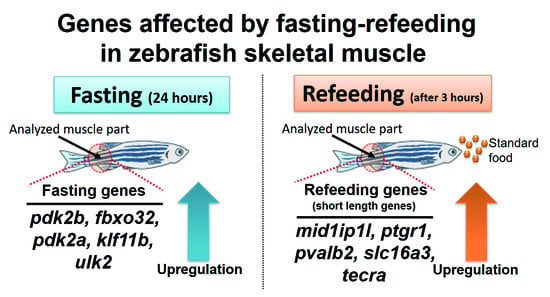
Gene Expression Profile Provides Novel Insights of Fasting-Refeeding Response in Zebrafish Skeletal Muscle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
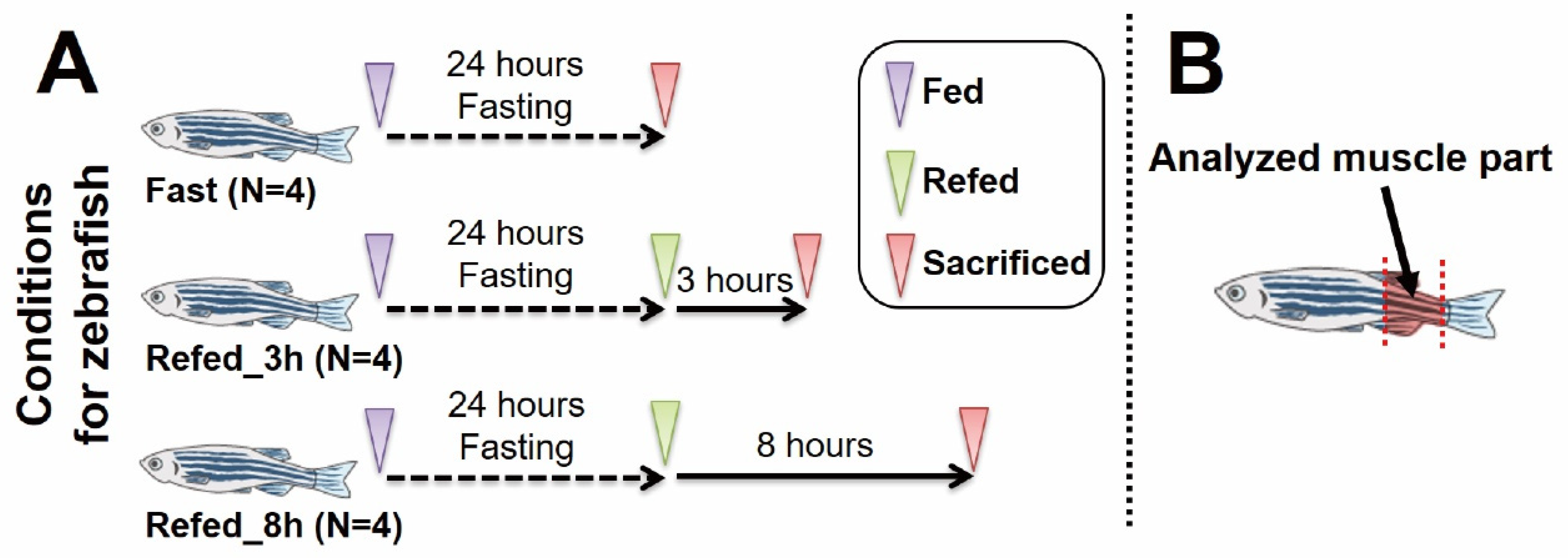
2.1. Zebrafish Experiments
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.3. mRNA-Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
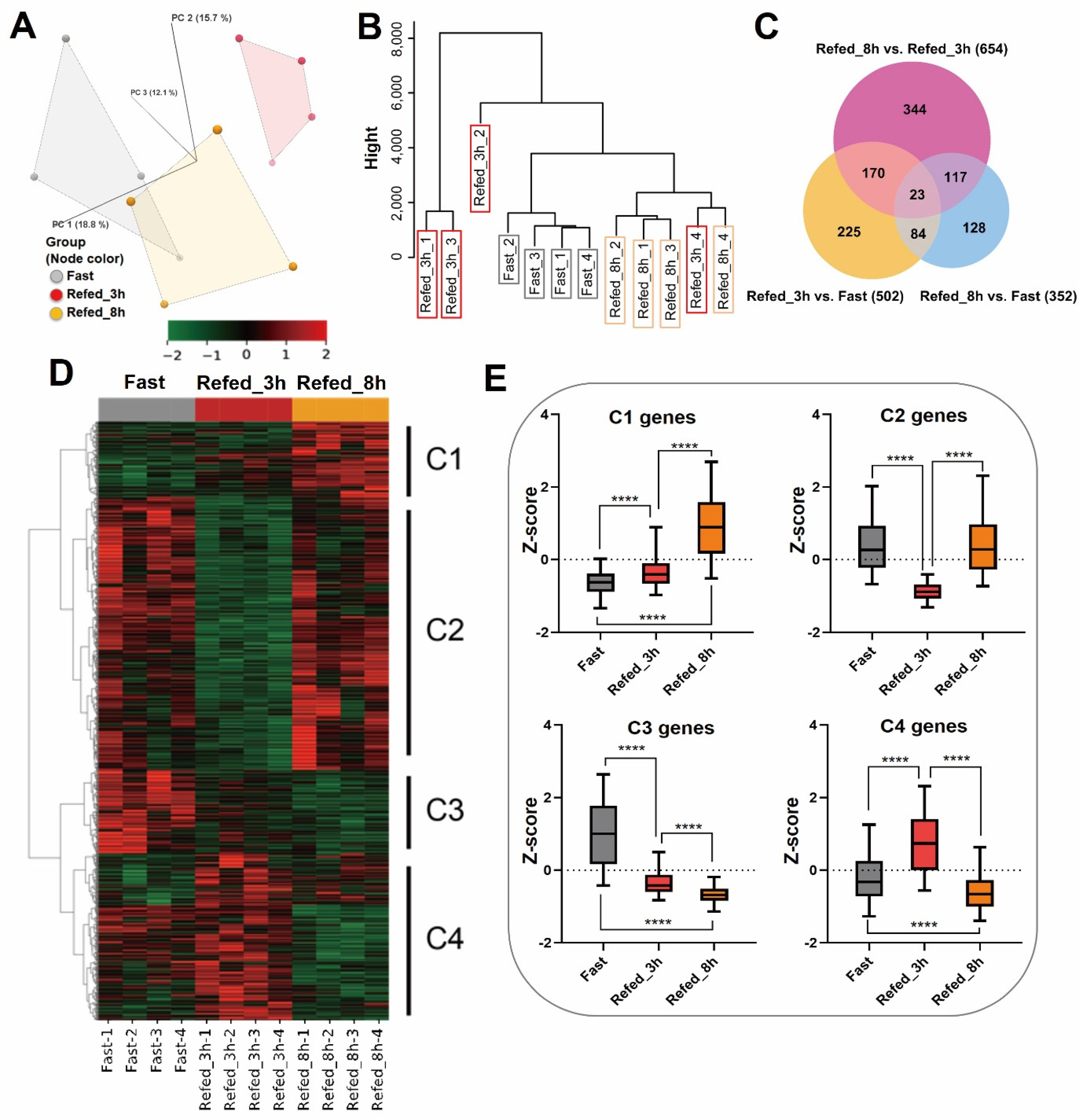
3.1. Overview of Gene Expression Profiling by Fasting-Refeeding
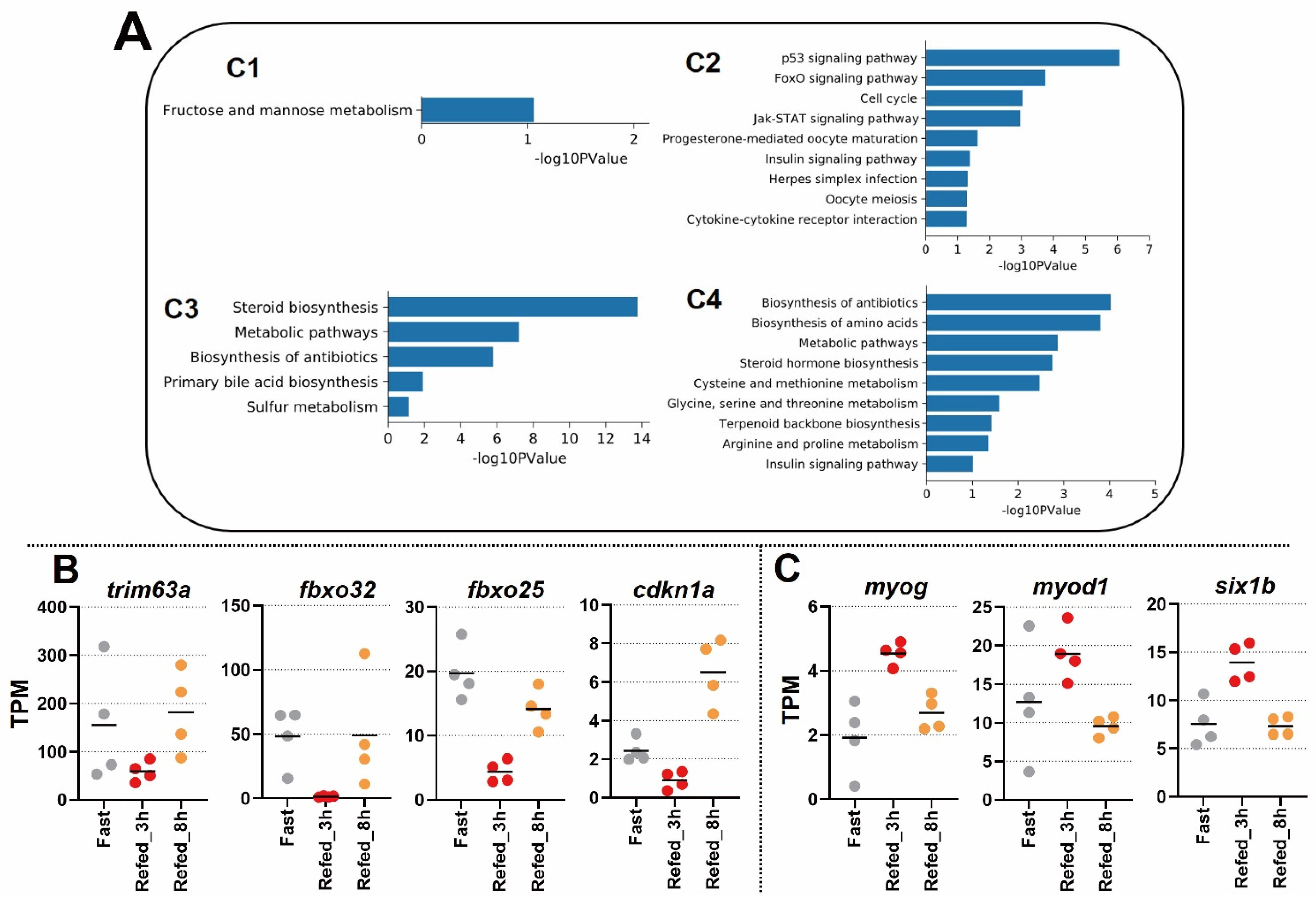
3.2. Enrichment Analysis of DEG Profiles Affected by the Fasting-Refeeding
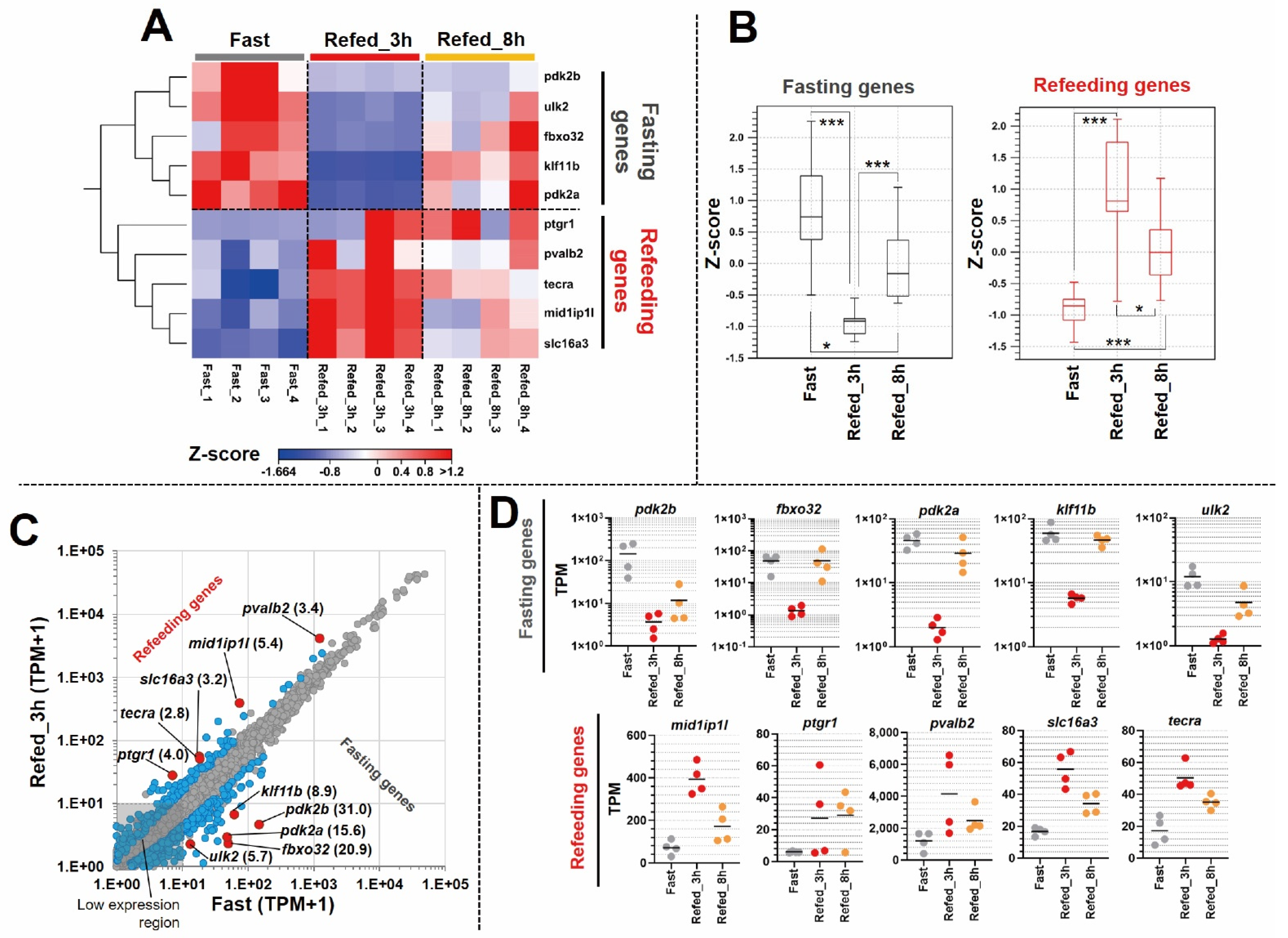
3.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes in Zebrafish Skeletal Muscle Affected by Fasting-Refeeding
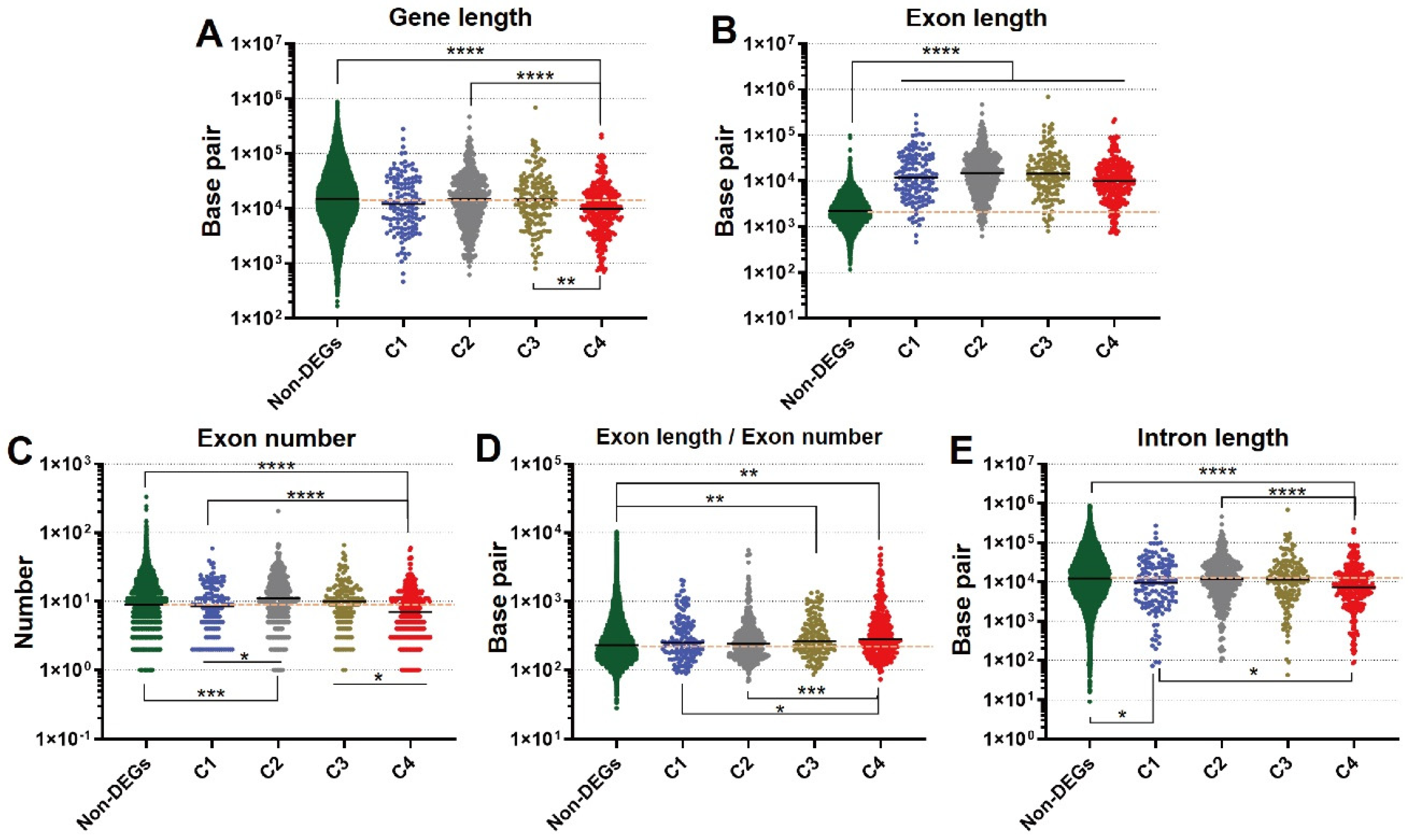
3.4. Novel Findings of Gene Length Associated with Refeeding
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Redman, L.M.; Ravussin, E. Caloric Restriction in Humans: Impact on Physiological, Psychological, and Behavioral Outcomes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, K.; Maekawa, T.; Ly, N.H.; Fujita, S.-I.; Muratani, M.; Ando, M.; Katou, Y.; Araki, H.; Miura, F.; Shirahige, K.; et al. ATF7-Dependent Epigenetic Changes Are Required for the Intergenerational Effect of a Paternal Low-Protein Diet. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 445–458.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varady, K. Intermittent fasting is gaining interest fast. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cabo, R.; Mattson, M.P. Effects of intermittent fasting on health, aging, and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, S.D.; Moehl, K.; Donahoo, W.T.; Marosi, K.; Lee, S.A.; Mainous, A.G.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Mattson, M.P. Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying the Health Benefits of Fasting. Obesity 2018, 26, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Longo, V.D.; Harvie, M. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 39, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrick, C.L.; Ingram, D.K.; Reynolds, M.A.; Freeman, J.R.; Cider, N.L. Effects of Intermittent Feeding Upon Growth and Life Span in Rats. Gerontology 1982, 28, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, P.M.; Moon, T.W. Fasted Zebrafish Mimic Genetic and Physiological Responses in Mammals: A Model for Obesity and Diabetes? Zebrafish 2011, 8, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoriello, C.; Zon, L.I. Hooked! Modeling human disease in zebrafish. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Currie, P.D. Animal models of human disease: Zebrafish swim into view. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gut, P.; Reischauer, S.; Stainier, D.Y.R.; Arnaout, R. Little Fish, Big Data: Zebrafish as a Model for Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 889–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, J.; Qin, J.; Yuan, X.; Liao, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, C.; Li, W. Microarray and metabolome analysis of hepatic response to fasting and subsequent refeeding in zebrafish (Danio rerio). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Qin, J.; Yang, G.; Yu, X.; Wang, B.; Sun, C.; Li, W. Reactive oxygen species participate in liver function recovery during compensatory growth in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescan, P.-Y.; Montfort, J.; Rallière, C.; Le Cam, A.; Esquerré, D.; Hugot, K. Dynamic gene expression in fish muscle during recovery growth induced by a fasting-refeeding schedule. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rescan, P.-Y.; Le Cam, A.; Rallière, C.; Montfort, J. Global gene expression in muscle from fasted/refed trout reveals up-regulation of genes promoting myofibre hypertrophy but not myofibre production. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, L.; Pei, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Global gene expression patterns of grass carp following compensatory growth. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauvigné, F.; Gabillard, J.; Weil, C.; Rescan, P. Effect of refeeding on IGFI, IGFII, IGF receptors, FGF2, FGF6, and myostatin mRNA expression in rainbow trout myotomal muscle. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2003, 132, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montserrat, N.; Gabillard, J.-C.; Capilla, E.; Navarro, M.; Gutiérrez, J. Role of insulin, insulin-like growth factors, and muscle regulatory factors in the compensatory growth of the trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2007, 150, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebo, C.; Portella, M.C.; Carani, F.R.; de Almeida, F.L.A.; Padovani, C.R.; Carvalho, R.F.; Dal-Pai-Silva, M. Short periods of fasting followed by refeeding change the expression of muscle growth-related genes in juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 164, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaral, I.; Johnston, I. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signalling and genome-wide transcriptional regulation in fast muscle of zebrafish following a single-satiating meal. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 2125–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drew, R.E.; Rodnick, K.J.; Settles, M.; Wacyk, J.; Churchill, E.; Powell, M.S.; Hardy, R.W.; Murdoch, G.K.; Hill, R.A.; Robison, B.D. Effect of starvation on transcriptomes of brain and liver in adult female zebrafish (Danio rerio). Physiol. Genom. 2008, 35, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seiliez, I.; Médale, F.; Aguirre, P.; Larquier, M.; Lanneretonne, L.; Alami-Durante, H.; Panserat, S.; Skiba-Cassy, S. Postprandial Regulation of Growth- and Metabolism-Related Factors in Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Xu, A.; Shen, P.; Gao, C.; Zang, J.; Qiu, C.; Ouyang, H.; Jiang, Y.; He, F. A two-level model for the role of complex and young genes in the formation of organism complexity and new insights into the relationship between evolution and development. EvoDevo 2018, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahakyan, A.B.; Balasubramanian, S. Long genes and genes with multiple splice variants are enriched in pathways linked to cancer and other multigenic diseases. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, S.; Sampath, K. Alternative splicing of SMADs in differentiation and tissue homeostasis. Dev. Growth Differ. 2010, 52, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chen, W.; Myers, S.J.; Yuan, H.; Traynelis, S.F. Human GRIN2B variants in neurodevelopmental disorders. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 132, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felder, M.; Kapur, A.; Gonzalez-Bosquet, J.; Horibata, S.; Heintz, J.; Albrecht, R.; Fass, L.; Kaur, J.; Hu, K.; Shojaei, H.; et al. MUC16 (CA125): Tumor biomarker to cancer therapy, a work in progress. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zylka, M.J.; Simon, J.M.; Philpot, B.D. Gene Length Matters in Neurons. Neuron 2015, 86, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, A.; Iida, K.; Tsubota, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Denawa, M.; Brown, J.; Ninomiya, K.; Ito, M.; Kimura, H.; Abe, T.; et al. Loss of Sfpq Causes Long-Gene Transcriptopathy in the Brain. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1326–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.J.; Fire, A.Z. Intron and gene size expansion during nervous system evolution. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, M.; Takeuchi, A.; Tanihata, J.; Iida, K.; Takeda, S.; Hagiwara, M. Loss of RNA-Binding Protein Sfpq Causes Long-Gene Transcriptopathy in Skeletal Muscle and Severe Muscle Mass Reduction with Metabolic Myopathy. iScience 2019, 13, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foletta, V.C.; White, L.J.; Larsen, A.E.; Léger, B.; Russell, A.P. The role and regulation of MAFbx/atrogin-1 and MuRF1 in skeletal muscle atrophy. Pflugers Arch. 2011, 461, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodine, S.C.; Baehr, L.M. Skeletal muscle atrophy and the E3 ubiquitin ligases MuRF1 and MAFbx/atrogin-1. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 307, E469–E484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peris-Moreno, D.; Taillandier, D.; Polge, C. MuRF1/TRIM63, Master Regulator of Muscle Mass. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula, T.G.; Zanella, B.T.T.; de Almeida Fantinatti, B.E.; de Moraes, L.N.; da Silva Duran, B.O.; de Oliveira, C.B.; Salomäo, R.A.S.; da Silva, R.N.; Padovani, C.R.; dos Santos, V.B.; et al. Food restriction increase the expression of mTORC1 complex genes in the skeletal muscle of juvenile pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlinger-Romero, F.; Guimarães-Ferreira, L.; Yonamine, C.Y.; Salgueiro, R.B.; Nunes, M.T. Effects of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) on the expression of ubiquitin ligases, protein synthesis pathways and contractile function in extensor digitorum longus (EDL) of fed and fasting rats. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 68, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, O.; Reznick, A.Z. The role of E3 ubiquitin-ligases MuRF-1 and MAFbx in loss of skeletal muscle mass. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 98, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, I.L.; Silva, W.J.; Artioli, G.G.; Guilherme, J.P.L.F.; Leal, M.L.; Aoki, M.S.; Miyabara, E.H.; Moriscot, A.S. Leucine and HMB Differentially Modulate Proteasome System in Skeletal Muscle under Different Sarcopenic Conditions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Guadamillas, E.; Fernandez-Marcos, P.J.; Pantoja, C.; Muñoz-Martin, M.; Martínez, D.; Gómez-López, G.; Campos-Olivas, R.; Valverde, A.M.; Serrano, M. p21Cip1 plays a critical role in the physiological adaptation to fasting through activation of PPARα. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep34542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talbot, J.C.; Teets, E.M.; Ratnayake, D.; Duy, P.Q.; Currie, P.D.; Amacher, S.L. Muscle precursor cell movements in zebrafish are dynamic and require six-family genes. Development 2019, 146, dev171421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roh, E.; Choi, K.M. Health Consequences of Sarcopenic Obesity: A Narrative Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, I.; Altab, G.; Raina, P.; de Magalhães, J.P. Gene Size Matters: An Analysis of Gene Length in the Human Genome. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Han, M.; Qi, L.S. Engineering 3D genome organization. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, S.J.; Madrigal-Matute, J.; Scheibye-Knudsen, M.; Fang, E.F.; Aon, M.; González-Reyes, J.A.; Cortassa, S.; Kaushik, S.; Gonzalez-Freire, M.; Patel, B.; et al. Effects of Sex, Strain, and Energy Intake on Hallmarks of Aging in Mice. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 1093–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontana, L.; Partridge, L.; Longo, V.D. Extending Healthy Life Span—From Yeast to Humans. Science 2010, 328, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sugasawa, T.; Komine, R.; Manevich, L.; Tamai, S.; Takekoshi, K.; Kanki, Y. Gene Expression Profile Provides Novel Insights of Fasting-Refeeding Response in Zebrafish Skeletal Muscle. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112239
Sugasawa T, Komine R, Manevich L, Tamai S, Takekoshi K, Kanki Y. Gene Expression Profile Provides Novel Insights of Fasting-Refeeding Response in Zebrafish Skeletal Muscle. Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112239
Chicago/Turabian StyleSugasawa, Takehito, Ritsuko Komine, Lev Manevich, Shinsuke Tamai, Kazuhiro Takekoshi, and Yasuharu Kanki. 2022. "Gene Expression Profile Provides Novel Insights of Fasting-Refeeding Response in Zebrafish Skeletal Muscle" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112239
APA StyleSugasawa, T., Komine, R., Manevich, L., Tamai, S., Takekoshi, K., & Kanki, Y. (2022). Gene Expression Profile Provides Novel Insights of Fasting-Refeeding Response in Zebrafish Skeletal Muscle. Nutrients, 14(11), 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112239