IL-1 Receptor Antagonist (IL-1Ra) Levels and Management of Metabolic Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. IL-1Ra Predicts T2DM at Population Level
3. Immune Regulation, Metabolism, and Glucose Homeostasis with IL-1Ra
4. IL-1Ra Measurements in Individuals with Metabolic Disorders
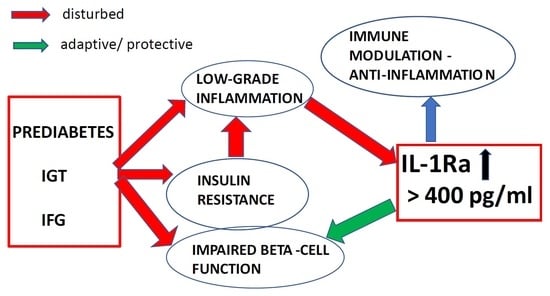
5. IL-1Ra Limit Values
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, H.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. An immune origin of type 2 diabetes? Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickup, J.C. Inflammation and activated innate immunity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellen, K.E.; Hotamisigil, G.S. Inflammation, stress and diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herder, C.; Baumert, J.; Thorand, B.; Koenig, W.; de Jager, W.; Meisinger, C.; Illig, T.; Martin, S.; Kolb, H. Chemokines as risk factors for type 2 diabetes: Results from the MONICA/KORA Augsburg study, 1984–2002. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, S.; Saberi, M.; Olefsky, J.M. Insulin sensitivity: Modulation by nutrients and inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2992–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomilehto, J.; Lindstrom, J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Valle, T.T.; Hämäläinen, H.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Keinänen Kiukaanniemi, S.; Laakso, M.; Louheranta, A.; Rastas, M.; et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M.; Diabetes Prevention Research Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar]
- Florez, H.; Marinella, G.; Tempro, M.G.; Orchard, T.J.; Mather, K.J.; Marcovina, S.M.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Horton, E.; Saudek, C.; Pi-Sunyer, X.F.; et al. Metabolic syndrome components and their response to lifestyle and metformin interventions are associated with differences in diabetes risk in persons with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W.H.; Pan, Q.; Edelstein, S.L.; Mather, K.J.; Perreault, L.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Dabelea, D.M.; Horton, E.; Kahn, S.E.; Knowler, W.C.; et al. Impact of lifestyle and metformin interventions on the risk of progression to diabetes and regression to normal glucose regulation in overweight or obese people with impaired glucose regulation. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn, L.; White, M.; Oldroyd, J.; Walker, M.; Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Mathers, J.C. Prevention of type 2 diabetes in adults with impaired glucose tolerance: The European Diabetes Prevention RCT in Newcastle upon Tyne, UK. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood 2011, 117, 3720–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenen, T.B.; Stienstra, R.; van Tits, L.J.; de Graaf, J.; Stalenhoef, A.F.H.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Tack, C.J.; Netea, M.G. Hyperglycemia Activates Caspase-1 and TXNIP-Mediated IL-1β Transcription in Human Adipose Tissue. Diabetes 2011, 60, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arend, W.P. The balance between IL-1 and IL-1Ra in disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002, 13, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herder, C.; Brunner, E.J.; Rathmann, W.; Strassburger, K.; Tabak, A.G.; Schloot, N.C.; Witte, D.R. Elevated levels of the anti-inflammatory interleukin-1 receptor antagonist precede the onset of type 2 diabetes: The Whitehall II study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, M.; Herder, C.; Kivimäki, M.; Jokela, M.; Roden, M.; Shipley, M.J.; Witte, D.R.; Brunner, E.J.; Tabak, A.G. Accelerated increase in seruminterleukin-1 receptor antagonist starts 6 years before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: Whitehall II prospective cohort study. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomaa, V.; Havulinna, A.; Saarela, O.; Zeller, T.; Jousilahti, P.; Jula, A.; Muenzel, T.; Aromaa, A.; Evans, A.; Kuulasmaa, K.; et al. Thirty-one novel biomarkers as predictors for clinically incident diabetes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksentijevich, I.; Masters, S.L.; Ferguson, P.J.; Dancey, P.; Frenkel, J.; van Royen-Kerkhoff, A.; Laxer, R.; Tedgård, U.; Cowen, E.W.; Pham, T.-H.; et al. An Autoinflammatory Disease with Deficiency of the Interleukin-1–Receptor Antagonist. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2426–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Jia, S.; Geoffrey, R.; Lorier Suchi, M.; Ulrich Broeckel, U.; Hessner, M.J.; Verbsky, J. An Autoinflammatory Disease Due to Homozygous Deletion of the IL1RN Locus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 36, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge-Aubry, C.E.; Somm, E.; Giusti, V.; Pernin, V.A.; Chicheportiche, R.; Chantal Verdumo, C.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; Burger, D.; Jean-Michel Dayer, J.-M.; Meier, C.A. Adipose tissue is a major source of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: Upregulation in obesity and inflammation. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrier, S.; Darakhshan, F.; Hajduch, E. IL-1 receptor antagonist in metabolic diseases: Dr Jekyll or Mr Hyde? FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 6289–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Shoelson, S.E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, C.A.; Bobbioni, E.; Gabay, C.; Assimacopoulos-Jeannet, F.; Golay, A.; Dayer, J.-M. IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Serum Levels Are Increased in Human Obesity: A Possible Link to the Resistance to Leptin? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luotola, K.; Pietilä, A.; Kinnunen, M.; Lanki, T.; Loo, B.-M.; Jula, A.; Perola, M.; Peters, A.; Zeller, T.; Blankenberg, S.; et al. Genetic variation of the interleukin-1 family and nongenetic factors determining the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist phenotypes. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2010, 59, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luotola, K.; Pääkkönen, R.; Alanne, M.; Lanki, T.; Moilanen, L.; Surakka, I.; Pietilä, A.; Mika Kähönen, M.; Nieminen, M.S.; Kesäniemi, Y.A.; et al. Association of variation in the interleukin-1 gene family with diabetes and glucose homeostasis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4575–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luotola, K.; Pietilä, A.; Zeller, T.; Moilanen, L.; Kähönen, M.; Nieminen, M.S.; Kesäniemi, Y.A.; Blankenberg, S.; Jula, A.; Perola, M.; et al. Associations between interleukin-1 (IL-1) gene variations or IL-1 receptor antagonist levels and the development of type 2 diabetes. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 269, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herder, C.; Nuotio, M.-L.; Shah, S.; Blankenberg, S.; Brunner, E.J.; Carstensen, M.; Gieger, C.; Grallert, H.; Jula, A.; Kähönen, M.; et al. Genetic Determinants of Circulating Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Levels and Their Association with Glycemic Traits. Diabetes 2014, 63, 4343–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, S.; Saint-Pierre, N.; Lamantia, V.; Cyr, Y.; Wassef, H.; Faraj, M. Plasma IL-1Ra: Linking hyper apoB to risk factors for type 2 diabetes independent of obesity in humans. Nutr. Diabetes 2015, 5, e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luotola, K.; Piltonen, T.T.; Puurunen, J.; Tapanainen, J.S. IL-1 receptor antagonist levels are associated with glucose tolerance in polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2016, 85, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luotola, K.; Piltonen, T.T.; Puurunen, J.; Morin-Papunen, L.C.; Tapanainen, J.S. Testosterone is associated with insulin resistance index independently of adiposity in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2018, 34, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusitupa, M.; Hermansen, K.; Savolainen, M.J.; Schwab, U.; Kolehmainen, M.; Brader, L.; Mortensen, L.; Cloetens, L.; Johansson-Persson, A.; Onning, G.; et al. Effects of an isocaloric healthy Nordic diet on insulin sensitivity, lipid profile and inflammation markers in metabolic syndrome–a randomized study (SYSDIET). J. Intern. Med. 2013, 274, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuomainen, M.; Kärkkäinen, O.; Leppänen, J.; Auriola, S.; Lehtonen, M.; Savolainen, M.J.; Hermansen, K.; Risérus, U.; Åkesson, B.; Thorsdottir, I.; et al. Quantitative assessment of betainized compounds and associations with dietary and metabolic biomarkers in the randomized study of the healthy Nordic diet (SYSDIET). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasson, J.; Guldbrand, H.; Lundberg, A.K.; Nystrom, F.H. Advice to follow a low-carbohydrate diet has a favourable impact on low-grade inflammation in type 2 diabetes compared with advice to follow a low-fat diet. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herder, C.; Bongaerts, B.W.C.; Rathmann, W.; Heier, M.; Kowall, B.; Koenig, W.; Thorand, B.; Roden, M.; Meisinger, C.; Ziegler, D. Association of subclinical inflammation with polyneuropathy in the older population: KORA F4 study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, V.; Schmitt, V.H.; Zeller, T.; Panova-Noeva, M.; Schulz, A.; Laubert-Reh, D.; Juenger, C.; Schnabel, R.B.; Abt, T.G.J.; Laskowski, R.; et al. Profile of the Immune and Inflammatory Response in Individuals with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Population Cohort Study (Ref.) | N—Case/ Non-Case | Female % | IL-1Ra Concentration (pg/mL) | IL-1Ra Concentration, Non-Case/Healthy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whitehall II [17] | baseline T2DM cases/ non-cases | 335/2475 | 30/27 | 308 (CI95%: 293–323) | 248 (CI95%: 244–252) |
| Health2000 [28] | men with MetS/ metabolically healthy | 1034/1403 | 0 | 343 (247–456) | 268 (191–364) |
| Health2000 [28] | women with MetS/ metabolically healthy | 964/1859 | 100 | 402 (272–570) | 306 (213–423) |
| FINRISK97 [28] | men with MetS/ metabolically healthy | 972/2499 | 0 | 284 (211–371) | 208 (159–267) |
| FINRISK97 [28] | women with MetS/ metabolically healthy | 666/2892 | 100 | 360 (255–458) | 240 (176–310) |
| Gutenberg Health Study [37] | prediabetes/ normoglycemia | 1425/12,152 | 52/50 | 351 (271–485) | 311 (233–408) |
| KORA F4 [36] | elderly polyneuropathy/ no polyneuropthy | 146/901 | 39/51 | 335 (248–472) | 304 (233–400) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luotola, K. IL-1 Receptor Antagonist (IL-1Ra) Levels and Management of Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163422
Luotola K. IL-1 Receptor Antagonist (IL-1Ra) Levels and Management of Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients. 2022; 14(16):3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163422
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuotola, Kari. 2022. "IL-1 Receptor Antagonist (IL-1Ra) Levels and Management of Metabolic Disorders" Nutrients 14, no. 16: 3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163422
APA StyleLuotola, K. (2022). IL-1 Receptor Antagonist (IL-1Ra) Levels and Management of Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients, 14(16), 3422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163422