Korean Red Ginseng Enhances Immunotherapeutic Effects of NK Cells via Eosinophils in Metastatic Liver Cancer Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Establishment of Experimental Metastatic Liver Cancer Model
2.3. Treatment
2.4. In Vivo Imaging
2.5. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Hematological Analysis
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Measurement of CD56dim+ NK Cells
2.10. Kaplan–Meier Plotter Database Analysis
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Combination of KRG and NK Cells Suppressed Metastatic Liver Cancer Progression
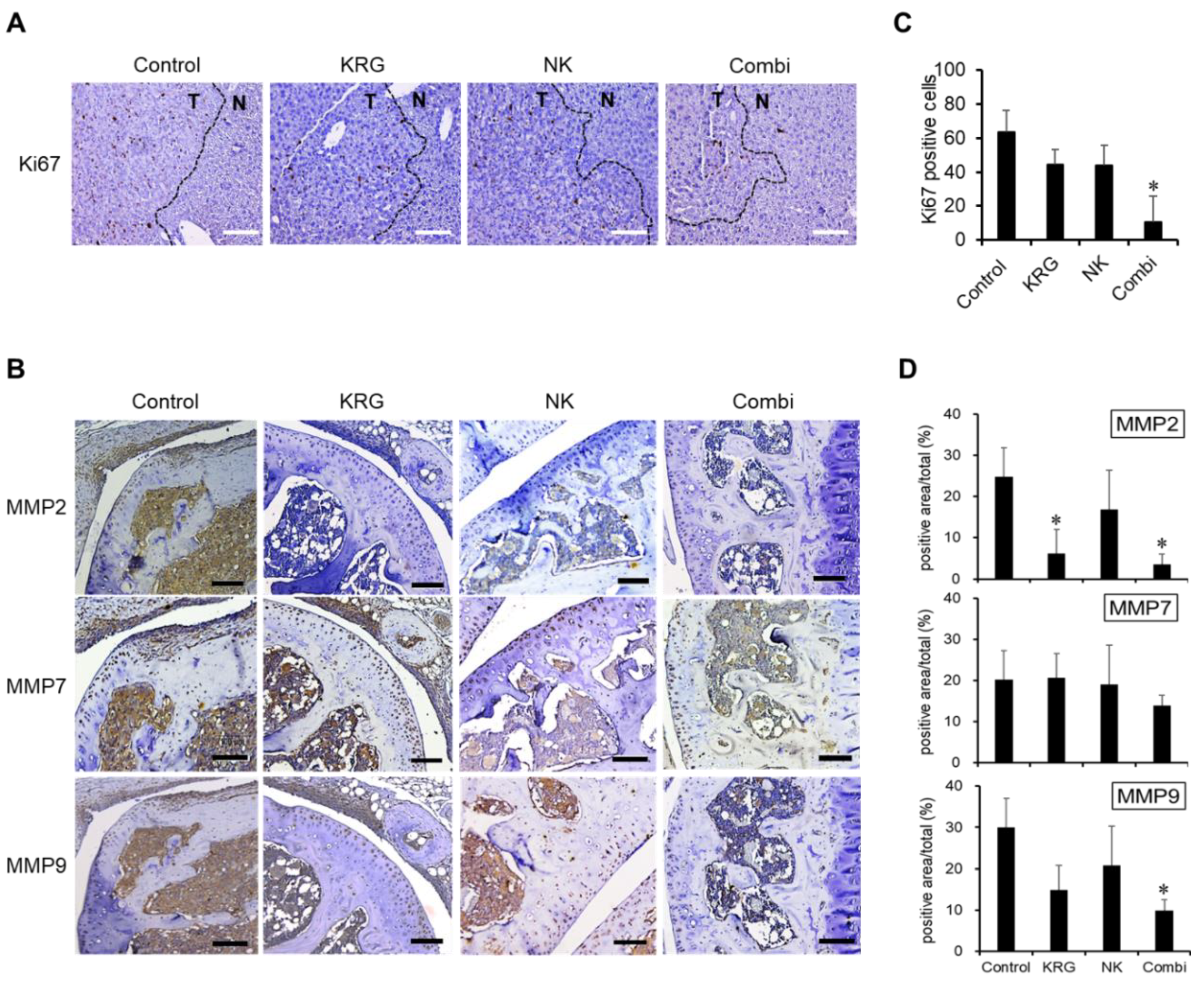
3.2. Combination of KRG and NK Cells Inhibited the Expression of Ki67 and MMPs in Metastatic Lesions
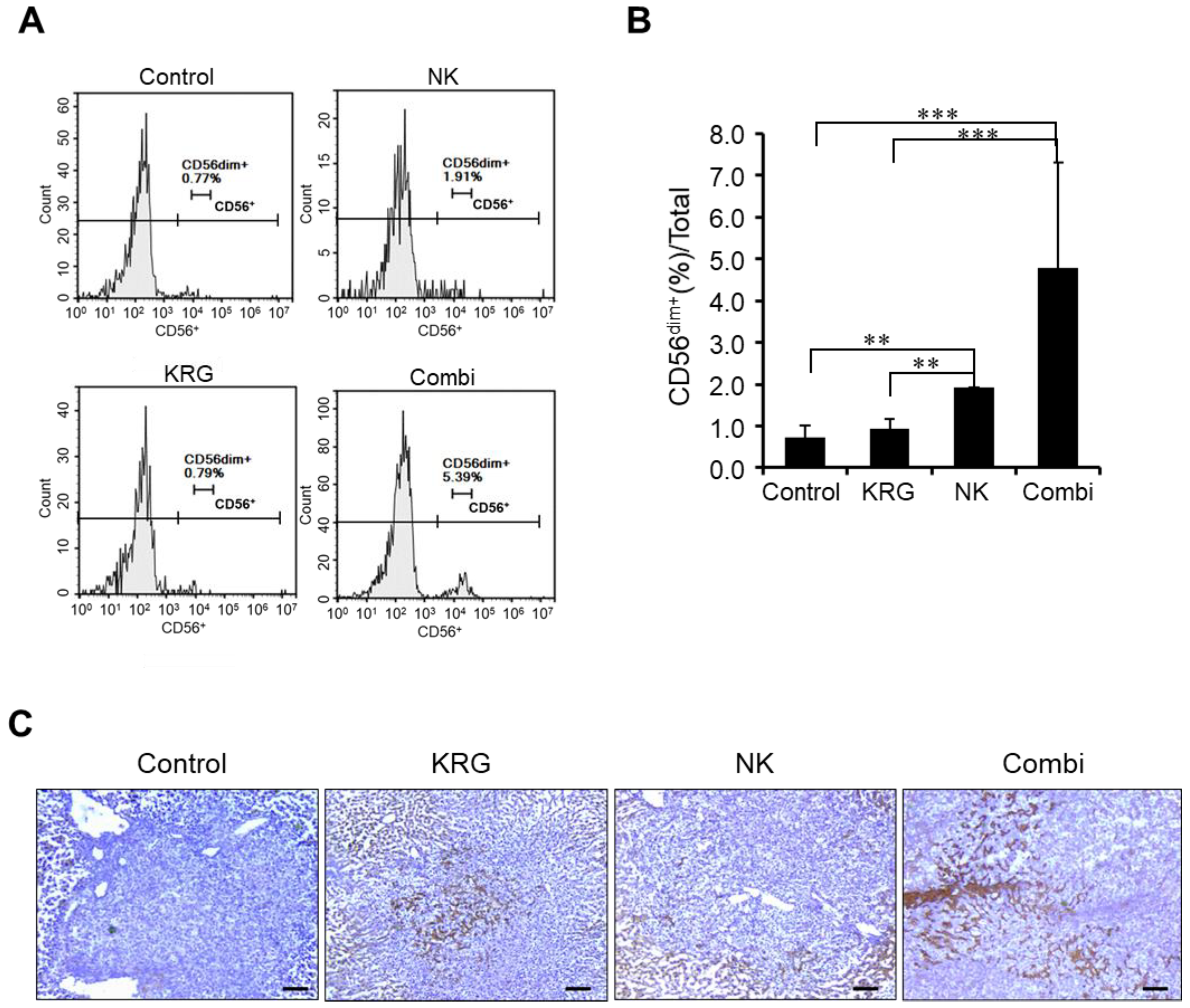
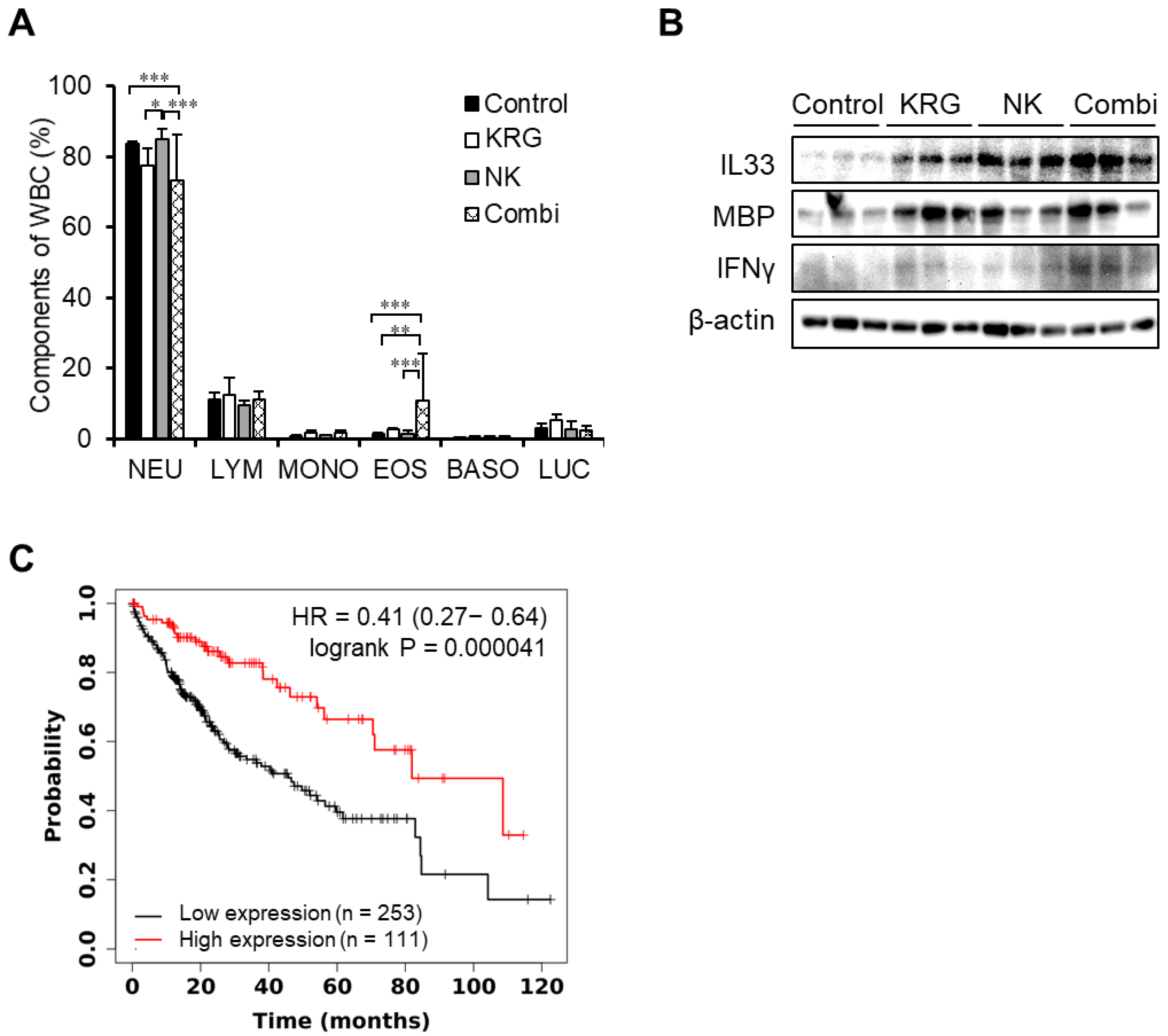
3.3. KRG Enhanced Anti-Metastatic Effects of NK Cells through Eosinophils
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. S1), 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.T.; Geer, D.A. Primary liver cancer: Pattern of metastasis. J. Surg. Oncol. 1987, 36, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.S.; Hanley, K.L.; Liang, Y.; Lin, X. Improving the Efficacy of Liver Cancer Immunotherapy: The Power of Combined Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. S1), 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiam-Galvez, K.J.; Allen, B.M.; Spitzer, M.H. Systemic immunity in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassim, S.; Pouyssegur, J. Tumor Microenvironment: A Metabolic Player that Shapes the Immune Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keenan, B.P.; Fong, L.; Kelley, R.K. Immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: The complex interface between inflammation, fibrosis, and the immune response. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. Natural Killer Cells in Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma and the NK Cell-Based Immunotherapy. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1206737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Min, H. Ginseng, the ‘Immunity Boost’: The Effects of Panax ginseng on Immune System. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hyun, S.H.; Ahn, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; So, S.H.; In, G.; Park, C.K.; Han, C.K. Immuno-enhancement effects of Korean Red Ginseng in healthy adults: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, E.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.H.; Hong, S.B.; Rhee, M.H. A comparative study on immune-stimulatory and antioxidant activities of various types of ginseng extracts in murine and rodent models. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Hyun, S.H.; Han, C.K. Red ginseng monograph. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, G.; Xu, J.; Qian, F.; Chen, Z. CD147, MMP-2, MMP-9 and MVD-CD34 are significant predictors of recurrence after liver transplantation in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Qin, G.; Dang, Y.W.; Yang, J. The prospective role of matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 and transforming growth factor beta 1 in accelerating the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2017, 6, S229–S231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Jung, J. Upregulation of G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor by Chrysin-Nanoparticles Inhibits Tumor Proliferation and Metastasis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Xenograft Model. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 560605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Shi, K.; Ran, C.; et al. SPARC Negatively Correlates With Prognosis After Transarterial Chemoembolization and Facilitates Proliferation and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via ERK/MMP Signaling Pathways. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.Y.; Kim, W.K. Red ginseng extract reduced metastasis of colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Ginseng Res. 2011, 35, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.; Lee, H.; Park, D.; Ahn, J.; Shin, S.S.; Yoon, M. Ginseng and Its Active Components Ginsenosides Inhibit Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Cells by Regulating MMP-2 and MMP-9. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. Ecam 2012, 2012, 265023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albertsson, P.; Kim, M.H.; Jonges, L.E.; Kitson, R.P.; Kuppen, P.J.; Johansson, B.R.; Nannmark, U.; Goldfarb, R.H. Matrix metalloproteinases of human NK cells. In Vivo 2000, 14, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.H.; Maki, G.; Klingemann, H.G. Characterization of a human cell line (NK-92) with phenotypical and functional characteristics of activated natural killer cells. Leukemia 1994, 8, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.W. Platelets impair natural killer cell reactivity and function in endometriosis through multiple mechanisms. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 32, 794–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placke, T.; Kopp, H.G.; Salih, H.R. Modulation of natural killer cell anti-tumor reactivity by platelets. J. Innate Immun. 2011, 3, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiola, I. Immune Circuits to Shape Natural Killer Cells in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.R.; Yu, J.Y.; Lee, J.J.; You, S.H.; Chung, J.H.; Noh, J.Y.; Im, J.H.; Han, X.H.; Kim, T.J.; Shin, K.S.; et al. Antithrombotic and antiplatelet activities of Korean red ginseng extract. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 100, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Kim, M.; Rhee, M.H. Anti-platelet role of Korean ginseng and ginsenosides in cardiovascular diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, K.E.; Mikkola, A.M.; Stepanek, A.M.; Vernet, A.; Hall, C.D.; Sun, C.C.; Yildirim, E.; Staropoli, J.F.; Lee, J.T.; Brown, D.E. Practical murine hematopathology: A comparative review and implications for research. Comp. Med. 2015, 65, 96–113. [Google Scholar]
- Sakkal, S.; Miller, S.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Nurgali, K. Eosinophils in Cancer: Favourable or Unfavourable? Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 650–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisaru-Tal, S.; Itan, M.; Klion, A.D.; Munitz, A. A new dawn for eosinophils in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichman, H.; Karo-Atar, D.; Munitz, A. Emerging Roles for Eosinophils in the Tumor Microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichman, H.; Itan, M.; Rozenberg, P.; Yarmolovski, T.; Brazowski, E.; Varol, C.; Gluck, N.; Shapira, S.; Arber, N.; Qimron, U.; et al. Activated Eosinophils Exert Antitumorigenic Activities in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Loffredo, S.; Lucarini, V.; Marone, G.; Mattei, F.; Marone, G.; Schiavoni, G. Eosinophils: The unsung heroes in cancer? Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1393134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, B.P.; Rothenberg, M.E. Eosinophils and cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogasawara, H.; Furuno, M.; Edamura, K.; Noguchi, M. Peptides of major basic protein and eosinophil cationic protein activate human mast cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 21, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, M.S.; Wheatley, C.L.; Slifman, N.R.; Gleich, G.J. Activation of platelets by eosinophil granule proteins. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattei, F.; Andreone, S.; Marone, G.; Gambardella, A.R.; Loffredo, S.; Varricchi, G.; Schiavoni, G. Eosinophils in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1273, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Zeng, P.; Xu, J.; Diao, H. The Contradictory Role of Interleukin-33 in Immune Cells and Tumor Immunity. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7527–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic, I.P.; Pejnovic, N.N.; Radosavljevic, G.D.; Pantic, J.M.; Milovanovic, M.Z.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Lukic, M.L. Interleukin-33/ST2 axis promotes breast cancer growth and metastases by facilitating intratumoral accumulation of immunosuppressive and innate lymphoid cells. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1669–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Razumilava, N.; Gores, G.J.; Walters, S.; Mizuochi, T.; Mourya, R.; Bessho, K.; Wang, Y.H.; Glaser, S.S.; Shivakumar, P.; et al. Biliary repair and carcinogenesis are mediated by IL-33-dependent cholangiocyte proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3241–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, K.; Qi, S.; Zhang, J.; Zgodzinski, W.; Majewski, M.; Wallner, G.; Gozdz, S.; Macek, P.; et al. IL33 Promotes Colon Cancer Cell Stemness via JNK Activation and Macrophage Recruitment. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dominguez, D.; Ye, C.; Geng, Z.; Chen, S.; Fan, J.; Qin, L.; Long, A.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Exogenous IL-33 Restores Dendritic Cell Activation and Maturation in Established Cancer. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Bai, L.; Dong, W.; Gao, K.; Shi, G.; Xia, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L. Transgenic expression of IL-33 activates CD8(+) T cells and NK cells and inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, S.; Kimura, M.; Ohnishi, M. Induction of neutrophil accumulation by red ginseng. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1990, 30, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Suk, K.T.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Sung, H.T.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, M.J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; et al. Anti-oxidant and natural killer cell activity of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) and urushiol (Rhus vernicifera Stokes) on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease of rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2013, 55, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Control | KRG | NK Cells | Combination | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||||
| RBC (×106 cells/μL) | 8.58 ± 0.66 | 8.06 ± 0.3 | 7.41 ± 1.06 | 7.95 ± 0.15 | |
| HGB (g/dL) | 14 ± 0.9 | 13 ± 0.36 | 12.87 ± 0.51 | 10 ± 5.74 | |
| HCT (%) | 47.3 ± 4.29 | 44.43 ± 0.45 | 40.6 ± 6.52 | 42.78 ± 1.79 | |
| RDW (%) | 15.27 ± 0.75 | 15.4 ± 0.62 | 15.33 ± 0.55 | 14.63 ± 0.62 | |
| MPV (fL) | 8.5 ± 1.67 | 12.57 ± 3.19 | 11.03 ± 3.32 | 8.2 ± 1.36 | |
| PLT (×103 cells/μL) | 257 ± 51.26 | 158.67 ± 27.54 * | 213.67 ± 136.7 | 484.5 ± 112.2 * | |
| WBC (×103 cells/μL) | NEU | 1.24 ± 0.18 | 1.33 ± 0.17 | 1.23 ± 0.24 | 0.93 ± 0.4 |
| LYM | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.11 | 0.13 ± 0 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | |
| MONO | 0.01 ± 0.05 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | |
| EOS | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | |
| BASO | 0.0 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | |
| LUC | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | |
| Total | 1.48 ± 0.21 | 1.73 ± 0.29 | 1.44 ± 0.24 | 1.23 ± 0.43 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, H.J.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.H.; Cho, H.; Jung, J. Korean Red Ginseng Enhances Immunotherapeutic Effects of NK Cells via Eosinophils in Metastatic Liver Cancer Model. Nutrients 2022, 14, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010134
Kwon HJ, Lee S, Lee HH, Cho H, Jung J. Korean Red Ginseng Enhances Immunotherapeutic Effects of NK Cells via Eosinophils in Metastatic Liver Cancer Model. Nutrients. 2022; 14(1):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010134
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Hee Jung, Sunyi Lee, Hwan Hee Lee, Hyosun Cho, and Joohee Jung. 2022. "Korean Red Ginseng Enhances Immunotherapeutic Effects of NK Cells via Eosinophils in Metastatic Liver Cancer Model" Nutrients 14, no. 1: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010134
APA StyleKwon, H. J., Lee, S., Lee, H. H., Cho, H., & Jung, J. (2022). Korean Red Ginseng Enhances Immunotherapeutic Effects of NK Cells via Eosinophils in Metastatic Liver Cancer Model. Nutrients, 14(1), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010134







