Magnesium Status and Ca/Mg Ratios in a Series of Children and Adolescents with Chronic Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site, Design, and Participants
2.2. Ethical Consideration
2.3. Assessment of Phenotypical Characteristics
2.4. Dietary Assessment
2.5. Clinical Evaluation
2.6. Laboratory Exploration
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Serum Magnesium Levels
4.2. Phenotypical Characteristics
4.3. Bone Densitometry
4.4. Dietary Intake Survey
4.5. Biochemical Analysis
4.6. Blood Analysis and Inflammatory Response
4.7. Calcium/Magnesium Ratios
4.8. Risk of Other Chronic Illnesses
4.9. Therapeutic Measures
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perrin, J.M.; Anderson, L.E.; Van Cleave, J. The rise in chronic conditions among infants, children, and youth can be met with continued health system innovations. Health Aff. 2014, 33, 2099–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mokkink, L.B.; van der Lee, J.H.; Grootenhuis, M.A.; Offringa, M.; Heymans, H.S. Dutch National Consensus Committee Chronic Diseases and Health Conditions in Childhood. Defining chronic diseases and health conditions in childhood (0–18 years of age): National consensus in the Netherlands. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2008, 167, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torpy, J.M.; Campbell, A.; Glass, R.M. Chronic Diseases of Children. JAMA 2010, 303, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Compas, B.E.; Jaser, S.S.; Dunn, M.J.; Rodriguez, E.M. Coping with chronic illness in childhood and adolescence. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2012, 8, 455–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denny, S.; de Silva, M.; Fleming, T.; Clark, T.; Merry, S.; Ameratunga, S.; Milfont, T.; Farrant, B.; Fortune, S.A. The prevalence of chronic health conditions impacting on daily functioning and the association with emotional well-being among a national sample of high school students. J. Adolesc. Health 2014, 54, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Survey of Children’s Health. NSCH 2018 19: Number of Current or Lifelong Health Conditions, Nationwide, Age in 3 Groups Website. Available online: https://www.childhealthdata.org (accessed on 28 February 2021).
- World Health Organization. Preventing Chronic Diseases a Vital Investment; Department of Chronic Diseases and Health Promotion: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Taylor, S.N. Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus, and Vitamin D. World Rev. Nutr. Diet 2021, 122, 122–139. [Google Scholar]
- Beto, J.A. The role of calcium in human aging. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2015, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, S.T.; Soman, S.S.; Yee, J. Mg balance and measurement. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.A.; Panonnummal, R. ‘Mg’-the master cation-as a drug-possibilities and evidences. Biometals 2021, 34, 955–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shrubsole, M.; Ness, R.M.; Hibler, E.; Cai, Q.; Long, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, M.; Hou, L.; et al. Calcium/magnesium intake ratio, but not magnesium intake, interacts with genetic polymorphism in relation to colorectal neoplasia in a two-phase study. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M. Magnesium in Man: Implications for Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Belvedere, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium homeostasis and aging. Magnes. Res. 2009, 22, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbagallo, M.; Veronese, N.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium in Aging, Health and Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. Electrolyte and Acid-Base Disturbances in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kostov, K.; Halacheva, L. Role of Magnesium Deficiency in Promoting Atherosclerosis, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Arterial Stiffening as Risk Factors for Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Xun, P.; Tang, Q.; Cai, W.; He, K. Circulating magnesium levels and incidence of coronary heart diseases, hyper-tension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebamowo, S.N.; Jimenez, M.C.; Chiuve, S.E.; Spiegelman, D.; Willett, W.C.; Rexrode, K.M. Plasma magnesium and risk of ischemic stroke among women. Stroke 2014, 45, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Liu, K.; Daviglus, M.L.; Morris, S.J.; Loria, C.M.; Van Horn, L.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Savage, P. Magnesium intake and incidence of metabolic syndrome among young adults. Circulation 2006, 113, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; Liu, J.; O’Keefe, J.H. Magnesium for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Ridker, P.M.; Manson, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Buring, J.E.; Liu, S. Magnesium intake, C-reactive protein, and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged and older U.S. Women. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrè, S.; Li, X.; Adams-Huet, B.; Maalouf, N.M.; Sakhaee, K.; Toto, R.D.; Moe, O.W.; Neyra, J.A. Association of serum magnesium with all-cause mortality in patients with and without chronic kidney disease in the Dallas Heart Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermes Sales, C.; Azevedo Nascimento, D.; Queiroz Medeiros, A.C.; Costa Lima, K.; Campos Pedrosa, L.F.; Colli, C. There is chronic latent magnesium deficiency in apparently healthy university students. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Iriti, M.; Varoni, E.M.; Vitalini, S. Healthy Diets and Modifiable Risk Factors for Non-Communicable Diseases-The European Perspective. Foods 2020, 9, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighi, J.; Nedjat, S.; Rostami, R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of iron-fortified flour on iron status of populations worldwide. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 22, 3465–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, R.B.; Rosanoff, A.; Dai, Q.; Saldanha, L.G.; Potischman, N.A. Perspective: Characterization of Dietary Supplements Containing Calcium and Magnesium and Their Respective Ratio—Is a Rising Ratio a Cause for Concern? Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Alonso, A.; Michos, E.D.; Loehr, L.R.; Astor, B.C.; Coresh, J.; Folsom, A.R. Serum magnesium, phosphorus, and calcium are associated with risk of incident heart failure: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Saito, A.; Kagaya, S.; Fukami, H.; Ojima, Y.; Nagasawa, T. Evaluation of the Predictive Value of the Serum Calcium-Magnesium Ratio for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Incident Dialysis Patients. Cardiorenal. Med. 2017, 8, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najeeb, S.; Zafar, M.S.; Khurshid, Z.; Zohaib, S.; Almas, K. The Role of Nutrition in Periodontal Health: An Update. Nutrients 2016, 8, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommisch, H.; Kuzmanova, D.; Jönsson, D.; Grant, M.; Chapple, I. Effect of Micronutrient Malnutrition on Periodontal Disease and Periodontal Therapy. Periodontology 2000 2018, 78, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, M.J.; Van Dael, P.; Eggersdorfer, M. The Role of Nutrients in Reducing the Risk for Noncommunicable Diseases during Aging. Nutrients 2019, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzago, M.; Santurbano, D.; Vitacolonna, E.; Stuppia, L. Genes and Diet in the Prevention of Chronic Diseases in Future Generations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for magnesium. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4186. [Google Scholar]
- Malakoutian, T.; Madadi, B.; Saber, S. A Novel Mutation in CLDN16 Gene Causing Familial Hypomagnesemia, Hypercalciuria, Nephrocalcinosis in An Iranian Family. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 16, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yousif, O.O.; Hassan, M.K.; Al-Naama, L.M. Red Blood Cell and Serum Magnesium Levels Among Children and Adolescents With Sickle Cell Anemia. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalny, A.V.; Mazaletskaya, A.L.; Ajsuvakova, O.P.; Bjørklund, G.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Chernova, L.N.; Skalny, A.A.; Tinkov, A.A. Magnesium Status in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and/or Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Korean Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 31, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.J.; Alvarez, J.A.; Smith, E.M.; Killilea, D.W.; Chmiel, J.F.; Joseph, P.M.; Grossmann, R.E.; Gaggar, G.A.; Ziegler, T.R.; Tangpricha, V. Vitamin D for Enhancing the Immune System in Cystic Fibrosis Investigators. Changes in Mineral Micronutrient Status During and After Pulmonary Exacerbation in Adults With Cystic Fibrosis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.C.; Tsweng, G.J.; Lee, C.F.; Chen, B.H.; Huang, Y.L. Magnesium, zinc, and chromium levels in children, adolescents, and young adults with type 1 diabetes. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Barrado, E.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Zinc Nutritional Status in a Series of Children with Chronic Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Copper and Copper/Zn Ratio in a Series of Children with Chronic Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Marcos-Temprano, M.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Magnesium Status and Calcium/Magnesium Ratios in a Series of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisancho, A.R. New norms of upper limb fat and muscle areas for assessment of nutritional status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 2540–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, M.; Sobradillo, B.; Aguirre, A.; Aresti, U.; Bilbao, A.; Fernández-Ramos, C.; Lizárraga, A.; Lorenzo, H.; Madariaga, L.; Rica, I. Curvas y Tablas de Crecimiento (Estudios Longitudinal y Transversal); Fundación Faustino Orbegozo: Bilbao, Spain, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, M.J.; Redondo, D.; Conde, F.; Redondo, P.; Franch, M.A. Gráficas Longitudinales de Velocidad de Conducción Media de Ultrasonidos en Falanges. In Estudio Nutricional de Castilla y León; de CyL, J., Ed.; Junta Castilla y León: Valladolid, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mataix Verdú, J.; Diaz, G.; Nutriber, J. V. 1.0; Fundación Universitaria Iberoamericana: Barcelona, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo, M.; Corbalán, M.; Baladía, E.; Cabrerizo, L.; Formiguera, X.; Iglesias, C.; Lorenzo, H.; Polanco, I.; Quiles, J.; De Avila, M.D.R.; et al. Comparison of dietary reference intakes (DRI) between different countries of the European Union, The United States and the World Health Organization. Nutr. Hosp. 2009, 24, 384–414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for calcium. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4101. [Google Scholar]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney 2012, 5, i3–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Eastham, K.M.; Wrightson, N.; Spencer, D.A. Hypomagnesemia in cystic fibrosis patients referred for lung transplant assessment. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2007, 6, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, F.; Mohammed, A. Mg2+: The forgotten electrolyte—A review on hypomagnesemia. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Cascella, M.; Vaqar, S. Hypermagnesemia. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, R.T.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Molecular determinants of magnesium homeostasis: Insights from human disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagana, K.D.; Pagana, T.J.; Pagana, T.N. Mosby’s Diagnostic & Laboratory Test Reference, 14th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Çullas İlarslan, N.E.; Şıklar, Z.; Berberoğlu, M. Childhood Sustained Hypercalcemia: A Diagnostic Challenge. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, R.B.; Elin, R.J.; Rosanoff, A.; Wallace, T.C.; Guerrero-Romero, F.; Hruby, A.; Lutsey, P.L.; Nielsen, F.H.; Rodriguez-Moran, M.; Song, Y.; et al. Perspective: The Case for an Evidence-Based Reference Interval for Serum Magnesium: The Time Has Come12345. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltzman, D. Approach to Hypercalcemia. In Endotext [Internet]; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., Kalra, S., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Pang, J.; Ma, J.; Ling, W.; Li, D. Associations of serum magnesium levels and calcium-magnesium ratios with mortality in patients with coronary artery disease. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 46, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosanoff, A.; Wolf, F.I. A guided tour of presentations at the xiv international magnesium symposium. Magnes. Res. 2016, 29, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bordelon, P.; Ghetu, M.V.; Langan, R.C. Recognition and management of vitamin D deficiency. Am. Fam. Physician 2009, 80, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gibson, R.S.; Hess, S.Y.; Hotz, C.; Brown, K.H. Indicators of zinc status at the population level: A review of the evidence. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, S14–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shenkin, A. Vitamins and trace elements. In Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnosis, 4th ed.; Bertis, S.A., Ashvud, E.R., Bruns, D., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow, J.E. Copper/Zinc Imbalance. Medical Board of California. Available online: http://www.mbc.ca.gov (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Eck, P.; Wilson, L. Toxic Metals in Human Health and Disease Eck; Institute of Applied Nutrition and Bioenergetics, Ltd.: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Leroy, Z.C.; Wallin, R.; Lee, S. The Role of School Health Services in Addressing the Needs of Students with Chronic Health Conditions. J. Sch. Nurs. 2017, 33, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortes, J.B.; Fernández, C.S.; de Oliveira, M.B.; Lagos, C.M.; Martínez, M.T.B.; Hernández, C.L.; González, I.D.C. Chronic diseases in the paediatric population: Comorbidities and use of primary care services. An. Pediatr. 2020, 93, 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Spatling, L.; Classen, H.G.; Kolpmann, W.R.; Manz, F.; Rob, P.M.; Schimatschek, H.F.; Vierling, W.; Vormann, J.; Weigert, A.; Wink, K. Diagnostik des Magnesiummangels. Aktuelle Empfehlungen der Gesellschaft für Magnesium-Forschung e. V. Fortschr. Med. Orig. 2000, 2, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Micke, O.; Vormann, J.; Kraus, A.; Kisters, K. Serum magnesium: Time for a standardized and evidence-based reference range. Magnes. Res. 2021, 34, 84–890. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaque, M.S. Magnesium: Are We Consuming Enough? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fulop, T. Hypomagnesemia. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2038394-overview (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Mataix, J.; Aranda, P.; López-Jurado, M.; Sánchez, C.; Planells, E.; Llopis, J. Factors influencing the intake and plasma levels of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium in southern Spain. Eur. J. Nutr. 2006, 45, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H. Chapter 25. Magnesium: Basic Nutritional Aspects. In Molecular, Genetic, and Nutritional Aspects of Major and Trace Minerals; Collins, J.F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- De la Cruz-Góngora, V.; Gaona, B.; Villalpando, S.; Shamah-Levy, T.; Robledo, R. Anemia and iron, zinc, copper and magnesium deficiency in Mexican adolescents: National Health and Nutrition Survey 2006. Salud Publica Mex. 2012, 54, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malinowska, J.; Małecka, M.; Ciepiela, O. Variations in Magnesium Concentration Are Associated with Increased Mortality: Study in an Unselected Population of Hospitalized Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, M.J. Update on the assessment of Mg status. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99 (Suppl. 3), S24–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welch, A.A.; Kelaiditi, E.; Jennings, A.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; MacGregor, A. Dietary Magnesium Is Positively Associated with Skeletal Muscle Power and Indices of Muscle Mass and May Attenuate the Association between Circulating C-Reactive Protein and Muscle Mass in Women. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gragossian, A.; Bashir, K.; Friede, R. Hypomagnesemia. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rondanelli, M.; Faliva, M.A.; Gasparri, C.; Peroni, G.; Naso, M.; Picciotto, G.; Riva, A.; Nichetti, M.; Infantino, V.; Alalwan, T.A.; et al. Micronutrients dietary supplementation advices for celiac patients on long-term gluten-free diet with good compliance: A review. Medicine 2019, 55, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adler, A.I.; Gunn, E.; Haworth, C.S.; Bilton, D. Characteristics of adults with and without cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2007, 24, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruis, W.; Phuong Nguyen, G. Iron Deficiency, Zinc, Mg, Vitamin Deficiencies in Crohn’s Disease: Substitute or Not? Dig. Dis. 2016, 34, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Wilson, W. Subclinical Mg deficiency: A principal driver of cardiovascular disease and a public health crisis. Open Heart Vol. 2018, 5, e000668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, S.W. A Quick Reference on Magnesium. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 47, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Mg in prevention and therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolati, S.; Rikhtegar, R.; Mehdizadeh, A.; Yousefi, M. The role of magnesium in pathophysiology and migraine treatment. Biol. Trace Elem Res. 2020, 196, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workinger, J.L.; Doyle, R.P.; Bortz, J. Challenges in the diagnosis of Mg status. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasdam, S.M.; Glasdam, S.; Peters, G.H. The importance of magnesium in the human body: A systematic literature review. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 73, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wyskida, K.; Witkowicz, J.; Chudek, J.; Więcek, A. Daily magnesium intake and hypermagnesemia in hemodialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2012, 22, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, C.G. Magnesium metabolism in health and disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2009, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietman, S.A.; Germain-Lee, E.L.; Levine, M.A. Hypercalcemia in children and adolescents. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2010, 22, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, S.A.; Ahmed, I.; Nasrullah, A.; Haq, S.; Ghazanfar, H.; Sheikh, A.B.; Zafar, R.; Askar, G.; Hamid, Z.; Khushdil, A.; et al. Comparison of Serum Mg Levels in Overweight and Obese Children and Normal Weight Children. Cureus 2017, 9, e1607. [Google Scholar]
- Cuadrado-Soto, E.; López-Sobaler, A.M.; Jiménez-Ortega, A.I.; Bermejo, L.M.; Bermejo, L.M.; Hernández-Ruiz, Á.; Villoslada, F.L.; Leis, R.; De Victoria, E.M.; Villares, J.M.M.; et al. Usual Dietary Intake, Nutritional Adequacy and Food Sources of Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium and Vitamin D of Spanish Children Aged One to <10 Years. Findings from the EsNuPI Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormick, G.; Betran, A.; Romero, I.; Cormick, M.; Belizán, J.; Bardach, A.; Ciapponi, A. Effect of Calcium Fortified Foods on Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, M.A.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Mahboob, S. Serum calcium, magnesium, phosphorous and lipid profile in healthy Iranian pre-menopausal women. Biochem. Med. 2011, 21, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Lu, Y.F.; Cheng, F.C.; Lee, J.N.; Tsai, L.C. Correlation of Mg intake with metabolic parameters, depression and physical activity in elderly type 2 diabetes patients: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rafiee, M.; Ghavami, A.; Rashidian, A.; Hadi, A.; Askari, G. The effect of magnesium supplementation on anthropometric indices: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of clinical trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lamas, C.; de Castro, M.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, Á.; Couce, M.L.; Leis, R. Effects of Dairy Product Consumption on Height and Bone Mineral Content in Children: A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S88–S96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- López-Sobaler, A.M.; Aparicio, A.; González-Rodríguez, L.G.; Cuadrado-Soto, E.; Rubio, J.; Marcos, V.; Sanchidrián, R.; Santos, S.; Pérez-Farinós, N.; Dal Re, M.Á.; et al. Adequacy of Usual Vitamin and Mineral Intake in Spanish Children and Adolescents: ENALIA Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Mg, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Balk, E.M.; Adam, G.P.; Langberg, V.N.; Earley, A.; Clark, P.; Ebeling, P.R.; Mithal, A.; Rizzoli, R.; Zerbini, C.A.F.; Dawson-Hughes, B. Global dietary calcium intake among adults: A systematic review. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 3315–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonjour, J.P. Calcium and phosphate: A duet of ions playing for bone health. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2011, 30, 438S–448S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröber, U. Magnesium and drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Julián-Almárcegui, C.; Gómez-Cabello, A.; Huybrechts, I.; González-Agüero, A.; Kaufman, J.M.; Casajus, J.A.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G. Combined effects of interaction between physical activity and nutrition on bone health in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orchard, T.S.; Larson, J.C.; Alghothani, N.; Bout-Tabaku, S.; Cauley, J.A.; Chen, Z.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Wactawski-Wende, J.W.; Jackson, R.D. Magnesium intake, bone mineral density, and fractures: Results from the women’s health initiative observational study. Am. J. Clin. Nut. 2014, 99, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrams, S.A.; Chen, Z.; Hawthorne, K.M. Magnesium Metabolism in 4-Year-Old to 8-Year-Old Children. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Alawi, A.M.; Majoni, S.W.; Falhammar, H. Magnesium and Human Health: Perspectives and Research Directions. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 9041694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Sanchez, J.J.; Alam, A.; Haque, A.; Mahfuz, M.; Ahmed, T.; Long, K.Z. Dietary Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Animal Protein Intake and Their Association to the Linear Growth Trajectory of Children from Birth to 24 Months of Age: Results From MAL-ED Birth Cohort Study Conducted in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Food Nutr. Bull. 2020, 41, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismail, A.A.A.; Ismail, Y.; Ismail, A.A. Chronic magnesium deficiency and human disease; time for reappraisal? QJM 2018, 111, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, B.; Alvarado, J.; Hazlewood, C.; Viteri, F. Magnesium supplementation in protein-calorie malnutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1978, 31, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singla, P.; Chand, P.; Kumar, A.; Kachhawaha, J. Serum magnesium levels in protein-energy malnutrition. J. Trop. Pediatr. 1998, 44, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estívariz, C.F.; Ziegler, T.R. Nutrition and the insulin-like growth factor system. Endocrine 1997, 7, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallach, S. Effects of magnesium on skeletal metabolism. Magnes. Trace Elem. 1990, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Rude, R.; Gruber, H.; Norton, H.; Wei, L.; Frausto, A.; Kilburn, J. Reduction of dietary magnesium by only 50% in the rat disrupts bone and mineral metabolism. Osteoporos. Int. 2006, 17, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, S.; Cazzaniga, A.; Albisetti, W.; Maier, J.A. Magnesium and osteoporosis: Current state of knowledge and future research directions. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3022–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elin, R.J. Assessment of magnesium status for diagnosis and therapy. Magnes. Res. 2010, 3, S194–S198. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, E.S.; Mokdad, A.H. Dietary magnesium intake in a national sample of U.S. adults. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 2879–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross, C.A.; Caballero, B.; Cousins, R.J.; Tucker, K.L.; Ziegler, T.R. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 11th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins y: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2014; pp. 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, L.M.; Ní Fhloinn, D.M.; Gaydadzhieva, G.T.; Mazurkiewicz, O.M.; Leeson, H.; Wright, C.P. Magnesium in pregnancy. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takaya, J.; Yamato, F.; Kaneko, K. Possible relationship between low birth weight and magnesium status: From the standpoint of “fetal origin” hypothesis. Magnes. Res. 2006, 19, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akizawa, Y.; Koizumi, S.; Itokawa, Y.; Ojima, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Tamura, T.; Kusaka, Y. Daily magnesium intake and serum magnesium concentration among Japanese people. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, C.D.; Johnson, L.K. Magnesium requirements: New estimations for men and women by cross-sectional statistical analysis of metabolic. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakır, B.; Şahin, H.; Doğan, A. Serum Magnesium Level and Dietary Magnesium Intake in Patients with Hypertension-Related Complications. Erciyes Med. J. 2021, 43, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, M.H.; Elin, R.J. Relationships between magnesium and protein concentrations in serum. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. Magnesium. In Dietary Reference Intakes: Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 190–249. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, J.B.; Frei, B.; Fulgoni, V.L.; Weaver, C.M.; Zeisel, S.H. Contribution of Dietary Supplements to Nutritional Adequacy in Various Adult Age Groups. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olza, J.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; González-Gross, M.; Ortega, R.; Serra-Majem, L.; Varela-Moreiras, G.; Gil, Á. Reported Dietary Intake, Disparity between the Reported Consumption and the Level Needed for Adequacy and Food Sources of Calcium, Phosphorus, Mg and Vitamin D in the Spanish Population: Findings from the ANIBES Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardt, J.P.; Hahn, A. Intestinal Absorption and Factors Influencing Bioavailability of Magnesium-An Update. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, F.L.; Rao, R.B.; Kim, W.W.; Kelsay, J.L. Magnesium intakes, balances, and blood levels of adults consuming self-selected diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosolova, H.; Mayer, O., Jr.; Reaven, G.M. Insulin-mediated glucose disposal is decreased in normal subjects with relatively low plasma magnesium concentrations. Metabolism 2000, 49, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilian, M.; Sabzevar, N.K.; Asemi, Z. The Effect of Magnesium and Vitamin E Co-Supplementation on Glycemic Control and Markers of Cardio-Metabolic Risk in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dibaba, D.T.; Xun, P.; He, K. Dietary Magnesium Intake is Inversely Associated with Serum Creactive Protein Levels: Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durlach, J. Magnesium in Clinical Practice; John Libbey: Paris, France, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Maktabi, M.; Jamilian, M.; Amirani, E.; Chamani, M.; Asemi, Z. The effects of magnesium and vitamin Eco-supplementation on parameters of glucose homeostasis and lipid profiles in patients with gestational diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaquero, M.P.; Sarria, B. Long-chain fatty acid supplemented infant formula does not influence calcium and Mg bioavailability in weanling rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srbely, V.; Janjua, I.; Buchholz, A.; Newton, G. Interventions Aimed at Increasing Dairy and/or Calcium Consumption of Preschool-Aged Children: A Systematic Literature Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-shehawy, E.L.; Allah, S.B.; Mahmoud, A.T.; Mansour, A.E.; Elsayed, O.M. The Impact of Serum Mg Level Disorders on Parathyroid Hormone and Alkaline Phosphatase Levels in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 under Maintenance Hemodialysis. Benha J. Appl. Sci. 2020, 5, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, I. Lipid metabolism and magnesium. Clin. Calcium. 2005, 15, 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Randell, E.W.; Mathews, M.; Gadag, V.; Zhang, H.; Sun, G. Relationship between serum magnesium values, lipids and anthropometric risk factors. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, T.; Peacock, J.M.; Iso, H.; Chambless, L.E.; Rosamond, W.D.; Folsom, A.R. Serum and dietary magnesium and risk of ischemic stroke: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norman, D.A.; Fordtran, J.S.; Brinkley, L.J.; Zerwekh, J.E.; Nicar, M.J.; Strowig, S.M.; Pak, C.Y. Jejunal and ileal adaptation to alterations in dietary calcium: Changes in calcium and magnesium absorption and pathogenetic role of parathyroid hormone and 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 67, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De, H.; Basu, K. Mutual influence of minerals in metabolism. Indian J. Med. Res. 1949, 37, 213–231. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, H.; Norris, C.; William, D. Inhibitory effects of zinc on magnesium balance and magnesium absorption in man. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1994, 13, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polzikov, M.; Blinov, D.; Barakhoeva, Z.; Vovk, L.; Fetisova, Y.; Ovchinnikova, M.; Tischenko, M.; Zorina, I.; Yurasov, V.; Ushakova, T.; et al. Association of the Serum Folate and Total Calcium and Magnesium Levels Before Ovarian Stimulation With Outcomes of Fresh In Vitro Fertilization Cycles in Normogonadotropic Women. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 732731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coşkun Benlidayı, İ.; Gökçen, N.; Sarpel, T. Serum magnesium level is not associated with inflammation in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 63, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M.T. Metals, toxicity, and oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, F.H. Dietary Magnesium and Chronic Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, M.; Gómez, S.; González-Gross, M.; Marcos, A. Possible roles of magnesium on immune system. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, J.; Romani, A.M.; Valentin-Torres, A.M.; Luciano, A.A.; Ramirez Kitchen, C.M.; Funderburg, N.; Mesiano, S.; Bernstein, H.B. Mg decreases inflammatory cytokine production: A novel innate immunomodulatory mechanism. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 6338–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feske, S.; Skolnik, E.Y.; Prakriya, M. Ion channels and transporters in lymphocyte function and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, C.; Perraud, A.-L.; Johnson, C.O.; Inabe, K.; Smith, M.K.; Penner, R.; Kurosaki, T.; Fleig, A.; Scharenberg, A.M. Regulation Mg2+ of Vertebrate Cellular Homeostasis by TRPM7. Cell 2003, 114, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Yu, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Q.; Lin, H.; Zhang, J. Association between serum magnesium and blood count: Influence of type 2 diabetes and central obesity. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubena, K.S. The role of magnesium in immunity. J. Nutr. Immunol. 1994, 2, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chaigne-delalande, B.; Kanellopoulou, C.; Jeremiah, C.; Lenardo, M.J. Signaling role for Mg2+ revealed by immunodeficiency due to loss of MagT1. Nature 2012, 475, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laires, M.J.; Monteiro, C. Exercise, magnesium and immune function. Magnes. Res. 2008, 21, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Rayssiguier, Y.; Libako, P.; Nowacki, W.; Rock, E. Magnesium deficiency and metabolic syndrome: Stress and inflammation may reflect calcium activation. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tonick, H.; Muneyyirci-Delale, O. Magnesium in women’s health and gynecology. Open J. Obstetr. Gynecol. 2016, 6, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosanoff, A.; Weaver, C.M.; Rude, R.K. Suboptimal magnesium status in the United States: Are the health consequences underestimated? Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisters, K.; Wessels, F.; Küper, H.; Tokmak, F.; Krefting, E.R.; Gremmler, B.; Kosch, M.; Barenbrock, M.; Hausberg, M. Increased calcium and decreased magnesium concentrations and an increased calcium/magnesium ratio in spontaneously hypertensive rats versus Wistar-Kyoto rats: Relation to arteriosclerosis. Am. J. Hypertens. 2004, 17, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kisters, K.; Wessels, F.; Tokmak, F.; Krefting, E.R.; Gremmler, B.; Kosch, M.; Hausberg, M. Early-onset increased calcium and decreased magnesium concentrations and an increased calcium/magnesium ratio in SHR versus WKY. Magnes. Res. 2004, 17, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, H.; Jin, L.; Ruan, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, Y. Higher levels of magnesium and lower levels of calcium in whole blood are positively correlated with the metabolic syndrome in a Chinese population: A Case-Control Study. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore-Schiltz, L.; Albert, J.M.; Singer, M.E.; Swain, J.; Nock, N.L. Dietary intake of calcium and Magnesium and the metabolic syndrome in the National Health and Nutrition Examination (NHANES) 2001–2010 data. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winarno, G.; Pribadi, A.; Maruli, H.J.; Achmad, E.D.; Anwar, R.; Mose, J.C.; Nisa, A.S.; Trianasari, N.T. Ratio of Serum Calcium to Magnesium Levels on Pregnancy with and without Preeclampsia. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2021, 27, e932032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosanoff, A.; Dai, Q.; Shapses, S.A. Essential Nutrient Interactions: Does Low or Suboptimal Magnesium Status Interact with Vitamin D and/or Calcium Status? Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Song, P.; Man, Q.; Mao, D.; Hu, Y.; Yang, L. Suggested Reference Ranges of Blood Mg and Ca Level in Childbearing Women of China: Analysis of China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015). Nutrients 2021, 13, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Mercado, M.; Rodriguez-Moran, M.; Ramírez-Renteria, C.; Martínez-Aguilar, G.; Marrero-Rodríguez, D.; Ferreira-Hermosillo, A.; Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Remba-Shapiro, I.; Gamboa-Gómez, C.I.; et al. Magnesium-to-Calcium Ratio and Mortality from COVID-19. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Shu, X.O.; Deng, X.; Xiang, Y.B.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Ji, B.; Cai, H.; Chow, W.H.; et al. Modifying effect of calcium/magnesium intake ratio and mortality: A population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e002111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hibler, E.A.; Zhu, X.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Hou, L.; Dai, Q. Physical activity, dietary calcium to Magnesium intake and mortality in the National Health and Examination Survey 1999–2006 cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 2979–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.; Koklu, M.; Gusoy, E.; Gungo, M.; Yasar, S.; Gormel, S.; Yildirim, E.; Gokoglan, Y.; Yuksel, U.C.; Kaul, H.K.; et al. The serum calcium to Magnesium ratio in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Acta Med. Mediterr. 2016, 32, 691–697. [Google Scholar]
- Kousa, A.; Havulinna, A.S.; Moltchanova, E.; Taskinen, O.; Nikkarinen, M.; Eriksson, J.; Karvonen, M. Calcium: Magnesium ratio in local groundwater and incidence of acute myocardial infarction among males in rural Finland. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Sandler, R.; Barry, E.; Summers, R.; Grau, M.; Baron, J. Calcium, magnesium, and colorectal cancer. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 504–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steck, S.E.; Omofuma, O.O.; Su, L.J.; Maise, A.A.; Woloszynska-Read, A.; Johnson, C.S.; Zhang, H.; Bensen, J.T.; Fontham, E.T.; Mohler, J.L.; et al. Calcium, magnesium, and whole-milk intakes and high-aggressive prostate cancer in the North Carolina-Louisiana Prostate Cancer Project (PCaP). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.-H.; Dai, Q.; Millen, A.E.; Nie, J.; Edge, S.B.; Trevisan, M.; Shields, P.G.; Freudenheim, J.L. Associations of intakes of magnesium and calcium and survival among women with breast cancer: Results from Western New York Exposures and Breast Cancer (WEB) Study. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 6, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Du, M.; Blumberg, J.B.; Chui, K.K.H.; Ruan, M.; Rogers, G.; Shan, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, F.F. Association among dietary supplement use, nutrient intake, and mortality among U.S. adults: A cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Lorente, H.; Herrera-Quintana, L.; Molina-López, J.; Gamarra-Morales, Y.; López-González, B.; Miralles-Adell, C.; Planells, E. Response of vitamin D after Magnesium intervention in a postmenopausal population from the province of Granada, Spain. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Giri, A.; Zhu, X.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ness, R.; Seidner, D.L.; Giovannucci, E.; Edwards, T.L.; et al. Calcium: Magnesium intake ratio and colorectal carcinogenesis, results from the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian cancer screening trial. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.C.; Dai, Q.; Zhu, X.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Roumie, C.; Shrubsole, M.J. Associations between calcium and Magnesium intake and the risk of incident oesophageal cancer: An analysis of the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study prospective cohort. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Saleem, A.F. On admission hypomagnesemia in critically ill children: Risk factors and outcome. Indian J. Pediatrics 2009, 76, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Jin, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, A.; Wu, Y.; Chen, C. Hypermagnesaemia, but Not Hypomagnesaemia, Is a Predictor of Inpatient Mortality in Critically Ill Children with Sepsis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 3893653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Hernández-Ronquillo, G.; Gómez-Díaz, R.; Pizano-Zarate, M.L.; Wacher, N.H.; Mondragón-González, R.; Simental-Mendia, L.E.; Network of Childhood Obesity of the Mexican Social Security Institute. Low Serum Magnesium Levels and Its Association with High Blood Pressure in Children. J. Pediatr. 2016, 168, 93–98.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Fang, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Chen, Q.; Fan, Z.; Aaseth, J.; Hiyoshi, A.; He, J.; et al. Dose-response relationship between dietary magnesium intake, serum magnesium concentration and risk of hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuryłowicz, A.; Cąkała-Jakimowicz, M.; Puzianowska-Kuźnicka, M. Targeting abdominal obesity and its complications with dietary phytoestrogens. Nutrients 2020, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaher, M.M.; Abdel-Salam, M.; Abdel-Salam, R.; Sabour, R.; Morsy, A.A.; Gamal, D. Serum magnesium level and vascular stiffness in children with chronic kidney disease on regular hemodialysis. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2016, 27, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplinsky, C.; Alon, U.S. Magnesium homeostasis and hypomagnesemia in children with malignancy. Pediatric. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Zeng, C.; Yang, T.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Xie, D.; Xu, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Association between serum magnesium concentration and metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension and hyperuricaemia in knee osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study in Hunan Province, China. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e01915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, M.G.; Roemmich, J.N.; Kington, M.L.; Bovbjerg, V.E.; Weltman, A.L.; Holmes, V.F.; Patrie, J.T.; Rogol, A.D.; Nadler, J.L. Magnesium deficiency is associated with insulin resistance in obese children. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.K.; Kim, G.; Jang, E.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Baek, K.H.; Oh, K.W.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, K.-H.; Lee, W.C.; Lee, K.W.; et al. Altered calcium homeostasis is correlated with the presence of metabolic syndrome and diabetes in middle-aged and elderly Korean subjects: The Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort study (CMC study). Atherosclerosis 2010, 212, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, B.; Jain, V.; Vikram, N.K.; Agarwala, A.; Saini, S. Serum magnesium in overweight children. Indian Pediatr. 2012, 49, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piuri, G.; Zocchi, M.; Della Porta, M.; Ficara, V.; Manoni, M.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Pinotti, L.; Maier, J.A.; Cazzola, R. Mg in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaakouk, A.M.; Hassan, M.A.; Tolba, O.A. Serum magnesium status among obese children and adolescents. Egypt. Pediatr. Assoc. Gaz. 2016, 64, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.Y.; Xun, P.; He, K.; Qin, L.Q. Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Mesa, J.E.; Galindo-Coral, S.; Montes, M.C.; Muñoz Martin, A.J. Thrombosis and Coagulopathy in COVID-19. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nägele, M.P.; Haubner, B.; Tanner, F.C.; Ruschitzka, F.; Flammer, A.J. Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: Current findings and therapeutic implications. Atherosclerosis 2020, 314, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babapoor-Farrokhran, S.; Gill, D.; Walker, J.; Rasekhi, R.T.; Bozorgnia, B.; Amanullah, A. Myocardial injury and COVID-19: Possible mechanisms. Life Sci. 2020, 253, 117723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapani, V.; Rosanoff, A.; Baniasadi, S.; Barbagallo, M.; Castiglioni, S.; Guerrero-Romero, F.; Iotti, S.; Mazur, A.; Micke, O.; Pourdowlat, G.; et al. The relevance of magnesium homeostasis in COVID-19. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosanoff, A.; Plesset, M.R. Oral magnesium supplements decrease high blood pressure (SBP > 155 mm Hg) in hypertensive subjects on anti-hypertensive medications: A targeted meta-analysis. Magnes. Res. 2013, 26, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Tangvoraphonkchai, K.; Davenport, A. Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-F.; Ding, H.; Jiao, R.-Q.; Wu, X.-X.; Kong, L.-D. Possibility of magnesium supplementation for supportive treatment in patients with COVID-19. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 886, 173546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Caterson, I.; Seidell, J.C.; James, W.P. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of excess weight gain and obesity. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 123–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hemamy, M.; Heidari-Beni, M.; Askari, G.; Karahmadi, M.; Maracy, M. Effect of Vitamin D and Magnesium Supplementation on Behavior Problems in Children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2021, 11, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Shahrami, A.; Assarzadegan, F.; Hatamabadi, H.R.; Asgarzadeh, M.; Sarehbandi, B.; Asgarzadeh, S. Comparison of therapeutic effects of magnesium sulfate vs. dexamethasone/metoclopramide on alleviating acute migraine headache. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 48, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keum, N.; Lee, D.H.; Greenwood, D.C.; Zhang, X.; Giovannucci, E.L. Calcium intake and colorectal adenoma risk: Dose-response meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Q.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Ness, R.M.; Schlundt, D.; Cai, Q.; Smalley, W.E.; Li, M.; Shyr, Y.; Zheng, W. The relation of Magnesium and calcium intakes and a genetic polymorphism in the Magnesium transporter to colorectal neoplasia risk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gantenbein, K.V.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C. Mediterranean Diet as an Antioxidant: The Impact on Metabolic Health and Overall Wellbeing. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Xun, P.; Shikany, J.M.; He, K. Mg intake is inversely associated with risk of obesity in a 30-year prospective follow-up study among American young adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3745–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisters, K. What is the correct magnesium supplement? Magnes. Res. 2013, 26, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total (n = 78) | Obesity (n = 24) | Undernutrition (n = 30) | Eutrophic (n = 24) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||
| Age (years) | 9.6 ± 4.8 | 11 ± 4 | 7 ± 5 | 10 ± 5 | 0.003 * |
| Children (age in years) | 6 ± 3 | 7 ± 3 | 4 ± 3 | 7 ± 3 | 0.026 * |
| Head circumference (cm) | 52 ± 4 | 55 ± 3 | 49 ± 3 | 53 ± 3 | 0.000 * |
| Weight-for-age (kg) | 38 ± 26 | 63 ± 24 | 18 ± 12 | 38 ± 18 | 0.000 * |
| Weight-for-age Z-score | 38 ± 26 | 63 ± 24 | 18 ± 12 | 38 ± 18 | 0.000 * |
| Height-for-age (cm) | 131 ± 31 | 147 ± 21 | 112 ± 30 | 139 ± 28 | 0.000 * |
| Height-for-age Z-score | −0.76 ± 1.5 | −0.7 ± 1.3 | −1.6 ± 1.6 | −0.4 ± 1.2 | 0.000 * |
| Body mass index (kg/cm2) | 19 ± 7.2 | 28 ± 5 | 13 ± 1.4 | 18 ± 2.8 | 0.000 * |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 63 ± 18 | 83 ± 15 | 48 ± 9 | 62 ± 10 | 0.000 * |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 76 ± 24 | 98 ± 17 | 56 ± 17 | 77 ± 18 | 0.000 * |
| Waist/height ratio | 0.49 ± 0.09 | 0.57 ± 0.07 | 0.45 ± 0.09 | 0.45 ± 0.05 | 0.000 * |
| Bicipital skinfold (mm) | 8.1 ± 6.9 | 11.1 ± 8.8 | 5.8 ± 4.2 | 7.9 ± 6.4 | 0.016 * |
| Sum of skinfolds Z-score | 47 ± 36 | 91 ± 24 | 18 ± 5 | 38 ± 25 | 0.000 * |
| Muscle mass by anthropometry (kg) | 28 ± 15 | 40 ± 15 | 16 ± 9 | 29 ± 12 | 0.000 * |
| Muscle mass by BIA (kg) | 30 ± 16 | 41 ± 15 | 19 ± 18 | 29 ± 13 | 0.000 * |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 97 ± 53 | 98 ± 48 | 80 ± 13 | 116 ± 53 | 0.040 * |
| Creatine (mg/dL) | 0.50 ± 0.19 | 0.52 ± 0.16 | 0.42 ± 0.14 | 0.58 ± 0.25 | 0.008 * |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.50 ± 0.34 | 0.47 ± 0.17 | 0.39 ± 0.24 | 0.65 ± 0.48 | 0.032 * |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 174 ± 38 | 161 ± 29 | 174 ± 40 | 187 ± 40 | 0.072 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 55 ± 16 | 48 ± 11 | 56 ± 18 | 61 ± 17 | 0.027 * |
| Aspartate amino transferase (U/L) | 28 ± 10 | 25 ± 9 | 34 ± 11 | 24 ± 7 | 0.000 * |
| Vitamin B 12 (pg/mL) | 690 ± 276 | 549 ± 182 | 786 ± 246 | 708 ± 338 | 0.006 * |
| Vitamin E (µg/mL) | 16 ± 6 | 13 ± 4 | 16 ± 6 | 17 ± 6 | 0.022 * |
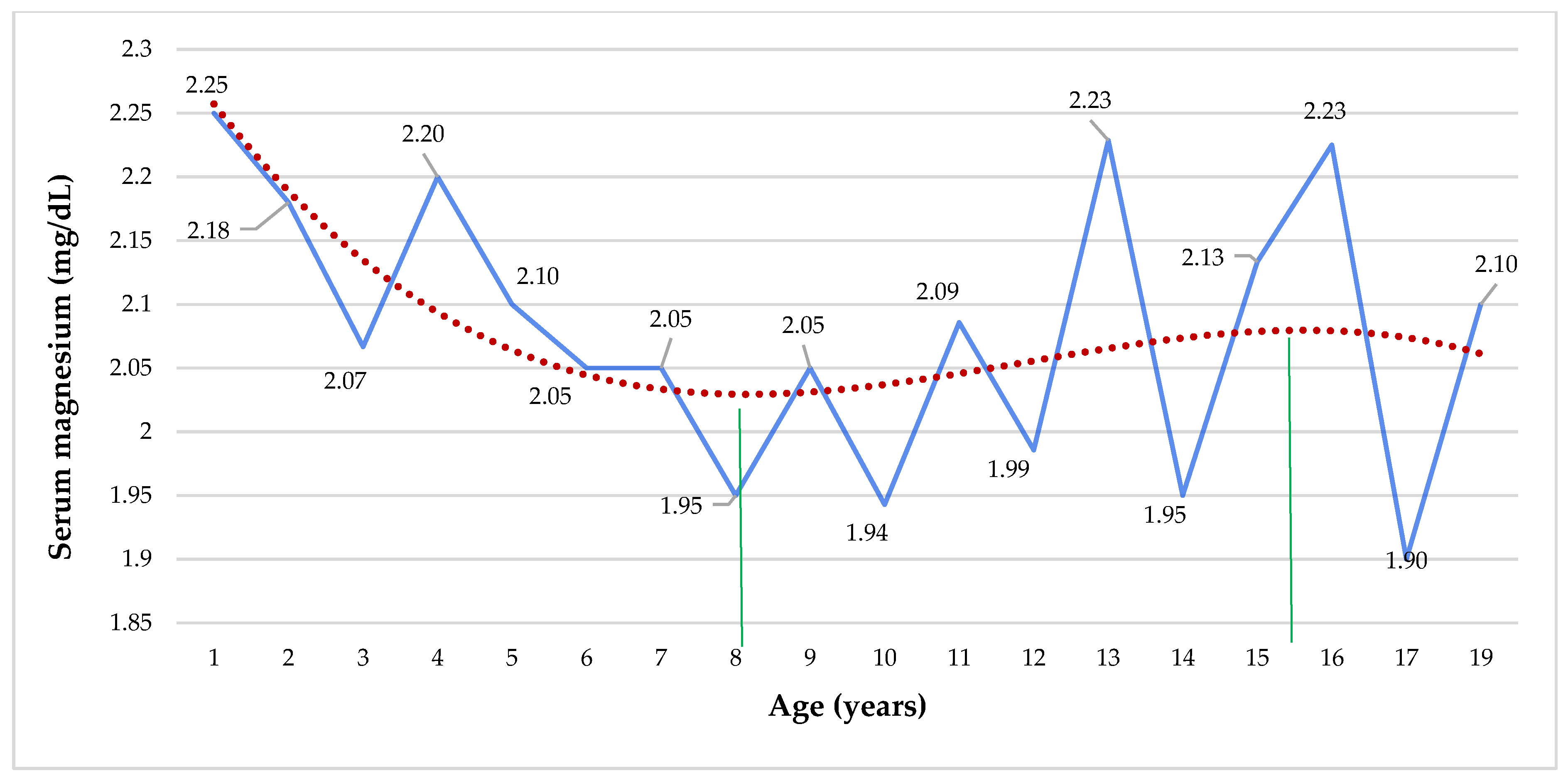
| Serum magnesium (mg/dL) | 2.08 ± 0.19 | 2.09 ± 0.19 | 2.1 ± 0.18 | 2.04 ± 0.20 | 0.461 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 9.9 ± 0.4 | 9.8 ± 0.4 | 10 ± 0.4 | 9.8 ± 0.4 | 0.118 |
| Serum calcium/magnesium ratio | 4.79 ± 0.47 | 4.72 ± 0.53 | 4.79 ± 0.44 | 4.86 ± 0.46 | 0.621 |
| IGF-1 (ng/mL) | 212 ± 136 | 264 ± 119 | 149 ± 115 | 241 ± 152 | 0.004 * |
| Leucocytes (cell/mm3) | 7465 ± 2239 | 7025 ± 2373 | 8344 ± 2349 | 6806 ± 1593 | 0.020 * |
| Lymphocytes (cell/mm3) | 3080 ± 1432 | 2887 ± 312 | 3606 ± 1641 | 2615 ± 719 | 0.028 * |
| Complement C3 (mg/dL) | 114 ± 21 | 126 ± 16 | 108 ± 19 | 111 ± 23 | 0.016 * |
| Complement C4 (mg/dL) | 21 ± 7 | 25 ± 6 | 18 ± 7 | 22 ± 8 | 0.005 * |
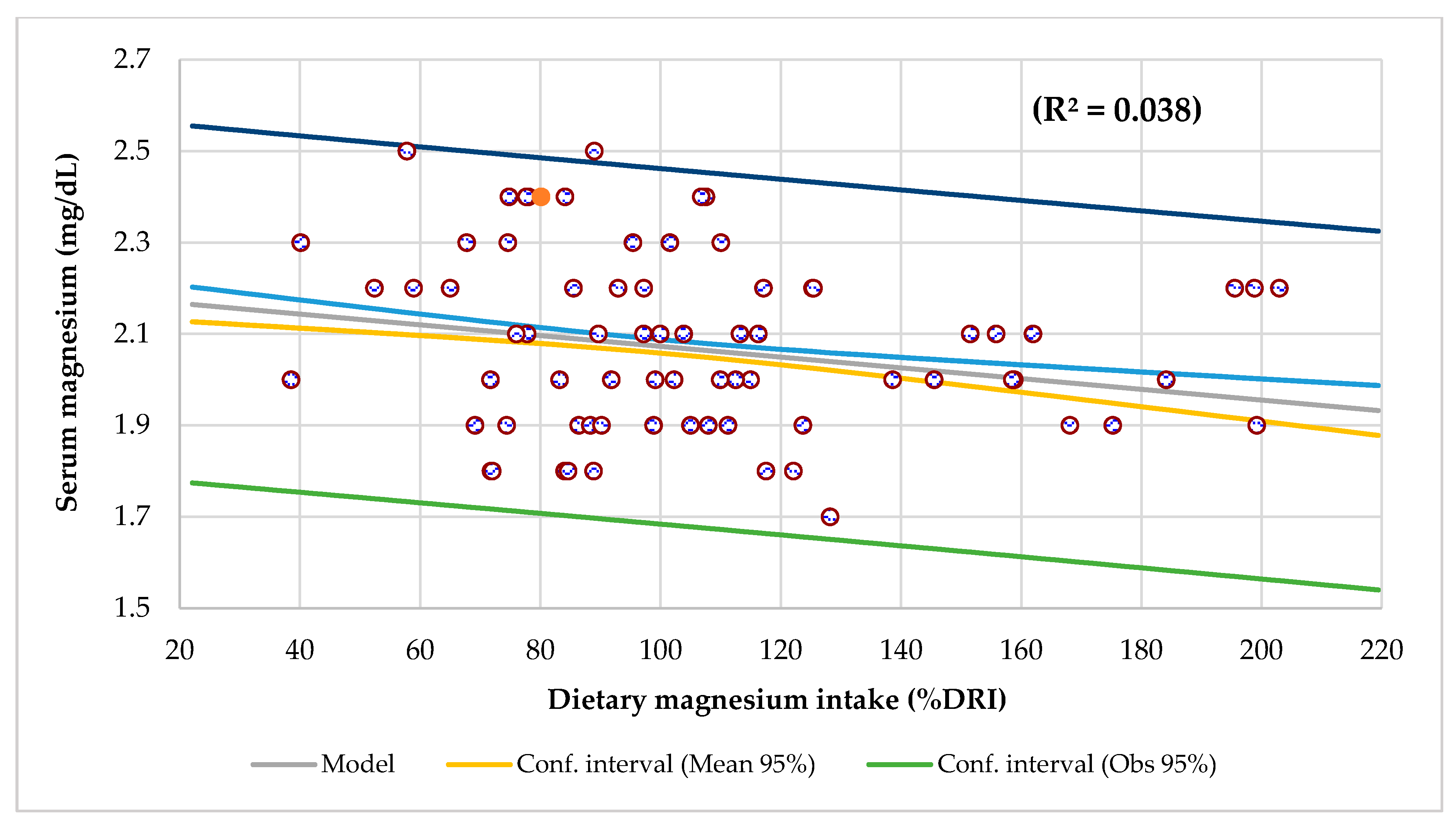
| Magnesium intake (%DRI) | 105 ± 39 | 107 ± 41 | 104 ± 41 | 104 ± 34 | 0.942 |
| Calcium intake (%DRI) | 102 ± 37 | 94 ± 28 | 103 ± 34 | 110 ± 46 | 0.338 |
| Calcium/magnesium intake ratio | 1.06 ± 0.51 | 0.97 ± 0.45 | 109 ± 0.49 | 1.11 ± 0.57 | 0.555 |
| Folic acid (%DRI) | 167 ± 86 | 189 ± 83 | 133 ± 69 | 187 ± 96 | 0.024 * |
| Hypomagnesemia (%) | 35 (45) | 11 (14) | 12 (15) | 12 (15) | |
| Hypermagnesemia (%) | 9 (11) | 4 (5) | 3 (4) | 2 (2) | |
| Low serum Ca/Mg ratio (%) | 3 (4) | 2 (3) | 1 (1) | 0 | |
| High serum Ca/Mg ratio (%) | 42 (54) | 11 (14) | 18 (23) | 13 (17) | |
| Deficient magnesium intake (%) | 20 (26) | 6 (8) | 9 (12) | 5 (6) | |
| Deficient calcium intake (%) | 27 (35) | 11 (14) | 7 (9) | 9 (12) | |
| High magnesium intake (%) | 19 (24) | 7 (9) | 7 (9) | 5 (6) | |
| High calcium intake | 22 (28) | 4 (5) | 7 (9) | 11 (14) | |
| Low Ca/Mg intake ratio (%) | 70 (90) | 22 (28) | 25 (32) | 23 (30) | |
| High Ca/Mg intake ratio (%) | 2 (2) | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (1) |
| Serum Magnesium Concentration | Dietary Magnesium Intake (n, %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deficiency | Normal | High | Total | |
| Asymptomatic hypomagnesemia | 1 (1.4) | 4 (5.1) | 3 (3.8) | 8 (10.3) |
| Chronic latent magnesium deficiency | 4 (5.1) | 14 (18) | 9 (11.5) | 27 (34.6) |
| Normal levels | 11 (14.1) | 16 (20.5) | 7 (9) | 34 (43.6) |
| Asymptomatic hypermagnesemia | 4 (5.1) | 5 (6.4) | 0 | 9 (11.5) |
| Total | 20 (25.7) | 39 (50) | 19 (24.3) | 78 (100) |
| Serum Calcium/Magnesium Ratio | Dietary Calcium/Magnesium Intake Ratio (n, %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Normal | High | Total | |
| Low | 3 (3.8) | 0 | 0 | 3 (3.8) |
| Normal | 27 (34.7) | 3 (3.8) | 3 (3.8) | 33 (42.3) |
| High | 40 (51.3) | 2 (2.6) | 0 | 42 (53.9) |
| Total | 70 (89.8) | 5 (6.4) | 3 (3.8) | 78 |
| Cases | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Female |
| Age (years) | 1 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 16 |
| Nutritional status by BMI | under | under | normal | under | obese | obese | obese | normal | obese |
| Calcium intake (% DRI) | 57 | 79 | 71 | 78 | 73 | 64 | |||
| Magnesium intake (% DRI) | 108 | 80 | 107 | 58 | 75 | 89 | 84 | 78 | 78 |
| Zinc intake (% DRI) | 22 | 31 | 45 | 55 | 74 | 74 | 58 | 48 | |
| Iodine intake (%DRI) | 55 | 31 | 54 | 45 | 68 | 55 | 47 | 41 | |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 289 | ||||||||
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 119 | 197 | 131 | ||||||
| Serum Mg (mg/dL) | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| Serum zinc (µg/dL) | 69 | 61 | |||||||
| Serum copper (µg/dL) | 175 | ||||||||
| High Cu/Zn ratio | 2.3 | ||||||||
| Leucocytes (cell/mm3) | 750 | ||||||||
| Lymphocytes (cell/mm3) | 490 | ||||||||
| ESR (mm/h) | 26 | 37 | 36 |
| Characteristics | Children < 5 y | Children ≥ 5 y | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum magnesium level (mg/dL) | 2.15 ± 0.18 | 2.05 ± 0.19 | 0.036 * | |
| Serum calcium level (mg/dL) | 10.1 ± 0.5 | 9.8 ± 0.4 | 0.021 * | |
| Dietary calcium intake (%DRI) | 115 ± 39 | 96 ± 34 | 0.044 * | |
| Age Group | Children | Adolescents | ||
| Dietary magnesium intake (%DRI) | 120 ± 45 | 87 ± 19 | 0.000 * | |
| Serum calcium level (mg/dL) | 10 ± 0.4 | 9.8 ± 0.4 | 0.015 * | |
| Dietary calcium intake (%DRI) | 119 ± 36 | 83 ± 27 | 0.000 * | |
| Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate | Normal | High | ||
| Serum magnesium level (mg/dL) | 2.06 ± 0.19 | 2.18 ± 0.15 | 0.024 * | |
| Serum calcium level (mg/dL) | 9.9 ± 0.4 | 10.1 ± 0.4 | 0.045 * | |
| Serum magnesium level | Low | Normal | High | |
| Dietary magnesium intake (%DRI) | 113 ± 34 | - | 84 ± 16 | 0.001 * |
| - | 106 ± 44 | 84 ± 16 | 0.032 * | |
| Serum magnesium (mg/dL) | 1.91 ± 0.85 | 2.18 ± 0.76 | 2.42 ± 0.4 | 0.000 * |
| Serum calcium/magnesium ratio | 5.19 ± 0.19 | 4.53 ± 0.22 | 4.12 ± 0.31 | 0.000 * |
| Dietary magnesium intake | Low | Normal | High | |
| Serum magnesium level (mg/dL) | 2.18 ± 0.19 | 2.08 ± 0.19 | 2.00 ± 0.15 | 0.018 * |
| Dietary calcium intake (%DRI) | 84 ± 39 | 100 ± 34 | 123 ± 28 | 0.003 * |
| Dietary magnesium intake (%DRI) | 64 ± 15 | 99 ± 11 | 159 ± 27 | 0.000 * |
| Serum calcium/magnesium ratio | 4.62 ± 0.47 | 4.77 ± 0.45 | 5.02 ± 0.39 | 0.027 * |
| Calcium/magnesium intake ratio | 1.39 ± 0.73 | 1.02 ± 0.36 | 0.80 ± 0.24 | 0.001 * |
| Fisher’s Exact Test | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | Cochran’s | Mantel–Haenszel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Dietary magnesium deficiency | ||||||
| Microcephaly | 0.030 | 3.556 | 1.133 | 11.154 | 0.025 | 0.055 |
| Children under 10-year-old | 0.015 | 1.397 | 1.045 | 1.866 | 0.015 | 0.032 |
| Deficient energy intake | 0.011 | 4.182 | 1.398 | 12.512 | 0.008 | 0.019 |
| Deficient total fat intake | 0.019 | 4.083 | 1.273 | 13.100 | 0.014 | 0.033 |
| Deficient calcium intake | 0.008 | 4.200 | 1.439 | 12.262 | 0.007 | 0.015 |
| High vitamin B1 intake | 0.004 | 5.844 | 1.789 | 19.094 | 0.002 | 0.006 |
| High vitamin B2 intake | 0.017 | 3.750 | 1.269 | 11.080 | 0.014 | 0.030 |
| High niacin intake | 0.000 | 7.897 | 2.528 | 24.670 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| High iron intake | 0.027 | 3.184 | 1.098 | 9.234 | 0.029 | 0.056 |
| High dietary magnesium intake | ||||||
| Deficient vitamin E intake | 0.027 | 3.257 | 1.108 | 9.572 | 0.028 | 0.055 |
| Deficient zinc intake | 0.001 | 6.571 | 2.127 | 20.304 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| Deficient iodine intake | 0.010 | 4.259 | 1.415 | 12.822 | 0.007 | 0.018 |
| High calcium intake | 0.010 | 4.259 | 1.415 | 12.822 | 0.007 | 0.018 |
| Total Series | Obesity | Undernutrition | Eutrophic | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | |
| Age (months) | 0.773 ** | 0.000 | 0.761 ** | 0.000 | 0.732 ** | 0.000 | 0.876 ** | 0.000 |
| Age-for-50° height | 0.638 ** | 0.539 * | 0.012 | 0.799 ** | 0.639 ** | 0.001 | ||
| Weight-for-age | 0.525 ** | 0.589 ** | 0.005 | 0.786 ** | 0.834 ** | 0.000 | ||
| Height-for-age | 0.742 ** | 0.700 ** | 0.000 | 0.791 ** | 0.834 ** | |||
| Weight-for-height | 0.287 * | 0.016 | - | - | - | - | 0.576 ** | 0.004 |
| Body mass index | 0.261 * | 0.029 | - | - | - | - | 0.626 ** | 0.001 |
| Muscle mass by A. (kg) | 0.622 ** | 0.000 | 0.653 ** | 0.001 | 0.765 ** | 0.000 | 0.889 ** | 0.000 |
| Fat mass by A. (kg) | 0.354 ** | 0.003 | 0.453 * | 0.039 | 0.737 ** | 0.598 ** | 0.003 | |
| Muscle mass by BIA | 0.490 ** | 0.000 | 0.492 * | 0.023 | - | - | 0.871 ** | 0.000 |
| Fat mass by BIA | 0.330 ** | 0.008 | 0.572 ** | 0.007 | - | - | 0.561 ** | 0.005 |
| Serum Magnesium | Serum Calcium | Serum Ca/Mg Ratio | Magnesium Intake | Calcium Intake | Ca/Mg Intake Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | regression | analyses | |||
| r = 0.135, p = 0.001 Age in years | r = 0.089, p = 0.008 Age in years | ||||
| r = 0.125, p = 0.005 Head circumference | r = 0.066, p = 0.047 Arm perimeter | r = 0.157, p = 0.001 Height-for-age | r = 0.143, p = 0.002 Height-for-age | ||
| r = 0.141, p = 0.008 Fat mass by BIA | r = 0.110, p = 0.022 kg mass muscular by BIA | ||||
| r = 0.071, p = 0.023 Vitamin E intake | |||||
| r = 0.081, p = 0.017 BCS absolute value | r = 0.057, p = 0.048 BCS absolute value | ||||
| r = 0.062, p = 0.043 Serum vitamin C | r = 0.138, p = 0.007 HDL-cholesterol | r = 0.059, p = 0.039 IGF-1 | r = 0.223, p = 0.000 Serum vitamin B12 | r = 0.091, p = 0.013 Serum vitamin B12 | |
| r = 0255, p = 0.000 Serum phosphorus | r = 0.046, p = 0.038 Serum magnesium | r = 0.062, p = 0.033 Serum phosphorus | |||
| r = 0.087, p = 0.016 MCH | r = 0.214, p = 0.000 Lymphocytes | r = 0.121, p = 0.004 MCH | r = 0.087, p = 0.030 IgA | r = 0.124, p = 0.003 Lymphocytes | r = 0.089, p = 0.029 T-lymphocytes CD16+56 |
| r = 0.119, p = 0.003 CV risk index | r = 0.109, p = 0.005 CV risk index | ||||
| Multilinear | regression | analyses | |||
| r = 0.650, p = 0.000 Energy, vitamin B12, folic acid, zinc, vitamin E and cholesterol intake | r = 0.274, p = 0.000 Energy, proteins, and iron intake | r = 0.391, p = 0.000 Magnesium, niacin, iron, and protein intake | |||
| r = 0.160, p = 0.004 Serum vitamin D, and beta-carotene | |||||
| r = 0.298, p = 0.001 HDL-cholesterol, total bilirubin, and LDL-cholesterol | r = 0.466, p = 0.000 Creatinine, albumin, alkaline phosphatase, and ESR | r = 0.990, p = 0.000 Serum Mg, Ca, and copper | |||
| r = 0.989, p = 0.000 Serum Ca/Mg ratio, calcium, and copper | r = 0.141, p = 0.005 Serum phosphorus, and Mg | ||||
| r = 0.249, p = 0.004 Complement C4, IgG3, and CD4/CD8 ratio | r = 0.269, p = 0.001 T-lymphocytes C4 and IgG3 | r = 0.188, p = 0.005 Transferrin, and BUN | r = 0.287, p = 0.001 T-lymphocytes CD16+56, CD4/CD8 ratio, and IgA | r = 0.162, p = 0.003 MVC, and platelets |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Magnesium Status and Ca/Mg Ratios in a Series of Children and Adolescents with Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142941
Escobedo-Monge MF, Barrado E, Parodi-Román J, Escobedo-Monge MA, Torres-Hinojal MC, Marugán-Miguelsanz JM. Magnesium Status and Ca/Mg Ratios in a Series of Children and Adolescents with Chronic Diseases. Nutrients. 2022; 14(14):2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142941
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscobedo-Monge, Marlene Fabiola, Enrique Barrado, Joaquín Parodi-Román, María Antonieta Escobedo-Monge, María Carmen Torres-Hinojal, and José Manuel Marugán-Miguelsanz. 2022. "Magnesium Status and Ca/Mg Ratios in a Series of Children and Adolescents with Chronic Diseases" Nutrients 14, no. 14: 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142941
APA StyleEscobedo-Monge, M. F., Barrado, E., Parodi-Román, J., Escobedo-Monge, M. A., Torres-Hinojal, M. C., & Marugán-Miguelsanz, J. M. (2022). Magnesium Status and Ca/Mg Ratios in a Series of Children and Adolescents with Chronic Diseases. Nutrients, 14(14), 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142941