NSAID-Induced Enteropathy Affects Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Production by Decreasing GLP-1 Secretion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Care
2.2. Study Design
2.3. NSAID Gavage Experiment
2.4. Energy Balance Calculations
2.5. Glucose Homeostasis Studies
2.6. Insulin Measurement by ELISA
2.7. GLP-1 Measurement Experiment
2.8. H & E Staining and Imaging
2.9. Immunofluorescence Antibody Staining
2.10. Confocal Imaging and Image Processing
2.11. GLP-1 Antagonist (Exendin-9) Experiment
2.12. Hyper-Insulinemic Euglycemic Clamp Study
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
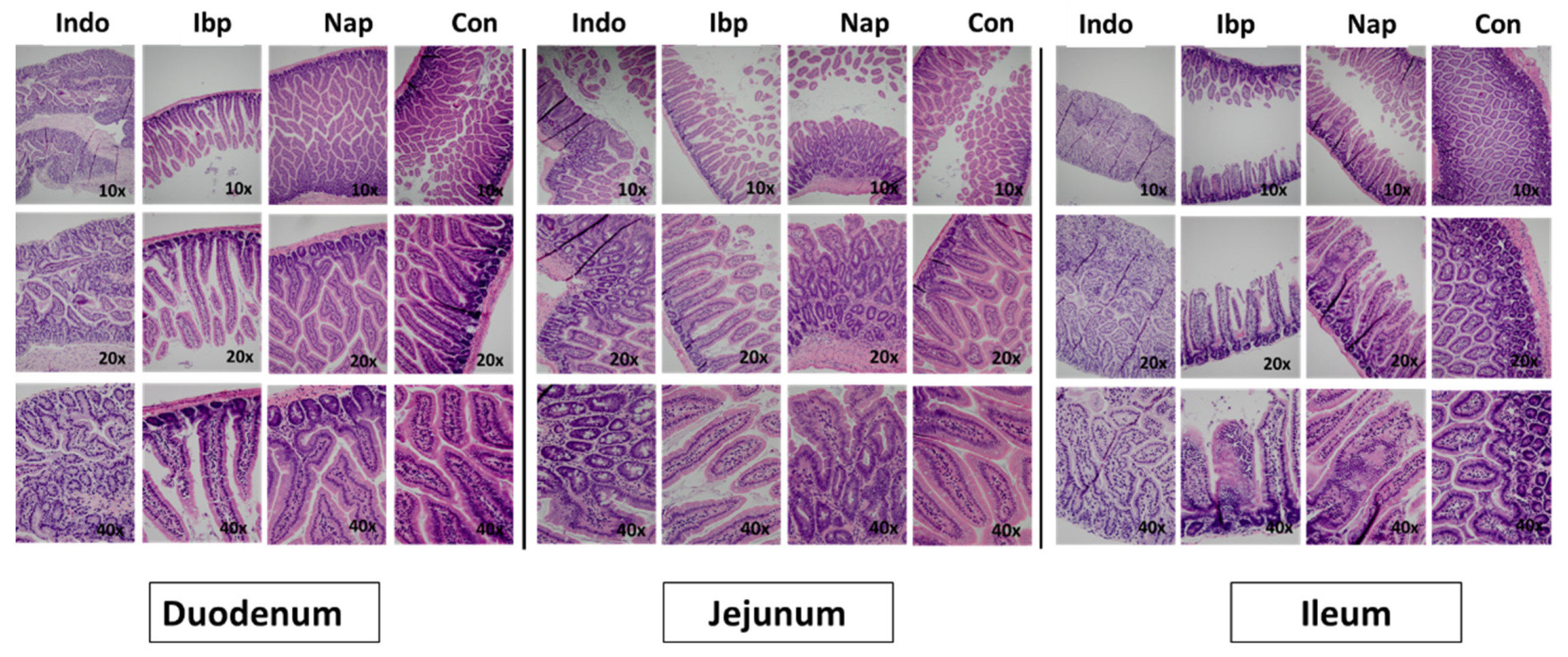
3.1. A Murine Model of NSAID-Induced Enteropathy
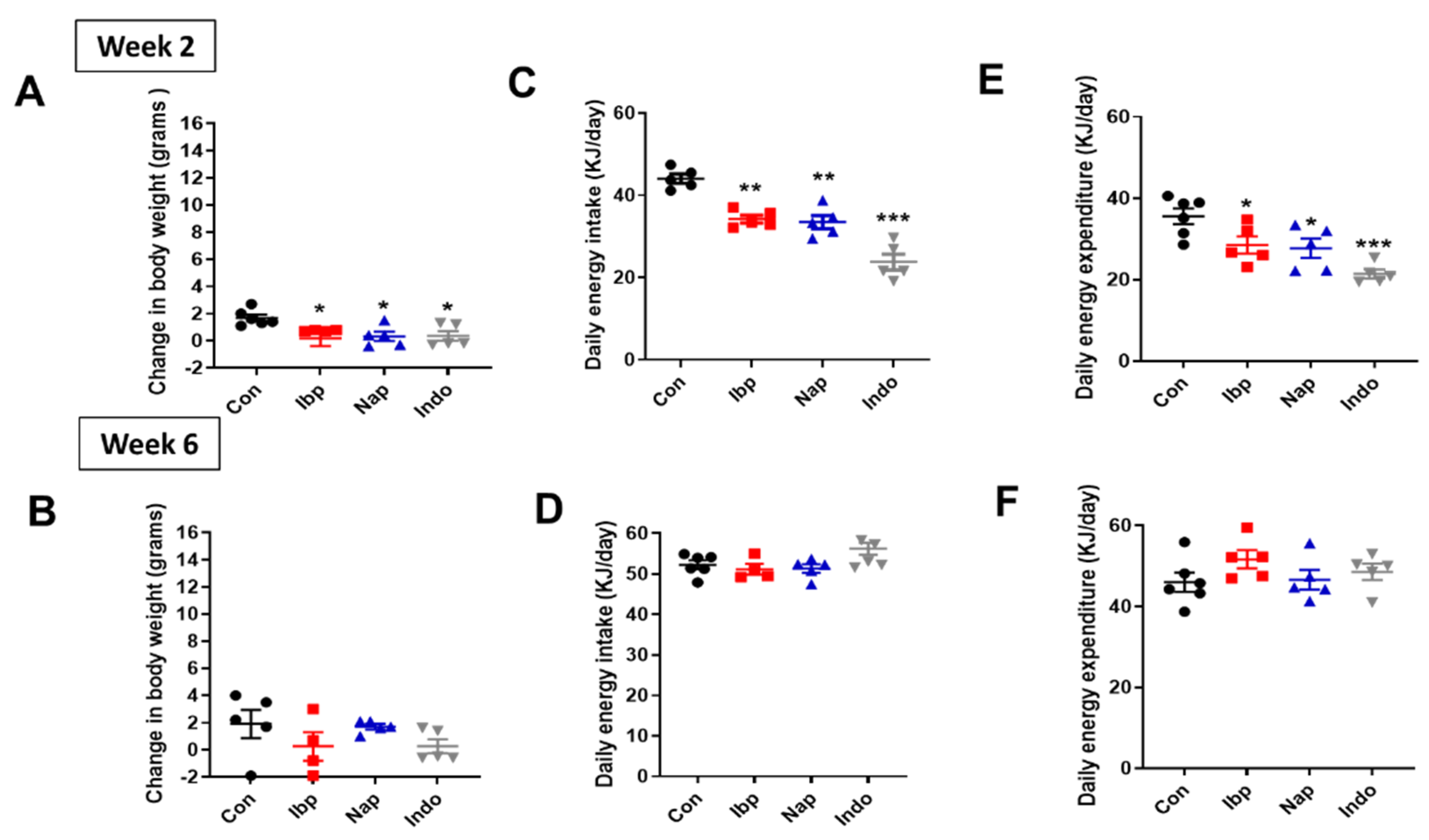
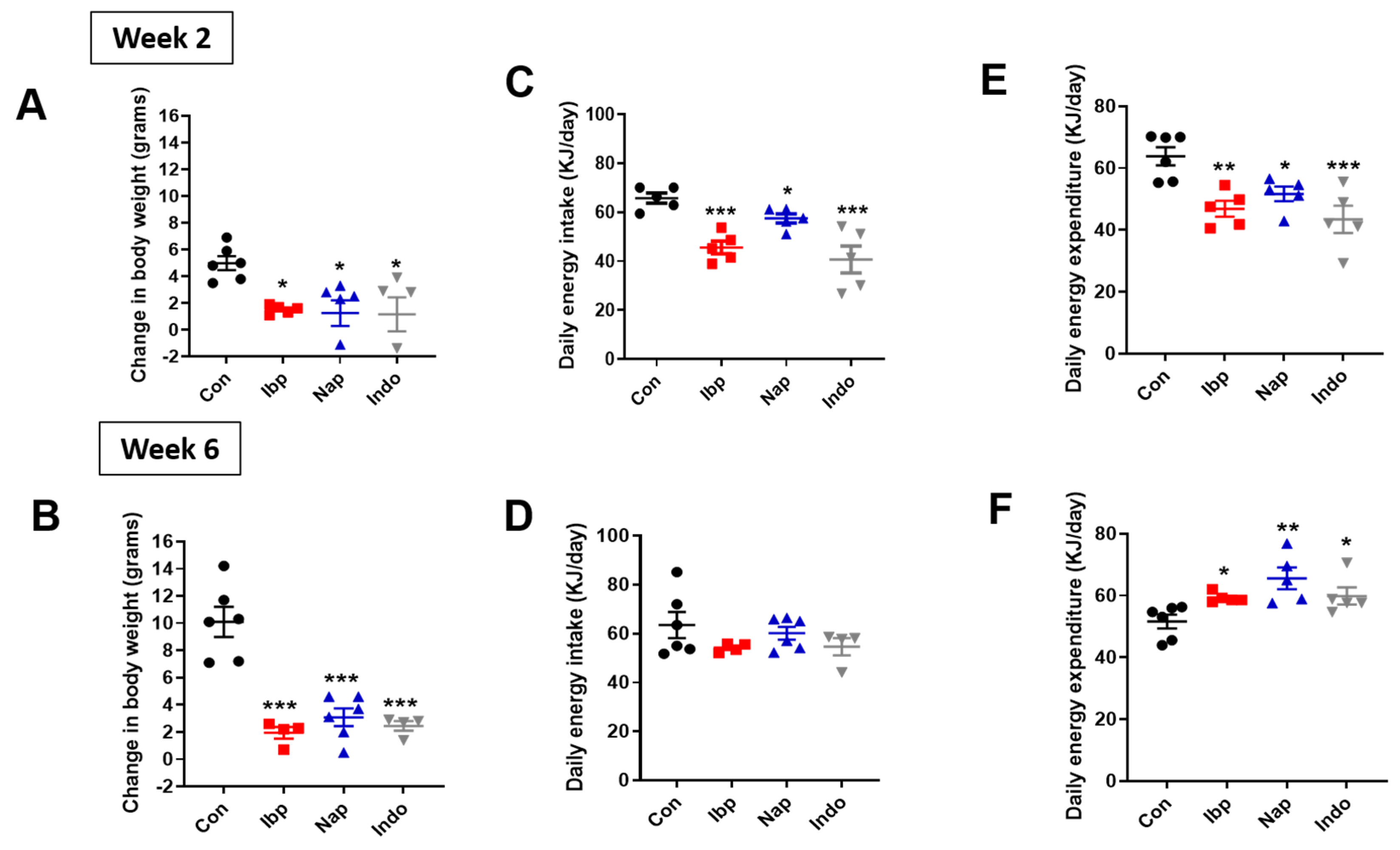
3.2. Prolonged NSAIDs Intake Protects against Weight Gain on HFD
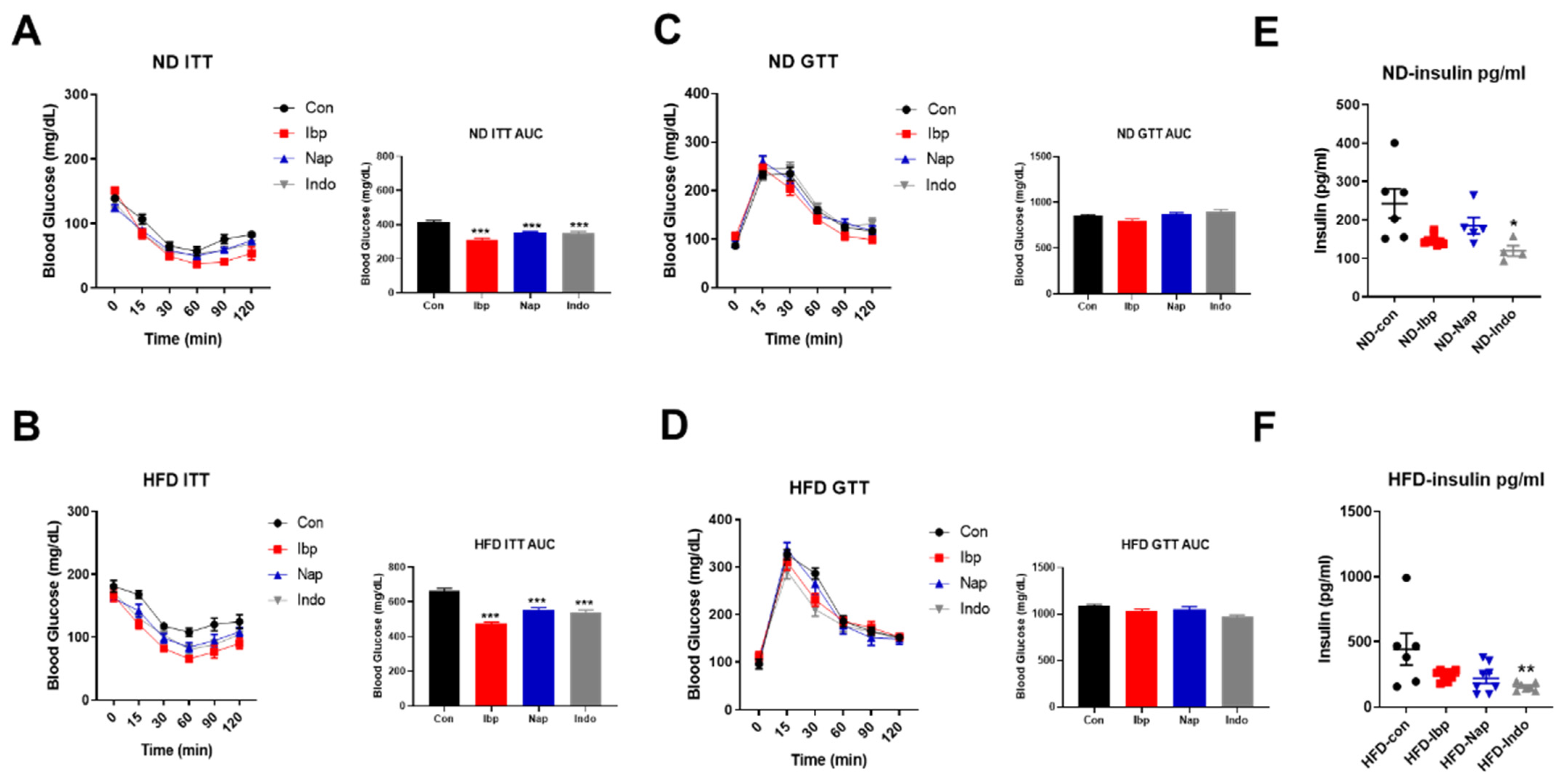
3.3. Mice Receiving NSAIDs Exhibit Improved Insulin Sensitivity but Not Glucose Tolerance
3.4. NSAIDs Attenuates Incretin GLP-1 Secretion
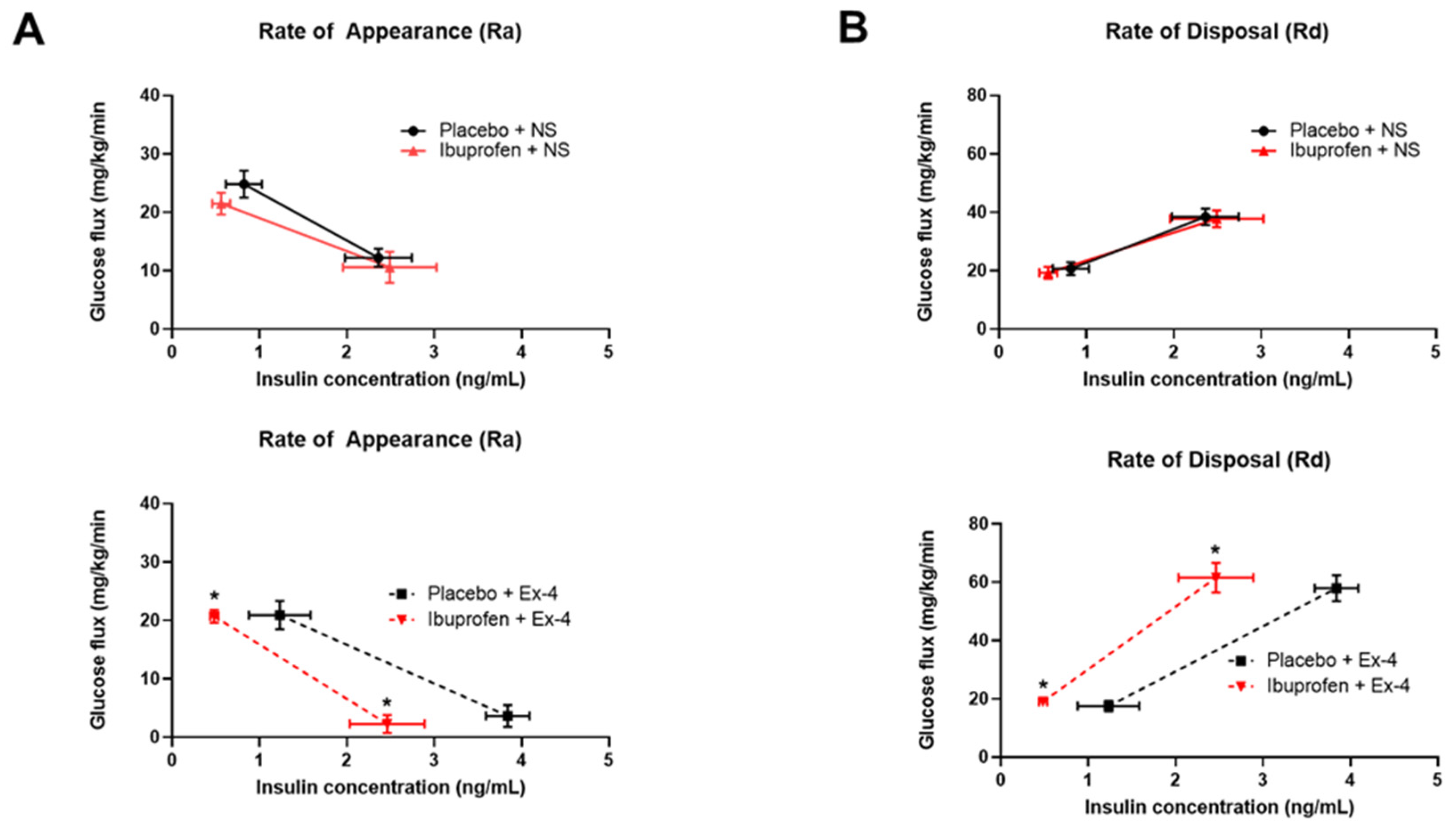
3.5. Exendin-9 Does Not Affect Oral Glucose Tolerance of Ibuprofen-Treated Mice While Exendin-4 Improves Their Insulin-Mediated Glucose Regulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shack, M.E. Drug induced ulceration and perforation of the small bowel. Ariz Med. 1966, 23, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kent, T.H.; Cardelli, R.M.; Stamler, F.W. Small Intestinal Ulcers and Intestinal Flora in Rats Given Indomethacin. Am. J. Pathol. 1969, 54, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, M.C.; Allan, G.H.; Torrance, C.J.; Lee, F.D.; Russell, R.I. Gastrointestinal Damage associated with the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. N. Eng. J. Med. 1992, 327, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnason, I.; Zanelli, G.; Smith, T.; Prouse, P.; Williams, P.; Smethurst, P.; Decacey, G.; Gumpel, M.J.; Levi, A.J. Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drug-Induced Intestinal Inflammation in Humans. Gastroenterology 1987, 93, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.; Williams, P.; So, J.D.; Zanelli, A.; Levi, A.J.; Gumpel, J.M.; Peters, T.J.; Ansell, B. Intestinal permeability and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis: Effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Lancet 1984, 8413, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.; Hayllar, J.; Macpherson, A.J.; Russell, A.S. Side Effects of Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs on the Small and Large Intestine in Humans. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 1832–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengeling, R.W.; Mitros, F.A.; Brennan, J.A.; Schulze, K.S. Ulcerative Ileitis Encountered at Ileo-Colonoscopy: Likely Role of Nonsteroidal Agents. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 1, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, L.; Thjodleifsson, B.; Seigal, A.; Bjarnason, I.I.; Scott, D.; Birgisson, S.; Bjarnason, I. Long-term effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cyclooxygenase-2 selective agents on the small bowel: A cross-sectional capsule enteroscopy study. Clin. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007, 5, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnason, I.; Scarpignato, C.; Holmgren, E.; Olszewski, M.; Rainsford, K.D.; Lanas, A. Mechanisms of Damage to the Gastrointestinal Tract From Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gummin, D.D.; Mowry, J.B.; Beuhler, M.C.; Spyker, D.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Dibert, K.W.; Rivers, L.J.; Pham, N.P.; Ryan, M.L. 2019 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 37th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol (Phila) 2020, 58, 1360–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spreckley, E.; Murphy, K.G. The L-Cell in Nutritional Sensing and the Regulation of Appetite. Front. Nutr. 2015, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Ionut, V.; Mooradian, V.; Stefanovski, D.; Bergman, R.N. Exenatide sensitizes insulin-mediated whole-body glucose disposal and promotes uptake of exogenous glucose by the liver. Diabetes 2009, 58, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, P.; Chepurny, O.G.; Holz, G.G. Regulation of glucose homeostasis by GLP-1. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2014, 121, 23–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadden, T.A.; Hollander, P.; Klein, S.; Niswender, K.; Woo, V.; Hale, P.M.; Aronne, L. NN8022-1923 Investigators. Weight maintenance and additional weight loss with liraglutide after low-calorie-diet-induced weight loss: The SCALE Maintenance randomized study. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, P.M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; McGowan, B.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; Wharton, S.; Carson, C.G.; Jepsen, C.H.; Kabisch, M.; Wilding, J.P.H. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide compared with liraglutide and placebo for weight loss in patients with obesity: A randomised, double-blind, placebo and active controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, J.; Finlayson, G.; Axelsen, M.; Flint, A.; Gibbons, C.; Kvist, T.; Hjerpsted, J.B. Effects of once-weekly semaglutide on appetite, energy intake, control of eating, food preference and body weight in subjects with obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J.; Nauck, M.A. The incretin system: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2006, 368, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, Y.; Gutman, R.; LeDuc, C.A.; Leibel, R.L. Estimating energy expenditure in mice using an energy balance technique. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, N.G.; Levitsky, D.A.; Strupp, B. Enhanced thermogenesis during recovery from diet-induced weight gain in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, R1380–R1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, S.W.; Trayhurn, P. Effect of high fat diets on energy balance and thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue of lean and genetically obese ob/ob mice. J. Nutr. 1987, 117, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, J.D.; Webster, A.J. The energy cost of fat and protein deposition in the rat. Br. J. Nutr. 1977, 37, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggert, D.L.; Nielsen, M.K. Comparison of feed energy costs of maintenance, lean deposition, and fat deposition in three lines of mice selected for heat loss. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mokadem, M.; Zechner, J.F.; Margolskee, R.F.; Drucker, D.J.; Aguirre, V. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on energy and glucose homeostasis are preserved in two mouse models of functional glucagon-like peptide-1 deficiency. Mol. Metab. 2013, 3, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, L.; Kieffer, T.J.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1, but not glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, regulates fasting glycemia and nonenteral glucose clearance in mice. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fang, W.F.; Broughton, A.; Jacobson, E.D. Indomethacin-induced intestinal inflammation. Amer. J. Dig. Dis. 1977, 22, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, D.A.; Cook, P.G.; Bauer, B.J.; Dagle, G.E. Indomethacin-induced intestinal lesions in the rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1970, 17, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, A.; Asano, T. Resistance of germfree rats to indomethacin-induced lesions. Prostaglandins 1977, 14, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.M.; Sun, E.W.; Keating, D.J. Review: Mechanisms Controlling Hormone Secretion in Human Gut and Its Relevance to Metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 244, R1–R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, J.; Trautmann, M.; Wilhelm, K.; Taylor, K.; Kendall, D.M. Exenatide once weekly for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, J.E.; Bracy, D.P.; James, F.D.; Burmeister, M.A.; Wasserman, D.H.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor knockout mice are protected from high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4678–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas, E.; Wood, J.A.; Stanojevic, V.; Habener, J.F. Glucagon-like peptide-1(9–36)amide metabolite inhibits weight gain and attenuates diabetes and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, W.; Shao, W.; Chiang, Y.T.; Jin, T. GLP-1-derived nonapeptide GLP-1(28–36)amide represses hepatic gluconeogenic gene expression and improves pyruvate tolerance in high-fat diet-fed mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E1348–E1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, M.A.; Ferre, T.; Ayala, J.E.; King, E.M.; Holt, R.M.; Ayala, J.E. Acute activation of central GLP-1 receptors enhances hepatic insulin action and insulin secretion in high-fat-fed, insulin resistant mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E334–E343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjære, E.; Aune, U.L.; Røen, K.; Keenan, A.H.; Ma, T.; Borkowski, K.; Kristensen, D.M.; Novotny, G.W.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Hudson, B.D.; et al. Indomethacin treatment prevents high fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance but not glucose intolerance in C57BL/6J mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 16032–16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimura, N.; Otani, K.; Watanabe, T.; Nakatsu, G.; Shimada, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Nadatani, Y.; Hosomi, S.; Tanaka, F.; Kamata, N.; et al. High-fat diet-mediated dysbiosis exacerbates NSAID-induced small intestinal damage through the induction of interleukin-17A. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.L.; Syer, S.; Denou, E.; dePalma, G.; Vong, L.; McKnight, W.; Jury, J.; Bolla, M.; Bercik, P.; Collins, S.M.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors exacerbate NSAID-induced small intestinal injury by inducing dysbiosis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Advani, M.A.; Peng, H.L.; Banfield, E.; Hawk, E.T.; Chang, S.; Frazier-Wood, A.C. Use on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug in US drugs: Change over time and by demographic. Open Heart 2015, 1, e000248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.J.; Noh, C.K.; Lim, S.G.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, K.J. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced enteropathy. Intest. Res. 2017, 15, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herz, H.; Song, Y.; Ye, Y.; Tian, L.; Linden, B.; Abu El Haija, M.; Chu, Y.; Grobe, J.L.; Lengeling, R.W.; Mokadem, M. NSAID-Induced Enteropathy Affects Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Production by Decreasing GLP-1 Secretion. Nutrients 2022, 14, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010120
Herz H, Song Y, Ye Y, Tian L, Linden B, Abu El Haija M, Chu Y, Grobe JL, Lengeling RW, Mokadem M. NSAID-Induced Enteropathy Affects Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Production by Decreasing GLP-1 Secretion. Nutrients. 2022; 14(1):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010120
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerz, Hussein, Yang Song, Yuanchao Ye, Liping Tian, Benjamin Linden, Marwa Abu El Haija, Yi Chu, Justin L. Grobe, Randall W. Lengeling, and Mohamad Mokadem. 2022. "NSAID-Induced Enteropathy Affects Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Production by Decreasing GLP-1 Secretion" Nutrients 14, no. 1: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010120
APA StyleHerz, H., Song, Y., Ye, Y., Tian, L., Linden, B., Abu El Haija, M., Chu, Y., Grobe, J. L., Lengeling, R. W., & Mokadem, M. (2022). NSAID-Induced Enteropathy Affects Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Production by Decreasing GLP-1 Secretion. Nutrients, 14(1), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010120






