Ethanol Extracts of Rice Bran and Whole Grain Adlay Seeds Mitigate Colonic Inflammation and Damage in Mice with Colitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Ethanol Extract Preparations and Experimental Diets
2.3. Induction of UC
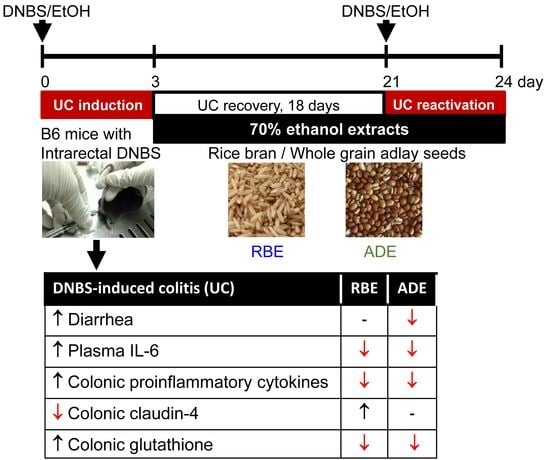
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Measurements
2.5.1. Body Weight, Food Intake, and Disease Activity Index (DAI)
2.5.2. Inflammatory Mediators in the Plasma and Colon
2.5.3. Macroscopic Injury Score of the Colon
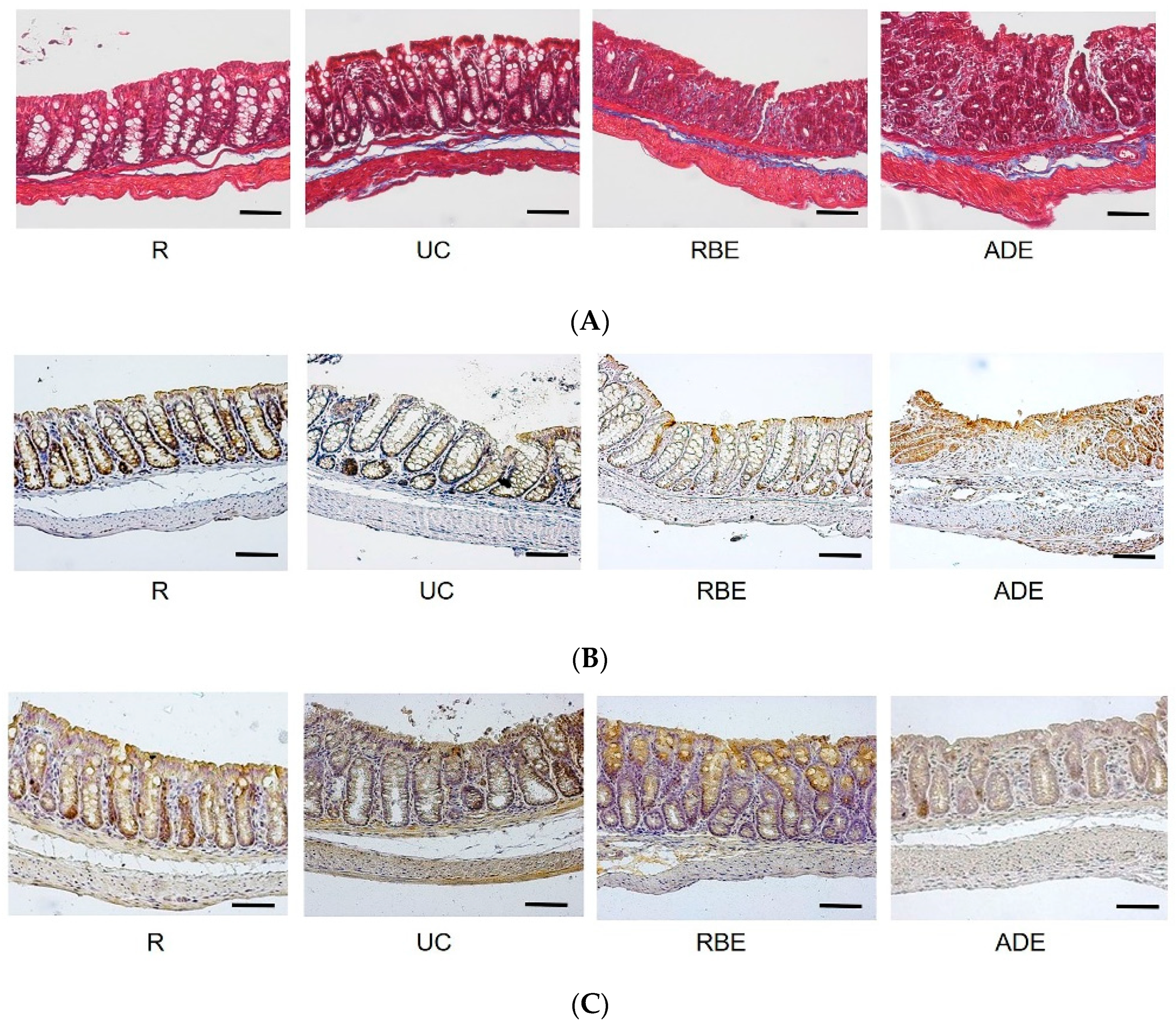
2.5.4. Collagenous Connective Tissue of the Colon: Masson’s Trichrome Stain
2.5.5. Histopathological (Microscopic) Assessment of the Colon
2.5.6. Tight Junction Proteins in the Colon
2.5.7. Indicators of Oxidative Stress in the Colon
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Food Intake, Body Weight, DAI, and Colon Length
3.2. Inflammatory Mediators in the Plasma
3.3. Macroscopic and Microscopic Injury Scores of the Colon
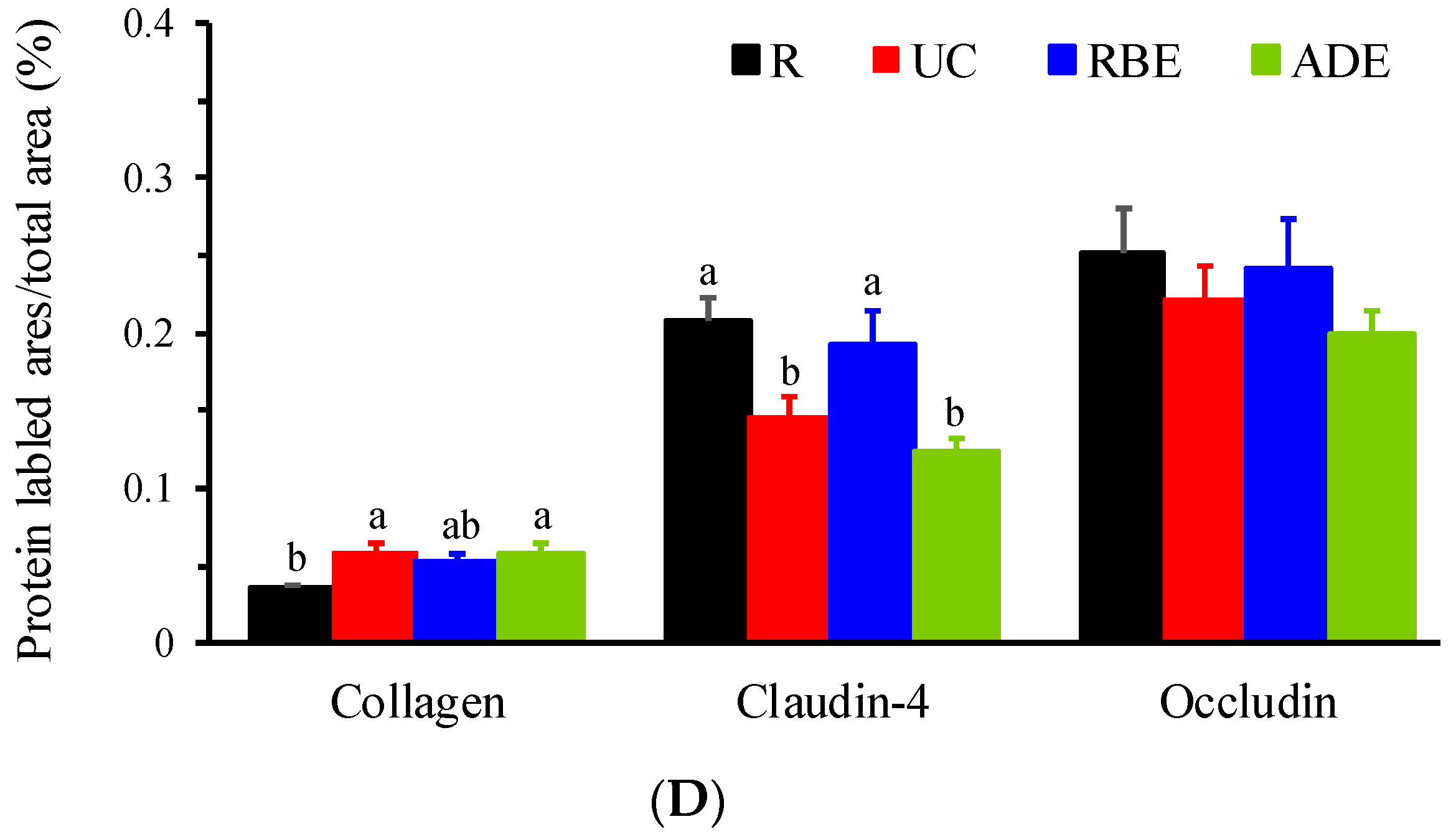
3.4. Collagen, Claudin-4, and Occludin Contents in the Colon
3.5. GSH, GSSG and TBARS Levels in the Colon
3.6. Inflammatory Mediators in the Colon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramos, G.P.; Papadakis, K.A. Mechanisms of disease: Inflammatory bowel diseases. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.H.; Weng, M.T.; Tung, C.C.; Wang, Y.T.; Chang, Y.T.; Chang, C.H.; Shieh, M.J.; Wong, J.M.; Wei, S.C. Epidemiological trend in inflammatory bowel disease in Taiwan from 2001 to 2015: A nationwide populationbased study. Intest. Res. 2019, 17, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.H.; Hsu, T.C.; Chen, M.W.; Su, P.Y.; Chen, Y.Y. Clinical features and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in a low-incidence area: A hospital-based retrospective cohort study in Taiwan. Medicine 2021, 100, e25090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shizuma, T. Anti-colitis effects of brown rice reported by experimental studies. J. Rice Res. 2014, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshteli, A.H.; Madsen, K.L.; Dieleman, L.A. Diet in the pathogenesis and management of ulcerative colitis; a review of randomized controlled dietary interventions. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnatyszyn, A.; Hryhorowicz, S.; Kaczmarek-Rys, M.; Lis, E.; Slomski, R.; Scott, R.J.; Plawski, A. Colorectal carcinoma in the course of inflammatory bowel diseases. Hered. Cancer Clin. Pract. 2019, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeputte, D.; Joossens, M. Effects of low and high FODMAP diets on human gastrointestinal microbiota composition in adults with intestinal diseases: A systematic review. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, K.J.; Pennings, B.; Javelli, D.; Wyatt, G.; Given, B. Dietary patterns, beliefs and behaviours among individuals with inflammatory bowel disease: A cross-sectional study. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 34, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Koseki, T.; Watanabe, K.; Ardiansyah; Budijanto, S.; Oikawa, A.; Alauddin, M.; Goto, T.; Aso, H.; Komai, M.; et al. Dietary supplementation of fermented rice bran effectively alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Nutrients 2017, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.; Francis, N.; Blanchard, C.L.; Schwarz, L.J.; Santhakumar, A.B. Rice bran phenolic compounds regulate genes associated with antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory activity in human umbilical vein endothelial cells with induced oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Li, S.; Chang, L.; Sun, P.; Lu, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Z.; et al. Total polysaccharides of adlay bran (Coix lachryma-jobi L.) improve TNF-alpha induced epithelial barrier dysfunction in Caco-2 cells via inhibition of the inflammatory response. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Chung, C.P.; Chiang, W.; Lin, Y.L. Anti-inflammatory effects and chemical study of a flavonoid-enriched fraction from adlay bran. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Appukuttan, J.P. Inhibition of LPS induced neurochemical imbalance and oxidative stress by pigmented and non-pigmented rice bran extracts. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohail, M.; Rakha, A.; Butt, M.S.; Iqbal, M.J.; Rashid, S. Rice bran nutraceutics: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3771–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapwarobol, S.; Saphyakhajorn, W.; Astina, J. Biological functions and activities of rice bran as a functional ingredient: A review. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2021, 14, 11786388211058559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agista, A.Z.; Rusbana, T.B.; Islam, J.; Ohsaki, Y.; Sultana, H.; Hirakawa, R.; Watanabe, K.; Nochi, T.; Ardiansyah; Budijanto, S.; et al. Fermented rice bran supplementation prevents the development of intestinal fibrosis due to DSS-induced inflammation in mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ren, G. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on immunological activities of polysaccharides from adlay. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.; Han, A.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, U.; Hong, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Seo, E.K. A comparative study on hulled adlay and unhulled adlay through evaluation of their LPS-induced anti-inflammatory effects, and isolation of pure compounds. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhu, D.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Su, G.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y. In vitro and in vivo studies on adlay-derived seed extracts: Phenolic profiles, antioxidant activities, serum uric acid suppression, and xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7771–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, G.J.; Lin, Y.T.; Hsu, C.H.; Tang, F.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chao, C.Y. Adlay hull extracts attenuate beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity and oxidative stress in PC12 cells through antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic activities. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 101020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kozukue, N.; Kim, H.J.; Friedman, M. Growth-inhibitory effects of pigmented rice bran extracts and three red bran fractions against human cancer cells: Relationships with composition and antioxidative activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9151–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Chain, F.; Miquel, S.; Lu, J.; Gratadoux, J.J.; Sokol, H.; Verdu, E.F.; Bercik, P.; Bermudez-Humaran, L.G.; Langella, P. The commensal bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is protective in DNBS-induced chronic moderate and severe colitis models. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Shajib, M.S.; Manocha, M.M.; Khan, W.I. Investigating intestinal inflammation in DSS-induced model of IBD. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 60, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morampudi, V.; Bhinder, G.; Wu, X.; Dai, C.; Sham, H.P.; Vallance, B.A.; Jacobson, K. DNBS/TNBS colitis models: Providing insights into inflammatory bowel disease and effects of dietary fat. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, e51297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Therapeutic potential of dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS)-induced colitis in mice by targeting IL-1beta and IL-18. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwazawa, R.; Kozakai, S.; Kitahashi, T.; Nakamura, K.; Hata, K.I. The therapeutic effects of adipose-derived stem cells and recombinant peptide pieces on mouse model of DSS colitis. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, C.; Long, G.; Wolf, J.; Okerberg, C.; Herbert, R. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of nonneoplastic lesions in toxicology studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2002, 30, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hissin, P.J.; Hilf, R. A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 74, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Cheon, J.H. Pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease and recent advances in biologic therapies. Immune Netw. 2017, 17, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.; Proenca, C.; Rocha, S.; Lima, J.; Carvalho, F.; Fernandes, E.; Freitas, M. Immunomodulatory effects of flavonoids in the prophylaxis and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases: A comprehensive review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3374–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damas, O.M.; Garces, L.; Abreu, M.T. Diet as adjunctive treatment for inflammatory bowel disease: Review and update of the latest literature. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2019, 17, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, K.; Staudacher, H. Low FODMAP diet in irritable bowel syndrome: A review of recent clinical trials and meta-analyses. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2022, 25, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Shi, R.; Tang, B.; Xie, S. Coix lachryma-jobi extract ameliorates inflammation and oxidative stress in a complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis model. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.-C.; Wang, K.-L.; Chen, Y.-C. An Animal Platform for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. In Proceedings of the 2019 R&D Results Presentation of Human Ecology College in Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan, 22 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lean, Q.Y.; Eri, R.D.; Randall-Demllo, S.; Sohal, S.S.; Stewart, N.; Peterson, G.M.; Gueven, N.; Patel, R.P. Orally administered enoxaparin ameliorates acute colitis by reducing macrophage-associated inflammatory responses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manetti, M.; Rosa, I.; Messerini, L.; Ibba-Manneschi, L. Telocytes are reduced during fibrotic remodelling of the colonic wall in ulcerative colitis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Oyama, T.; Sugie, S. Dietary tricin suppresses inflammation-related colon carcinogenesis in mice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, S100–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtys, E.; Eisel, U.L.M.; Hageman, R.J.J.; Verkuyl, J.M.; Broersen, L.M.; Dierckx, R.; de Vries, E.F.J. Anti-inflammatory effects of rice bran components. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Fu, L.; Cao, S.; Yin, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhang, W. The anti-inflammatory effect of bovine bone-gelatin-derived peptides in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages cells and dextran sulfate sodium-induced C57BL/6 mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredient (g) | R/UC Groups | RBE Group | ADE Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn starch | 465.7 | 464.2 | 464.9 |
| Rice bran extract | 0 | 1.5 | 0 |
| Whole-grain adlay seeds’ extract | 0 | 0 | 0.8 |
| Dextrin | 155 | 155 | 155 |
| Casein, vitamin-free | 140 | 140 | 140 |
| Sucrose, granular | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Cellulose | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Soybean oil | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| AIN-93M Mineral Mix | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| AIN-93M Vitamin Mix | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Choline bitartrate | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| L-cystine | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Total | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Group | Diarrhea | Bloody Stool | DAI | Colon Length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0 (0, 0) b | 0 (0, 0) b | 0 (0, 0) b | 6.93 ± 0.26 |
| UC | 2 (0, 2) a | 0.5 (0, 2) a | 1 (0.33, 1) a | 6.90 ± 0.38 |
| RBE | 0 (0, 2) ab | 0 (0, 1) ab | 0.67 (0.33, 1.33) a | 6.53 ± 0.16 |
| ADE | 0 (0, 0) b | 0 (0, 2) ab | 0 (0, 1.33) ab | 6.44 ± 0.19 |
| Group | TNF-α | IL-6 | IFN-γ | IL-10 | IL-12p70 | MCP-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (pg/mL) | ||||||
| R | 38.4 ± 0.9 a | 53.4 ± 0.5 b | 12.00 ± 0.27 a | 409 ± 5 a | 106.8 ± 3.3 a | 10.05 ± 0.13 a |
| UC | 37.7 ± 3.2 a | 67.1 ± 8.8 a | 11.38 ± 0.29 a | 393 ± 4 a | 97.0 ± 3.9 a | 10.81 ± 1.29 a |
| RBE | 29.2 ± 1.3 b | 53.3 ± 2.5 b | 9.79 ± 0.17 b | 364 ± 5 b | 71.8 ± 4.2 b | 8.30 ± 0.21 b |
| ADE | 30.3 ± 1.8 b | 50.2 ± 0.9 b | 9.82 ± 0.45 b | 364 ± 4 b | 81.6 ± 4.7 b | 8.36 ± 0.32 b |
| Group | Area of Ulceration | Edema | Immune-Cell Infiltration | Goblet-Cell Loss | Inflammation | Total Injury Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 0) b | 0 (0, 0) b | 0 (0, 0) b | 0 (0, 0) b | 0 (0, 0) b |
| UC | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (0, 1) a | 1 (0, 3) a | 0.5 (0, 1) a | 2 (0, 3) a | 4.5 (0, 10) a |
| RBE | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (0, 1) a | 1 (0, 3) a | 1 (0, 1) a | 2 (0, 3) a | 6 (0, 9) a |
| ADE | 0 (0, 1) | 1 (1, 1) a | 2 (1, 3) a | 1 (1, 2) a | 2 (1, 3) a | 8 (4, 11) a |
| Group | GSH (μmol/g Colon) | GSSG (μmol/g Colon) | GSH/GSSG | TBARS (nmol/g Colon) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 33.8 ± 2.0 b | 6.23 ± 0.44 | 5.60 ± 0.31 b | 132.5 ± 13.7 |
| UC | 43.9 ± 3.4 a | 5.49 ± 0.37 | 8.60 ± 0.50 a | 143.3 ± 29.6 |
| RBE | 30.0 ± 1.3 b | 5.60 ± 0.31 | 5.10 ± 0.39 b | 138.1 ± 22.6 |
| ADE | 35.3 ± 1.8 b | 6.63 ± 0.19 | 5.30 ± 0.30 b | 158.2 ± 25.0 |
| Group | TNF-α | IL-6 | IFN-γ | IL-10 | IL-12p70 | MCP-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (pg/g Colon) | ||||||
| R | 31.2 ± 1.5 b | 8.92 ± 0.85 b | 2.08 ± 0.16 b | 3.08 ± 0.15 a | 56.8 ± 4.3 c | 0.25 ± 0.08 b |
| UC | 55.4 ± 4.1 a | 18.11 ± 2.84 a | 5.49 ± 0.37 a | 1.52 ± 0.14 b | 112.0 ± 8.9 a | 0.51 ± 0.10 a |
| RBE | 40.3 ± 3.3 b | 10.85 ± 2.57 b | 4.81 ± 0.28 a | 3.42 ± 0.20 a | 72.4 ± 9.2 b | 0.32 ± 0.08 b |
| ADE | 44.8 ± 2.6 b | 13.02 ± 1.99 ab | 4.92 ± 0.34 a | 2.15 ± 0.23 ab | 83.9 ± 6.7 b | 0.40 ± 0.17 ab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lo, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wu, W.-T. Ethanol Extracts of Rice Bran and Whole Grain Adlay Seeds Mitigate Colonic Inflammation and Damage in Mice with Colitis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3877. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183877
Lo H-C, Chen Y-H, Wu W-T. Ethanol Extracts of Rice Bran and Whole Grain Adlay Seeds Mitigate Colonic Inflammation and Damage in Mice with Colitis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3877. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183877
Chicago/Turabian StyleLo, Hui-Chen, Yu-Hsin Chen, and Wen-Tzu Wu. 2022. "Ethanol Extracts of Rice Bran and Whole Grain Adlay Seeds Mitigate Colonic Inflammation and Damage in Mice with Colitis" Nutrients 14, no. 18: 3877. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183877
APA StyleLo, H.-C., Chen, Y.-H., & Wu, W.-T. (2022). Ethanol Extracts of Rice Bran and Whole Grain Adlay Seeds Mitigate Colonic Inflammation and Damage in Mice with Colitis. Nutrients, 14(18), 3877. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183877