Metabolomic Profile of Different Dietary Patterns and Their Association with Frailty Index in Community-Dwelling Older Men and Women
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Dietary Assessment and Construction of Diet Scores
2.3. Frailty Index (FI)
2.4. Assessment of Plasma Metabolites
2.5. Assessment of Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Association of Dietary Patterns with Frailty Index
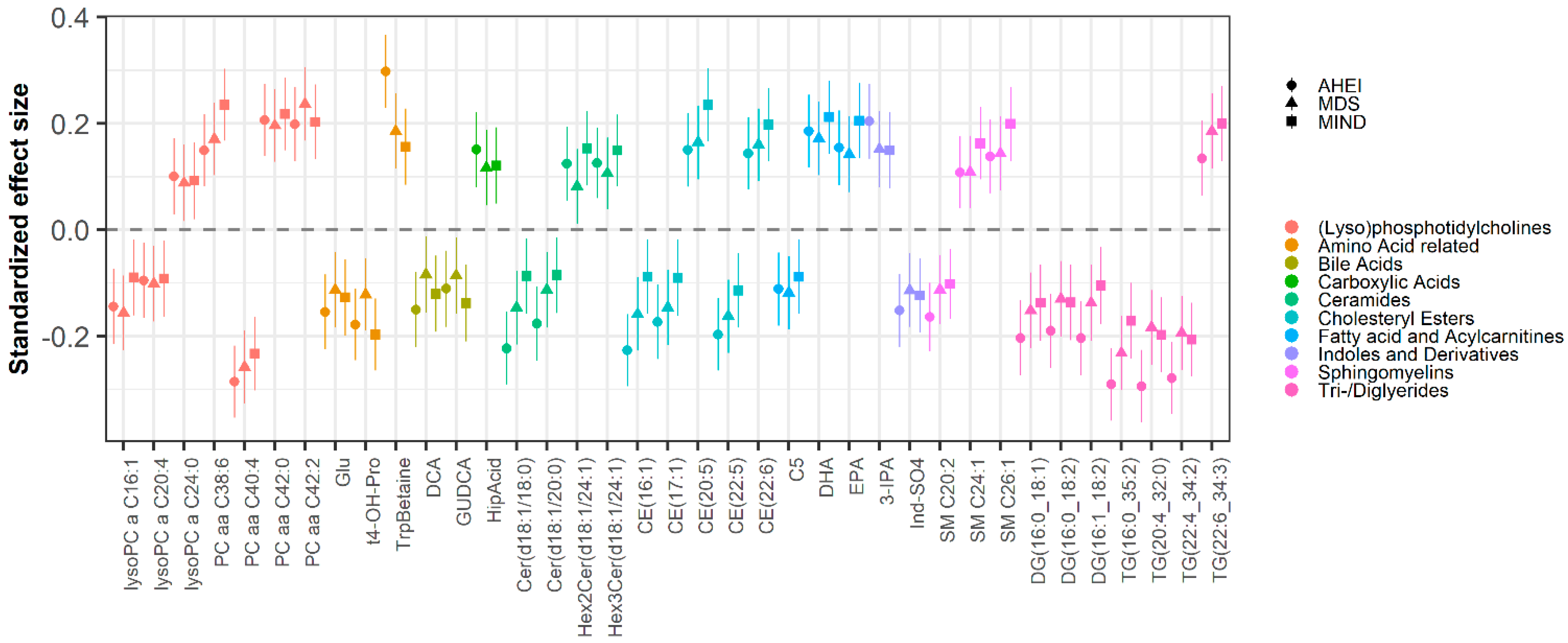
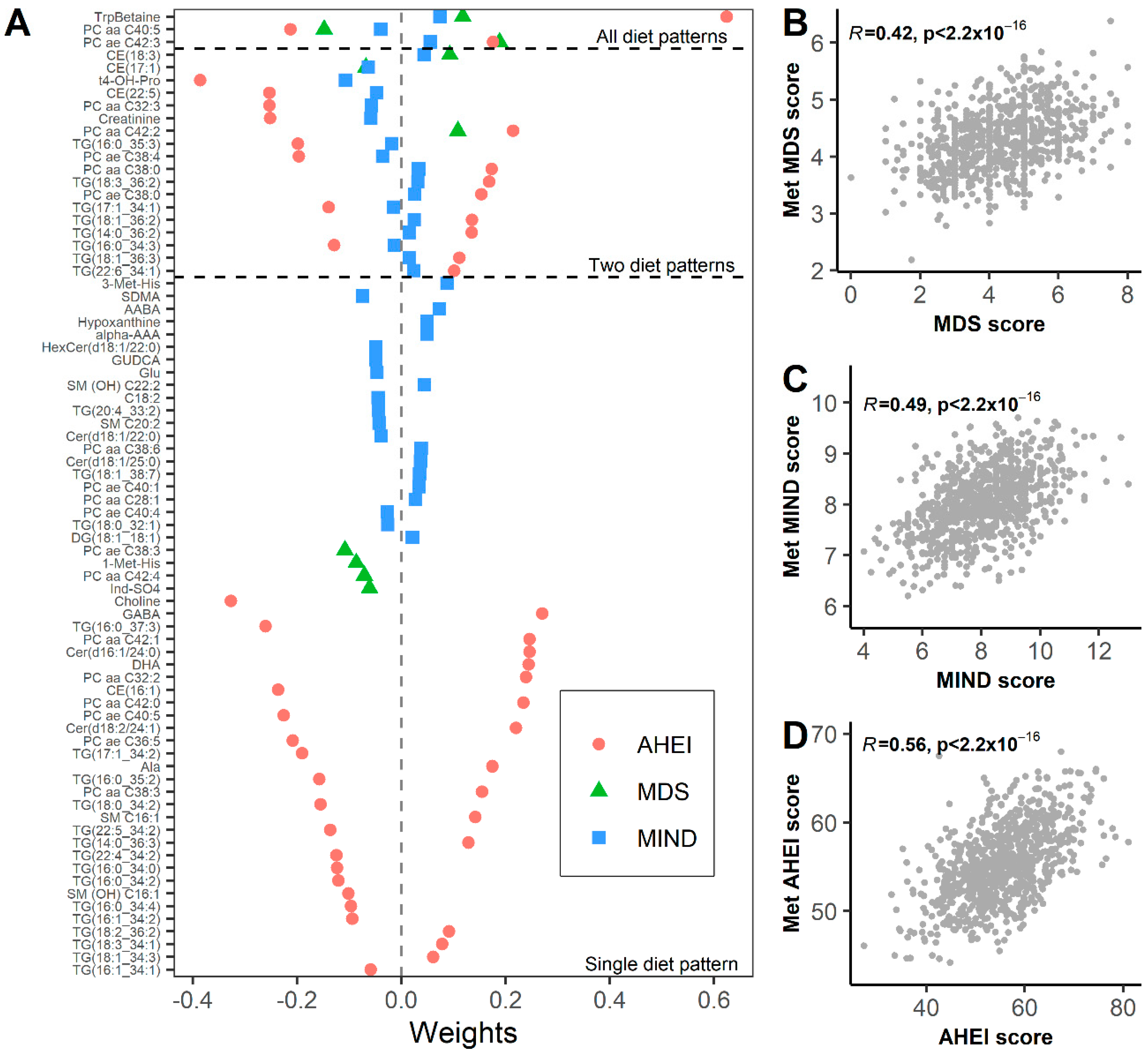
3.2. Metabolomic Biomarkers of Dietary Patterns
3.3. Metabolomic Signature Mediate Associations between Diet and Frailty Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Ageing and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- US Department of Agriculture; Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion; Nutrition Evidence Library; Dietary Patterns Technical Expert Collaborative. A Series of Systematic Reviews on the Relationship between Dietary Patterns and Health Outcomes. Available online: https://nesr.usda.gov/sites/default/files/2019-06/DietaryPatternsReport-FullFinal2.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet and Survival in a Greek Population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiuve, S.E.; Fung, T.T.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B.; McCullough, M.L.; Wang, M.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C. Alternative Dietary Indices Both Strongly Predict Risk of Chronic Disease. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, M.C.; Tangney, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Sacks, F.M.; Barnes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Aggarwal, N.T. Mind diet slows cognitive decline with aging. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.; Talegawkar, S.; Jin, Y.; Bandinelli, S.; Ferrucci, L. Association of Adherence to the Mediterranean-Style Diet with Lower Frailty Index in Older Adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talegawkar, S.A.; Bandinelli, S.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Chen, P.; Milaneschi, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Semba, R.D.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. A Higher Adherence to a Mediterranean-Style Diet Is Inversely Associated with the Development of Frailty in Community-Dwelling Elderly Men and Women. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ma, Y.; Bandinelli, S.; Ferrucci, L.; Talegawkar, S.A. Cardiovascular Health Is Associated with Disability Among Older Community Dwelling Men and Women. J. Aging Health 2018, 31, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talegawkar, S.A.; Jin, Y.; Simonsick, E.M.; Tucker, K.L.; Ferrucci, L.; Tanaka, T. The Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) diet is associated with physical function and grip strength in older men and women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 115, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.A.N.; Zhang, S.; Gu, H.; Asiago, V.; Shanaiah, N.; Raftery, D. Metabolomics-based methods for early disease diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 8, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, D.P.; Park, Y.; Ziegler, T.R. Nutritional Metabolomics: Progress in Addressing Complexity in Diet and Health. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 32, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picó, C.; Serra, F.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Keijer, J.; Palou, A. Biomarkers of Nutrition and Health: New Tools for New Approaches. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shock, N.W.; Greulick, R.C.; Andres, R.; Arenberg, D.; Costa., P.; Lakatta., E.; Tobin, J.D. Normal Human Aging: The Baltimore Study of Aging; NIH Publication No.84-2450; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1984.
- Searle, S.D.; Mitnitski, A.; Gahbauer, E.A.; Gill, T.M.; Rockwood, K. A standard procedure for creating a frailty index. BMC Geriatr. 2008, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Zampino, M.; Moaddel, R.; Chen, T.K.; Tian, Q.; Ferrucci, L.; Semba, R.D. Plasma metabolites associated with chronic kidney disease and renal function in adults from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Bosch, J.P.; Lewis, J.B.; Greene, T.; Rogers, N.; Roth, D. A More Accurate Method to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate from Serum Creatinine: A New Prediction Equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candia, J.; Tsang, J.S. eNetXplorer: An R package for the quantitative exploration of elastic net families for generalized linear models. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tingley, D.; Yamamoto, T.; Hirose, K.; Keele, L.; Imai, K. Mediation: R Package for Causal Mediation Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 59, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, T.Y.; Koulman, A.; Griffin, J.L.; Wareham, N.; Forouhi, N.; Imamura, F. A Combination of Metabolites Predicts Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Pattern and Its Associations with Insulin Sensitivity and Lipid Homeostasis in the General Population: The Fenland Study, United Kingdom. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Rebholz, C.M. Metabolomic Biomarkers of Healthy Dietary Patterns and Cardiovascular Outcomes. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Willett, W.; Townsend, M.K.; Kraft, P.; Ivey, K.L.; Rimm, E.B.; Wilson, K.M.; Costenbader, K.H.; Karlson, E.W.; Poole, E.M.; et al. A lipid-related metabolomic pattern of diet quality. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1613–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Marin, B.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Lopez-Moreno, J.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Jimenez-Lucena, R.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Ortiz-Morales, A.M.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Malagon, M.D.M.; et al. Long-term consumption of a Mediterranean diet improves postprandial lipemia in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Cordioprev randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grösch, S.; Schiffmann, S.; Geisslinger, G. Chain length-specific properties of ceramides. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 51, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albeituni, S.; Stiban, J. Roles of Ceramides and Other Sphingolipids in Immune Cell Function and Inflammation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1161, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayssac, M.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Role of sphingolipids in senescence: Implication in aging and age-related diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2702–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodcock, J. Sphingosine and ceramide signalling in apoptosis. IUBMB Life 2006, 58, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoliu, I.; Scherer, M.; Beguelin, F.; DaSilva, L.; Mari, D.; Salvioli, S.; Martin, F.-P.; Capri, M.; Bucci, L.; Ostan, R.; et al. Serum profiling of healthy aging identifies phospho- and sphingolipid species as markers of human longevity. Aging 2014, 6, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Nevado-Holgado, A.; Whiley, L.; Snowden, S.G.; Soininen, H.; Kloszewska, I.; Mecocci, P.; Tsolaki, M.; Vellas, B.; Thambisetty, M.; et al. Association between Plasma Ceramides and Phosphatidylcholines and Hippocampal Brain Volume in Late Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 60, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kajander, K.; Myllyluoma, E.; Kyronpalo, S.; Rasmussen, M.; Sipponen, P.; Mattila, I.; Seppanen-Laakso, T.; Vapaatalo, H.; Oresic, M.; Korpela, R. Elevated pro-inflammatory and lipotoxic mucosal lipids characterise irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 6068–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.E.; Xanthakis, V.; Peterson, L.R.; Duncan, M.S.; Lee, J.; Ma, J.; Bigornia, S.; Moore, L.L.; Quatromoni, P.A.; Vasan, R.S.; et al. Dietary Patterns, Ceramide Ratios, and Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality: The Framingham Offspring Study. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2994–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, P.; Balasubramanian, R.; Paynter, N.; Giulianini, F.; Fung, T.; Tinker, L.F.; Snetselaar, L.; Liu, S.; Eaton, C.; Tobias, D.K.; et al. Metabolic signatures associated with Western and Prudent dietary patterns in women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guertin, K.A.; Moore, S.C.; Sampson, J.N.; Huang, W.-Y.; Xiao, Q.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Sinha, R.; Cross, A.J. Metabolomics in nutritional epidemiology: Identifying metabolites associated with diet and quantifying their potential to uncover diet-disease relations in populations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Yu, B.; Alexander, D.; Steffen, L.M.; Boerwinkle, E. Human Metabolome Associates with Dietary Intake Habits Among African Americans in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, X.; Cai, W.; Qiu, L. Hypaphorine Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Inflammation via Regulation of TLR4 and PPAR-gamma Dependent on PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signal Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerra, A.; Folesani, G.; Mena, P.; Ticinesi, A.; Allegri, F.; Nouvenne, A.; Pinelli, S.; Del Rio, D.; Borghi, L.; Meschi, T. Hippuric acid in 24 h urine collections as a biomarker of fruits and vegetables intake in kidney stone formers. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, G.; Balducci, C.; Forloni, G.; Pastorelli, R.; Brunelli, L. Hippuric acid: Could became a barometer for frailty and geriatric syndromes? Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 72, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, L.; Davin, A.; Sestito, G.; Mimmi, M.C.; De Simone, G.; Balducci, C.; Pansarasa, O.; Forloni, G.; Cereda, C.; Pastorelli, R.; et al. Plasmatic Hippuric Acid as a Hallmark of Frailty in an Italian Cohort: The Mediation Effect of Fruit–Vegetable Intake. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2021, 76, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Tarng, D.-C. Diet, gut microbiome and indoxyl sulphate in chronic kidney disease patients. Nephrology 2018, 23 (Suppl. S4), 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mafra, D.; Borges, N.; Alvarenga, L.; Esgalhado, M.; Cardozo, L.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Dietary Components That May Influence the Disturbed Gut Microbiota in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imazu, M.; Fukuda, H.; Kanzaki, H.; Amaki, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Takahama, H.; Hitsumoto, T.; Tsukamoto, O.; Morita, T.; Ito, S.; et al. Plasma indoxyl sulfate levels predict cardiovascular events in patients with mild chronic heart failure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, N.A.; Carmo, F.L.; Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; de Brito, J.S.; Dolenga, C.J.; Ferreira, D.; Nakao, L.; Rosado, A.; Fouque, D.; Mafra, D. Probiotic Supplementation in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Sawrey-Kubicek, L.; Beals, E.; Rhodes, C.H.; Houts, H.E.; Sacchi, R.; Zivkovic, A.M. Human gut microbiome composition and tryptophan metabolites were changed differently by fast food and Mediterranean diet in 4 days: A pilot study. Nutr. Res. 2020, 77, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbownik, M.; Stasiak, M.; Zygmunt, A.; Zasada, K.; Lewiński, A. Protective effects of melatonin and indole-3-propionic acid against lipid peroxidation, caused by potassium bromate in the rat kidney. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2006, 24, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendheim, P.E.; Poeggeler, B.; Neria, E.; Ziv, V.; Pappolla, M.A.; Chain, D.G. Development of indole-3-propionic acid (OXIGON™) for alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2002, 19, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, R.; Aoki-Yoshida, A.; Suzuki, C.; Takayama, Y. Indole-3-Pyruvic Acid, an Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activator, Suppresses Experimental Colitis in Mice. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3683–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Sun, S.; Liang, L.; Lou, C.; He, Q.; Ran, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C.; Yuan, H.; et al. Role of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites Indole-3-Acetic Acid in Sulforaphane Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis in Mice. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 756565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopelski, P.; Mogilnicka, I. Biological Effects of Indole-3-Propionic Acid, a Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolite, and Its Precursor Tryptophan in Mammals’ Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomova, A.; Bukovsky, I.; Rembert, E.; Yonas, W.; Alwarith, J.; Barnard, N.D.; Kahleova, H. The Effects of Vegetarian and Vegan Diets on Gut Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y. New Insights into Gut-Bacteria-Derived Indole and Its Derivatives in Intestinal and Liver Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 769501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roager, H.M.; Licht, T.R. Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gesper, M.; Nonnast, A.B.H.; Kumowski, N.; Stoehr, R.; Schuett, K.; Marx, N.; Kappel, B.A. Gut-Derived Metabolite Indole-3-Propionic Acid Modulates Mitochondrial Function in Cardiomyocytes and Alters Cardiac Function. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 648259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Value * (n = 806) | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 73.3 (7.1, 65–95) |
| Men, n (%) | 391 (48.5) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| White | 577 (71.6) |
| Black | 183 (22.7) |
| Other | 46 (5.7) |
| MIND score | 8.0 (1.4, 4–13) |
| MDS score | 4.3 (1.3, 0–8) |
| AHEI score | 55.2 (8.1, 27.2–81.1) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 69.1 (15.4, 15.3–127.2) |
| Frailty Index | 0.1 (0.1, 0–0.4) |
| MDS | MIND | AHEI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | 95% CI | p | Estimate | 95% CI | p | Estimate | 95% CI | p | |
| ACME | −0.001 | (−0.003, −0.00001) | 0.076 | −0.003 | (−0.004, −0.001) | <0.001 | −0.0005 | (−0.0008, −0.0003) | <0.001 |
| ADE | −0.003 | (−0.006, 0.0004) | 0.052 | −0.002 | (−0.005, 0.001) | 0.256 | −0.0004 | (−0.001, 0.0002) | 0.14 |
| TE | −0.004 | (−0.007, −0.001) | 0.012 | −0.005 | (−0.008, −0.001) | 0.004 | −0.001 | (−0.0015, −0.0004) | <0.001 |
| PM | 0.29 | (−0.05, 0.97) | 0.088 | 0.55 | (0.21, 0.95) | 0.004 | 0.61 | (0.26, 1.31) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, T.; Talegawkar, S.A.; Jin, Y.; Candia, J.; Tian, Q.; Moaddel, R.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L. Metabolomic Profile of Different Dietary Patterns and Their Association with Frailty Index in Community-Dwelling Older Men and Women. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112237
Tanaka T, Talegawkar SA, Jin Y, Candia J, Tian Q, Moaddel R, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L. Metabolomic Profile of Different Dietary Patterns and Their Association with Frailty Index in Community-Dwelling Older Men and Women. Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112237
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Toshiko, Sameera A. Talegawkar, Yichen Jin, Julián Candia, Qu Tian, Ruin Moaddel, Eleanor M. Simonsick, and Luigi Ferrucci. 2022. "Metabolomic Profile of Different Dietary Patterns and Their Association with Frailty Index in Community-Dwelling Older Men and Women" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112237
APA StyleTanaka, T., Talegawkar, S. A., Jin, Y., Candia, J., Tian, Q., Moaddel, R., Simonsick, E. M., & Ferrucci, L. (2022). Metabolomic Profile of Different Dietary Patterns and Their Association with Frailty Index in Community-Dwelling Older Men and Women. Nutrients, 14(11), 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112237







