Nobiletin Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Placental Damage via Modulating P53 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals and Treatment
2.3. Reverse Transcription (RT)-and Real-Time Quantitative (q) PCR
2.4. Hypoxia-Related Biomarkers
2.5. Hematoxylin-Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.6. TUNEL Staining
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Cells, Lentiviral Transfection, and Treatment with NOB
2.9. CCK-8 Assay
2.10. Cell Morphology
2.11. Cell Cycle Distribution
2.12. WesTM Automatic Western Blot Quantitative Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
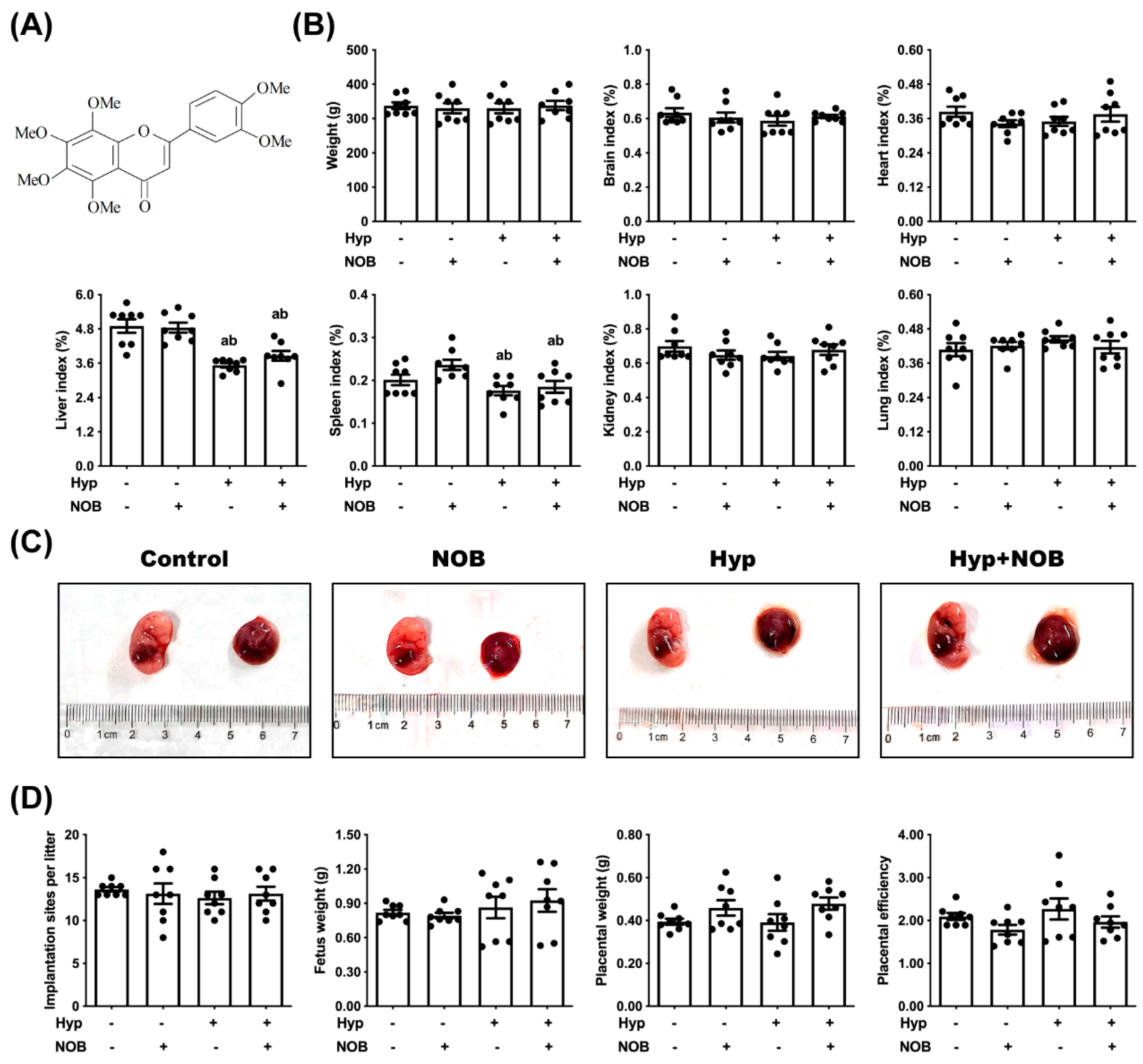
3.1. NOB Inhibited Placental Damage in RUPP Rats
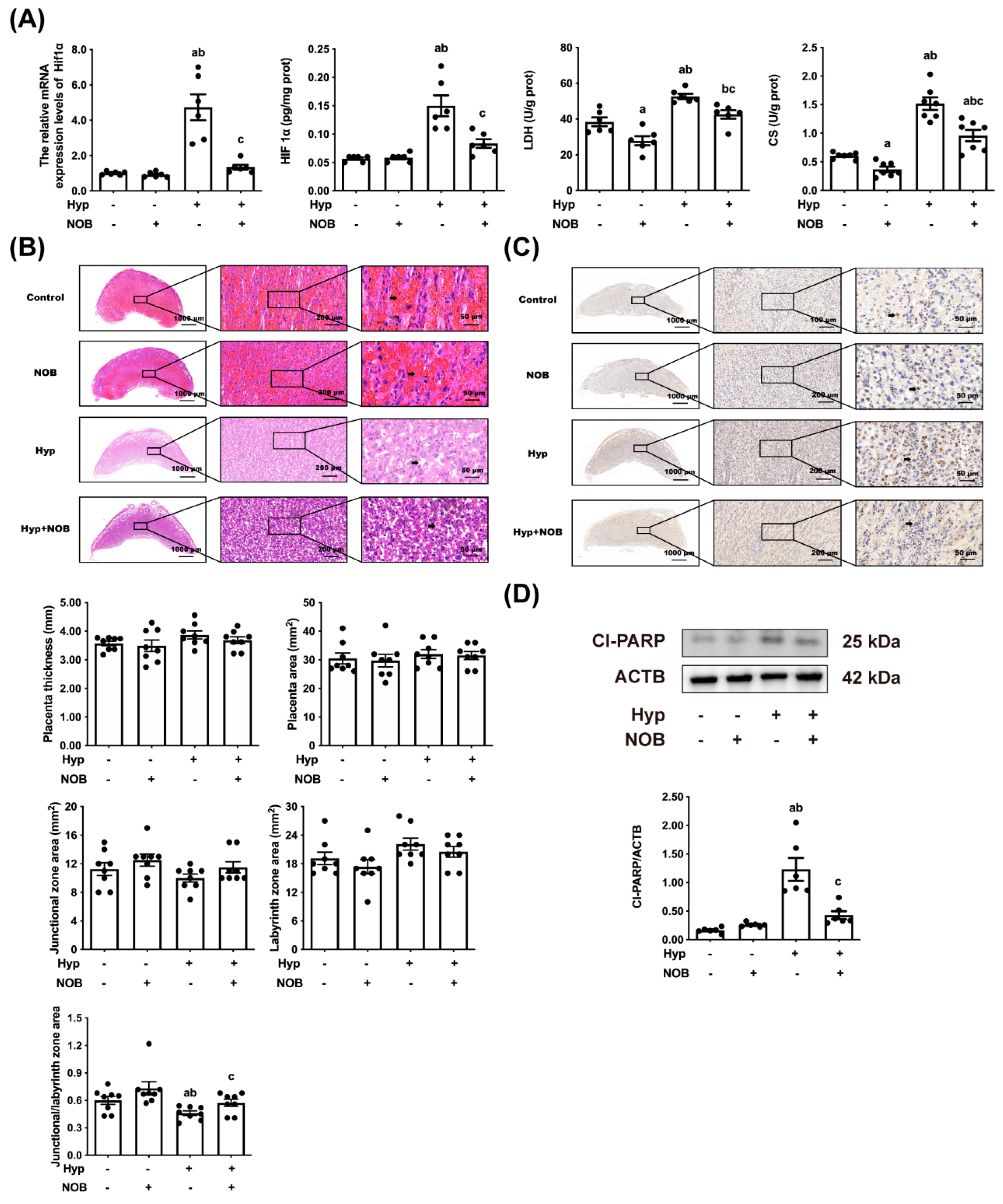
3.1.1. NOB Alleviated Placental Hypoxia in RUPP Rats
3.1.2. NOB Alleviated Placental Pathological Injury in RUPP Rats
3.1.3. NOB Alleviated Placental Apoptosis in RUPP Rats
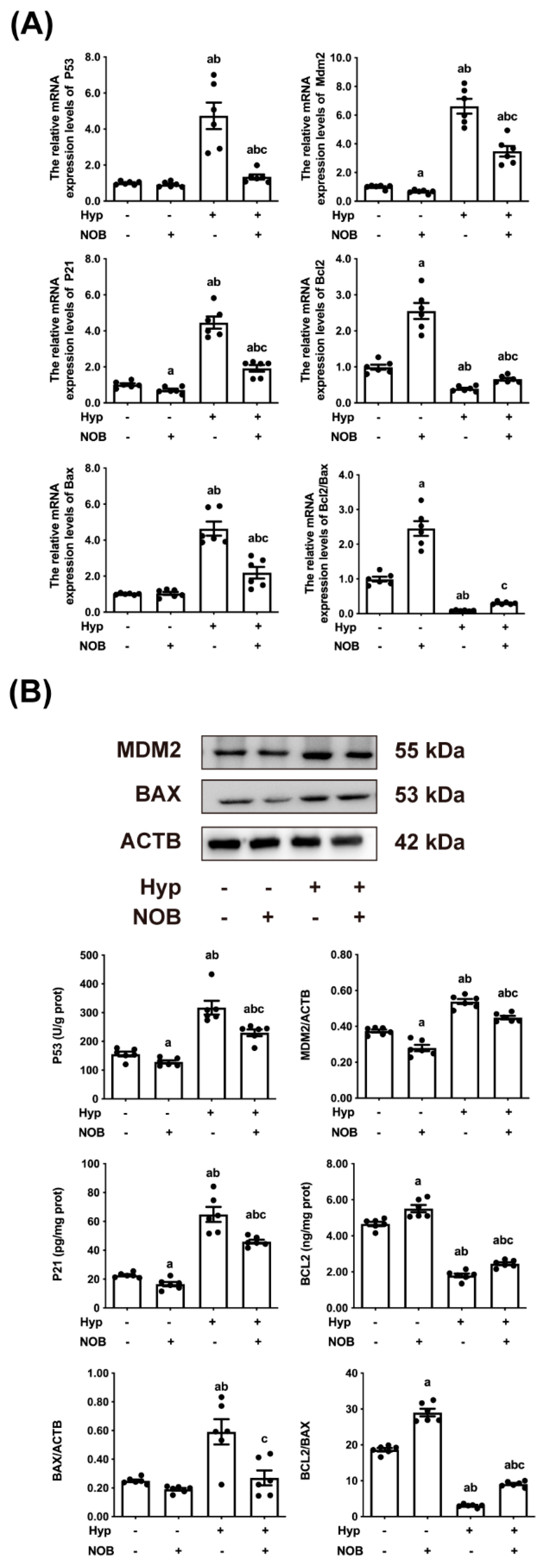
3.1.4. NOB Inhibited the Activation of Placental P53 in RUPP Rats
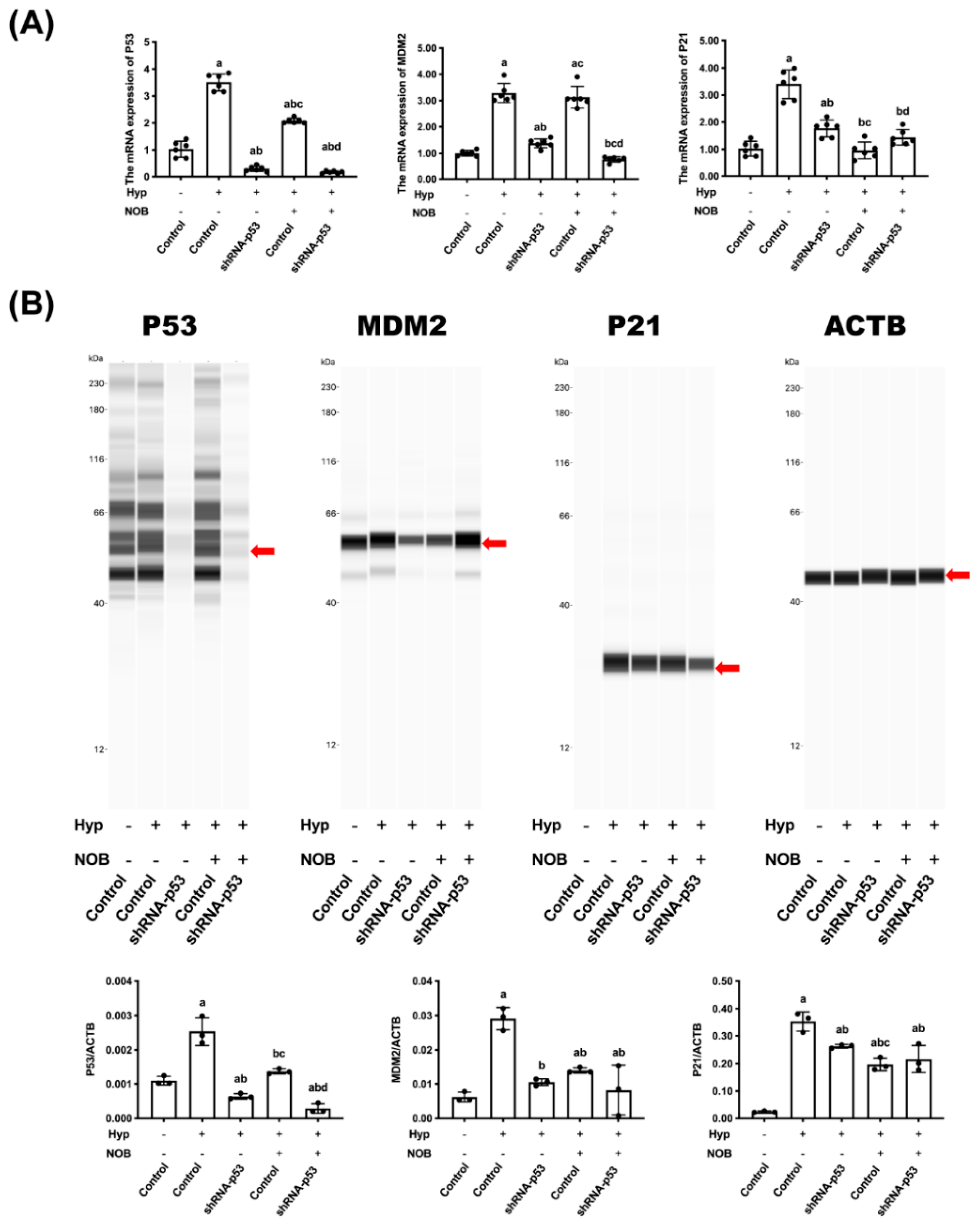
3.2. The Anti-Apoptotic Effect of NOB Partly Depended on the Inhibition of P53
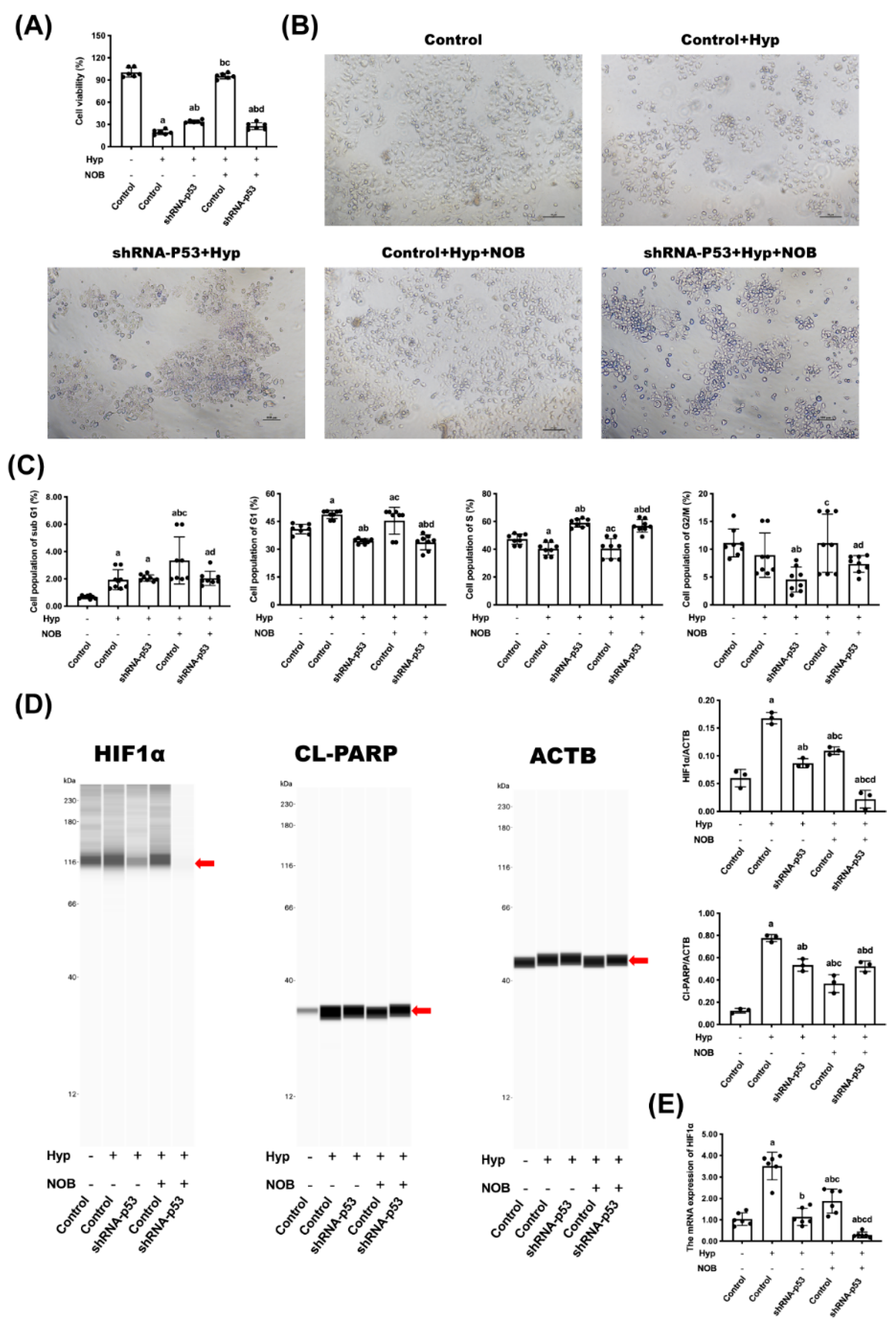
3.2.1. Effects of NOB on Cell Proliferation of BeWo Cell Line with p53 Knockdown
3.2.2. Effects of NOB on Cell Apoptosis of BeWo Cell Line with p53 Knockdown
3.2.3. Effects of NOB on P53 Signaling Pathway of BeWo Cell Line with p53 Knockdown
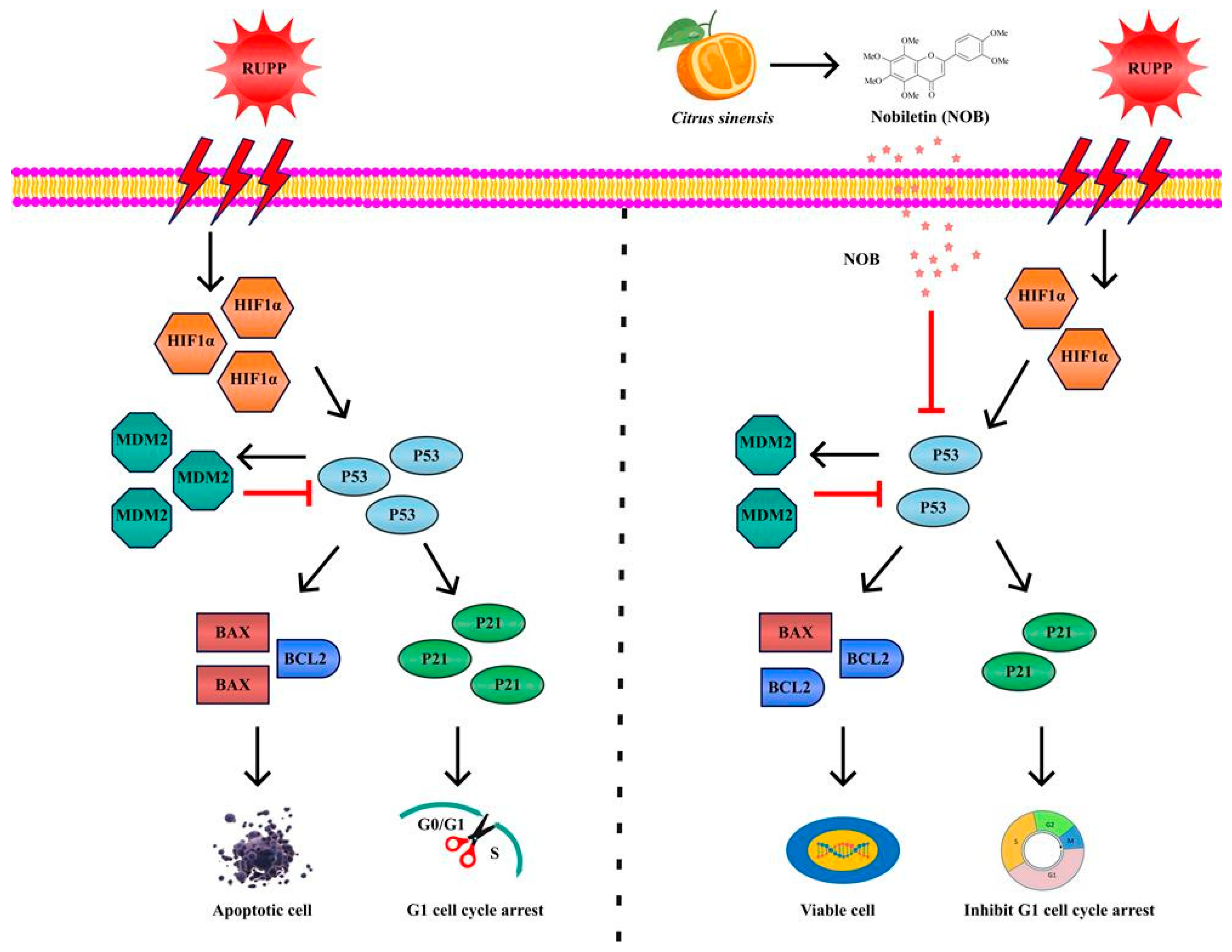
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NOB | Nobiletin |
| SD | Sprague–Dawley |
| RUPP | Reduce uterine perfusion pressure |
| HIF1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| CS | Citrate synthase |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline |
| ACTB | β-Actin |
| cl-PARP | cleaved-PARP |
| GD | Days of pregnancy |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
References
- Colson, A.; Sonveaux, P.; Debieve, F.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N. Adaptations of the human placenta to hypoxia: Opportunities for interventions in fetal growth restriction. Hum. Reprod. Update 2021, 27, 531–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassen, S.; Jansson, T. Complex, coordinated and highly regulated changes in placental signaling and nutrient transport capacity in IUGR. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridder, A.; Giorgione, V.; Khalil, A.; Thilaganathan, B. Preeclampsia: The Relationship between Uterine Artery Blood Flow and Trophoblast Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aplin, J.D.; Myers, J.E.; Timms, K.; Westwood, M. Tracking placental development in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, D.J.; Powell, T.L.; Barrett, E.S.; Hardy, D.B. Developmental origins of metabolic diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 739–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekimoto, A.; Tanaka, K.; Hashizume, Y.; Sato, E.; Sato, H.; Ikeda, T.; Takahashi, N. Tadalafil alleviates preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction in RUPP model of preeclampsia in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 521, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ives, C.W.; Sinkey, R.; Rajapreyar, I.; Tita, A.T.N.; Oparil, S. Preeclampsia-Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentations: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajas, Y.N.; Canon-Beltran, K.; Ladron de Guevara, M.; Millan de la Blanca, M.G.; Ramos-Ibeas, P.; Gutierrez-Adan, A.; Rizos, D.; Gonzalez, E.M. Antioxidant Nobiletin Enhances Oocyte Maturation and Subsequent Embryo Development and Quality. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Mao, L.; Guo, Y.; Hao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Liao, W.; Yuan, M. Nobiletin Triggers Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Pyroptosis through Regulating Autophagy in Ovarian Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngo, C.; Salomon, C.; Quak, S.; Lai, A.; Willcox, J.C.; Lappas, M. Nobiletin exerts anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects in an in vitro human model and in vivo murine model of gestational diabetes. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Lv, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Guan, W.; Liu, J.; et al. Nobiletin Protects against Acute Liver Injury via Targeting c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK)-Induced Apoptosis of Hepatocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7112–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, F.; Yu, L.; Li, Z. Nobiletin alleviates cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury via MAPK signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 5967–5977. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yin, T.; Shi, M.; Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Wang, K.; Cheang, I.; Li, Y.; Shang, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Nobiletin Attenuates Pathological Cardiac Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction via Activating PPARgamma and PGC1alpha. PPAR Res. 2021, 2021, 9947656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knofler, M.; Haider, S.; Saleh, L.; Pollheimer, J.; Gamage, T.; James, J. Human placenta and trophoblast development: Key molecular mechanisms and model systems. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3479–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Shan, Y.; Yu, H. The Effects of 5,6,7,8,3′,4′-Hexamethoxyflavone on Apoptosis of Cultured Human Choriocarcinoma Trophoblast Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Liang, Z.; Ding, S.; Yu, H.; Shan, Y. Nobiletin, a hexamethoxyflavonoid from citrus pomace, attenuates G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hypoxia-induced human trophoblast cells of JEG-3 and BeWo via regulating the p53 signaling pathway. Food Nutr. Res. 2021, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, R.D.; McCarthy, F.P.; Manna, S.; Groarke, E.; Kell, D.B.; Kenny, L.C.; McCarthy, C.M. L-(+)-Ergothioneine Significantly Improves the Clinical Characteristics of Preeclampsia in the Reduced Uterine Perfusion Pressure Rat Model. Hypertension 2020, 75, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, M.W., Jr.; Castillo, J.; Ibrahim, T.; Cornelius, D.C.; Campbell, N.; Amaral, L.; Vaka, V.R.; Usry, N.; Williams, J.M.; LaMarca, B. AT1-AA (Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Agonistic Autoantibody) Blockade Prevents Preeclamptic Symptoms in Placental Ischemic Rats. Hypertension 2018, 71, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Blayney, A.; Liu, X.; Gandy, L.; Jin, W.; Yan, L.; Ha, J.H.; Canning, A.J.; Connelly, M.; Yang, C.; et al. EGCG binds intrinsically disordered N-terminal domain of p53 and disrupts p53-MDM2 interaction. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Borrero, L.J.; El-Deiry, W.S. Tumor suppressor p53: Biology, signaling pathways, and therapeutic targeting. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, C.F.A.; Wong-Brown, M.W.; Bowden, N.A. BCL-2 family isoforms in apoptosis and cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; LaMarca, B.; Reckelhoff, J.F. A model of preeclampsia in rats: The reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) model. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 303, H1–H8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natale, B.V.; Mehta, P.; Vu, P.; Schweitzer, C.; Gustin, K.; Kotadia, R.; Natale, D.R.C. Reduced Uteroplacental Perfusion Pressure (RUPP) causes altered trophoblast differentiation and pericyte reduction in the mouse placenta labyrinth. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, L.; Richards, C.; Patel, N.; Chen, H.; Sesperez, K.; Bubb, K.J.; Karlstaedt, A.; Aksentijevic, D. Impact of reduced uterine perfusion pressure model of preeclampsia on metabolism of placenta, maternal and fetal hearts. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, J.; Ahmad, S.; Rezai, H.; Litvinova, K.; Sparatore, A.; Alzahrani, F.A.; Wang, K.; Ahmed, A. Hydrogen sulfide releasing molecule MZe786 inhibits soluble Flt-1 and prevents preeclampsia in a refined RUPP mouse model. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Martinez-Portilla, R.J.; Rolnik, D.L.; Poon, L.C. ASPRE trial: Risk factors for development of preterm pre-eclampsia despite aspirin prophylaxis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 58, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluver, C.A.; Hiscock, R.; Decloedt, E.H.; Hall, D.R.; Schell, S.; Mol, B.W.; Brownfoot, F.; Kaitu’u-Lino, T.J.; Walker, S.P.; Tong, S. Use of metformin to prolong gestation in preterm pre-eclampsia: Randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial. BMJ 2021, 374, n2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, S.; Calcaterra, V.; Pelizzo, G.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Prenatal Hypoxia and Placental Oxidative Stress: Insights from Animal Models to Clinical Evidences. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasture, V.; Kale, A.; Randhir, K.; Sundrani, D.; Joshi, S. Effect of maternal omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E supplementation on placental apoptotic markers in rat model of early and late onset preeclampsia. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuffa, L.G.A.; Lupi, L.A.; Cucielo, M.S.; Silveira, H.S.; Reiter, R.J.; Seiva, F.R.F. Melatonin Promotes Uterine and Placental Health: Potential Molecular Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazarico, E.; Molinet-Coll, C.; Martinez-Portilla, R.J.; Figueras, F. Heparin therapy in placental insufficiency: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.H.; Kwan, S.T.C.; Yan, J.; Jiang, X.; Fomin, V.G.; Levine, S.P.; Wei, E.; Roberson, M.S.; Caudill, M.A. Maternal Choline Supplementation Modulates Placental Markers of Inflammation, Angiogenesis, and Apoptosis in a Mouse Model of Placental Insufficiency. Nutrients 2019, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boutelle, A.M.; Attardi, L.D. p53 and Tumor Suppression: It Takes a Network. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Yang, F.; Shao, C.; Wei, K.; Xie, M.; Shen, H.; Shu, Y. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Gene | Species | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hif1α | Rat | CGGCGAGAACGAGAAGAAAAATAGG | GACTCTTTGCTTCGCCGAGA |
| P53 | Rat | CCCCTGAAGACTGGATAACTGT | TTAGGTGACCCTGTCGCTGT |
| Mdm2 | Rat | CGAGCGAAATGGTCTCTCAAG | TGCAGACCGCTGCTACT |
| P21 | Rat | AACAGGCTCAGGAGTTAGCA | CATCGTCAACACCCTGTCTT |
| Bcl2 | Rat | AGTACCTGAACCGGCATCTG | TATAGTTCCACAAAGGCATCCCAG |
| Bax | Rat | ACCAAGAAGCTGAGCGAGTG | TCCACATCAGCAATCATCCTCT |
| Actb | Rat | ACCCGCGAGTACAACCTTCTT | TATCGTCATCCATGGCGAACTGG |
| HIF1α | Human | GGCGCGAACGACAAGAAAAAG | CCTTATCAAGATGCGAACTCACA |
| P53 | Human | AAAAGTCTAGAGCCACCGTCC | AGTCTGGCCAATCCAGGGAAG |
| MDM2 | Human | TCTCCTGCCTCAGCCTTCCAAG | GCCAGGTGCCTCACATCTGTAATC |
| P21 | Human | CCTGTCACTGTCTTGTACCCT | GCGTTTGGAGTGGTAGAAATCT |
| ACTB | Human | TCCTTCCGCAGCTATTTATGAT | CACAGTATAGGATGGTCTGGAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.-L.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Y.-D.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Dang, Q.-Y.; Huang, D.-X.; Zhang, M.-Y.; et al. Nobiletin Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Placental Damage via Modulating P53 Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112332
Zhang M-L, Yang Q, Zhu Y-D, Zhang Y-D, Zhang R, Liu J, Zhao X-Y, Dang Q-Y, Huang D-X, Zhang M-Y, et al. Nobiletin Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Placental Damage via Modulating P53 Signaling Pathway. Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112332
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Meng-Ling, Qian Yang, Yan-Di Zhu, Ya-Di Zhang, Rui Zhang, Jian Liu, Xiao-Yan Zhao, Qin-Yu Dang, Dong-Xu Huang, Ming-Yuan Zhang, and et al. 2022. "Nobiletin Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Placental Damage via Modulating P53 Signaling Pathway" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112332
APA StyleZhang, M.-L., Yang, Q., Zhu, Y.-D., Zhang, Y.-D., Zhang, R., Liu, J., Zhao, X.-Y., Dang, Q.-Y., Huang, D.-X., Zhang, M.-Y., Wei, Y.-C., Hu, Z., Cai, X.-X., Gao, L.-F., Shan, Y., & Yu, H.-L. (2022). Nobiletin Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Placental Damage via Modulating P53 Signaling Pathway. Nutrients, 14(11), 2332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112332







