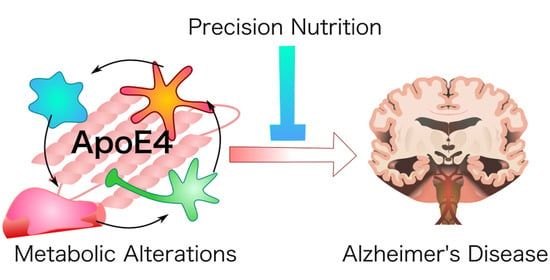
Precision Nutrition for Alzheimer’s Prevention in ApoE4 Carriers
Abstract
1. Introduction
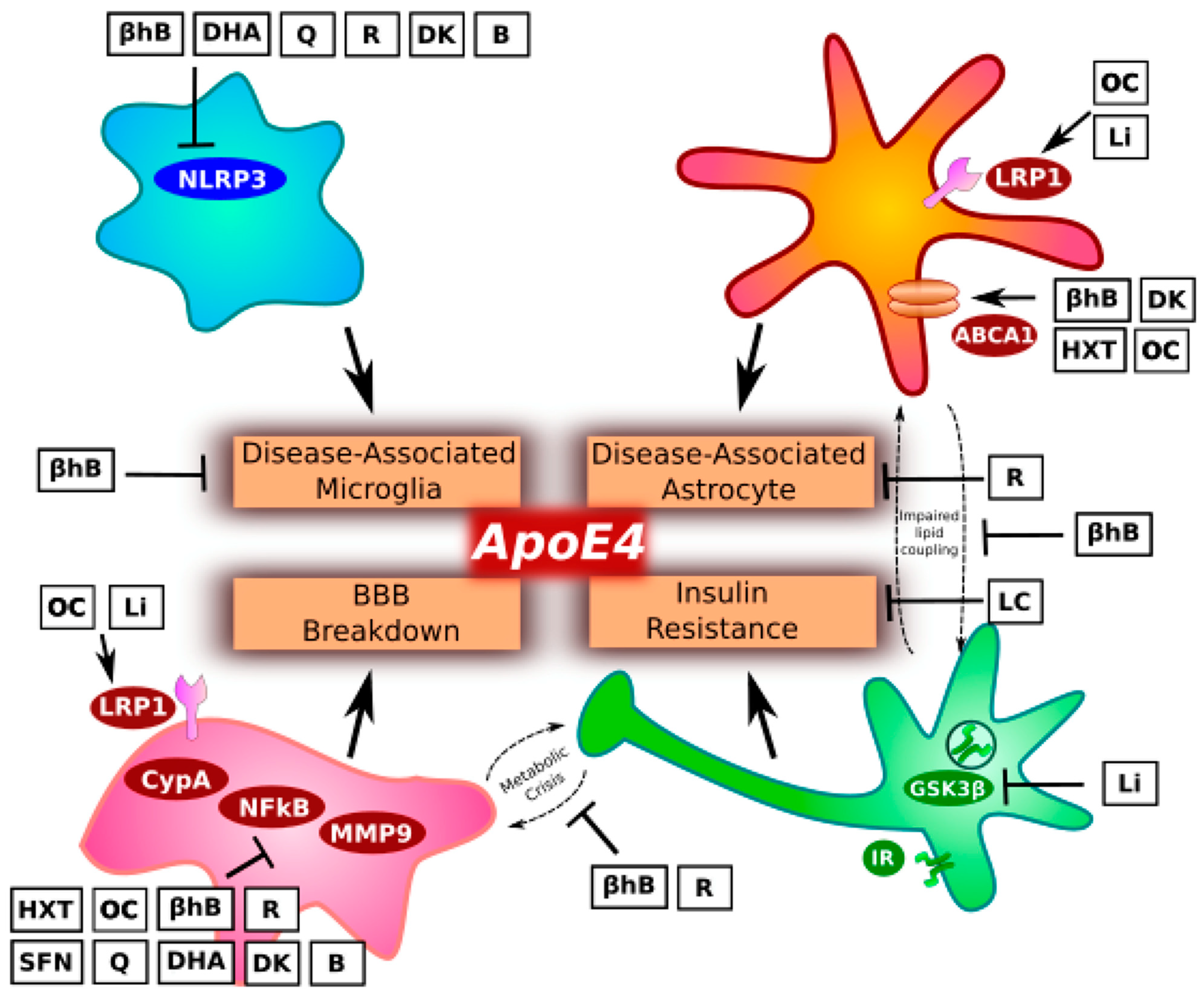
2. Microglia and Inflammation
3. Astrocytes and Lipid Metabolism
4. Pericytes and Blood–Brain Barrier
5. Insulin Resistance and Glucose Metabolism
6. Precision Nutrition Considerations
6.1. Low-Glycemic Index and Low-Carbohydrate Diets
6.2. Ketogenic Diets and β-Hydroxybutyrate
6.3. Mediterranean Dietary Components
6.3.1. Extra Virgin Olive Oil
6.3.2. Certain Vegetables
6.3.3. Fatty Fish
6.3.4. Limit Alcohol
6.4. Supplementation
6.4.1. DHA
6.4.2. Quercetin
6.4.3. Resveratrol
6.4.4. Vitamins D3 and K2
6.4.5. B Vitamins
6.4.6. Lithium
7. Ethical Considerations
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cummings, J.L.; Morstorf, T.; Zhong, K. Alzheimer’s disease drug-development pipeline: Few candidates, frequent failures. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, L.E.; Weuve, J.; Scherr, P.A.; Evans, D.A. Alzheimer disease in the United States (2010–2050) estimated using the 2010 census. Neurology 2013, 80, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association. Is Alzheimer’s Genetic? Available online: https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers/causes-and-risk-factors/genetics (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Michaelson, D.M. APOE epsilon4: The most prevalent yet understudied risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2014, 10, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuntokun, B.O.; Sahota, A.; Ogunniyi, A.O.; Gureje, O.; Baiyewu, O.; Adeyinka, A.; Oluwole, S.O.; Komolafe, O.; Hall, K.S.; Unverzagt, F.W.; et al. Lack of an association between apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 and Alzheimer’s disease in elderly Nigerians. Ann. Neurol 1995, 38, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaria, R.N.; Ogeng’O, J.A.; Patel, N.B.; Sayi, J.G.; Kitinya, J.N.; Chande, H.M.; Matuja, W.B.; Mtui, E.P.; Kimani, J.K.; Premkumar, D.R.; et al. Evaluation of risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease in elderly east Africans. Brain Res. Bull 1997, 44, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrie, H.C.; Ogunniyi, A.; Hall, K.S.; Baiyewu, O.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Gureje, O.; Gao, S.; Evans, R.M.; Ogunseyinde, A.O.; Adeyinka, A.O.; et al. Incidence of dementia and Alzheimer disease in 2 communities: Yoruba residing in Ibadan, Nigeria, and African Americans residing in Indianapolis, Indiana. JAMA 2001, 285, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurinovich, A.; Andersen, S.L.; Puca, A.; Atzmon, G.; Barzilai, N.; Sebastiani, P. Varying Effects of APOE Alleles on Extreme Longevity in European Ethnicities. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, S45–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, B.D.; Leurgans, S.E.; Hebert, L.E.; Scherr, P.A.; Yaffe, K.; Bennett, D.A. Contribution of Alzheimer disease to mortality in the United States. Neurology 2014, 82, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngandu, T.; Lehtisalo, J.; Solomon, A.; Levalahti, E.; Ahtiluoto, S.; Antikainen, R.; Backman, L.; Hanninen, T.; Jula, A.; Laatikainen, T.; et al. A 2 year multidomain intervention of diet, exercise, cognitive training, and vascular risk monitoring versus control to prevent cognitive decline in at-risk elderly people (FINGER): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellas, B.; Carrie, I.; Gillette-Guyonnet, S.; Touchon, J.; Dantoine, T.; Dartigues, J.F.; Cuffi, M.N.; Bordes, S.; Gasnier, Y.; Robert, P.; et al. Mapt Study: A Multidomain Approach for Preventing Alzheimer’s Disease: Design and Baseline Data. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 1, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal, J.A.; Smith, P.J.; Mabe, S.; Hinderliter, A.; Welsh-Bohmer, K.; Browndyke, J.N.; Doraiswamy, P.M.; Lin, P.H.; Kraus, W.E.; Burke, J.R.; et al. Longer Term Effects of Diet and Exercise on Neurocognition: 1-Year Follow-up of the ENLIGHTEN Trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPRINT MIND Investigators for the SPRINT Research Group; Williamson, J.D.; Pajewski, N.M.; Auchus, A.P.; Bryan, R.N.; Chelune, G.; Cheung, A.K.; Cleveland, M.L.; Coker, L.H.; Crowe, M.G.; et al. Effect of Intensive vs Standard Blood Pressure Control on Probable Dementia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solomon, A.; Turunen, H.; Ngandu, T.; Peltonen, M.; Levalahti, E.; Helisalmi, S.; Antikainen, R.; Backman, L.; Hanninen, T.; Jula, A.; et al. Effect of the Apolipoprotein E Genotype on Cognitive Change During a Multidomain Lifestyle Intervention: A Subgroup Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. What is Precision Medicine? U.S. National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018.
- Friedberg, J.S.; Aytan, N.; Cherry, J.D.; Xia, W.; Standring, O.J.; Alvarez, V.E.; Nicks, R.; Svirsky, S.; Meng, G.; Jun, G.; et al. Associations between brain inflammatory profiles and human neuropathology are altered based on apolipoprotein E epsilon4 genotype. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauro, C.; Limatola, C. Metabolic Reprograming of Microglia in the Regulation of the Innate Inflammatory Response. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fann, D.Y.; Santro, T.; Manzanero, S.; Widiapradja, A.; Cheng, Y.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Chunduri, P.; Jo, D.G.; Stranahan, A.M.; Mattson, M.P.; et al. Intermittent fasting attenuates inflammasome activity in ischemic stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 257, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Mi, Y.; Shi, X.; Gu, H.; Brinton, R.D.; Yin, F. ApoE4 Impairs Neuron-Astrocyte Coupling of Fatty Acid Metabolism. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagne, A.; Nation, D.A.; Sagare, A.P.; Barisano, G.; Sweeney, M.D.; Chakhoyan, A.; Pachicano, M.; Joe, E.; Nelson, A.R.; D’Orazio, L.M.; et al. APOE4 leads to blood-brain barrier dysfunction predicting cognitive decline. Nature 2020, 581, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Liu, C.C.; Yamazaki, A.; Shue, F.; Martens, Y.A.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, W.; Kurti, A.; Oue, H.; Ren, Y.; et al. Vascular ApoE4 Impairs Behavior by Modulating Gliovascular Function. Neuron 2021, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, C.C.; Van Ingelgom, A.J.; Martens, Y.A.; Linares, C.; Knight, J.A.; Painter, M.M.; Sullivan, P.M.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E4 Impairs Neuronal Insulin Signaling by Trapping Insulin Receptor in the Endosomes. Neuron 2017, 96, 115–129.e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peila, R.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Launer, L.J.; Honolulu-Asia Aging, S. Type 2 diabetes, APOE gene, and the risk for dementia and related pathologies: The Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacson, R.S.; Ganzer, C.A.; Hristov, H.; Hackett, K.; Caesar, E.; Cohen, R.; Kachko, R.; Melendez-Cabrero, J.; Rahman, A.; Scheyer, O.; et al. The clinical practice of risk reduction for Alzheimer’s disease: A precision medicine approach. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphis, N.; Xu, G.; Kokiko-Cochran, O.N.; Jiang, S.; Cardona, A.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Lamb, B.T.; Bhaskar, K. Reactive microglia drive tau pathology and contribute to the spreading of pathological tau in the brain. Brain 2015, 138, 1738–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, A.; Kawarabayashi, T.; Murakami, T.; Matsubara, E.; Ikeda, M.; Hagiwara, H.; Westaway, D.; George-Hyslop, P.S.; Shoji, M.; Nakazato, Y. Microglial activation in brain lesions with tau deposits: Comparison of human tauopathies and tau transgenic mice TgTauP301L. Brain Res. 2008, 1214, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Walsh, D.M.; Selkoe, D.J. Large Soluble Oligomers of Amyloid beta-Protein from Alzheimer Brain Are Far Less Neuroactive Than the Smaller Oligomers to Which They Dissociate. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Kummer, M.P.; Stutz, A.; Delekate, A.; Schwartz, S.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Griep, A.; Axt, D.; Remus, A.; Tzeng, T.C.; et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 2013, 493, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ising, C.; Venegas, C.; Zhang, S.; Scheiblich, H.; Schmidt, S.V.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Schwartz, S.; Albasset, S.; McManus, R.M.; Tejera, D.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology. Nature 2019, 575, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas, C.; Kumar, S.; Franklin, B.S.; Dierkes, T.; Brinkschulte, R.; Tejera, D.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Schwartz, S.; Santarelli, F.; Kummer, M.P.; et al. Microglia-derived ASC specks cross-seed amyloid-beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2017, 552, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanzel, C.E.; Pichet-Binette, A.; Pimentel, L.S.; Iulita, M.F.; Allard, S.; Ducatenzeiler, A.; Do Carmo, S.; Cuello, A.C. Neuronal driven pre-plaque inflammation in a transgenic rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, A.; Edison, P.; Archer, H.A.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Kennedy, J.; Bullock, R.; Walker, Z.; Kennedy, A.; Fox, N.; Rossor, M.; et al. Microglial activation and amyloid deposition in mild cognitive impairment: A PET study. Neurology 2009, 72, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streit, W.J.; Braak, H.; Xue, Q.S.; Bechmann, I. Dystrophic (senescent) rather than activated microglial cells are associated with tau pathology and likely precede neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: Where do we go from here? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maezawa, I.; Nivison, M.; Montine, K.S.; Maeda, N.; Montine, T.J. Neurotoxicity from innate immune response is greatest with targeted replacement of E4 allele of apolipoprotein E gene and is mediated by microglial p38MAPK. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasemann, S.; Madore, C.; Cialic, R.; Baufeld, C.; Calcagno, N.; El Fatimy, R.; Beckers, L.; O’Loughlin, E.; Xu, Y.; Fanek, Z.; et al. The TREM2-APOE Pathway Drives the Transcriptional Phenotype of Dysfunctional Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Immunity 2017, 47, 566–581.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren-Shaul, H.; Spinrad, A.; Weiner, A.; Matcovitch-Natan, O.; Dvir-Szternfeld, R.; Ulland, T.K.; David, E.; Baruch, K.; Lara-Astaiso, D.; Toth, B.; et al. A Unique Microglia Type Associated with Restricting Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 2017, 169, 1276–1290.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yamada, K.; Liddelow, S.A.; Smith, S.T.; Zhao, L.; Luo, W.; Tsai, R.M.; Spina, S.; Grinberg, L.T.; Rojas, J.C.; et al. ApoE4 markedly exacerbates tau-mediated neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Nature 2017, 549, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Seo, J.; Gao, F.; Feldman, H.M.; Wen, H.L.; Penney, J.; Cam, H.P.; Gjoneska, E.; Raja, W.K.; Cheng, J.; et al. APOE4 Causes Widespread Molecular and Cellular Alterations Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease Phenotypes in Human iPSC-Derived Brain Cell Types. Neuron 2018, 98, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; McCabe, C.; Medina, S.; Varshavsky, M.; Kitsberg, D.; Dvir-Szternfeld, R.; Green, G.; Dionne, D.; Nguyen, L.; Marshall, J.L.; et al. Disease-associated astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease and aging. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophir, G.; Amariglio, N.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Elkon, R.; Rechavi, G.; Michaelson, D.M. Apolipoprotein E4 enhances brain inflammation by modulation of the NF-kappaB signaling cascade. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 20, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, D.; Campbell, F.M.; Grant, C.; Morris, A.C.; Bachmair, E.M.; Koch, C.; McLean, F.H.; Muller, A.; Hoggard, N.; de Roos, B.; et al. SerpinA3N is a novel hypothalamic gene upregulated by a high-fat diet and leptin in mice. Genes Nutr. 2018, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, J.L.; Xu, L.; Foo, L.C.; Nouri, N.; Zhou, L.; Giffard, R.G.; Barres, B.A. Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6391–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Garcia, G., Jr.; Tian, E.; Cui, Q.; Chen, X.; Sun, G.; Wang, J.; Arumugaswami, V.; Shi, Y. ApoE-Isoform-Dependent SARS-CoV-2 Neurotropism and Cellular Response. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 331–342.e335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, H.; Rao, R. Amyloid clearance defect in ApoE4 astrocytes is reversed by epigenetic correction of endosomal pH. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6640–E6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, H.; Rao, R. Histone deacetylase-mediated regulation of endolysosomal pH. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6721–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Basak, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. The role of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2009, 63, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.S.; Kobayashi, M.; Hayashi, H.; Zou, K.; Sawamura, N.; Fujita, S.C.; Yanagisawa, K.; Michikawa, M. Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoform-dependent lipid release from astrocytes prepared from human ApoE3 and ApoE4 knock-in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 29919–29926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddell, D.R.; Zhou, H.; Atchison, K.; Warwick, H.K.; Atkinson, P.J.; Jefferson, J.; Xu, L.; Aschmies, S.; Kirksey, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. Impact of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) polymorphism on brain ApoE levels. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11445–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietschy, J.M.; Turley, S.D. Cholesterol metabolism in the brain. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2001, 12, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisvert, M.M.; Erikson, G.A.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Allen, N.J. The Aging Astrocyte Transcriptome from Multiple Regions of the Mouse Brain. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, V.; Wang, S.; Sima, J.; Bar, R.; Liraz, O.; Gundimeda, U.; Parekh, T.; Chan, J.; Johansson, J.O.; Tang, C.; et al. ApoE4 Alters ABCA1 Membrane Trafficking in Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9611–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; He, C.; He, K.; Xue, T.; Wan, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q. Astrocytic ApoE reprograms neuronal cholesterol metabolism and histone-acetylation-mediated memory. Neuron 2021, 109, 957–970.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.D.; Winkler, E.A.; Singh, I.; Sagare, A.P.; Deane, R.; Wu, Z.; Holtzman, D.M.; Betsholtz, C.; Armulik, A.; Sallstrom, J.; et al. Apolipoprotein E controls cerebrovascular integrity via cyclophilin A. Nature 2012, 485, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willette, A.A.; Bendlin, B.B.; Starks, E.J.; Birdsill, A.C.; Johnson, S.C.; Christian, B.T.; Okonkwo, O.C.; La Rue, A.; Hermann, B.P.; Koscik, R.L.; et al. Association of Insulin Resistance With Cerebral Glucose Uptake in Late Middle-Aged Adults at Risk for Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, W.; Mansourian, S.; Chang, Y.; Lindsley, L.; Eckman, E.A.; Frosch, M.P.; Eckman, C.B.; Tanzi, R.E.; Selkoe, D.J.; Guenette, S. Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4162–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, A.; Morelli, L.; Cresto, J.C.; Castano, E.M. Degradation of soluble amyloid beta-peptides 1-40, 1-42, and the Dutch variant 1-40Q by insulin degrading enzyme from Alzheimer disease and control brains. Neurochem. Res. 2000, 25, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.Q.; Walsh, D.M.; Ye, Z.; Vekrellis, K.; Zhang, J.; Podlisny, M.B.; Rosner, M.R.; Safavi, A.; Hersh, L.B.; Selkoe, D.J. Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates extracellular levels of amyloid beta-protein by degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32730–32738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens-Martin, M.; Jurado, J.; Hernandez, F.; Avila, J. GSK-3beta, a pivotal kinase in Alzheimer disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leroy, K.; Yilmaz, Z.; Brion, J.P. Increased level of active GSK-3beta in Alzheimer’s disease and accumulation in argyrophilic grains and in neurones at different stages of neurofibrillary degeneration. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, J.J.; Hernandez, F.; Gomez-Ramos, P.; Moran, M.A.; Hen, R.; Avila, J. Decreased nuclear beta-catenin, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration in GSK-3beta conditional transgenic mice. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwitz, N.G.; Mota, A.S.; Norwitz, S.G.; Clarke, K. Multi-Loop Model of Alzheimer Disease: An Integrated Perspective on the Wnt/GSK3beta, alpha-Synuclein, and Type 3 Diabetes Hypotheses. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiman, E.M.; Caselli, R.J.; Yun, L.S.; Chen, K.; Bandy, D.; Minoshima, S.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Osborne, D. Preclinical evidence of Alzheimer’s disease in persons homozygous for the epsilon 4 allele for apolipoprotein E. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiman, E.M.; Chen, K.; Alexander, G.E.; Caselli, R.J.; Bandy, D.; Osborne, D.; Saunders, A.M.; Hardy, J. Correlations between apolipoprotein E epsilon4 gene dose and brain-imaging measurements of regional hypometabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8299–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ervin, R.B. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among adults 20 years of age and over, by sex, age, race and ethnicity, and body mass index: United States, 2003–2006. Natl. Health Stat. Rep. 2009, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, J.; Cai, J.; Stevens, J. Prevalence of Optimal Metabolic Health in American Adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2016. Metab Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2019, 17, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, N.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Liu, S.; Saltzman, E.; Wilson, P.W.; Jacques, P.F. Carbohydrate nutrition, insulin resistance, and the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partsalaki, I.; Karvela, A.; Spiliotis, B.E. Metabolic impact of a ketogenic diet compared to a hypocaloric diet in obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab 2012, 25, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, P.N.; Sapper, T.N.; Crabtree, C.D.; LaFountain, R.A.; Bowling, M.L.; Buga, A.; Fell, B.; McSwiney, F.T.; Dickerson, R.M.; Miller, V.J.; et al. Dietary carbohydrate restriction improves metabolic syndrome independent of weight loss. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athinarayanan, S.J.; Adams, R.N.; Hallberg, S.J.; McKenzie, A.L.; Bhanpuri, N.H.; Campbell, W.W.; Volek, J.S.; Phinney, S.D.; McCarter, J.P. Long-Term Effects of a Novel Continuous Remote Care Intervention Including Nutritional Ketosis for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A 2-Year Non-randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.T. High carbohydrate diets and Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Hypotheses 2004, 62, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unwin, D.J.; Tobin, S.D.; Murray, S.W.; Delon, C.; Brady, A.J. Substantial and Sustained Improvements in Blood Pressure, Weight and Lipid Profiles from a Carbohydrate Restricted Diet: An Observational Study of Insulin Resistant Patients in Primary Care. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffont, I.; Shuvaev, V.V.; Briand, O.; Lestavel, S.; Barbier, A.; Taniguchi, N.; Fruchart, J.C.; Clavey, V.; Siest, G. Early-glycation of apolipoprotein E: Effect on its binding to LDL receptor, scavenger receptor A and heparan sulfates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1583, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Dickson, D.W. Enhanced binding of advanced glycation endproducts (AGE) by the ApoE4 isoform links the mechanism of plaque deposition in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 226, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vitek, M.P.; Bhattacharya, K.; Glendening, J.M.; Stopa, E.; Vlassara, H.; Bucala, R.; Manogue, K.; Cerami, A. Advanced glycation end products contribute to amyloidosis in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4766–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunnane, S.C.; Courchesne-Loyer, A.; Vandenberghe, C.; St-Pierre, V.; Fortier, M.; Hennebelle, M.; Croteau, E.; Bocti, C.; Fulop, T.; Castellano, C.A. Can Ketones Help Rescue Brain Fuel Supply in Later Life? Implications for Cognitive Health during Aging and the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newport, M.T.; VanItallie, T.B.; Kashiwaya, Y.; King, M.T.; Veech, R.L. A new way to produce hyperketonemia: Use of ketone ester in a case of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrill, S.J.; Gibas, K.J. Ketogenic diet rescues cognition in ApoE4+ patient with mild Alzheimer’s disease: A case study. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019, 13, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Deprez, L.; Mortimer, G.; Murtagh, D.; McCoy, S.; Mylchreest, R.; Gilbertson, L.; Clark, K.; Simpson, P.; McManus, E.; et al. Randomized crossover trial of a modified ketogenic diet in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res.Ther. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.T.; Vogel, J.L.; Barr, L.J.; Garvin, F.; Jones, J.J.; Costantini, L.C. Study of the ketogenic agent AC-1202 in mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. Human ApoE Isoforms Differentially Modulate Brain Glucose and Ketone Body Metabolism: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Reduction and Early Intervention. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 6665–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwitz, N.G.; Hu, M.T.; Clarke, K. The Mechanisms by Which the Ketone Body D-beta-Hydroxybutyrate May Improve the Multiple Cellular Pathologies of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Argenio, V.; Sarnataro, D. New Insights into the Molecular Bases of Familial Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2006, 66, S79–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, F.M.; Brecht, W.J.; Xu, Q.; Tesseur, I.; Kekonius, L.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Fish, J.D.; Masliah, E.; Hopkins, P.C.; Scearce-Levie, K.; et al. Carboxyl-terminal-truncated apolipoprotein E4 causes Alzheimer’s disease-like neurodegeneration and behavioral deficits in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10966–10971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, M.F.; DiNicolantonio, J.J.; O’Keefe, J.H. Ketosis may promote brain macroautophagy by activating Sirt1 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Med. Hypotheses 2015, 85, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alirezaei, M.; Kemball, C.C.; Flynn, C.T.; Wood, M.R.; Whitton, J.L.; Kiosses, W.B. Short-term fasting induces profound neuronal autophagy. Autophagy 2010, 6, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Kashiwaya, Y.; Keon, C.A.; Tsuchiya, N.; King, M.T.; Radda, G.K.; Chance, B.; Clarke, K.; Veech, R.L. Insulin, ketone bodies, and mitochondrial energy transduction. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwaya, Y.; Takeshima, T.; Mori, N.; Nakashima, K.; Clarke, K.; Veech, R.L. D-beta-hydroxybutyrate protects neurons in models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5440–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versele, R.; Corsi, M.; Fuso, A.; Sevin, E.; Businaro, R.; Gosselet, F.; Fenart, L.; Candela, P. Ketone Bodies Promote Amyloid-beta1-40 Clearance in a Human in Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shippy, D.C.; Wilhelm, C.; Viharkumar, P.A.; Raife, T.J.; Ulland, T.K. β-Hydroxybutyrate inhibits inflammasome activation to attenuate Alzheimer’s disease pathology. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youm, Y.H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’Agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.D.; et al. The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, T.; Hirschey, M.D.; Newman, J.; He, W.; Shirakawa, K.; Le Moan, N.; Grueter, C.A.; Lim, H.; Saunders, L.R.; Stevens, R.D.; et al. Suppression of oxidative stress by beta-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science 2013, 339, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.C.; Verdin, E. Ketone bodies as signaling metabolites. Trends. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, M.H.; Ha, S.; Bang, E.J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, A.K.; Lee, J.; Yu, B.P.; Chung, H.Y. Anti-inflammatory action of beta-hydroxybutyrate via modulation of PGC-1alpha and FoxO1, mimicking calorie restriction. Aging 2019, 11, 1283–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.P.; Wang, J.F.; Xue, W.J.; Liu, H.M.; Liu, B.R.; Zeng, Y.L.; Li, S.N.; Huang, B.X.; Lv, Q.K.; Wang, W.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of BHBA in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson’s disease models are mediated by GPR109A-dependent mechanisms. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, F.; Siebert, H.C.; Zheng, X. Ketogenic Diet Elicits Antitumor Properties through Inducing Oxidative Stress, Inhibiting MMP-9 Expression, and Rebalancing M1/M2 Tumor-Associated Macrophage Phenotype in a Mouse Model of Colon Cancer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11182–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujica-Parodi, L.R.; Amgalan, A.; Sultan, S.F.; Antal, B.; Sun, X.; Skiena, S.; Lithen, A.; Adra, N.; Ratai, E.M.; Weistuch, C.; et al. Diet modulates brain network stability, a biomarker for brain aging, in young adults. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6170–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarmeas, N.; Stern, Y.; Tang, M.X.; Mayeux, R.; Luchsinger, J.A. Mediterranean diet and risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarmeas, N.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Mayeux, R.; Stern, Y. Mediterranean diet and Alzheimer disease mortality. Neurology 2007, 69, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Parsaik, A.K.; Mielke, M.M.; Erwin, P.J.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Roberts, R.O. Association of mediterranean diet with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 39, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuznait, A.H.; Qosa, H.; Busnena, B.A.; El Sayed, K.A.; Kaddoumi, A. Olive-oil-derived oleocanthal enhances beta-amyloid clearance as a potential neuroprotective mechanism against Alzheimer’s disease: In vitro and in vivo studies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, M.C.; Margarucci, L.; Tosco, A.; Riccio, R.; Casapullo, A. New insights on the interaction mechanism between tau protein and oleocanthal, an extra-virgin olive-oil bioactive component. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardiello, P.; Pantano, D.; Lapucci, A.; Stefani, M.; Casamenti, F. Diet Supplementation with Hydroxytyrosol Ameliorates Brain Pathology and Restores Cognitive Functions in a Mouse Model of Amyloid-beta Deposition. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 63, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daccache, A.; Lion, C.; Sibille, N.; Gerard, M.; Slomianny, C.; Lippens, G.; Cotelle, P. Oleuropein and derivatives from olives as Tau aggregation inhibitors. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qosa, H.; Batarseh, Y.S.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; El Sayed, K.A.; Keller, J.N.; Kaddoumi, A. Oleocanthal enhances amyloid-beta clearance from the brains of TgSwDI mice and in vitro across a human blood-brain barrier model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoditti, E.; Calabriso, N.; Massaro, M.; Pellegrino, M.; Storelli, C.; Martines, G.; De Caterina, R.; Carluccio, M.A. Mediterranean diet polyphenols reduce inflammatory angiogenesis through MMP-9 and COX-2 inhibition in human vascular endothelial cells: A potentially protective mechanism in atherosclerotic vascular disease and cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, O.; Berrougui, H.; Loued, S.; Khalil, A. Extra-virgin olive oil consumption improves the capacity of HDL to mediate cholesterol efflux and increases ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression in human macrophages. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2003; 20p.
- Egert, S.; Wolffram, S.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Wagner, A.E.; Frank, J.; Rimbach, G.; Mueller, M.J. Daily quercetin supplementation dose-dependently increases plasma quercetin concentrations in healthy humans. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, B.; Rojas-Sutterlin, S.; Laroche, M.; Lachambre, M.P.; Moumdjian, R.; Beliveau, R. The diet-derived sulforaphane inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9-activated human brain microvascular endothelial cell migration and tubulogenesis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Noh, E.M.; Han, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Hwang, B.M.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, S.H.; Youn, H.J.; Chung, E.Y.; et al. Sulforaphane controls TPA-induced MMP-9 expression through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway, but not AP-1, in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. BMB Rep. 2013, 46, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukiw, W.J.; Cui, J.G.; Marcheselli, V.L.; Bodker, M.; Botkjaer, A.; Gotlinger, K.; Serhan, C.N.; Bazan, N.G. A role for docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 in neural cell survival and Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2774–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, M.R.; Lovell, M.A.; Yatin, M.; Dhillon, H.; Markesbery, W.R. Regional membrane phospholipid alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 1998, 23, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.C.; Evans, D.A.; Bienias, J.L.; Tangney, C.C.; Bennett, D.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Aggarwal, N.; Schneider, J. Consumption of fish and n-3 fatty acids and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudrault, C.; Bazinet, R.P.; Ma, D.W. Experimental models and mechanisms underlying the protective effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, G.P.; Calon, F.; Morihara, T.; Yang, F.; Teter, B.; Ubeda, O.; Salem, N., Jr.; Frautschy, S.A.; Cole, G.M. A diet enriched with the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid reduces amyloid burden in an aged Alzheimer mouse model. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3032–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.N.; Martinez-Coria, H.; Khashwji, H.; Hall, E.B.; Yurko-Mauro, K.A.; Ellis, L.; LaFerla, F.M. Dietary docosahexaenoic acid and docosapentaenoic acid ameliorate amyloid-beta and tau pathology via a mechanism involving presenilin 1 levels. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4385–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, A.; de Rosny, C.; Kieu, T.L.; Perrey, S.; Berger, H.; Fluckiger, A.; Muller, T.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Pichon, L.; Hichami, A.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits both NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and JNK-mediated mature IL-1beta secretion in 5-fluorouracil-treated MDSC: Implication in cancer treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madore, C.; Leyrolle, Q.; Morel, L.; Rossitto, M.; Greenhalgh, A.D.; Delpech, J.C.; Martinat, M.; Bosch-Bouju, C.; Bourel, J.; Rani, B.; et al. Essential omega-3 fatty acids tune microglial phagocytosis of synaptic elements in the mouse developing brain. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.K.; Yu, H.N.; Noh, E.M.; Kim, J.M.; Hong, O.Y.; Youn, H.J.; Jung, S.H.; Kwon, K.B.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.R. DHA blocks TPA-induced cell invasion by inhibiting MMP-9 expression via suppression of the PPAR-gamma/NF-kappaB pathway in MCF-7 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard-Watkins, R.; Plourde, M. Fatty acid metabolism in carriers of apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele: Is it contributing to higher risk of cognitive decline and coronary heart disease? Nutrients 2014, 6, 4452–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Khalil, H.; Nicolazzo, J.A. The Impact of Docosahexaenoic Acid on Alzheimer’s Disease: Is There a Role of the Blood-Brain Barrier? Curr. Clin Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 222–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.L.; Zandi, P.P.; Tucker, K.L.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Kuller, L.H.; Fried, L.P.; Burke, G.L.; Carlson, M.C. Benefits of fatty fish on dementia risk are stronger for those without APOE epsilon4. Neurology 2005, 65, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassine, H.N.; Croteau, E.; Rawat, V.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Rapoport, S.I.; Cunnane, S.C.; Umhau, J.C. DHA brain uptake and APOE4 status: A PET study with [1-(11)C]-DHA. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstey, K.J.; Mack, H.A.; Cherbuin, N. Alcohol consumption as a risk factor for dementia and cognitive decline: Meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2009, 17, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivipelto, M.; Rovio, S.; Ngandu, T.; Kareholt, I.; Eskelinen, M.; Winblad, B.; Hachinski, V.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Soininen, H.; Tuomilehto, J.; et al. Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 magnifies lifestyle risks for dementia: A population-based study. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2762–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downer, B.; Zanjani, F.; Fardo, D.W. The relationship between midlife and late life alcohol consumption, APOE e4 and the decline in learning and memory among older adults. Alcohol Alcohol. 2014, 49, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, T.; Helkala, E.L.; Viitanen, M.; Kareholt, I.; Fratiglioni, L.; Winblad, B.; Soininen, H.; Tuomilehto, J.; Nissinen, A.; Kivipelto, M. Alcohol drinking in middle age and subsequent risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia in old age: A prospective population based study. BMJ 2004, 329, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, R.P. Role of phosphatidylcholine-DHA in preventing APOE4-associated Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidlaw, M.; Cockerline, C.A.; Rowe, W.J. A randomized clinical trial to determine the efficacy of manufacturers’ recommended doses of omega-3 fatty acids from different sources in facilitating cardiovascular disease risk reduction. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domiciano, T.P.; Wakita, D.; Jones, H.D.; Crother, T.R.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Arditi, M.; Shimada, K. Quercetin Inhibits Inflammasome Activation by Interfering with ASC Oligomerization and Prevents Interleukin-1 Mediated Mouse Vasculitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Wang, F.M.; Kong, L.D. Quercetin and allopurinol ameliorate kidney injury in STZ-treated rats with regulation of renal NLRP3 inflammasome activation and lipid accumulation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.H.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Kong, L.D. Allopurinol, quercetin and rutin ameliorate renal NLRP3 inflammasome activation and lipid accumulation in fructose-fed rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Lu, X.Y.; Shi, J.J.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, Q.B.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhang, S.J. Quercetin protects against diabetic encephalopathy via SIRT1/NLRP3 pathway in db/db mice. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 3449–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, C.; Hebron, M.; Huang, X.; Ahn, J.; Rissman, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Turner, R.S. Resveratrol regulates neuro-inflammation and induces adaptive immunity in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, T.; Saitoh, T.; Kozaki, T.; Park, S.; Takahama, M.; Akira, S. Resveratrol inhibits the acetylated alpha-tubulin-mediated assembly of the NLRP3-inflammasome. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, L. Resveratrol Suppresses Abeta-Induced Microglial Activation Through the TXNIP/TRX/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Ma, L.; Ruan, L.; Kong, Y.; Mou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.M.; Le, Y. Resveratrol differentially modulates inflammatory responses of microglia and astrocytes. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, L.; Liu, X.; Lu, T.; Xie, C.; Jia, J. Resveratrol Attenuates Microglial Activation via SIRT1-SOCS1 Pathway. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 8791832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagouge, M.; Argmann, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Meziane, H.; Lerin, C.; Daussin, F.; Messadeq, N.; Milne, J.; Lambert, P.; Elliott, P.; et al. Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 2006, 127, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Resveratrol: How Much Wine Do You Have to Drink to Stay Healthy? Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boocock, D.J.; Faust, G.E.; Patel, K.R.; Schinas, A.M.; Brown, V.A.; Ducharme, M.P.; Booth, T.D.; Crowell, J.A.; Perloff, M.; Gescher, A.J.; et al. Phase I dose escalation pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers of resveratrol, a potential cancer chemopreventive agent. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2007, 16, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginde, A.A.; Liu, M.C.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. Demographic differences and trends of vitamin D insufficiency in the US population, 1988–2004. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresz, K. Proper Calcium Use: Vitamin K2 as a Promoter of Bone and Cardiovascular Health. Integr. Med. 2015, 14, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; et al. Vitamin D Receptor Inhibits NLRP3 Activation by Impeding Its BRCC3-Mediated Deubiquitination. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Hou, Y.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wang, X.; Gong, T.; Jiang, W. Synthetic vitamin K analogs inhibit inflammation by targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Baek, M.S.; Yoon, D.S.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, B.W.; Oh, B.S.; Park, J.; Kim, H.J. Vitamin D Inhibits Expression and Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase in Human Lung Fibroblasts (HFL-1) Cells. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2014, 77, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, P.M.; Mannan, N.; Hitman, G.A.; Noonan, K.; Mills, P.G.; Syndercombe-Court, D.; Aganna, E.; Price, C.P.; Boucher, B.J. Circulating MMP9, vitamin D and variation in the TIMP-1 response with VDR genotype: Mechanisms for inflammatory damage in chronic disorders? QJM 2002, 95, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, N.; Fadaei, R.; Ahmadi, R.; Mohammad, M.H.; Shahmohamadnejad, S.; Tavakoli-Yaraki, M.; Aghajani, H.; Fallah, S. Role of serum MMP-9 levels and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in the susceptibility to coronary artery disease: An association study in Iranian population. Gene 2017, 628, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, D.; Kocyigit, D.; Adorni, M.P.; Marchi, C.; Ronda, N.; Bernini, F.; Gurses, K.M.; Canpinar, H.; Guc, D.; Oguz, S.H.; et al. Vitamin D replacement ameliorates serum lipoprotein functions, adipokine profile and subclinical atherosclerosis in pre-menopausal women. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; You, Y.; Swier, V.; Tang, L.; Radwan, M.M.; Pandya, A.N.; Agrawal, D.K. Vitamin D Protects Against Atherosclerosis via Regulation of Cholesterol Efflux and Macrophage Polarization in Hypercholesterolemic Swine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 2432–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddock, J.; Cavadino, A.; Power, C.; Hypponen, E. 25-hydroxyvitamin D, APOE varepsilon4 genotype and cognitive function: Findings from the 1958 British birth cohort. Eur. J. Clin Nutr. 2015, 69, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Khemka, V.K.; Ganguly, A.; Roy, D.; Ganguly, U.; Chakrabarti, S. Vitamin D and Alzheimer’s Disease: Neurocognition to Therapeutics. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 2015, 192747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.D. The worldwide challenge of the dementias: A role for B vitamins and homocysteine? Food Nutr. Bull 2008, 29, S143–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, K.; Gustafson, L.; Nornholm, M.; Hultberg, B. Plasma homocysteine, apolipoprotein E status and vascular disease in elderly patients with mental illness. Clin Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusca, V.G.; Mihai, A.D.; Fuior, E.V.; Fenyo, I.M.; Gafencu, A.V. High levels of homocysteine downregulate apolipoprotein E expression via nuclear factor kappa B. World J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 7, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonn, E.; Yusuf, S.; Arnold, M.J.; Sheridan, P.; Pogue, J.; Micks, M.; McQueen, M.J.; Probstfield, J.; Fodor, G.; Held, C.; et al. Homocysteine lowering with folic acid and B vitamins in vascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jerneren, F.; Elshorbagy, A.K.; Oulhaj, A.; Smith, S.M.; Refsum, H.; Smith, A.D. Brain atrophy in cognitively impaired elderly: The importance of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamin status in a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, S.M.; Zhu, X.; Zeisel, S.H. Phosphatidylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase activity and dietary choline regulate liver-plasma lipid flux and essential fatty acid metabolism in mice. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3386–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magret, V.; Elkhalil, L.; Nazih-Sanderson, F.; Martin, F.; Bourre, J.M.; Fruchart, J.C.; Delbart, C. Entry of polyunsaturated fatty acids into the brain: Evidence that high-density lipoprotein-induced methylation of phosphatidylethanolamine and phospholipase A2 are involved. Biochem. J. 1996, 316 Pt 3, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selley, M.L. A metabolic link between S-adenosylhomocysteine and polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijk, N.; Watkins, C.J.; Hageman, R.J.; Sijben, J.C.; Kamphuis, P.G.; Wurtman, R.J.; Broersen, L.M. Combined dietary folate, vitamin B-12, and vitamin B-6 intake influences plasma docosahexaenoic acid concentration in rats. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Lee, G.S. Riboflavin, vitamin B2, attenuates NLRP3, NLRC4, AIM2, and non-canonical inflammasomes by the inhibition of caspase-1 activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Kushiyama, H.; Suidasari, S.; Hatakeyama, M.; Imura, H.; Kato, N.; Suda, T. Vitamin B6 Prevents IL-1beta Protein Production by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 24517–24527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.; Mutti, E.; Tacchini, L.; Gammella, E.; Tredici, G.; Scalabrino, G. Indirect down-regulation of nuclear NF-kappaB levels by cobalamin in the spinal cord and liver of the rat. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, S.; Zhai, L.; Yao, S.; Sang, H.; Yang, N.; Song, G.; Gu, J.; et al. Niacin inhibits vascular inflammation via downregulating nuclear transcription factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 263786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappacosta, B.; Graziano, M.; Persichilli, S.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Mastroiacovo, P.; Iacoviello, L. 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T and A1298C polymorphisms: Genotype frequency and association with homocysteine and folate levels in middle-southern Italian adults. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2014, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Short, J.L.; Newman, S.A.; Choy, K.H.C.; Tiwari, D.; Yap, C.; Senyschyn, D.; Banks, W.A.; Nicolazzo, J.A. Cognitive benefits of lithium chloride in APP/PS1 mice are associated with enhanced brain clearance of beta-amyloid. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 70, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, W.T.; Klein, P.S. Validating GSK3 as an in vivo target of lithium action. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Kessing, L.V.; Gerds, T.A.; Knudsen, N.N.; Jorgensen, L.F.; Kristiansen, S.M.; Voutchkova, D.; Ernstsen, V.; Schullehner, J.; Hansen, B.; Andersen, P.K.; et al. Association of Lithium in Drinking Water With the Incidence of Dementia. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajardo, V.A.; Fajardo, V.A.; LeBlanc, P.J.; MacPherson, R.E.K. Examining the Relationship between Trace Lithium in Drinking Water and the Rising Rates of Age-Adjusted Alzheimer’s Disease Mortality in Texas. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 61, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, M.A.; Viel, T.A.; Buck, H.S. Microdose lithium treatment stabilized cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2013, 10, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeyasingam, N. Lithium to Treat—Or Prevent—Dementia: A Short Discussion. J. Neurol. Expir. Neurosci. 2020, 6, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mullins, V.A.; Bresette, W.; Johnstone, L.; Hallmark, B.; Chilton, F.H. Genomics in Personalized Nutrition: Can You “Eat for Your Genes”? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, S.; Roberts, J.S.; Marteau, T.M.; Silliman, R.; Cupples, L.A.; Green, R.C. Health behavior changes after genetic risk assessment for Alzheimer disease: The REVEAL Study. Alzheimer. Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2008, 22, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, R.S.; Hristov, H.; Saif, N.; Hackett, K.; Hendrix, S.; Melendez, J.; Safdieh, J.; Fink, M.; Thambisetty, M.; Sadek, G.; et al. Individualized clinical management of patients at risk for Alzheimer’s dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 15, 1588–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diet Options | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Low-glycemic index/ Low-carbohydrate diets |
|
| Ketogenic diet (On the spectrum of low-carbohydrate diets) |
|
| Extra virgin olive oil |
|
| Cruciferous vegetables Capers and red onion |
|
| Fatty fish (≥2 times/week) |
|
| Limit alcohol |
|
| Supplement | Dose |
|---|---|
| DHA |
|
| Quercetin |
|
| Resveratrol |
|
| Vitamin D3 |
|
| Vitamin K2 MK7 |
|
| B-vitamin complex |
|
| Lithium |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Norwitz, N.G.; Saif, N.; Ariza, I.E.; Isaacson, R.S. Precision Nutrition for Alzheimer’s Prevention in ApoE4 Carriers. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041362
Norwitz NG, Saif N, Ariza IE, Isaacson RS. Precision Nutrition for Alzheimer’s Prevention in ApoE4 Carriers. Nutrients. 2021; 13(4):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041362
Chicago/Turabian StyleNorwitz, Nicholas G., Nabeel Saif, Ingrid Estrada Ariza, and Richard S. Isaacson. 2021. "Precision Nutrition for Alzheimer’s Prevention in ApoE4 Carriers" Nutrients 13, no. 4: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041362
APA StyleNorwitz, N. G., Saif, N., Ariza, I. E., & Isaacson, R. S. (2021). Precision Nutrition for Alzheimer’s Prevention in ApoE4 Carriers. Nutrients, 13(4), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041362