Association between Food Insecurity and Sarcopenia among Adults Aged ≥65 Years in Low- and Middle-Income Countries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sarcopenia
2.2. Food Insecurity
2.3. Control Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings and Comparison with Previous Literature
4.2. Interpretation of Findings
4.3. Public Health Implications and Areas for Future Research
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woo, J. Sarcopenia. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2017, 33, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Morley, J.E.; von Haehling, S. Welcome to the ICD-10 code for sarcopenia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D.; Von Haehling, S. Prevalence, incidence, and clinical impact of sarcopenia: Facts, numbers, and epidemiology—update 2014. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Haehling, S.; Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D. From muscle wasting to sarcopenia and myopenia: Update 2012. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2012, 3, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, A.; Jarjou, L.M.; Prentice, A.; Cooper, C.; Ebeling, P.R.; Ward, K.A. The prevalence of sarcopenia and relationships between muscle and bone in ageing West-African Gambian men and women. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, N.; Demurtas, J.; Soysal, P.; Smith, L.; Torbahn, G.; Schoene, D.; Schwingshackl, L.; Sieber, C.; Bauer, J.; Cesari, M. Sarcopenia and health-related outcomes: An umbrella review of observational studies. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 10, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, E.; Choi, K.M. Health Consequences of Sarcopenic Obesity: A Narrative Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: Aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, N.F.; Lee, D. Physical activity and sarcopenia in older adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 32, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koyanagi, A.; Veronese, N.; Solmi, M.; Oh, H.; Shin, J.I.; Jacob, L.; Yang, L.; Haro, J.M.; Smith, L. Fruit and vegetable consumption and sarcopenia among older adults in low-and middle-income countries. Nutrients 2020, 12, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganapathy, A.; Nieves, J.W. Nutrition and Sarcopenia—What Do We Know? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Chen, H.; Huang, S.; Liou, T. The role of muscle mass gain following protein supplementation plus exercise therapy in older adults with sarcopenia and frailty risks: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized trials. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, S.; Cooper, C.; Aihie Sayer, A. Nutrition and sarcopenia: A review of the evidence and implications for preventive strategies. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 510801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nord, M.; Andrews, M.; Carlson, S. Household Food Security in the United States, 2005; United States Department of Agriculture USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi, A.; Stubbs, B.; Oh, H.; Veronese, N.; Smith, L.; Haro, J.M.; Vancampfort, D. Food insecurity (hunger) and suicide attempts among 179,771 adolescents attending school from 9 high-income, 31 middle-income, and 4 low-income countries: A cross-sectional study. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 248, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, K.; Faeh, D.; Stettler, R.; Debard, C.; Loizon, E.; Vidal, H.; Boesch, C.; Ravussin, E.; Tappy, L. Effects of four-week high-fructose diet on gene expression in skeletal muscle of healthy men. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 34, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.; Petersen, C.; Gooding, T. Association of Food Insecurity and Sarcopenia: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Innov. Aging 2020, 4, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Zepeda, M.U. Food Insecurity and its association with sarcopenia elements. Innov. Aging 2017, 1, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, G.; Heshmat, R.; Ostovar, A.; Nabipour, I.; Larijani, B. Sarcopenia disease in Iran: An overview. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2019, 18, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2020: Transforming Food Systems for Affordable Healthy Diets; Food & Agriculture Org.: Rome, Italy, 2020; Volume 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kowal, P.; Chatterji, S.; Naidoo, N.; Biritwum, R.; Fan, W.; Lopez Ridaura, R.; Maximova, T.; Arokiasamy, P.; Phaswana-Mafuya, N.; Williams, S. Data resource profile: The World Health Organization Study on global AGEing and adult health (SAGE). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrovolas, S.; Koyanagi, A.; Olaya, B.; Ayuso-Mateos, J.L.; Miret, M.; Chatterji, S.; Tobiasz-Adamczyk, B.; Koskinen, S.; Leonardi, M.; Haro, J.M. Factors associated with skeletal muscle mass, sarcopenia, and sarcopenic obesity in older adults: A multi-continent study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Smith, L.; Barbagallo, M.; Yang, L.; Zou, L.; Haro, J.M.; Koyanagi, A. Sarcopenia and fall-related injury among older adults in five low-and middle-income countries. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 147, 111262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, T.; Peters, K.W.; Fragala, M.; Cawthon, P.M.; Harris, T.B.; McLean, R.; Shardell, M.; Alley, D.E.; Kenny, A.; Ferrucci, L. An evidence-based comparison of operational criteria for the presence of sarcopenia. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Wang, Z.; Heo, M.; Ross, R.; Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B. Total-body skeletal muscle mass: Development and cross-validation of anthropometric prediction models. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M. The FNIH sarcopenia project: Rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, O.; Russell, M.; Daley, T.L.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Waki, M.; Lichtman, S.; Wang, J.; Pierson Jr, R.N.; Heymsfield, S.B. Differences in skeletal muscle and bone mineral mass between black and white females and their relevance to estimates of body composition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 55, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrovolas, S.; Koyanagi, A.; Olaya, B.; Ayuso-Mateos, J.L.; Miret, M.; Chatterji, S.; Tobiasz-Adamczyk, B.; Koskinen, S.; Leonardi, M.; Haro, J.M. The role of muscle mass and body fat on disability among older adults: A cross-national analysis. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 69, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capistrant, B.D.; Glymour, M.M.; Berkman, L.F. Assessing mobility difficulties for cross-national comparisons: Results from the World Health Organization Study on Global AGEing and Adult Health. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrock, J.M.; McClure, H.H.; Snodgrass, J.J.; Liebert, M.A.; Charlton, K.E.; Arokiasamy, P.; Naidoo, N.; Kowal, P. Food insecurity partially mediates associations between social disadvantage and body composition among older adults in india: Results from the study on global AGE ing and adult health (SAGE). Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2017, 29, e23033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, A.; Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Vancampfort, D.; Stickley, A.; Oh, H.; Shin, J.I.; Jackson, S.; Smith, L.; Lara, E. Food insecurity is associated with mild cognitive impairment among middle-aged and older adults in South Africa: Findings from a nationally representative survey. Nutrients 2019, 11, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bull, F.C.; Maslin, T.S.; Armstrong, T. Global physical activity questionnaire (GPAQ): Nine country reliability and validity study. J. Phys. Act. Health 2009, 6, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stubbs, B.; Vancampfort, D.; Veronese, N.; Schofield, P.; Lin, P.; Tseng, P.; Solmi, M.; Thompson, T.; Carvalho, A.F.; Koyanagi, A. Multimorbidity and perceived stress: A population-based cross-sectional study among older adults across six low-and middle-income countries. Maturitas 2018, 107, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, B.; Vancampfort, D.; Firth, J.; Schuch, F.B.; Hallgren, M.; Smith, L.; Gardner, B.; Kahl, K.G.; Veronese, N.; Solmi, M. Relationship between sedentary behavior and depression: A mediation analysis of influential factors across the lifespan among 42,469 people in low-and middle-income countries. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 229, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conti, V.; Izzo, V.; Corbi, G.; Russomanno, G.; Manzo, V.; De Lise, F.; Di Donato, A.; Filippelli, A. Antioxidant supplementation in the treatment of aging-associated diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Yoshida, H.; Kim, H.; Shimada, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Iwasa, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Handa, S. A significant relationship between plasma vitamin C concentration and physical performance among Japanese elderly women. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Pahor, M.; Bartali, B.; Cherubini, A.; Penninx, B.W.; Williams, G.R.; Atkinson, H.; Martin, A.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. Antioxidants and physical performance in elderly persons: The Invecchiare in Chianti (InCHIANTI) study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davison, K.M.; Gondara, L.; Kaplan, B.J. Food insecurity, poor diet quality, and suboptimal intakes of folate and iron are independently associated with perceived mental health in Canadian adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, L.; Lee, W.; Peng, L.; Chen, L. Epidemiology of sarcopenia and factors associated with it among community-dwelling older adults in Taiwan. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 357, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurpad, A.V.; Muthayya, S.; Vaz, M. Consequences of inadequate food energy and negative energy balance in humans. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 1053–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazerghi, C.; McKay, F.H.; Dunn, M. The role of food banks in addressing food insecurity: A systematic review. J. Community Health 2016, 41, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOV.UK Get Meals at Home (Meals on Wheels). Available online: https://www.gov.uk/meals-home (accessed on 24 April 2021).
- Encyclopedia of Food Safety Meals on Wheels. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/meals-on-wheels (accessed on 24 April 2021).
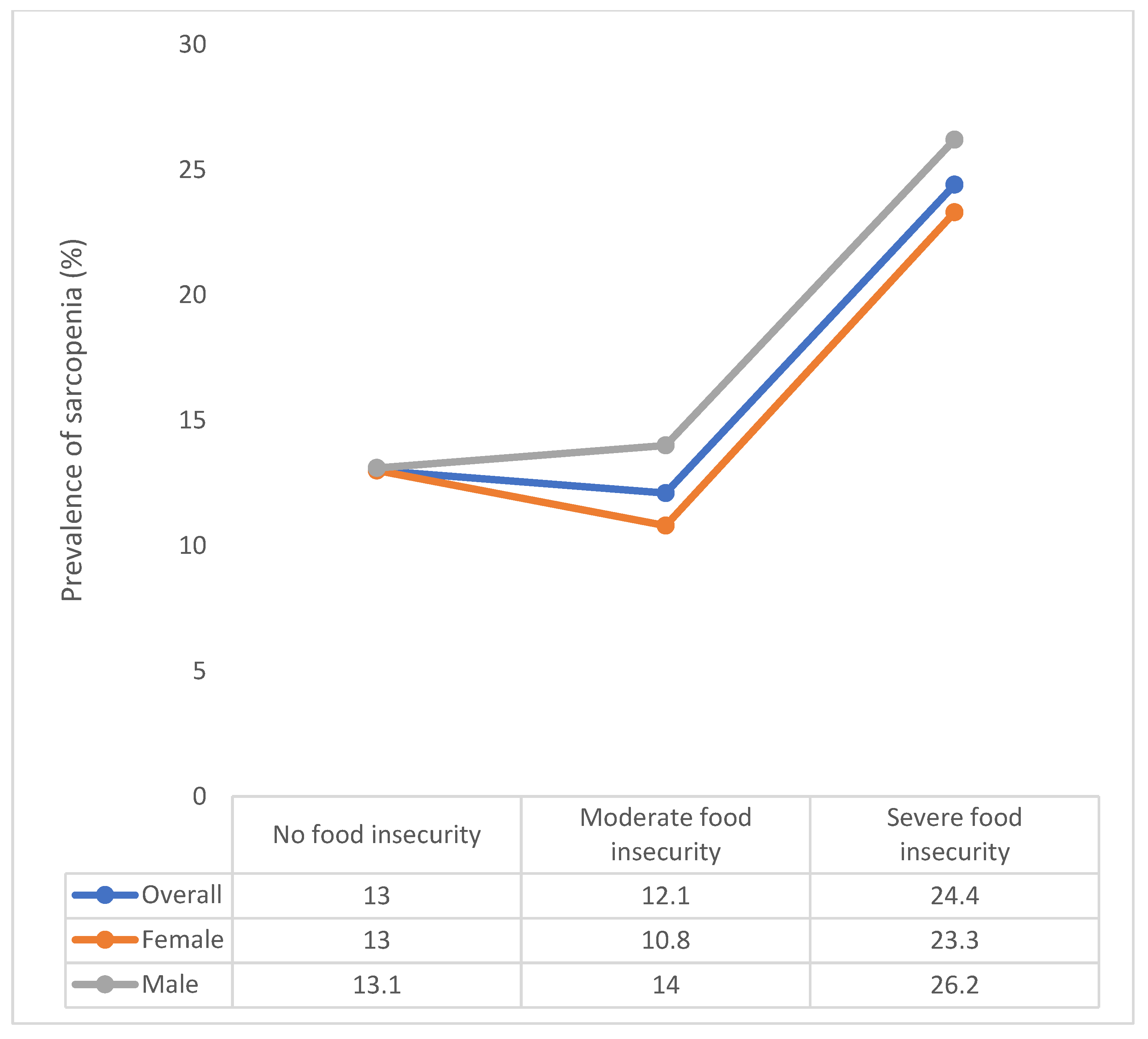
| Food Insecurity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Overall | None | Moderate | Severe | p-Value a | |
| Sex | Male | 45.0 | 46.1 | 37.7 | 37.8 | 0.009 |
| Female | 55.0 | 53.9 | 62.3 | 62.2 | ||
| Age (years) | Mean (SD) | 72.6 (11.5) | 72.5 (11.0) | 71.9 (12.6) | 72.5 (14.9) | 0.177 |
| Wealth | Poorest | 21.7 | 19.5 | 35.3 | 41.6 | <0.001 |
| Poorer | 21.0 | 20.0 | 29.3 | 26.9 | ||
| Middle | 20.4 | 20.4 | 22.3 | 18.6 | ||
| Richer | 17.5 | 18.8 | 8.0 | 7.6 | ||
| Richest | 19.4 | 21.4 | 5.1 | 5.3 | ||
| Education (years) | Mean (SD) | 5.2 (9.3) | 5.4 (9.1) | 3.9 (9.7) | 3.6 (10.7) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol consumption | No | 86.1 | 85.9 | 87.2 | 87.1 | 0.755 |
| Yes | 13.9 | 14.1 | 12.8 | 12.9 | ||
| Smoking | Never | 62.2 | 62.9 | 57.3 | 56.8 | 0.139 |
| Current | 29.3 | 28.6 | 33.2 | 35.7 | ||
| Quit | 8.5 | 8.5 | 9.5 | 7.5 | ||
| Physical activity | High | 35.2 | 34.0 | 45.1 | 43.7 | <0.001 |
| Moderate | 25.2 | 26.3 | 17.8 | 15.1 | ||
| Low | 39.6 | 39.7 | 37.1 | 41.2 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | <18.5 | 19.3 | 17.5 | 32.4 | 34.8 | <0.001 |
| 18.5–24.9 | 46.4 | 47.3 | 42.6 | 35.5 | ||
| 25.0–29.9 | 23.9 | 25.1 | 14.7 | 14.9 | ||
| ≥30 | 10.4 | 10.2 | 10.3 | 14.8 | ||
| No. of chronic diseases | Mean (SD) | 2.1 (2.8) | 2.1 (2.7) | 2.4 (3.7) | 2.6 (4.1) | <0.001 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | OR | 95%CI | OR | 95%CI | OR | 95%CI | OR | 95%CI | |
| Food insecurity | None | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Moderate | 0.82 | [0.56,1.21] | 0.84 | [0.57,1.25] | 0.87 | [0.59,1.28] | 0.87 | [0.59,1.30] | |
| Severe | 1.98 * | [1.10,3.58] | 2.04 * | [1.13,3.68] | 2.11 * | [1.16,3.85] | 2.05 * | [1.12,3.73] | |
| Sex | Male | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Female | 0.81 * | [0.66,0.99] | 0.77 * | [0.60,0.99] | 0.72 * | [0.56,0.93] | 0.72 ** | [0.56,0.92] | |
| Age (years) | 1.12 *** | [1.10,1.14] | 1.11 *** | [1.10,1.13] | 1.12 *** | [1.10,1.14] | 1.12 *** | [1.10,1.14] | |
| Wealth | Poorest | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Poorer | 0.76 | [0.56,1.04] | 0.77 | [0.56,1.05] | 0.73 | [0.53,1.01] | 0.76 | [0.55,1.04] | |
| Middle | 0.78 | [0.55,1.10] | 0.79 | [0.55,1.11] | 0.75 | [0.52,1.07] | 0.74 | [0.51,1.06] | |
| Richer | 0.66 ** | [0.49,0.89] | 0.65 ** | [0.48,0.87] | 0.60 ** | [0.44,0.82] | 0.60 ** | [0.44,0.82] | |
| Richest | 0.54 ** | [0.35,0.81] | 0.53 ** | [0.35,0.80] | 0.45 *** | [0.28,0.71] | 0.46 ** | [0.29,0.73] | |
| Education (years) | 0.95 *** | [0.92,0.98] | 0.95 *** | [0.92,0.98] | 0.94 *** | [0.92,0.97] | 0.95 *** | [0.92,0.98] | |
| Alcohol consumption | No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| Yes | 0.74 | [0.52,1.04] | 0.75 | [0.53,1.06] | 0.75 | [0.53,1.08] | |||
| Smoking | Never | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| Current | 0.98 | [0.74,1.30] | 1.04 | [0.78,1.39] | 1.02 | [0.76,1.37] | |||
| Quit | 1.19 | [0.83,1.69] | 1.18 | [0.83,1.68] | 1.12 | [0.78,1.60] | |||
| Physical activity | High | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||
| Moderate | 1.23 | [0.97,1.55] | 1.21 | [0.95,1.54] | 1.14 | [0.89,1.45] | |||
| Low | 1.22 | [0.97,1.53] | 1.20 | [0.95,1.52] | 1.12 | [0.89,1.42] | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.5–24.9 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||||
| 25.0–29.9 | 1.36 ** | [1.08,1.70] | 1.36 ** | [1.09,1.70] | |||||
| ≥30 | 2.60 *** | [1.65,4.10] | 2.48 *** | [1.55,3.97] | |||||
| <18.5 | 0.63 ** | [0.44,0.89] | 0.64 * | [0.45,0.92] | |||||
| No. of chronic diseases | 1.14 *** | [1.06,1.22] | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, L.; Jacob, L.; Barnett, Y.; Butler, L.T.; Shin, J.I.; López-Sánchez, G.F.; Soysal, P.; Veronese, N.; Haro, J.M.; Koyanagi, A. Association between Food Insecurity and Sarcopenia among Adults Aged ≥65 Years in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061879
Smith L, Jacob L, Barnett Y, Butler LT, Shin JI, López-Sánchez GF, Soysal P, Veronese N, Haro JM, Koyanagi A. Association between Food Insecurity and Sarcopenia among Adults Aged ≥65 Years in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Nutrients. 2021; 13(6):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061879
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Lee, Louis Jacob, Yvonne Barnett, Laurie T. Butler, Jae Il Shin, Guillermo F. López-Sánchez, Pinar Soysal, Nicola Veronese, Josep Maria Haro, and Ai Koyanagi. 2021. "Association between Food Insecurity and Sarcopenia among Adults Aged ≥65 Years in Low- and Middle-Income Countries" Nutrients 13, no. 6: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061879
APA StyleSmith, L., Jacob, L., Barnett, Y., Butler, L. T., Shin, J. I., López-Sánchez, G. F., Soysal, P., Veronese, N., Haro, J. M., & Koyanagi, A. (2021). Association between Food Insecurity and Sarcopenia among Adults Aged ≥65 Years in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Nutrients, 13(6), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061879









