Neuroprotective Effects of Cranberry Juice Treatment in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
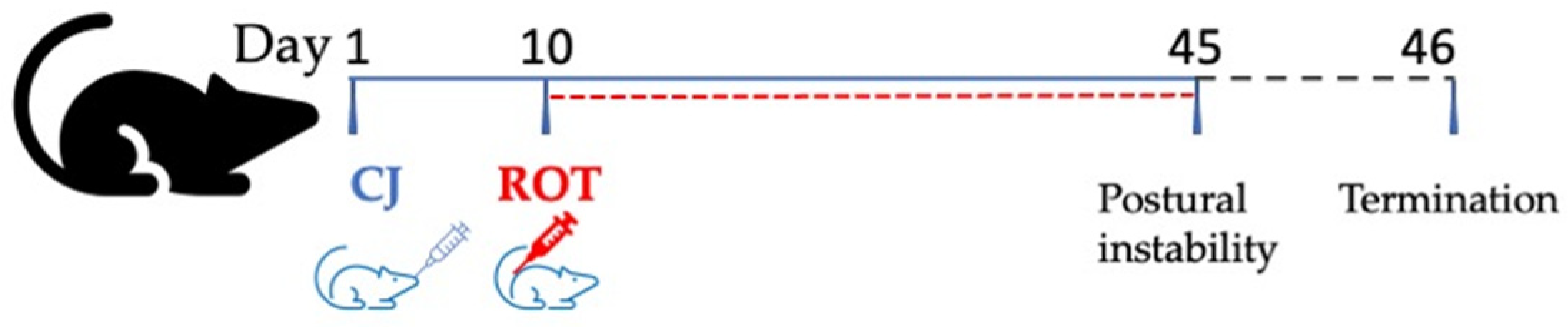
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Postural Instability Test
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Western Blotting
3. Results
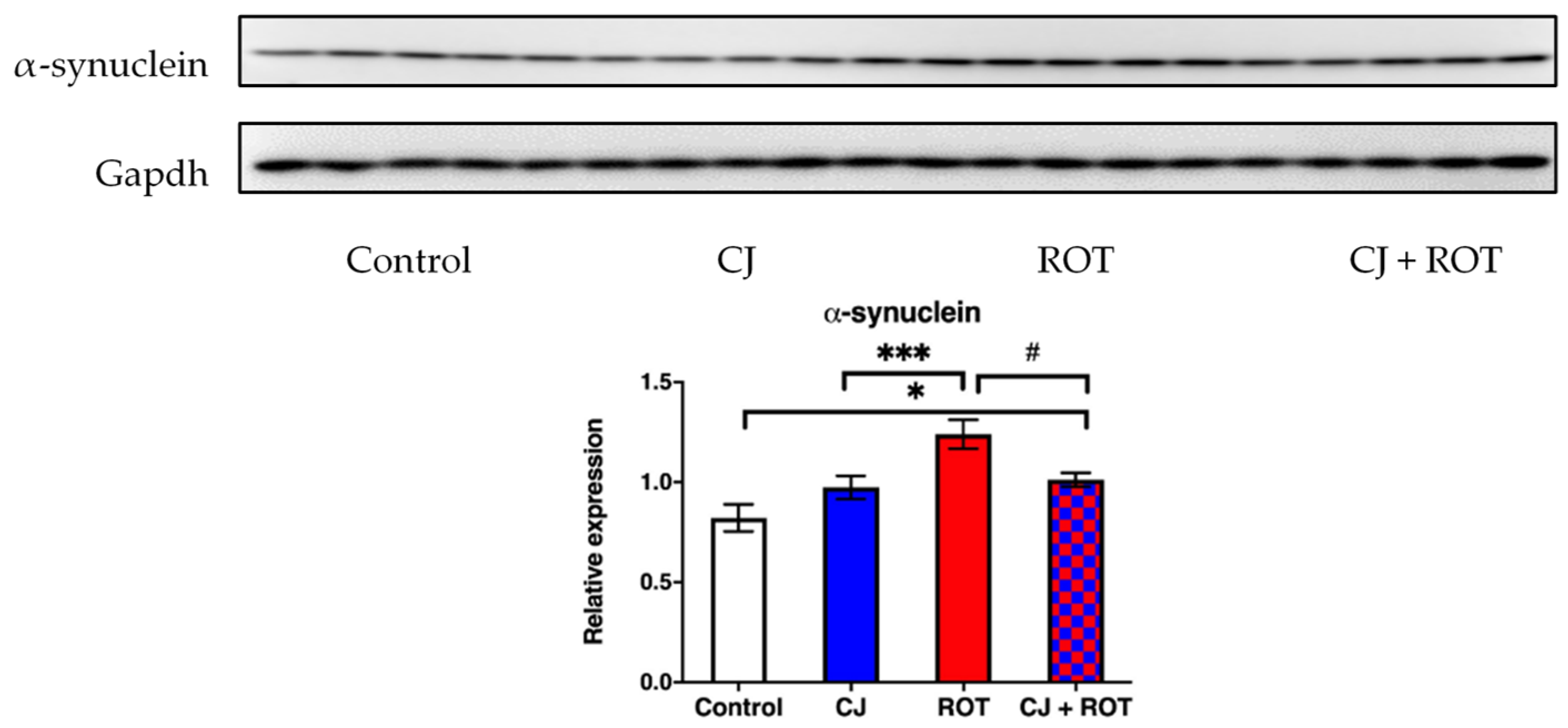
3.1. α-Synuclein Expression
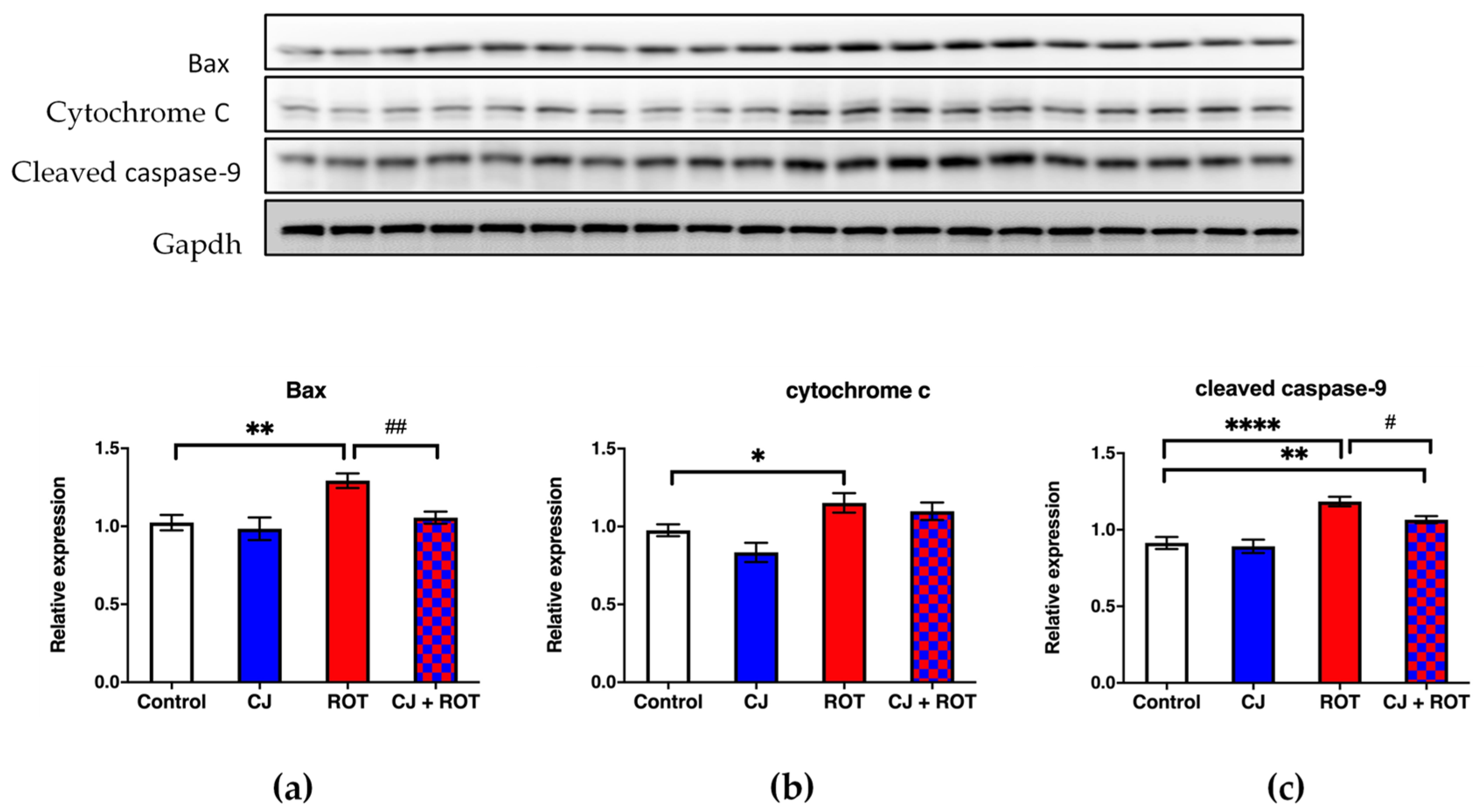
3.2. Apoptosis Markers
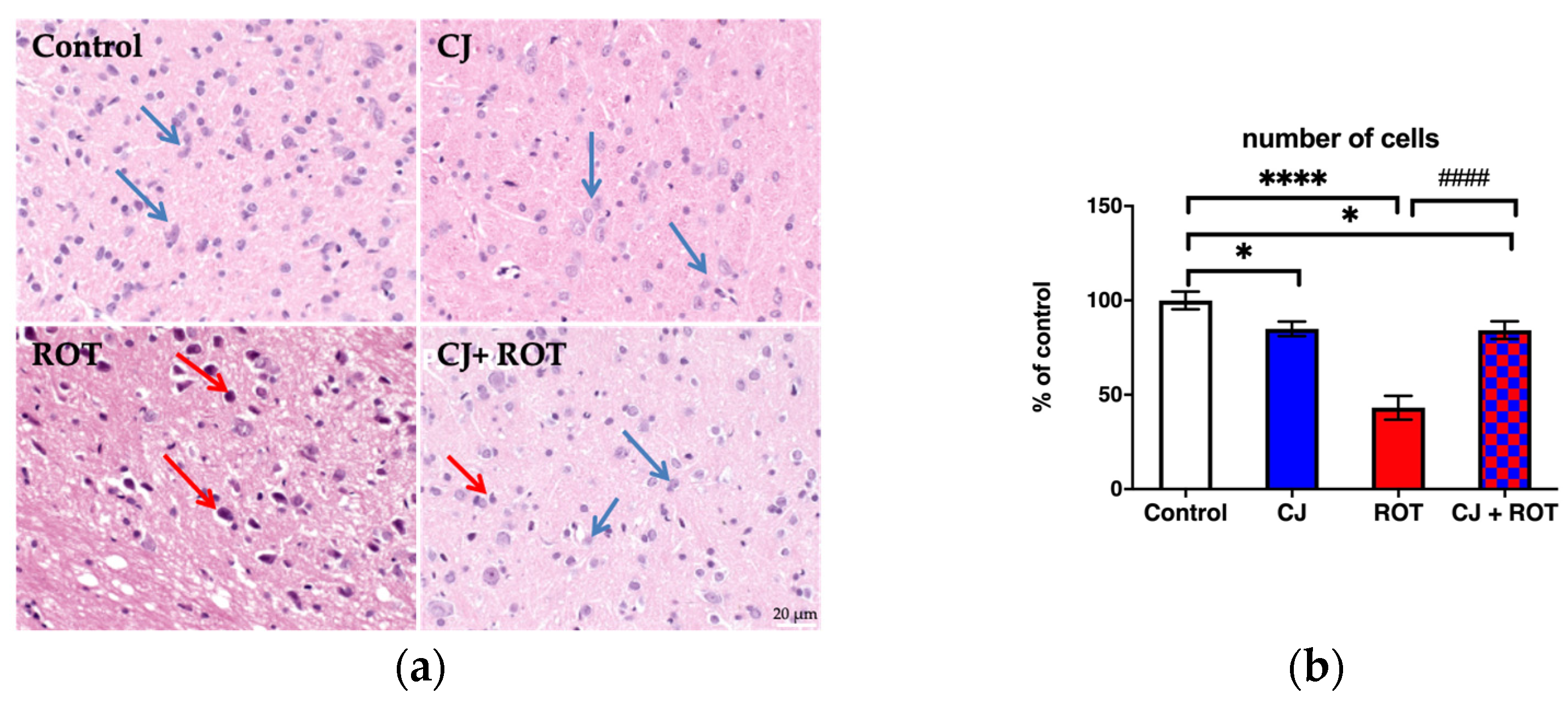
3.3. Histopathological Analysis
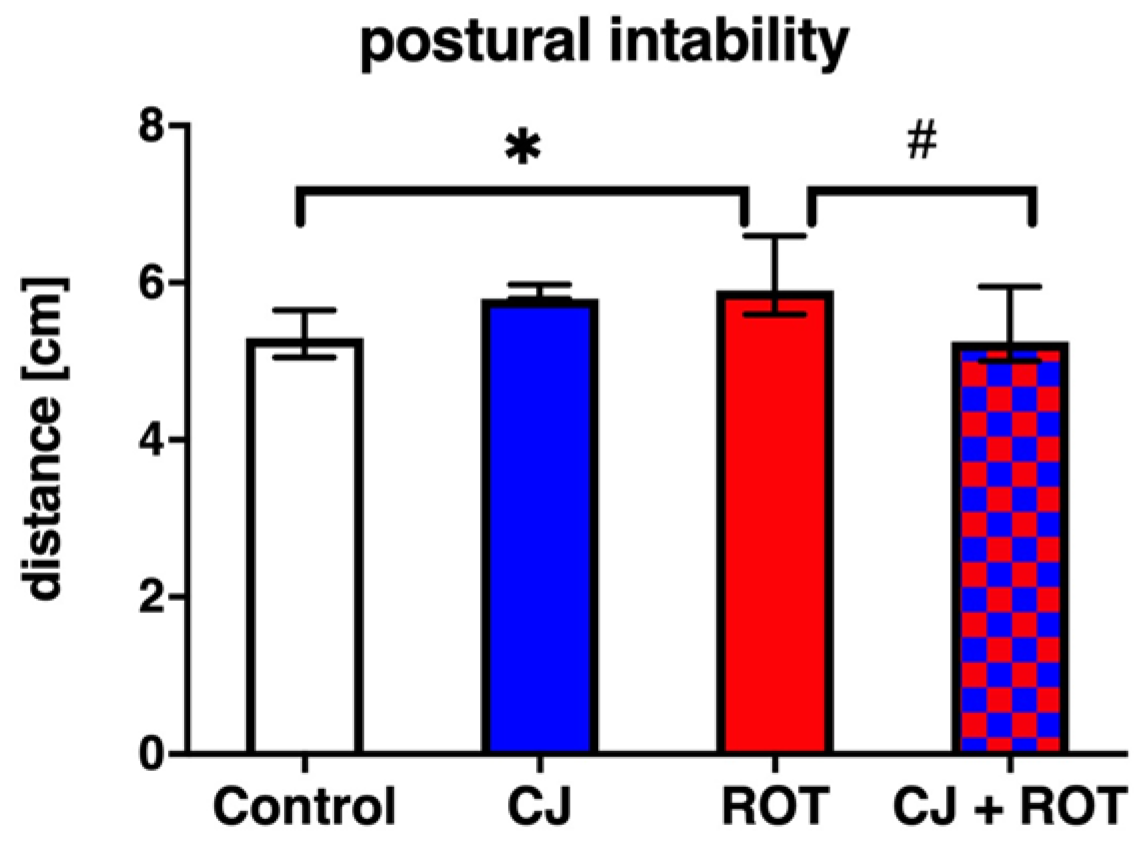
3.4. Postural Instability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson′s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, H.; Mizuta, I.; Li, Y.; Funayama, M.; Yoshino, H.; Li, L.; Murata, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kubo, S.I.; Mizuno, Y.; et al. LRRK2 P755L variant in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 53, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.D.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.R.; Liu, X.L. Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson′s disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Xia, Y.; Wan, F.; Ma, K.; Guo, X.; Kou, L.; Yin, S.; Han, C.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; et al. New Perspectives on Roles of Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattson, M.P.; Gleichmann, M.; Cheng, A. Mitochondria in neuroplasticity and neurological disorders. Neuron 2008, 60, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cannon, J.R.; Tapias, V.; Na, H.M.; Honick, A.S.; Drolet, R.E.; Greenamyre, J.T. A highly reproducible rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kujawska, M.; Jourdes, M.; Kurpik, M.; Szulc, M.; Szaefer, H.; Chmielarz, P.; Kreiner, G.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Mikołajczak, P.; Teissedre, P.L.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate Juice against Parkinson’s Disease and Presence of Ellagitannins-Derived Metabolite-Urolithin A-In the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Giampieri, F.; Gasparrini, M.; Mazzoni, L.; Quiles, J.L.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Battino, M. The effects of bioactive compounds from plant foods on mitochondrial function: A focus on apoptotic mechanisms. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 154–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palikova, I.; Vostalova, J.; Zdarilova, A.; Svobodova, A.; Kosina, P.; Vecera, R.; Stejskal, D.; Proskova, J.; Hrbac, J.; Bednar, P.; et al. Long-term effects of three commercial cranberry products on the antioxidative status in rats: A pilot study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Spencer, J.P.; Tognolini, M.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Dietary (poly)phenolics in human health: Structures, bioavailability, and evidence of protective effects against chronic diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2013, 18, 1818–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Vauzour, D.; Krueger, C.G.; Shanmuganayagam, D.; Reed, J.; Calani, L.; Mena, P.; Del Rio, D.; Crozier, A. Bioavailability, bioactivity and impact on health of dietary flavonoids and related compounds: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1803–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, G.; Kay, C.D.; Crozier, A. The Bioavailability, Transport, and Bioactivity of Dietary Flavonoids: A Review from a Historical Perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1054–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brickman, A.M.; Khan, U.A.; Provenzano, F.A.; Yeung, L.K.; Suzuki, W.; Schroeter, H.; Wall, M.; Sloan, R.P.; Small, S.A. Enhancing dentate gyrus function with dietary flavanols improves cognition in older adults. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desideri, G.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Grassi, D.; Necozione, S.; Ghiadoni, L.; Mastroiacovo, D.; Raffaele, A.; Ferri, L.; Bocale, R.; Lechiara, M.C.; et al. Benefits in cognitive function, blood pressure, and insulin resistance through cocoa flavanol consumption in elderly subjects with mild cognitive impairment: The Cocoa, Cognition, and Aging (CoCoA) study. Hypertension 2012, 60, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mastroiacovo, D.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Grassi, D.; Necozione, S.; Raffaele, A.; Pistacchio, L.; Righetti, R.; Bocale, R.; Lechiara, M.C.; Marini, C.; et al. Cocoa flavanol consumption improves cognitive function, blood pressure control, and metabolic profile in elderly subjects: The Cocoa, Cognition, and Aging (CoCoA) Study—A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathearn, K.E.; Yousef, G.G.; Grace, M.H.; Roy, S.L.; Tambe, M.A.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Wu, Q.L.; Simon, J.E.; Lila, M.A.; Rochet, J.C. Neuroprotective effects of anthocyanin- and proanthocyanidin-rich extracts in cellular models of Parkinson׳s disease. Brain Res. 2014, 1555, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pipingas, A.; Silberstein, R.B.; Vitetta, L.; Rooy, C.V.; Harris, E.V.; Young, J.M.; Frampton, C.M.; Sali, A.; Nastasi, J. Improved cognitive performance after dietary supplementation with a Pinus radiata bark extract formulation. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Croft, K.; Mori, T.; Wesnes, K.; Spong, J.; Downey, L.; Kure, C.; Lloyd, J.; Stough, C. An examination of the effects of the antioxidant Pycnogenol on cognitive performance, serum lipid profile, endocrinological and oxidative stress biomarkers in an elderly population. J. Psychopharmacol. 2008, 22, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.T.; Head, K.; Morris, P.G.; Macdonald, I.A. The effect of flavanol-rich cocoa on the fMRI response to a cognitive task in healthy young people. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47 (Suppl. S2), S215–S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ho, L.; Zhao, W.; Ono, K.; Rosensweig, C.; Chen, L.; Humala, N.; Teplow, D.B.; Pasinetti, G.M. Grape-derived polyphenolics prevent Abeta oligomerization and attenuate cognitive deterioration in a mouse model of Alzheimer′s disease. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 6388–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, M.; Mori, K.; Misawa, T.; Takaki, T.; Demizu, Y.; Shibanuma, M.; Fukuhara, K. Inhibition of β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity by planar analogues of procyanidin B3. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 2659–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Johnson, S.L.; Liu, W.; DaSilva, N.A.; Meschwitz, S.; Dain, J.A.; Seeram, N.P. Evaluation of Polyphenol Anthocyanin-Enriched Extracts of Blackberry, Black Raspberry, Blueberry, Cranberry, Red Raspberry, and Strawberry for Free Radical Scavenging, Reactive Carbonyl Species Trapping, Anti-Glycation, Anti-β-Amyloid Aggregation, and Microglial Neuroprotective Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cásedas, G.; Les, F.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P.; Smith, C.; López, V. Anthocyanin profile, antioxidant activity and enzyme inhibiting properties of blueberry and cranberry juices: A comparative study. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4187–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukitt-Hale, B.; Galli, R.L.; Meterko, V.; Carey, A.; Bielinski, D.F.; McGhie, T.; Joseph, J.A. Dietary supplementation with fruit polyphenolics ameliorates age-related deficits in behavior and neuronal markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. Age 2005, 27, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurpik, M.; Zalewski, P.; Kujawska, M.; Ewertowska, M.; Ignatowicz, E.; Cielecka-Piontek, J.; Jodynis-Liebert, J. Can Cranberry Juice Protect against Rotenone-Induced Toxicity in Rats? Nutrients 2021, 13, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson′s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, J.C. Natural Compounds for the Management of Parkinson′s Disease and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. BioMed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kujawska, M.; Jodynis-Liebert, J. Polyphenols in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review of In Vivo Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stacchiotti, A.; Corsetti, G. Natural Compounds and Autophagy: Allies Against Neurodegeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 555409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, M.; Jourdes, M.; Witucki, Ł.; Karaźniewicz-Łada, M.; Szulc, M.; Górska, A.; Mikołajczak, P.Ł.; Teissedre, P.-L.; Jodynis-Liebert, J. Pomegranate Juice Ameliorates Dopamine Release and Behavioral Deficits in a Rat Model of Parkinson′s Disease. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reglodi, D.; Renaud, J.; Tamas, A.; Tizabi, Y.; Socías, S.B.; Del-Bel, E.; Raisman-Vozari, R. Novel tactics for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease: Role of antibiotics, polyphenols and neuropeptides. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 155, 120–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.Y.; Xie, X.X.; Liu, R.T. The Role of α-Synuclein Oligomers in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, S.; Skinner, T.; Bridges, B.; Weber, J.T. The Pathology of Parkinson′s Disease and Potential Benefit of Dietary Polyphenols. Molecules 2020, 25, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, H.L.; Teismann, P. Glutathione--a review on its role and significance in Parkinson′s disease. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3263–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marino, A.; Battaglini, M.; Desii, A.; Lavarello, C.; Genchi, G.; Petretto, A.; Ciofani, G. Liposomes loaded with polyphenol-rich grape pomace extracts protect from neurodegeneration in a rotenone-based. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 8171–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, M.A.; Tikhonova, N.G.; Tenditnik, M.V.; Ovsyukova, M.V.; Akopyan, A.A.; Dubrovina, N.I.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Khlestkina, E.K. Effects of Grape Polyphenols on the Life Span and Neuroinflammatory Alterations Related to Neurodegenerative Parkinson Disease-Like Disturbances in Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, G.; Chakrabarti, S.; Chatterjee, U.; Saso, L. Proteinopathy, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: Cross talk in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, D.S. The Catecholaldehyde Hypothesis for the Pathogenesis of Catecholaminergic Neurodegeneration: What We Know and What We Do Not Know. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, P. Oxidative stress in Parkinson′s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53 (Suppl. S3), S26–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Meeran, M.F.N.; Azimullah, S.; Bader Eddin, L.; Dwivedi, V.D.; Jha, N.K.; Ojha, S. α-Bisabolol, a Dietary Bioactive Phytochemical Attenuates Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Apoptosis in Rotenone-Induced Rat Model of Parkinson′s Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margabandhu, G.; Vanisree, A.J. Dopamine, a key factor of mitochondrial damage and neuronal toxicity on rotenone exposure and also parkinsonic motor dysfunction-Impact of asiaticoside with a probable vesicular involvement. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2020, 106, 101788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Gao, S.S.; Yang, H.J.; Wang, M.; Cheng, B.F.; Feng, Z.W.; Wang, L. Neuroprotective Effects of Proanthocyanidins, Natural Flavonoids Derived From Plants, on Rotenone-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Lv, Y.; He, P.; Liu, C.; Jiao, J.; Li, S.; Mao, X.; Xue, X. Proanthocyanidins exert a neuroprotective effect via ROS/JNK signaling in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease models in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 4913–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhen, J.; Qu, Z.; Fang, H.; Fu, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zang, H.; Wang, W. Effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling and associated cognitive impairment in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Chang, J.; Zhao, W.; Gao, Y. Proanthocyanidins regulate the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway and protect neurons from cypermethrin-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 177, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Chen, L.; Hu, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Bai, Y. Grape seed proanthocyanidins attenuate apoptosis in ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2021, 121, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; He, X.; Zhang, W.; Chu, D.; Feng, C. Alleviation Effect of Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins on Neuronal Apoptosis in Rats with Iron Overload. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cassidy, A.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Rimm, E.B.; Ascherio, A. Habitual intake of dietary flavonoids and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 2012, 78, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, B.; Wang, G.; Jia, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, X. A-Type Cinnamon Procyanidin Oligomers Protect Against 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine-Induced Neurotoxicity in Mice Through Inhibiting the P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/P53/BCL-2 Associated X Protein Signaling Pathway. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.H.; Yang, D.J.; Kwan, H.Y.; Lyu, A.P.; Chen, G.Q.; Bian, Z.X. Cell death mechanisms induced by synergistic effects of halofuginone and artemisinin in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujawska, M.; Kant, P.; Mayoral, I.H.; Ignatowicz, E.; Sikora, J.; Oszmianski, J.; Czapski, J.; Jodynis-Liebert, J. Effect of Chokeberry Juice on N-Nitrosodiethylamine-Induced Rat Liver Carcinogenesis. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2016, 35, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Ortiz, J.M.; Alguacil, L.F.; Salas, E.; Hermosín-Gutiérrez, I.; Gómez-Alonso, S.; González-Martín, C. Antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of grape pomace and grape seed extracts on colorectal cancer cell lines. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2948–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angelino, D.; Carregosa, D.; Domenech-Coca, C.; Savi, M.; Figueira, I.; Brindani, N.; Jang, S.; Lakshman, S.; Molokin, A.; Urban, J.F.; et al. 5-(Hydroxyphenyl)-γ-Valerolactone-Sulfate, a Key Microbial Metabolite of Flavan-3-ols, Is Able to Reach the Brain: Evidence from Different in. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Group (n) | Treatment | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st–10th Day | 11th–45th Day | |
| Control (n = 11) | water (i.g.) | water (i.g.) + oleum (s.c.) |
| CJ 1 (n = 11) | CJ 1 (i.g.) | CJ 1 (i.g.) + oleum (s.c.) |
| ROT 2 (n = 11) | water (i.g.) | water (i.g.) + ROT 2 (s.c.) |
| CJ + ROT (n = 11) | CJ 1 (i.g.) | CJ 1 (i.g.) + ROT 2 (s.c.) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Witucki, Ł.; Kurpik, M.; Jakubowski, H.; Szulc, M.; Łukasz Mikołajczak, P.; Jodynis-Liebert, J.; Kujawska, M. Neuroprotective Effects of Cranberry Juice Treatment in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102014
Witucki Ł, Kurpik M, Jakubowski H, Szulc M, Łukasz Mikołajczak P, Jodynis-Liebert J, Kujawska M. Neuroprotective Effects of Cranberry Juice Treatment in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients. 2022; 14(10):2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102014
Chicago/Turabian StyleWitucki, Łukasz, Monika Kurpik, Hieronim Jakubowski, Michał Szulc, Przemysław Łukasz Mikołajczak, Jadwiga Jodynis-Liebert, and Małgorzata Kujawska. 2022. "Neuroprotective Effects of Cranberry Juice Treatment in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease" Nutrients 14, no. 10: 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102014
APA StyleWitucki, Ł., Kurpik, M., Jakubowski, H., Szulc, M., Łukasz Mikołajczak, P., Jodynis-Liebert, J., & Kujawska, M. (2022). Neuroprotective Effects of Cranberry Juice Treatment in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients, 14(10), 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14102014










