Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Chinese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in Shanghai, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Physical Examination and Biochemical Assays
2.3. Diagnostic Criteria
2.4. Assessment of Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
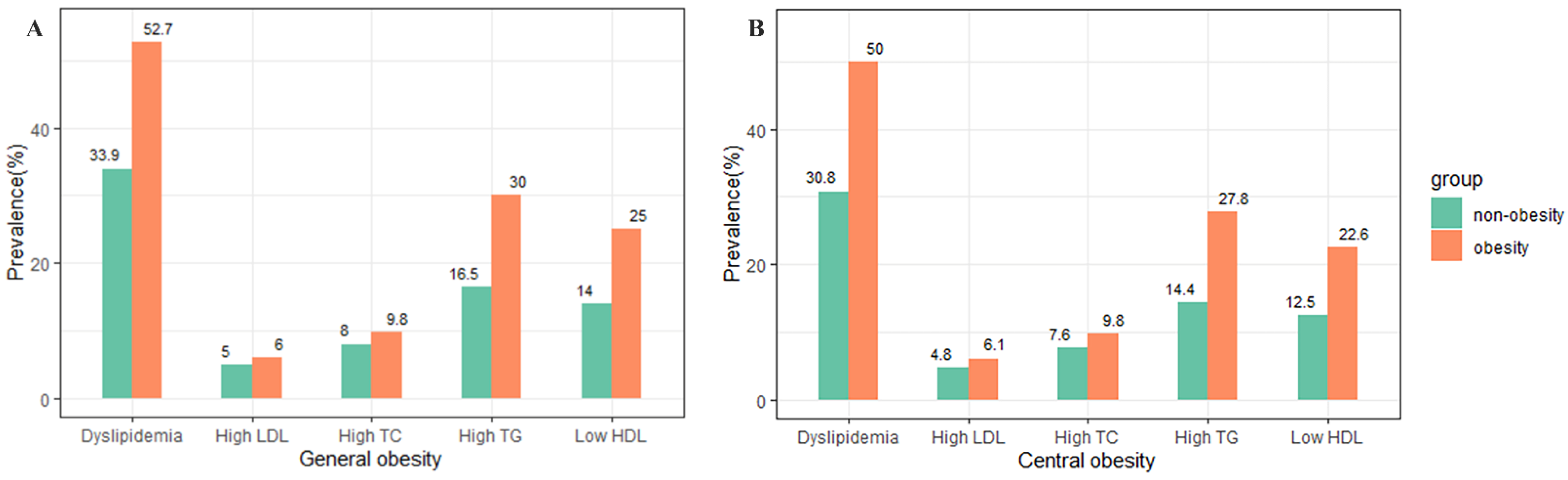
3.2. Prevalence of Different Forms of Dyslipidemia
3.3. Association of Obesity with Different Forms of Dyslipidemia
3.4. Stratified Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSACB | The Shanghai Suburban Adult Cohort and Biobank study |
| OR | Odds ratios |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| WC | Waist circumference |
| FPG | Fasting plasma glucose |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| CHDI | China Healthy Diet Index |
| MET | Metabolic equivalent of task |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| DALYs | Disability-adjusted life years |
References
- Nagasawa, S.Y.; Okamura, T.; Iso, H.; Tamakoshi, A.; Yamada, M.; Watanabe, M.; Murakami, Y.; Miura, K.; Ueshima, H.; Evidence for Cardiovascular Prevention from Observational Cohorts in Japan Research Group. Relation between serum total cholesterol level and cardiovascular disease stratified by sex and age group: A pooled analysis of 65 594 individuals from 10 cohort studies in Japan. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2012, 1, e001974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Angelantonio, E.; Gao, P.; Pennells, L.; Kaptoge, S.; Caslake, M.; Thompson, A.; Butterworth, A.S.; Sarwar, N.; Wormser, D.; Saleheen, D.; et al. Lipid-Related Markers and Cardiovascular Disease Prediction. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 307, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, R.D.; Anderson, T.J.; Gregoire, J.; Pearson, G.J. 2016 Guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia and the prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults by pharmacists. Can. Pharm. J. 2017, 150, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katulanda, P.; Dissanayake, H.A.; De Silva, S.D.N.; Katulanda, G.W.; Liyanage, I.K.; Constantine, G.R.; Sheriff, R.; Matthews, D.R. Prevalence, patterns, and associations of dyslipidemia among Sri Lankan adults-Sri Lanka Diabetes and Cardiovascular Study in 2005–2006. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Chang, P.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kizer, J.R.; Best, L.G.; Howard, B.V. Triglyceride and HDL-C Dyslipidemia and Risks of Coronary Heart Disease and Ischemic Stroke by Glycemic Dysregulation Status: The Strong Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, F.; Kocer, D.; Gundogan, K.; Kaya, A.; Demir, O.; Coskun, R.; Sabuncu, T.; Karaman, A.; Cesur, M.; Rizzo, M.; et al. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors in Turkish adults. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 8, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latifi, S.M.; Moradi, L.; Shahbazian, H.; Aleali, A.M. A study of the prevalence of dyslipidemia among the adult population of Ahvaz, Iran. Diabetes Metab. Synd. 2016, 10, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, J.; Ding, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Tan, L.; Mu, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Availability of Lipid-Lowering Medications Among Primary Health Care Settings in China. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2127573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS) [DB/OL]. Available online: http://www.cpc.unc.edu/projects/china/data/datasets (accessed on 26 May 2022).
- Opoku, S.; Gan, Y.; Fu, W.; Chen, D.; Addo-Yobo, E.; Trofimovitch, D.; Yue, W.; Yan, F.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z. Prevalence and risk factors for dyslipidemia among adults in rural and urban China: Findings from the China National Stroke Screening and prevention project (CNSSPP). BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, W.Q.; Tang, W.W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.X.; Xu, R.H.; Zhao, S.P.; Wang, T.D.; Huang, X.B. Prevalence and related factors of dyslipidemia among urban adults aged 35 to 79 years in Southwestern China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Niu, L.; Cao, N.; Bao, H.; Xu, X.; Zhu, H.; Yan, T.; Zhang, N.; Qiao, L.; Han, K.; et al. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors among adults aged ≥35 years in northern China: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekic, J.; Zeljkovic, A.; Stefanovic, A.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V. Obesity and dyslipidemia. Metabolism 2019, 92, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonestedt, E.; Hellstrand, S.; Drake, I.; Schulz, C.A.; Ericson, U.; Hlebowicz, J.; Persson, M.M.; Gullberg, B.; Hedblad, B.; Engstrom, G.; et al. Diet Quality and Change in Blood Lipids during 16 Years of Follow-up and Their Interaction with Genetic Risk for Dyslipidemia. Nutrients 2016, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Duan, X.Y.; Li, L.; Dai, F.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, X.J.; Fan, J.G. Dyslipidemia in Shanghai, China. Prev. Med. 2010, 51, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, A.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Mu, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Associations of sedentary behavior and physical activity with physical measurements and dyslipidemia in school-age children: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, B.; Wang, R.; Zhu, M.; Shao, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, F.; Wang, W.; et al. Cohort profile: Protocol and baseline survey for the Shanghai Suburban Adult Cohort and Biobank (SSACB) study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lu, F.C. The guidelines for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.C.; Lyu, J.; Gao, M.; Yu, C.Q.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Z.; Pei, P.; Du, H.D.; Chen, J.S.; Chen, Z.M.; et al. Association of body mass index and waist circumference with major chronic diseases in Chinese adults. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2019, 40, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Committee for Developing Chinese guidelines on Prevention and Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Adults. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in Chinese adults (2016 revision). Chin. Circ. J. 2016, 31, 937–953. [Google Scholar]
- Chobanian, A.V.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Cushman, W.C.; Green, L.A.; Izzo, J.L., Jr.; Jones, D.W.; Materson, B.J.; Oparil, S.; Wright, J.T., Jr.; et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: The JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003, 289, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S13–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu-na, H.; Yue-hui, F.; Xiao-guang, Y.; Gang-qiang, D. Establishment and application of china healthy diet index. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2017, 39, 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaacks, L.M.; Vandevijvere, S.; Pan, A.; McGowan, C.J.; Wallace, C.; Imamura, F.; Mozaffarian, D.; Swinburn, B.; Ezzati, M. The obesity transition: Stages of the global epidemic. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Deng, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol targets in Chinese adults: A nationally representative survey of 163,641 adults. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 260, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, M.; Kuwabara, R.; Niwa, K.; Hisatome, I.; Smits, G.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; MacLean, P.S.; Yracheta, J.M.; Ohno, M.; Lanaspa, M.A.; et al. Different Risk for Hypertension, Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, and Hyperuricemia According to Level of Body Mass Index in Japanese and American Subjects. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yin, R.X.; Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, B.; Zhang, L. The prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of dyslipidemia among adults in China. Atherosclerosis 2016, 248, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, P.A.; Otero, J.; Pérez, M.; Arcos, E.; García, H.; Narvaez, C.; Molina, D.I.; Sanchez, G.; Duran, M.; Cure, C.; et al. The spectrum of the dyslipidemia in Colombia: The PURE study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 284, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, R.; Elorriaga, N.; Gutierrez, L.; Irazola, V.; Rubinstein, A.; Danaei, G. Associations between dietary patterns and serum lipids, apo and C-reactive protein in an adult population: Evidence from a multi-city cohort in South America. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Alsalhe, T.A.; Chalghaf, N.; Riccò, M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Wu, J. The global burden of disease attributable to high body mass index in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliaki, C.; Liatis, S.; Kokkinos, A. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Revisiting an old relationship. Metabolism 2019, 92, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagidipati, N.J.; Zheng, Y.; Green, J.B.; McGuire, D.K.; Mentz, R.J.; Shah, S.; Aschner, P.; Delibasi, T.; Rodbard, H.W.; Westerhout, C.M.; et al. Association of obesity with cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Insights from TECOS. Am. Heart J. 2020, 219, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, F.D.C.; Pereira, F.E.F.; Pereira, A.F.; Ribeiro, B.G. Overweight or obesity and abdominal obesity and their association with cardiometabolic risk factors in Brazilian schoolchildren: A cross-sectional study. Nutrition 2020, 78, 110780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors for Chronic Diseases Collaboration (BMI Mediated Effects); Lu, Y.; Hajifathalian, K.; Ezzati, M.; Woodward, M.; Rimm, E.B.; Danaei, G. Metabolic Mediators of the Effects of Body-Mass Index, Overweight, and Obesity on Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke: A Pooled Analysis of 97 Prospective Cohorts with 1.8 Million Participants. Lancet 2014, 383, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Luo, Q.; Xu, D.; Yu, B. Interaction between adipocytes and high-density lipoprotein:new insights into the mechanism of obesity-induced dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangrós, F.J.; Torrecilla, J.; Giráldez-García, C.; Carrillo, L.; Mancera, J.; Mur, T.; Franch, J.; Díez, J.; Goday, A.; Serrano, R.; et al. Association of General and Abdominal Obesity With Hypertension, Dyslipidemia and Prediabetes in the PREDAPS Study. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 71, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Munker, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Xu, L.; Ye, H.; Chen, H.T.; Xu, G.Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.H.; Yu, C.H.; et al. Association between alcohol intake, overweight, and serum lipid Levels and the risk analysis associated with the development of dyslipidemia. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 8, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirrakhimov, E.M.; Kerimkulova, A.S.; Lunegova, O.S.; Mirrakhimov, A.E.; Nabiev, M.P.; Neronova, K.V.; Bayramukova, A.A.; Alibaeva, N.T.; Satarov, N. The association of leptin with dyslipidemia, arterial hypertension and obesity in Kyrgyz (Central Asian nation) population. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Z.Y.; Zhao, L.H.; Yang, X.; Xu, F.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, L.H.; et al. Sedentary lifestyle and body composition in type 2 diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz Contreras, A.M.; Bedoya Berrío, G.; Velásquez, R.C. An approach to the etiology of metabolic syndrome. Colomb. Med. 2013, 44, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lee, H.A.; Tinkov, A.A.; Skalny, A.V.; Wang, W.H.; Chao, J.C. Gender difference in the association of dietary patterns and metabolic parameters with obesity in young and middle-aged adults with dyslipidemia and abnormal fasting plasma glucose in Taiwan. Nutr. J. 2019, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, W.; Sa, R.; Liu, F. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Hypertension, Diabetes, and Dyslipidemia among Adults in Northwest China. Int. J. Hypertens. 2021, 2021, 5528007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, P.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Xiao, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, S. Dynamic development of metabolic syndrome and its risk prediction in Chinese population: A longitudinal study using Markov model. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erem, C.; Hacihasanoglu, A.; Deger, O.; Kocak, M.; Topbas, M. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors among Turkish adults: Trabzon lipid study. Endocrine 2008, 34, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Jonas, J.B.; You, Q.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Yang, H. Prevalence and associated factors of dyslipidemia in the adult Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | BMI | p | WC | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Subjects (n = 40,406) | Non-General Obesity (n = 35,207) | General Obesity a (n = 5199) | Non-Central Obesity (n = 28,761) | Central Obesity b (n = 11,645) | |||
| Age (years) | 56 ± 11 | 56 ± 11 | 57 ± 10 | <0.001 | 55 ± 11 | 59 ± 10 | <0.001 |
| Gender | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| Male | 16,793 (41.6) | 14,471 (41.1) | 2322 (44.7) | 11,789 (41.0) | 5004 (43.0) | ||
| Female | 23,613 (58.4) | 20,736 (58.9) | 2877 (55.3) | 16,972 (59.0) | 6641 (57.0) | ||
| Education level | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| 0–6 years | 16,557 (41.0) | 14,072 (40.0) | 2485 (47.8) | 10,823 (37.6) | 5734 (49.2) | ||
| 7–12 years | 21,017 (52.0) | 18,561 (52.7) | 2456 (47.2) | 15,561 (54.1) | 5456 (46.9) | ||
| >12 years | 2832 (7.0) | 2574 (7.3) | 258 (5.0) | 2377 (8.3) | 455 (3.9) | ||
| Marriage | 0.73 | 0.61 | |||||
| Married | 37,584 (93.0) | 32,754 (93.0) | 4830 (92.9) | 26,764 (93.1) | 10,820 (92.9) | ||
| Other | 2822 (7.0) | 2453 (7.0) | 369 (7.1) | 1997 (6.9) | 825 (7.1) | ||
| Physical activity | 0.38 | <0.001 | |||||
| Low | 13,237 (32.8) | 11,574 (32.9) | 1663 (32.0) | 9587 (33.3) | 3650 (31.3) | ||
| Moderate | 13,771 (34.1) | 11,994 (34.1) | 1777 (34.2) | 9840 (34.2) | 3931 (33.8) | ||
| High | 13,398 (33.2) | 11,639 (33.1) | 1759 (33.8) | 9334 (32.5) | 4064 (34.9) | ||
| Smoking | 0.14 | 0.003 | |||||
| Ever | 10,082 (25.0) | 8742 (24.8) | 1340 (25.8) | 7059 (24.5) | 3023 (26) | ||
| Never | 30,324 (75.1) | 26,465 (75.2) | 3859 (74.2) | 21,702 (75.5) | 8622 (74) | ||
| Alcohol drinking | 0.002 | <0.001 | |||||
| Ever | 5563 (13.8) | 4774 (13.6) | 789 (15.2) | 3758 (13.1) | 1805 (15.5) | ||
| Never | 34,843 (86.2) | 30,433 (86.4) | 4410 (84.8) | 25,003 (86.9) | 9840 (84.5) | ||
| Diabetes | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| Yes | 5738 (14.2) | 4420 (12.6) | 1318 (25.4) | 3154 (11.0) | 2584 (22.2) | ||
| No | 34,668 (85.8) | 30,787 (87.5) | 3881 (74.7) | 25,607 (89) | 9061 (77.8) | ||
| Hypertension | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| Yes | 19,696 (48.8) | 15,948 (45.3) | 3748 (72.1) | 11,227 (45.0) | 7102 (70.2) | ||
| No | 20,710 (51.3) | 19,259 (54.7) | 1451 (27.9) | 16,769 (58.3) | 3941 (33.8) | ||
| CHDI | 70.05 ± 9.29 | 70.2 ± 9.31 | 69.04 ± 9.13 | <0.001 | 70.51 ± 9.28 | 68.91 ± 9.22 | <0.001 |
| HBA1c (%) | 4.9 (4.4, 5.5) | 4.8 (4.4, 5.4) | 5.1 (4.5, 5.9) | <0.001 | 4.8 (4.4, 5.4) | 5.0 (4.4, 5.8) | <0.001 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 5.81 ± 0.85 | 5.77 ± 0.81 | 6.09 ± 1.00 | <0.001 | 5.72 ± 0.78 | 6.03 ± 0.97 | <0.001 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.91 ± 0.94 | 4.90 ± 0.93 | 4.99 ± 0.99 | <0.001 | 4.88 ± 0.92 | 4.99 ± 0.97 | <0.001 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.70 ± 1.26 | 1.64 ± 1.2 | 2.11 ± 1.55 | <0.001 | 1.56 ± 1.12 | 2.03 ± 1.49 | <0.001 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.4 ± 0.35 | 1.42 ± 0.35 | 1.26 ± 0.31 | <0.001 | 1.44 ± 0.35 | 1.29 ± 0.32 | <0.001 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.74 ± 0.83 | 2.74 ± 0.83 | 2.78 ± 0.88 | 0.004 | 2.73 ± 0.82 | 2.78 ± 0.87 | <0.001 |
| Variables | High TC | High LDL-C | Low HDL-C | High TG | Dyslipidemia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||||
| <60 | 1.26 (1.09, 1.45) | 1.28 (1.07, 1.52) | 1.87 (1.68, 2.07) | 1.81 (1.65, 1.99) | 1.88 (1.72, 2.05) |
| ≥60 | 0.97 (0.84, 1.13) | 0.89 (0.74, 1.07) | 1.66 (1.49, 1.84) | 1.65 (1.49, 1.82) | 1.60 (1.47, 1.75) |
| p for Interaction | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.14 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 1.53 (1.29, 1.81) | 1.41 (1.14, 1.74) | 1.94 (1.76, 2.14) | 2.05 (1.85, 2.26) | 2.24 (2.04, 2.46) |
| Female | 0.90 (0.79, 1.02) | 0.92 (0.78, 1.08) | 1.48 (1.31, 1.67) | 1.45 (1.31, 1.59) | 1.40 (1.29, 1.53) |
| p for Interaction | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.01 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | |||||
| Yes | 1.05 (0.94, 1.19) | 1.05 (0.90, 1.21) | 1.63 (1.49, 1.78) | 1.63 (1.50, 1.76) | 1.65 (1.53, 1.77) |
| No | 1.25 (1.02, 1.53) | 1.19 (0.93, 1.53) | 2.21 (1.93, 2.54) | 2.16 (1.90, 2.46) | 2.10 (1.88, 2.34) |
| p for Interaction | 0.15 | 0.40 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| Diabetes | |||||
| Yes | 1.03 (0.85, 1.26) | 1.07 (0.83, 1.37) | 1.50 (1.30, 1.74) | 1.62 (1.42, 1.85) | 1.63 (1.43, 1.86) |
| No | 1.13 (1.01, 1.28) | 1.10 (0.94, 1.27) | 1.89 (1.74, 2.06) | 1.83 (1.69, 1.98) | 1.83 (1.71, 1.96) |
| p for Interaction | 0.46 | 0.84 | 0.007 | 0.06 | 0.17 |
| Variables | High TC | High LDL-C | Low HDL-C | High TG | Dyslipidemia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||||
| <60 | 1.23 (1.10, 1.38) | 1.37 (1.19, 1.58) | 2.04 (1.87, 2.21) | 2.13 (1.98, 2.30) | 2.10 (1.96, 2.24) |
| ≥60 | 1.02 (0.91, 1.13) | 0.97 (0.85, 1.11) | 1.68 (1.55, 1.83) | 1.70 (1.57, 1.85) | 1.64 (1.53, 1.75) |
| p for Interaction | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 1.31 (1.14, 1.51) | 1.28 (1.08, 1.52) | 2.03 (1.88, 2.19) | 2.22 (2.05, 2.40) | 2.25 (2.10, 2.42) |
| Female | 0.99 (0.90, 1.09) | 1.04 (0.93, 1.17) | 1.60 (1.45, 1.76) | 1.64 (1.51, 1.76) | 1.52 (1.43, 1.62) |
| p for Interaction | 0.003 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.04 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | |||||
| Yes | 1.11 (1.01, 1.22) | 1.10 (0.98, 1.25) | 1.75 (1.63, 1.89) | 1.79 (1.67, 1.92) | 1.75 (1.65, 1.85) |
| No | 1.17 (1.02, 1.33) | 1.24(1.06, 1.46) | 2.20 (2.00, 2.42) | 2.41 (2.20, 2.63) | 2.18 (2.02, 2.35) |
| p for Interaction | 0.11 | 0.09 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | |||||
| Yes | 1.08 (0.91, 1.28) | 1.09 (0.88, 1.36) | 1.76 (1.54, 2.00) | 1.73 (1.54, 1.95) | 1.74 (1.56, 1.94) |
| No | 1.13 (1.04, 1.24) | 1.16 (1.04, 1.30) | 1.96 (1.83, 2.09) | 2.07 (1.94, 2.20) | 1.94 (1.85, 2.04) |
| p for Interaction | 0.34 | 0.47 | 0.12 | 0.001 | 0.048 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Tong, X.; Yu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Cui, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, N.; et al. Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Chinese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in Shanghai, China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112321
Zhu J, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Xiang Y, Tong X, Yu Y, Qiu Y, Cui S, Zhao Q, Wang N, et al. Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Chinese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in Shanghai, China. Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112321
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Junjie, Yue Zhang, Yiling Wu, Yu Xiang, Xin Tong, Yuting Yu, Yun Qiu, Shuheng Cui, Qi Zhao, Na Wang, and et al. 2022. "Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Chinese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in Shanghai, China" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112321
APA StyleZhu, J., Zhang, Y., Wu, Y., Xiang, Y., Tong, X., Yu, Y., Qiu, Y., Cui, S., Zhao, Q., Wang, N., Jiang, Y., & Zhao, G. (2022). Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Chinese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in Shanghai, China. Nutrients, 14(11), 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112321






