Effects of Acute Vitamin C plus Vitamin E Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Runners: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
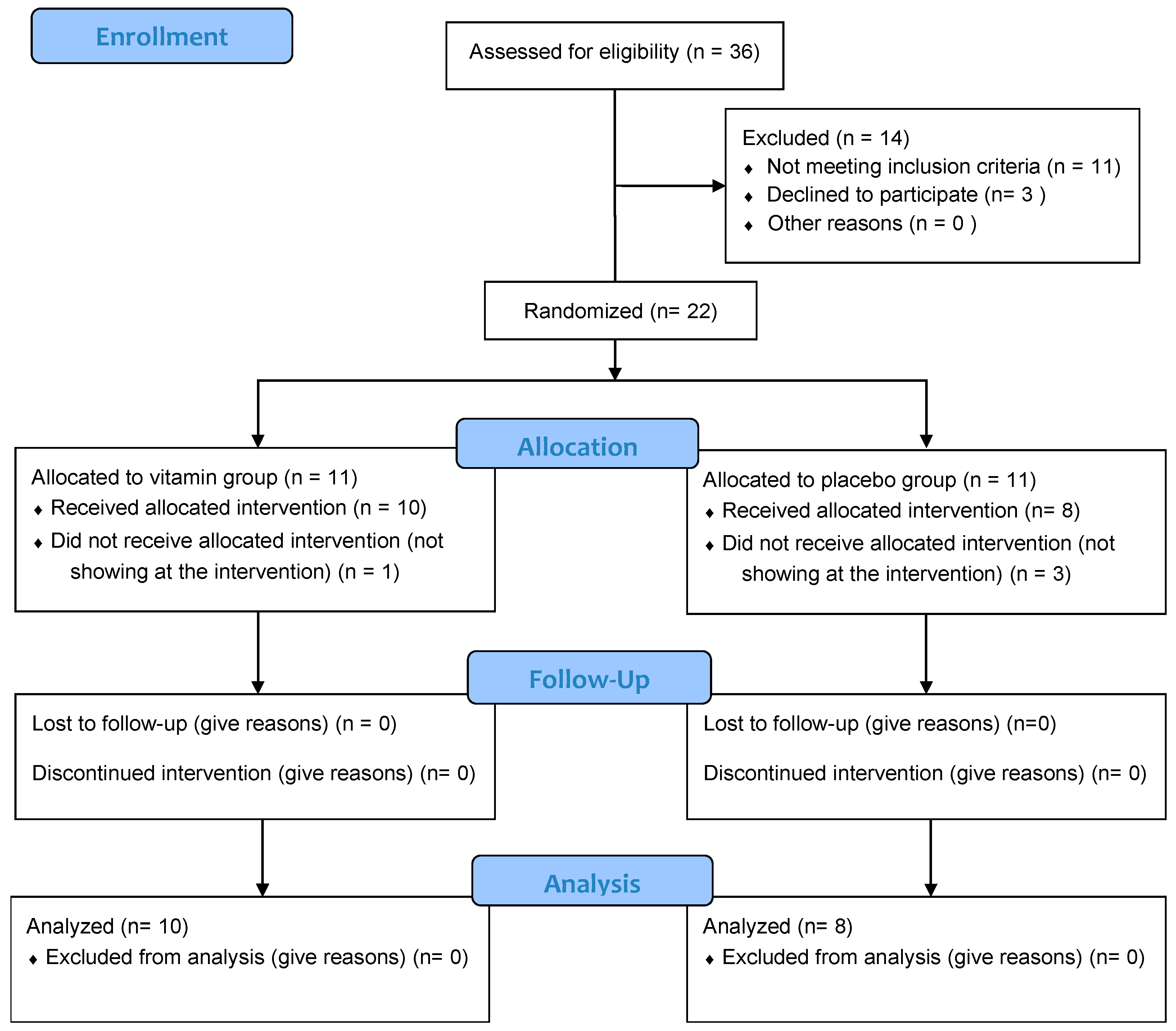
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Supplementation with Antioxidant Vitamins
2.4. Diet Control and Body Composition Anaylsis
2.5. Outcome Measures
2.5.1. Muscle Damage
2.5.2. Lactate
2.5.3. Physical Performance
2.5.4. DOMS and RPE
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Muscle Damage
3.3. Lactate Levels
3.4. Performance
3.5. DOMS and RPE
4. Discussion
Limitations and Strength
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harty, P.S.; Cottet, M.L.; Malloy, J.K.; Kerksick, C.M. Nutritional and Supplementation Strategies to Prevent and Attenuate Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: A Brief Review. Sport. Med. 2019, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, I.; Constantini, K.; Hoffman, J.R.; Bartolomei, S.; Gepner, Y. Exercise-induced muscle damage: Mechanism, assessment and nutritional factors to accelerate recovery. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 969–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howatson, G.; Van Someren, K.A. The prevention and treatment of exercise-induced muscle damage. Sport. Med. 2008, 38, 483–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, J.M. Recovery after exercise: What is the current state of play? Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2019, 10, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.T.; Erdman, K.A.; Buker, L.M. American College of Sports Medicine Joint Position Statement. Nutrition and Athletic Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, A.H.; Garten, R.S.; Cho, C.; Chee, P.D.M.; Chambers, L.A. Effects of a fruit/berry/vegetable supplement on muscle function and oxidative stress. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ives, S.J.; Bloom, S.; Matias, A.; Morrow, N.; Martins, N.; Roh, Y.; Ebenstein, D.; O’Brien, G.; Escudero, D.; Brito, K.; et al. Effects of a combined protein and antioxidant supplement on recovery of muscle function and soreness following eccentric exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasiakos, S.M.; Lieberman, H.R.; McLellan, T.M. Effects of protein supplements on muscle damage, soreness and recovery of muscle function and physical performance: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, K.; Robinson, N.; Ives, S.J. Exercise performance and physiological responses: The potential role of redox imbalance. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ferran, M.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Lavie, C.J.; Lippi, G.; Pareja-Galeano, H. Do Antioxidant Vitamins Prevent Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage? A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, M.F.; Martinez-Ferran, M.; Vallecillo, N.; Jiménez, S.L.S.L.; Romero-Morales, C.; Pareja-Galeano, H. Supplementation with Vitamins C and E and Exercise-Induced Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Institute of Sport Vitamin E. Available online: https://www.ais.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0015/1000419/36182_Supplements-fact-sheets_Vitamin-E-v2.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Australian Institute of Sport Vitamin C. Available online: https://www.ais.gov.au/nutrition/supplements/group_b#vitamin_c (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Armstrong, R.B. Mechanisms of exercise-induced delayed onset muscular soreness: A brief review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1984, 16, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.L.; Leichtweis, S. Exercise and oxidative stress: Sources of free radicals and their impact on antioxidant systems. Age 1997, 20, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frei, B. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant vitamins: Mechanisms of action. Am. J. Med. 1994, 97, S5–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.R.; Izadi, A.; Kaviani, M. Antioxidants and exercise performance: With a focus on vitamin e and c supplementation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viña, J.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Martinez-Bello, V.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C. Exercise acts as a drug; The pharmacological benefits of exercise. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Viña, J.; Li Li, J. Role of redox signaling and inflammation in skeletal muscle adaptations to training. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadley, G.D. A role for reactive oxygen species in the regulation of skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Acta Physiol. 2013, 208, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Domenech, E.; Romagnoli, M.; Arduini, A.; Borras, C.; Pallardo, F.V.; Sastre, J.; Viña, J. Oral administration of vitamin C decreases muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and hampers training-induced adaptations in endurance performance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.; Hughes, J.; Della Gatta, P.A.; Mason, S.; Lamon, S.; Russell, A.P.; Wadley, G.D. Vitamin C and E supplementation prevents some of the cellular adaptations to endurance-training in humans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, M.T.; Martins, W.R.; Ribeiro, A.L.A.; Bottaro, M. The Effects of Strength Training Combined with Vitamin C and E Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle Mass and Strength: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Sport. Med. 2020, 2020, 3505209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merry, T.L.; Ristow, M. Do antioxidant supplements interfere with skeletal muscle adaptation to exercise training? J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 5135–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beil, L. Tough to swallow: Athletes who use antioxidant supplements may not be getting the boost they expect. Sci. News 2015, 187, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penry, J.T.; Wilcox, A.R.; Yun, J. Validity and reliability analysis of Cooper’s 12-minute run and the multistage shuttle run in healthy adults. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescatello, L.S. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 9th ed.; Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health: Philladelphia, PA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-6091-3955. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, K.; Getzin, A. Nutrition and Supplement Update for the Endurance Athlete: Review and Recommendations. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeukendrup, A.E. Nutrition for endurance sports: Marathon, triathlon, and road cycling. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, S91–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, P.; Maffulli, N.; Limongelli, F.M. Creatine kinase monitoring in sport medicine. Br. Med. Bull. 2007, 81–82, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, J.M.; Sharpe, K.; Knight, E.; Fuller, K.L.; Tanner, R.K.; Gore, C.J. Reliability and Accuracy of Six Hand-Held Blood Lactate Analysers. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2015, 14, 203. [Google Scholar]
- Crotty, N.M.; Boland, M.; Mahony, N.; Donne, B.; Fleming, N. Reliability and Validity of the Lactate Pro 2 Analyzer. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 25, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Reyes, P.; Pareja-Blanco, F.; Balsalobre-Fernández, C.; Cuadrado-Peñafiel, V.; Ortega-Becerra, M.A.; González-Badillo, J.J. Jump-Squat Performance and Its Relationship With Relative Training Intensity in High-Level Athletes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Reyes, P.; Cuadrado-Peñafiel, V.; Párraga-Montilla, J.A.; Romero-Franco, N.; Casado, A. Anaerobic Speed Reserve, Sprint Force–Velocity Profile, Kinematic Characteristics, and Jump Ability among Elite Male Speed-and Endurance-Adapted Milers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalleau, G.; Belli, A.; Viale, F.; Lacour, J.R.; Bourdin, M. A simple method for field measurements of leg stiffness in hopping. Int. J. Sports Med. 2004, 25, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, D.C.; Rosa, F.T.; Simões-Ambrósio, L.; Jordao, A.A.; Deminice, R. Antioxidant vitamin supplementation prevents oxidative stress but does not enhance performance in young football athletes. Nutrition 2019, 63–64, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G. Psychophysical Scaling with Applications in Physical Work and the Perception of Exertion. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 1990, 16, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, C.; Hector, L.L.; Welsh, R.; Schrager, M.; Green, M.A.; Snyder, A.C. Effects of specific versus cross-training on running performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1995, 70, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive Statistics for Studies in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge Academic: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bohlooli, S.; Rahmani-Nia, F.; Babaei, P.; Nakhostin-Roohi, B. Influence of vitamin C moderate dose supplementation on exercise-induced lipid peroxidation, muscle damage and inflammation. Med. Dello Sport 2012, 65, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Nakhostin-Roohi, B.; Babaei, P.; Rahmani-Nia, F.; Bohlooli, S.; NAkhostin-Roohi, B.; Babaei, P.; Rahmani-Nia, F.; Bohlooli, S. Effect of vitamin C supplementation on lipid peroxidation, muscle damage and inflammation after 30-min exercise at 75% V.O(2max). J. Sport. Med. Phys. Fit. 2008, 48, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Lin, H. Effects of vitamin C supplementation on recovery from eccentric exercise-induced muscle soreness and damage in junior athletes. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2004, 2, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, S.A.; Silva, E.T.; Caris, A.V.; Lira, F.S.; Tufik, S.; dos Santos, R.V.T.T. Vitamin E supplementation inhibits muscle damage and inflammation after moderate exercise in hypoxia. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.; Williams, C.; Kingsley, M.; Nicholas, C.W.; Lakomy, H.K.A.; McArdle, F.; Jackson, M.J. Muscle soreness and damage parameters after prolonged intermittent shuttle-running following acute vitamin C supplementation. Int. J. Sports Med. 2001, 22, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, D.; Williams, C.; Garcia-Roves, P.; McGregor, S.J.; McArdle, F.; Jackson, M.J. Post-exercise vitamin C supplementation and recovery from demanding exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 89, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, B.; Henry, G.J.J.; Goodman, C.; Gillam, I.; Beilby, J.R.R.; Ching, S.; Fabian, V.; Dasig, D.; Morling, P.; Kakulus, B.A.A. Effect of vitamin C and E supplementation on biochemical and ultrastructural indices of muscle damage after a 21 km run. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2002, 23, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastaloudis, A.; Traber, M.G.; Carstensen, K.; Widrick, J.J. Antioxidants did not prevent muscle damage in response to an ultramarathon run. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.W.; Ostrowski, K.; Ibfelt, T.; Richelle, M.; Offord, E.; Halkjær-Kristensen, J.; Pedersen, B.K.; Halkjaer-Kristensen, J.; Pedersen, B.K.; Halkjær-Kristensen, J.; et al. Effect of vitamin supplementation on cytokine response and on muscle damage after strenuous exercise. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokitzki, L.; Logemann, E.; Sagredos, A.N.; Murphy, M.; Wetzel-Roth, W.; Keul, J. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidative vitamins under extreme endurance stress. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1994, 151, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.G.; Orencole, S.F.; Fielding, R.A.; Meydani, M.; Meydani, S.N.; Fiatarone, M.A.; Blumberg, J.B.; Evans, W.J. Acute phase response in exercise: Interaction of age and vitamin E on neutrophils and muscle enzyme release. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1990, 259, R1214–R1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.M.; Anderson, R.; Theron, A.J. Attenuation of increase in circulating cortisol and enhancement of the acute phase protein response in vitamin C-supplemented ultramarathoners. Int. J. Sports Med. 2001, 22, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Ohkuwa, T.; Yamazaki, Y.; Shimoda, T.; Wakayama, A.; Tamura, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Sato, Y.; Miyamura, M. Vitamin E supplementation attenuates leakage of enzymes following 6 successive days of running training. Int. J. Sports Med. 2000, 21, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranchordas, M.K.; Rogerson, D.; Soltani, H.; Costello, J.T. Antioxidants for preventing and reducing muscle soreness after exercise. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Jackson, M.J. Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress: Cellular Mechanisms and Impact on Muscle Force Production. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1243–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pinillos, F.; Soto-Hermoso, V.M.; Latorre-Román, P.A. Acute effects of extended interval training on countermovement jump and handgrip strength performance in endurance athletes: Postactivation potentiation. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervasi, M.; Calavalle, A.R.; Amatori, S.; Grassi, E.; Benelli, P.; Sestili, P.; Sisti, D. Post-Activation Potentiation Increases Recruitment of Fast Twitch Fibers: A Potential Practical Application in Runners. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 65, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabita, G.; Couturier, A.; Dorel, S.; Hausswirth, C.; Le Meur, Y. Changes in spring-mass behavior and muscle activity during an exhaustive run at VO2max. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braakhuis, A.J.; Hopkins, W.G. Impact of Dietary Antioxidants on Sport Performance: A Review. Sport. Med. 2015, 45, 939–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.-C.; Sung, Y.-C.; Davison, G.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liao, Y.-H. Short-Term High-Dose Vitamin C and E Supplementation Attenuates Muscle Damage and Inflammatory Responses to Repeated Taekwondo Competitions: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.M.; Kraemer, W.J.; Triplett-McBride, T.; Sebastianelli, W. Effect of resistance exercise on free radical production. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niess, A.M.; Fehrenbach, E.; Schlotz, E.; Sommer, M.; Angres, C.; Tschositsch, K.; Battenfeld, N.; Golly, I.C.; Biesalski, H.K.; Northoff, H.; et al. Effects of RRR-α-tocopherol on leukocyte expression of HSP72 in response to exhaustive treadmill exercise. Int. J. Sports Med. 2002, 23, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.M.; Jawis, M.N.; Ahmed, S.A.; Krasilshchikov, O. Effects of Dietary Vitamin C and E Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage among Young Kelantan Weightlifters. Biol. Exerc. 2015, 11, 41–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokitzki, L.; Logemann, E.; Huber, G.; Keck, E.; Keul, J. Alpha tocopherol supplementation in Racing Cyclist During Extreme Endurance Training. Int. J. Sport Nutr. 1994, 4, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, N.G.; Kaiser, J.L.; Sharman, M.J.; Scheet, T.E.; Barnes, D.M.; Gómez, A.L.; Kraemer, W.J.; Volek, J.S. Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation on Recovery From Repeated Bouts of Resistance Exercise. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2003, 17, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakeman, P.; Maxwell, S. Effect of antioxidant vitamin supplementation on muscle function after eccentric exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1993, 67, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group VIT | Group PLA | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 47.90 (5.75) | 46.76 (4.60) | 0.656 a |
| VO2max (mL/min) | 53.64 (11.77) | 49.65 (9.27) | 0.460 a |
| HRmax (BPM) | 174.75 (4.15) | 174.53 (4.00) | 0.655 a |
| Body mass (kg) | 74.84 (10.94) | 75.00 (9.82) | 1.00 b |
| Body fat (%) | 21.81 (5.37) | 19.31 (4.32) | 0.302 a |
| Muscle mass (kg) | 55.22 (5.60) | 57.40 (7.10) | 0.476 a |
| Bone mass (kg) | 2.90 (0.28) | 3.025 (0.35) | 0.416 a |
| Total body water | 55.58 (4.04) | 57.64 (3.34) | 0.264 a |
| Visceral adipose tissue | 9.00 (3.20) | 8.25 (1.98) | 0.571 a |
| Group | PRE | POST | 24 h | Effect Size | p–Value (Intragroup × Time) | Observed Power | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMJ | VIT | 22.63 (5.02) | 26.71 (6.27) * | 25.41 (6.54) * | 0.696 | 0.000 a | 1.000 |
| PLA | 20.97 (4.21) | 25.29 (5.32) * | 21.89 (5.02) ** | 0.750 | 0.000 a | 1.000 | |
| SJ | VIT | 21.65 (4.67) | 24.74 (6.10) * | 22.78 (5.73) ** | 0.603 | 0.000 a | 0.994 |
| PLA | 20.29 (4.38) | 22.91 (5.32) * | 20.21 (4.31) ** | 0.656 | 0.001 a | 0.989 | |
| EI (%) | VIT | 4.48 (4.01) | 8.25 (4.66) | 11.52 (5.13) * | 0.400 | 0.010 a | 0.820 |
| PLA | 4.16 (9.19) | 11.25 (9.52) | 8.02 (5.85) | 0.208 | 0.195 a | 0.319 | |
| Kvert | VIT | 159.65 (63.14) | 173.45 (56.72) | 173.92 (57.68) | 0.068 | 0.533 a | 0.142 |
| PLA | 161.51 (28.28) | 177.86 (56.25) | 157.27 (38.88) | 0.152 | 0.315 a | 0.228 | |
| Lactate | VIT | 1.64 (0.40) | 6.02 (2.25) | - | −1.006 y | 0.000 b | - |
| PLA | 1.86 (1.01) | 5.73 (2.36) | - | −0.891 yy | 0.012 c | - | |
| CK | VIT | 103.03 (15.45) | - | 302.40 (66.76) | −0.886 yy | 0.005 c | - |
| PLA | 125.06 (65.64) | - | 233.86 (47.48) | −2.493 y | 0.000 b | - |
| Mean Differences | Effect Size (η2) | 95% CI | p-Value (Intergroup × Time) | Observed Power | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMJ | 2.20 | 0.007 | (−3.23, 7.63) | 0.072 a | 0.522 |
| SJ | 1.92 | 0.002 | (−3.18, 7.02) | 0.377 a | 0.196 |
| IE (%) | 0.27 | 0.038 | (−4.09, 4.63) | 0.282 a | 0.264 |
| KVERT | 3.46 | 0.009 | (−43.44, 50.36) | 0.526 a | 0.150 |
| CK | 90.27 | 0.077 | (−71.07, 251.60) | 0.252 b | 0.201 |
| Lactate | 0.13 | 0.009 | (−2.25, 2.52) | 0.907 b | 0.051 |
| Group VIT | Group PLA | p-Value (Intergroup) a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RPE | 5.30 (2.71) | 5.00 (2.00) | 0.829 |
| DOMS 24 h upper body | 1.60 (0.84) | 2.25 (1.91) | 0.762 |
| DOMS 24 h upper legs | 2.90 (2.18) | 3.88 (2.30) | 0.408 |
| DOMS 24 h lower legs | 2.50 (2.22) | 4.00 (3.02) | 0.408 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Ferrán, M.; Cuadrado-Peñafiel, V.; Sánchez-Andreo, J.M.; Villar-Lucas, M.; Castellanos-Montealegre, M.; Rubio-Martín, A.; Romero-Morales, C.; Casla-Barrio, S.; Pareja-Galeano, H. Effects of Acute Vitamin C plus Vitamin E Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Runners: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4635. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214635
Martínez-Ferrán M, Cuadrado-Peñafiel V, Sánchez-Andreo JM, Villar-Lucas M, Castellanos-Montealegre M, Rubio-Martín A, Romero-Morales C, Casla-Barrio S, Pareja-Galeano H. Effects of Acute Vitamin C plus Vitamin E Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Runners: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2022; 14(21):4635. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214635
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Ferrán, María, Víctor Cuadrado-Peñafiel, Juan Manuel Sánchez-Andreo, Marta Villar-Lucas, Mónica Castellanos-Montealegre, Agustín Rubio-Martín, Carlos Romero-Morales, Soraya Casla-Barrio, and Helios Pareja-Galeano. 2022. "Effects of Acute Vitamin C plus Vitamin E Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Runners: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 14, no. 21: 4635. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214635
APA StyleMartínez-Ferrán, M., Cuadrado-Peñafiel, V., Sánchez-Andreo, J. M., Villar-Lucas, M., Castellanos-Montealegre, M., Rubio-Martín, A., Romero-Morales, C., Casla-Barrio, S., & Pareja-Galeano, H. (2022). Effects of Acute Vitamin C plus Vitamin E Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Runners: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 14(21), 4635. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214635









