Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Tendency to Orthorexia Nervosa in Professional Athletes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Questionnaires
- Walking MET min/week = 3.3 × walking minutes × walking days
- Moderate MET min/week = 4.0 × moderate activity minutes × moderate days
- Vigorous MET min/week = 8.0 × vigorous activity minutes × vigorous days
- Total MET min/week = walking + moderate + vigorous MET min/week scores
2.4. Survey Pre-Testing
2.5. Statistical Analyses
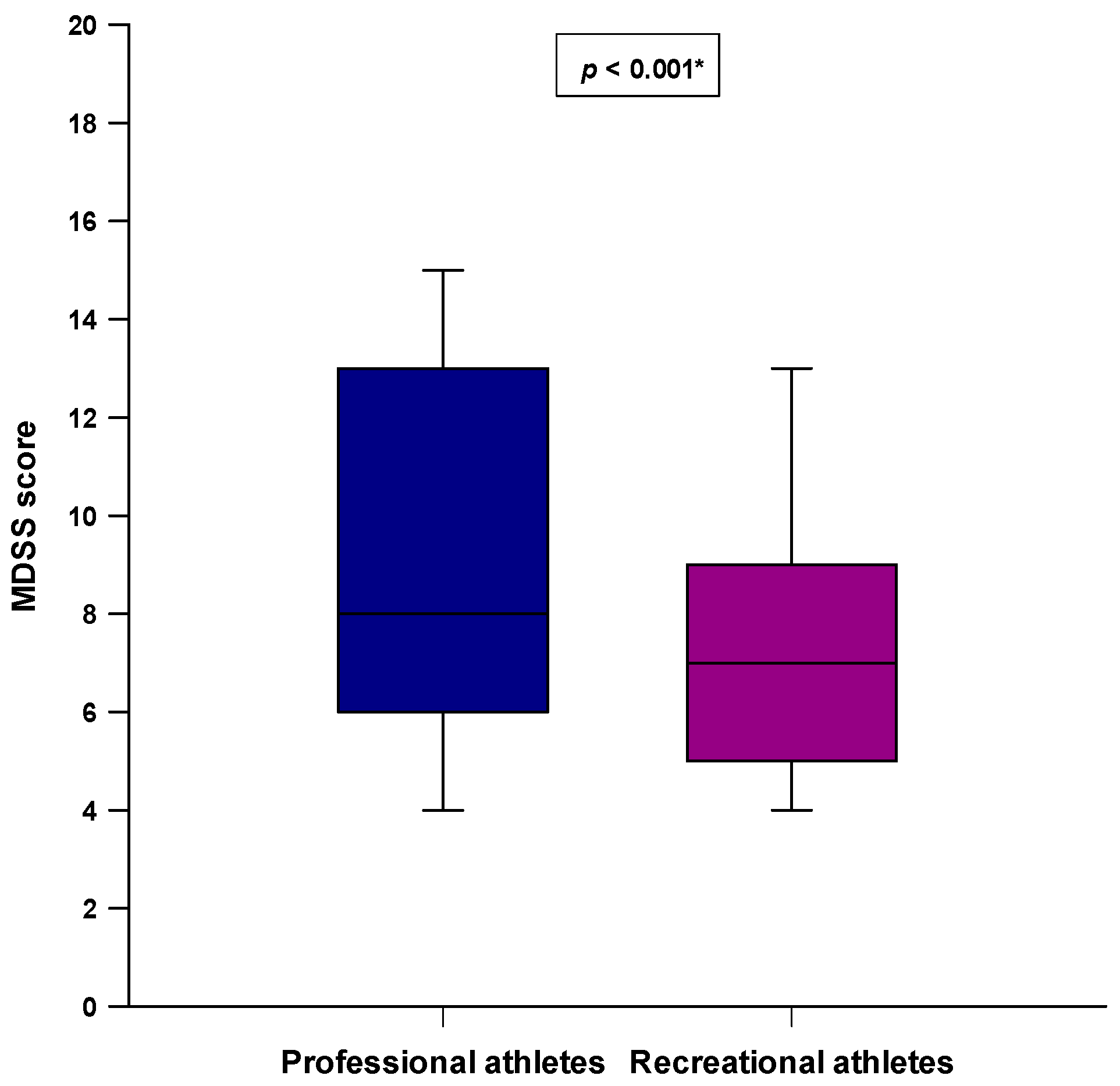
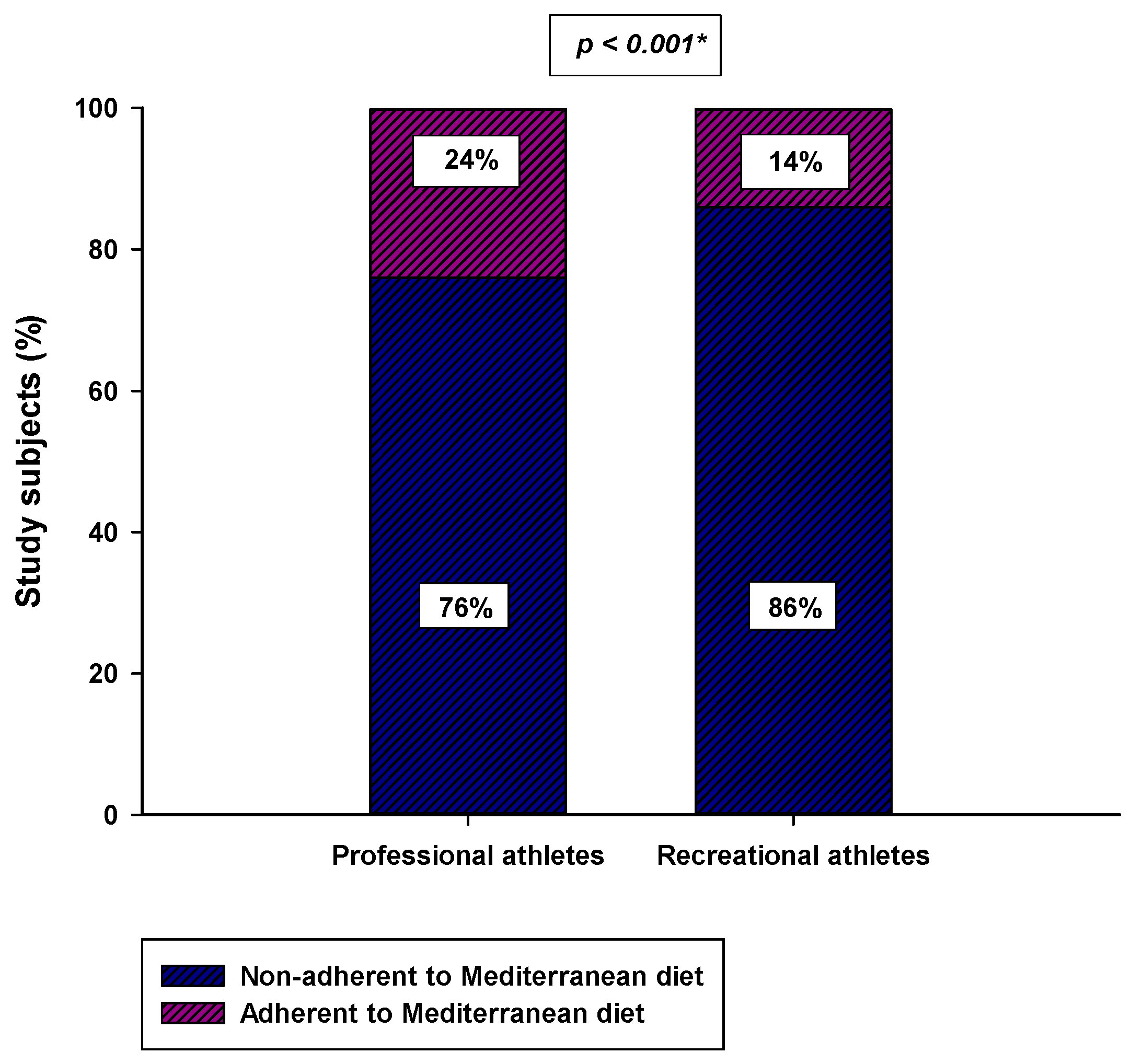
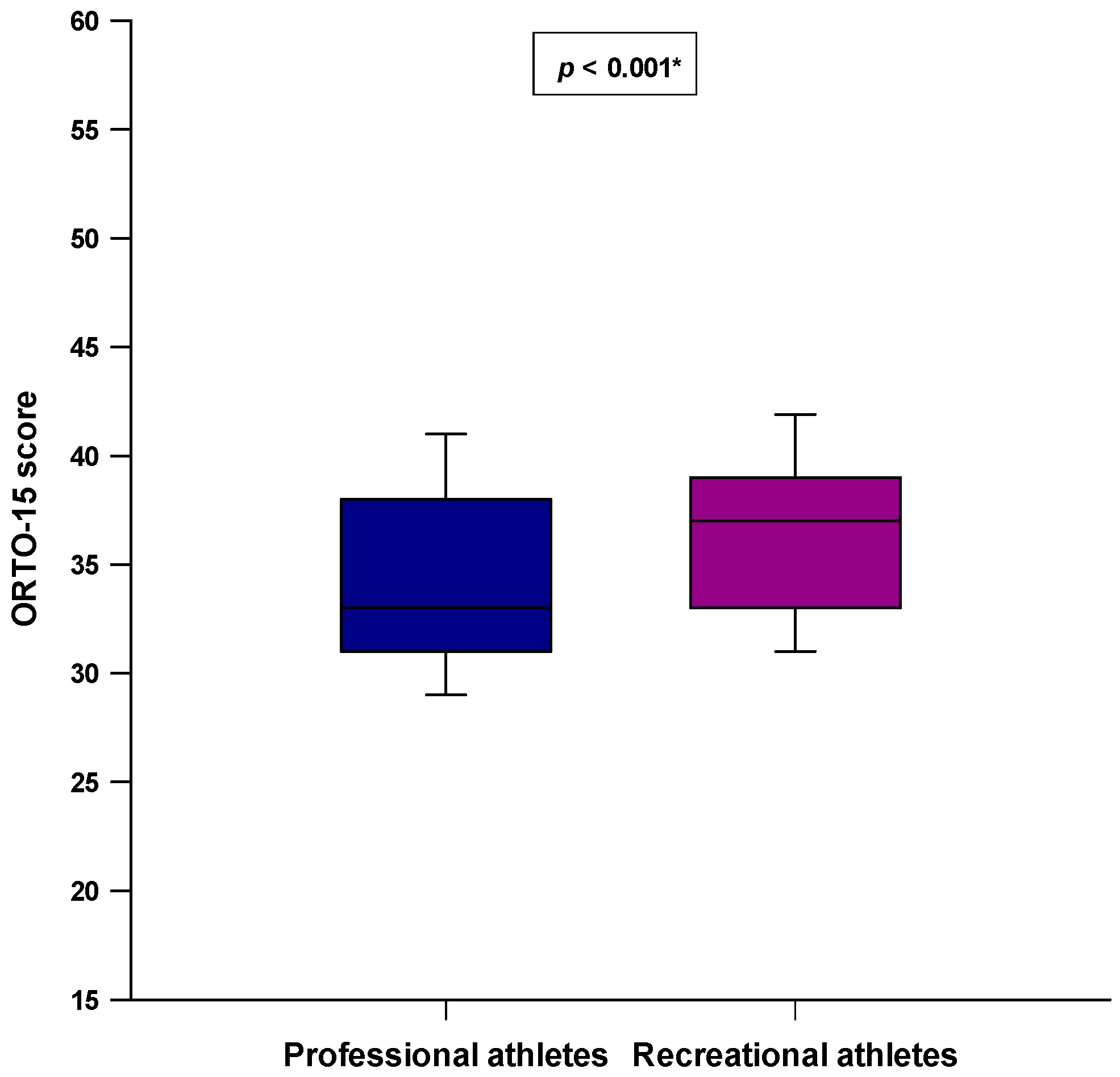
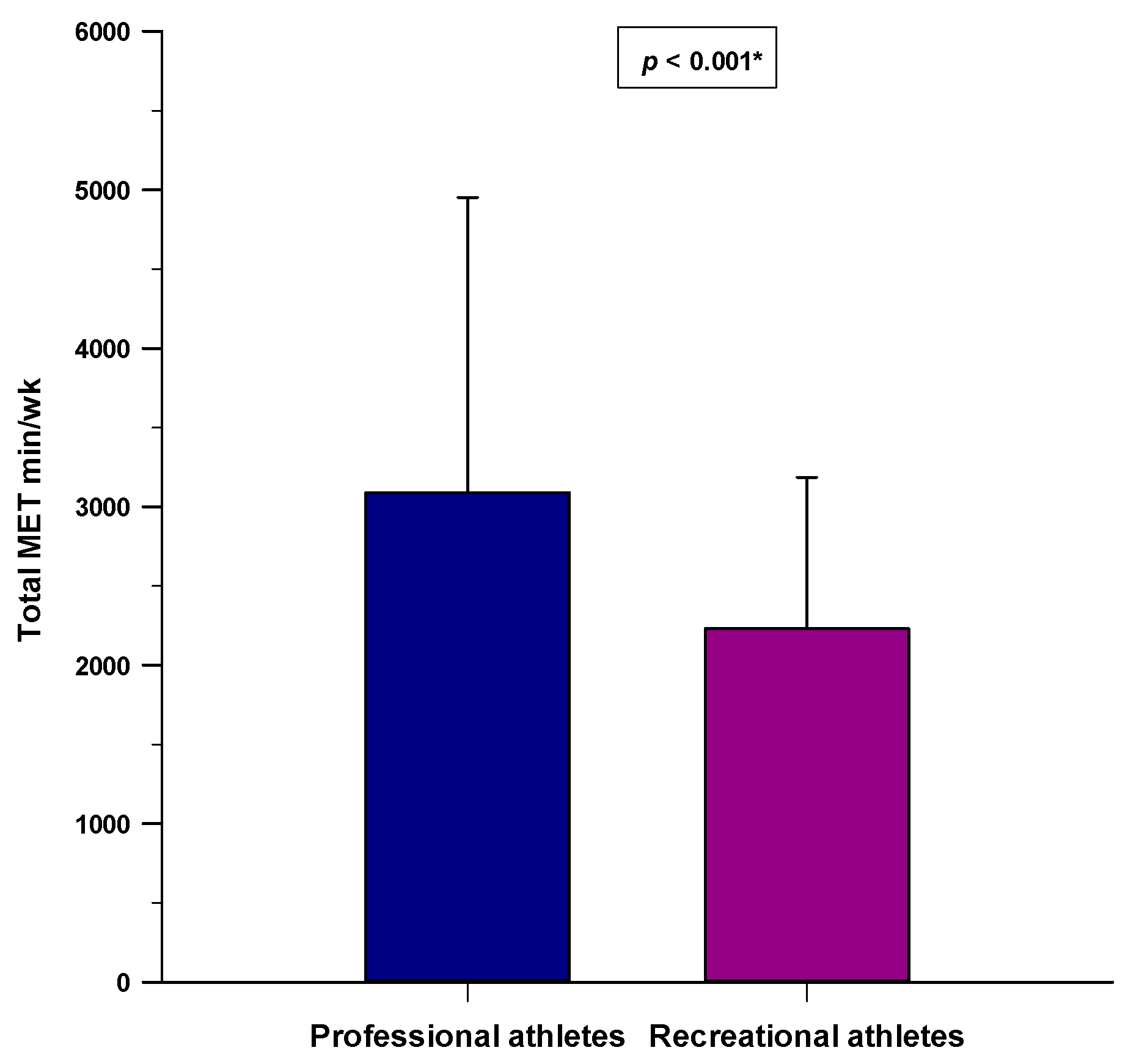
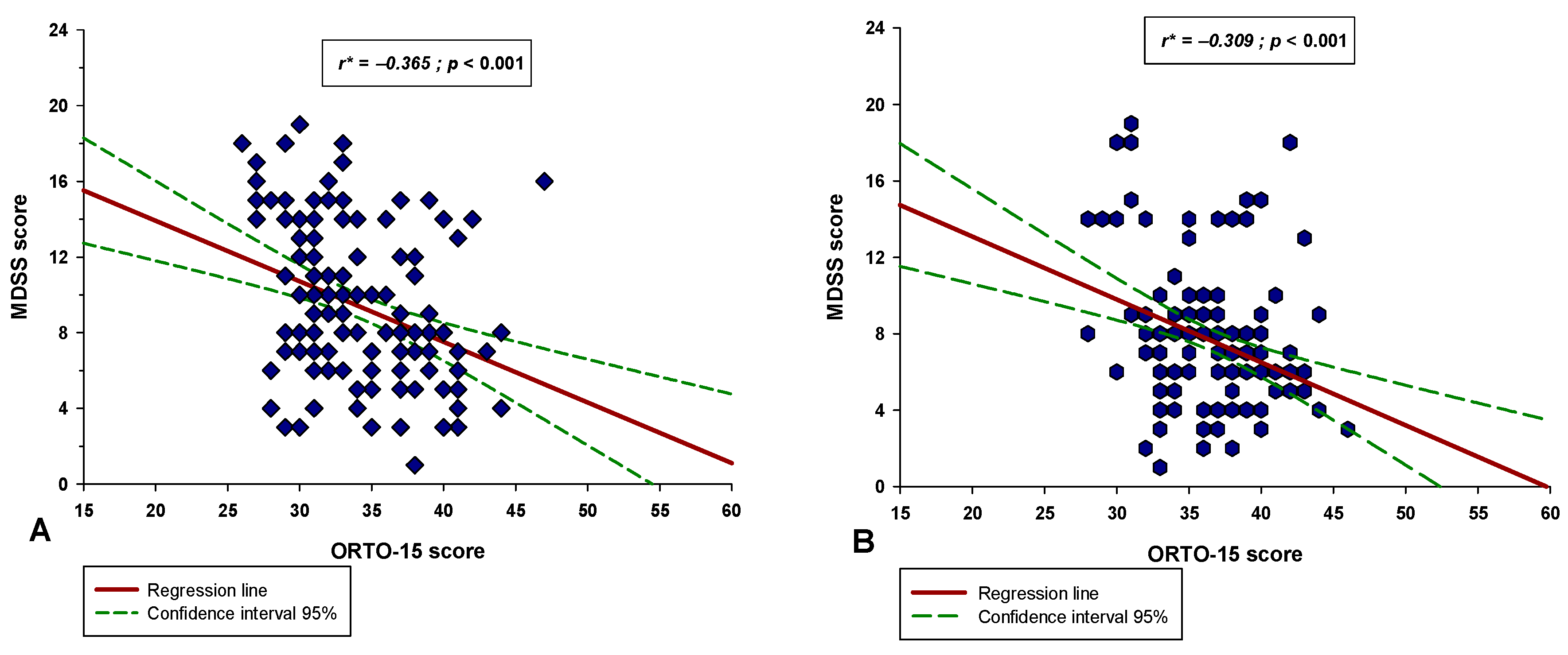
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guest, N.S.; Horne, J.; Vanderhout, S.; El-Sohemy, A. Sport Nutrigenomics: Personalized Nutrition for Athletic Performance. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.; Thomson, J.S.; Swift, R.J.; von Hurst, P.R. Role of nutrition in performance enhancement and postexercise recovery. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2015, 6, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinovic, D.; Tokic, D.; Vilovic, M.; Rusic, D.; Bukic, J.; Bozic, J. Sport Dietary Supplements and Physical Activity in Biomedical Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerksick, C.M.; Arent, S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Stout, J.R.; Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.D.; Taylor, L.; Kalman, D.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Kreider, R.B.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Nutrient timing. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cena, H.; Calder, P.C. Defining a Healthy Diet: Evidence for the Role of Contemporary Dietary Patterns in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinovic, D.; Tokic, D.; Martinovic, L.; Kumric, M.; Vilovic, M.; Rusic, D.; Vrdoljak, J.; Males, I.; Kurir, T.T.; Lupi-Ferandin, S.; et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Its Association with the Level of Physical Activity in Fitness Center Users: Croatian-Based Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.; Bryan, J.; Hodgson, J.; Murphy, K. Definition of the Mediterranean Diet; A Literature Review. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9139–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Willett, W.C. The Mediterranean diet and health: A comprehensive overview. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minzer, S.; Estruch, R.; Casas, R.; Ding, C.; O’Neill, D.; Bell, S.; Stamatakis, E.; Britton, A.; Zatońska, K.; Psikus, P.; et al. Wine Intake in the Framework of a Mediterranean Diet and Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases: A Short Literature Review of the Last 5 Years. Molecules 2020, 25, 5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lăcătușu, C.-M.; Grigorescu, E.-D.; Floria, M.; Onofriescu, A.; Mihai, B.-M. The Mediterranean Diet: From an Environment-Driven Food Culture to an Emerging Medical Prescription. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klimova, B.; Novotny, M.; Schlegel, P.; Valis, M. The Effect of Mediterranean Diet on Cognitive Functions in the Elderly Population. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milenkovic, T.; Bozhinovska, N.; Macut, D.; Bjekic-Macut, J.; Rahelic, D.; Asimi, Z.V.; Burekovic, A. Mediterranean Diet and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Perpetual Inspiration for the Scientific World. A Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nani, A.; Murtaza, B.; Khan, A.S.; Khan, N.; Hichami, A. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Polyphenols Contained in Mediterranean Diet in Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms. Molecules 2021, 26, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, R.J.; Flammer, A.J.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. The Mediterranean Diet, its Components, and Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skarupski, K.A.; Tangney, C.C.; Li, H.; Evans, D.A.; Morris, M.C. Mediterranean diet and depressive symptoms among older adults over time. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tosti, V.; Bertozzi, B.; Fontana, L. Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sureda, A.; Del Mar Bibiloni, M.; Julibert, A.; Bouzas, C.; Argelich, E.; Llompart, I.; Pons, A.; Tur, J.A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Inflammatory Markers. Nutrients 2018, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarff, J.R. Orthorexia nervosa: An obsession with healthy eating. Fed. Pract. 2017, 34, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Strahler, J.; Hermann, A.; Walter, B.; Stark, R. Orthorexia nervosa: A behavioral complex or a psychological condition? J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håman, L.; Barker-Ruchti, N.; Patriksson, G.; Lindgren, E.-C. Orthorexia nervosa: An integrative literature review of a lifestyle syndrome. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well-Being 2015, 10, 26799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.G.; Lefevre, C.E. Instagram use is linked to increased symptoms of orthorexia nervosa. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2017, 22, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alacid, F.; Vaquero-Cristóbal, R.; Sánchez-Pato, A.; Muyor, J.M.; López-Miñarro, P. Ángel [Habit based consumptions in the mediterranean diet and the relationship with anthropometric parameters in young female kayakers]. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 29, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Benito, J.L.; Sánchez-Soriano, E.; Suárez, J.G. Assessment of the Mediterranean Diet Adequacy Index of a collective of young cyclists. Nutr. Hosp. 2009, 24, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio-Arias, J.; Ramos Campo, D.J.; Ruiloba Nuñez, J.M.; Carrasco Poyatos, M.; Alcaraz Ramón, P.E.; Jiménez Díaz, F.J. Adherence to a mediterranean diet and sport performance in a elite female athletes futsal population. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 2276–2282. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, C.M.; Simón-Grima, J.; Peñarrubia-Lozano, C.; Izquierdo, D.M.; Moliner-Urdiales, D.; Arrese, A.L. Exercise addiction risk and health in male and female amateur endurance cyclists. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muros, J.J.; Zabala, M. Differences in Mediterranean Diet Adherence between Cyclists and Triathletes in a Sample of Spanish Athletes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passariello, C.L.; Marchionni, S.; Carcuro, M.; Casali, G.; Della Pasqua, A.; Hrelia, S.; Malaguti, M.; Lorenzini, A. The Mediterranean Athlete’s Nutrition: Are Protein Supplements Necessary? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bert, F.; Gualano, M.R.; Voglino, G.; Rossello, P.; Perret, J.P.; Siliquini, R. Orthorexia Nervosa: A cross-sectional study among athletes competing in endurance sports in Northern Italy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surała, O.; Malczewska-Lenczowska, J.; Sadowska, D.; Grabowska, I.; Białecka-Dębek, A. Traits of Orthorexia Nervosa and the Determinants of These Behaviors in Elite Athletes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-García, C.; Papaianni, M.C.; Caglioti, F.; Procopio, L.; Nisticò, C.G.; Bombardiere, L.; Ammendolia, A.; Rizza, P.; De Fazio, P.; Capranica, L. Orthorexia nervosa: A frequent eating disordered behavior in athletes. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2012, 17, e226–e233. [Google Scholar]
- Sember, V.; Meh, K.; Sorić, M.; Starc, G.; Rocha, P.; Jurak, G. Validity and Reliability of International Physical Activity Questionnaires for Adults across EU Countries: Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Whitt, M.C.; Irwin, M.L.; Swartz, A.M.; Strath, S.J.; O’Brien, W.L.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Schmitz, K.H.; Emplaincourt, P.O.; et al. Compendium of Physical Activities: An update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, S498–S516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monteagudo, C.; Mariscal-Arcas, M.; Rivas, A.; Lorenzo-Tovar, M.L.; Tur, J.A.; Olea-Serrano, F. Proposal of a Mediterranean Diet Serving Score. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marendić, M.; Polić, N.; Matek, H.; Oršulić, L.; Polašek, O.; Kolčić, I. Mediterranean diet assessment challenges: Validation of the Croatian Version of the 14-item Mediterranean Diet Serving Score (MDSS) Questionnaire. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Marsili, D.; Graziani, M.P.; Imbriale, M.; Cannella, C. Orthorexia nervosa: Validation of a diagnosis questionnaire. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2005, 10, e28–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, M.; Thege, B.K.; Dukay-Szabó, S.; Túry, F.; Van Furth, E.F. When eating healthy is not healthy: Orthorexia nervosa and its measurement with the ORTO-15 in Hungary. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramacciotti, C.E.; Perrone, P.; Coli, E.; Burgalassi, A.; Conversano, C.; Massimetti, G.; Dell’Osso, L. Orthorexia nervosa in the general population: A preliminary screening using a self-administered questionnaire (ORTO-15). Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2011, 16, e127–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Zoccali, R.; Ponzo, V.; Soldati, L.; De Carli, L.; Benso, A.; Fea, E.; Rainoldi, A.; Durazzo, M.; Fassino, S.; et al. University courses, eating problems and muscle dysmorphia: Are there any associations? J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosele, J.I.; Motilva, M.-J. Phenol Biological Metabolites as Food Intake Biomarkers, a Pending Signature for a Complete Understanding of the Beneficial Effects of the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Ortega, F.; Román-Mata, S.S.; Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Castro-Sánchez, M.; Muros, J.J. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Is Associated with Physical Activity, Self-Concept and Sociodemographic Factors in University Student. Nutrients 2018, 10, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobo-Cuenca, A.I.; Garrido-Miguel, M.; Soriano-Cano, A.; Ferri-Morales, A.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Espínosa, N.M.M. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Its Association with Body Composition and Physical Fitness in Spanish University Students. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clifford, T.; Blyth, C. A pilot study comparing the prevalence of orthorexia nervosa in regular students and those in University sports teams. Eat. Weight Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2019, 24, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yılmaz, H.; Karakuş, G.; Tamam, L.; Demirkol, M.E.; Namlı, Z.; Yeşiloğlu, C. Association of Orthorexic Tendencies with Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms, Eating Attitudes and Exercise. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 3035–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Study Sample N = 300 | Professional Group N = 150 | Recreational Group N = 150 | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex (N, %) | 165 (55.0) | 87 (58.0) | 78 (52.0) | 0.353 |
| Age (years) | 24.2 ± 4.8 | 24.5 ± 4.0 | 24.0 ± 5.5 | 0.314 |
| Weight (kg) | 80.8 ± 15.5 | 84.1 ± 16.5 | 77.6 ± 13.8 | <0.001 |
| Height (cm) | 180.3 ± 10.4 | 183.2 ± 10.8 | 177.4 ± 9.2 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.2 ± 4.4 | 24.8 ± 3.3 | 23.8 ± 3.0 | <0.001 |
| Education level | ||||
| Elementary school (N, %) | 2 (0.7) | 2 (1.3%) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| High school (N, %) | 108 (36.0) | 55 (36.7) | 53 (35.3) | |
| Bachelor’s degree (N, %) | 73 (24.3) | 52 (34.7) | 21 (14.0) | |
| Master’s degree (N, %) | 117 (39.0) | 41 (27.3) | 76 (50.7) |
| Parameter | Study Sample N = 300 | Professional N = 150 | Recreational N = 150 | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cereals (N, %) | 61 (20.3) | 27 (18.0) | 34 (22.7) | 0.389 |
| Potatoes (N, %) | 272 (90.7) | 135 (90.0) | 137 (91.3) | 0.842 |
| Olive oil (N, %) | 70 (23.3) | 52 (34.7) | 21 (14.0) | <0.001 |
| Nuts (N, %) | 104 (34.7) | 56 (37.3) | 48 (32.0) | 0.395 |
| Fruits (N, %) | 68 (22.7) | 42 (28.0) | 28 (18.7) | 0.076 |
| Vegetables (N, %) | 80 (26.7) | 52 (34.7) | 32 (21.3) | 0.014 |
| Dairy (N, %) | 64 (21.3) | 45 (30.0) | 19 (12.7) | <0.001 |
| Legumes (N, %) | 221 (73.7) | 95 (63.3) | 126 (84.4) | <0.001 |
| Eggs (N, %) | 171 (57.0) | 79 (52.7) | 93 (62.0) | 0.129 |
| Fish (N, %) | 182 (60.7) | 102 (68.0) | 81 (54.0) | 0.017 |
| White meat (N, %) | 249 (83.0) | 110 (73.3) | 142 (94.7) | <0.001 |
| Red meat (N, %) | 76 (38.0) | 57 (38.0) | 22 (14.7) | <0.001 |
| Sweets (N, %) | 143 (47.7) | 95 (63.3) | 52 (34.7) | <0.001 |
| Wine (N, %) | 15 (5.0) | 1 (0.7) | 15 (10.0) | <0.001 |
| Parameter | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.025 | 0.971 to 1.081 | 0.369 |
| Female sex 1 | 1.401 | 0.826 to 2.376 | 0.210 |
| BMI | 0.994 | 0.938 to 1.053 | 0.834 |
| MDSS score | 1.074 | 0.997 to 1.058 | 0.049 |
| Total MET min/week | 1.0005 | 1.0003 to 1.0007 | <0.001 |
| Professional athlete group 2 | 1.966 | 1.160 to 3.332 | 0.012 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinovic, D.; Tokic, D.; Martinovic, L.; Vilovic, M.; Vrdoljak, J.; Kumric, M.; Bukic, J.; Ticinovic Kurir, T.; Tavra, M.; Bozic, J. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Tendency to Orthorexia Nervosa in Professional Athletes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020237
Martinovic D, Tokic D, Martinovic L, Vilovic M, Vrdoljak J, Kumric M, Bukic J, Ticinovic Kurir T, Tavra M, Bozic J. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Tendency to Orthorexia Nervosa in Professional Athletes. Nutrients. 2022; 14(2):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020237
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinovic, Dinko, Daria Tokic, Lovre Martinovic, Marino Vilovic, Josip Vrdoljak, Marko Kumric, Josipa Bukic, Tina Ticinovic Kurir, Marino Tavra, and Josko Bozic. 2022. "Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Tendency to Orthorexia Nervosa in Professional Athletes" Nutrients 14, no. 2: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020237
APA StyleMartinovic, D., Tokic, D., Martinovic, L., Vilovic, M., Vrdoljak, J., Kumric, M., Bukic, J., Ticinovic Kurir, T., Tavra, M., & Bozic, J. (2022). Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Tendency to Orthorexia Nervosa in Professional Athletes. Nutrients, 14(2), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020237








