Oats Lower Age-Related Systemic Chronic Inflammation (iAge) in Adults at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Randomization and Concealment
2.3. Study Cohort and Treatment
2.4. iAge® Determination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
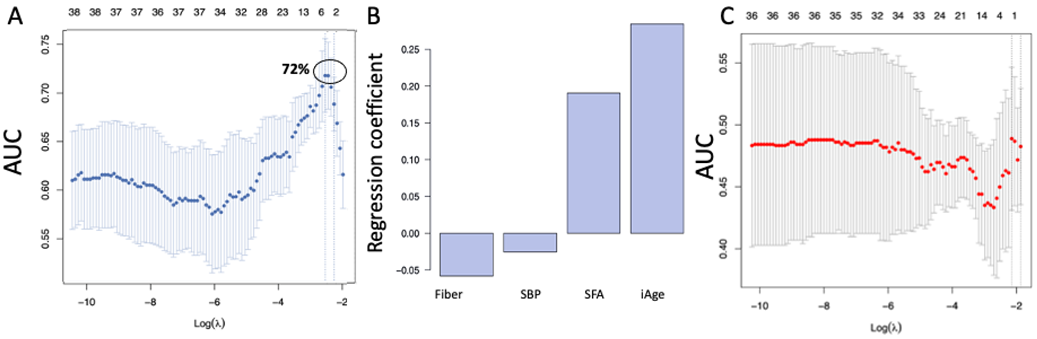
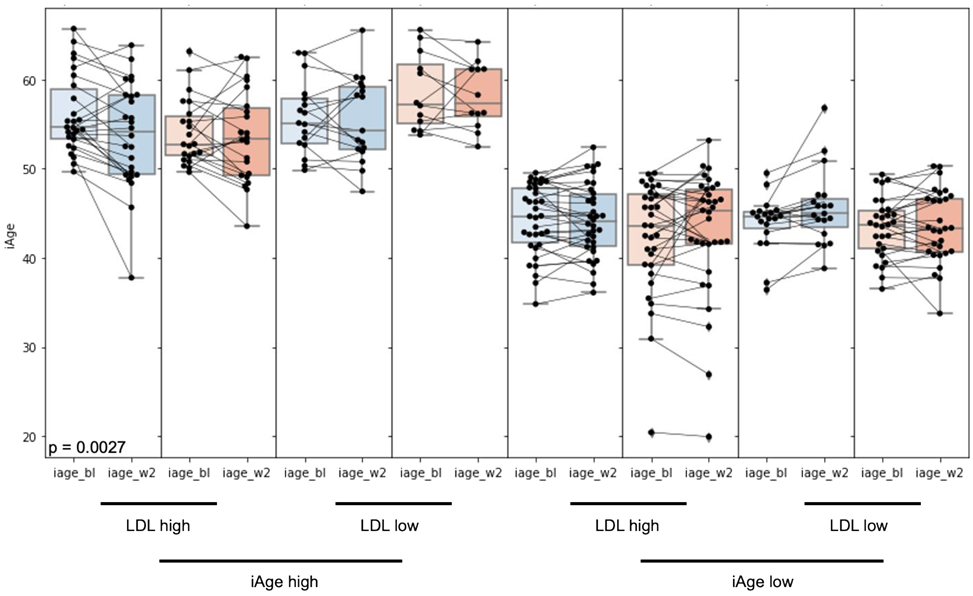
3.1. High Baseline iAge® Predicts the Effectiveness of Oats Intervention
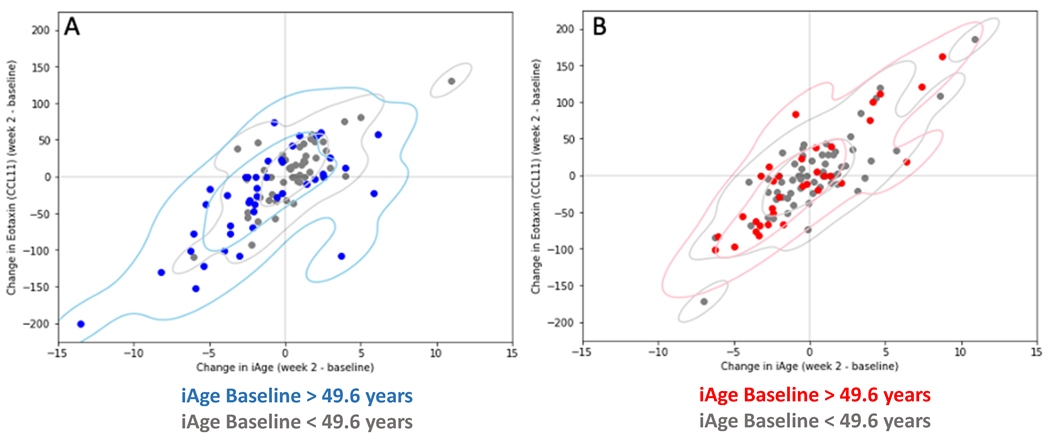
3.2. Changes in iAge® Induced by the Oat Product Are Correlated with a Decrease in CCL11
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Control, U.S.C.f.D. Underlying Cause of Death, 1999–2018. CDC WONDER Online Database. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2018. Available online: https://wonder.cdc.gov/ (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Foundations of Immunometabolism and Implications for Metabolic Health and Disease. Immunity 2017, 47, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Flavell, R.A. Innate sensors of pathogen and stress: Linking inflammation to obesity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, D.; Chang, J.; Lartigue, L.; Bolen, C.R.; Haddad, F.; Gaudilliere, B.; Ganio, E.A.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; Spitzer, M.H.; Douchet, I.; et al. Expression of specific inflammasome gene modules stratifies older individuals into two extreme clinical and immunological states. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gistera, A.; Hansson, G.K. The immunology of atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.H.; Raison, C.L. The role of inflammation in depression: From evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaria, R.N.; Maestre, G.E.; Arizaga, R.; Friedland, R.P.; Galasko, D.; Hall, K.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Ogunniyi, A.; Perry, E.K.; Potocnik, F.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia in developing countries: Prevalence, management, and risk factors. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.M.; Reeves, G.; Billman, G.E.; Sturmberg, J.P. Inflammation–Nature’s Way to Efficiently Respond to All Types of Challenges: Implications for Understanding and Managing “the Epidemic” of Chronic Diseases. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2018, 5, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Spinelli, C.C.; Martucciello, S.; Nori, S.L.; Capunzo, M.; Puca, A.A.; Ciaglia, E. Innate immunity and cellular senescence: The good and the bad in the developmental and aged brain. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, K.; Smolen, J.S. Inflammatory bone loss: Pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, R.H.; Cutolo, M.; Pacifici, R. Evolutionary medicine and bone loss in chronic inflammatory diseases—A theory of inflammation-related osteopenia. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Balkwill, F.; Chonchol, M.; Cominelli, F.; Donath, M.Y.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Golenbock, D.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Heneka, M.T.; Hoffman, H.M.; et al. A guiding map for inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotas, M.E.; Medzhitov, R. Homeostasis, inflammation, and disease susceptibility. Cell 2015, 160, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Vitale, G.; Capri, M.; Salvioli, S. Inflammaging and ‘Garb-aging’. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.; Vince, J.E. Pyroptosis versus necroptosis: Similarities, differences, and crosstalk. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, A.; Masters, S.L. Homeostasis-altering molecular processes as mechanisms of inflammasome activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, R.H. Concepts of evolutionary medicine and energy regulation contribute to the etiology of systemic chronic inflammatory diseases. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, R.H. The brain and immune system prompt energy shortage in chronic inflammation and ageing. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C.; Bosco, N.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Capuron, L.; Delzenne, N.; Dore, J.; Franceschi, C.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Recker, T.; Salvioli, S.; et al. Health relevance of the modification of low grade inflammation in ageing (inflammageing) and the role of nutrition. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beharka, A.A.; Meydani, M.; Wu, D.; Leka, L.S.; Meydani, A.; Meydani, S.N. Interleukin-6 production does not increase with age. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, B81–B88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyczalkowska-Tomasik, A.; Czarkowska-Paczek, B.; Zielenkiewicz, M.; Paczek, L. Inflammatory Markers Change with Age, but do not Fall Beyond Reported Normal Ranges. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz) 2016, 64, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, N.; Yingxiang, H.; Keheim, N.; Krejciova-Rajaniemi, Z.; Davis, M.M.; Furman, D. An Inflammatory aging clock (iAge) based on deep learning tracks multimorbiditiy, immunosenescence, fraility and cardiovascular aging. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Diepen, J.A.; Berbee, J.F.; Havekes, L.M.; Rensen, P.C. Interactions between inflammation and lipid metabolism: Relevance for efficacy of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Lipoprotein Apheresis. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Angelovich, T.A.; Hearps, A.C.; Jaworowski, A. Inflammation-induced foam cell formation in chronic inflammatory disease. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Thuren, T.; Everett, B.M.; Libby, P.; Glynn, R.J.; Group, C.T. Effect of interleukin-1beta inhibition with canakinumab on incident lung cancer in patients with atherosclerosis: Exploratory results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetvicka, V.; Gover, O.; Hayby, H.; Danay, O.; Ezov, N.; Hadar, Y.; Schwartz, B. Immunomodulating Effects Exerted by Glucans Extracted from the King Oyster Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom Pleurotus eryngii (Agaricomycetes) Grown in Substrates Containing Various Concentrations of Olive Mill Waste. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2019, 21, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Peng, S.; Song, Z.; Bai, F.; Li, X.; Fang, J. Oat polyphenol avenanthramide-2c confers protection from oxidative stress by regulating the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway in PC12 cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 706, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrelli, A.; Goitre, L.; Salzano, A.M.; Moglia, A.; Scaloni, A.; Retta, S.F. Biological Activities, Health Benefits, and Therapeutic Properties of Avenanthramides: From Skin Protection to Prevention and Treatment of Cerebrovascular Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6015351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, O.; Mah, E.; Dioum, E.; Marwaha, A.; Shanmugam, S.; Malleshi, N.; Sudha, V.; Gayathri, R.; Unnikrishnan, R.; Anjana, R.M.; et al. The Role of Oat Nutrients in the Immune System: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, E.; Sapa, H.; Negrea, L.; Bame, K.; Hostetter, T.; Barkoukis, H.; Dusso, A.; Dobre, M. Effect of Oat beta-Glucan Supplementation on Chronic Kidney Disease: A Feasibility Study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2020, 30, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurbau, A.; Noronha, J.C.; Khan, T.A.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Wolever, T.M.S. The effect of oat beta-glucan on postprandial blood glucose and insulin responses: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 1540–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, A.; Beck, E.J.; Tosh, S.; Wolever, T.M. Cholesterol-lowering effects of oat beta-glucan: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolever, T.M.; Tosh, S.M.; Gibbs, A.L.; Brand-Miller, J.; Duncan, A.M.; Hart, V.; Lamarche, B.; Thomson, B.A.; Duss, R.; Wood, P.J. Physicochemical properties of oat beta-glucan influence its ability to reduce serum LDL cholesterol in humans: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolever, T.M.S.; Rahn, M.; Dioum, E.H.; Jenkins, A.L.; Ezatagha, A.; Campbell, J.E.; Chu, Y. Effect of Oat beta-Glucan on Affective and Physical Feeling States in Healthy Adults: Evidence for Reduced Headache, Fatigue, Anxiety and Limb/Joint Pains. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, C.; Landberg, R.; Andersson, K.; Heyman-Linden, L.; Rascon, A.; Magnuson, A.; Khalili, P.; Karegren, A.; Nilsson, J.; Pirazzi, C.; et al. Effects of Bilberry and Oat intake on lipids, inflammation and exercise capacity after Acute Myocardial Infarction (BIOAMI): Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Trials 2021, 22, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Veronesi, M.; Strocchi, E.; Grandi, E.; Rizzoli, E.; Poli, A.; Marangoni, F.; Borghi, C. A randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Medium-Term Effects of Oat Fibers on Human Health: The Beta-Glucan Effects on Lipid Profile, Glycemia and inTestinal Health (BELT) Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Malipatlolla, D.K.; Devarakonda, S.; Bull, C.; Rascon, A.; Nyman, M.; Stringer, A.; Tremaroli, V.; Steineck, G.; Sjoberg, F. Dietary Oat Bran Reduces Systemic Inflammation in Mice Subjected to Pelvic Irradiation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Kim, S.; Guo, W.; Collins, F.W.; Wise, M.L.; Meydani, M. High Levels of Avenanthramides in Oat-Based Diet Further Suppress High Fat Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Ldlr(−/−) Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Wise, M.L.; Collins, F.W.; Meydani, M. Avenanthramides, polyphenols from oats, inhibit IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovska, M.; Abdi, Z.; Murdjeva, M.; Macedo, D.; Maes, A.; Maes, M. CCL-11 or Eotaxin-1: An Immune Marker for Ageing and Accelerated Ageing in Neuro-Psychiatric Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ms Wolever, T.; Rahn, M.; Dioum, E.; Spruill, S.E.; Ezatagha, A.; Campbell, J.E.; Jenkins, A.L.; Chu, Y. An Oat beta-Glucan Beverage Reduces LDL Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Men and Women with Borderline High Cholesterol: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, N.; Gao, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Hastie, T.; Cui, L.; Kuznetsova, T.; Rosenberg-Hasson, Y.; Ostan, R.; Monti, D.; Lehallier, B.; et al. An Inflammatory Clock Predicts Multi-morbidity, Immunosenescence and Cardiovascular Aging in Humans. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Virani, S.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Delling, F.N.; Deo, R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e67–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feingold, K.R. The Effect of Diet on Cardiovascular Disease and Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Orr, S.S.; Furman, D. Variability in the immune system: Of vaccine responses and immune states. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaluddin, M.S.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Rafael, C.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Eotaxin increases monolayer permeability of human coronary artery endothelial cells. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccoli, G.; Calvieri, C.; Flego, D.; Scalone, G.; Imaeva, A.; Sabato, V.; Schiavino, D.; Liuzzo, G.; Crea, F. Allergic Inflammation Is Associated With Coronary Instability and a Worse Clinical Outcome After Acute Myocardial Infarction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 8, e002554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccoli, G.; Cosentino, N. Eosinophils: A new player in coronary atherosclerotic disease. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Bobryshev, Y.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Macrophage-mediated cholesterol handling in atherosclerosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, R.; van Klinken, B.J. The future of oats in the food and health continuum. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112 (Suppl. S2), S75–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, D.J. Impact of whole grains on the gut microbiota: The next frontier for oats? Br. J. Nutr 2014, 112 (Suppl. S2), S44–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, S.A.; Kamil, A.; Fleige, L.; Gahan, C.G.M. The Cholesterol-Lowering Effect of Oats and Oat Beta Glucan: Modes of Action and Potential Role of Bile Acids and the Microbiome. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, N.; Browne, R.W.; Fellows Maxwell, K.; Bodziak, M.L.; Jakimovski, D.; Hagemeier, J.; Bergsland, N.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Zivadinov, R.; Ramanathan, M. Cholesterol and neurodegeneration: Longitudinal changes in serum cholesterol biomarkers are associated with new lesions and gray matter atrophy in multiple sclerosis over 5 years of follow-up. Eur. J. Neurol 2020, 27, 188–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.P.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Toh, B.H.; McLean, C.; Li, H. Cholesterol involvement in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2010, 43, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, U.; Park, S.J.; Park, S.M. Cholesterol Metabolism in the Brain and Its Association with Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Neurobiol. 2019, 28, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Lee, H.-J.; Yang, J.Y.; Shin, H.-L.; Choi, S.-W.; Kim, J.-K.; Seo, W.D.; Kim, E.H. The Potential Neuroprotective Effects of Extracts from Oat Seedlings against Alzheimer’s Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, F.; Masson, L.F.; Boffetta, P.; Kris-Etherton, P. Oats and bowel disease: A systematic literature review. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112 (Suppl. S2), S31–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, M.L.; Tzounis, X.; Tuohy, K.M.; Lovegrove, J.A. Hypocholesterolemic and Prebiotic Effects of a Whole-Grain Oat-Based Granola Breakfast Cereal in a Cardio-Metabolic “At Risk” Population. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, C.R.; Fulgoni, V.L., 3rd; Devareddy, L. Ten-year trends in fiber and whole grain intakes and food sources for the United States population: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001–2010. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dioum, E.H.M.; Schneider, K.L.; Vigerust, D.J.; Cox, B.D.; Chu, Y.; Zachwieja, J.J.; Furman, D. Oats Lower Age-Related Systemic Chronic Inflammation (iAge) in Adults at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4471. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214471
Dioum EHM, Schneider KL, Vigerust DJ, Cox BD, Chu Y, Zachwieja JJ, Furman D. Oats Lower Age-Related Systemic Chronic Inflammation (iAge) in Adults at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients. 2022; 14(21):4471. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214471
Chicago/Turabian StyleDioum, El Hadji M., Kevin L. Schneider, David J. Vigerust, Bryan D. Cox, YiFang Chu, Jeffery J. Zachwieja, and David Furman. 2022. "Oats Lower Age-Related Systemic Chronic Inflammation (iAge) in Adults at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease" Nutrients 14, no. 21: 4471. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214471
APA StyleDioum, E. H. M., Schneider, K. L., Vigerust, D. J., Cox, B. D., Chu, Y., Zachwieja, J. J., & Furman, D. (2022). Oats Lower Age-Related Systemic Chronic Inflammation (iAge) in Adults at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients, 14(21), 4471. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214471





