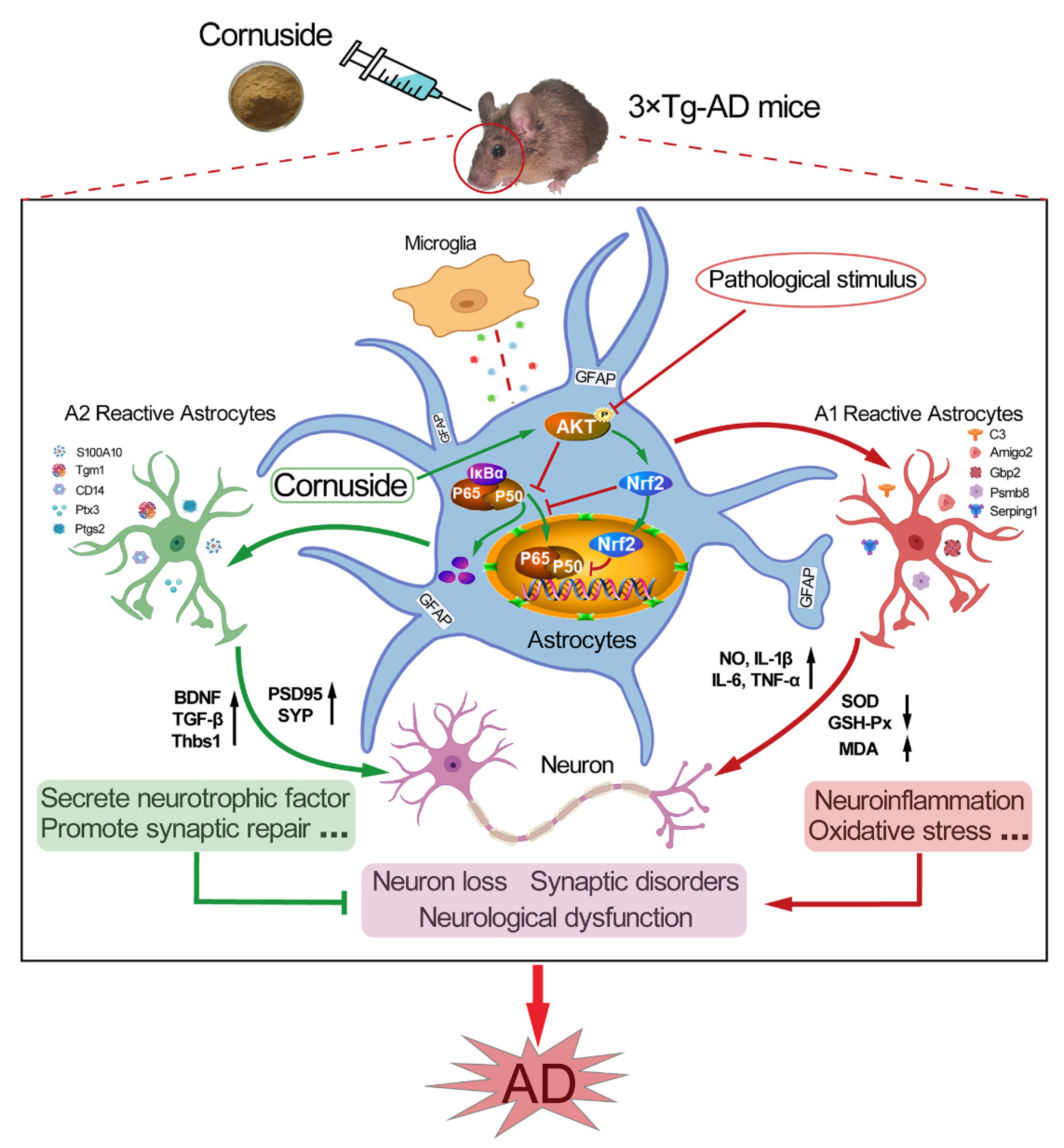
Cornuside Is a Potential Agent against Alzheimer’s Disease via Orchestration of Reactive Astrocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Morris Water Maze Test (MWM)
2.5. Nissl Staining
2.6. Thioflavin S-Staining
2.7. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.8. Immunofluorescence Double Staining
2.9. Cell Culture
2.10. Preparation of MCM
2.11. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.12. ELISA
2.13. NO Testing
2.14. Measurement of MDA, SOD, and GSH-Px
2.15. Western Blot
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
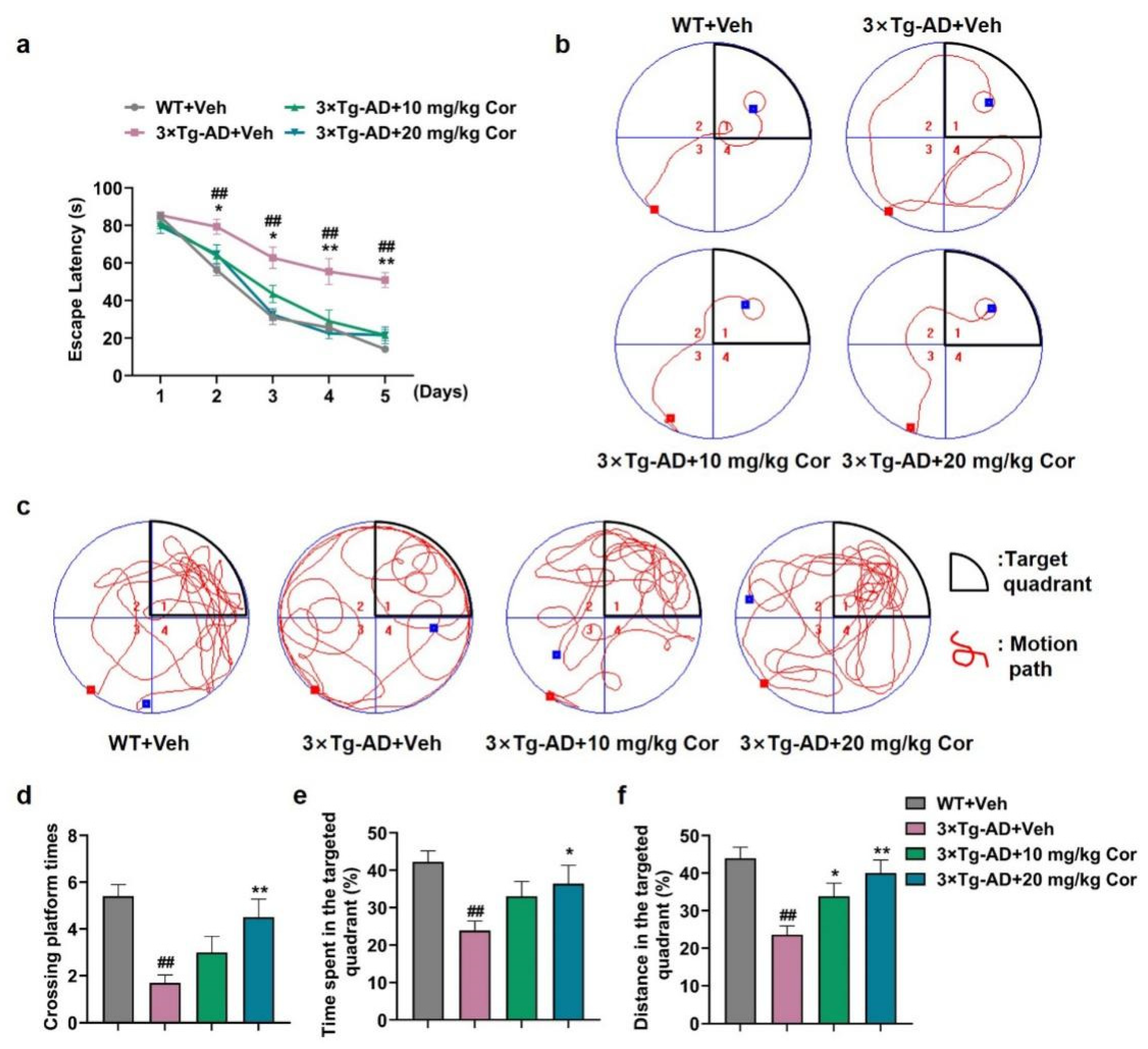
3.1. Cornuside Ameliorated Cognitive Deficits in 3 × Tg-AD Mice
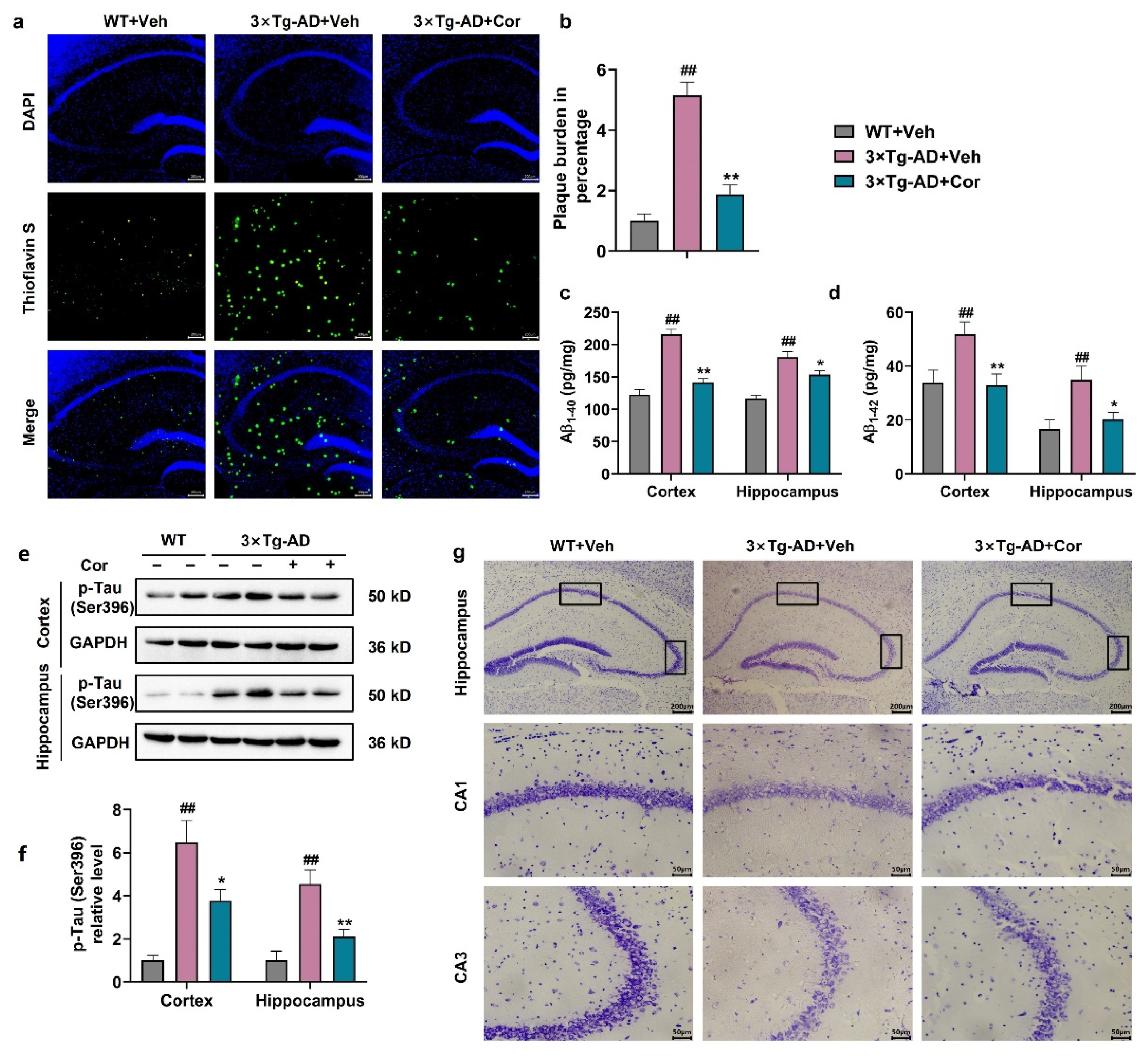
3.2. Cornuside Improved the Histomorphology, Reduced Amyloid Plaque and Inhibited Tau Phosphorylation in Brains of 3 × Tg-AD Mice
3.3. Cornuside Inhibited the Activation of Glial Cells in 3 × Tg-AD Mice
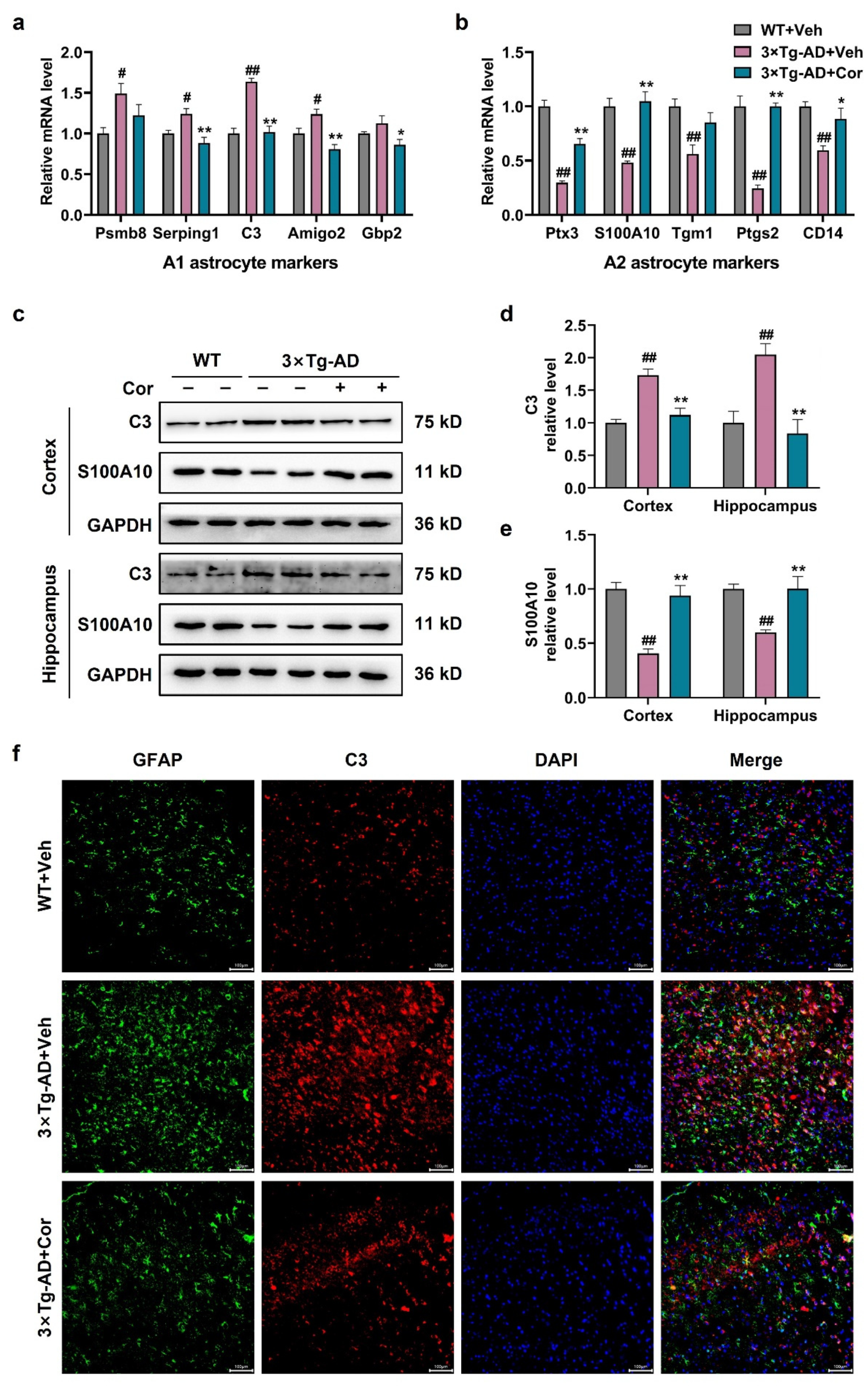
3.4. Cornuside Regulated A1/A2 Astrocytic Phenotype Alteration in 3 × Tg-AD Mice
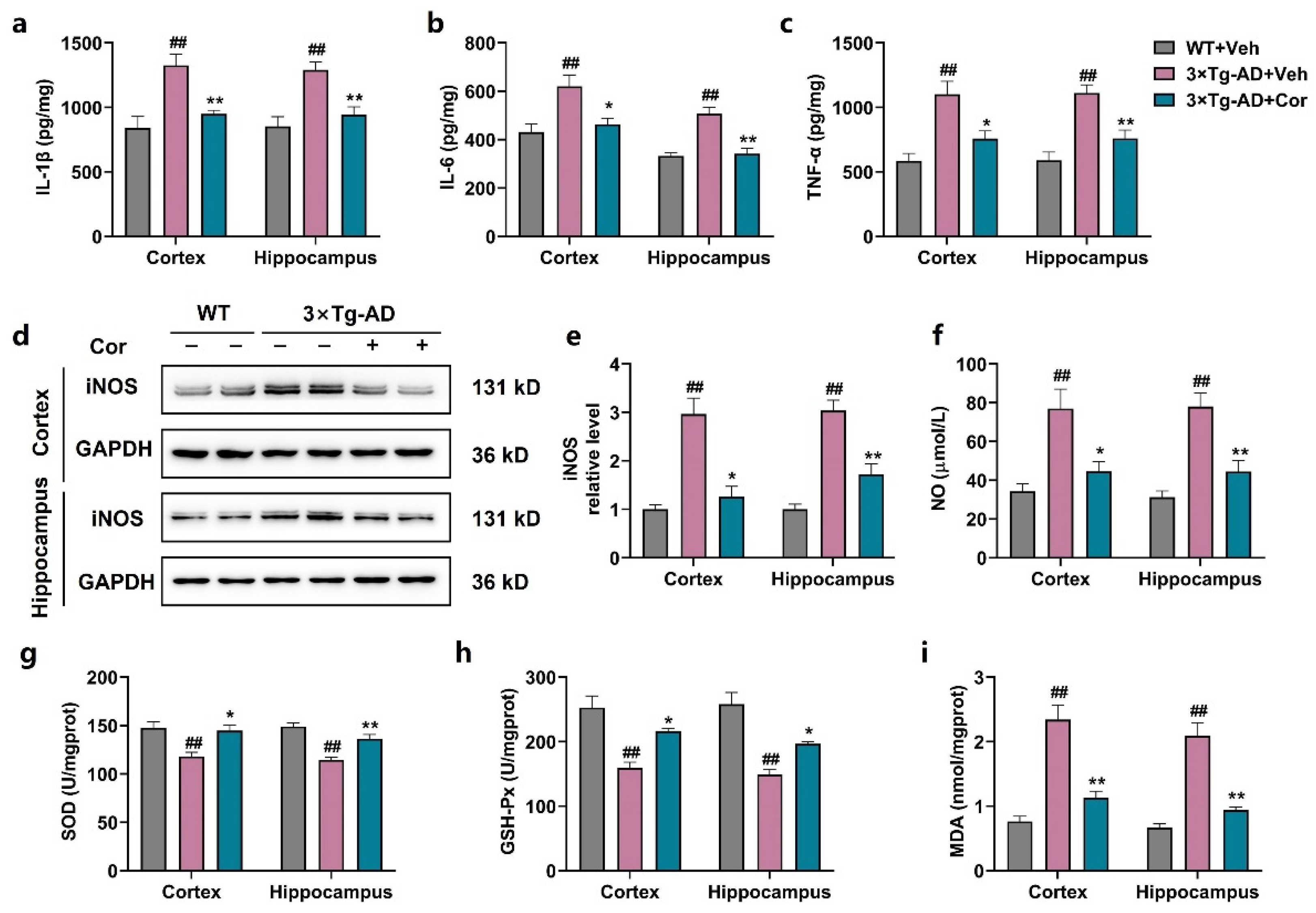
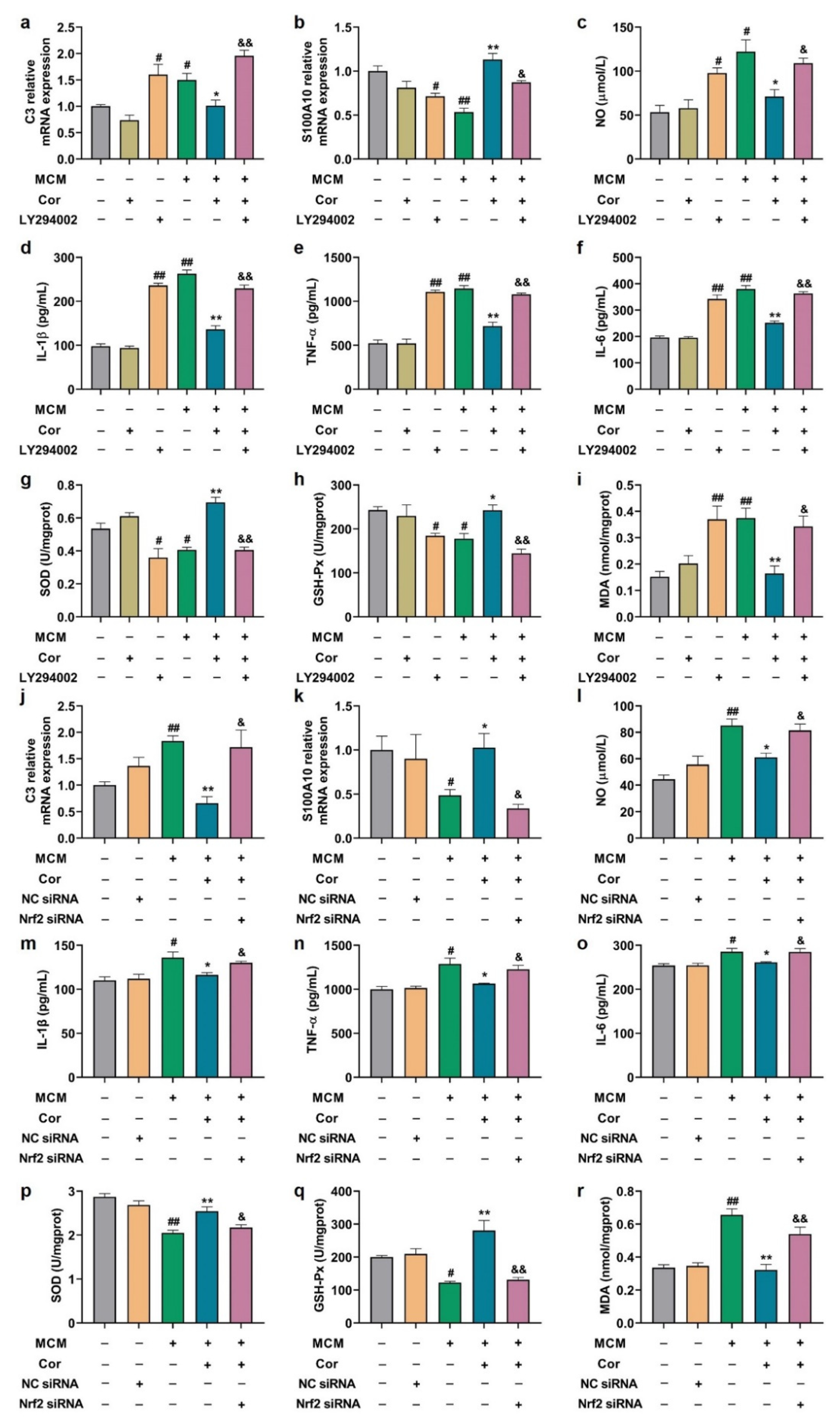
3.5. Cornuside Reduced Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in Brains of 3 × Tg-AD Mice
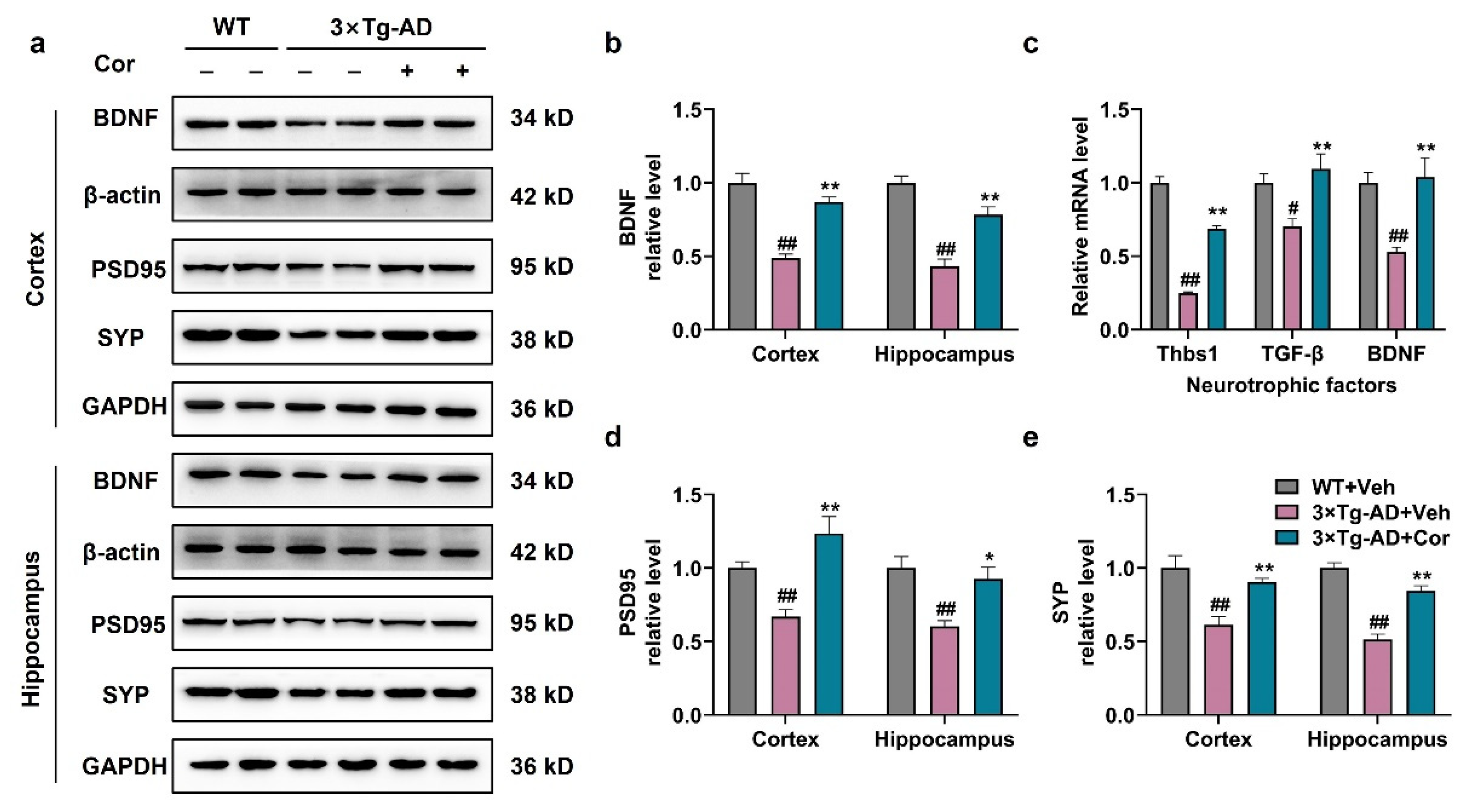
3.6. Cornuside Increased Neurotrophic Factors and Synapse-Associated Proteins in 3 × Tg-AD Mice
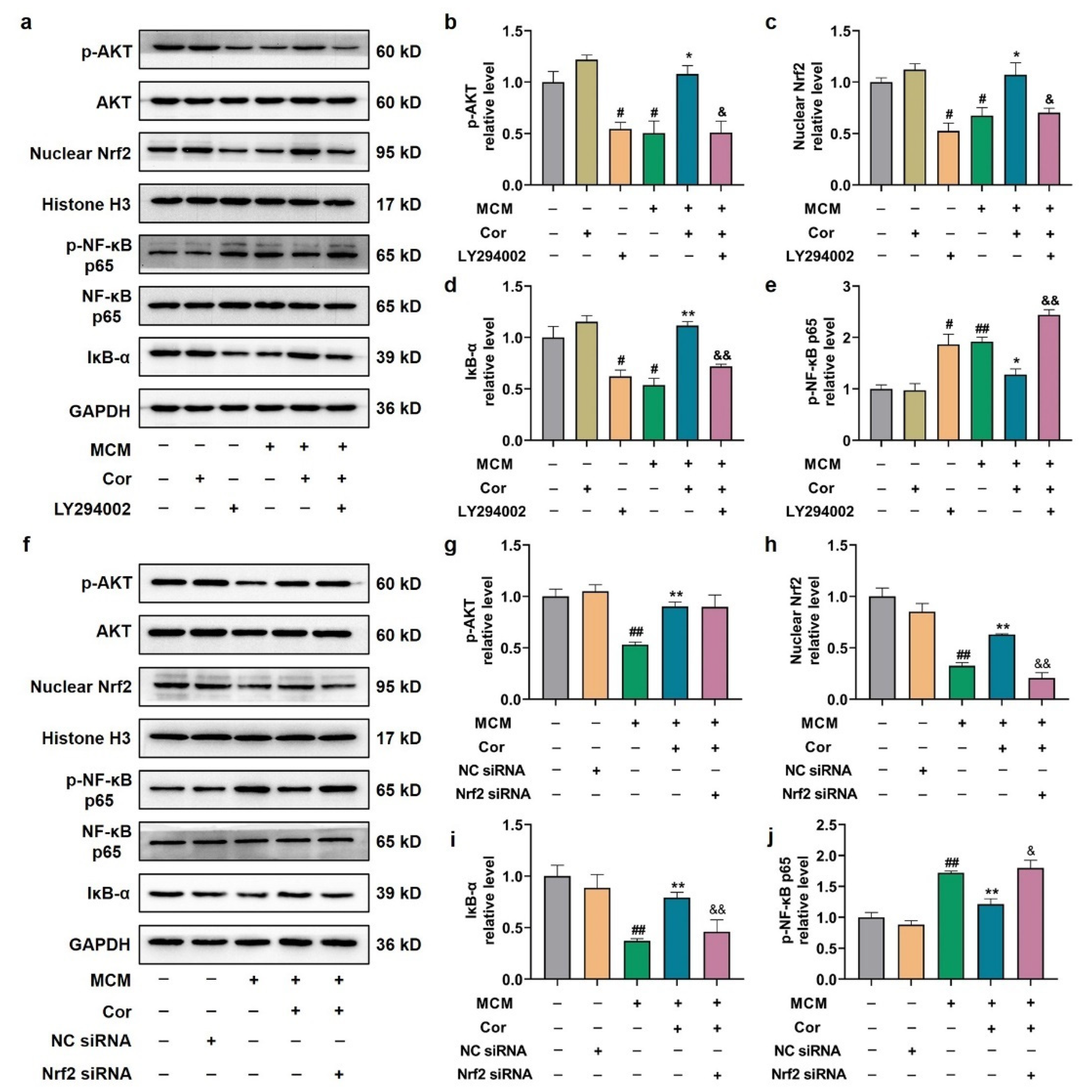
3.7. Cornuside Activated AKT/Nrf2 Pathway and Inhibited NF-κB Signaling in 3 × Tg-AD Mice
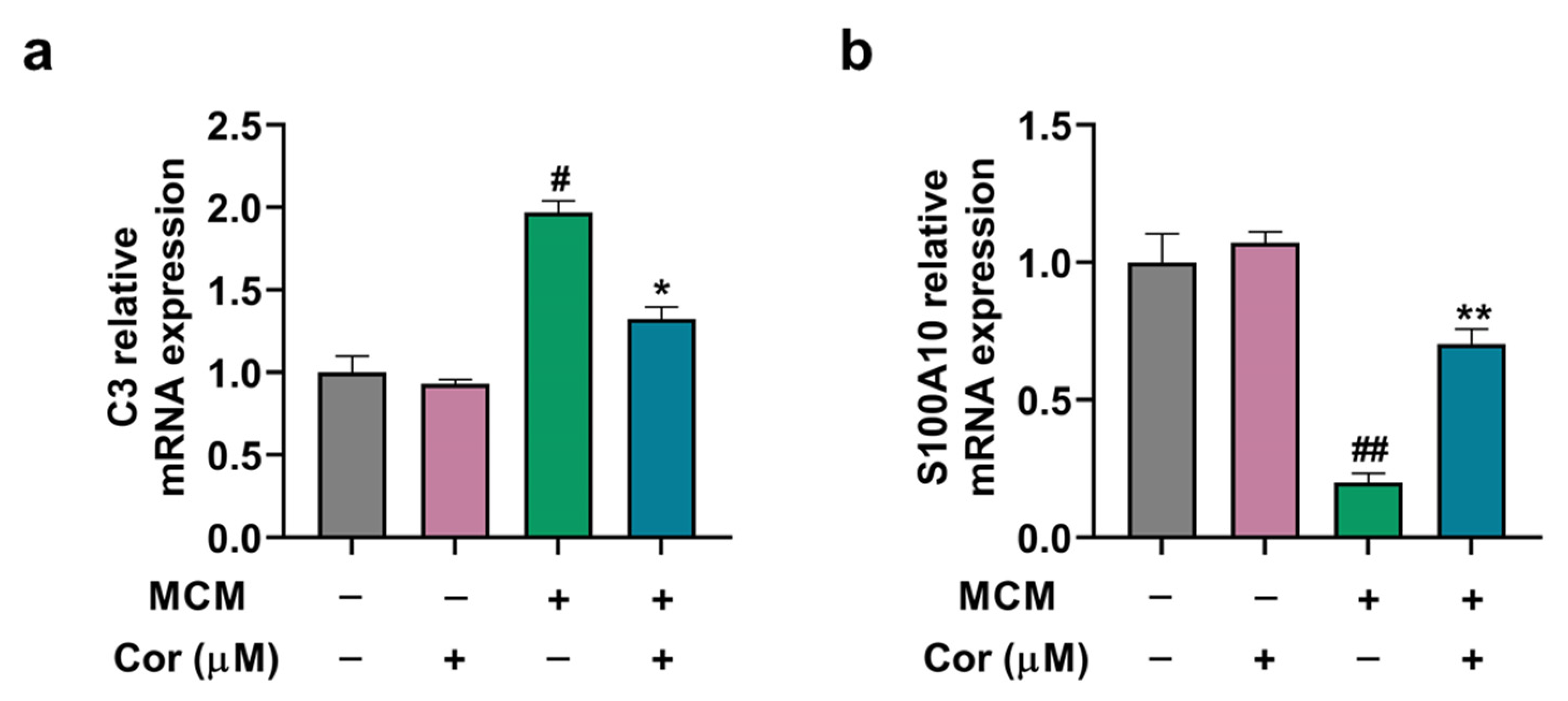
3.8. Cornuside Regulated A1/A2 Phenotypic Switch of C6 Cells Induced by MCM
3.9. Cornuside Protected C6 Cells Induced by MCM via AKT/Nrf2/NF-κB
3.10. Effects of PI3K Inhibitor and Nrf2 Silencing on Astrocyte Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Strooper, B.; Karran, E. The Cellular Phase of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 2016, 164, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Xu, H.; Huang, Y.; Mo, D.; Song, L.; Jia, B.; Wang, B.; Jin, Z.; Miao, Z. Deposition of BACE-1 Protein in the Brains of APP/PS1 Double Transgenic Mice. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8380618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Villain, N.; Frisoni, G.B.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Sabbagh, M.; Cappa, S.; Bejanin, A.; Bombois, S.; Epelbaum, S.; Teichmann, M.; et al. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations of the International Working Group. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Aducanumab: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.B.; de Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, D.M.; Morris, J.C.; Goate, A.M. Alzheimer’s disease: The challenge of the second century. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 77sr71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisbet, R.M.; Gotz, J. Amyloid-beta and Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease: Novel Pathomechanisms and Non-Pharmacological Treatment Strategies. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2018, 64, S517–S527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2017, 57, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calsolaro, V.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Current evidence and future directions. Alzheimers. Dement. 2016, 12, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox. Biol. 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.F.; Santos, A.E.; Moreira, P.I.; Pereira, A.C.; Sousa, F.J.; Cardoso, S.M.; Cruz, M.T. Is Alzheimer’s disease an inflammasomopathy? Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 56, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; Khoury, J.E.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaman, I.; Belanger, M.; Magistretti, P.J. Astrocyte-neuron metabolic relationships: For better and for worse. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydon, P.G.; Carmignoto, G. Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1009–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogsdill, J.A.; Ramirez, J.; Liu, D.; Kim, Y.H.; Baldwin, K.T.; Enustun, E.; Ejikeme, T.; Ji, R.R.; Eroglu, C. Astrocytic neuroligins control astrocyte morphogenesis and synaptogenesis. Nature 2017, 551, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Munch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escartin, C.; Guillemaud, O.; Carrillo-de Sauvage, M.A. Questions and (some) answers on reactive astrocytes. Glia 2019, 67, 2221–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Tian, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, R.; Ning, B. Reactive Astrogliosis: Implications in Spinal Cord Injury Progression and Therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 9494352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, Y.; He, W.; Di, W.; Fang, Y.; Shi, X. MFG-E8 reverses microglial-induced neurotoxic astrocyte (A1) via NF-kappaB and PI3K-Akt pathways. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 234, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Gong, F.; Rong, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tang, P.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, T.; Jiang, T.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury by Suppressing the Activation of A1 Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes. J. Neurotraum. 2019, 36, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Fu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Lou, J.; et al. Cottonseed oil alleviates ischemic stroke injury by inhibiting the inflammatory activation of microglia and astrocyte. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vismara, I.; Papa, S.; Veneruso, V.; Mauri, E.; Mariani, A.; De Paola, M.; Affatato, R.; Rossetti, A.; Sponchioni, M.; Moscatelli, D.; et al. Selective Modulation of A1 Astrocytes by Drug-Loaded Nano-Structured Gel in Spinal Cord Injury. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Lu, J.; Mei, S.; Wu, H.; Sun, Z.; Fang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Xu, W.; et al. Ceria nanoparticles ameliorate white matter injury after intracerebral hemorrhage: Microglia-astrocyte involvement in remyelination. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.O.; Kim, S.Y.; Han, S.M.; Kim, H.M.; Ham, S.S.; Kang, I.J. Corni fructus scavenges hydroxy radicals and decreases oxidative stress in endothelial cells. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Kwak, J.H. A furan derivative from Cornus officinalis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1998, 21, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.J.; Zhong, X.J.; Zhang, B.; Juan, J.; Shang, X.Y. New Iridoid Derivatives from the Fruits of Cornus officinalis and Their Neuroprotective Activities. Molecules 2019, 24, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozanski, T.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Szumny, A.; Magdalan, J.; Bielska, K.; Merwid-Lad, A.; Wozniak, A.; Dzimira, S.; Piorecki, N.; Trocha, M. The protective effect of the Cornus mas fruits (cornelian cherry) on hypertriglyceridemia and atherosclerosis through PPARalpha activation in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.; Niu, D.; Guo, C.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Bai, J.; Li, X.; Kang, J. Comparative Study of Crude and Wine-Processing Corni Fructus on Chemical Composition and Antidiabetic Effects. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 2019, 3986964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Gao, Q.; Yin, L.; Quan, H.; Chen, R.; Fu, X.; Lin, D. Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 213, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, E.-B.; Birhanu, B.T.; Ali, M.S.; Abbas, M.A.; Boby, N.; Im, Z.-E.; Park, S.-C. Cornus officinalis Ethanolic Extract with Potential Anti-Allergic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antioxidant Activities. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Lim, E.; Yeo, S.; Yong, Y.; Yang, J.; Jeong, S.-Y. Anti-Menopausal Effects of Cornus officinalis and Ribes fasciculatum Extract In Vitro and In Vivo. Nutrients 2020, 12, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, M.Y.; Ji, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Hwangbo, H.; Park, C.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, G.-Y.; Choi, Y.H. The Protective Effect of Oral Application of Corni Fructus on the Disorders of the Cornea, Conjunctiva, Lacrimal Gland and Retina by Topical Particulate Matter 2.5. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.G.; Moon, M.K.; Lee, A.S.; Kwon, T.O.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.S. Cornuside suppresses cytokine-induced proinflammatory and adhesion molecules in the human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1796–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Song, S.Z.; Choi, Y.H.; Jin, G.Y.; Li, G.Z.; Yan, G.H. Protective effect of cornuside against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic injury. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jin, G.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, M.; Jin, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, G.; Choi, Y.; Yan, G. Cornuside inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic response by down-regulating MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.L.; Chen, X.G.; Zhu, H.B.; Hou, J.; Tian, J.W. Cornuside attenuates apoptosis and ameliorates mitochondrial energy metabolism in rat cortical neurons. Pharmacology 2009, 84, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakta, H.K.; Park, C.H.; Yokozawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Potential anti-cholinesterase and beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 inhibitory activities of cornuside and gallotannins from Cornus officinalis fruits. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 836–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Wang, M.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H.; Pu, X.; Song, S.; Yang, C.; Yan, Y.; Doring, Y.; Xie, X.; et al. Curcumin Reduces Cognitive Deficits by Inhibiting Neuroinflammation through the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway in Apolipoprotein E4 Transgenic Mice. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 6654–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.J.; Shi, J.Z.; He, Y.Y.; Hao, J.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Luo, D.M.; Song, J.K.; Yan, Y.; Xie, X.M.; Du, G.H.; et al. Luteolin alleviates cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent neuroinflammation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilg, A.; Bechstein, P.; Saade, A.; Dick, M.; Li, T.X.; Tosini, G.; Rami, A.; Zemmar, A.; Stehle, J.H. Melatonin modulates daytime-dependent synaptic plasticity and learning efficiency. J. Pineal. Res. 2019, 66, e12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; He, Y.Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.W.; Zhao, J.H.; Ye, J.; Lian, T.Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.J.; et al. DNA methyltransferase 3B deficiency unveils a new pathological mechanism of pulmonary hypertension. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Y.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, J.H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, S.S.; Ye, J.; Lian, T.Y.; et al. Spermine promotes pulmonary vascular remodelling and its synthase is a therapeutic target for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Su, Y.L.; Wang, Q.; Huang, S.W.; Pan, Z.F.; Chen, Y.P.; Liang, J.J.; Zhang, M.L.; Xie, X.Q.; et al. Baicalein ameliorates ulcerative colitis by improving intestinal epithelial barrier via AhR/IL-22 pathway in ILC3s. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loera-Valencia, R.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Kenigsberg, P.A.; Page, G.; Duarte, A.I.; Giusti, P.; Zusso, M.; Robert, P.; Frisoni, G.B.; Cattaneo, A.; et al. Current and emerging avenues for Alzheimer’s disease drug targets. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 286, 398–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttenplan, K.A.; Liddelow, S.A. Astrocytes and microglia: Models and tools. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekny, M.; Pekna, M. Astrocyte reactivity and reactive astrogliosis: Costs and benefits. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1077–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Barres, B.A. Reactive Astrocytes: Production, Function, and Therapeutic Potential. Immunity 2017, 46, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.E.; Liddelow, S.A.; Chakraborty, C.; Munch, A.E.; Heiman, M.; Barres, B.A. Normal aging induces A1-like astrocyte reactivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1896–E1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, A.; Dirnagl, U.; Urra, X.; Planas, A.M. Neuroprotection in acute stroke: Targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Tian, D.C.; Li, Z.G.; Ducruet, A.F.; Lawton, M.T.; Shi, F.D. Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, C.; Anderson, H.D.; Anderson, C.M. Astrocyte dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 2430–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Reyes, R.E.; Nava-Mesa, M.O.; Vargas-Sanchez, K.; Ariza-Salamanca, D.; Mora-Munoz, L. Involvement of Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease from a Neuroinflammatory and Oxidative Stress Perspective. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xi, J.; Xiao, B.; Li, Y.; Ma, C. Neuroprotective effect of fasudil on inflammation through PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin dependent pathways in a mice model of Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 2354–2364. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, F.; Li, H.; Chen, B. Ginkgetin aglycone ameliorates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by activating SIRT1 via inhibiting the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Han, J.; Yuan, R.; Xue, L.; Pang, W. Berberine ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natoli, G.; De Santa, F. Shaping alternative NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression programs: New clues to specificity. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabel, S.; Koncina, E.; Dorban, G.; Heurtaux, T.; Birck, C.; Glaab, E.; Michelucci, A.; Heuschling, P.; Grandbarbe, L. Inflammation Promotes a Conversion of Astrocytes into Neural Progenitor Cells via NF-kappaB Activation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5041–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Feng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, L.; Zhang, C.; Yao, W. Microglia induce the transformation of A1/A2 reactive astrocytes via the CXCR7/PI3K/Akt pathway in chronic post-surgical pain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, G. Fortunellin protects against high fructose-induced diabetic heart injury in mice by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress via AMPK/Nrf-2 pathway regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; An, Z. Hesperidin attenuates learning and memory deficits in APP/PS1 mice through activation of Akt/Nrf2 signaling and inhibition of RAGE/NF-kappaB signaling. Arch Pharm. Res. 2018, 41, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Li, C.C.; Liu, K.L.; Lii, C.K.; Chen, H.W. Andrographolide inhibits TNFalpha-induced ICAM-1 expression via suppression of NADPH oxidase activation and induction of HO-1 and GCLM expression through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt/AP-1 pathways in human endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 91, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.S.; Lin, A.H.; Yang, T.C.; Liu, K.L.; Chen, H.W.; Lii, C.K. Shikonin inhibits oxidized LDL-induced monocyte adhesion by suppressing NFkappaB activation via up-regulation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent antioxidation in EA.hy926 endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.H.; Kuo, C.T.; Chang, G.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Lai, Y.J.; Cheng, M.L.; Chen, W.J. Rosuvastatin suppresses atrial tachycardia-induced cellular remodeling via Akt/Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 pathway. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2015, 82, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.-Z.; Zheng, X.-M.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Yun, L.-Y.; Luo, D.-M.; Hao, J.-J.; Liu, P.-F.; Zhang, W.-K.; Xu, J.-K.; Yan, Y.; et al. Cornuside Is a Potential Agent against Alzheimer’s Disease via Orchestration of Reactive Astrocytes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153179
Shi J-Z, Zheng X-M, Zhou Y-F, Yun L-Y, Luo D-M, Hao J-J, Liu P-F, Zhang W-K, Xu J-K, Yan Y, et al. Cornuside Is a Potential Agent against Alzheimer’s Disease via Orchestration of Reactive Astrocytes. Nutrients. 2022; 14(15):3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153179
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jun-Zhuo, Xiao-Ming Zheng, Yun-Feng Zhou, Lu-Yao Yun, Dong-Mei Luo, Jiao-Jiao Hao, Peng-Fei Liu, Wei-Ku Zhang, Jie-Kun Xu, Yi Yan, and et al. 2022. "Cornuside Is a Potential Agent against Alzheimer’s Disease via Orchestration of Reactive Astrocytes" Nutrients 14, no. 15: 3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153179
APA StyleShi, J.-Z., Zheng, X.-M., Zhou, Y.-F., Yun, L.-Y., Luo, D.-M., Hao, J.-J., Liu, P.-F., Zhang, W.-K., Xu, J.-K., Yan, Y., Xie, X.-M., He, Y.-Y., & Pang, X.-B. (2022). Cornuside Is a Potential Agent against Alzheimer’s Disease via Orchestration of Reactive Astrocytes. Nutrients, 14(15), 3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153179






