Mulberry Leaf and Neochlorogenic Acid Alleviates Glucolipotoxicity-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Proliferation/Migration via Downregulating Ras and FAK Signaling Pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of OH Medium, MLE and nCGA on Cell Viability and Proliferation of VSMCs
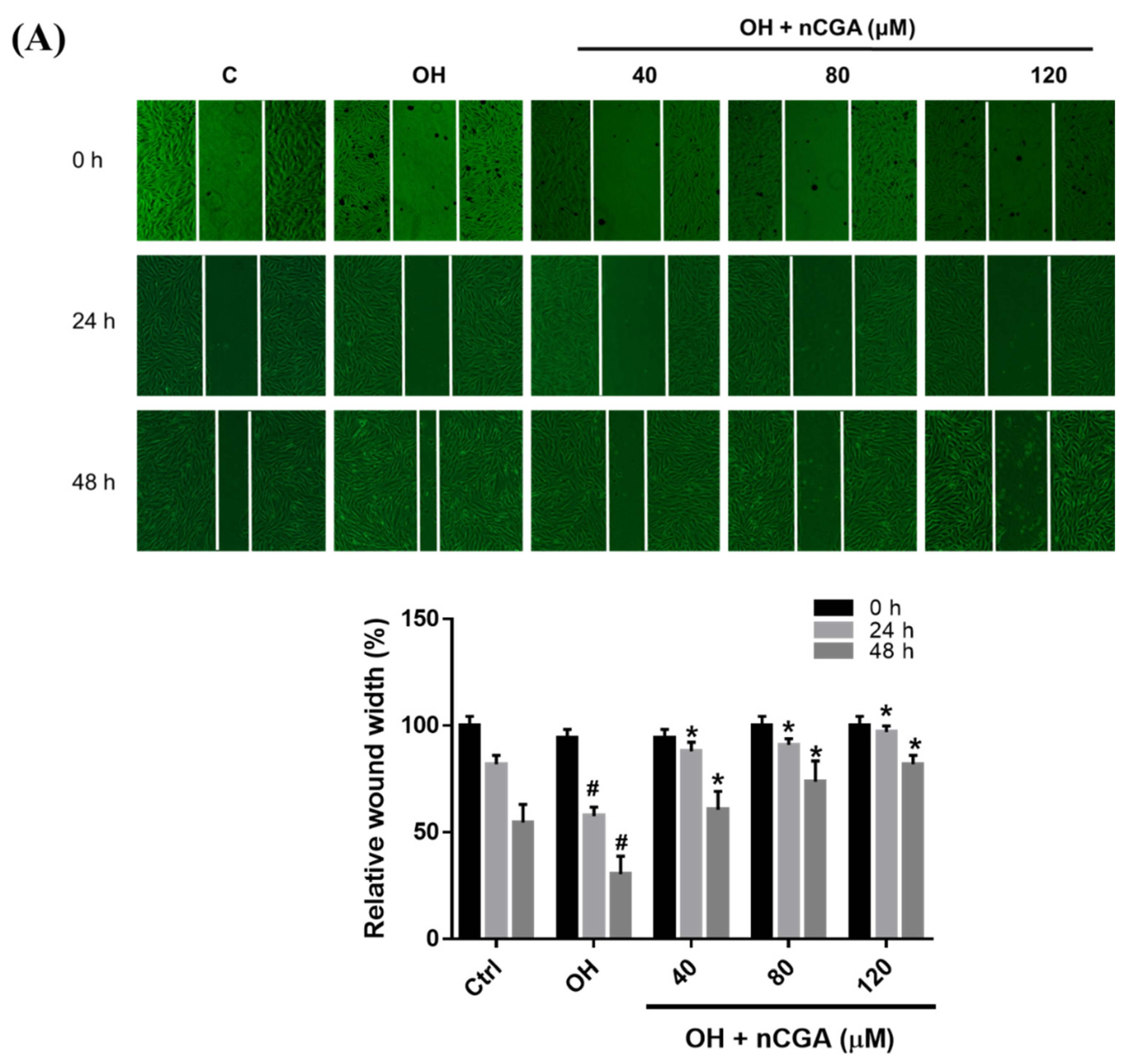
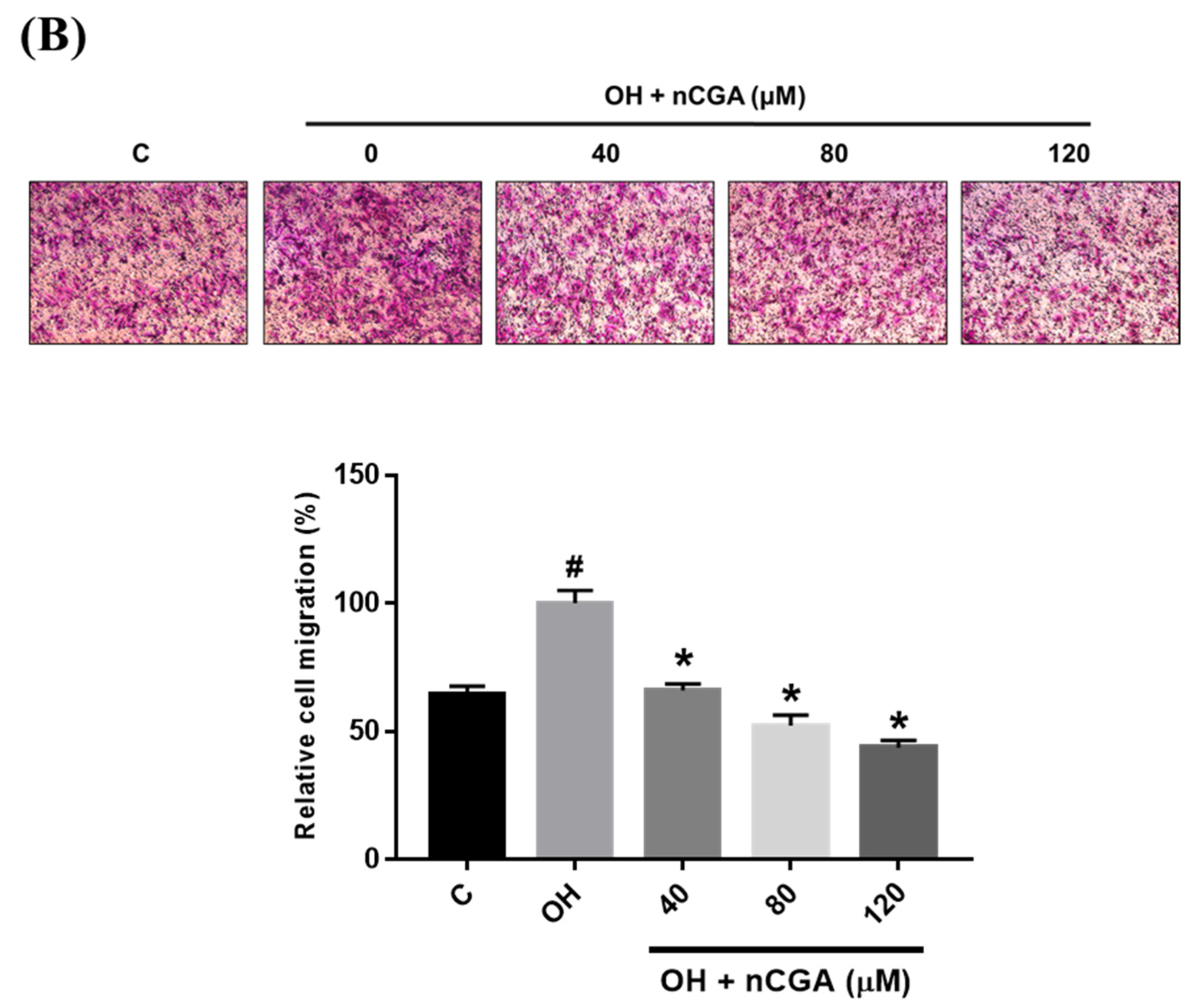
2.2. MLE and nCGA Inhibit the Migration of VSMCs Cultured in OH
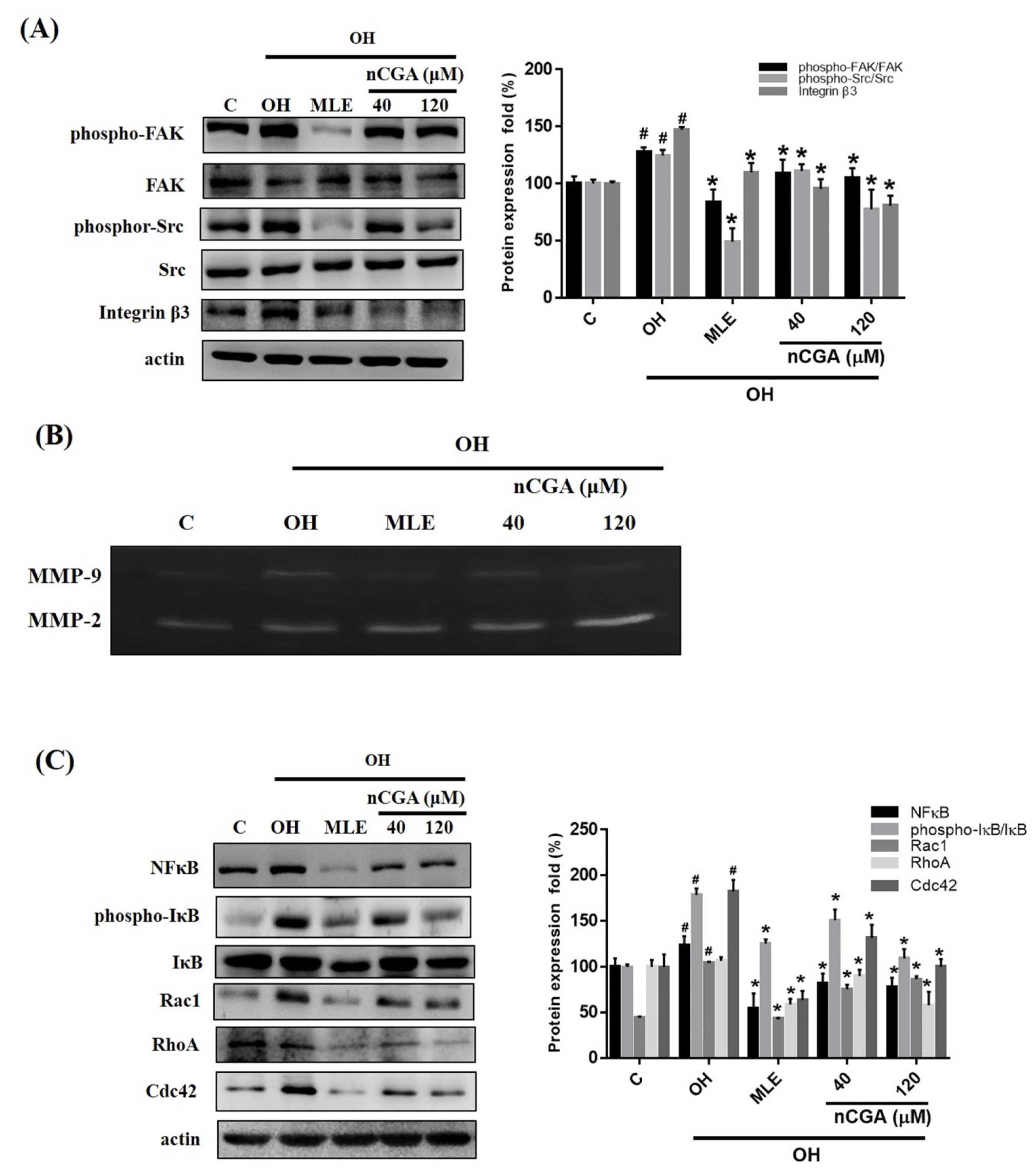
2.3. MLE and nCGA Decrease the Expression of FAK-Related Signaling Proteins in OH Cultured VSMCs
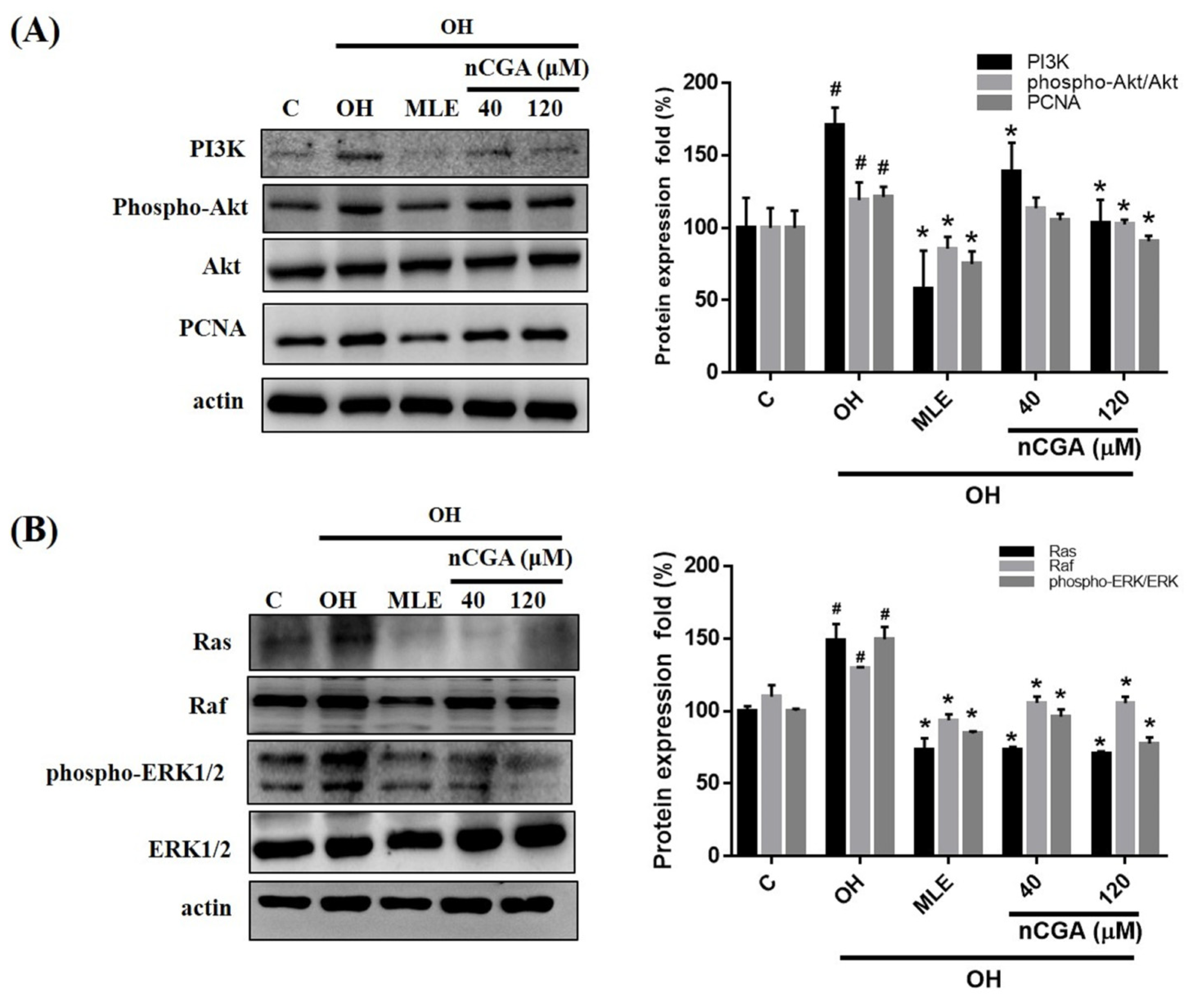
2.4. MLE and nCGA Inhibit Proliferation Related Proteins in OH Cultured VSMCs
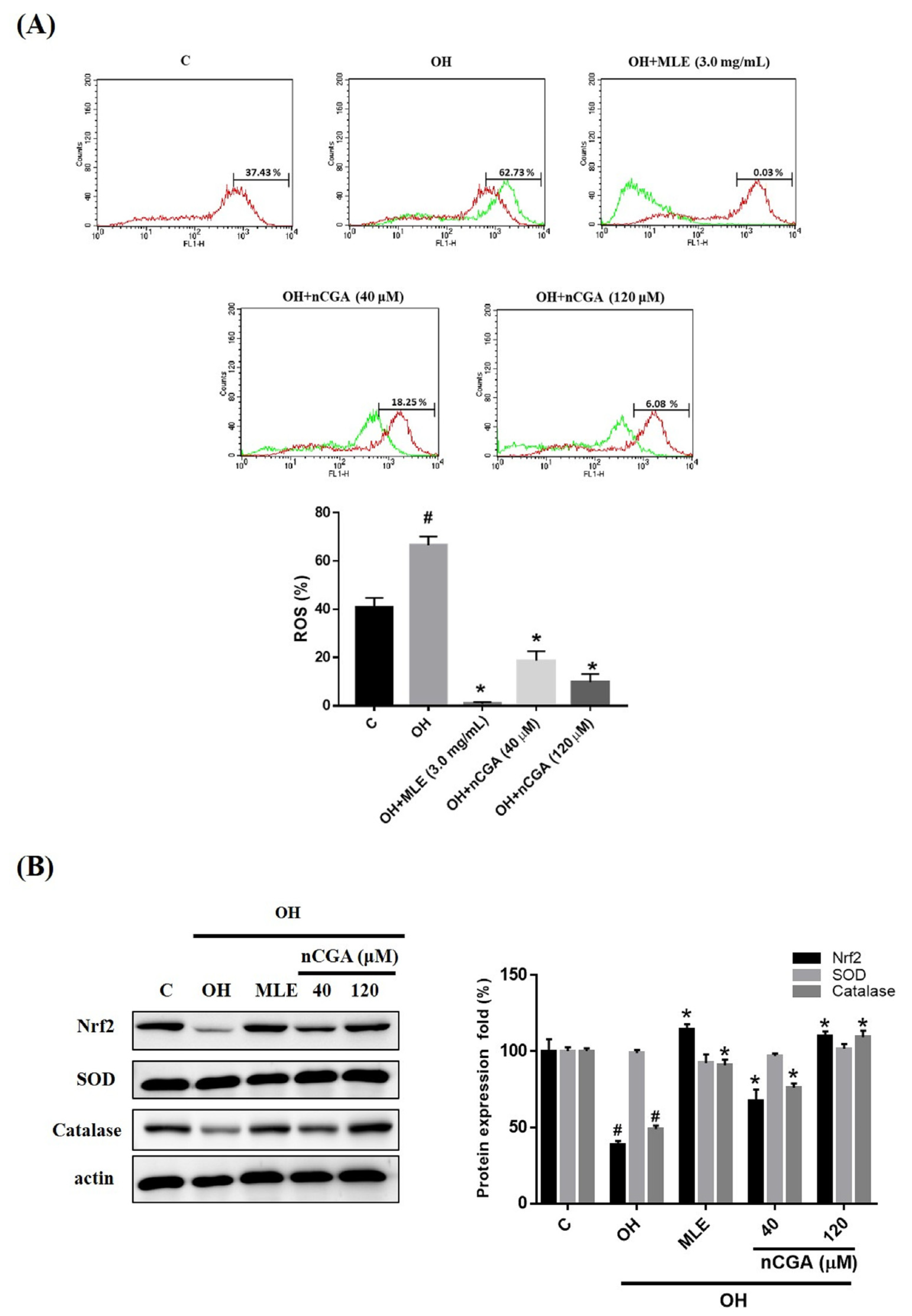
2.5. MLE and nCGA Decreased Levels of OH-Induced ROS
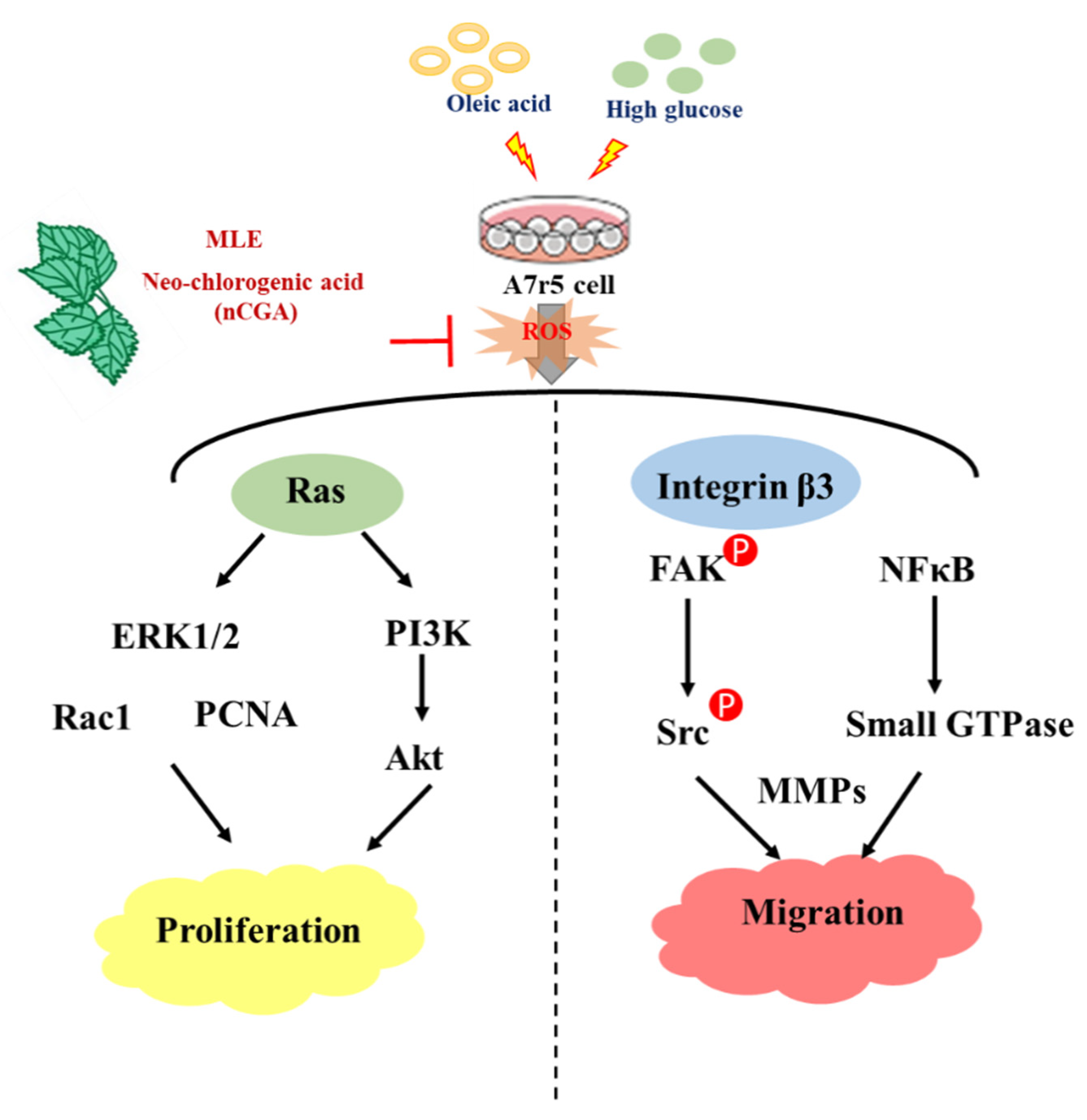
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Diabetic Conditions In Vitro Model and Experimental Design
4.4. Preparation of MLE
4.5. Cell Viability/Proliferation Assay
4.6. Wound Healing Assay
4.7. Transwell Migration Analysis
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Gelatin Zymography
4.10. Measurement of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AlJaroudi, W.A.; Petersen, J.L. Obesity, diabetes, and associated risk factors. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2006, 8, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Wang, X.; Meng, L.-B.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Luo, Y.; Gong, T.; Liu, D.-P.; Chen, Z.-G.; Li, Y.-J. Recent Progress of Chronic Stress in the Development of Atherosclerosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 4121173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, S.; Paul, C.; Alvarez, S.; Mine, Y.; Majumder, K. Dietary γ-Glutamyl Valine Ameliorates TNF-α-Induced Vascular Inflammation via Endothelial Calcium-Sensing Receptors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9139–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, N.; Formoso, G.; Pandolfi, A. Physiology and pathophysiology of oxLDL uptake by vascular wall cells in atherosclerosis. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2016, 84, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, A.L.; Speer, M.Y.; Scatena, M.; Giachelli, C.M.; Shanahan, C.M. Role of smooth muscle cells in vascular calcification: Implications in atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Niu, X.; Yu, J.; Xiao, X.; Zang, L.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, W. Imperatorin alleviates the abnormal proliferation, migration, and foaming of ox-LDL-induced VSMCs through regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-H.; Yang, T.-Y.; Ho, H.-H.; Huang, H.-P.; Chan, K.-C.; Wang, C.-J. Mulberry polyphenol extract inhibits FAK/Src/PI3K complex and related signaling to regulate the migration in A7r5 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3860–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunschmann, T.; Puder, S.; Fischer, T.; Steffen, A.; Rottner, K.; Mierke, C.T. The small GTPase Rac1 increases cell surface stiffness and enhances 3D migration into extracellular matrices. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Gordon, E.; Claesson-Welsh, L. Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, N.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Tian, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, N.; Tan, B.; Feng, H.; Feng, X.; Zou, L. Curcumol inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of melanoma via the miR-152-3p/PI3K/AKT and ERK/NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, N.-N.; Zhang, R.-R.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.-K.; Guo, X.; Wang, P.-P.; Sun, J.-Y. PDB-1 from Potentilla discolor Bunge suppresses lung cancer cell migration and invasion via FAK/Src and MAPK signaling pathways. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, Q.; Alam, A.; Cui, J.; Suen, K.C.; Soo, A.P.; Eguchi, S.; Gu, J.; Ma, D. The role of osteopontin in the progression of solid organ tumour. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, W.-Y.; Yu, M.-H.; Yang, T.-Y.; Chan, K.-C.; Wang, C.-J. Acarbose attenuates migration/proliferation via targeting microRNA-143 in vascular smooth muscle cells under diabetic conditions. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhao, L. The Mulberry (Morus alba L.) Fruit-A Review of Characteristic Components and Health Benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10383–10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-Y.; Wan, Y.; Hao, J.-Y.; Hu, R.-Z.; Chen, C.; Yao, X.-H.; Zhao, W.-G.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Li, L. Evaluation of the alkaloid, polyphenols, and antioxidant contents of various mulberry cultivars from different planting areas in eastern China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 122, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-C.; Wang, C.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hung, T.-W.; Lai, C.-J.; Kuo, C.-W.; Huang, H.-P. Mulberry fruits extracts induce apoptosis and autophagy of liver cancer cell and prevent hepatocarcinogenesis in vivo. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Shehabi, T.S.; Iratni, R.; Eid, A.H. Anti-atherosclerotic plants which modulate the phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.-C.; Lin, M.-C.; Huang, C.-N.; Chang, W.-C.; Wang, C.-J. Mulberry 1-deoxynojirimycin pleiotropically inhibits glucose-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell migration by activation of AMPK/RhoB and down-regulation of FAK. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9867–9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, J.; Corti, A.; Lerouge, L.; Pompella, A.; Gaucher, C. Phenotypic Modulation of Macrophages and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis—Nitro-Redox Interconnections. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Bian, F.; Hu, H.; Zhu, T.; Li, C.; Zhou, Q. Effects of Kindlin-2 on proliferation and migration of VSMC and integrinβ1 andβ3 activity via FAK-PI3K signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Zhu, N.; Niu, L.; Ding, X.; Xie, Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, F. Oleic Acid and Eicosapentaenoic Acid Reverse Palmitic Acid-induced Insulin Resistance in Human HepG2 Cells via the Reactive Oxygen Species/JUN Pathway. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 754–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogdu, M.; Canan, I.; Gecer, M.K.; Kan, T.; Ercisli, S. Phenolic compounds, bioactive content and antioxidant capacity of the fruits of mulberry (Morus spp.) germplasm in Turkey. Folia Hortic. 2017, 29, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Hsu, J.-D.; Lin, W.-L.; Kao, S.-H.; Wang, C.-J. Upregulation of caveolin-1 by mulberry leaf extract and its major components, chlorogenic acid derivatives, attenuates alcoholic steatohepatitis via inhibition of oxidative stress. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.-W.; Wong, C.N.-Y.; Pin, W.-K.; Wong, M.H.-Y.; Kwok, C.-Y.; Chan, R.Y.-K.; Yu, P.H.-F.; Chan, S.-W. Chlorogenic acid exhibits cholesterol lowering and fatty liver attenuating properties by up-regulating the gene expression of PPAR-α in hypercholesterolemic rats induced with a high-cholesterol diet. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.-W.; Hsu, A.; Tan, B.K.-H. Anti-diabetic and anti-lipidemic effects of chlorogenic acid are mediated by ampk activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sęczyk, Ł.; Świeca, M.; Kapusta, I.; Gawlik-Dziki, U. Protein–phenolic interactions as a factor affecting the physicochemical properties of white bean proteins. Molecules 2019, 24, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.-Y.; Huang, C.-N.; Chan, K.-C.; Yang, Y.-S.; Peng, C.-H.; Wang, C.-J. Mulberry leaf polyphenols possess antiatherogenesis effect via inhibiting LDL oxidation and foam cell formation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1985–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.B.; Tanwar, R.S.; Rini, A.; Singh, U.R.; Gupta, S.; Shukla, S.K. Protective effect of Morus rubra L. leaf extract on diet-induced atherosclerosis in diabetic rats. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 47, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.-C.; Ho, H.-H.; Peng, C.-H.; Lan, K.-P.; Lin, M.-C.; Chen, H.-M.; Wang, C.-J. Polyphenol-rich extract from mulberry leaf inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation involving upregulation of p53 and inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2536–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.-C.; Yang, M.-Y.; Lin, M.-C.; Lee, Y.-J.; Chang, W.-C.; Wang, C.-J. Mulberry leaf extract inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits and in cultured aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Guo, K.; Zhou, F.; Yang, H. Use of Chlorogenic Acid against Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 9680508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Su, C.-P.; Wang, Q.; Wu, F.-J.; Bai, R.; Zhang, H.-M.; Liu, J.-Y.; Lu, W.-J.; Wang, W.; Lan, F. Chlorogenic acid: A potent molecule that protects cardiomyocytes from TNF-α–induced injury via inhibiting NF-κB and JNK signals. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4666–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.-H.; Lin, M.-C.; Huang, C.-N.; Chan, K.-C.; Wang, C.-J. Acarbose inhibits the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via targeting Ras signaling. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2018, 103, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Wang, Y.-L.; Xia, L.-M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.-S.; Mei, Y.-Q. High shear stress suppresses proliferation and migration but promotes apoptosis of endothelial cells co-cultured with vascular smooth muscle cells via down-regulating MAPK pathway. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanessa Fiorentino, T.; Prioletta, A.; Zuo, P.; Folli, F. Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and its role in diabetes mellitus related cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5695–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Tian, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X. Chlorogenic acid: A comprehensive review of the dietary sources, processing effects, bioavailability, beneficial properties, mechanisms of action, and future directions. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3130–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Dou, C.; Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Ma, X.; Liu, J. Upregulated 14-3-3β aggravates restenosis by promoting cell migration following vascular injury in diabetic rats with elevated levels of free fatty acids. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1074–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adan, A.; Kiraz, Y.; Baran, Y. Cell proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.-Y.; Wu, Y.-L.; Yu, M.-H.; Hung, T.-W.; Chan, K.-C.; Wang, C.-J. Mulberry Leaf and Neochlorogenic Acid Alleviates Glucolipotoxicity-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Proliferation/Migration via Downregulating Ras and FAK Signaling Pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153006
Yang T-Y, Wu Y-L, Yu M-H, Hung T-W, Chan K-C, Wang C-J. Mulberry Leaf and Neochlorogenic Acid Alleviates Glucolipotoxicity-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Proliferation/Migration via Downregulating Ras and FAK Signaling Pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell. Nutrients. 2022; 14(15):3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153006
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tsung-Yuan, Yi-Liang Wu, Meng-Hsun Yu, Tung-Wei Hung, Kuei-Chuan Chan, and Chau-Jong Wang. 2022. "Mulberry Leaf and Neochlorogenic Acid Alleviates Glucolipotoxicity-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Proliferation/Migration via Downregulating Ras and FAK Signaling Pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell" Nutrients 14, no. 15: 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153006
APA StyleYang, T.-Y., Wu, Y.-L., Yu, M.-H., Hung, T.-W., Chan, K.-C., & Wang, C.-J. (2022). Mulberry Leaf and Neochlorogenic Acid Alleviates Glucolipotoxicity-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Proliferation/Migration via Downregulating Ras and FAK Signaling Pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell. Nutrients, 14(15), 3006. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14153006





