Impact of Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss on Anterior Eye Health in Patients with Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
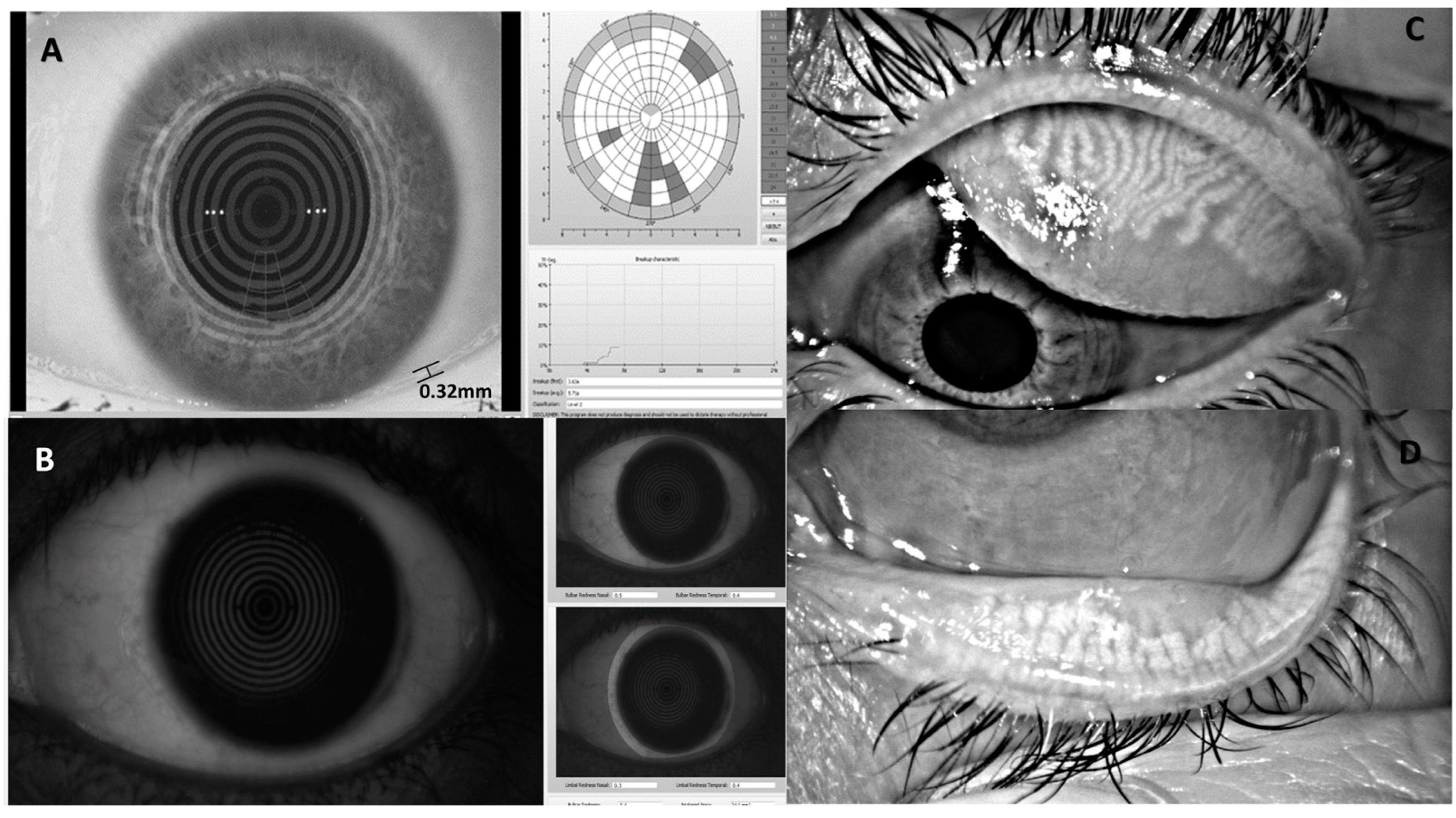
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Bohlman, H. Communicating the Ocular and Systemic Complications of Obesity to Patients. Optometry 2005, 76, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, R.; Ee, N.; Peters, J.; Beckett, N.; Booth, A.; Rockwood, K.; Anstey, K.J. Common Risk Factors for Major Noncommunicable Disease, a Systematic Overview of Reviews and Commentary: The Implied Potential for Targeted Risk Reduction. Ther. Adv. Chronic. Dis. 2019, 10, 2040622319880392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Impact of Obesity and Lifestyle-Related Risk Indicators in Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Review|University of Toronto Medical Journal. Available online: https://www.utmj.org/index.php/UTMJ/article/view/169 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Patterson, R.E.; Frank, L.L.; Kristal, A.R.; White, E. A Comprehensive Examination of Health Conditions Associated with Obesity in Older Adults. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2004, 27, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iroku-Malize, T.; Kirsch, S. Eye Conditions in Older Adults: Cataracts. FP Essent. 2016, 445, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Acer, S.; Ağladıoğlu, S.Y.; Pekel, G.; Özhan, B.; Çetin, E.N.; Yağci, R.; Yildirim, C. Density of the Crystalline Lens in Obese and Nonobese Children. J. AAPOS 2016, 20, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leiden, H.A.; Dekker, J.M.; Moll, A.C.; Nijpels, G.; Heine, R.J.; Bouter, L.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Polak, B.C.P. Blood Pressure, Lipids, and Obesity Are Associated with Retinopathy: The Hoorn Study. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leiden, H.A.; Dekker, J.M.; Moll, A.C.; Nijpels, G.; Heine, R.J.; Bouter, L.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Polak, B.C.P. Risk Factors for Incident Retinopathy in a Diabetic and Nondiabetic Population: The Hoorn Study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliveau, M.J.; Harvey, J.T. Floppy Eyelid Syndrome. CMAJ 2015, 187, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Uchino, M.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Michikawa, T.; Shirakawa, K.; Kuwahara, E.; Yamada, M.; Dogru, M.; Schaumberg, D.A.; Kawakita, T.; Takebayashi, T.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Dry Eye Disease in Japan: Koumi Study. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 2361–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. Obesity and Dyslipidemia; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rathnakumar, K.; Ramachandran, K.; Baba, D.; Ramesh, V.; Anebaracy, V.; Vidhya, R.; Vinothkumar, R.; Poovitha, R.; Geetha, R. Prevalence of Dry Eye Disease and Its Association with Dyslipidemia. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 29, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokr, H.; Wolffsohn, J.S.; Trave Huarte, S.; Scarpello, E.; Gherghel, D. Dry Eye Disease Is Associated with Retinal Microvascular Dysfunction and Possible Risk for Cardiovascular Disease. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021, 99, aos.14782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.C.; Jalbert, I.; Watt, K.; Golebiowski, B. A Possible Association Between Dry Eye Symptoms and Body Fat: A Prospective, Cross-Sectional Preliminary Study. Eye Contact Lens Sci. Clin. Pract. 2017, 43, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdur, S.K.; Aydin, R.; Ozsutcu, M.; Olmuscelik, O.; Eliacik, M.; Demirci, G.; Kocabora, M.S. The Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome, Its Components, and Dry Eye: A Cross-Sectional Study. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.L.; Ren, Y.P.; Yu, X.N.; Shentu, X.C. Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors and Dry Eye Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 9, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Z.; Huang, Y.L.; Wu, C.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Pan, H.J.; Huang, C.K.; Yeh, L.R.; Wu, M.T. Differential Effects of Bariatric Surgery versus Exercise on Excessive Visceral Fat Deposits. Medicine 2016, 95, e2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, S.S. Nutritional and Metabolic Complications of Bariatric Surgery. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 331, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socorro Sánchez-Sánchez, A.; Rodríguez-Murguía, N.; Martinez-Cordero, C.; Chávez-Cerda, S. Protein Diet in Bariatric Patients Could Modify Tear Film. Obes. Surg. 2019, 30, 2053–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, N.P.N.; Felberg, S.; De Barros, J.N.; Malheiros, C.A. Evaluation of the Ocular Surface Following Bariatric Surgery. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2017, 80, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bartolomé, F.; Sanz-Pozo, C.; Martínez-de la Casa, J.M.; Arriola-Villalobos, P.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; García-Feijoó, J. Assessment of Ocular Redness Measurements Obtained with Keratograph 5M and Correlation with Subjective Grading Scales. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2018, 41, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hong, J.; Tian, L.; Cui, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, J. Assessment of Bulbar Redness with a Newly Developed Keratograph. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2015, 92, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokr, H.; Gherghel, D. European Society of Cardiology/European Society of Hypertension versus the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Guidelines on the Cut-off Values for Early Hypertension: A Microvascular Perspective. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the Concentration of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Plasma, without Use of the Preparative Ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Qu, J.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, X.G. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Noninvasive Keratograph 5m Measurements in Patients with Dry Eye Disease. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 2016, 8013621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Montero, M.; Rico-del-Viejo, L.; Lorente-Velázquez, A.; Martínez-Alberquilla, I.; Hernández-Verdejo, J.L.; Madrid-Costa, D. Repeatability of Noninvasive Keratograph 5M Measurements Associated With Contact Lens Wear. Eye Contact Lens Sci. Clin. Pract. 2019, 45, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, R.; Suehiro, J.; Haraguchi, T.; Shirakawa, R.; Tokoro, H.; Amano, S. Objective Image Analysis of the Meibomian Gland Area. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pult, H.; Riede-Pult, B. Comparison of Subjective Grading and Objective Assessment in Meibography. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2013, 36, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pult, H.; Nichols, J.J. A Review of Meibography. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2012, 89, E760–E769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Tahhan, M.; Vidal-Rohr, M.; Hunt, O.A.; Bhogal-Bhamra, G. Best Technique for Upper Lid Eversion. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2019, 42, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Arita, R.; Chalmers, R.; Djalilian, A.; Dogru, M.; Dumbleton, K.; Gupta, P.K.; Karpecki, P.; Lazreg, S.; Pult, H.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Diagnostic Methodology Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 539–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.C.; Wolffsohn, J.S.; Fowler, C.W. Optimization of Anterior Eye Fluorescein Viewing. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 142, 572–575.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. In Proceedings of the Behavior Research Methods; Psychonomic Society Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2007; Volume 39, pp. 175–191. [Google Scholar]
- Pult, H.; Riede-Pult, B.H. Non-Contact Meibography: Keep It Simple but Effective. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2012, 35, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, Y.; Shimazaki-Den, S.; Tsubota, K.; Shimazaki, J. Morphological Evaluation of Meibomian Glands Using Noncontact Infrared Meibography. Ocul. Surf. 2013, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, J.P.; Muntz, A.; Wang, M.T.M.; Luensmann, D.; Tan, J.; Trave Huarte, S.; Xue, A.L.; Jones, L.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Wolffsohn, J.S. Developing Evidence-Based Guidance for the Treatment of Dry Eye Disease with Artificial Tear Supplements: A Six-Month Multicentre, Double-Masked Randomised Controlled Trial. Ocul. Surf. 2021, 20, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, N.; Katritsis, D.; Raggi, P. Visceral Adipose Tissue as a Source of Inflammation and Promoter of Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2014, 233, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikama, Y.; Kurosawa, M.; Furukawa, M.; Ishimaru, N.; Matsushita, K. Involvement of Adiponectin in Age-Related Increases in Tear Production in Mice. Aging 2019, 11, 8329–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilkhu, P.; Vidal-Rohr, M.; Trave-Huarte, S.; Wolffsohn, J.S. Effect of Meibomian Gland Morphology on Functionality with Applied Treatment. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2021, 45, 101402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, K.; Aarts, E.O.; Koehestanie, P.; Betzel, B.; Ploeger, N.; De Boer, H.; Aufenacker, T.J.; Van Laarhoven, K.J.H.M.; Janssen, I.M.C.; Berends, F.J. Optimization of Vitamin Suppletion after Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery Can Lower Postoperative Deficiencies:A Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicine 2014, 93, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz, S.P.; Matos, A.; Pereira, S.; Saboya, C.; da Cruz, S.P.; Ramalho, A. Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass Aggravates Vitamin A Deficiency in the Mother-Child Group. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C. The Eye Signs of Vitamin A Deficiency. Community Eye Health J. 2013, 26, 66–67. [Google Scholar]
- Malm, E.; Ghosh, F. Chronic Conjunctivitis in a Patient with Folic Acid Deficiency. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2006, 85, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, S.; Ozer, M.A.; Akdemir, M.O. Vitamin B12 Deficiency Evaluation and Treatment in Severe Dry Eye Disease with Neuropathic Ocular Pain. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekeryapan, B.; Oner, V.; Kirbas, A.; Turkyilmaz, K.; Durmus, M. Plasma Homocysteine Levels in Dry Eye Patients. Cornea 2013, 32, e94–e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.D.; Martin, N.; Dodson, P.M. Homocysteine, Folates, and the Eye. Eye 2008, 22, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roedl, J.B.; Bleich, S.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; Von Ahsen, N.; Kornhuber, J.; Naumann, G.O.H.; Kruse, F.E.; Jünemann, A.G.M. Increased Homocysteine Levels in Tear Fluid of Patients with Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Ophthalmic Res. 2008, 40, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, S.Y.; Zarshenas, N.; Jorgensen, J. Prevalence of Nutrient Deficiencies in Bariatric Patients. Nutrition 2009, 25, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodard, G.A.; Peraza, J.; Bravo, S.; Toplosky, L.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Morton, J.M. One Year Improvements in Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Comparative Trial of Laparoscopic Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass vs. Adjustable Gastric Banding. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeotikar, N.S.; Zhu, H.; Markoulli, M.; Nichols, K.K.; Naduvilath, T.; Papas, E.B. Functional and Morphologic Changes of Meibomian Glands in an Asymptomatic Adult Population. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 3996–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osae, E.A.; Steven, P.; Redfern, R.; Hanlon, S.; Smith, C.W.; Rumbaut, R.E.; Burns, A.R. Dyslipidemia and Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: Utility of Lipidomics and Experimental Prospects with a Diet-Induced Obesity Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, E.; Thorell, A. Insulin Resistance in Bariatric Surgery. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirra, F.; Richards, S.M.; Liu, M.; Suzuki, T.; Yamagami, H.; Sullivan, D.A. Androgen Regulation of Lipogenic Pathways in the Mouse Meibomian Gland. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Baseline | Follow-Up | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) | 49.20 (7.69) | 38.38 (7.84) | <0.001 * |
| SBP (mmHg) | 144.24 (14.35) | 128.75 (13.23) | <0.001 * |
| DBP (mmHg) | 78.96 (11.35) | 73.34 (10.84) | 0.039 * |
| MAP (mmHg) | 100.72 (10.58) | 92.48 (10.94) | <0.001 * |
| HR (bpm) | 74.10 (13.45) | 69.17 (9.88) | 0.046 * |
| CHOL (mmol/L) | 4.90 (1.21) | 4.53 (0.97) | 0.003 * |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.24 (0.35) | 1.51 (0.40) | <0.001 * |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.97 (1.01) | 2.49 (0.81) | <0.001 * |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.44 (0.72) | 1.13 (0.50) | 0.002 * |
| Parameter | Baseline | Follow Up | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| TMH (mm) | 0.30 (0.10) | 0.27 (0.08) | 0.074 |
| Fluorescein staining (%) | 1.76 (2.46) | 2.73 (4.53) | 0.333 |
| Lissamine staining (%) | 12.10 (9.32) | 11.03 (4.72) | 0.372 |
| NIBUT | |||
| First (sec) | 10.08 (7.08) | 10.29 (6.72) | 0.875 |
| Average (sec) | 11.92 (6.71) | 12.14 (6.53) | 0.849 |
| Hyperemia | |||
| Bulbar temporal | 0.86 (9.36) | 0.86 (0.44) | 0.952 |
| Bulbar nasal | 0.99 (0.47) | 0.93 (0.41) | 0.451 |
| Limbal temporal | 0.57 (0.32) | 0.57 (0.39) | 0.948 |
| Limbal nasal | 0.71 (0.33) | 0.62 (0.32) | 0.082 |
| MG Dropout | |||
| Superior loss (%) | 22.12 (11.73) | 18.64 (10.88) | 0.062 |
| Inferior loss (%) | 16.99 (9.94) | 14.39 (11.06) | 0.181 |
| BMI | SBP | DBP | MAP | HR | CHOL | HDL-C | LDL-C | TG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| − | 0.310 | 0.201 | 0.138 | 0.179 | 0.116 | 0.155 | −0.120 | 0.268 | −0.108 | |
| Staining | Fluorescein | −0.010 | −0.075 | −0.050 | −0.078 | 0.025 | −0.151 | −0.164 | −0.150 | 0.083 |
| Lissamine | 0.219 | 0.046 | −0.176 | −0.103 | 0.341 | 0.011 | −10.49 | 0.041 | 0.110 | |
| NIBUT | First | 0.050 | 0.115 | 0.048 | 0.080 | 0.322 | −00.41 | −0.114 | 0.048 | −0.069 |
| Average | 0.033 | 0.131 | 0.034 | 0.080 | 0.348 | −00.86 | −0.191 | 0.001 | −0.035 | |
| Hyperemia | Bulbar Temporal | −0.129 | 0.103 | −0.032 | 0.036 | −0.191 | −0.097 | −0.063 | −0.107 | 0.121 |
| Bulbar Nasal | −0.049 | 0.114 | −0.102 | −0.010 | −0.048 | −0.153 | −0.037 | −0.096 | 0.016 | |
| Limbal Temporal | −0.115 | 0.169 | 0.024 | 0.119 | −0.307 | 0.012 | −0.094 | −0.001 | 0.181 | |
| Limbal Nasal | 0.003 | 0.245 | 0.037 | 0.144 | −0.126 | 0.124 | 0.062 | 0.137 | 0.089 | |
| MG Dropout | Upper | 0.112 | 0.310 | 0.150 | 0.237 | 0.049 | −0.041 | −0.051 | 0.003 | −0.026 |
| Lower | 0.204 | 0.213 | −0.001 | 0.076 | −0.123 | 0.280 | −0.031 | 0.325 | 0.083 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karimzad, S.; Bilkhu, P.S.; Wolffsohn, J.S.; Bellary, S.; Shokr, H.; Singhal, R.; Gherghel, D. Impact of Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss on Anterior Eye Health in Patients with Obesity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122462
Karimzad S, Bilkhu PS, Wolffsohn JS, Bellary S, Shokr H, Singhal R, Gherghel D. Impact of Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss on Anterior Eye Health in Patients with Obesity. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122462
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarimzad, Said, Paramdeep S. Bilkhu, James S. Wolffsohn, Srikanth Bellary, Hala Shokr, Rishi Singhal, and Doina Gherghel. 2022. "Impact of Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss on Anterior Eye Health in Patients with Obesity" Nutrients 14, no. 12: 2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122462
APA StyleKarimzad, S., Bilkhu, P. S., Wolffsohn, J. S., Bellary, S., Shokr, H., Singhal, R., & Gherghel, D. (2022). Impact of Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss on Anterior Eye Health in Patients with Obesity. Nutrients, 14(12), 2462. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122462








