TRPV1-Mediated Sensing of Sodium and Osmotic Pressure in POMC Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Measurement of Cytosolic Calcium Concentration ([Ca2+]i)
2.3. Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
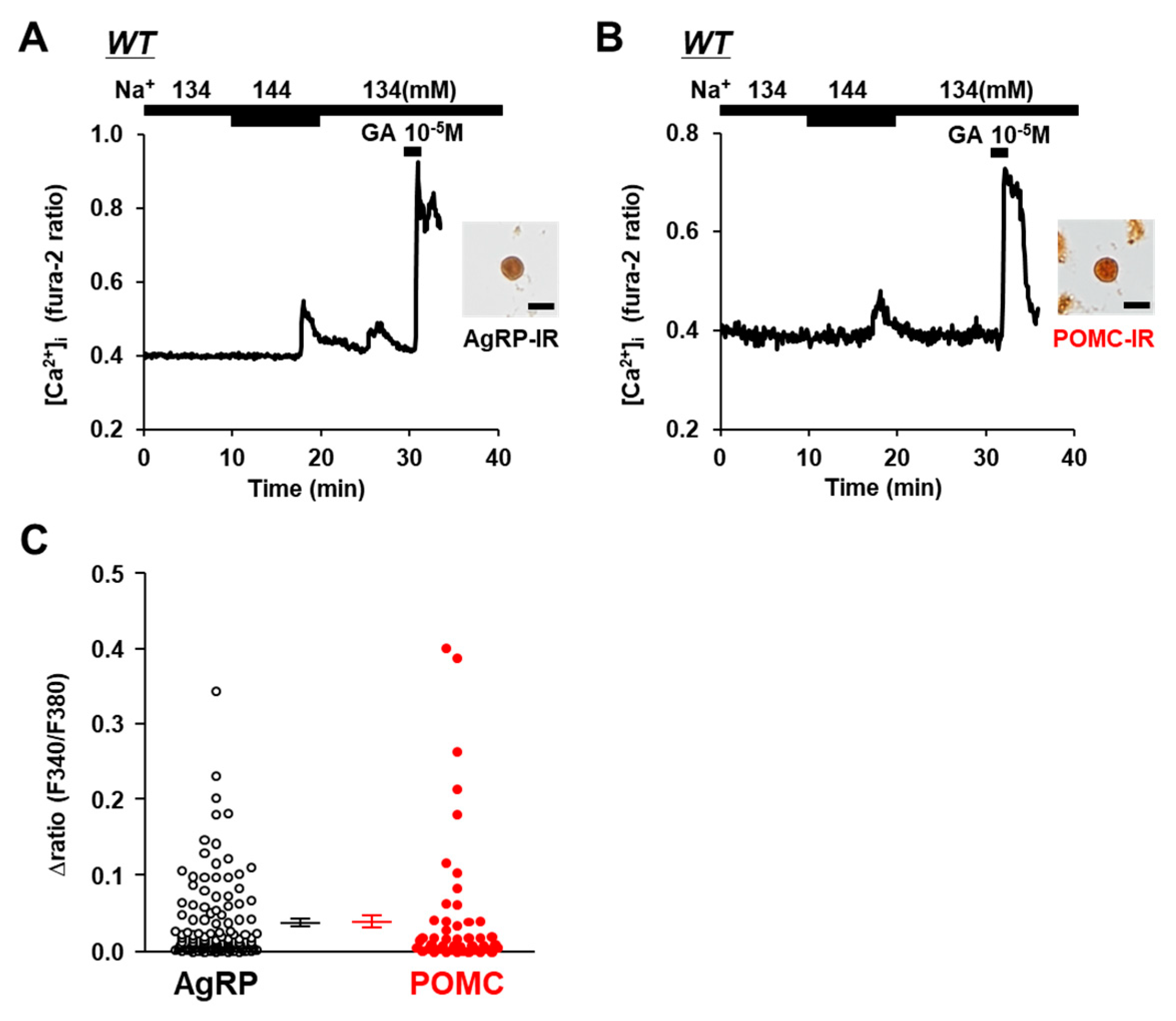
3.1. AgRP and POMC Neurons in ARC Sense Na+
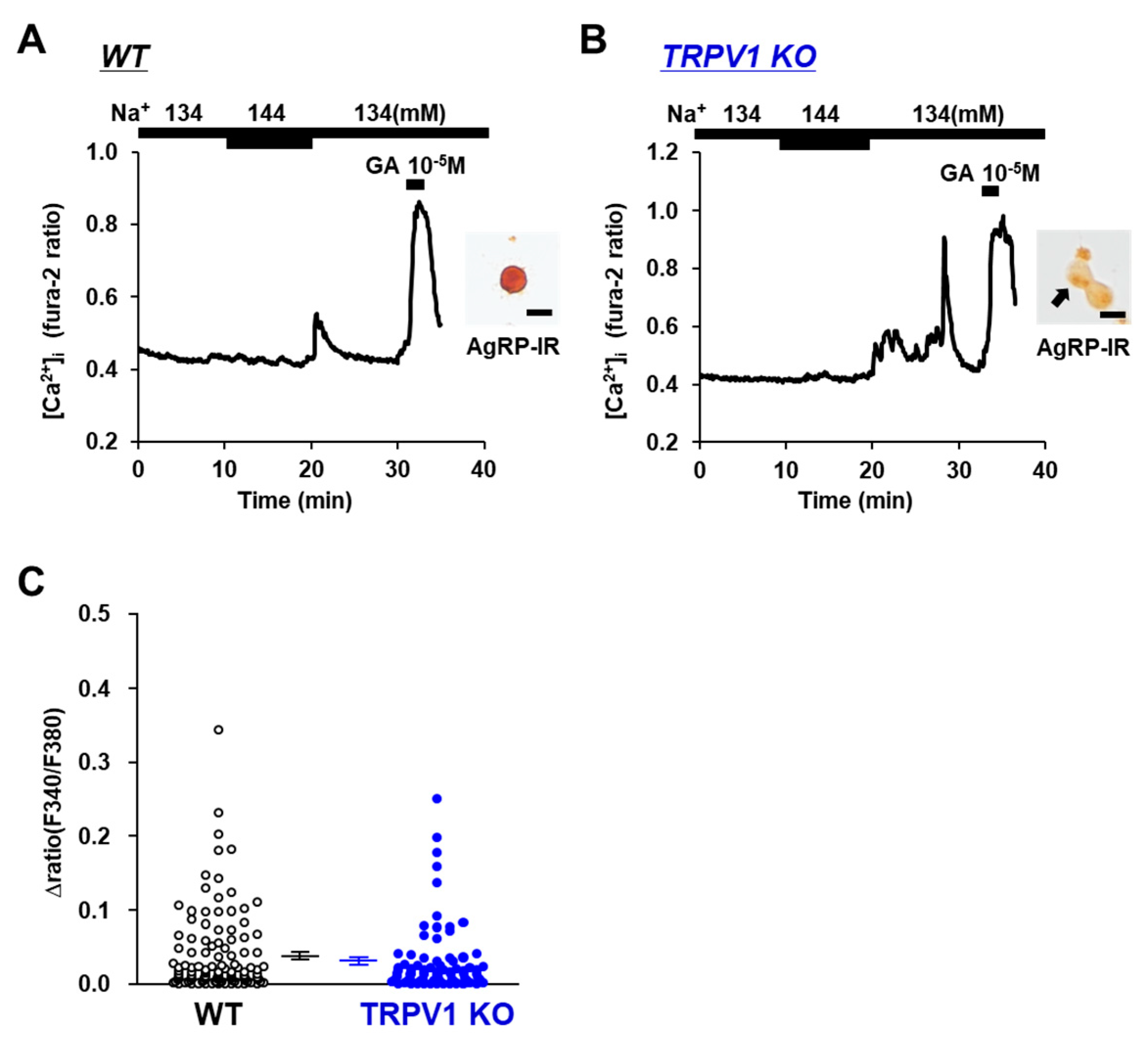
3.2. [Na+] Sensing in POMC Neurons Is Abolished in TRPV1 KO Mice
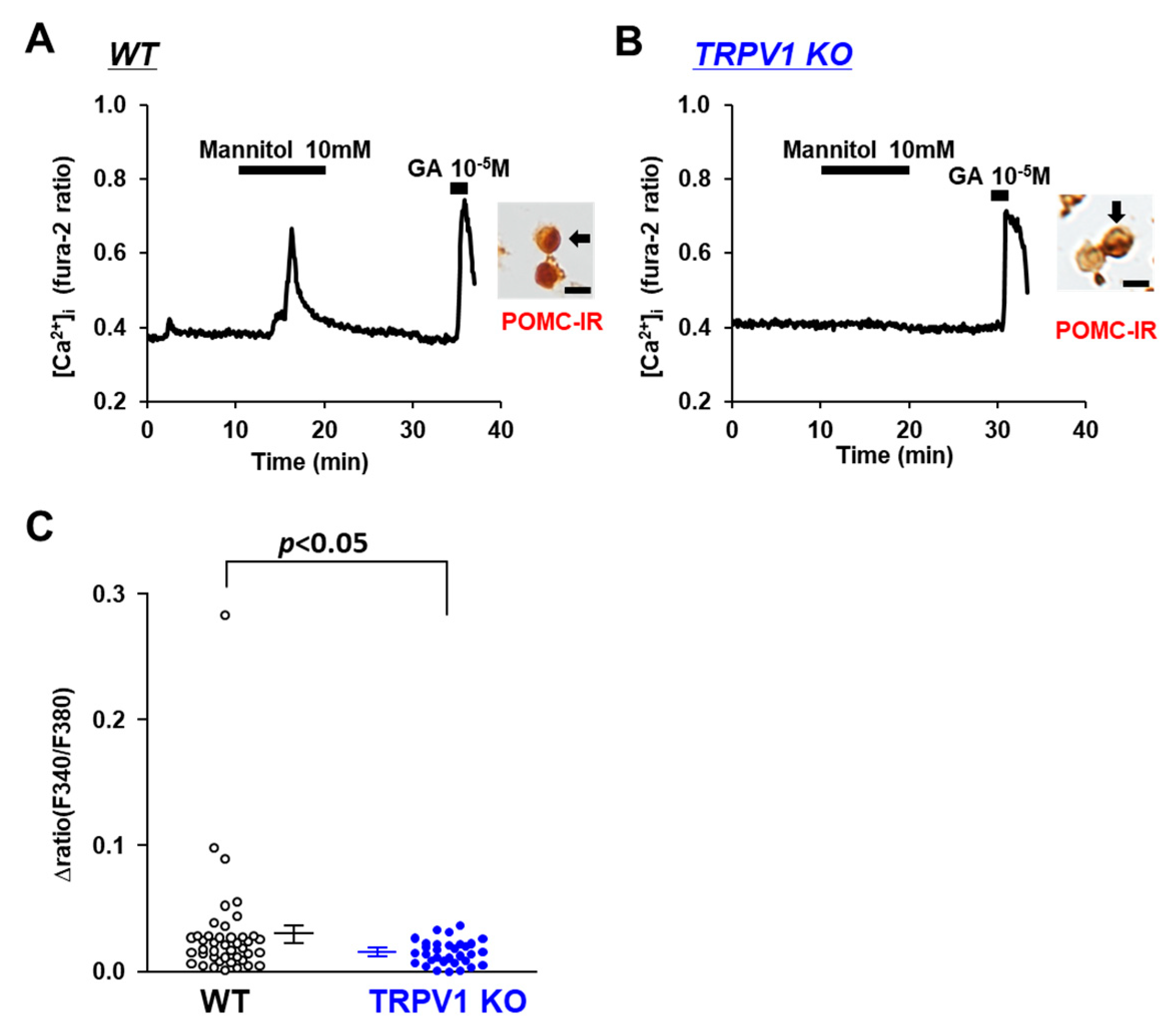
3.3. Osmolarity Increase Activates POMC Neurons via TRPV1
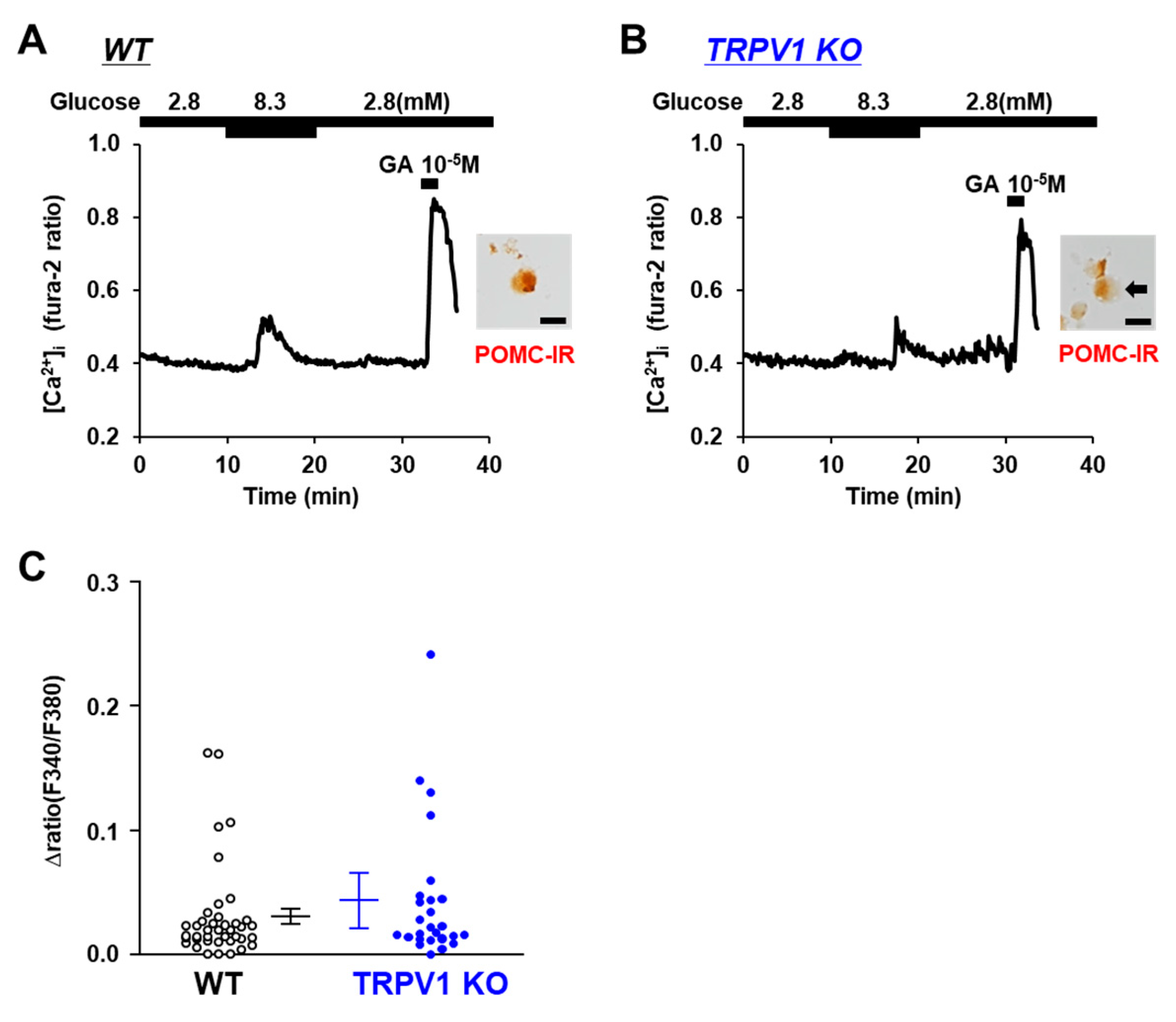
3.4. Glucose-Sensing in POMC Neurons Is Unaltered in TRPV1 KO Mice
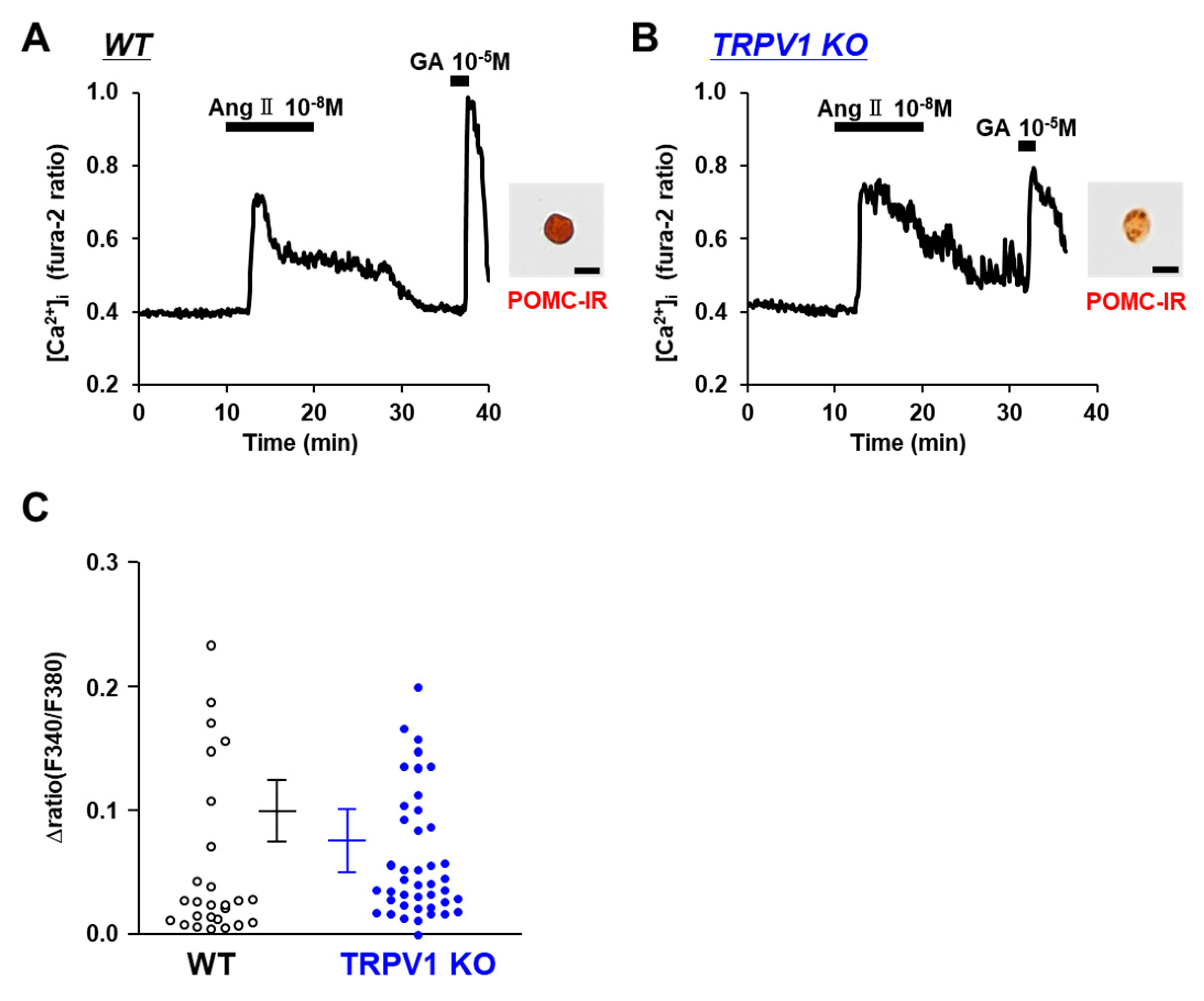
3.5. Angiotensin II Activates POMC Neurons in WT and TRPV1 KO Mice
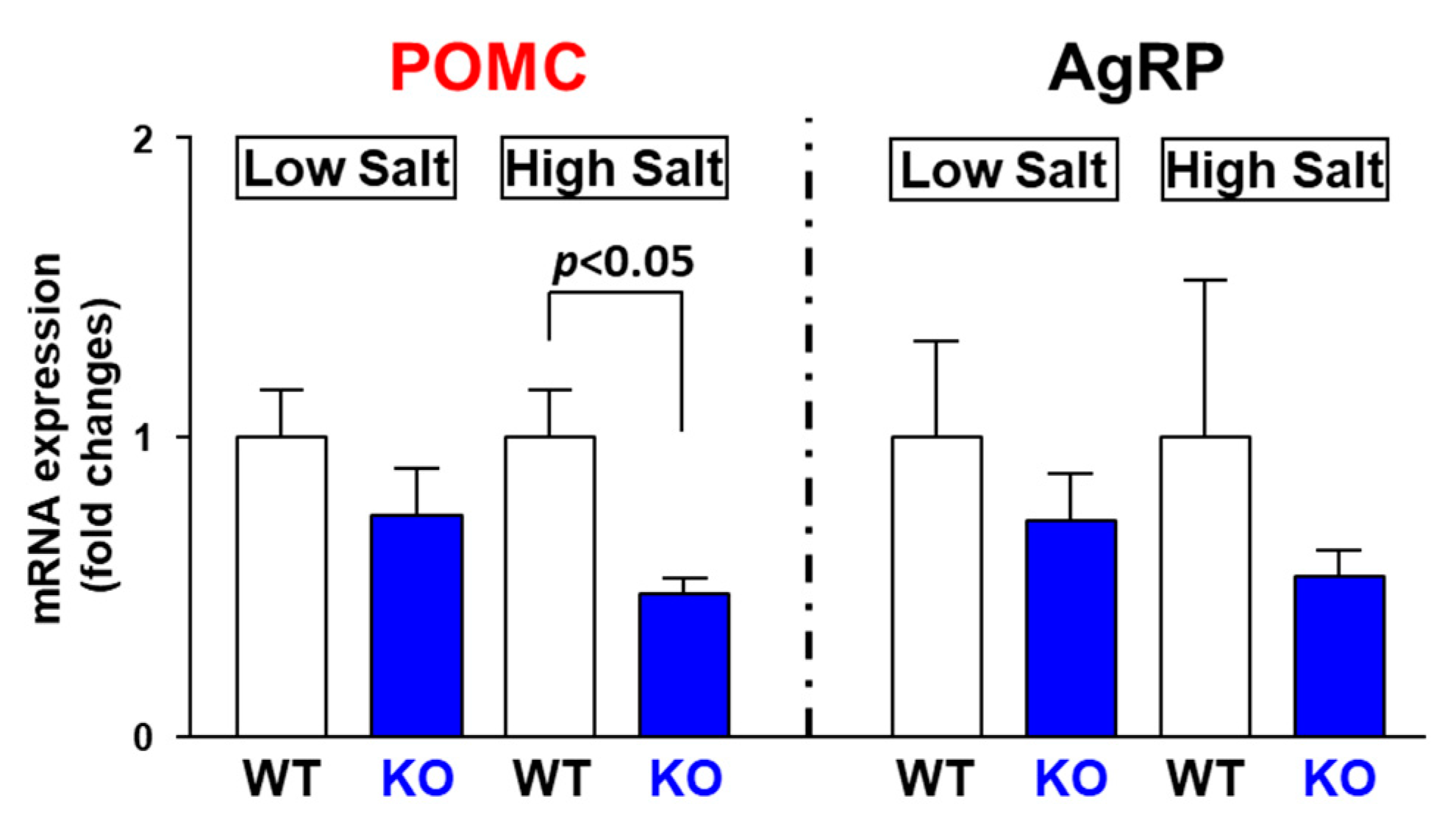
3.6. High Salt Intake Decreases POMC mRNA Expression in TRPV1 KO Mice
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Elena, V.; Massimo, S.; Francesco, C. Neuroendocrine control of food intake. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 158–168. [Google Scholar]
- Konturek, S.J.; Konturek, J.W.; Pawlik, T.; Brzozowski, T. Brain-gut axis and its role in the control of food intake. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2004, 55, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bunner, W.; Landry, T.; Laing, B.T.; Li, P.; Rao, Z.J.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, H. ARC AgRP/NPY Neuron Activity Is Required for Acute Exercise-Induced Food Intake in Un-Trained Mice. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Woods, S.C.; Porte, D., Jr.; Seeley, R.J.; Baskin, D.G. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 2000, 404, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ollmann, M.M.; Wilson, B.D.; Yang, Y.K.; Kerns, J.A.; Chen, Y.R.; Gantz, I.; Barsh, G.S. Antagonism of central melanocortin receptors in vitro and in vivo by agouti-related protein. Science 1997, 278, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, A.R.; Hentges, S.T. The Relevance of AgRP Neuron-Derived GABA Inputs to POMC Neurons Differs for Spontaneous and Evoked Release. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 7362–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, M.A.; Pronchuk, N.; Wei, F.; Dinulescu, D.M.; Colmers, W.F.; Cone, R.D. Integration of NPY, AGRP, and melanocortin signals in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: Evidence of a cellular basis for the adipostat. Neuron 1999, 24, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smart, J.L.; Rubinstein, M.; Cerdán, M.G.; Diano, S.; Horvath, T.L.; Cone, R.D.; Low, M.J. Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature 2001, 411, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.A.; Kuo, J.J.; Hall, J.E. Role of hypothalamic melanocortin 3/4-receptors in mediating chronic cardiovascular, renal, and metabolic actions of leptin. Hypertension 2004, 43, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo, J.M.; Tallam, L.S.; Roberts, J.V.; Brandon, E.L.; Biglane, J.; da Silva, A.A.; Hall, J.E. Impact of obesity on renal structure and function in the presence and absence of hypertension: Evidence from melanocortin-4 receptor-deficient mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 297, R803–R812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmouni, K.; Haynes, W.G.; Morgan, D.A.; Mark, A.L. Role of melanocortin-4 receptors in mediating renal sympathoactivation to leptin and insulin. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 5998–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallam, L.S.; Stec, D.E.; Willis, M.A.; da Silva, A.A.; Hall, J.E. Melanocortin-4 receptor-deficient mice are not hypertensive or salt-sensitive despite obesity, hyperinsulinemia, and hyperleptinemia. Hypertension 2005, 46, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaques, D.A.; Wuerzner, G.; Ponte, B. Sodium Intake as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Kawamura, M.; Yoshimi, H.; Ashida, T.; Abe, H.; Imanishi, M.; Kimura, G.; Kojima, S.; Kuramochi, M.; et al. Sodium and noradrenaline in cerebrospinal fluid and blood in salt-sensitive and non-salt-sensitive essential hypertension. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1992, 19, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, K.; Hiyama, T.Y.; Sakuta, H.; Matsuda, T.; Lin, C.; Kobayashi, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Kuwaki, T.; Takahashi, K.; Matsui, S.; et al. [Na+] Increases in Body Fluids Sensed by Central Nax Induce Sympathetically Mediated Blood Pressure Elevations via H+-Dependent Activation of ASIC1a. Neuron 2019, 101, 60–75.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.S.; Van Vliet, B.N.; Leenen, F.H.H. Increases in CSF [Na+] precede the increases in blood pressure in Dahl S rats and SHR on a high-salt diet. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H1160–H1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, M.C.; Peters, J.H. TRPV1, hypertension, and cardiovascular regulation. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, F.; Xiong, S.Q.; Zhu, Z.M. Dietary Capsaicin Protects Cardiometabolic Organs from Dysfunction. Nutrients 2016, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ma, S.; Wang, D.H. Selective ablation of TRPV1 by intrathecal injection of resiniferatoxin in rats increases renal sympathoexcitatory responses and salt sensitivity. Hypertens. Res. 2018, 41, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ma, S.; Wang, D.H. TRPV1 Activation Prevents Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury-Induced Increase in Salt Sensitivity by Suppressing Renal Sympathetic Nerve Activity. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2019, 16, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, F.E.; Sugino, K.; Tozer, A.; Branco, T.; Sternson, S.M. Cell type-specific transcriptomics of hypothalamic energy-sensing neuron responses to weight-loss. eLife 2015, 4, e09800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.H.; Lee, D.K.; Liu, S.; Chua Jr, S.C.; Schwartz, G.J.; Jo, Y. Activation of temperature-sensitive TRPV1-like receptors in ARC POMC neurons reduces food intake. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2004399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caterina, M.J.; Leffler, A.; Malmberg, A.B.; Martin, W.J.; Trafton, J.; Petersen-Zeitz, K.R.; Koltzenburg, M.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science 2000, 288, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Nakata, M.; Nakae, J.; Ogawa, W.; Yada, T. Central insulin action induces activation of paraventricular oxytocin neurons to release oxytocin into circulation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Kurosumi, K. A certain step of proteolytic processing of proopiomelanocortin occurs during the transition between two distinct stages of secretory granule maturation in rat anterior pituitary corticotrophs. Endocrinology 1992, 131, 779–786. [Google Scholar]
- Nakata, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Okada, T.; Gantulga, D.; Okano, H.; Ozawa, K.; Yada, T. IL-10 gene transfer upregulates arcuate POMC and ameliorates hyperphagia, obesity and diabetes by substituting for leptin. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parton, L.E.; Ye, C.P.; Coppari, R.; Enriori, P.J.; Choi, B.; Zhang, C.; Xu, C.; Vianna, C.R.; Balthasar, N.; Lee, C.E.; et al. Glucose sensing by POMC neurons regulates glucose homeostasis and is impaired in obesity. Nature 2007, 449, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Bosch, M.A.; Smart, J.L.; Qiu, J.; Rubinstein, M.; Ronnekleiv, O.K.; Low, M.J.; Kelly, M.J. Hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin neurons are glucose responsive and express K(ATP) channels. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coble, J.P.; Grobe, J.L.; Johnson, A.K.; Sigmund, C.D. Mechanisms of brain renin angiotensin system-induced drinking and blood pressure: Importance of the subfornical organ. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 308, R238–R249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, P.M. Circumventricular organ capillaries. Prog. Brain Res. 1992, 91, 219–333. [Google Scholar]
- Morita-Takemura, S.; Wanaka, A. Blood-to-brain communication in the hypothalamus for energy intake regulation. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 128, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.A.; Hauptfleisch, S.; Fleissner, G.; Lemmer, B. Localization of angiotensin II (AT1)-receptor-immunoreactive fibres in the hypothalamus of rats: Angiotensin II-sensitive tanycytes in the ependyma of the third ventricle? Brain Res. 2003, 967, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquenne, M.; Folgueira, C.; Bourouh, C.; Millet, M.; Silva, A.; Clasadonte, J.; Imbernon, M.; Fernandois, D.; Martinez-Corral, I.; Kusumakshi, S.; et al. Leptin brain entry via a tanycytic LepR-EGFR shuttle controls lipid metabolism and pancreas function. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1071–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudbury, J.R.; Bourque, C.W. Dynamic and permissive roles of TRPV1 and TRPV4 channels for thermosensation in mouse supraoptic magnocellular neurosecretory neurons. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 17160–17165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cone, R.D. Anatomy and regulation of the central melanocortin system. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Ye, C.; Jones, J.E.; Elmquist, J.K.; Lowell, B.B. Synaptic release of GABA by AgRP neurons is required for normal regulation ofenergy balance. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeltser, L.M.; Seeley, R.J.; Tschöp, M.H. Synaptic plasticity in neuronal circuits regulating energy balance. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancardi, V.C.; Son, S.J.; Ahmadi, S.; Filosa, J.A.; Stern, J.E. Circulating Angiotensin II Gains Access to the Hypothalamus and Brain Stem during Hypertension via Breakdown of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Hypertension 2014, 63, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Mao, Y.; Ramirez, S.H.; Tuma, R.F.; Chabrashvili, T. Angiotensin II induced cerebral microvascular inflammation and increased blood-brain barrier permeability via oxidative stress. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kloet, A.D.; Pioquinto, D.J.; Nguyen, D.; Wang, L.; Smith, J.A.; Hiller, H.; Sumners, C. Obesity induces neuroinflammation mediated by altered expression of the renin-angiotensin system in mouse forebrain nuclei. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 136, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claflin, K.E.; Sandgren, J.A.; Lambertz, A.M.; Weidemann, B.J.; Littlejohn, N.K.; Burnett, C.M.L.; Pearson, N.A.; Morgan, D.A.; Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Rahmouni, K.; et al. Angiotensin AT1A receptors on leptin receptor-expressing cells control resting metabolism. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Morgan, D.A.; Cui, H.; Rahmouni, K. Activation of hypothalamic AgRP and POMC neurons evokes disparate sympathetic and cardiovascular responses. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 319, H1069–H1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Nakata, M.; Lu, M.; Nakae, J.; Okada, T.; Ogawa, W.; Yada, T. Protective role of AgRP neuron’s PDK1 against salt-induced hypertension. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Kario, K.; Yada, T.; Nakata, M. TRPV1-Mediated Sensing of Sodium and Osmotic Pressure in POMC Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132600
Zhang B, Kario K, Yada T, Nakata M. TRPV1-Mediated Sensing of Sodium and Osmotic Pressure in POMC Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus. Nutrients. 2022; 14(13):2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132600
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Boyang, Kazuomi Kario, Toshihiko Yada, and Masanori Nakata. 2022. "TRPV1-Mediated Sensing of Sodium and Osmotic Pressure in POMC Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus" Nutrients 14, no. 13: 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132600
APA StyleZhang, B., Kario, K., Yada, T., & Nakata, M. (2022). TRPV1-Mediated Sensing of Sodium and Osmotic Pressure in POMC Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus. Nutrients, 14(13), 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14132600




