Estrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) and the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Mediate the Effect of the Coumarin Derivative Umbelliferon on Bone Mineralization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
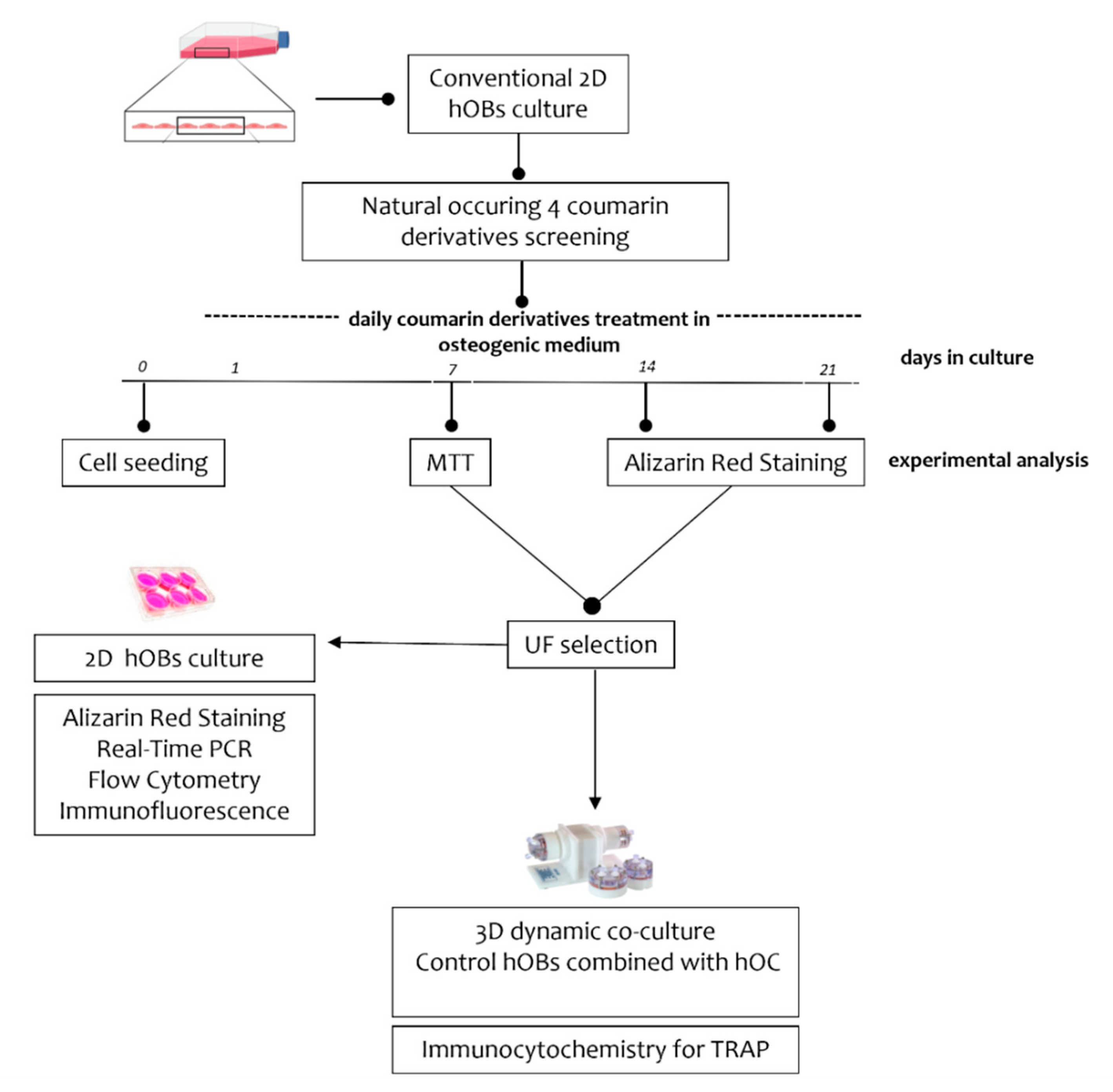
2.1. Experimental Plan
2.2. Cell Cultures
2.3. 3-(4, 5-Dimethylthiazolyl-2-yl)-2, 5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Cell Metabolic Activity
2.4. Alizarin Red Staining
2.5. Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR)
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Immunocytochemistry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
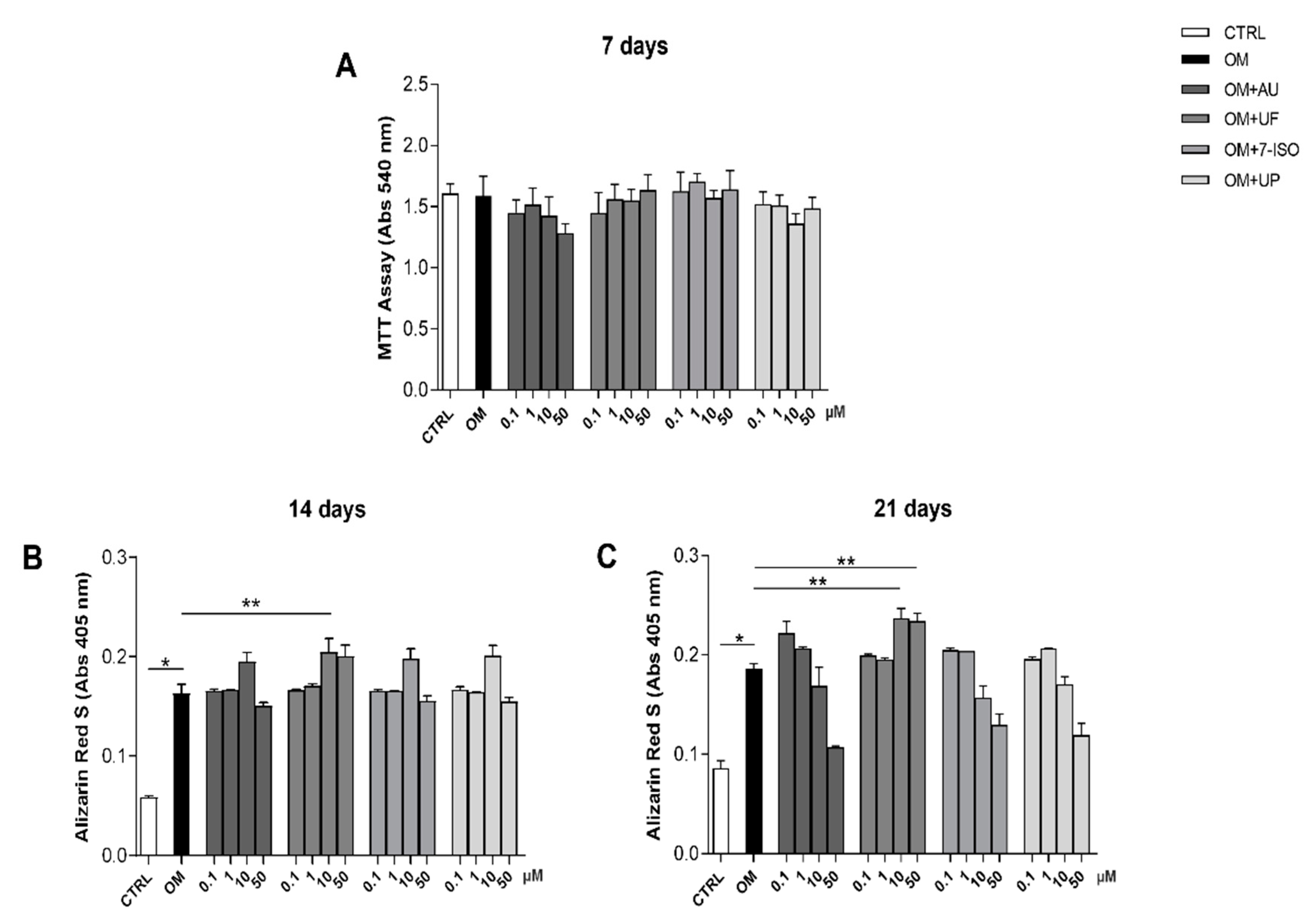
3.1. Effects of Coumarin Derivatives on hOBs’ Viability and Bone Matrix Deposition Ability
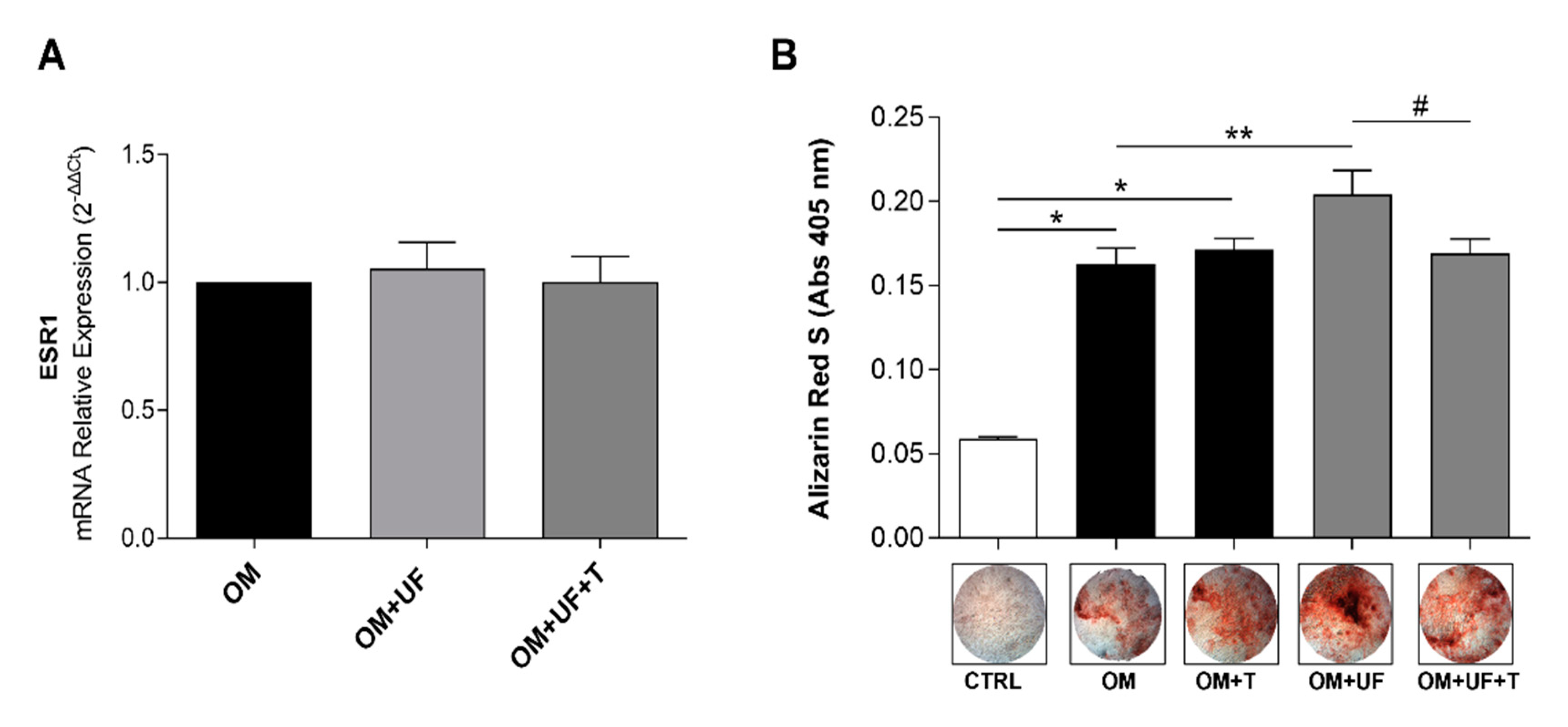
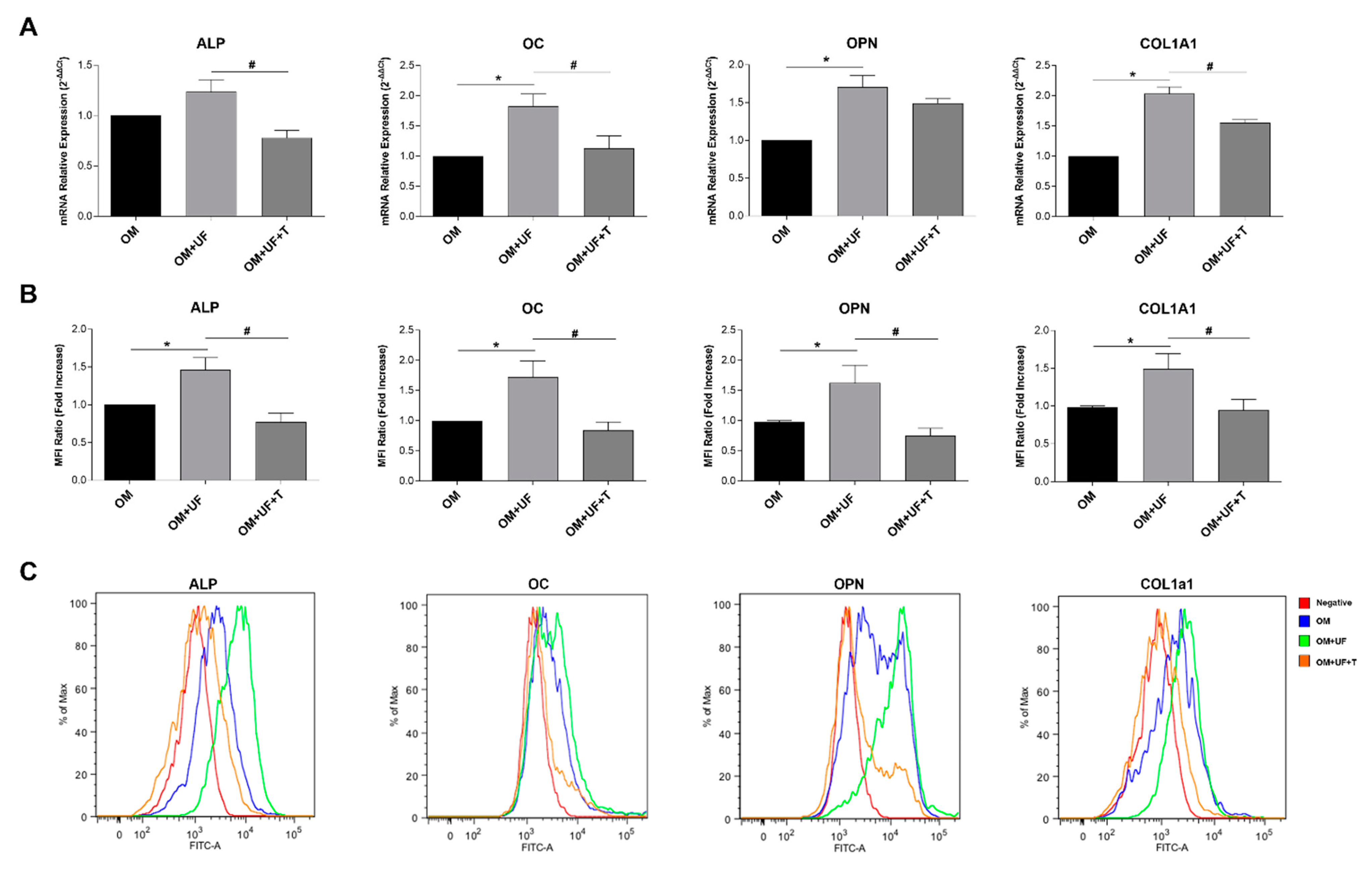
3.2. hOBs’ Responsiveness to UF and Estrogen Receptor 1 Involvement
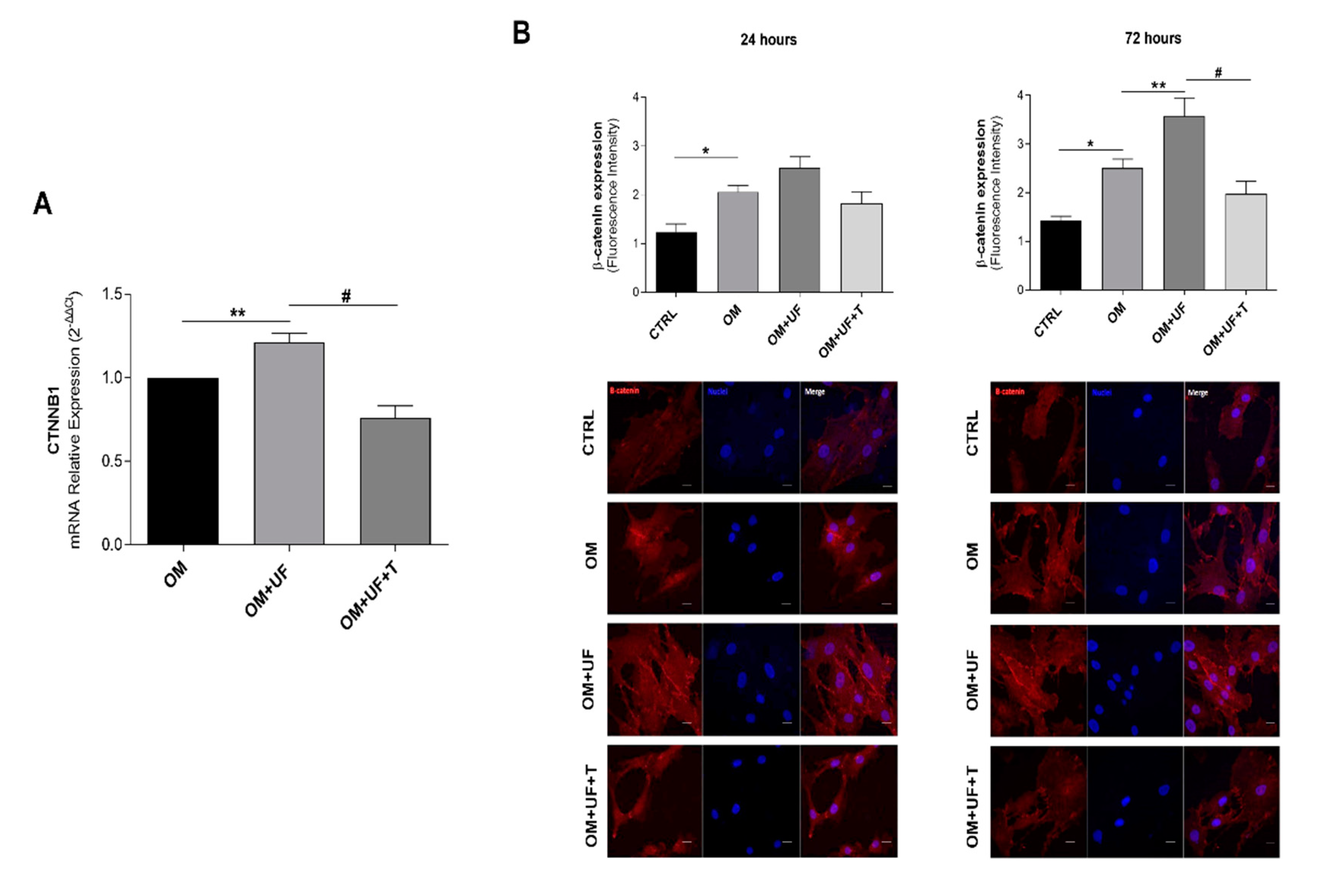
3.3. β-Catenin Pathway
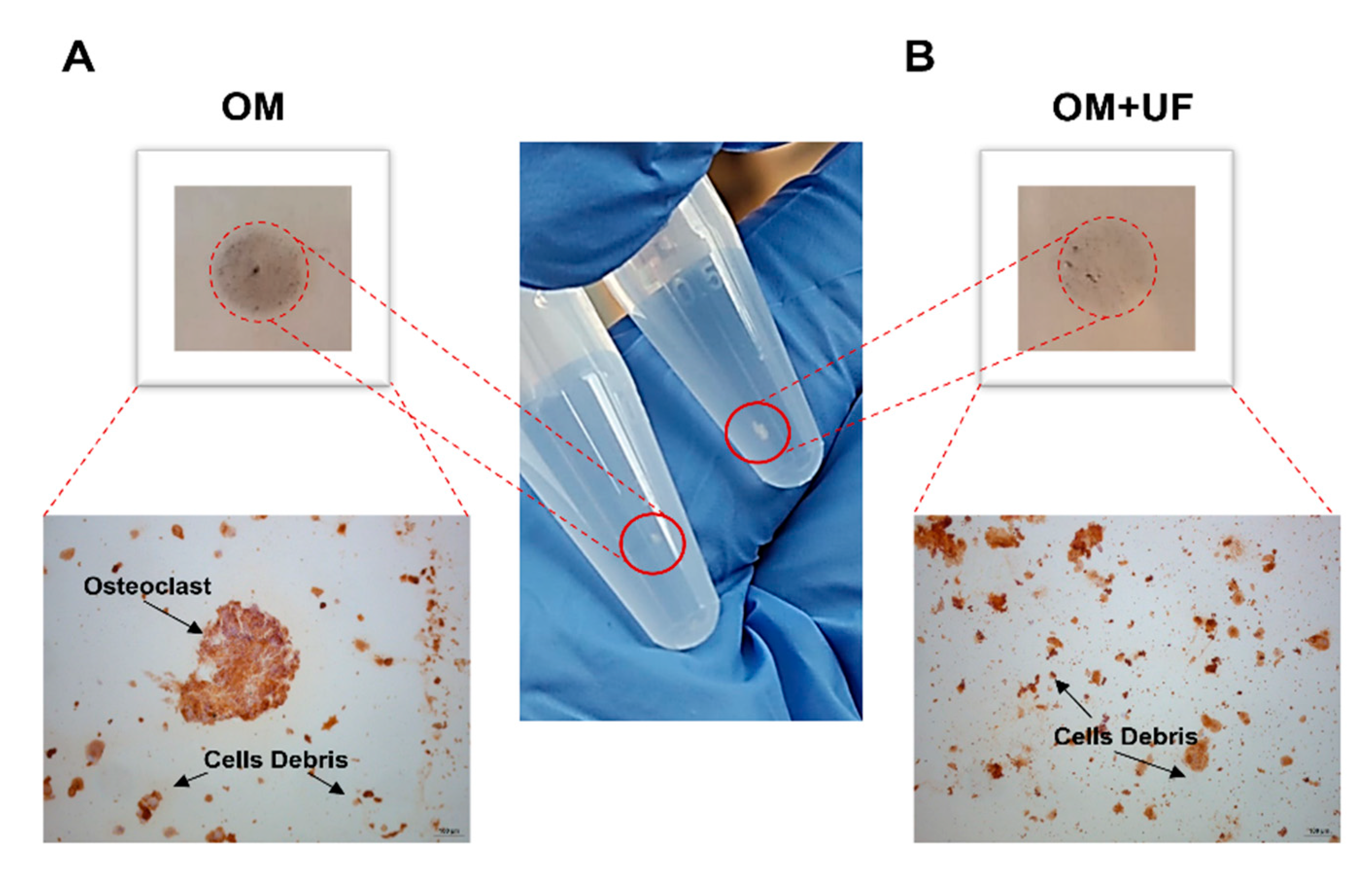
3.4. UF’s Effects on the hOBs/hOCs 3D Co-Culture System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasqualetti, S.; Banfi, G. The Zebrafish Scale as Model to Study the Bone Mineralization Process. J. Mol. Histol. 2012, 43, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, Y.; Farlay, D. Bone Mineralization: From Tissue to Crystal in Normal and Pathological Contexts. Osteoporos. Int. 2013, 24, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirckx, N.; Moorer, M.C. The Role of Osteoblasts in Energy Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeuerlein, E.; Behrens, P. Handbook of Biomineralization.; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 9783527318063. [Google Scholar]
- Teti, A.; Econs, M.J. Osteopetroses, Emphasizing Potential Approaches to Treatment. Bone 2017, 102, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Appelman-Dijkstra, N.M.; Papapoulos, S.E. Modulating Bone Resorption and Bone Formation in Opposite Directions in the Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Drugs 2015, 75, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Streicher, C.; Heyny, A. Estrogen Regulates Bone Turnover by Targeting RANKL Expression in Bone Lining Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, H.; Liu, J. Integrated Strategy of Network Pharmacological Prediction and Experimental Validation Elucidate Possible Mechanism of Bu-Yang Herbs in Treating Postmenopausal Osteoporosis via ESR1. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilezikian, J.P. Anabolic Therapy for Osteoporosis. Women’s Health 2007, 3, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeman, E.; Martin, T.J. Antiresorptive and Anabolic Agents in the Prevention and Reversal of Bone Fragility. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Sambrook, P.N. Antiresorptive Therapies for Osteoporosis: A Clinical Overview. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, S. Full Length Parathyroid Hormone, PTH(1-84), for the Treatment of Severe Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2008, 24, 3259–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjødt, M.K.; Frost, M. Side Effects of Drugs for Osteoporosis and Metastatic Bone Disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miranda, L.L.; Guimarães-Lopes, V.D.P. Plant Extracts in the Bone Repair Process: A Systematic Review. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnam, S.E.; Scutt, A.M. Natural Products as Alternative Treatments for Metabolic Bone Disorders and for Maintenance of Bone Health. Phytother. Res 2007, 21, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Kim, J. Scopolin Attenuates Osteoporotic Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhong, S. Estrogenic Properties of Coumarins and Meroterpene from the Fruits of Cullen Corylifolium: Experimental and Computational Studies. Phytochemistry 2018, 152, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandatori, D.; Penolazzi, L. Three-Dimensional Co-Culture System of Human Osteoblasts and Osteoclast Precursors from Osteoporotic Patients as an Innovative Model to Study the Role of Nutrients: Focus on Vitamin K2. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Jiang, J.G. Pharmacological and Nutritional Effects of Natural Coumarins and Their Structure–Activity Relationships. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1701073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.-M.; Damu, G.L. Current developments of coumarin compounds in medicinal chemistry. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 3884–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, S.J.S.; Lima, V. Bone Anti-Resorptive Effects of Coumarins on RANKL Downstream Cellular Signaling: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Fitoterapia 2021, 150, 104842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.C.; Baek, J.M. Umbelliferone Prevents Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Bone Loss and Suppresses Rankl-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Attenuating Akt-c-Fos-Nfatc1 Signaling. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, L. Osthole Inhibits Osteoclasts Formation and Bone Resorption by Regulating NF-ΚB Signaling and NFATc1 Activations Stimulated by RANKL. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 16052–16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, W.; Lee, E.J. Aesculetin Inhibits Osteoclastic Bone Resorption through Blocking Ruffled Border Formation and Lysosomal Trafficking. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, B.M.; Ali, E.M. 5′-Hydroxy Auraptene Stimulates Osteoblast Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells via a BMP-Dependent Mechanism. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorito, S.; Epifano, F. Natural Oxyprenylated Coumarins Are Modulators of Melanogenesis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, J.; Fodera, D.M. Estrogen Depletion Alters Osteogenic Differentiation and Matrix Production by Osteoblasts in Vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 408, 112814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preziuso, F.; Genovese, S. 7-Isopentenyloxycoumarin: What Is New across the Last Decade. Molecules 2020, 25, 5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, I.; Russo, D. Screening of in Vitro and in Silico α-Amylase, α-Glucosidase, and Lipase Inhibitory Activity of Oxyprenylated Natural Compounds and Semisynthetic Derivatives. Phytochemistry 2021, 187, 112781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, S.; Epifano, F. Biomolecular Targets of Oxyprenylated Phenylpropanoids and Polyketides. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 2019, 108, 143–205. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L. Progress in the Chemistry of Naturally Occurring Coumarins. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 2017, 106, 241–304. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, B.Y.K.; Sagun, J.E. Reduced Serum and Hypoxic Culture Conditions Enhance the Osteogenic Potential of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem. Cell Rev. Rep. 2015, 11, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabavi, N.; Khandani, A. Effects of Microgravity on Osteoclast Bone Resorption and Osteoblast Cytoskeletal Organization and Adhesion. Bone 2011, 49, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, M.P.; Risin, D. The Current State of Bone Loss Research: Data from Spaceflight and Microgravity Simulators. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tomo, P.; Pipino, C. Calcium Sensing Receptor Expression in Ovine Amniotic Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells and the Potential Role of R-568 during Osteogenic Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, E. Crosstalk between Wnt/β-Catenin and Estrogen Receptor Signaling Synergistically Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, M.; Laurent, M.R.; Claessens, F.; O’brien, C.A.; Bouillon, R.; Vanderschueren, D.; Manolagas, S.C. Estrogens and Androgens in Skeletal Physiology and Patho-Physiology. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xie, L. Bergapten: A Review of Its Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Toxicity. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6131–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, W.; Kang, M.K. Aesculetin Accelerates Osteoblast Differentiation and Matrix-Vesicle-Mediated Mineralization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, H.; Dharun, V.N. Osteogenic Stimulatory Effect of Heraclenin Purified from Bael in Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Vitro. Chem. -Biol. Interact. 2019, 310, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Han, W. Psoralen Accelerates Bone Fracture Healing by Activating Both Osteoclasts and Osteoblasts. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 5399–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alimonte, I.; Lannutti, A. Wnt Signaling Behaves as a “Master Regulator” in the Osteogenic and Adipogenic Commitment of Human Amniotic Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem. Cell Rev. Rep. 2013, 9, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamos, J.L.; Weis, W.I. The Beta-Catenin Destruction Complex. EMBO J. 2012, 5, 31. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelusi, L.; Mandatori, D.; Di Pietrantonio, N.; Del Pizzo, F.; Di Tomo, P.; Di Pietro, N.; Buda, R.; Genovese, S.; Epifano, F.; Pandolfi, A.; et al. Estrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) and the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Mediate the Effect of the Coumarin Derivative Umbelliferon on Bone Mineralization. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3209. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153209
Pelusi L, Mandatori D, Di Pietrantonio N, Del Pizzo F, Di Tomo P, Di Pietro N, Buda R, Genovese S, Epifano F, Pandolfi A, et al. Estrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) and the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Mediate the Effect of the Coumarin Derivative Umbelliferon on Bone Mineralization. Nutrients. 2022; 14(15):3209. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153209
Chicago/Turabian StylePelusi, Letizia, Domitilla Mandatori, Nadia Di Pietrantonio, Francesco Del Pizzo, Pamela Di Tomo, Natalia Di Pietro, Roberto Buda, Salvatore Genovese, Francesco Epifano, Assunta Pandolfi, and et al. 2022. "Estrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) and the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Mediate the Effect of the Coumarin Derivative Umbelliferon on Bone Mineralization" Nutrients 14, no. 15: 3209. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153209
APA StylePelusi, L., Mandatori, D., Di Pietrantonio, N., Del Pizzo, F., Di Tomo, P., Di Pietro, N., Buda, R., Genovese, S., Epifano, F., Pandolfi, A., Fiorito, S., & Pipino, C. (2022). Estrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) and the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Mediate the Effect of the Coumarin Derivative Umbelliferon on Bone Mineralization. Nutrients, 14(15), 3209. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153209