Choline Supplementation Modifies the Effects of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Immune Responses in Adult Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
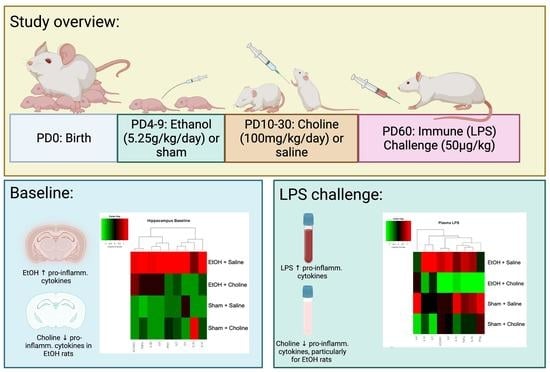
2.2. Design and Treatment
2.3. Developmental Alcohol Exposure
2.4. Peak Blood Alcohol Concentrations
2.5. Choline Supplementation
2.6. Immune Challenge and Tissue Collection
2.7. Tissue Homogenization
2.8. Protein Measurements
2.9. Cytokine Measurements
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Blood Alcohol Concentrations
3.2. Hippocampus Cytokine Levels at Baseline and after LPS Challenge
3.2.1. Hippocampal Cytokine Profile
3.2.2. Hippocampal Cytokine Levels
3.3. Plasma Cytokine Levels Pre- and Post-LPS Challenge
3.3.1. Plasma Cytokine Profile
3.3.2. Plasma Cytokine Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- May, P.A.; Hasken, J.M.; Hooper, S.R.; Hedrick, D.M.; Jackson-Newsom, J.; Mullis, C.E.; Dobyns, E.; Kalberg, W.O.; Buckley, D.; Robinson, L.K.; et al. Estimating the community prevalence, child traits, and maternal risk factors of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) from a random sample of school children. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 227, 108918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, P.A.; Chambers, C.D.; Kalberg, W.O.; Zellner, J.; Feldman, H.; Buckley, D.; Kopald, D.; Hasken, J.M.; Xu, R.; Honerkamp-Smith, G.; et al. Prevalence of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders in 4 US Communities. JAMA 2018, 319, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozen, S.; Peters, G.J.; Kok, G.; Townend, D.; Nijhuis, J.; Curfs, L. Worldwide Prevalence of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Literature Review Including Meta-Analysis. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kable, J.A.; O’Connor, M.J.; Olson, H.C.; Paley, B.; Mattson, S.N.; Anderson, S.M.; Riley, E.P. Neurobehavioral Disorder Associated with Prenatal Alcohol Exposure (ND-PAE): Proposed DSM-5 Diagnosis. Child. Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2016, 47, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, C.J.M.; Drew, P.D. Neuroinflammatory contribution of microglia and astrocytes in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. J Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 1973–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deverman, B.E.; Patterson, P.H. Cytokines and CNS development. Neuron 2009, 64, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noto, C.; Ota, V.K.; Santoro, M.L.; Gouvea, E.S.; Silva, P.N.; Spindola, L.M.; Cordeiro, Q.; Bressan, R.A.; Gadelha, A.; Brietzke, E.; et al. Depression, Cytokine, and Cytokine by Treatment Interactions Modulate Gene Expression in Antipsychotic Naive First Episode Psychosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5701–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakowiak, P.; Goines, P.E.; Tancredi, D.J.; Ashwood, P.; Hansen, R.L.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Van de Water, J. Neonatal Cytokine Profiles Associated With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agostinho, P.; Cunha, R.A.; Oliveira, C. Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 2766–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, T.S.; Hill, L.A.; Weinberg, J. Evidence for an immune signature of prenatal alcohol exposure in female rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 58, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drew, P.D.; Johnson, J.W.; Douglas, J.C.; Phelan, K.D.; Kane, C.J. Pioglitazone blocks ethanol induction of microglial activation and immune responses in the hippocampus, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex in a mouse model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boschen, K.E.; Ruggiero, M.J.; Klintsova, A.Y. Neonatal binge alcohol exposure increases microglial activation in the developing rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 2016, 324, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruggiero, M.J.; Boschen, K.E.; Roth, T.L.; Klintsova, A.Y. Sex Differences in Early Postnatal Microglial Colonization of the Developing Rat Hippocampus Following a Single-Day Alcohol Exposure. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasaki, L.S.; Schwarz, J.M. Effects of Moderate Prenatal Alcohol Exposure during Early Gestation in Rats on Inflammation across the Maternal-Fetal-Immune Interface and Later-Life Immune Function in the Offspring. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chastain, L.G.; Franklin, T.; Gangisetty, O.; Cabrera, M.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Shrivastava, P.; Jabbar, S.; Sarkar, D.K. Early life alcohol exposure primes hypothalamic microglia to later-life hypersensitivity to immune stress: Possible epigenetic mechanism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gano, A.; Prestia, L.; Middleton, F.A.; Youngentob, S.L.; Ignacio, C.; Deak, T. Gene expression profiling reveals a lingering effect of prenatal alcohol exposure on inflammatory-related genes during adolescence and adulthood. Cytokine 2020, 133, 155126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doremus-Fitzwater, T.L.; Youngentob, S.L.; Youngentob, L.; Gano, A.; Vore, A.S.; Deak, T. Lingering Effects of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure on Basal and Ethanol-Evoked Expression of Inflammatory-Related Genes in the CNS of Adolescent and Adult Rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, B.; Wesley, B.; Adeyiga, O.; Smith, D.M.; Da-Silva, A.; Rajguru, S. Alcohol modulates cytokine secretion and synthesis in human fetus: An in vivo and in vitro study. Alcohol 2000, 21, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, T.S.; Raineki, C.; Wertelecki, W.; Yevtushok, L.; Plotka, L.; Zymak-Zakutnya, N.; Honerkamp-Smith, G.; Wells, A.; Rolland, M.; Woodward, T.S.; et al. Altered maternal immune networks are associated with adverse child neurodevelopment: Impact of alcohol consumption during pregnancy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, T.S.; Raineki, C.; Wertelecki, W.; Yevtushok, L.; Plotka, L.; Granovska, I.; Zymak-Zakutnya, N.; Pashtepa, A.; Wells, A.; Honerkamp-Smith, G.; et al. Immune network dysregulation associated with child neurodevelopmental delay: Modulatory role of prenatal alcohol exposure. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, A.M.; Gimbel, B.A.; de Water, E.; Eckerle, J.K.; Radke, J.P.; Georgieff, M.K.; Wozniak, J.R. Prenatal and Postnatal Choline Supplementation in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients 2022, 14, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, S.H. Nutritional importance of choline for brain development. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 621S–626S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, S.H. Is maternal diet supplementation beneficial? Optimal development of infant depends on mother’s diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 685S–687S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeisel, S.H. Choline: Needed for normal development of memory. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2000, 19, 528S–531S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, S.H.; Niculescu, M.D. Perinatal choline influences brain structure and function. Nutr. Rev. 2006, 64, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blusztajn, J.K.; Slack, B.E.; Mellott, T.J. Neuroprotective Actions of Dietary Choline. Nutrients 2017, 9, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derbyshire, E.; Obeid, R. Choline, Neurological Development and Brain Function: A Systematic Review Focusing on the First 1000 Days. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamiz, F.; Gallo, M. A Systematic Review of the Dietary Choline Impact on Cognition from a Psychobiological Approach: Insights from Animal Studies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.D.; La Fiette, M.H.; Quinn, V.R.; Riley, E.P. Neonatal choline supplementation ameliorates the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on a discrimination learning task in rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2000, 22, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.D.; Biane, J.S.; O’Bryan, K.A.; O’Neill, T.M.; Dominguez, H.D. Choline supplementation following third-trimester-equivalent alcohol exposure attenuates behavioral alterations in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 2007, 121, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.H.; Williams, J.K.; Thomas, J.D. Choline supplementation attenuates learning deficits associated with neonatal alcohol exposure in the rat: Effects of varying the timing of choline administration. Brain Res. 2008, 1237, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.D.; Abou, E.J.; Dominguez, H.D. Prenatal choline supplementation mitigates the adverse effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on development in rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2009, 31, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.D.; Idrus, N.M.; Monk, B.R.; Dominguez, H.D. Prenatal choline supplementation mitigates behavioral alterations associated with prenatal alcohol exposure in rats. Birth. Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.D.; Tran, T.D. Choline supplementation mitigates trace, but not delay, eyeblink conditioning deficits in rats exposed to alcohol during development. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grafe, E.L.; Wade, M.M.M.; Hodson, C.E.; Thomas, J.D.; Christie, B.R. Postnatal Choline Supplementation Rescues Deficits in Synaptic Plasticity Following Prenatal Ethanol Exposure. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warton, F.L.; Molteno, C.D.; Warton, C.M.R.; Wintermark, P.; Lindinger, N.M.; Dodge, N.C.; Zollei, L.; van der Kouwe, A.J.W.; Carter, R.C.; Jacobson, J.L.; et al. Maternal choline supplementation mitigates alcohol exposure effects on neonatal brain volumes. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 45, 1762–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, S.W.; Carter, R.C.; Molteno, C.D.; Stanton, M.E.; Herbert, J.S.; Lindinger, N.M.; Lewis, C.E.; Dodge, N.C.; Hoyme, H.E.; Zeisel, S.H.; et al. Efficacy of Maternal Choline Supplementation During Pregnancy in Mitigating Adverse Effects of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure on Growth and Cognitive Function: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, J.R.; Fuglestad, A.J.; Eckerle, J.K.; Fink, B.A.; Hoecker, H.L.; Boys, C.J.; Radke, J.P.; Kroupina, M.G.; Miller, N.C.; Brearley, A.M.; et al. Choline supplementation in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wozniak, J.R.; Fink, B.A.; Fuglestad, A.J.; Eckerle, J.K.; Boys, C.J.; Sandness, K.E.; Radke, J.P.; Miller, N.C.; Lindgren, C.; Brearley, A.M.; et al. Four-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial of choline for neurodevelopment in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2020, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Brain Behav. Immun. 2005, 19, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, S.V.; Williams, C.L. The Cholinergic System Modulates Memory and Hippocampal Plasticity via Its Interactions with Non-Neuronal Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.L.; Adams, C.E.; Stevens, K.E.; Chow, K.H.; Freedman, R.; Patterson, P.H. The interaction between maternal immune activation and alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in regulating behaviors in the offspring. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 46, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Jones, S.; Andrew, B.Y.; Ganti, A.; Malysheva, O.V.; Giallourou, N.; Brannon, P.M.; Roberson, M.S.; Caudill, M.A. Choline inadequacy impairs trophoblast function and vascularization in cultured human placental trophoblasts. J. Cell Physiol. 2014, 229, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, S.T.C.; King, J.H.; Yan, J.; Jiang, X.; Wei, E.; Fomin, V.G.; Roberson, M.S.; Caudill, M.A. Maternal choline supplementation during murine pregnancy modulates placental markers of inflammation, apoptosis and vascularization in a fetal sex-dependent manner. Placenta 2017, 53, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.H.; Kwan, S.T.C.; Yan, J.; Jiang, X.; Fomin, V.G.; Levine, S.P.; Wei, E.; Roberson, M.S.; Caudill, M.A. Maternal Choline Supplementation Modulates Placental Markers of Inflammation, Angiogenesis, and Apoptosis in a Mouse Model of Placental Insufficiency. Nutrients 2019, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Han, X.; Bao, J.; Yang, J.; Shi, S.Q.; Garfield, R.E.; Liu, H. Choline Supplementation During Pregnancy Protects Against Gestational Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 25, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, W.X.; Du, C.Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.D.; Jin, S.Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, Z.G. Choline improves lipopolysaccharide-induced central nervous system inflammatory response and cognitive dysfunction in mice. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2017, 37, 600–606. [Google Scholar]
- Workman, A.D.; Charvet, C.J.; Clancy, B.; Darlington, R.B.; Finlay, B.L. Modeling transformations of neurodevelopmental sequences across mammalian species. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 7368–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbing, J.; Sands, J. Comparative aspects of the brain growth spurt. Early Hum. Dev. 1979, 3, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Mohapel, J.; Boehme, F.; Kainer, L.; Christie, B.R. Hippocampal cell loss and neurogenesis after fetal alcohol exposure: Insights from different rodent models. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 64, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.D.; Garrison, M.; O’Neill, T.M. Perinatal choline supplementation attenuates behavioral alterations associated with neonatal alcohol exposure in rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodlett, C.R.; Johnson, T.B. Neonatal binge ethanol exposure using intubation: Timing and dose effects on place learning. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1997, 19, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, R.F.; Heilig, M.; Cunningham, C.L.; Stephens, D.N.; Duka, T.; O’Malley, S.S. Ethanol consumption: How should we measure it? Achieving consilience between human and animal phenotypes. Addict. Biol. 2010, 15, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, S.J.; Bonthius, D.J.; West, J.R. Developmental changes in alcohol pharmacokinetics in rats. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1987, 11, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P. The Laboratory Rat: Relating Its Age With Human’s. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blom, G. Statistical Estimates and Transformed Beta-Variables; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1958; 176p. [Google Scholar]
- Crews, F.T.; Sarkar, D.K.; Qin, L.; Zou, J.; Boyadjieva, N.; Vetreno, R.P. Neuroimmune Function and the Consequences of Alcohol Exposure. Alcohol Res. 2015, 37, 331–341, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Lawrimore, C.J.; Walter, T.J.; Coleman, L.G., Jr. The role of neuroimmune signaling in alcoholism. Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerri, C.; Pascual, M. Impact of neuroimmune activation induced by alcohol or drug abuse on adolescent brain development. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2019, 77, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topper, L.A.; Baculis, B.C.; Valenzuela, C.F. Exposure of neonatal rats to alcohol has differential effects on neuroinflammation and neuronal survival in the cerebellum and hippocampus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahlers, K.E.; Karacay, B.; Fuller, L.; Bonthius, D.J.; Dailey, M.E. Transient activation of microglia following acute alcohol exposure in developing mouse neocortex is primarily driven by BAX-dependent neurodegeneration. Glia 2015, 63, 1694–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantacorps, L.; Montagud-Romero, S.; Valverde, O. Curcumin treatment attenuates alcohol-induced alterations in a mouse model of foetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 100, 109899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galic, M.A.; Riazi, K.; Pittman, Q.J. Cytokines and brain excitability. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 33, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monteiro, S.; Ferreira, F.M.; Pinto, V.; Roque, S.; Morais, M.; de Sa-Calcada, D.; Mota, C.; Correia-Neves, M.; Cerqueira, J.J. Absence of IFNgamma promotes hippocampal plasticity and enhances cognitive performance. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; He, H.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, T.; He, H.; Yi, S.; Zhang, L.; Mo, L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, W.; et al. Priming of microglia with IFN-gamma impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis and leads to depression-like behaviors and cognitive defects. Glia 2020, 68, 2674–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, S.; Milligan, E.D. Lifelong Impacts of Moderate Prenatal Alcohol Exposure on Neuroimmune Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, L.S.; Schwarz, J.M. Impact of Prenatal and Subsequent Adult Alcohol Exposure on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression in Brain Regions Necessary for Simple Recognition Memory. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topper, L.A.; Valenzuela, C.F. Effect of repeated alcohol exposure during the third trimester-equivalent on messenger RNA levels for interleukin-1beta, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2, and interleukin 10 in the developing rat brain after injection of lipopolysaccharide. Alcohol 2014, 48, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowell, K.D.; Uriu-Adams, J.Y.; Van de Water, J.; Chambers, C.D.; Coles, C.D.; Kable, J.A.; Yevtushok, L.; Zymak-Zakutnya, N.; Wertelecki, W.; Keen, C.L.; et al. Implications of altered maternal cytokine concentrations on infant outcomes in children with prenatal alcohol exposure. Alcohol 2018, 68, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bake, S.; Pinson, M.R.; Pandey, S.; Chambers, J.P.; Mota, R.; Fairchild, A.E.; Miranda, R.C.; Sohrabji, F. Prenatal alcohol-induced sex differences in immune, metabolic and neurobehavioral outcomes in adult rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 98, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Turnbull, A.V.; Lee, S.Y.; Rivier, C.L. Effects of prenatal exposure to alcohol on the release of adenocorticotropic hormone, corticosterone, and proinflammatory cytokines. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1999, 23, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappelli, F.; Kung, M.A.; Tio, D.L.; Tritt, S.H.; Yirmiya, R.; Taylor, A.N. Fetal alcohol exposure augments the blunting of tumor necrosis factor production in vitro resulting from in vivo priming with lipopolysaccharide in young adult male but not female rats. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1997, 21, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourrier, C.; Remus-Borel, J.; Greenhalgh, A.D.; Guichardant, M.; Bernoud-Hubac, N.; Lagarde, M.; Joffre, C.; Laye, S. Docosahexaenoic acid-containing choline phospholipid modulates LPS-induced neuroinflammation in vivo and in microglia in vitro. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.Y.; Wang, H. Synergistic interaction between choline and aspirin against acute inflammation induced by carrageenan and lipopolysaccharide. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 20, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; West, A.A.; Caudill, M.A. Maternal choline supplementation: A nutritional approach for improving offspring health? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, J.; Buendia, I.; Parada, E.; Navarro, E.; Leon, R.; Lopez, M.G. Anti-inflammatory role of microglial alpha7 nAChRs and its role in neuroprotection. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 97, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, E.; Egea, J.; Buendia, I.; Negredo, P.; Cunha, A.C.; Cardoso, S.; Soares, M.P.; Lopez, M.G. The microglial alpha7-acetylcholine nicotinic receptor is a key element in promoting neuroprotection by inducing heme oxygenase-1 via nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Jonge, W.J.; Ulloa, L. The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor as a pharmacological target for inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 151, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallowitsch-Puerta, M.; Pavlov, V.A. Neuro-immune interactions via the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 2325–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benfante, R.; Di Lascio, S.; Cardani, S.; Fornasari, D. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors targeting the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: A new therapeutic perspective in aging-related disorders. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raineki, C.; Bodnar, T.S.; Holman, P.J.; Baglot, S.L.; Lan, N.; Weinberg, J. Effects of early-life adversity on immune function are mediated by prenatal environment: Role of prenatal alcohol exposure. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, N.; Moritz, K.M.; Akison, L.K. Adverse health outcomes associated with fetal alcohol exposure: A systematic review focused on immune-related outcomes. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 30, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, T.W. Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and the Developing Immune System. Alcohol Res. 2015, 37, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oleson, D.R.; Magee, R.M.; Donahoe, R.M.; Falek, A.; Coles, C.D. Immunity and prenatal alcohol exposure. A pilot study in human adolescents. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 437, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Libster, R.; Ferolla, F.M.; Hijano, D.R.; Acosta, P.L.; Erviti, A.; Polack, F.P.; Network, I.R. Alcohol during pregnancy worsens acute respiratory infections in children. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, e494–e499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, T.W.; Ping, X.D.; Gabelaia, L.; Brown, L.A. Delayed neonatal lung macrophage differentiation in a mouse model of in utero ethanol exposure. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L8–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauthier, T.W.; Ping, X.D.; Harris, F.L.; Wong, M.; Elbahesh, H.; Brown, L.A. Fetal alcohol exposure impairs alveolar macrophage function via decreased glutathione availability. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gauthier, T.W.; Young, P.A.; Gabelaia, L.; Tang, S.M.; Ping, X.D.; Harris, F.L.; Brown, L.A. In utero ethanol exposure impairs defenses against experimental group B streptococcus in the term Guinea pig lung. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.K.; Gaur, S.N.; Arora, N.; Singh, B.P. Effect of choline chloride in allergen-induced mouse model of airway inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baker, J.A.; Breit, K.R.; Bodnar, T.S.; Weinberg, J.; Thomas, J.D. Choline Supplementation Modifies the Effects of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Immune Responses in Adult Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142868
Baker JA, Breit KR, Bodnar TS, Weinberg J, Thomas JD. Choline Supplementation Modifies the Effects of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Immune Responses in Adult Rats. Nutrients. 2022; 14(14):2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142868
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaker, Jessica A., Kristen R. Breit, Tamara S. Bodnar, Joanne Weinberg, and Jennifer D. Thomas. 2022. "Choline Supplementation Modifies the Effects of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Immune Responses in Adult Rats" Nutrients 14, no. 14: 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142868
APA StyleBaker, J. A., Breit, K. R., Bodnar, T. S., Weinberg, J., & Thomas, J. D. (2022). Choline Supplementation Modifies the Effects of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Immune Responses in Adult Rats. Nutrients, 14(14), 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142868