Intergenerational Transmission of Obesity from Mothers to Their Offspring: Trends and Associated Factors Derived from the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethical Approval
2.3. Study Sample
2.4. Body Mass Index (BMI) of the Participants
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Mother–Child Pairs
3.2. The Prevalence of Different BMI Categories by Mother–Child Pair
3.3. Factors Associated with Overweight Mother/Overweight Child Pair (OWM/OWC)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Description | 2006 | 2011 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of households (N) | 15,316 | 7638 | 8427 |
| Reasons for exclusion | |||
| No data on child in the household | 3797 | 1893 | 2063 |
| Living alone | 2144 | 1015 | 1325 |
| Child’s age above 17 years old in the household | 1373 | 890 | 1062 |
| Living with friends | 207 | 167 | 142 |
| Relationship to the head of the household cannot be determined | 1216 | 441 | 992 |
| Missing data on height and weight | 574 | 275 | 258 |
| Mother–child pairs obtained | 6005 | 2957 | 2871 |
Appendix B
| Quintile Income | Household Income Range (RM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2011 | 2015 | |
| Quintile 1 (lowest income) | <500 | <950 | <1200 |
| Quintile 2 | 500–949 | 950–1727 | 1200–1999 |
| Quintile 3 | 950–1499 | 1728–2799 | 2000–3181 |
| Quintile 4 | 1500–2499 | 2800–4599 | 3182–5299 |
| Quintile 5 (highest income) | 2500 and above | 4600 and above | 5300 and above |
References
- Global Burden of Disease 2015 Obesity Collaborators Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The Epidemiology of Obesity. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization Global Health Observatory (GHO) Data: Prevalence of Overweight among Children and Adolescents, Ages 5–19, 1975–2016 (Crude Estimate): Both Sexes. Available online: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/overweight_obesity/overweight_adolescents/en/ (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Dolton, P.; Xiao, M. The Intergenerational Transmission of Body Mass Index across Countries. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2017, 24, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wang, F. Is Economic Environment Associated with the Physical Activity Levels and Obesity in Chinese Adults? A Cross-Sectional Study of 30 Regions in China. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heslehurst, N.; Vieira, R.; Akhter, Z.; Bailey, H.; Slack, E.; Ngongalah, L.; Pemu, A.; Rankin, J. The Association between Maternal Body Mass Index and Child Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.M.; Wan, Y.P.; Gao, X. A Two-Year Study of Parental Obesity Status and Childhood Obesity in China. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduano, S.; Borsari, L.; Salvia, C.; Arletti, S.; Tripodi, A.; Pinca, J.; Borella, P. Risk Factors for Overweight and Obesity in Children Attending the First Year of Primary Schools in Modena, Italy. J. Community Health 2020, 45, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, T.J.; Thompson, O. Genes and the Intergenerational Transmission of BMI and Obesity. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2016, 23, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.L.; Johnson, S.B.; Goodman, E. Breaking the Intergenerational Cycle of Disadvantage: The Three Generation Approach. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20152467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newnham, J.P.; Ross, M.G. Early Life Origins of Human Health and Disease; Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2009; ISBN 978-3-8055-9139-3. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, E. The Childhood Obesity Epidemic as a Result of Nongenetic Evolution: The Maternal Resources Hypothesis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Archer, E.; Lavie, C.J.; Hill, J.O. The Contributions of ‘Diet’, ‘Genes’, and Physical Activity to the Etiology of Obesity: Contrary Evidence and Consilience. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Xue, Y. Pediatric Obesity: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention and Treatment (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flieh, S.M.; Miguel-Berges, M.L.; González-Gil, E.M.; Gottrand, F.; Censi, L.; Widhalm, K.; Manios, Y.; Kafatos, A.; Molnár, D.; Dallongeville, J.; et al. The Association between Portion Sizes from High-Energy-Dense Foods and Body Composition in European Adolescents: The HELENA Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuri, S.K.; Onywera, V.O.; Tremblay, M.S.; Broyles, S.T.; Chaput, J.-P.; Fogelholm, M.; Hu, G.; Kuriyan, R.; Kurpad, A.; Lambert, E.V.; et al. Relationships between Parental Education and Overweight with Childhood Overweight and Physical Activity in 9–11 Year Old Children: Results from a 12-Country Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, C.C.; Desai, M.M.; Park, J.J.; Frame, E.A.; Thompson, A.A.; Naseri, T.; Reupena, M.S.; Duckham, R.L.; Deziel, N.C.; Hawley, N.L. Child, Maternal and Household-Level Correlates of Nutritional Status: A Cross-Sectional Study among Young Samoan Children. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Partap, U.; Young, E.H.; Allotey, P.; Sandhu, M.S.; Reidpath, D.D. Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Parents and Child Obesity in Segamat, Malaysia. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- John, C.; Ichikawa, T.; Abdu, H.; Ocheke, I.; Diala, U.; Modise-Letsatsi, V.; Wada, T.; Okolo, S.; Yamamoto, T. Maternal Overweight/Obesity Characteristics and Child Anthropometric Status in Jos, Nigeria. Niger. Med. J. 2015, 56, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Kishawi, R.R.; Soo, K.L.; Abed, Y.A.; Muda, W.A.M.W. Prevalence and Associated Factors for Dual Form of Malnutrition in Mother-Child Pairs at the Same Household in the Gaza Strip-Palestine. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cauich-Viñas, P.; Azcorra, H.; Rodríguez, L.; Datta Banik, S.; Varela-Silva, M.I.; Dickinson, F. Body Mass Index in Mother and Child Dyads and Its Association with Household Size and Parents’ Education in 2 Urban Settings of Yucatan, Mexico. Food Nutr. Bull. 2019, 40, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, A.W.; Mâsse, L.C.; Barr, S.I.; Lovato, C.Y.; Hanning, R.M. Parent-Child Associations in Selected Food Group and Nutrient Intakes among Overweight and Obese Adolescents. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawloski, L.R.; Curtin, K.M.; Gewa, C.; Attaway, D. Maternal-Child Overweight/Obesity and Undernutrition in Kenya: A Geographic Analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bralić, I.; Vrdoljak, J.; Kovačić, V. Associations between Parental and Child Overweight and Obesity. Coll. Antropol. 2005, 29, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Institute for Public Health. National Health and Morbidity Survey 2015 (NHMS 2015). Vol. I: Methodology and General Findings; Ministry of Health: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2015; Volume I.
- Institute for Public Health. National Health and Morbidity Survey 2011 (NHMS 2011). Vol. I: Methodology and General Findings; Ministry of Health Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2011; Volume I.
- Institute for Public Health. The Third National Health and Morbidity Survey 2006 (NHMS III): General Findings; Ministry of Health: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2008.
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). Convention on the Rights of the Child; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Tamiya, N.; Izumida, N.; Kawamura, A.; Takahashi, H.; Noguchi, H. The Relationship between Raising a Child with a Disability and the Mental Health of Mothers Compared to Raising a Child without Disability in Japan. SSM Popul. Health 2016, 2, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ihab, A.N.; Rohana, A.J.; Wan Manan, W.M.; Wan Suriati, W.N.; Zalilah, M.S.; Rusli, A.M. The Coexistence of Dual Form of Malnutrition in a Sample of Rural Malaysia. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sellers, R.; Hammerton, G.; Harold, G.T.; Mahedy, L.; Potter, R.; Langley, K.; Thapar, A.; Rice, F.; Thapar, A.; Collishaw, S. Examining Whether Offspring Psychopathology Influences Illness Course in Mothers with Recurrent Depression Using a High-Risk Longitudinal Sample. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2016, 125, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochiai, H.; Shirasawa, T.; Ohtsu, T.; Nishimura, R.; Morimoto, A.; Obuchi, R.; Hoshino, H.; Tajima, N.; Kokaze, A. Number of Siblings, Birth Order, and Childhood Overweight: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study in Japan. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinovic, M.; Belojevic, G.; Evans, G.W.; Lausevic, D.; Asanin, B.; Samardzic, M.; Terzic, N.; Pantovic, S.; Jaksic, M.; Boljevic, J. Prevalence of and Contributing Factors for Overweight and Obesity among Montenegrin Schoolchildren. Eur. J. Public Health 2015, 25, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosli, R.H.; Miller, A.L.; Pterson, K.E.; Kaciroti, N.; Rosenblum, K.; Baylin, A.; Lumeng, J.C. Birth Order and Sibship Composition as Predictors of Overweight or Obesity among Low-Income 4- to 8-Year-Old Children. Pediatr. Obes. 2016, 11, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Cormier, E. Influence of Siblings on Child Health Behaviors and Obesity: A Systematic Review. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2018, 27, 2069–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shloim, N.; Edelson, L.R.; Martin, N.; Hetherington, M.M. Parenting Styles, Feeding Styles, Feeding Practices, and Weight Status in 4–12 Year-Old Children: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Onis, M.; Lobstein, T. Defining Obesity Risk Status in the General Childhood Population: Which Cut-Offs Should We Use? Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2010, 5, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Report of a WHO Consultation on Obesity; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- de Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO Growth Reference for School-Aged Children and Adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.P.; Maclean, G.; Dalziel, P. Household Size Economies: Malaysian Evidence. Econ. Anal. Policy 2011, 41, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Labour Organization; The Commissioner of Law Revision. Laws of Malaysia: Education Act 1996 (Act 550). Available online: http://www.ilo.org/dyn/natlex/docs/ELECTRONIC/95631/112655/F1187461074/MYS95631.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780470582473. [Google Scholar]
- Bursac, Z.; Gauss, C.H.; Williams, D.K.; Hosmer, D.W. Purposeful Selection of Variables in Logistic Regression. Source Code Biol. Med. 2008, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z. Model Building Strategy for Logistic Regression: Purposeful Selection. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aitsi-Selmi, A.; Chandola, T.; Friel, S.; Nouraei, R.; Shipley, M.J.; Marmot, M.G. Interaction between Education and Household Wealth on the Risk of Obesity in Women in Egypt. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, N.; Song, S.; Fan, Q.; Wen, D. Interaction between Parental Education and Household Wealth on Children’s Obesity Risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health Artic. 2018, 15, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolodziejczyk, J.K.; Norman, G.J.; Rock, C.L.; Arredondo, E.M.; Roesch, S.C.; Madanat, H.; Patrick, K. Reliability and Concurrent and Construct Validity of the Strategies for Weight Management Measure for Adults. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 10, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonsson, K.; Hartvigsson, O.; Sandin, A.; Wold, A.E.; Sandberg, A.-S.; Barman, M. Food and Nutrient Intake during Pregnancy in Relation to Maternal Characteristics: Results from the NICE Birth Cohort in Northern Sweden. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fichman, H.C.; Fernandes, C.S.; Nitrini, R.; Lourenço, R.A.; de Paiva Paradela, E.M.; Carthery-Goulart, M.T.; Caramelli, P. Age and Educational Level Effects on the Performance of Normal Elderly on Category Verbal Fluency Tasks. Dement. e Neuropsychol. 2009, 3, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, N.D.; Patel, S.A.; Venkat Narayan, K.M. Obesity in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Burden, Drivers, and Emerging Challenges. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2017, 38, 11.1–11.20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The Global Obesity Pandemic: Shaped by Global Drivers and Local Environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M.; Adair, L.S.; Ng, S.W. Global Nutrition Transition and the Pandemic of Obesity in Developing Countries. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzioumis, E.; Adair, L.S. Childhood Dual Burden of Under-and Overnutrition in Low-and Middle-Income Countries: A Critical Review. Food Nutr. Bull. 2014, 35, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chong, P.N.; Teh, C.P.W.; Poh, B.K.; Noor, M.I. Etiology of Obesity over the Life Span: Ecological and Genetic Highlights from Asian Countries. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2014, 3, 16–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsina, K.; Dibaba, D.T.; Akinyemiju, T. Association between Life-Course Socio-Economic Status and Prevalence of Cardio-Metabolic Risk Ractors in Five Middle-Income Countries. J. Glob. Health 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonchoo, W.; Takemi, Y.; Hayashi, F.; Koiwai, K.; Ogata, H. Dietary Intake and Weight Status of Urban Thai Preadolescents in the Context of Food Environment. Prev. Med. Reports 2017, 8, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkawi, I.; Mohamed, Z.; Rezai, G. Healthy Eating: The Preventive Factors among Malaysians. J. Econ. Bus. Manag. 2014, 2, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Overweight and Obesity in the Western Pacific Region: An Equity Perspective; World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific: Manila, Philippines, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.N. The Nutrition and Health Transition in Malaysia. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khor, G.-L. Food Availability and the Rising Obesity Prevalence in Malaysia. Int. e-J. Sci. Med. Educ. 2012, 6, S61–S68. [Google Scholar]
- Davey, T.M.; Allotey, P.; Reidpath, D.D. Is Obesity an Ineluctable Consequence of Development? A Case Study of Malaysia. Public Health 2013, 127, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, J.; Prusty, R.K. Overweight and Obesity among Women by Economic Stratum in Urban India. J. Health. Popul. Nutr. 2014, 32, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Beydoun, M.A.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Moreno, L.A. Do Children and Their Parents Eat a Similar Diet? Resemblance in Child and Parental Dietary Intake: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2011, 65, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smetanina, N.; Albaviciute, E.; Babinska, V.; Karinauskiene, L.; Albertsson-Wikland, K.; Petrauskiene, A.; Verkauskiene, R. Prevalence of Overweight/Obesity in Relation to Dietary Habits and Lifestyle among 7–17 Years Old Children and Adolescents in Lithuania. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.; Zulaily, N.; Shahril, M.R.; Abdullah, E.F.H.S.; Ahmed, A. Association between Socioeconomic Status and Obesity among 12-Year-Old Malaysian Adolescents. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zobel, E.H.; Hansen, T.W.; Rossing, P.; von Scholten, B.J. Global Changes in Food Supply and the Obesity Epidemic. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2016, 5, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S.A.; Wall, M.; Mitchell, N.R. Household Income Differences in Food Sources and Food Items Purchased. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pell, C.; Allotey, P.; Evans, N.; Hardon, A.; Imelda, J.D.; Soyiri, I.; Reidpath, D.D. Coming of Age, Becoming Obese: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Obesity among Adolescents and Young Adults in Malaysia. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariapun, J.; Ng, C.-W.; Hairi, N.N. The Gradual Shift of Overweight, Obesity, and Abdominal Obesity towards the Poor in a Multi-Ethnic Developing Country: Findings from the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Surveys. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, T.; Tibère, L.; Laporte, C.; Mognard, E.; Ismail, M.N.; Sharif, S.P.; Poulain, J.-P. Eating Patterns and Prevalence of Obesity. Lessons Learned from the Malaysian Food Barometer. Appetite 2016, 107, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.F.; Teo, P.S.; Foo, L.H. Ethnic Differences in the Food Intake Patterns and Its Associated Factors of Adolescents in Kelantan, Malaysia. Nutrients 2016, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chong, K.H.; Lee, S.T.; Ng, S.A.; Khouw, I.; Poh, B.K. Fruit and Vegetable Intake Patterns and Their Associations with Sociodemographic Characteristics, Anthropometric Status and Nutrient Intake Profiles among Malaysian Children Aged 1–6 Years. Nutrients 2017, 9, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, H.C.; Poh, B.K.; Lee, S.T.; Chong, K.H.; Bragt, M.C.E.; Abd Talib, R. Are Malaysian Children Achieving Dietary Guideline Recommendations? Asia Pacific J. Public Health 2016, 28, 8S–20S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolnicka, K.; Taraszewska, A.M.; Jaczewska-Schuetz, J.; Jarosz, M. Factors within the Family Environment Such as Parents’ Dietary Habits and Fruit and Vegetable Availability Have the Greatest Influence on Fruit and Vegetable Consumption by Polish Children. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 2705–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhurosy, T.; Jeewon, R. Food Habits, Socioeconomic Status and Body Mass Index among Premenopausal and Post-Menopausal Women in Mauritius. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics of Mother–Child Pairs | 2006 | 2011 | 2015 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Maternal age in years, mean (SD) | 40.9 (7.5) | 41.5 (7.3) | 41.7 (7.7) | |||
| <30 | 529 | 8.8 | 187 | 6.3 | 206 | 7.2 |
| 31–40 | 2335 | 38.9 | 1175 | 39.7 | 1106 | 38.5 |
| 41–50 | 2490 | 41.5 | 1248 | 42.2 | 1170 | 40.8 |
| 51 and above | 651 | 10.8 | 347 | 11.7 | 389 | 13.5 |
| Total | 6005 | 2957 | 2871 | |||
| Ethnicity | ||||||
| Malays | 3659 | 60.9 | 1842 | 62.3 | 1915 | 66.7 |
| Chinese | 926 | 15.4 | 443 | 15.0 | 331 | 11.5 |
| Indian | 485 | 8.1 | 212 | 7.2 | 194 | 6.8 |
| Others | 935 | 15.6 | 460 | 15.6 | 431 | 15.0 |
| Total | 6005 | 2957 | 2871 | |||
| Maternal education level | ||||||
| Tertiary | 401 | 6.7 | 510 | 17.4 | 614 | 21.6 |
| Secondary | 3246 | 54.3 | 1662 | 56.6 | 1606 | 56.4 |
| Primary | 1832 | 30.7 | 609 | 20.7 | 527 | 18.5 |
| None | 497 | 8.3 | 156 | 5.3 | 101 | 3.5 |
| Total | 5976 | 2937 | 2848 | |||
| Household size, mean (SD) | 5.16 (1.82) | 5.23 (1.72) | 4.87 (1.62) | |||
| Small (<5 persons) | 2393 | 39.9 | 1091 | 37.0 | 1319 | 45.9 |
| Medium (5–7 persons) | 3034 | 50.5 | 1594 | 54.0 | 1394 | 48.6 |
| Large (>7 persons) | 577 | 9.6 | 266 | 9.0 | 158 | 5.5 |
| Total | 6004 | 2951 | 2871 | |||
| Household income | ||||||
| Quintile 5 | 1429 | 24.5 | 665 | 22.5 | 677 | 23.6 |
| Quintile 4 | 1396 | 23.9 | 633 | 21.4 | 607 | 21.1 |
| Quintile 3 | 960 | 16.4 | 536 | 18.1 | 635 | 22.1 |
| Quintile 2 | 1310 | 22.4 | 559 | 18.9 | 461 | 16.1 |
| Quintile 1 | 747 | 12.8 | 432 | 14.6 | 491 | 17.1 |
| Total | 5842 | 2825 | 2871 | |||
| Family structure | ||||||
| Dual-parent family | 5682 | 94.7 | 2803 | 94.8 | 2671 | 93.0 |
| Single-parent family | 319 | 5.3 | 154 | 5.2 | 200 | 7.0 |
| Total | 6001 | 2957 | 2871 | |||
| Residential area | ||||||
| Rural | 2613 | 43.5 | 1265 | 42.8 | 1233 | 42.9 |
| Urban | 3392 | 56.5 | 1692 | 57.2 | 1638 | 57.1 |
| Total | 6005 | 2957 | 2871 | |||
| Child age in years, mean (SD) | 9.2 (3.6) | 9.7 (3.7) | 9.6 (3.7) | |||
| 5–9 | 3587 | 59.7 | 1629 | 55.1 | 1603 | 55.8 |
| 10–14 | 1730 | 28.8 | 892 | 30.2 | 876 | 30.5 |
| 15–17 | 688 | 11.5 | 436 | 14.7 | 392 | 13.7 |
| Total | 6005 | 2957 | 2871 | |||
| Sex of child | ||||||
| Girls | 2906 | 48.4 | 1464 | 49.5 | 1405 | 48.9 |
| Boys | 3099 | 51.6 | 1493 | 50.5 | 1466 | 51.1 |
| Total | 6005 | 2957 | 2871 | |||
| Characteristics of Mother–Child Pairs | 2006 | 2011 | 2015 | p-Value a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 6005) | (n = 2957) | (n = 2871) | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Maternal BMI, mean (SD) | 26.19 (5.19) | 26.66 (5.39) | 27.36 (5.55) | <0.001 b | |||
| Underweight | 248 | 4.1 | 100 | 3.4 | 81 | 2.8 | |
| Normal weight | 2438 | 40.6 | 1130 | 38.2 | 970 | 33.8 | |
| Overweight | 2060 | 34.3 | 1041 | 35.2 | 1003 | 34.9 | |
| Obese | 1259 | 21.0 | 686 | 23.2 | 817 | 28.5 | |
| Child BMI, mean (SD) | 17.26 (4.45) | 17.78 (4.66) | 18.28 (5.05) | <0.001 b | |||
| Underweight | 617 | 10.2 | 299 | 10.1 | 219 | 7.6 | |
| Normal weight | 4034 | 67.2 | 1961 | 66.3 | 1839 | 64.1 | |
| Overweight | 774 | 12.9 | 367 | 12.4 | 374 | 13.0 | |
| Obese | 580 | 9.7 | 330 | 11.2 | 439 | 15.3 | |
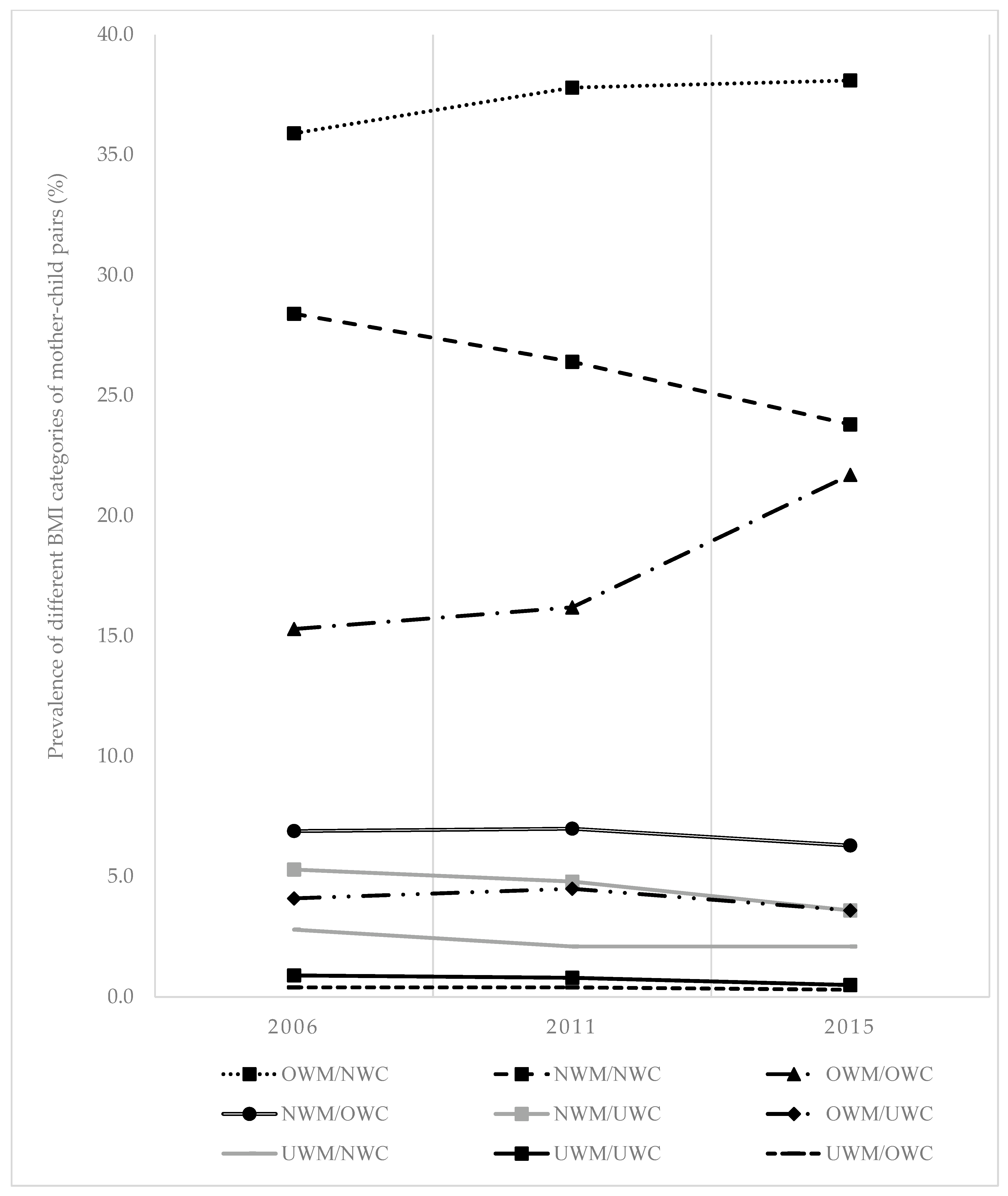
| Mother–Child Pairs Categories | 2006 | 2011 | 2015 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 6005) | (n = 2957) | (n = 2871) | ||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| UWM/UWC | 52 | 0.9 | 25 | 0.8 | 13 | 0.5 |
| UWM/NWC | 171 | 2.8 | 62 | 2.1 | 60 | 2.1 |
| UWM/OWC | 25 | 0.4 | 13 | 0.4 | 8 | 0.3 |
| NWM/UWC | 320 | 5.3 | 142 | 4.8 | 104 | 3.6 |
| NWM/NWC | 1705 | 28.4 | 782 | 26.4 | 684 | 23.8 |
| NWM/OWC | 413 | 6.9 | 206 | 7.0 | 182 | 6.3 |
| OWM/UWC | 245 | 4.1 | 132 | 4.5 | 102 | 3.6 |
| OWM/NWC | 2158 | 35.9 | 1117 | 37.8 | 1095 | 38.1 |
| OWM/OWC | 916 | 15.3 | 478 | 16.2 | 623 | 21.7 |
| Risk Factors | 2006 (n = 2621) | 2011 (n = 1260) | 2015 (n = 1307) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||||
| Maternal age | ||||||||||||
| ≤30 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| 31–40 | 1.74 | 1.21, 2.49 | 0.003 | 1.19 | 0.71, 2.01 | 0.510 | 1.51 | 0.96, 2.38 | 0.078 | |||
| 41–50 | 3.22 | 2.25, 4.60 | <0.001 | 1.66 | 0.99, 2.78 | 0.054 | 1.72 | 1.09, 2.70 | 0.019 | |||
| 51 and above | 3.21 | 2.12, 4.87 | <0.001 | 2.07 | 1.15, 3.74 | 0.015 | 2.01 | 1.20, 3.38 | 0.008 | |||
| Child age | ||||||||||||
| 5–9 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| 10–14 | 2.13 | 1.78, 2.55 | <0.001 | 1.96 | 1.52, 2.53 | <0.001 | 1.47 | 1.15, 1.88 | 0.002 | |||
| 15–17 | 1.44 | 1.11, 1.87 | 0.006 | 1.25 | 0.89, 1.76 | 0.193 | 0.83 | 0.60, 1.13 | 0.235 | |||
| Child sex | ||||||||||||
| Girl | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Boy | 0.90 | 0.76, 1.05 | 0.180 | 1.13 | 0.90, 1.42 | 0.294 | 1.08 | 0.87, 1.35 | 0.465 | |||
| Household size a | ||||||||||||
| Small | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Medium | 0.83 | 0.70, 0.99 | 0.033 | 0.80 | 0.63, 1.01 | 0.062 | 0.99 | 0.79, 1.24 | 0.923 | |||
| Large | 0.64 | 0.47, 0.87 | 0.005 | 0.64 | 0.41, 1.01 | 0.055 | 0.52 | 0.31, 0.87 | 0.013 | |||
| Ethnicity | ||||||||||||
| Malay | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Chinese | 0.43 | 0.34, 0.55 | <0.001 | 0.38 | 0.27, 0.53 | <0.001 | 0.43 | 0.31, 0.61 | <0.001 | |||
| Indian | 1.39 | 1.03, 1.88 | 0.031 | 1.44 | 0.93, 2.22 | 0.100 | 1.23 | 0.79, 1.92 | 0.359 | |||
| Other | 0.53 | 0.41, 0.67 | <0.001 | 0.56 | 0.39, 0.79 | 0.001 | 0.79 | 0.58, 1.07 | 0.122 | |||
| Maternal education level | ||||||||||||
| Tertiary | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Secondary | 1.49 | 1.07, 2.08 | 0.018 | 1.29 | 0.95, 1.74 | 0.100 | 1.60 | 1.21, 2.12 | 0.001 | |||
| Primary | 1.77 | 1.26, 2.50 | 0.001 | 1.20 | 0.83, 1.74 | 0.330 | 1.62 | 1.15, 2.29 | 0.006 | |||
| None | 0.84 | 0.53, 1.31 | 0.438 | 1.74 | 1.01, 2.99 | 0.044 | 1.66 | 0.91, 3.02 | 0.097 | |||
| Household income ᵇ | ||||||||||||
| Quintile 5 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Quintile 4 | 1.24 | 0.99, 1.56 | 0.064 | 1.08 | 0.78, 1.51 | 0.637 | 1.01 | 0.73, 1.40 | 0.932 | |||
| Quintile 3 | 1.23 | 0.96, 1.58 | 0.107 | 1.19 | 0.84, 1.69 | 0.328 | 1.34 | 0.98, 1.84 | 0.067 | |||
| Quintile 2 | 0.82 | 0.64, 1.04 | 0.094 | 1.09 | 0.76, 1.55 | 0.649 | 0.92 | 0.65, 1.31 | 0.649 | |||
| Quintile 1 | 0.53 | 0.39, 0.72 | <0.001 | 1.14 | 0.78, 1.67 | 0.510 | 1.22 | 0.87, 1.72 | 0.247 | |||
| Family structure | ||||||||||||
| Dual-parent family | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Single-parent family | 0.88 | 0.61, 1.26 | 0.474 | 1.41 | 0.84, 2.37 | 0.191 | 1.08 | 0.69, 1.67 | 0.739 | |||
| Residential area | ||||||||||||
| Rural | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Urban | 1.12 | 0.95, 1.32 | 0.184 | 1.00 | 0.80, 1.27 | 0.971 | 0.77 | 0.62, 0.96 | 0.019 | |||
| Risk Factors | 2006 (n = 2621) | 2011 (n = 1260) | 2015 (n = 1307) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOR | 95% CI | p-Value | AOR | 95% CI | p-Value | AOR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Maternal age | |||||||||
| ≤30 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| 31–40 | 1.72 | 1.17, 2.53 | 0.005 | 0.94 | 0.54, 1.65 | 0.836 | 1.47 | 0.92, 2.37 | 0.108 |
| 41–50 | 2.82 | 1.91, 4.18 | <0.001 | 1.14 | 0.64, 2.02 | 0.657 | 1.68 | 1.03, 2.74 | 0.038 |
| 51 and above | 2.87 | 1.77, 4.66 | <0.001 | 1.27 | 0.64, 2.54 | 0.497 | 2.11 | 1.16, 3.84 | 0.015 |
| Child age | |||||||||
| 5–9 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| 10–14 | 1.59 | 1.30, 1.96 | <0.001 | 1.76 | 1.30, 2.36 | <0.001 | 1.21 | 0.91, 1.61 | 0.185 |
| 15–17 | 0.92 | 0.67, 1.26 | 0.594 | 1.02 | 0.67, 1.55 | 0.937 | 0.60 | 0.40, 0.89 | 0.012 |
| Household size a | |||||||||
| Small | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Medium | 0.87 | 0.72, 1.04 | 0.132 | 0.82 | 0.63, 1.07 | 0.150 | 0.93 | 0.73, 1.19 | 0.573 |
| Large | 0.62 | 0.44, 0.86 | 0.005 | 0.56 | 0.34, 0.91 | 0.019 | 0.44 | 0.25, 0.76 | 0.003 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||||
| Malay | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Chinese | 0.33 | 0.25, 0.43 | <0.001 | 0.30 | 0.21, 0.43 | <0.001 | 0.44 | 0.31, 0.63 | <0.001 |
| Indian | 1.31 | 0.95, 1.82 | 0.101 | 1.29 | 0.82, 2.04 | 0.273 | 1.31 | 0.83, 2.07 | 0.254 |
| Other | 0.69 | 0.53, 0.89 | 0.005 | 0.57 | 0.39, 0.84 | 0.005 | 0.78 | 0.56, 1.09 | 0.142 |
| Maternal education level | |||||||||
| Tertiary | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Secondary | 1.74 | 1.20, 2.52 | 0.003 | 1.26 | 0.88, 1.79 | 0.209 | 1.73 | 1.26, 2.38 | 0.001 |
| Primary | 2.24 | 1.49, 3.36 | <0.001 | 1.21 | 0.76, 1.92 | 0.423 | 2.00 | 1.32, 3.03 | 0.001 |
| None | 1.15 | 0.67, 1.95 | 0.615 | 1.65 | 0.84, 3.23 | 0.147 | 1.93 | 1.00, 3.73 | 0.052 |
| Household income ᵇ | |||||||||
| Quintile 5 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Quintile 4 | 1.05 | 0.81, 1.35 | 0.726 | 1.01 | 0.71, 1.45 | 0.960 | 0.76 | 0.54, 1.10 | 0.149 |
| Quintile 3 | 1.06 | 0.80, 1.40 | 0.684 | 0.99 | 0.66, 1.47 | 0.954 | 0.90 | 0.63, 1.29 | 0.577 |
| Quintile 2 | 0.67 | 0.50, 0.89 | 0.005 | 0.86 | 0.57, 1.29 | 0.471 | 0.61 | 0.41, 0.92 | 0.017 |
| Quintile 1 | 0.45 | 0.31, 0.64 | <0.001 | 0.83 | 0.52, 1.32 | 0.434 | 0.81 | 0.55, 1.21 | 0.309 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, N.N.; Rohana, A.J.; Hamid, N.A.A.; Hu, F.B.; Malik, V.S.; Mohd Yusoff, M.F.; Aris, T.; The Global Nutrition and Epidemiologic Transition Initiative (GNET). Intergenerational Transmission of Obesity from Mothers to Their Offspring: Trends and Associated Factors Derived from the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS). Nutrients 2022, 14, 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112186
Mohamed NN, Rohana AJ, Hamid NAA, Hu FB, Malik VS, Mohd Yusoff MF, Aris T, The Global Nutrition and Epidemiologic Transition Initiative (GNET). Intergenerational Transmission of Obesity from Mothers to Their Offspring: Trends and Associated Factors Derived from the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS). Nutrients. 2022; 14(11):2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112186
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Nur Nadia, Abdul Jalil Rohana, Noor Aman A Hamid, Frank B. Hu, Vasanti S. Malik, Muhammad Fadhli Mohd Yusoff, Tahir Aris, and The Global Nutrition and Epidemiologic Transition Initiative (GNET). 2022. "Intergenerational Transmission of Obesity from Mothers to Their Offspring: Trends and Associated Factors Derived from the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS)" Nutrients 14, no. 11: 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112186
APA StyleMohamed, N. N., Rohana, A. J., Hamid, N. A. A., Hu, F. B., Malik, V. S., Mohd Yusoff, M. F., Aris, T., & The Global Nutrition and Epidemiologic Transition Initiative (GNET). (2022). Intergenerational Transmission of Obesity from Mothers to Their Offspring: Trends and Associated Factors Derived from the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS). Nutrients, 14(11), 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14112186







