Healthy Lifestyle, Genetic Risk and Brain Health: A Gene-Environment Interaction Study in the UK Biobank
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Healthy Lifestyle Factors
2.3. Neuroimaging Outcomes
2.4. Genetic Risk Score
2.5. Statistical Analysis
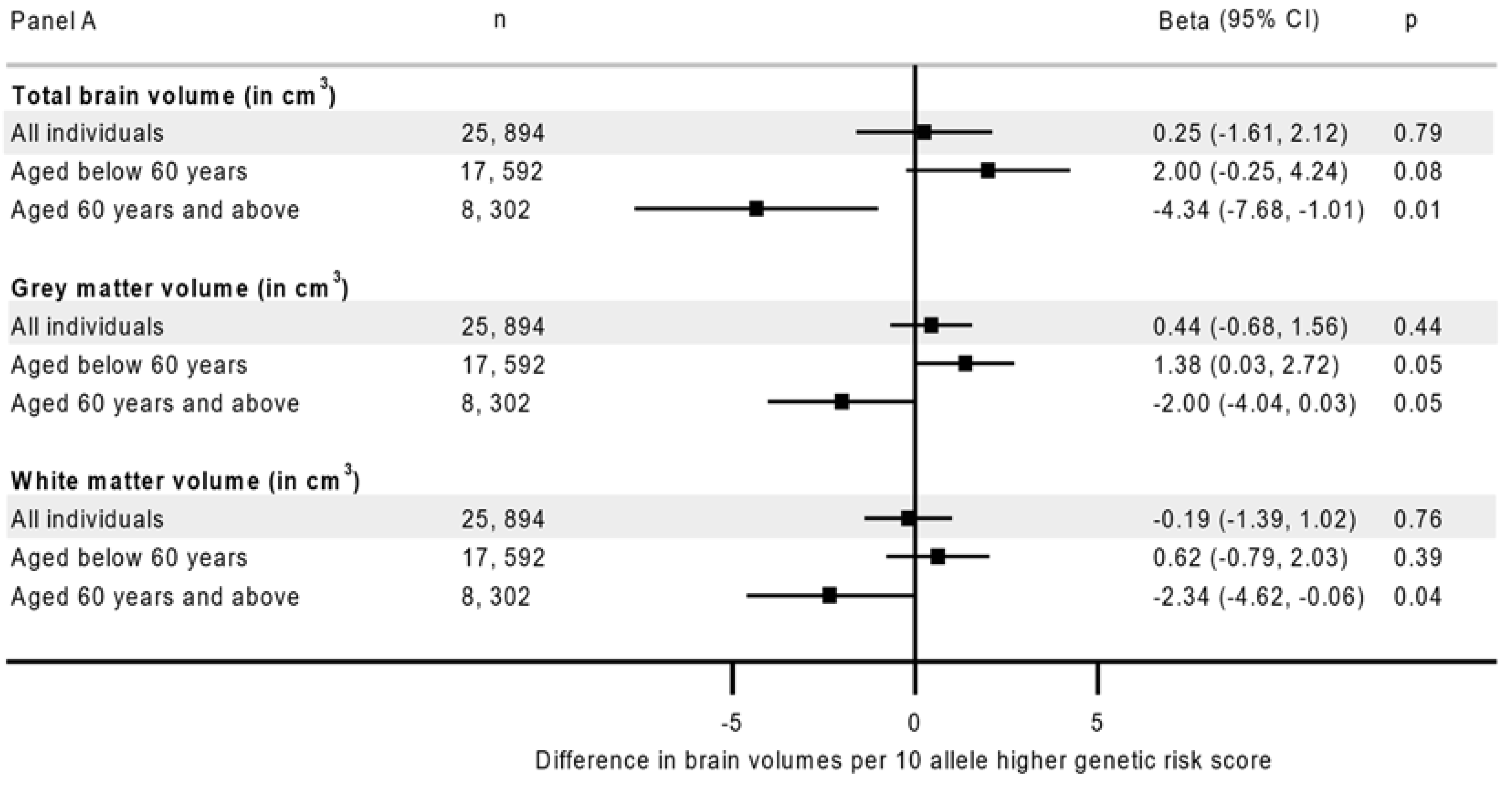
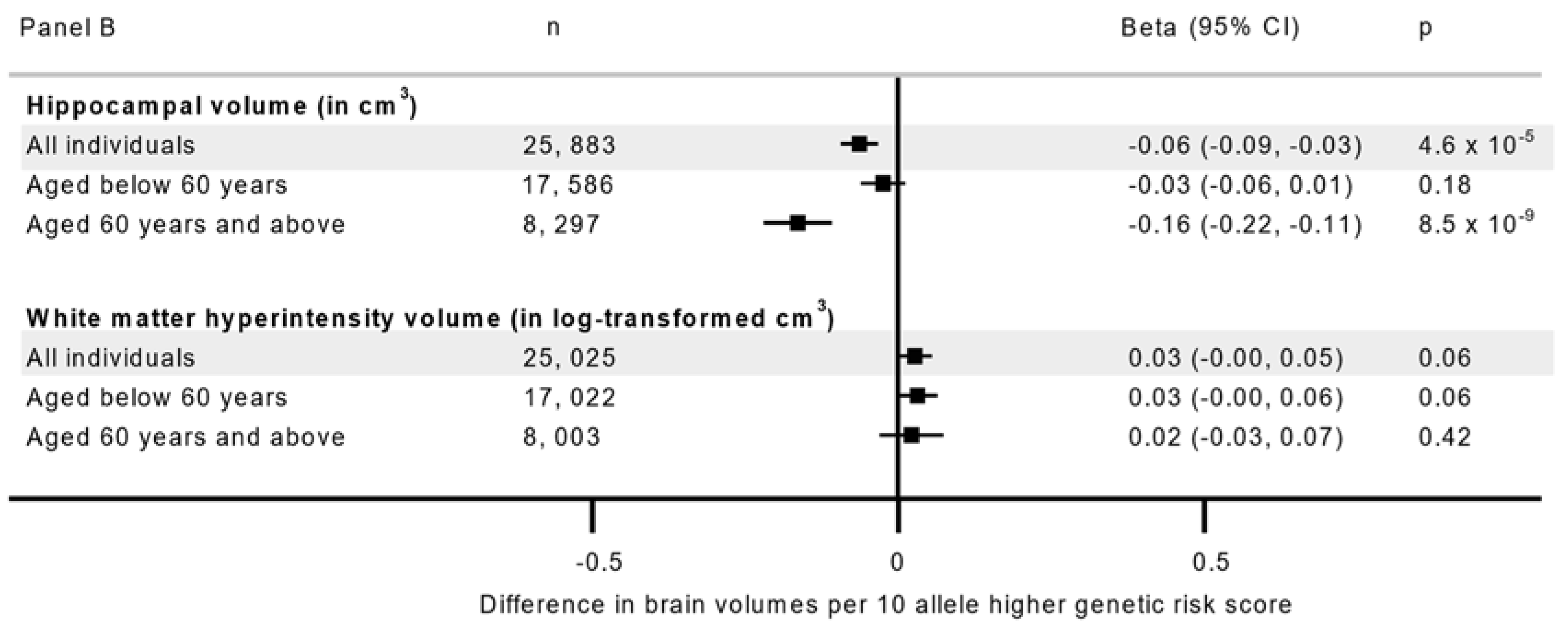
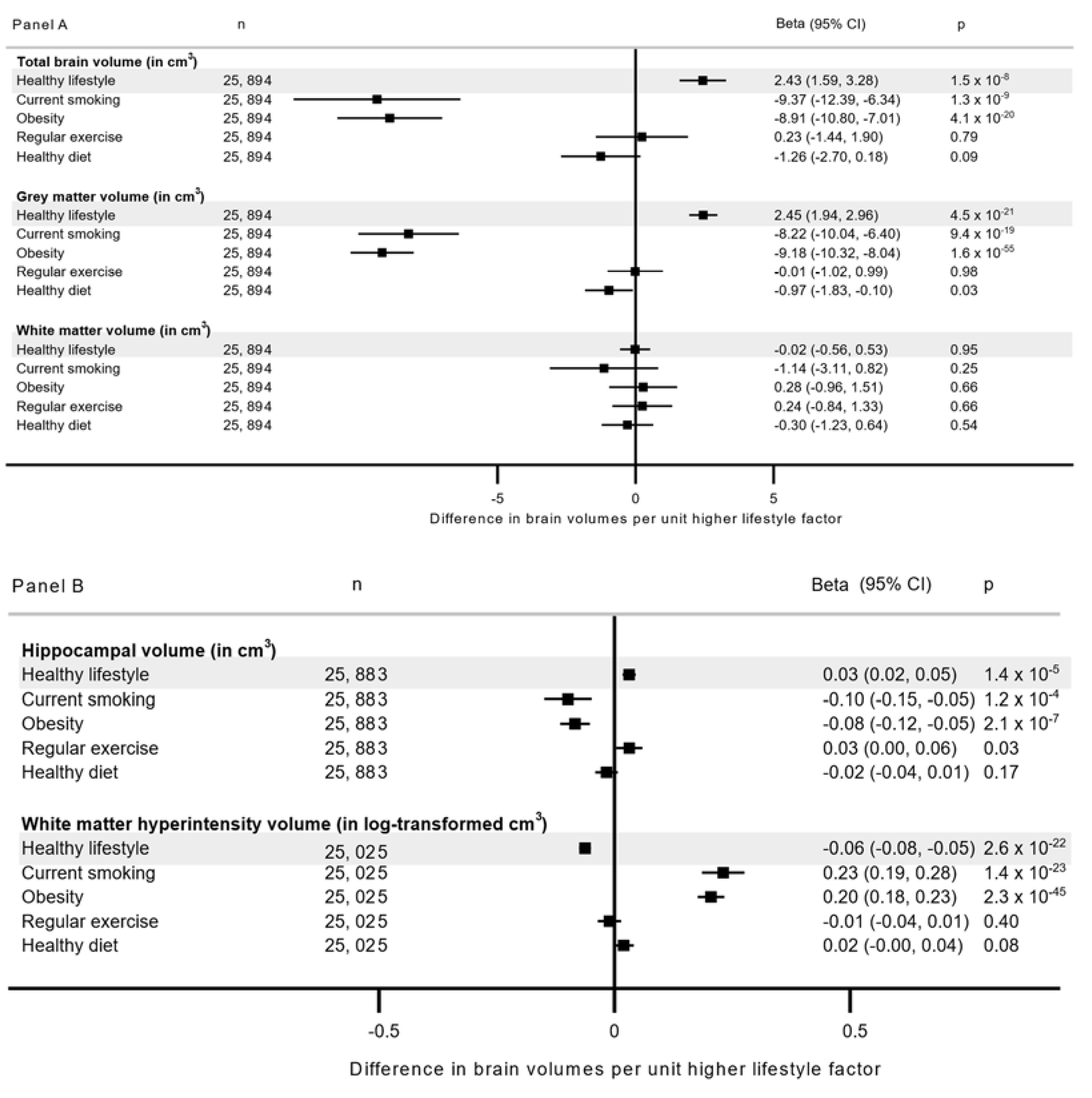
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Dementia; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Livingston, G.; Sommerlad, A.; Orgeta, V.; Costafreda, S.G.; Huntley, J.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care. Lancet 2017, 390, 2673–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentreau, M.; Maller, J.J.; Meslin, C.; Cyprien, F.; Ritchie, K.; Artero, S. Is hippocampal volume an accurate and reliable early marker of Alzheimer’s disease? Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, e042742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, N.D.; van Dijk, E.J.; den Heijer, T.; Vermeer, S.E.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Oudkerk, M.; Hofman, A.; Breteler, M.M.B. Cerebral White Matter Lesions and the Risk of Dementia. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Muralidharan, A.; Hakim Mohammed, A.R.; Malik, B.H. Neuroimaging in Dementia: A Brief Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navale, S.S.; Mulugeta, A.; Zhou, A.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Hyppönen, E. Vitamin D and brain health: An observational and Mendelian randomization study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Beydoun, H.A.; Gamaldo, A.A.; Teel, A.; Zonderman, A.B.; Wang, Y. Epidemiologic studies of modifiable factors associated with cognition and dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-T.; Xu, W.; Tan, C.-C.; Andrieu, S.; Suckling, J.; Evangelou, E.; Pan, A.; Zhang, C.; Jia, J.; Feng, L. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, C.; Pêgo, J.; Santos, N. Effects of physical activity on brain function and structure in older adults: A systematic review. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 402, 113061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.E.; Leoni, V.; Klein-Flügge, M.C.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Suri, S. Associations of dietary markers with brain volume and connectivity: A systematic review of MRI studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngandu, T.; Lehtisalo, J.; Solomon, A.; Levälahti, E.; Ahtiluoto, S.; Antikainen, R.; Bäckman, L.; Hänninen, T.; Jula, A.; Laatikainen, T.; et al. A 2 year multidomain intervention of diet, exercise, cognitive training, and vascular risk monitoring versus control to prevent cognitive decline in at-risk elderly people (FINGER): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, R.; Liu, Y.; Ngandu, T.; Antikainen, R.; Hulkkonen, J.; Koikkalainen, J.; Kemppainen, N.; Lötjönen, J.; Levälahti, E.; Parkkola, R.; et al. Brain volumes and cortical thickness on MRI in the Finnish Geriatric Intervention Study to Prevent Cognitive Impairment and Disability (FINGER). Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Andújar, M.; Morales-García, E.; García-Casares, N. Obesity and Gray Matter Volume Assessed by Neuroimaging: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbejjani, M.; Auer, R.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Haight, T.; Davatzikos, C.; Goff, D.C., Jr.; Bryan, R.N.; Launer, L.J. Cigarette smoking and gray matter brain volumes in middle age adults: The CARDIA Brain MRI sub-study. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.C.; Thompson, M.; Bachman, C.; Owens, M.M.; Murphy, M.; Palmer, R. Associations of cigarette smoking with gray and white matter in the UK Biobank. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 45, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pase, M.P.; Himali, J.J.; Jacques, P.F.; DeCarli, C.; Satizabal, C.L.; Aparicio, H.; Vasan, R.S.; Beiser, A.S.; Seshadri, S. Sugary beverage intake and preclinical Alzheimer’s disease in the community. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Brickman, A.M.; Stern, Y.; Habeck, C.G.; Razlighi, Q.R.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Manly, J.J.; Schupf, N.; Mayeux, R.; Scarmeas, N. Mediterranean diet and brain structure in a multiethnic elderly cohort. Neurology 2015, 85, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.C.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Harold, D.; Naj, A.C.; Sims, R.; Bellenguez, C.; DeStafano, A.L.; Bis, J.C.; Beecham, G.W.; Grenier-Boley, B.; et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK biobank: An open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlejohns, T.J.; Holliday, J.; Gibson, L.M.; Garratt, S.; Oesingmann, N.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Bell, J.D.; Boultwood, C.; Collins, R.; Conroy, M.C.; et al. The UK Biobank imaging enhancement of 100,000 participants: rationale, data collection, management and future directions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.L.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Bangerter, N.K.; Thomas, D.L.; Yacoub, E.; Xu, J.; Bartsch, A.J.; Jbabdi, S.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Andersson, J.L.; et al. Multimodal population brain imaging in the UK Biobank prospective epidemiological study. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Jenkinson, M.; Bangerter, N.K.; Andersson, J.L.R.; Griffanti, L.; Douaud, G.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Jbabdi, S.; Hernandez-Fernandez, M.; Vallee, E.; et al. Image processing and Quality Control for the first 10,000 brain imaging datasets from UK Biobank. NeuroImage 2018, 166, 400–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’Connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulugeta, A.; Lumsden, A.; Hyppönen, E. Unlocking the causal link of metabolically different adiposity subtypes with brain volumes and the risks of dementia and stroke: A Mendelian randomization study. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 102, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, H.; McNaughton, S.A.; Lamb, K.E.; Milte, C.M. Associations of Diet Quality with Midlife Brain Volume: Findings from the UK Biobank Cohort Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 84, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, G.; Adams, H.H.; Bis, J.C.; Weinstein, G.; Yu, L.; Töglhofer, A.M.; Smith, A.V.; Van Der Lee, S.J.; Gottesman, R.F.; Thomson, R. Association of Alzheimer’s disease GWAS loci with MRI markers of brain aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1765.e7–1765.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, R.; Ward, J.; Flegal, K.E.; Smith, D.J.; Bailey, M.E.S.; Cavanagh, J.; Lyall, D.M. Association between polygenic risk for Alzheimer’s disease, brain structure and cognitive abilities in UK Biobank. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 47, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, A.; Anderson, C.D.; Desikan, R.S.; Sabuncu, M.; Cortellini, L.; Schmansky, N.; Salat, D.; Rosand, J.; Initiative, A.s.D.N. Genetic Variation and Neuroimaging Measures in Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, A.L.; Mulugeta, A.; Zhou, A.; Hyppönen, E. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotype-associated disease risks: A phenome-wide, registry-based, case-control study utilising the UK Biobank. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondadori, C.R.; de Quervain, D.J.; Buchmann, A.; Mustovic, H.; Wollmer, M.A.; Schmidt, C.F.; Boesiger, P.; Hock, C.; Nitsch, R.M.; Papassotiropoulos, A.; et al. Better memory and neural efficiency in young apolipoprotein E epsilon4 carriers. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 1934–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourida, I.; Hannon, E.; Littlejohns, T.J.; Langa, K.M.; Hyppönen, E.; Kuźma, E.; Llewellyn, D.J. Association of lifestyle and genetic risk with incidence of dementia. Jama 2019, 322, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampe, L.; Zhang, R.; Beyer, F.; Huhn, S.; Kharabian Masouleh, S.; Preusser, S.; Bazin, P.L.; Schroeter, M.L.; Villringer, A.; Witte, A.V. Visceral obesity relates to deep white matter hyperintensities via inflammation. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, P.; Hinder, L.M.; Callaghan, B.C.; Feldman, E.L. Neurological consequences of obesity. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, T.C.; Mattsson, N.; Weiner, M.W.; Initiative, A.s.D.N. Smoking and increased Alzheimer’s disease risk: A review of potential mechanisms. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, S122–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haast, R.A.M.; Kiliaan, A.J. Impact of fatty acids on brain circulation, structure and function. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2015, 92, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchio, L.M.; Meng, Y.; Xhima, K.; Lipsman, N.; Hamani, C.; Aubert, I. The Neuroprotective Effects of Exercise: Maintaining a Healthy Brain Throughout Aging. Brain Plast. 2018, 4, 17–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, N.; Okamura, T. Cigarette smoking impairs nitric oxide-mediated cerebral blood flow increase: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 131, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, A.; Littlejohns, T.J.; Sudlow, C.; Doherty, N.; Adamska, L.; Sprosen, T.; Collins, R.; Allen, N.E. Comparison of sociodemographic and health-related characteristics of UK Biobank participants with those of the general population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 186, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaresko, J.; Lellmann, A.W.; Schmidt, A.; Lehmann, A.; Amini, A.M.; Egert, S.; Schlesinger, S.; Nöthlings, U. Dietary Factors and Neurodegenerative Disorders: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Prospective Studies. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2020, 11, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, H.L.; Igo, I. Genetics of Dementia. Skull Base 2011, 31, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marden, J.R.; Walter, S.; Tchetgen, E.J.T.; Kawachi, I.; Glymour, M.M. Validation of a polygenic risk score for dementia in black and white individuals. Brain Behav. 2014, 4, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, G.; Einstein, S.G. Chapter 4-structural magnetic resonance imaging as a biomarker for the diagnosis, progression, and treatment of alzheimer disease. In Translational Neuroimaging, 1st ed; McArthur, R.A., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013; pp. 87–129. [Google Scholar]
- Vemuri, P.; Jackjr, C.R. Role of structural MRI in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Res. Ther. 2010, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, E.; Vermunt, L.; van der Flier, W.M.; Visser, P.J.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Tijms, B.M. Modeling grey matter atrophy as a function of time, aging or cognitive decline show different anatomical patterns in Alzheimer's disease. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 22, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hase, Y.; Horsburgh, K.; Ihara, M.; Kalaria, R.N. White matter degeneration in vascular and other ageing-related dementias. J. Neurochem. 2018, 144, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Hong, Y.; Labarthe, D.; Mozaffarian, D.; Appel, L.J.; Van Horn, L.; Greenlund, K.; Daniels, S.; Nichol, G.; Tomaselli, G.F.; et al. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: The American heart association’s strategic impact goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation 2010, 121, 586–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten-Jacobs, L.C.; Larsson, S.C.; Malik, R.; Rannikmäe, K.; Sudlow, C.; Dichgans, M.; Markus, H.S.; Traylor, M. MEGASTROKE consortium; International Stroke Genetics Consortium Genetic risk, incident stroke, and the benefits of adhering to a healthy lifestyle: Cohort study of 306 473 UK Biobank participants. BMJ 2018, 363, k4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | N(%) | Grey Matter Volume Median (IQR) | Hippocampal Volume Median (IQR) | White Matter Hyperintensities Median (IQR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 25,894 | 7792.6 (760.7, 825.2) | 10.0 (9.2, 10.7) | 3.7 (2.0, 7.4) |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 12,286 (47.4) | 776.8 (746.8, 806.4) * | 9.6 (8.9, 10.3) * | 3.8 (2.0, 7.7) |
| Women | 13,608 (52.6) | 806.9 (7768., 839.2) | 10.2 (9.6, 10.9) | 3.5 (1.9, 7.1) |
| Age | ||||
| 39–49 years | 6839 (26.4) | 829.7 (80.2, 855.8) | 10.3 (9.7, 10.9) | 2.0 (1.2, 3.4) |
| 50–59 years | 10,753 (41.5) | 794.9 (7689, 821.3) | 10.1 (9.4, 10.7) | 3.6 (2.1, 6.5) |
| 60–73 years | 8302 (32.1) | 760.9 (734.2, 786.9) * | 9.5 (8.8, 10.2) * | 6.5 (3.5, 12.4) * |
| Education | ||||
| None | 1535 (5.9) | 777.3 (749.1, 807.5) * | 9.8 (9.1, 10.5) * | 5.5 (2.9, 10.2) * |
| NVQ/CSE/A-levels | 8071 (31.2) | 796.2 (762.1, 829.9) | 10.0 (9.3, 10.7) | 3.6 (2.0, 7.2) |
| Degree/professional | 16,288 (62.9) | 792.4 (761.1, 824.2) | 10.0 (9.2, 10.7) | 3.5 (1.9, 7.1) |
| Employment | ||||
| None | 1493 (5.8) | 803.1 (772.4, 835.2) | 10.1 (9.4, 10.8) | 3.3 (1.8, 6.3) |
| Retired | 6580 (25.4) | 764.4 (736.8, 792.4) * | 9.6 (8.9, 10.3) | 6.2 (3.3, 11.9) |
| Lowest working hour (1st quartile) | 4085 (15.8) | 801.1 (769.3, 835.3) | 10.1 (9.4, 10.8) | 3.4 (1.8, 7.0) |
| 2nd quartile | 2999 (11.6) | 807.6 (775.9, 839.8) | 10.2 (9.4, 10.8) | 3.0 (1.7, 5.8) |
| 3rd quartile | 5732 (22.1) | 8804.8 (773.9, 835.5) | 10.1 (9.4, 10.8) | 2.9 (1.7, 5.4) |
| Highest working hour (4th quartile) | 5005 (19.3) | 797.1 (768.6, 826.1) | 10.0 (9.3, 10.8) | 3.0 (1.7, 5.6) |
| Townsend deprivation index | ||||
| Highly deprived | 10,232 (39.5) | 791.3 (759.6, 824.0) | 10.0 (9.2, 10.7) | 3.7 (2.0, 7.5) |
| Less deprived | 15,662 (60.5) | 794.3 (761.9, 827.0) | 10.0 (9.3, 10.7) | 3.6 (1.9, 7.2) |
| Alcohol | ||||
| Non-drinker | 1040 (4.0) | 795.3 (764.8, 826.3) | 10.0 (9.3, 10.7) | 3.9 (2.1, 8.4) |
| Special occasion only | 1929 (7.4) | 801.0 (770.4, 832.9) | 10.1 (9.4, 10.8) | 3.7 (2.0, 7.8) |
| 1–3 times/month | 2737 (10.6) | 805.2 (771.5, 838.1) | 10.1 (9.4, 10.8) | 3.3 (1.8, 6.7) |
| 1–2 times/week | 6682 (25.8) | 798.6 (767.6, 830.8) | 10.0 (9.3, 10.7) | 3.4 (1.8, 6.9) |
| 3–4 times/week | 7527 (29.1) | 790.8 (760.2, 822.2) | 9.9 (9.2, 10.6) | 3.6 (1.9, 7.2) |
| Daily or almost daily | 5979 (23.1) | 779.0 (747.8, 810.6) * | 9.8 (9.1, 10.5) * | 4.1 (2.2, 8.1) |
| Long standing illness | ||||
| No | 19,920 (76.9) | 795.0 (763.0, 827.2) | 10.0 (9.3, 10.7) | 3.5 (1.9, 6.9) |
| Yes | 5974 (23.1) | 784.3 (753.0, 817.6) * | 9.8 (9.1, 10.6) * | 4.3 (2.2, 8.8) * |
| Current smoking | ||||
| No | 24,379 (94.1) | 792.7 (761.0, 825.2) | 10.0 (9.2, 10.7) | 3.6 (2.0, 7.3) |
| Yes | 1515 (5.9) | 790.1 (755.8, 824.9) * | 9.9 (9.2, 10.6) * | 3.8 (2.1, 8.4) * |
| Body mass index < 30 | ||||
| No | 21,403 (82.7) | 785.4 (753.4, 818.1) * | 9.9 (9.2, 110.6) * | 4.4 (2.3, 8.6) * |
| Yes | 4491 (17.3) | 793.9 (762.2, 826.5) | 10.0 (9.2, 10.6) | 3.5 (1.9, 7.1) |
| Regular physical activity | ||||
| No | 6323 (24.4) | 793.9 (761.7, 826.4) | 9.9 (9.2, 10.7) * | 3.7 (2.0, 7.4) |
| Yes | 19,571 (75.6) | 792.1 (760.4, 824.7) | 10.0 (9.2, 10.7) | 3.6 (1.9, 7.3) |
| Healthy diet | ||||
| No | 13,303 (51.4) | 793.5 (760.9, 826.9) | 10.0 (9.2, 10.7) | 3.5 (1.8, 7.0) |
| Yes | 12,591 (48.6) | 791.8 (760.4, 823.5) | 10.0 (9.2, 10.7) | 3.8 (2.1, 7.8) |
| Healthy lifestyle score | ||||
| 0 (least healthy) | 73 (0.3) | 770.3 (736.5, 813.3) * | 9.7 (9.1, 10.6) * | 6.1 (3.6, 9.0) * |
| 1 | 1178 (4.5) | 789.9 (756.6, 824.5) | 9.9 (9.2, 10.6) | 4.3 (2.3, 8.6) |
| 2 | 5357 (20.7) | 791.4 (758.4, 824.8) | 9.9 (9.2, 10.7) | 3.7 (2.0, 7.5) |
| 3 | 11,092 (42.8) | 793.9 (761.5, 826.4) | 10.0 (9.2, 10.7) | 3.5 (1.9, 7.1) |
| 4 (most healthy) | 8194 (31.6) | 792.2 (761.7, 824.1) | 10.0 (9.3, 10.7) | 3.7 (2.0, 7.5) |
| Risk Group | Grey Matter Volume (in cm3) | Hippocampal Volume (in cm3) | White Matter Hyperintensity (in Log-Transformed cm3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 25,894) | (n = 25,883) | (n = 25,025) | |||||
| N * | Beta (95% CI) | p | Beta (95% CI) | p | Beta (95% CI) | p | |
| All | |||||||
| Favorable lifestyle and low genetic risk | 12,829 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Unfavorable lifestyle and low genetic risk | 4319 | −4.92 (−6.14, −3.70) | 1.6 × 10−14 | −0.07 (−0.10, −0.03) | 1.2 × 10−4 | 0.11 (0.08, 0.14) | 2.4 × 10−13 |
| Favorable lifestyle and high genetic risk | 6457 | 0.40 (−0.65, 1.44) | 0.46 | −0.05 (−0.07, −0.02) | 0.002 | 0.01 (−0.01, 0.04) | 0.42 |
| Unfavorable lifestyle and high genetic risk | 2289 | −4.44 (−6.01, −2.88) | 1.7 × 10−7 | −0.08 (−0.12, −0.03) | 4.8 × 10−4 | 0.11 (0.08, 0.15) | 7.8 × 10−9 |
| pGRS-interaction † | 0.88 | 0.09 | 0.61 | ||||
| <60 years | |||||||
| Favorable lifestyle and low genetic risk | 8458 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Unfavorable lifestyle and low genetic risk | 3059 | −4.60 (−6.06, −3.13) | 1.7 × 10−9 | −0.08 (−0.12, −0.04) | 1.3 × 10−4 | 0.11 (0.08, 0.15) | 7.6 × 10−10 |
| Favorable lifestyle and high genetic risk | 4392 | 1.05 (−0.22, 2.33) | 0.11 | −0.03 (−0.06, −0.01) | 0.15 | 0.01 (−0.02, 0.04) | 0.39 |
| Unfavorable lifestyle and high genetic risk | 1683 | −3.61 (−5.45, −1.77) | 3.9 × 10−4 | −0.05 (−0.10, −0.00) | 0.04 | 0.11 (0.07, 0.15) | 1.6 × 10−6 |
| pGRS-interaction † | 0.96 | 0.13 | 0.51 | ||||
| ≥60 years | |||||||
| Favorable lifestyle and low genetic risk | 4371 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Unfavorable lifestyle and low genetic risk | 1260 | −5.49 (−7.72, −3.28) | 3.1 × 10−6 | −0.04 (−0.10, −0.02) | 0.24 | 0.11 (0.06, 0.17) | 7.6 × 10−5 |
| Favorable lifestyle and high genetic risk | 2065 | −1.07 (−2.90, 0.76) | 0.25 | −0.10 (−0.15, −0.05) | 1.1 × 10−4 | 0.01 (−0.04, 0.05) | 0.76 |
| Unfavorable lifestyle and high genetic risk | 606 | −6.84 (−9.83, −3.86) | 1.8 × 10−5 | −0.16 (−0.25, −0.08) | 1.6 × 10−4 | 0.12 (0.04, 0.20) | 0.002 |
| pGRS-interaction † | 0.89 | 0.67 | 0.85 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mulugeta, A.; Navale, S.S.; Lumsden, A.L.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Hyppönen, E. Healthy Lifestyle, Genetic Risk and Brain Health: A Gene-Environment Interaction Study in the UK Biobank. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3907. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193907
Mulugeta A, Navale SS, Lumsden AL, Llewellyn DJ, Hyppönen E. Healthy Lifestyle, Genetic Risk and Brain Health: A Gene-Environment Interaction Study in the UK Biobank. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):3907. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193907
Chicago/Turabian StyleMulugeta, Anwar, Shreeya S. Navale, Amanda L. Lumsden, David J. Llewellyn, and Elina Hyppönen. 2022. "Healthy Lifestyle, Genetic Risk and Brain Health: A Gene-Environment Interaction Study in the UK Biobank" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 3907. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193907
APA StyleMulugeta, A., Navale, S. S., Lumsden, A. L., Llewellyn, D. J., & Hyppönen, E. (2022). Healthy Lifestyle, Genetic Risk and Brain Health: A Gene-Environment Interaction Study in the UK Biobank. Nutrients, 14(19), 3907. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193907






