Metabolic Control of Patients with Phenylketonuria in a Portuguese Metabolic Centre Comparing Three Different Recommendations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Nutritional Intake
- -
- PKU diet only: Phe restricted diet supplemented with PS and SLPFs
- -
- BH4 + diet: BH4 treated patients with Phe restriction and ±PS
- -
- Non-restricted diet: without PS or BH4 prescription
2.3.2. BH4
2.3.3. Metabolic Control
2.4. Ethical Statement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Cohort
3.2. Nutritional Intake
3.3. Metabolic Control—Portuguese Consensus
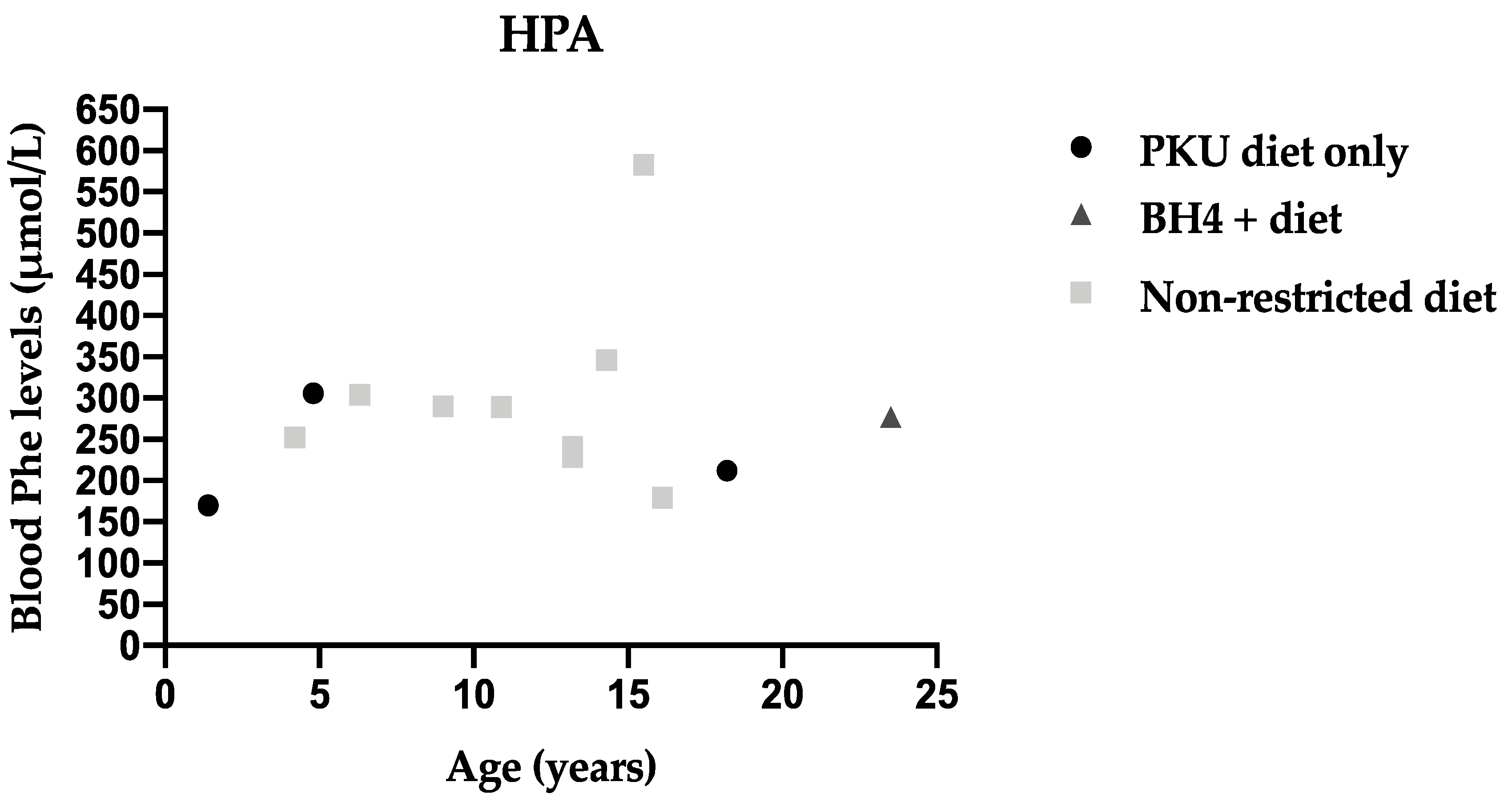
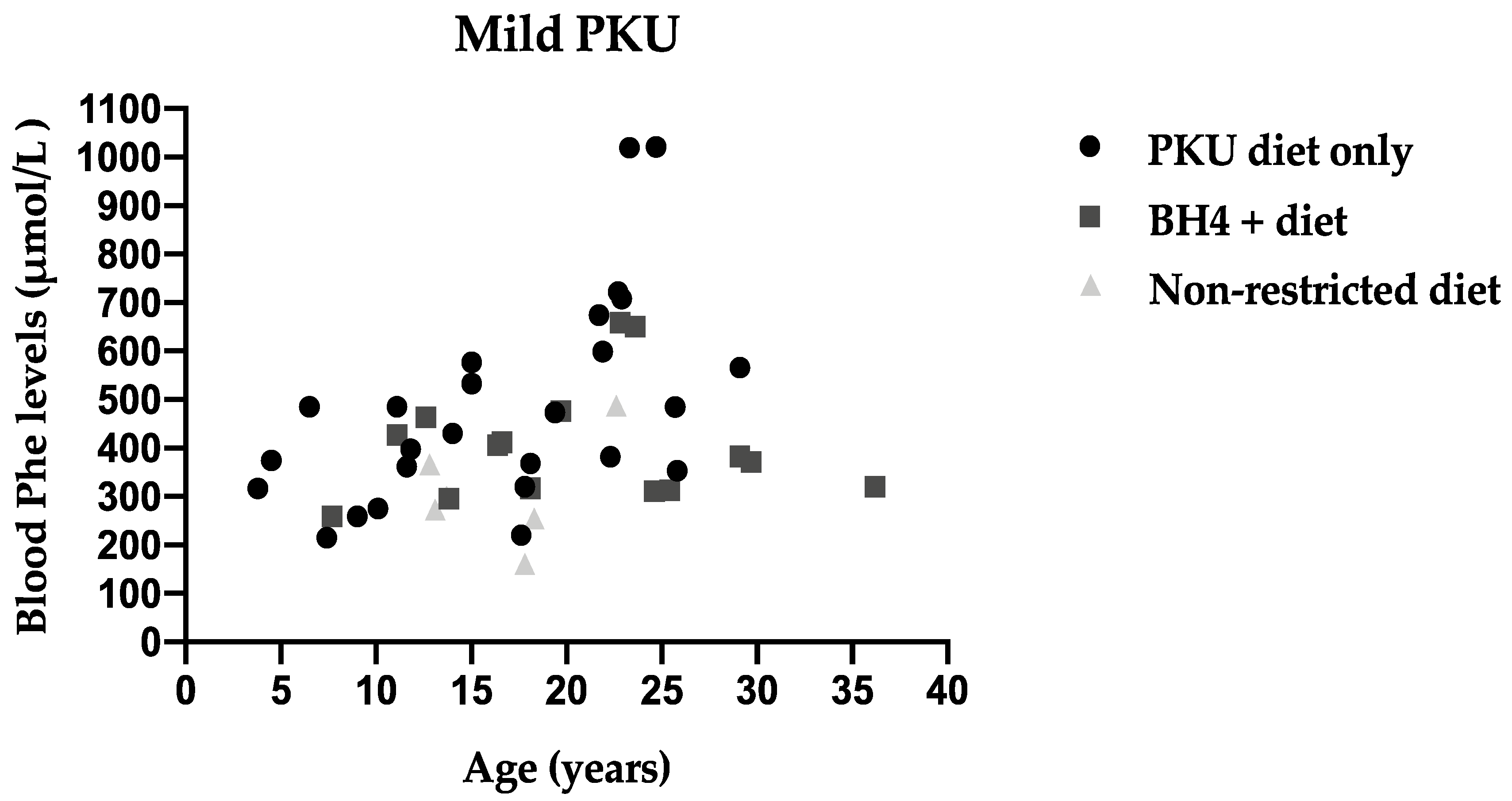
3.4. Metabolic Control Comparing Three Different Recommendations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Wegberg, A.M.J.; MacDonald, A.; Ahring, K.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Blau, N.; Bosch, A.M.; Burlina, A.; Campistol, J.; Feillet, F.; Giżewska, M.; et al. The complete European guidelines on phenylketonuria: Diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Didycz, B.; Nitecka, M.; Bik-Multanowski, M. The Use of d2 and Benton Tests for Assessment of Attention Deficits and Visual Memory in Teenagers with Phenylketonuria. JIMD Rep. 2018, 40, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, A.; van Wegberg, A.M.J.; Ahring, K.; Beblo, S.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Burlina, A.; Campistol, J.; Coşkun, T.; Feillet, F.; Giżewska, M.; et al. PKU dietary handbook to accompany PKU guidelines. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, A.; Rocha, J.C.; van Rijn, M.; Feillet, F. Nutrition in phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, S10–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, M.J.; Almeida, M.F.; van Dam, E.; Ahring, K.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Dokoupil, K.; Gokmen-Ozel, H.; Lammardo, A.M.; MacDonald, A.; Robert, M.; et al. Special low protein foods for phenylketonuria: Availability in Europe and an examination of their nutritional profile. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pena, M.J.; de Almeida, M.F.; van Dam, E.; Ahring, K.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Dokoupil, K.; Gokmen-Ozel, H.; Lammardo, A.M.; MacDonald, A.; Robert, M.; et al. Protein substitutes for phenylketonuria in Europe: Access and nutritional composition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.; Evans, S.; Chahal, S.; Santra, S.; Pinto, A.; Jackson, R.; Gingell, C.; Rocha, J.C.; Van Spronsen, F.J.; MacDonald, A. Glycomacropeptide: Long-term use and impact on blood phenylalanine, growth and nutritional status in children with PKU. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, M.J.; Pinto, A.; de Almeida, M.F.; de Sousa Barbosa, C.; Ramos, P.C.; Rocha, S.; Guimas, A.; Ribeiro, R.; Martins, E.; Bandeira, A.; et al. Continuous use of glycomacropeptide in the nutritional management of patients with phenylketonuria: A clinical perspective. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.; Almeida, M.F.; Ramos, P.C.; Rocha, S.; Guimas, A.; Ribeiro, R.; Martins, E.; Bandeira, A.; MacDonald, A.; Rocha, J.C. Nutritional status in patients with phenylketonuria using glycomacropeptide as their major protein source. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurecki, E.R.; Cederbaum, S.; Kopesky, J.; Perry, K.; Rohr, F.; Sanchez-Valle, A.; Viau, K.S.; Sheinin, M.Y.; Cohen-Pfeffer, J.L. Adherence to clinic recommendations among patients with phenylketonuria in the United States. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.H.; White, F.J.; Hall, S.K.; MacDonald, A.; Rylance, G.; Boneh, A.; Francis, D.E.; Shortland, G.J.; Schmidt, M.; Vail, A. How practical are recommendations for dietary control in phenylketonuria? Lancet 2002, 360, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntau, A.C.; Adams, D.J.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Bushueva, T.V.; Cerone, R.; Chien, Y.H.; Chiesa, A.; Coşkun, T.; de Las Heras, J.; Feillet, F.; et al. International best practice for the evaluation of responsiveness to sapropterin dihydrochloride in patients with phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, N.; Dimmock, D.; Levy, H.; Viau, K.; Bausell, H.; Bilder, D.A.; Burton, B.; Gross, C.; Northrup, H.; Rohr, F.; et al. Evidence- and consensus-based recommendations for the use of pegvaliase in adults with phenylketonuria. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1851–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waisbren, S.E.; Schnell, R.R.; Levy, H.L. Diet termination in children with phenylketonuria: A review of psychological assessments used to determine outcome. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1980, 3, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisbren, S.E.; Noel, K.; Fahrbach, K.; Cella, C.; Frame, D.; Dorenbaum, A.; Levy, H. Phenylalanine blood levels and clinical outcomes in phenylketonuria: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2007, 92, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, L.; Geberhiwot, T.; MacDonald, A.; Limback, E.; Hall, S.K.; Romani, C. Cognitive outcomes in early-treated adults with phenylketonuria (PKU): A comprehensive picture across domains. Neuropsychology 2017, 31, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahja, R.; Huijbregts, S.C.J.; de Sonneville, L.M.J.; van der Meere, J.J.; Legemaat, A.M.; Bosch, A.M.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Rubio-Gozalbo, M.E.; Brouwers, M.; Hofstede, F.C.; et al. Cognitive profile and mental health in adult phenylketonuria: A PKU-COBESO study. Neuropsychology 2017, 31, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, R.; Burton, B.; Hoganson, G.; Peterson, R.; Rhead, W.; Rouse, B.; Scott, R.; Wolff, J.; Stern, A.M.; Guttler, F.; et al. Phenylketonuria in adulthood: A collaborative study. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2002, 25, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, C.; Palermo, L.; MacDonald, A.; Limback, E.; Hall, S.K.; Geberhiwot, T. The impact of phenylalanine levels on cognitive outcomes in adults with phenylketonuria: Effects across tasks and developmental stages. Neuropsychology 2017, 31, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vockley, J.; Andersson, H.C.; Antshel, K.M.; Braverman, N.E.; Burton, B.K.; Frazier, D.M.; Mitchell, J.; Smith, W.E.; Thompson, B.H.; Berry, S.A. Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency: Diagnosis and management guideline. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burgard, P.; Ullrich, K.; Ballhausen, D.; Hennermann, J.B.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Langeveld, M.; Karall, D.; Konstantopoulou, V.; Maier, E.M.; Lang, F.; et al. Issues with European guidelines for phenylketonuria. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha, J.C.; Vilarinho, L.; Cabral, A.; Osório, R.V.; Almeida, M.F. Consenso para o tratamento nutricional de fenilcetonúria (Article in Portuguese). Acta Pediatr. Port. 2007, 38, 44–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, C.; Almeida, M.F.; Sousa Barbosa, C.; Martins, E.; Janeiro, P.; Tavares de Almeida, I.; MacDonald, A.; Rocha, J.C. The European Phenylketonuria Guidelines and the challenges on management practices in Portugal. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 32, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint WHO/FAO/UNU Expert Consultation. Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in Human Nutrition; World Health Organization Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kraleva, D.; Evans, S.; Pinto, A.; Daly, A.; Ashmore, C.; Pointon-Bell, K.; Rocha, J.C.; MacDonald, A. Protein Labelling Accuracy for UK Patients with PKU Following a Low Protein Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbould, E.; Pinto, A.; Evans, S.; Ford, S.; O’Driscoll, M.; Ashmore, C.; Daly, A.; MacDonald, A. Accidental Consumption of Aspartame in Phenylketonuria: Patient Experiences. Nutrients 2021, 13, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weglage, J.; Fromm, J.; van Teeffelen-Heithoff, A.; Möller, H.E.; Koletzko, B.; Marquardt, T.; Rutsch, F.; Feldmann, R. Neurocognitive functioning in adults with phenylketonuria: Results of a long term study. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2013, 110, S44–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotto, A.; Zipser, C.M.; Leks, E.; Haas, D.; Gramer, G.; Freisinger, P.; Schaeffer, E.; Liepelt-Scarfone, I.; Brockmann, K.; Maetzler, W.; et al. Phenylalanine Effects on Brain Function in Adult Phenylketonuria. Neurology 2021, 96, e399–e411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaulent, P.; Charriere, S.; Feillet, F.; Douillard, C.; Fouilhoux, A.; Thobois, S. Neurological manifestations in adults with phenylketonuria: New cases and review of the literature. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, K.; van Ginkel, W.G.; van Dam, E.; de Blaauw, P.; Koehorst, M.; Kingma, H.A.; van Spronsen, F.J.; Heiner-Fokkema, M.R. Dried blood spot versus venous blood sampling for phenylalanine and tyrosine. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

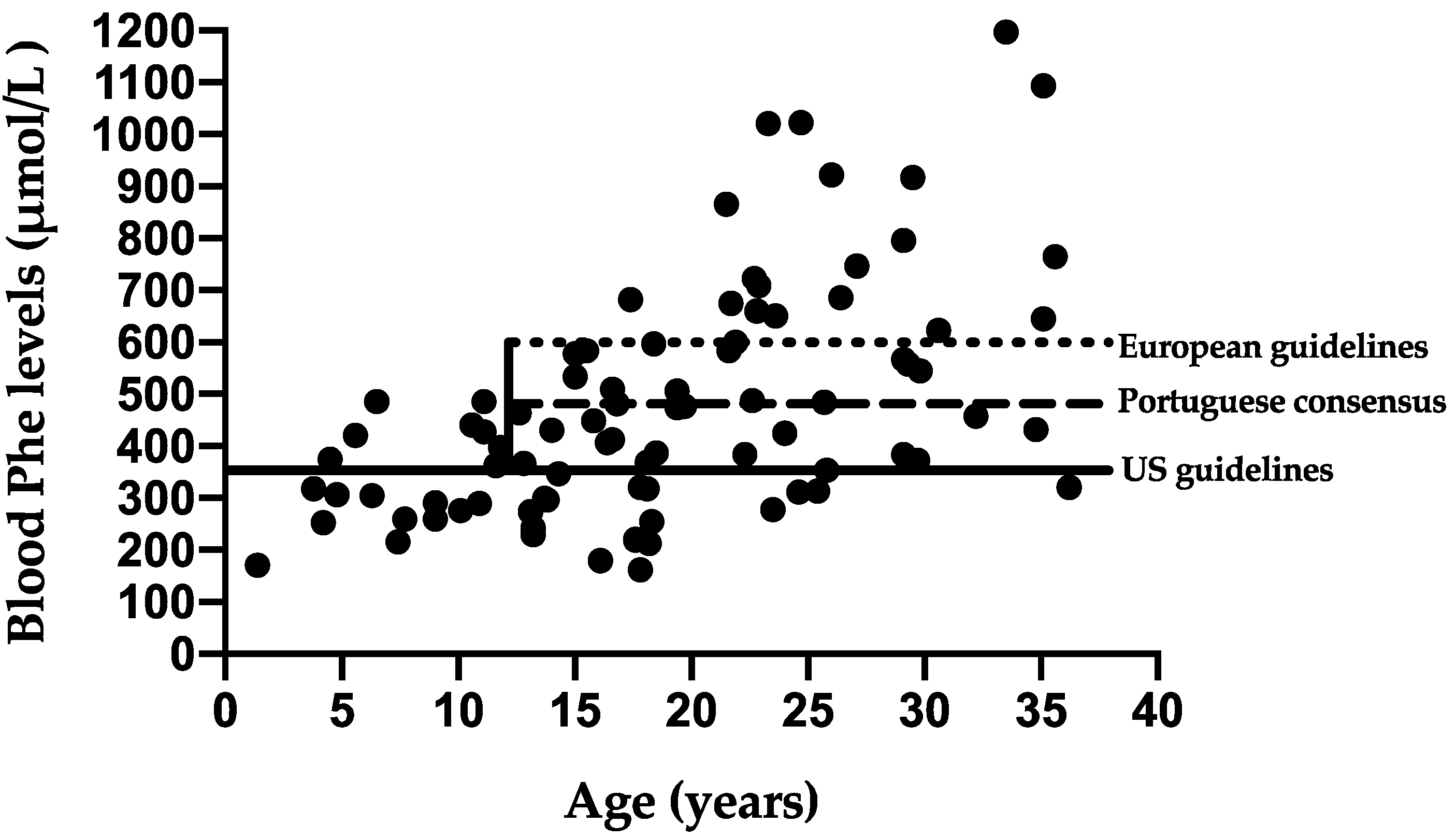
| Variable | <12 Years n (%) | ≥12 Years n (%) | Total n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 19 (22) | 68 (78) | 87 (100) | |
| Gender | Female | 8 (42) | 34 (50) | 42 (48) |
| Male | 11 (58) | 34 (50) | 45 (52) | |
| PKU severity | Classical PKU | 2 (11) | 25 (37) | 27 (31) |
| Mild PKU | 11 (58) | 36 (53) | 47 (54) | |
| HPA | 6 (32) | 7 (10) | 13 (15) | |
| Type of treatment | PKU diet only | 12 (63) | 38 (56) | 50 (57) |
| BH4 + diet | 3 (16) | 19 (28) | 22 (26) | |
| Non-restricted diet | 4 (21) | 11 (16) | 15 (17) | |
| Variable | Median Natural Protein (P25–P75) g/kg/Day | Median Protein Equivalent (P25–P75) g/kg/Day | Median Total Protein (P25–P75) g/kg/Day | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 0.69 (0.12–4.09) | 0.74 (0.00–1.55) | 1.54 (0.68–4.09) | |
| Age | <12 y (n = 19) | 0.69 (0.28–4.09) | 0.89 (0.00–1.55) | 1.84 (1.23–4.09) |
| ≥12 y (n = 68) | 0.69 (0.12–2.55) | 0.72 (0.00–1.32) | 1.46 (0.68–2.55) | |
| PKU Severity | Classical PKU (n = 27) | 0.40 (0.17–1.80) | 0.85 (0.00–1.32) | 1.37 (0.95–1.80) |
| Mild PKU (n = 47) | 0.69 (0.12–2.4) | 0.74 (0.00–1.55) | 1.54 (0.68–2.40) | |
| HPA (n = 13) | 1.97 (1.39–4.09) | 0.00 (0.00–0.51) | 2.10 (1.60–4.09) | |
| Type of treatment | PKU diet only (n = 50) | 0.48 (0.17–1.80) | 0.87 (0.08–1.55) | 1.47 (0.95–3.60) |
| BH4 + diet (n = 22) | 0.99 (0.24–1.84) | 0.63 (0.00–1.07) | 1.53 (0.68–2.19) | |
| Non-restricted diet (n = 15) | 1.97 (1.26–4.09) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 1.97 (1.26–4.09) | |
| <12 Years | ≥12 Years | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Median % of Blood Phe Levels within Target Range * | Median % of Blood Phe Levels within Target Range * | ||
| Sex | Female (n = 42) | 74 | 66 |
| Male (n = 45) | 45 | 41 | |
| PKU severity | Classical PKU (n = 27) | 34 | 28 |
| Mild PKU (n = 47) | 49 | 77 | |
| HPA (n = 13) | 91 | 100 | |
| Type of treatment | PKU diet only (n = 50) | 54 | 27 |
| BH4 + diet (n = 22) | 49 | 84 | |
| Non-restricted diet (n = 15) | 73 | 100 | |
| Median % of Blood Phe Levels within Target Range | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Portuguese Consensus % (p25–p75) | European Guidelines % (p25–p75) | US Guidelines % (p25–p75) | |
| Total | 56 (19–94) | 83 (36–100) | 26 (0–78) | |
| Age | <12 years (n = 19) | 56 (23–87) | 56 (23–87) | 56 (23–87) |
| ≥12 years (n = 68) | 54 (13–96) | 84 (38–100) | 17 (0–60) | |
| Gender | Female (n = 42) | 70 (23–98) | 89 (42–100) | 29 (0–81) |
| Male (n = 45) | 41 (13–89) | 66 (22–99) | 22 (0–59) | |
| PKU severity | HPA (n = 13) | 100 (84–100) | 100 (85–100) | 96 (7–100) |
| Mild PKU (n = 47) | 63 (19–94) | 84 (39–84) | 41 (0–76) | |
| Classical PKU (n = 27) | 27 (0–44) | 47 (4–83) | 6 (0–26) | |
| Type of treatment | PKU diet only (n = 50) | 32 (8–74) | 59 (14–91) | 15 (0–51) |
| BH4 diet (n = 22) | 76 (44–92) | 91 (66–100) | 32 (17–76) | |
| Non-restricted diet (n = 15) | 97 (33–100) | 100 (83–100) | 83 (13–100) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanufre, V.; Almeida, M.F.; Barbosa, C.S.; Carmona, C.; Bandeira, A.; Martins, E.; Rocha, S.; Guimas, A.; Ribeiro, R.; MacDonald, A.; et al. Metabolic Control of Patients with Phenylketonuria in a Portuguese Metabolic Centre Comparing Three Different Recommendations. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093118
Kanufre V, Almeida MF, Barbosa CS, Carmona C, Bandeira A, Martins E, Rocha S, Guimas A, Ribeiro R, MacDonald A, et al. Metabolic Control of Patients with Phenylketonuria in a Portuguese Metabolic Centre Comparing Three Different Recommendations. Nutrients. 2021; 13(9):3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093118
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanufre, Viviane, Manuela Ferreira Almeida, Catarina Sousa Barbosa, Carla Carmona, Anabela Bandeira, Esmeralda Martins, Sara Rocha, Arlindo Guimas, Rosa Ribeiro, Anita MacDonald, and et al. 2021. "Metabolic Control of Patients with Phenylketonuria in a Portuguese Metabolic Centre Comparing Three Different Recommendations" Nutrients 13, no. 9: 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093118
APA StyleKanufre, V., Almeida, M. F., Barbosa, C. S., Carmona, C., Bandeira, A., Martins, E., Rocha, S., Guimas, A., Ribeiro, R., MacDonald, A., Pinto, A., & Rocha, J. C. (2021). Metabolic Control of Patients with Phenylketonuria in a Portuguese Metabolic Centre Comparing Three Different Recommendations. Nutrients, 13(9), 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093118









