Postoperative Diet with an Oligomeric Hyperproteic Normocaloric Supplement versus a Supplement with Immunonutrients in Colorectal Cancer Surgery: Results of a Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Interventions
2.4. Variable Description and Outcome Measures
2.5. Sample Size
2.6. Randomization and Blinding
2.7. Statistical Methods
3. Results
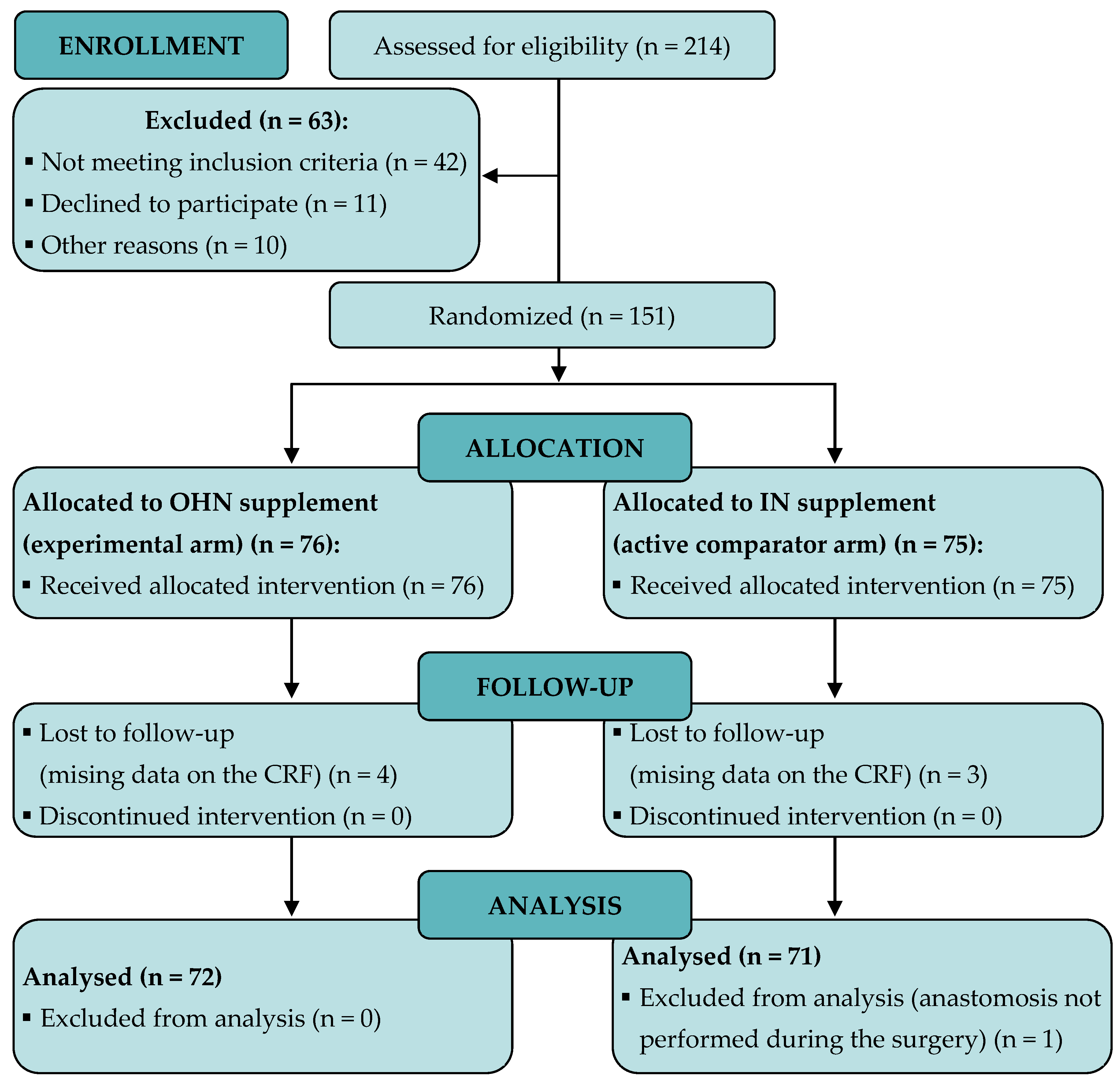
3.1. Patient Recruitment and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Primary Endpoint: Clinical Complications after Intestinal Anastomosis
3.3. Secondary Endpoint: Safety Analysis of OHN versus IN Supplement
3.4. Tolerance to Oral Dietary Supplement and Blood Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kreymann, K.G. Early Nutrition Support in Critical Care: A European Perspective. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, C. Immunonutrition. J. Visc. Surg. 2015, 152, S14–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanden-Berghe, C.; Sanz-Valero, J.; Arroyo-Sebastián, A.; Cheikh-Moussa, K.; Moya-Forcen, P. Effects of a Nutritional Intervention in a Fast-Track Program for a Colorectal Cancer Surgery: Systematic Review. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 983–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipworth, R.J.E.; Fearon, K.C.H. The Scientific Rationale for Optimizing Nutritional Support in Cancer. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 19, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finco, C.; Magnanini, P.; Sarzo, G.; Vecchiato, M.; Luongo, B.; Savastano, S.; Bortoliero, M.; Barison, P.; Merigliano, S. Prospective Randomized Study on Perioperative Enteral Immunonutrition in Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2007, 21, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, L.; Hogan, S.; Allman-Farinelli, M.; Carey, S. Oral Nutrition Interventions in Patients Undergoing Gastrointestinal Surgery for Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 5673–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, P.; Soriano-Irigaray, L.; Ramirez, J.M.; Garcea, A.; Blasco, O.; Blanco, F.J.; Brugiotti, C.; Miranda, E.; Arroyo, A. Perioperative Standard Oral Nutrition Supplements Versus Immunonutrition in Patients Undergoing Colorectal Resection in an Enhanced Recovery (ERAS) Protocol: A Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial (SONVI Study). Medicine 2016, 95, e3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornblade, L.W.; Varghese, T.K.; Shi, X.; Johnson, E.K.; Bastawrous, A.; Billingham, R.P.; Thirlby, R.; Fichera, A.; Flum, D.R. Preoperative Immunonutrition and Elective Colorectal Resection Outcomes. Dis. Colon Rectum 2017, 60, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, T.W. Immunonutrition in Critical Illness: Limited Benefit, Potential Harm. JAMA 2014, 312, 490–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimann, A.; Braga, M.; Carli, F.; Higashiguchi, T.; Hübner, M.; Klek, S.; Laviano, A.; Ljungqvist, O.; Lobo, D.N.; Martindale, R.; et al. ESPEN Guideline: Clinical Nutrition in Surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 623–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Zanten, A.R.H.; Sztark, F.; Kaisers, U.X.; Zielmann, S.; Felbinger, T.W.; Sablotzki, A.R.; De Waele, J.J.; Timsit, J.F.; Honing, M.L.H.; Keh, D.; et al. High-Protein Enteral Nutrition Enriched with Immune-Modulating Nutrients vs Standard High-Protein Enteral Nutrition and Nosocomial Infections in the ICU: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2014, 312, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Hopewell, S.; Schulz, K.F.; Montori, V.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Devereaux, P.J.; Elbourne, D.; Egger, M.; Altman, D.G. CONSORT 2010 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Parallel Group Randomised Trials. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 10, 28–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asociación Española de Cirujanos. Colorectal Surgery, 2nd ed.; Ortiz Hurtado, H., Ed.; Arán Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2012; ISBN 978-84-92977-34-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wittekind, C.; Asamura, H.; Sobin, L.H. TNM Atlas: Illustrated Guide to the TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 6th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1-118-69564-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, C.; Compher, C.; Ellen, D.M. A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines: Nutrition Screening, Assessment, and Intervention in Adults. J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2011, 35, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, K.C.H.; Ljungqvist, O.; Von Meyenfeldt, M.; Revhaug, A.; Dejong, C.H.C.; Lassen, K.; Nygren, J.; Hausel, J.; Soop, M.; Andersen, J.; et al. Enhanced Recovery after Surgery: A Consensus Review of Clinical Care for Patients Undergoing Colonic Resection. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA). ASA Physical Status Classification System. 2014. Available online: https://www.asahq.org/standards-and-guidelines/asa-physical-status-classification-system (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of Surgical Complications: A New Proposal with Evaluation in a Cohort of 6336 Patients and Results of a Survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berriós-Torres, S.I.; Umscheid, C.A.; Bratzler, D.W.; Leas, B.; Stone, E.C.; Kelz, R.R.; Reinke, C.E.; Morgan, S.; Solomkin, J.S.; Mazuski, J.E.; et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017. JAMA Surg. 2017, 152, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.; Capretti, G.; Beretta, L.; Gemma, M.; Pecorelli, N.; Braga, M. Enhanced Recovery Program in Colorectal Surgery: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. World J. Surg. 2014, 38, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colebatch, E.; Lockwood, C. Enhanced Perioperative Nutritional Care for Patients Undergoing Elective Colorectal Surgery at Calvary North Adelaide Hospital: A Best Practice Implementation Project. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 224–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, U.O.; Scott, M.J.; Schwenk, W.; Demartines, N.; Roulin, D.; Francis, N.; McNaught, C.E.; MacFie, J.; Liberman, A.S.; Soop, M.; et al. Guidelines for Perioperative Care in Elective Colonic Surgery: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS®) Society Recommendations. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, S.E.; Hilkewich, L.; Gillis, C.; Heine, J.A.; Fenton, T.R. Protein Intakes Are Associated with Reduced Length of Stay: A Comparison between Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) and Conventional Care after Elective Colorectal Surgery. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, S.T.; Gibson, D.J.; Lal, S.; Hill, J.; Pilling, M.; Soop, M.; Ramesh, A.; Todd, C. Pre-Operative Oral Nutritional Supplementation with Dietary Advice versus Dietary Advice Alone in Weight-Losing Patients with Colorectal Cancer: Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burden, S.T.; Hill, J.; Shaffer, J.L.; Campbell, M.; Todd, C. An Unblinded Randomised Controlled Trial of Preoperative Oral Supplements in Colorectal Cancer Patients. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2011, 24, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, C.; Loiselle, S.E.; Fiore, J.F.; Awasthi, R.; Wykes, L.; Liberman, A.S.; Stein, B.; Charlebois, P.; Carli, F. Prehabilitation with Whey Protein Supplementation on Perioperative Functional Exercise Capacity in Patients Undergoing Colorectal Resection for Cancer: A Pilot Double-Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Paris, A.; Martinez-Trufero, J.; Lambea-Sorrosal, J.; Calvo-Gracia, F.; Milà-Villarroel, R. Clinical and Nutritional Effectiveness of a Nutritional Protocol with Oligomeric Enteral Nutrition in Patients with Oncology Treatment-Related Diarrhea. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreiro, B.; Llopis-Salinero, S.; Lardies, B.; Granados-Colomina, C.; Milà-Villarroel, R. Clinical and Nutritional Impact of a Semi-Elemental Hydrolyzed Whey Protein Diet in Patients with Active Crohn’s Disease: A Prospective Observational Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | OHN Supplement Group (n = 72) | IN Supplement Group (n = 71) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years): Mean ± SD | 69.8 ± 11.7 | 69.6 ± 11.8 | 0.657 |
| Sex (men): n (%) | 39 (54.2%) | 45 (63.4%) | 0.263 |
| Previous diagnosis of diverticular disease, n (%) | 11 (15.3%) | 7 (9.9%) | 0.329 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 11 (15.3%) | 18 (25.4%) | 0.134 |
| Smoking habit, n (%) | 17 (23.6%) | 15 (21.1%) | 0.722 |
| Kidney failure, n (%) | 2 (2.8%) | 5 (7.0%) | 0.237 |
| Previous abdominal surgery | 29 (40.3%) | 25 (35.2%) | 0.532 |
| Obesity (BMI > 30) | 18 (25.0%) | 15 (21.1%) | 0.583 |
| ASA III | 20 (27.8%) | 20 (28.2%) | 0.958 |
| Laparoscopic approach | 55 (76.4%) | 59 (83.1%) | 0.604 |
| Variable | Occurrence/Grade | Total (n = 143) | OHN Supplement Group (n = 72) | IN Supplement Group (n = 71) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complications, n (%) | Yes | 41 (28.7%) | 18 (25.0%) | 23 (32.4%) | 0.328 |
| No | 102 (71.3%) | 54 (75.0%) | 48 (67.6%) | ||
| Severity of complications 1, n (%) | I | 7 (4.9%) | 5 (6.9%) | 2 (2.8%) | ND |
| II | 16 (11.2%) | 5 (6.9%) | 11 (15.5%) | ||
| IIIA | 6 (4.2%) | 3 (4.2%) | 3 (4.2%) | ||
| IIIB | 9 (6.3%) | 4 (5.6%) | 5 (7.0%) | ||
| IVA | 2 (1.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (2.8%) | ||
| IVB | --- | --- | --- | ||
| V | 1 (0.7%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Variable | Test | P1 (OHN) | P2 (IN) | Difference in Proportions (P1-P2) | Statistical Test Score | Probability Level | Rejection of Null Hypothesis? 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postoperative complications | F-M Score | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.07 | −0.35 | 0.36 | No |
| M-N Score | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.07 | −0.34 | 0.37 | No | |
| Surgical site infections | F-M Score | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.04 | −1.02 | 0.15 | No |
| M-N Score | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.04 | −1.01 | 0.16 | No | |
| Hospital readmissions | F-M Score | 0.92 | 0.96 | −0.04 | −0.89 | 0.00 | Yes |
| M-N Score | 0.92 | 0.96 | −0.04 | −0.88 | 0.00 | Yes | |
| <7 days hospital stays | F-M Score | 0.33 | 0.41 | −0.08 | −2.17 | 0.01 | Yes |
| M-N Score | 0.33 | 0.41 | −0.08 | −2.17 | 0.02 | Yes |
| Variable | Occurrence | Total (n = 143) | OHN Supplement Group (n = 72) | IN Supplement Group (n = 71) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical site infections, n (%) | Yes | 17 (11.9%) | 7 (9.7%) | 10 (14.1%) | 0.420 |
| No | 126 (88.1%) | 65 (90.3%) | 61 (85.9%) | ||
| Readmissions, n (%) | Yes | 9 (6.3%) | 6 (8.3%) | 3 (4.2%) | 0.312 |
| No | 134 (93.7%) | 66 (91.7%) | 68 (95.8%) | ||
| Deaths, n (%) | Yes | 1 (0.7%) | 1 (1.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | ND |
| No | 142 (99.3%) | 71 (98.6%) | 71 (100.0%) |
| OHN Supplement Group (n = 72) | IN Supplement Group (n = 71) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postoperative Day | Compl. Tolerance (400 mL) | Part. Tolerance (200 mL) | No Tolerance (<200 mL) | Compl. Tolerance (400 mL) | Part. Tolerance (200 mL) | No Tolerance (<200 mL) | p Value |
| 1 | 45 (62.5%) | 18 (25.0%) | 9 (12.5%) | 41 (57.7%) | 18 (25.4%) | 12 (16.9%) | 0.738 |
| 2 | 45 (62.5%) | 12 (16.7%) | 15 (20.8%) | 46 (64.8%) | 13 (18.3%) | 12 (16.9%) | 0.828 |
| 3 | 40 (55.6%) | 10 (13.9%) | 22 (30.6%) | 43 (60.6%) | 11 (15.5%) | 17 (23.9%) | 0.674 |
| 4 | 44 (61.1%) | 11 (15.3%) | 17 (23.6%) | 43 (60.6%) | 11 (15.4%) | 17 (23.4%) | 0.998 |
| 5 | 51 (70.8%) | 7 (9.7%) | 14 (19.4%) | 45 (63.4%) | 10 (14.1%) | 16 (22.5%) | 0.597 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benavides-Buleje, J.A.; Fernández-Fernández, P.V.; Ruiz-Úcar, E.; Solana-Bueno, A.; Parra-Baños, P.A.; Martínez-Torres, B.; Lozoya-Trujillo, R.; Ruiz-Carmona, M.D.; Alarcón-Iranzo, M.; Rentero-Redondo, L.; et al. Postoperative Diet with an Oligomeric Hyperproteic Normocaloric Supplement versus a Supplement with Immunonutrients in Colorectal Cancer Surgery: Results of a Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3062. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153062
Benavides-Buleje JA, Fernández-Fernández PV, Ruiz-Úcar E, Solana-Bueno A, Parra-Baños PA, Martínez-Torres B, Lozoya-Trujillo R, Ruiz-Carmona MD, Alarcón-Iranzo M, Rentero-Redondo L, et al. Postoperative Diet with an Oligomeric Hyperproteic Normocaloric Supplement versus a Supplement with Immunonutrients in Colorectal Cancer Surgery: Results of a Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2022; 14(15):3062. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153062
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenavides-Buleje, Jorge Alejandro, Pedro Vicente Fernández-Fernández, Elena Ruiz-Úcar, Amparo Solana-Bueno, Pedro Antonio Parra-Baños, Beatriz Martínez-Torres, Roberto Lozoya-Trujillo, María Dolores Ruiz-Carmona, Marina Alarcón-Iranzo, Lorena Rentero-Redondo, and et al. 2022. "Postoperative Diet with an Oligomeric Hyperproteic Normocaloric Supplement versus a Supplement with Immunonutrients in Colorectal Cancer Surgery: Results of a Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial" Nutrients 14, no. 15: 3062. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153062
APA StyleBenavides-Buleje, J. A., Fernández-Fernández, P. V., Ruiz-Úcar, E., Solana-Bueno, A., Parra-Baños, P. A., Martínez-Torres, B., Lozoya-Trujillo, R., Ruiz-Carmona, M. D., Alarcón-Iranzo, M., Rentero-Redondo, L., Peña-Ros, E., Muñoz-Camarena, J. M., Carrasco-Prats, M., Ramírez-Faraco, M., Portillo-Ortega, P., & Albarracín-Marín-Blázquez, A. (2022). Postoperative Diet with an Oligomeric Hyperproteic Normocaloric Supplement versus a Supplement with Immunonutrients in Colorectal Cancer Surgery: Results of a Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 14(15), 3062. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153062







