Infant Gut Microbiota Associated with Fine Motor Skills
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects, Experimental Design and Ethical Guidelines
2.2. DNA Extraction from Stool Samples
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Data Processing
2.4. Assessment of Infant Cognitive Development
2.5. Statistical and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population Characteristics and Bayley®-III Scores
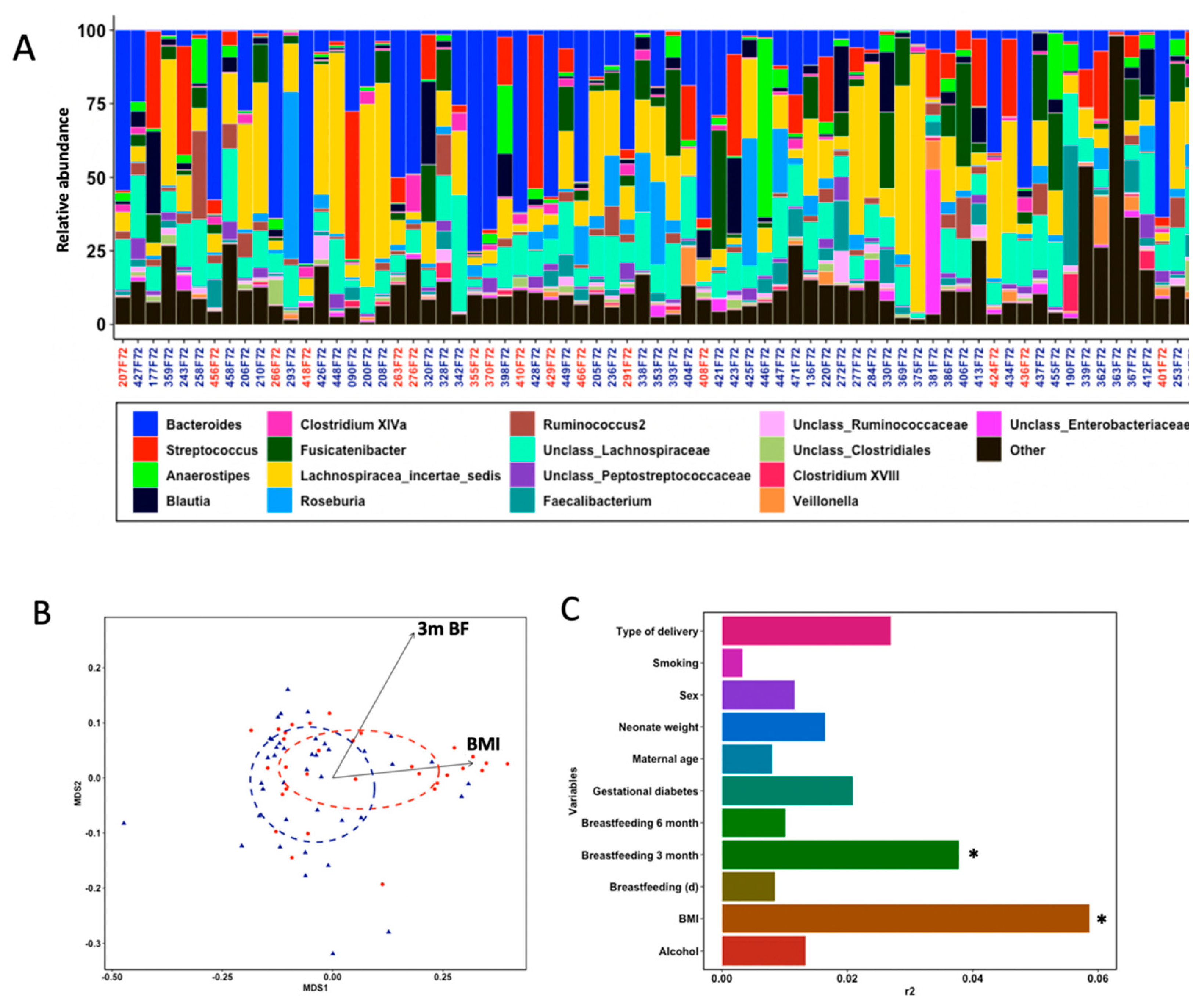
3.2. Taxonomic Profiling of Infants’ Gut Microbiota
3.3. Gut Microbial Structure Is Different Regarding Fine Motor Skills
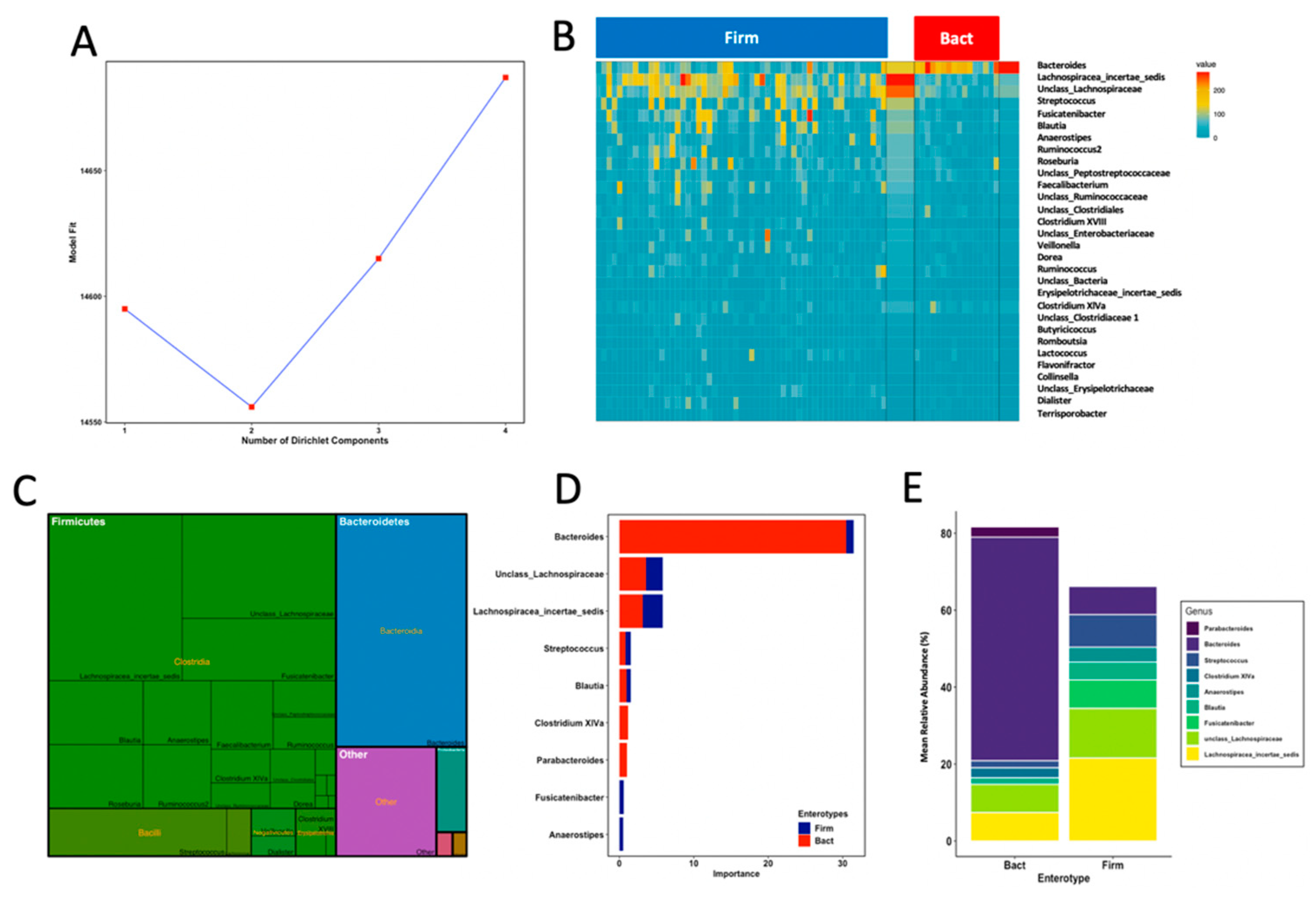
3.4. Enterotypes Are Associated with Fine Motor Activity in Infants
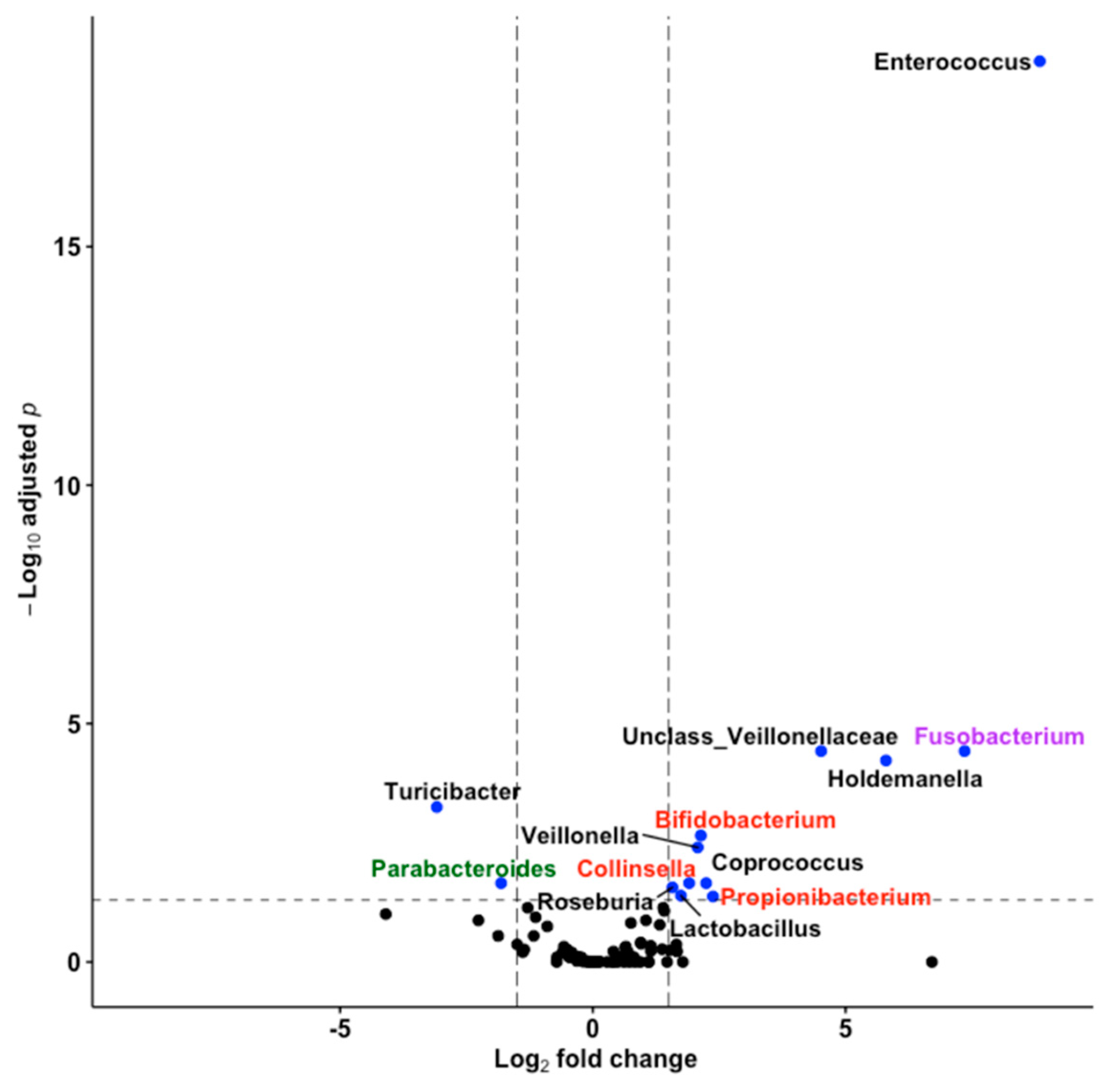
3.5. Thirteen Genera including Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Differentiated Fine Motricity Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemente, J.C.; Ursell, L.K.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. The Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Human Health: An Integrative View. Cell 2012, 148, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tau, G.Z.; Peterson, B.S. Normal Development of Brain Circuits. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Saavedra, P.; Mendez-Vilabrille, V.; Miranda, J.M.; Nebot, C.; Cardelle-Cobas, A.; Franco, C.M.; Cepeda, A. Food Additives, Contaminants and Other Minor Components: Effects on Human Gut Microbiota—A Review. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 74, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.P.; Rochat, F.; Chassard, C. Vertical Mother-Neonate Transfer of Maternal Gut Bacteria via Breastfeeding. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2891–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, C.; Liu, M.; Fang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zeng, L.; Chen, J.; Fan, S.; Du, X.; et al. Gut Microbiome Remodeling Induces Depressive-like Behaviors through a Pathway Mediated by the Host’s Metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palma, G.; Blennerhassett, P.; Lu, J.; Deng, Y.; Park, A.J.; Green, W.; Denou, E.; Silva, M.A.; Santacruz, A.; Sanz, Y.; et al. Microbiota and Host Determinants of Behavioural Phenotype in Maternally Separated Mice. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz Heijtz, R.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Björkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. Normal Gut Microbiota Modulates Brain Development and Behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, E.E.; Farzi, A.; Mayerhofer, R.; Reichmann, F.; Jac, A.; Wagner, B.; Zinser, E.; Bordag, N.; Magnes, C.; Fröhlich, E.; et al. Cognitive Impairment by Antibiotic-Induced Gut Dysbiosis: Analysis of Gut Microbiota-Brain Communication. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 56, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savignac, H.M.; Tramullas, M.; Kiely, B.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Bifidobacteria Modulate Cognitive Processes in an Anxious Mouse Strain. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 287, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, K.M.; Kang, N.; Bienenstock, J.; Foster, J.A.; Kang, N.; Bienenstock, J.; Foster, J.A. Effects of Intestinal Microbiota on Anxiety-like Behavior. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Grenham, S.; Scully, P.; Fitzgerald, P.; Moloney, R.D.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis during Early Life Regulates the Hippocampal Serotonergic System in a Sex-Dependent Manner. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbonnet, L.; Garrett, L.; Clarke, G.; Bienenstock, J.; Dinan, T.G. The Probiotic Bifidobacteria Infantis: An Assessment of Potential Antidepressant Properties in the Rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2009, 43, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, K.M.; Kang, N.; Bienenstock, J.; Foster, J.A. Reduced Anxiety-like Behavior and Central Neurochemical Change in Germ-Free Mice. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 255.e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, N.; Chida, Y.; Aiba, Y.; Sonoda, J.; Oyama, N.; Yu, X.; Kubo, C.; Koga, Y. Postnatal Microbial Colonization Programs the Hypothalamic—Pituitary—Adrenal System for Stress Response in Mice. J. Physiol. 2004, 558, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercik, P.; Denou, E.; Collins, J.; Jackson, W.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.; Macri, J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. The Intestinal Microbiota Affect Central Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor and Behavior in Mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luczynski, P.; Whelan, S.O.; O’Sullivan, C.; Clarke, G.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Adult Microbiota-Deficient Mice Have Distinct Dendritic Morphological Changes: Differential Effects in the Amygdala and Hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2016, 44, 2654–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegold, S.M.; Dowd, S.E.; Gontcharova, V.; Liu, C.; Henley, K.E.; Wolcott, R.D.; Youn, E.; Summanen, P.H.; Granpeesheh, D.; Dixon, D.; et al. Pyrosequencing Study of Fecal Microflora of Autistic and Control Children. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Christophersen, C.T.; Sorich, M.J.; Gerber, J.P.; Angley, M.T.; Conlon, M.A. Increased Abundance of Sutterella Spp. and Ruminococcus Torques in Feces of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Autism 2013, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomova, A.; Husarova, V.; Lakatosova, S.; Bakos, J.; Vlkova, B.; Babinska, K.; Ostatnikova, D. Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Children with Autism in Slovakia. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 138, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, L.M.; Galley, J.D.; Hade, E.M.; Schoppe-Sullivan, S.; Kamp Dush, C.; Bailey, M.T. Gut Microbiome Composition Is Associated with Temperament during Early Childhood. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2015, 45, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, A.L.; Xia, K.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Goldman, B.D.; Ahn, M.; Styner, M.A.; Thompson, A.L.; Geng, X.; Gilmore, J.H.; Knickmeyer, R.C. Infant Gut Microbiome Associated With Cognitive Development. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordillo, J.E.; Korrick, S.; Laranjo, N.; Carey, V.; Weinstock, G.M.; Gold, D.R.; Connor, G.O. Association of the Infant Gut Microbiome With Early Childhood Neurodevelopmental Outcomes An Ancillary Study to the VDAART Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open 2020, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, N. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, 3rd ed.; Harcourt Assessment, Inc.: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Berglund, S.K.; García-Valdés, L.; Torres-Espinola, F.J.; Segura, M.T.; Martínez-Zaldívar, C.; Aguilar, M.J.; Agil, A.; Lorente, J.A.; Florido, J.; Padilla, C.; et al. Maternal, Fetal and Perinatal Alterations Associated with Obesity, Overweight and Gestational Diabetes: An Observational Cohort Study (PREOBE). BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.; Ruiz, A.; Lanza, F.; Haange, S.; Oberbach, A.; Till, H.; Bargiela, R.; Campoy, C.; Segura, M.T.; Richter, M.; et al. Microbiota from the Distal Guts of Lean and Obese Adolescents Exhibit Partial Functional Redundancy besides Clear Differences in Community Structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarinha-Silva, A.; Jáuregui, R.; Chaves-Moreno, D.; Oxley, A.P.A.; Schaumburg, F.; Becker, K.; Wos-Oxley, M.L.; Pieper, D.H. Comparing the Anterior Nare Bacterial Community of Two Discrete Human Populations Using Illumina Amplicon Sequencing. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2939–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing Mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of RRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bittinger, K.; Charlson, E.S.; Hoffmann, C.; Lewis, J.; Wu, G.D.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Li, H. Associating Microbiome Composition with Environmental Covariates Using Generalized UniFrac Distances. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-6. 2019. Available online: http://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=vegan (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Holmes, I.; Harris, K.; Quince, C. Dirichlet Multinomial Mixtures: Generative Models for Microbial Metagenomics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 30126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential Expression Analysis for Sequence Count Data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Parenti, M.; Grip, T.; Lönnerdal, B.; Timby, N.; Domellöf, M.; Hernell, O.; Slupsky, C.M. Fecal Microbiome and Metabolome of Infants Fed Bovine MFGM Supplemented Formula or Standard Formula with Breast-Fed Infants as Reference: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J. Effects of Intestinal Microbiota on Brain Development in Humanized Gnotobiotic Mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Sandhu, K.; Peterson, V.; Dinan, T.G. The Gut Microbiome in Neurological Disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdó, T.; García-Valdés, L.; Altmäe, S.; Ruíz, A.; Suárez, A.; Campoy, C. Role of Microbiota Function during Early Life on Child’s Neurodevelopment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccarini, M.; Guarini, A.; Savini, S.; Faldella, G.; Sansavini, A. Do 6-Month Motor Skills Have Cascading Effects on 12-Month Motor and Cognitive Development in Extremely Preterm and Full-Term Infants? Front. Psychol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Chung, J.; Battaglia, T.; Henderson, N.; Jay, M.; Li, H.; Lieber, A.D.; Wu, F.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Chen, Y.; et al. Antibiotics, Birth Mode, and Diet Shape Microbiome Maturation during Early Life. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planer, J.D.; Peng, Y.; Kau, A.L.; Blanton, L.V.; Ndao, I.M.; Tarr, P.I.; Warner, B.B.; Gordon, J.I. Development of the Gut Microbiota and Mucosal IgA Responses in Twins and Gnotobiotic Mice. Nature 2016, 534, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, A.; Cerdó, T.; Jáuregui, R.; Pieper, D.H.; Marcos, A.; Clemente, A.; García, F.; Margolles, A.; Ferrer, M.; Campoy, C.; et al. One-Year Calorie Restriction Impacts Gut Microbial Composition but Not Its Metabolic Performance in Obese Adolescents. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1536–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, M.; Lord, C.; Ulrich, D.A. Motor Skills and Calibrated Autism Severity in Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Adapt. Phys. Activ. Q. 2014, 31, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-W.; Park, J.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Wallstrom, G.; LaBaer, J.; Adams, J.B.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Reduced Incidence of Prevotella and Other Fermenters in Intestinal Microflora of Autistic Children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus Strain Regulates Emotional Behavior and Central GABA Receptor Expression in a Mouse via the Vagus Nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davari, S.; Talaei, S.A.; Alaei, H.; Salami, M. Probiotics Treatment Improves Diabetes-Induced Impairment of Synaptic Activity and Cognitive Function: Behavioral and Electrophysiological Proofs for Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis. Neuroscience 2013, 240, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Violle, N.; Bisson, J.F.; Desor, D.; Javelot, H.; Rougeot, C. Beneficial Psychological Effects of a Probiotic Formulation (Lactobacillus Helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium Longum R0175) in Healthy Human Volunteers. Gut Microbes 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R.; van Hemert, S.; Bosch, J.A.; Colzato, L.S. A Randomized Controlled Trial to Test the Effect of Multispecies Probiotics on Cognitive Reactivity to Sad Mood. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerdó, T.; Ruíz, A.; Suárez, A.; Campoy, C. Probiotic, Prebiotic, and Brain Development. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Below the Median | Above the Median | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal characteristics | |||
| Age (years) | 32.87 (5.37) | 33.57 (2.97) | 0.485 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI | 0.034 * | ||
| Normal-Weight | 12 (38.71%) | 9 (22.5%) | |
| Overweight | 9 (29.03%) | 24 (60.0%) | |
| Obesity | 10 (32.26%) | 7 (17.5%) | |
| Pre-pregnancy weight (kg) | 72.12 (14.3) | 72.38 (15.17) | 0.966 |
| Weight gain (kg) | 8.71 (4.23) | 8.35 (7.62) | 0.832 |
| Diabetes | 0.515 | ||
| No | 17 (54.84%) | 25 (62.5%) | |
| Yes | 14 (45.16%) | 15 (37.5%) | |
| Education | 0.154 | ||
| Primary/Secondary | 20 (64.52%) | 18 (45.0%) | |
| University | 11 (35.48%) | 20 (50.0%) | |
| Smoking during pregnancy | 0.744 | ||
| No | 28 (90.32%) | 37 (92.5%) | |
| Yes | 3 (9.68%) | 3 (7.5%) | |
| Drinking alcohol during pregnancy | 0.855 | ||
| No | 30 (96.77%) | 39 (97.5%) | |
| Yes | 1 (3.23%) | 1 (2.5%) | |
| Type of delivery | 0.644 | ||
| Eutocic | 20 (64.52%) | 22 (55.0%) | |
| Dystocic | 4 (12.90%) | 5 (12.5%) | |
| Cesarean | 7 (22.58%) | 13 (32.5%) | |
| Infant characteristics | |||
| Sex | |||
| Male | 22 (70.97%) | 23 (57.5%) | 0.243 |
| Female | 9 (29.03%) | 17 (42.5%) | |
| Birth weight (g) | 3253.87 (467.99) | 3287.25 (578.51) | 0.794 |
| Birth length (cm) | 50.68 (1.96) | 49.83 (2.02) | 0.098 |
| Birth head Circumference (cm) | 34.75 (1.29) | 34.66 (1.47) | 0.803 |
| Placenta (g) | 498.52 (108.69) | 532.06 (127.56) | 0.281 |
| Breastfeeding † | 0.032 * | ||
| Exclusive | 14 (45.16%) | 29 (72.5%) | |
| Mixed | 4 (12.90%) | 5 (12.5%) | |
| Artificial | 13 (41.94%) | 6 (15.0%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acuña, I.; Cerdó, T.; Ruiz, A.; Torres-Espínola, F.J.; López-Moreno, A.; Aguilera, M.; Suárez, A.; Campoy, C. Infant Gut Microbiota Associated with Fine Motor Skills. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051673
Acuña I, Cerdó T, Ruiz A, Torres-Espínola FJ, López-Moreno A, Aguilera M, Suárez A, Campoy C. Infant Gut Microbiota Associated with Fine Motor Skills. Nutrients. 2021; 13(5):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051673
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcuña, Inmaculada, Tomás Cerdó, Alicia Ruiz, Francisco J. Torres-Espínola, Ana López-Moreno, Margarita Aguilera, Antonio Suárez, and Cristina Campoy. 2021. "Infant Gut Microbiota Associated with Fine Motor Skills" Nutrients 13, no. 5: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051673
APA StyleAcuña, I., Cerdó, T., Ruiz, A., Torres-Espínola, F. J., López-Moreno, A., Aguilera, M., Suárez, A., & Campoy, C. (2021). Infant Gut Microbiota Associated with Fine Motor Skills. Nutrients, 13(5), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051673










