Waist Circumference-Years Construct Analysis and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes: China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1997–2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Variable Measurement
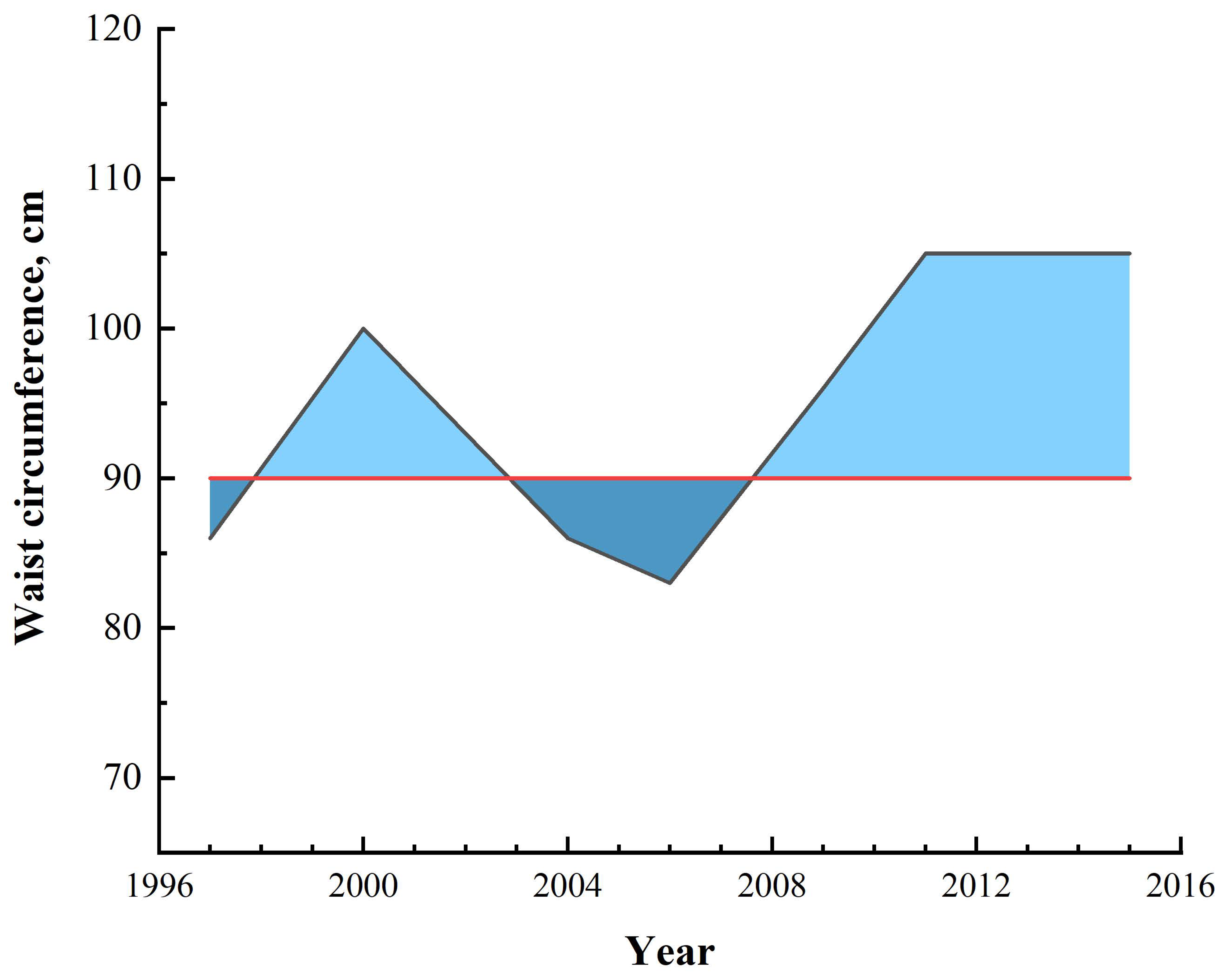
2.3. The Measurement of Waist Circumference–Years
2.4. Measurement of the Outcome and Time to Event
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. Incidence Rate and Odds Ratios of Type 2 Diabetes
3.3. Subgroup Analysis Results
3.4. ROC Comparison of Different Indexes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaiser, A.B.; Zhang, N.; Pluijm, W.V.D. Global Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes over the Next Ten Years (2018–2028). Diabetes 2018, 67, 202-LB. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Salpea, P.; Karuranga, S.; Petersohn, I.; Malanda, B.; Gregg, E.W.; Unwin, N.; Wild, S.H.; Williams, R. Mortality attributable to diabetes in 20–79 years old adults, 2019 estimates: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisinger, C.; Döring, A.; Thorand, B.; Heier, M.; Löwel, H. Body fat distribution and risk of type 2 diabetes in the general population: Are there differences between men and women? The MONICA/KORA Augsburg cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhou, W.; Sun, J.; Lin, R.; Ding, L.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Bi, Y.; et al. Visceral adiposity is significantly associated with type 2 diabetes in middle-aged and elderly Chinese women: A cross-sectional study. J. Diabetes 2017, 9, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, E.H.; Bae, S.J.; Park, J.Y. Impact of body mass index on the predictive ability of body fat distribution for type 2 diabetes risk in Koreans. Diabet. Med. 2012, 29, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.; Neeland, I.J.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R.D.; Arsenault, B.; Cuevas, A.; Hu, F.B.; et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: A Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.P.; Hankinson, A.L.; Loria, C.M.; Lewis, C.E.; Powell-Wiley, T.; Wei, G.S.; Liu, K. Duration of abdominal obesity beginning in young adulthood and incident diabetes through middle age: The CARDIA study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, R.; Ding, L.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Hu, G.; Liu, M. Waist Circumference and its Changes Are More Strongly Associated with the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes than Body Mass Index and Changes in Body Weight in Chinese Adults. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.F.; Wang, J.W.; Lu, J.X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.X. Waist-to-height ratio has a stronger association with cardiovascular risks than waist circumference, waist-hip ratio and body mass index in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, M.L.; Mukamal, K.J.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Ix, J.H.; Carnethon, M.R.; Newman, A.B.; de Boer, I.H.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Mozaffarian, D.; Siscovick, D.S. Association between adiposity in midlife and older age and risk of diabetes in older adults. Jama 2010, 303, 2504–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.P.; Allen, N.; Gunderson, E.P.; Lee, J.M.; Lewis, C.E.; Loria, C.M.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Rana, J.S.; Sidney, S.; Wei, G.; et al. Excess body mass index- and waist circumference-years and incident cardiovascular disease: The CARDIA study. Obesity 2015, 23, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhai, F.Y.; Du, S.F.; Popkin, B.M. The China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1989–2011. Obes Rev. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 1), 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Su, C.; Zhang, B.; Qin, G.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. Changes in distributions of waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio and waist-to-height ratio over an 18-year period among Chinese adults: A longitudinal study using quantile regression. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Weng, J.; Zhu, D.; Ji, L.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zou, D.; Guo, L.; Ji, Q.; Chen, L.; et al. Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmer, S.N.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.J. New Horizons in the impact of frailty on pharmacokinetics: Latest developments. Age Ageing 2021, 50, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Hodge, A.; Hendryx, M.; Byles, J.E. Age of obesity onset, cumulative obesity exposure over early adulthood and risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Wolfe, R.; Mannan, H.; Stoelwinder, J.U.; Stevenson, C.; Peeters, A. Epidemiologic merit of obese-years, the combination of degree and duration of obesity. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 176, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Gunn, P.; Gibson, S. Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Amin, F.A.; Hanum, F.; Stoelwinder, J.; Tanamas, S.; Wolf, R.; Wong, E.; Peeters, A. Estimating the risk of type-2 diabetes using obese-years in a contemporary population of the Framingham Study. Glob. Health Action 2016, 9, 30421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumvoll, M.; Goldstein, B.J.; van Haeften, T.W. Type 2 diabetes: Principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 2005, 365, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Papacosta, O.; Whincup, P.H.; Carson, C.; Thomas, M.C.; Lawlor, D.A.; Ebrahim, S.; Sattar, N. Assessing prediction of diabetes in older adults using different adiposity measures: A 7 year prospective study in 6,923 older men and women. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Wang, Z.M.; Ross, R. Skeletal muscle mass and distribution in 468 men and women aged 18–88 yr. J. Appl Physiol. 2000, 89, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Gender differences in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 187, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlamov, O.; Bethea, C.L.; Roberts, C.T., Jr. Sex-specific differences in lipid and glucose metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinders, I.; Visser, M.; Schaap, L. Body weight and body composition in old age and their relationship with frailty. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.; Katz, E.G.; Huxley, R.R. Associations between gender, age and waist circumference. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuk, J.L.; Lee, S.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Ross, R. Waist circumference and abdominal adipose tissue distribution: Influence of age and sex. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Savina, C.; Gennaro, E.; De Felice, M.R.; Rosano, A.; Pandolfo, M.M.; Del Balzo, V.; Cannella, C.; Ritz, P.; Chumlea, W.C. A systematic review of the literature concerning the relationship between obesity and mortality in the elderly. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautzky-Willer, A.; Harreiter, J.; Pacini, G. Sex and Gender Differences in Risk, Pathophysiology and Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 278–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Rawshani, A.; Franzén, S.; Rawshani, A.; Svensson, A.M.; Rosengren, A.; McGuire, D.K.; Eliasson, B.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S. Age at Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Associations With Cardiovascular and Mortality Risks. Circulation 2019, 139, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, N.S.; Richardson, A.S.; Gordon-Larsen, P. Timing and duration of obesity in relation to diabetes: Findings from an ethnically diverse, nationally representative sample. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree-Green, M.; Triolo, T.M.; Nadeau, K.J. Etiology of insulin resistance in youth with type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2013, 13, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Steinberger, J.; Hong, C.P.; Prineas, R.; Luepker, R.; Sinaiko, A.R. Insulin resistance during puberty: Results from clamp studies in 357 children. Diabetes 1999, 48, 2039–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Hodge, A.; Hendryx, M.; Byles, J.E. BMI trajectory and subsequent risk of type 2 diabetes among middle-aged women. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Nyamdorj, R. Is the association of type II diabetes with waist circumference or waist-to-hip ratio stronger than that with body mass index? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, S.; Horikawa, C.; Fujihara, K.; Heianza, Y.; Hirasawa, R.; Yachi, Y.; Sugawara, A.; Tanaka, S.; Shimano, H.; Iida, K.T.; et al. Comparisons of the strength of associations with future type 2 diabetes risk among anthropometric obesity indicators, including waist-to-height ratio: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 176, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.C.; Choe, S.; Torabi, M.R. Is waist circumference ≥ 102/88cm better than body mass index ≥30 to predict hypertension and diabetes development regardless of gender, age group, and race/ethnicity? Meta-analysis. Prev. Med. 2017, 97, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, K.C.; Ghazali, S.M.; Hock, L.K.; Subenthiran, S.; Huey, T.C.; Kuay, L.K.; Mustapha, F.I.; Yusoff, A.F.; Mustafa, A.N. The discriminative ability of waist circumference, body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio in identifying metabolic syndrome: Variations by age, sex and race. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2015, 9, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Chen, S.; Hu, G.; Chen, P.; Wu, J.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Jia, W. Stronger associations of waist circumference and waist-to-height ratio with diabetes than BMI in Chinese adults. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 147, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.H.; Nayak, K.S.; Goran, M.I. Assessment of abdominal adipose tissue and organ fat content by magnetic resonance imaging. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e504–e515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoufas, E.; Kanellakis, S.; Apostolidou, E.; Makridi, T.; Piggiou, E.; Papassotiriou, I.; Georgopoulou, C.; Manios, Y. Development and validation of two anthropometric models estimating abdominal fat percentage in Greek adult women and men. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 28, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Overall (n = 6616) | Diabetes (n = 315) | No Diabetes (n = 6301) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 43.4 ± 14.6 | 50.2 ± 11.4 | 43.0 ± 14.7 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 77.4 ± 9.2 | 85.3 ± 9.9 | 77.3 ± 9.0 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference-years | 25.1 ± 0.8 | 76.3 ± 5.8 | 22.5 ± 0.7 | <0.001 |
| Sex | 0.337 | |||
| Men, n (%) | 3241 (49.0) | 146 (46.3) | 3095 (49.1) | |
| Women, n (%) | 3375 (51.0) | 169 (53.7) | 3206 (50.9) | |
| Area | <0.001 | |||
| Urban, n (%) | 2233 (33.8) | 143 (45.4) | 2090 (33.2) | |
| Rural, n (%) | 4383 (66.2) | 172 (54.6) | 4211 (66.8) | |
| Smoking | 0.408 | |||
| Never, n (%) | 4416 (66.7) | 217 (68.9) | 4199 (66.6) | |
| Smoker, n (%) | 2200 (33.3) | 98 (31.1) | 2102 (33.4) | |
| Alcohol drinking | 0.056 | |||
| never | 4212 (63.7) | 202 (64.1) | 4009 (63.6) | |
| no more than 1 time per month | 700 (10.6) | 44 (14.0) | 656 (10.4) | |
| 1–2 times per month | 390 (5.9) | 24 (7.6) | 366 (5.8) | |
| 1–2 times per week | 585 (8.8) | 22 (7.0) | 563 (8.9) | |
| 3 or more times per week | 728 (11.0) | 23 (7.3) | 446 (11.2) | |
| Marital status | <0.001 | |||
| Single | 683 (10.4) | 9 (2.9) | 674 (10.8) | |
| Married | 5491 (83.6) | 284 (90.7) | 5207 (83.2) | |
| Widowed, divorced or separated | 396 (6.0) | 20 (6.4) | 376 (6.0) | |
| Educational | 0.231 | |||
| Primary school or lower | 3563 (54.4) | 184 (59.0) | 3379 (54.2) | |
| Junior or Senior Secondary | 2867 (43.8) | 122 (39.1) | 2745 (44.0) | |
| Junior college or above | 116 (1.8) | 6 (1.9) | 110 (1.8) |
| Waist Circumference-Years (cm·Years) | Per 50 Waist Circumference-Years | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (n = 5052) | 1–49.9 (n = 505) | 50–99.9 (n = 387) | 100–149.9 (n = 283) | ≥150 (n = 389) | p-Trend | ||
| No. of events | 137 | 39 | 39 | 36 | 64 | ||
| No. of person-years | 66,945 | 7043 | 4888 | 3811 | 4770 | ||
| Incidence rate a | 2.05 | 5.54 | 7.98 | 9.45 | 13.42 | ||
| Model 1 b | 1.00 (ref) | 2.86 (1.98–4.14) | 3.68 (2.52–5.36) | 4.83 (3.26–7.16) | 6.05 (4.37–8.37) | <0.001 | 1.40 (1.32–1.48) |
| Model 2 c | 1.00 (ref) | 2.64 (1.81–3.84) | 3.60 (2.46–5.25) | 4.43 (2.97–6.62) | 5.78 (4.16–8.02) | <0.001 | 1.38 (1.31–1.47) |
| Model 3 d | 1.00 (ref) | 2.63 (1.80–3.83) | 3.56 (2.43–5.20) | 4.39 (2.94–6.56) | 5.75 (4.14–8.00) | <0.001 | 1.38 (1.31–1.47) |
| Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Men | |||
| 0 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) |
| 1–49.9 | 2.61 (1.53–4.45) | 2.25 (1.30–3.89) | 2.19 (1.26–3.80) |
| 50–99.9 | 3.34 (1.83–6.08) | 2.97 (1.62–5.42) | 2.87 (1.56–5.26) |
| 100–149.9 | 3.78 (1.98–7.22) | 3.22 (1.68–6.29) | 3.12 (1.62–6.03) |
| ≥150 | 5.43 (3.28–9.00) | 4.75 (2.85–7.90) | 4.70 (2.81–7.85) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Per 50 waist circumference-years | 1.39 (1.27–1.52) | 1.35 (1.23–1.48) | 1.35 (1.23–1.48) |
| Women | |||
| 0 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) |
| 1–49.9 | 3.20 (1.91–5.37) | 3.02 (1.78–5.10) | 3.04 (1.79–5.15) |
| 50–99.9 | 4.11 (2.50–6.73) | 4.21 (2.55–6.95) | 4.17 (2.53–6.89) |
| 100–149.9 | 5.86 (3.53–9.74) | 5.50 (3.26–8.28) | 5.49 (3.25–9.29) |
| ≥150 | 6.82 (4.42–10.54) | 6.83 (4.38–10.65) | 6.82 (4.38–10.64) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Per 50 waist circumference-years | 1.41 (1.31–1.52) | 1.41 (1.30–1.51) | 1.41 (1.30–1.52) |
| <60 | |||
| 0 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) |
| 1–49.9 | 2.50 (1.63–3.84) | 2.42 (1.57–3.72) | 2.41 (1.56–3.70) |
| 50–99.9 | 3.99 (2.59–6.15) | 3.88 (2.52–5.98) | 3.76 (2.44–5.80) |
| 100–149.9 | 5.46 (3.54–8.42) | 5.16 (3.32–8.02) | 5.03 (3.23–7.84) |
| ≥150 | 6.82 (4.68–9.95) | 6.45 (4.41–9.43) | 6.36 (4.34–9.32) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Per 50 waist circumference-years | 1.44 (1.35–1.54) | 1.43 (1.33–1.52) | 1.42 (1.33–1.52) |
| ≥60 | |||
| 0 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) |
| 1–49.9 | 3.16 (1.48–6.75) | 2.51 (1.11–5.66) | 2.44 (1.07–5.58) |
| 50–99.9 | 2.44 (1.11–5.34) | 2.37 (1.05–5.31) | 2.32 (1.03–5.26) |
| 100–149.9 | 2.35 (0.87–6.37) | 1.99 (0.77–5.50) | 1.84 (0.66–5.12) |
| ≥150 | 3.57 (1.87–6.83) | 3.47 (1.77–6.80) | 3.41 (1.73–6.71) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Per 50 waist circumference-years | 1.25 (1.12–1.41) | 1.25 (1.11–1.41) | 1.24 (1.10–1.40) |
| Category | AUC | 95% CI | p Value | Cutoff Value | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waist circumference | 0.731 | 0.703–0.759 | <0.001 | 81.500 | 0.631 | 0.715 |
| Waist height ratio | 0.728 | 0.700–0.757 | <0.001 | 0.508 | 0.666 | 0.703 |
| Waist circumference-years | 0.743 | 0.715–0.770 | <0.001 | 0 | 0.720 | 0.688 |
| Men | ||||||
| Waist circumference | 0.725 | 0.682–0.767 | <0.001 | 84.500 | 0.596 | 0.762 |
| Waist height ratio | 0.724 | 0.681–0.768 | <0.001 | 0.508 | 0.616 | 0.769 |
| Waist circumference-years | 0.733 | 0.692–0.774 | <0.001 | 0 | 0.788 | 0.604 |
| Women | ||||||
| Waist circumference | 0.741 | 0.704–0.779 | <0.001 | 81.500 | 0.601 | 0.750 |
| Waist height ratio | 0.732 | 0.695–0.770 | <0.001 | 0.509 | 0.708 | 0.648 |
| Waist circumference-years | 0.754 | 0.716–0.791 | <0.001 | 0 | 0.768 | 0.659 |
| <60 | ||||||
| Waist circumference | 0.744 | 0.713–0.776 | <0.001 | 81.500 | 0.640 | 0.735 |
| Waist height ratio | 0.742 | 0.710–0.774 | <0.001 | 0.508 | 0.657 | 0.736 |
| Waist circumference-years | 0.754 | 0.723–0.786 | <0.001 | 0 | 0.715 | 0.703 |
| ≥60 | ||||||
| Waist circumference | 0.669 | 0.605–0.733 | <0.001 | 86.333 | 0.528 | 0.745 |
| Waist height ratio | 0.652 | 0.587–0.718 | <0.001 | 0.524 | 0.625 | 0.633 |
| Waist circumference-years | 0.689 | 0.630–0.748 | <0.001 | 0 | 0.722 | 0.636 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Ku, C.; Wu, B.; Dai, M.; Liu, L.; Ping, Z. Waist Circumference-Years Construct Analysis and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes: China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1997–2015. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214654
Xi L, Yang X, Wang R, Ku C, Wu B, Dai M, Liu L, Ping Z. Waist Circumference-Years Construct Analysis and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes: China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1997–2015. Nutrients. 2022; 14(21):4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214654
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Lijing, Xueke Yang, Ruizhe Wang, Chaoyue Ku, Binbin Wu, Man Dai, Li Liu, and Zhiguang Ping. 2022. "Waist Circumference-Years Construct Analysis and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes: China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1997–2015" Nutrients 14, no. 21: 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214654
APA StyleXi, L., Yang, X., Wang, R., Ku, C., Wu, B., Dai, M., Liu, L., & Ping, Z. (2022). Waist Circumference-Years Construct Analysis and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes: China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1997–2015. Nutrients, 14(21), 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214654






