Fast Eating Is Associated with Increased BMI among High-School Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
Aims
2. Materials and Methods
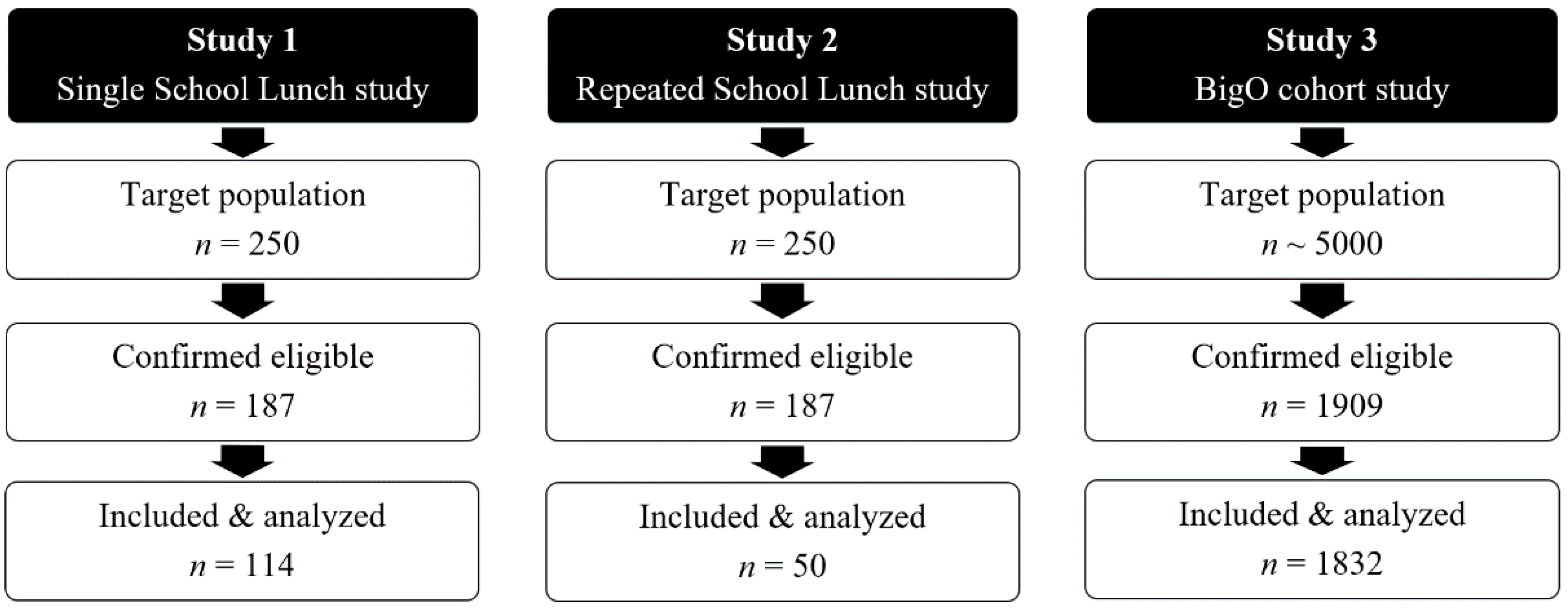
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting
2.3. Participants
2.4. Data Sources/Measurements
2.5. Served Food
2.6. Study Size
2.7. Statistics
2.8. Bias
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Descriptive Data
3.3. Main Results
3.3.1. Study 1. Single School Lunch Study
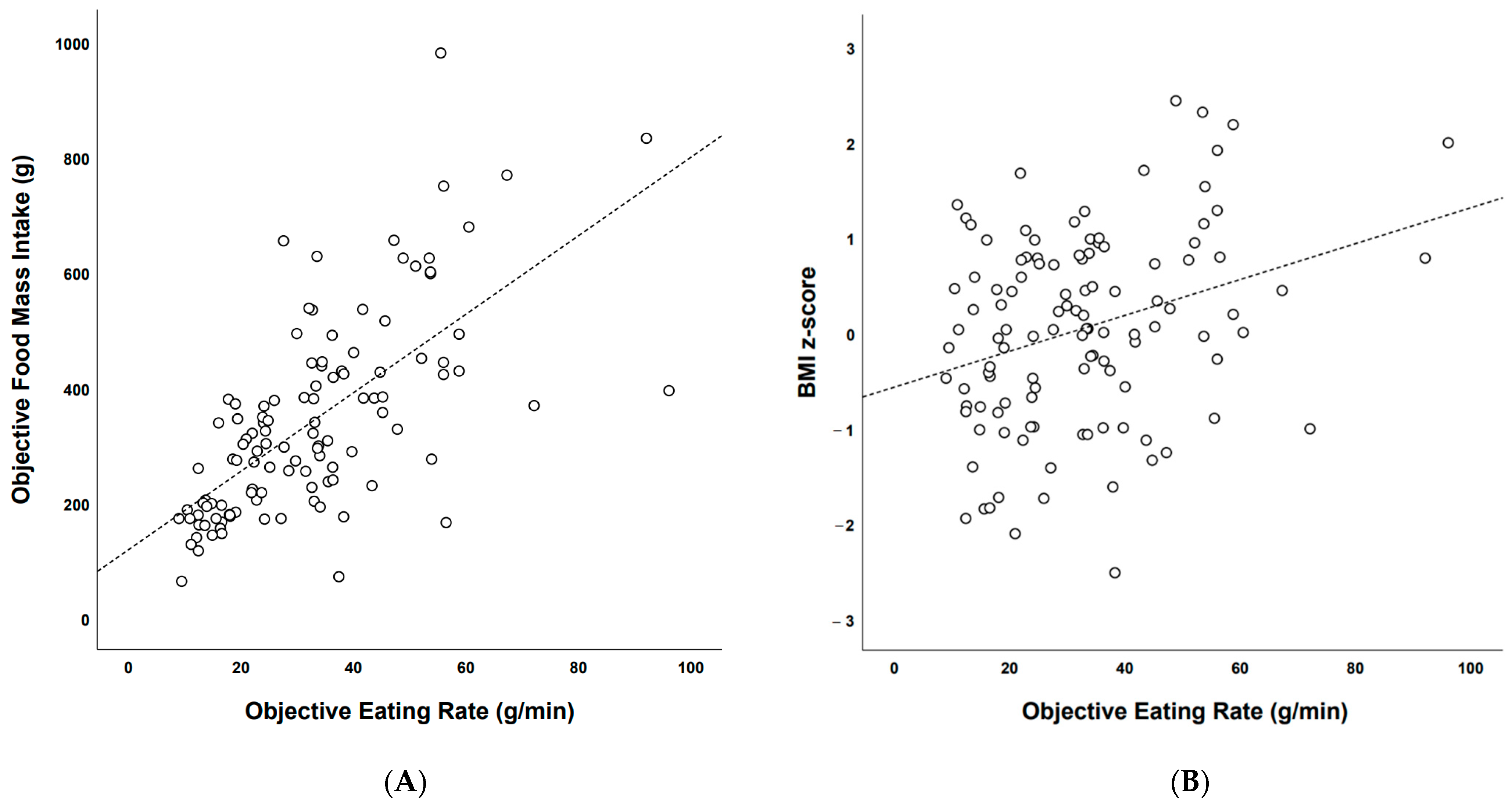
Association between Objective Eating Rate and Objective Food Mass Intake (g)
Association between Objective Eating Rate (g/min) and BMI z-Scores
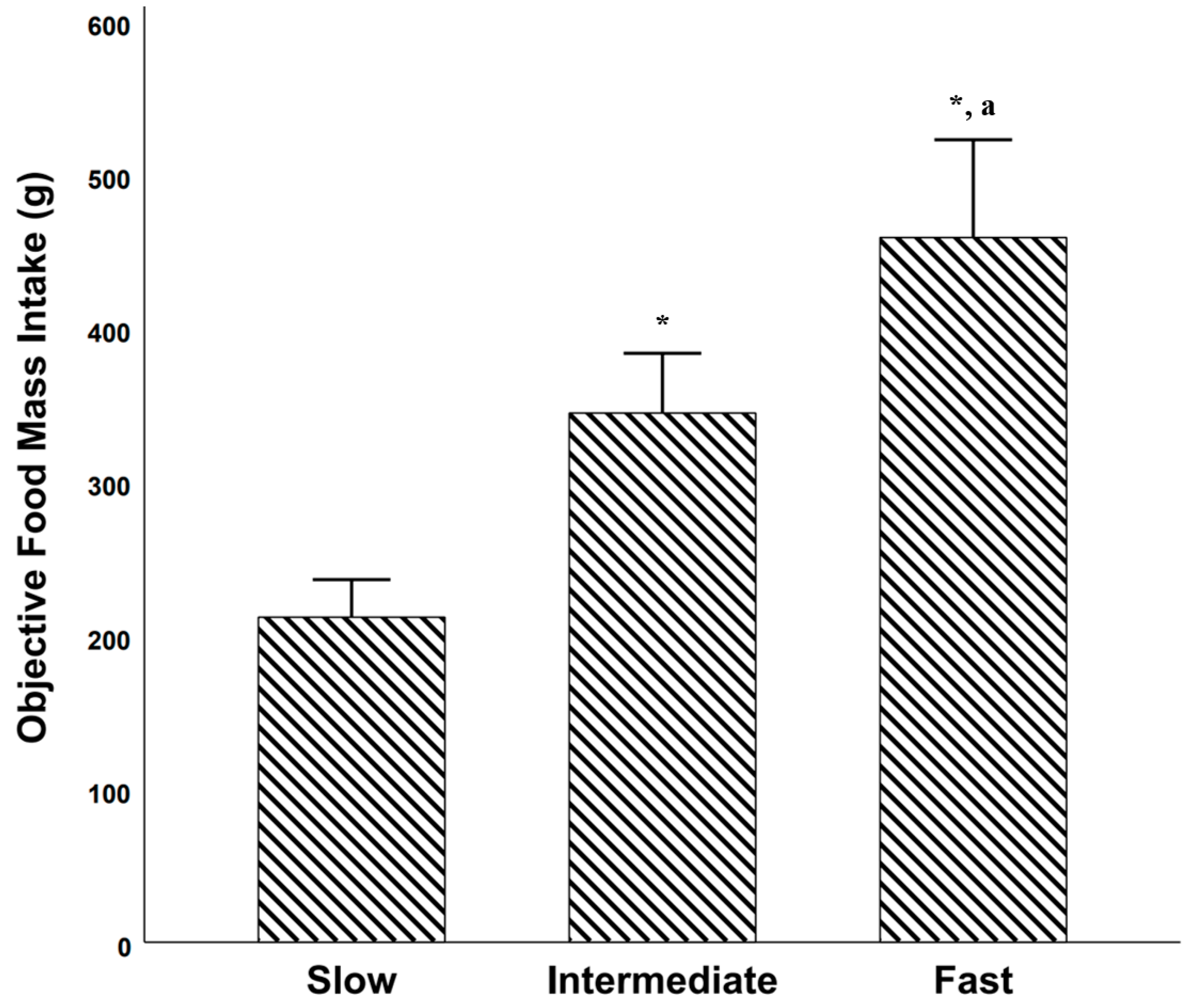
Objective Food Mass Intake among Objectively Established Eating Rate Categories
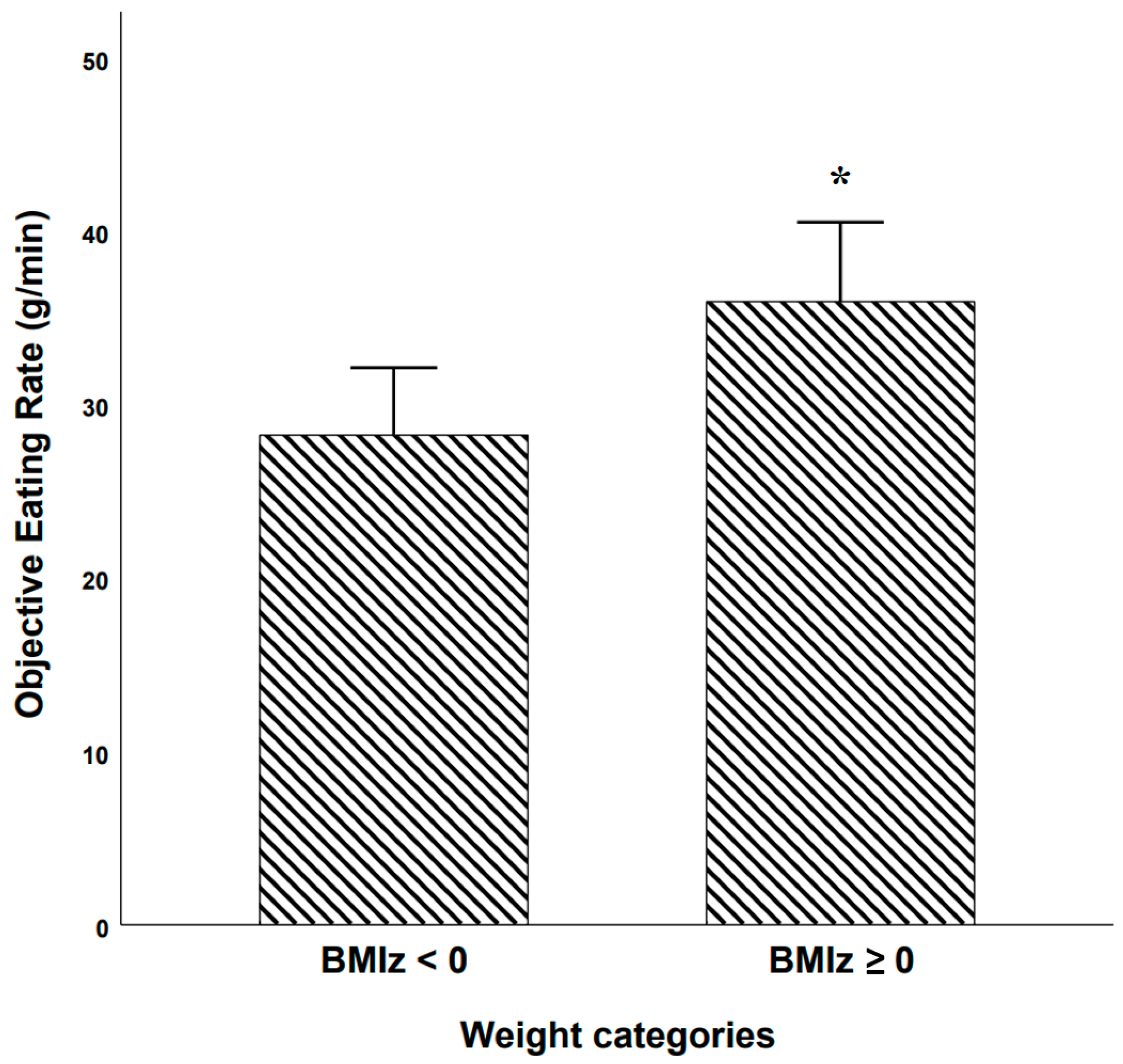
Objective Eating Rate among BMI z-Score Based Weight Categories
Objective Eating Rate among Self-Reported Slow, Intermediate, and Fast Eaters
Categorical Agreement: Self-Reported vs. Objective Eating Rate Categories
3.3.2. Study 2. Repeated School Lunch Study
Categorical Agreement: Self-Reported vs. Objectively Established Eating Rate Categories Lunches 1 and 2
Categorical Agreement: Self-Reported Eating Rate Categories Lunch 1 vs. Lunch 2
Categorical Agreement: Objective Eating Rate Categories Lunch 1 vs. Lunch 2
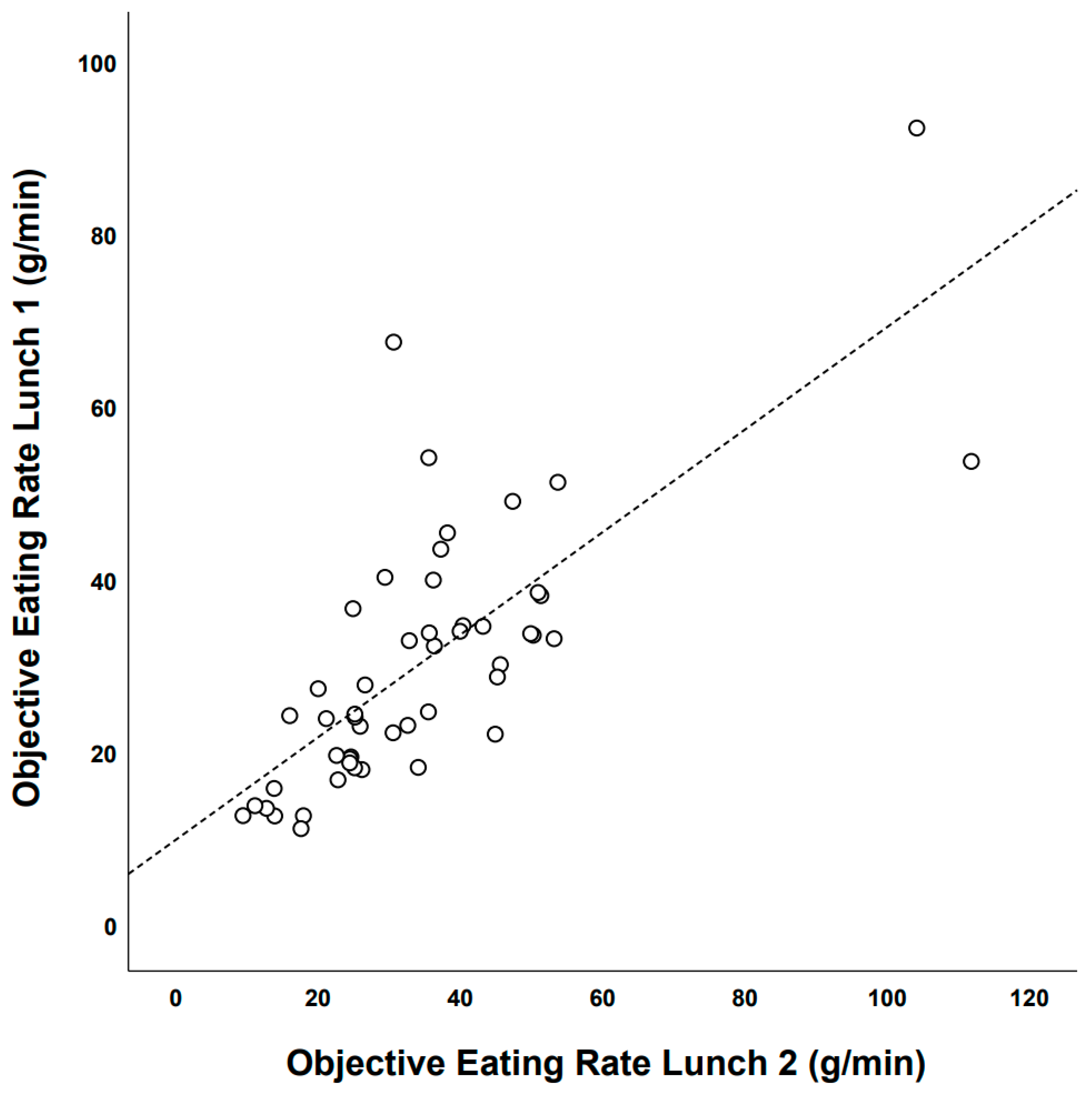
Test–Retest Reliability of Objective Eating Rate: Lunch Meal 1 vs. Lunch Meal 2
3.3.3. Study 3. BigO Cohort Study
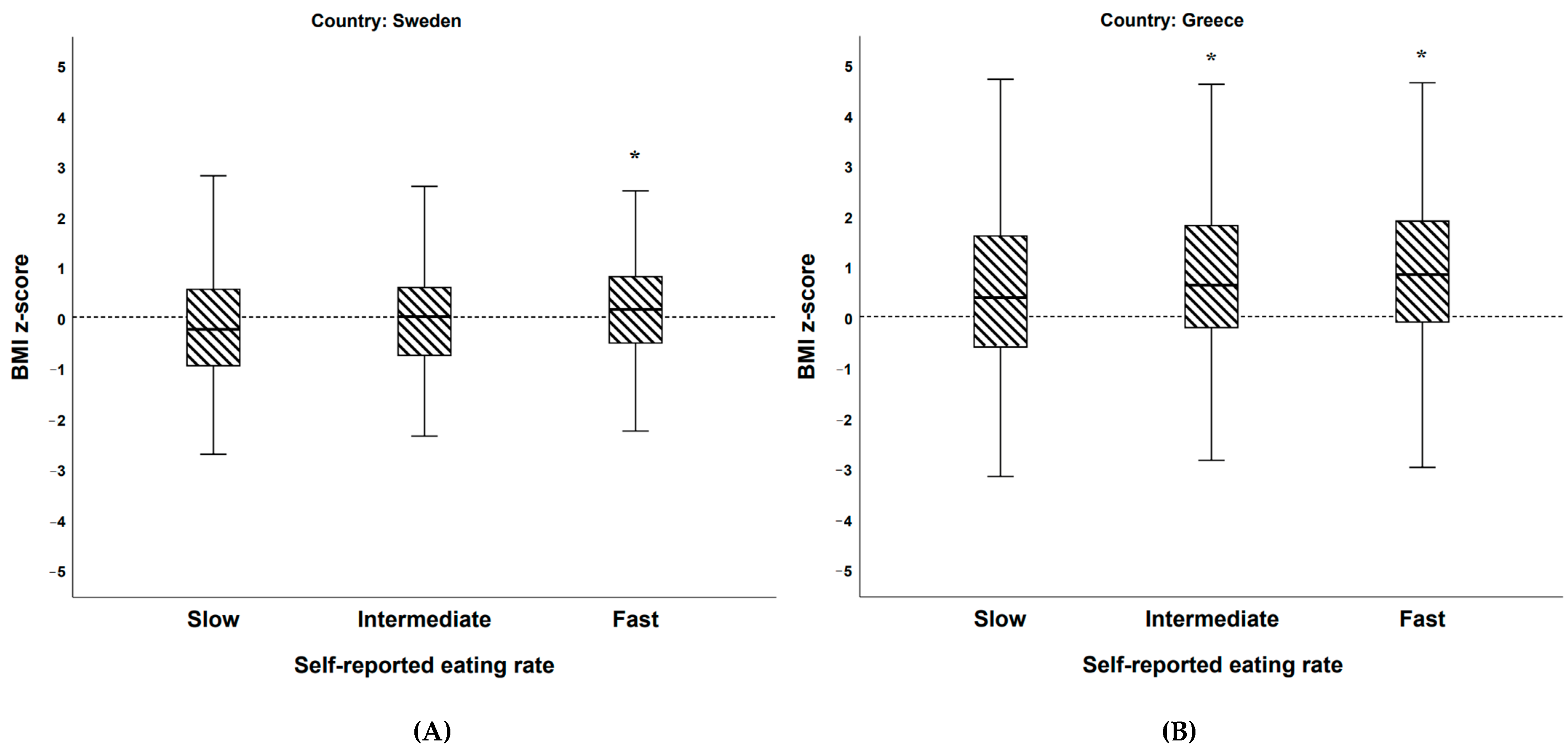
The BigO Cohort: BMI z-Scores among Self-Reported Eating Rate (Categorical)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riaz, H.; Khan, M.S.; Siddiqi, T.J.; Usman, M.S.; Shah, N.; Goyal, A.; Khan, S.S.; Mookadam, F.; Krasuski, R.A.; Ahmed, H. Association Between Obesity and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, 183788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppino, F.S.; de Wit, L.M.; Bouvy, P.F.; Stijnen, T.; Cuijpers, P.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Zitman, F.G. Overweight, Obesity, and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Douglas, I.; Forbes, H.; Dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Leon, D.A.; Smeeth, L. Body-Mass Index and Risk of 22 Specific Cancers: A Population-Based Cohort Study of 5·24 Million UK Adults. Lancet 2014, 384, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Obesity Is a Common, Serious, and Costly Disease. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html (accessed on 11 December 2020).
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Lo, S.K.; Westerterp, K.R.; Rush, E.C.; Rosenbaum, M.; Luke, A.; Schoeller, D.A.; DeLany, J.P.; Butte, N.F.; et al. Estimating the Changes in Energy Flux That Characterize the Rise in Obesity Prevalence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- How the World Could Better Fight Obesity | McKinsey. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/healthcare-systems-and-services/our-insights/how-the-world-could-better-fight-obesity (accessed on 17 May 2019).
- Hill, J.O.; Wyatt, H.R.; Peters, J.C. Energy Balance and Obesity. Circulation 2012, 126, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Kraak, V.I.; Allender, S.; Atkins, V.J.; Baker, P.I.; Bogard, J.R.; Brinsden, H.; Calvillo, A.; De Schutter, O.; Devarajan, R.; et al. The Global Syndemic of Obesity, Undernutrition, and Climate Change: The Lancet Commission Report. Lancet 2019, 393, 791–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The Global Obesity Pandemic: Shaped by Global Drivers and Local Environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.O.; Liu, Y.; Birch, L.L.; Rolls, B.J. Effects of Portion Size and Energy Density on Young Children’s Intake at a Meal. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrad, H.; Llewellyn, C.H.; Johnson, L.; Boniface, D.; Jebb, S.A.; Van Jaarsveld, C.H.M.; Wardle, J. Meal Size Is a Critical Driver of Weight Gain in Early Childhood. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, R.I.; Moore, R.H.; Faith, M.S.; Stallings, V.A.; Kral, T.V.E.; Stunkard, A.J. Identification of an Obese Eating Style in 4-Year-Old Children Born at High and Low Risk for Obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2010, 18, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, E.; Almiron-Roig, E.; Rutters, F.; De Graaf, C.; Forde, C.G.; Tudur Smith, C.; Nolan, S.J.; Jebb, S.A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Examining the Effect of Eating Rate on Energy Intake and Hunger. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 123–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, P.; Langlet, B.; Glossner, A.; Ioakimidis, I. Food Intake during School Lunch Is Better Explained by Objectively Measured Eating Behaviors than by Subjectively Rated Food Taste and Fullness: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, A.; Goh, A.T.; Fries, L.R.; Sadananthan, S.A.; Velan, S.S.; Michael, N.; Tint, M.-T.; Fortier, M.V.; Chan, M.J.; Toh, J.Y.; et al. Faster Eating Rates Are Associated with Higher Energy Intakes during an Ad Libitum Meal, Higher BMI and Greater Adiposity among 4·5-Year-Old Children: Results from the Growing Up in Singapore Towards Healthy Outcomes (GUSTO) Cohort. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, A.; McCrickerd, K.; Aris, I.M.; Goh, A.T.; Chong, Y.-S.; Tan, K.H.; Yap, F.; Shek, L.P.; Meaney, M.J.; Broekman, B.F.P.; et al. Eating Behaviors Moderate the Associations between Risk Factors in the First 1000 Days and Adiposity Outcomes at 6 Years of Age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Hirakawa, Y.; Nakamura, U.; Kiyohara, Y.; Kitazono, T.; Ninomiya, T. Association between Eating Rate and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2015, 39, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.L.; Bergh, C.; Södersten, P.; Sabin, M.A.; Hollinghurst, S.; Hunt, L.P.; Shield, J.P.H. Treatment of Childhood Obesity by Retraining Eating Behaviour: Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ 2009, 340, 5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioakimidis, I.; Zandian, M.; Bergh, C.; Södersten, P. A Method for the Control of Eating Rate: A Potential Intervention in Eating Disorders. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandian, M.; Ioakimidis, I.; Bergh, C.; Södersten, P. Cause and Treatment of Anorexia Nervosa. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhurandhar, N.V.; Schoeller, D.; Brown, A.W.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Thomas, D.; Sørensen, T.I.A.; Speakman, J.R.; Jeansonne, M.; Allison, D.B. Energy Balance Measurement Working Group Energy Balance Measurement: When Something Is Not Better than Nothing. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2015, 39, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A. Implausible Results in Human Nutrition Research. BMJ 2013, 347, 6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, J.D.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Is Everything We Eat Associated with Cancer? A Systematic Cookbook Review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Boer, J.H.W.; Kranendonk, J.; Van de Wiel, A.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Geelen, A.; Mars, M. Self-Reported Eating Rate Is Associated with Weight Status in a Dutch Population: A Validation Study and a Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petty, A.J.; Melanson, K.J.; Greene, G.W. Self-Reported Eating Rate Aligns with Laboratory Measured Eating Rate but Not with Free-Living Meals. Appetite 2013, 63, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, E.; Haszard, J.; Worsfold, A.; Venn, B. Comparison of Self-Reported Speed of Eating with an Objective Measure of Eating Rate. Nutrients 2020, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Katagiri, A.; Tsuji, T.; Shimoda, T.; Amano, K. Self-Reported Rate of Eating Correlates with Body Mass Index in 18-y-Old Japanese Women. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, H.; Miyake, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Hirota, Y. Rate of Eating in Early Life Is Positively Associated with Current and Later Body Mass Index among Young Japanese Children: The Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. Nutr. Res. 2017, 37, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, R.; Tamakoshi, K.; Yatsuya, H.; Murata, C.; Sekiya, A.; Wada, K.; Zhang, H.M.; Matsushita, K.; Sugiura, K.; Takefuji, S.; et al. Eating Fast Leads to Obesity: Findings Based on Self-Administered Questionnaires among Middle-Aged Japanese Men and Women. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 16, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.L.; Madden, C.; Gray, A.; Waters, D.; Horwath, C. Faster Self-Reported Speed of Eating Is Related to Higher Body Mass Index in a Nationwide Survey of Middle-Aged Women. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, P.S.; Van Dam, R.M.; Whitton, C.; Tan, L.W.L.; Forde, C.G. Association Between Self-Reported Eating Rate, Energy Intake, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in a Multi-Ethnic Asian Population. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, D.H.; Jang, J.S.; Nam, G.E.; Shin, Y.N.; Bok, A.R.; Kim, M.J.; Cho, K.H. Eating Rate Is Associated with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Korean Adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Splendid. Available online: https://splendid-program.eu/ (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Maramis, C.; Diou, C.; Ioakeimidis, I.; Lekka, I.; Dudnik, G.; Mars, M.; Maglaveras, N.; Bergh, C.; Delopoulos, A. Preventing Obesity and Eating Disorders through Behavioural Modifications: The SPLENDID Vision. In Proceedings of the 2014 4th International Conference on Wireless Mobile Communication and Healthcare–Transforming Healthcare Through Innovations in Mobile and Wireless Technologies (MOBIHEALTH), Athens, Greece, 3–5 November 2014; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- BigO. Available online: https://bigoprogram.eu/ (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Diou, C.; Sarafis, I.; Papapanagiotou, V.; Alagialoglou, L.; Lekka, I.; Filos, D.; Stefanopoulos, L.; Kilintzis, V.; Maramis, C.; Karavidopoulou, Y.; et al. BigO: A Public Health Decision Support System for Measuring Obesogenic Behaviors of Children in Relation to Their Local Environment. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2020, 2020, 5864–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Canadian Pediatric Endocrine Group (CPEG) Working Committee for National Growth Charts; Rodd, C.; Metzger, D.L.; Sharma, A. Extending World Health Organization Weight-for-Age Reference Curves to Older Children. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Child. Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age; Methods and Development; De Onis, M., Ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; ISBN 978-92-4-154693-5. [Google Scholar]
- Esfandiari, M.; Papapanagiotou, V.; Diou, C.; Zandian, M.; Nolstam, J.; Södersten, P.; Bergh, C. Control of Eating Behavior Using a Novel Feedback System. J. Vis. Exp. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlet, B.; Anvret, A.; Maramis, C.; Moulos, I.; Papapanagiotou, V.; Diou, C.; Lekka, E.; Heimeier, R.; Delopoulos, A.; Ioakimidis, I. Objective Measures of Eating Behaviour in a Swedish High School. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2017, 36, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Universität Düsseldorf: Gpower. Available online: https://www.psychologie.hhu.de/arbeitsgruppen/allgemeine-psychologie-und-arbeitspsychologie/gpower.html (accessed on 7 December 2020).
- Hallgren, K.A. Computing Inter-Rater Reliability for Observational Data: An Overview and Tutorial. Tutor. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2012, 8, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.G. Measures of Reliability in Sports Medicine and Science. Sports Med. 2000, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreadsheets for Analysis of Validity and Reliability. Available online: http://www.sportsci.org/2015/ValidRely.htm (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- New View of Statistics: Effect Magnitudes. Available online: https://www.sportsci.org/resource/stats/effectmag.html (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater Reliability: The Kappa Statistic. Biochem. Med. (Zagreb) 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Must, A.; Anderson, S.E. Body Mass Index in Children and Adolescents: Considerations for Population-Based Applications. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, A.; Goh, A.T.; Fries, L.R.; Sadananthan, S.A.; Velan, S.S.; Michael, N.; Tint, M.T.; Fortier, M.V.; Chan, M.J.; Toh, J.Y.; et al. A Description of an “obesogenic” Eating Style That Promotes Higher Energy Intake and Is Associated with Greater Adiposity in 4.5year-Old Children: Results from the GUSTO Cohort. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, C.H.; Van Jaarsveld, C.H.M.; Boniface, D.; Carnell, S.; Wardle, J. Eating Rate Is a Heritable Phenotype Related to Weight in Children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, I.P.; Elliott, S.A.; Siervo, M.; Padwal, R.; Bertoli, S.; Battezzati, A.; Prado, C.M. Is Obesity Associated with Altered Energy Expenditure? Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.J.; Ponnalagu, S.; Bi, X.; Forde, C. Does Basal Metabolic Rate Drive Eating Rate? Physiol. Behav. 2018, 189, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, R.J.; O’Reilly, L.M.; Whybrow, S.; Fuller, Z.; Johnstone, A.M.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Ritz, P.; Horgan, G.W. Measuring the Difference between Actual and Reported Food Intakes in the Context of Energy Balance under Laboratory Conditions. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 2032–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustachio Colombo, P.; Patterson, E.; Elinder, L.S.; Lindroos, A.K. The Importance of School Lunches to the Overall Dietary Intake of Children in Sweden: A Nationally Representative Study. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyritsis, K.; Tatli, C.L.; Diou, C.; Delopoulos, A. Automated Analysis of in Meal Eating Behavior Using a Commercial Wristband IMU Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju Island, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 2843–2846. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinidis, D.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Langlet, B.; Daras, P.; Ioakimidis, I. Validation of a Deep Learning System for the Full Automation of Bite and Meal Duration Analysis of Experimental Meal Videos. Nutrients 2020, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.; Kersbergen, I.; Brunstrom, J.M.; Field, M. I’m Watching You. Awareness That Food Consumption Is Being Monitored Is a Demand Characteristic in Eating-Behaviour Experiments. Appetite 2014, 83, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.; Gabriel, K.; Nehme, E.K.; Mandell, D.J.; Hoelscher, D.M. Measuring the Bias, Precision, Accuracy, and Validity of Self-Reported Height and Weight in Assessing Overweight and Obesity Status among Adolescents Using a Surveillance System. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, M.M.; Anderson, A.S.; Norton, G.N.M.; Newson, L. Situational Effects on Meal Intake: A Comparison of Eating Alone and Eating with Others. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 88, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Study 1. Single School Lunch Study | Study 2. Repeated School Lunch Study | Study 3. BigO Cohort Study | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 114 | 50 | 1832 |
| % females | 58.8% | 58.0% | 51.1% |
| Age, y | 16.5 ± 0.8 | 16.7 ± (0.6) | 15.8 ± 0.9 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 21.4 ± 3.1 | 21.6 ± 3.4 | 23.1 ± 6.0 |
| BMIz | 0.04 ± 1.0 | 0.08 ± 1.0 | 0.47 ± 1.4 |
| % with BMIz < 0 | 45.6% | 44.0% | 39.6% |
| % with BMIz ≥ 0 and ≤ 1.96 | 50.9% | 52.0% | 46.3% |
| % with BMIz > 1.96 | 3.5% | 4.0% | 14.1% |
| Weight, kg | 62.0 ± 11.7 | 61.8 ± 11.8 | 66.6 ± 18.0 |
| Height, cm | 170.1 ± 9.8 | 168.7 ± 8.9 | 169.9 ± 10.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fagerberg, P.; Charmandari, E.; Diou, C.; Heimeier, R.; Karavidopoulou, Y.; Kassari, P.; Koukoula, E.; Lekka, I.; Maglaveras, N.; Maramis, C.; et al. Fast Eating Is Associated with Increased BMI among High-School Students. Nutrients 2021, 13, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030880
Fagerberg P, Charmandari E, Diou C, Heimeier R, Karavidopoulou Y, Kassari P, Koukoula E, Lekka I, Maglaveras N, Maramis C, et al. Fast Eating Is Associated with Increased BMI among High-School Students. Nutrients. 2021; 13(3):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030880
Chicago/Turabian StyleFagerberg, Petter, Evangelia Charmandari, Christos Diou, Rachel Heimeier, Youla Karavidopoulou, Penio Kassari, Evangelia Koukoula, Irini Lekka, Nicos Maglaveras, Christos Maramis, and et al. 2021. "Fast Eating Is Associated with Increased BMI among High-School Students" Nutrients 13, no. 3: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030880
APA StyleFagerberg, P., Charmandari, E., Diou, C., Heimeier, R., Karavidopoulou, Y., Kassari, P., Koukoula, E., Lekka, I., Maglaveras, N., Maramis, C., Pagkalos, I., Papapanagiotou, V., Riviou, K., Sarafis, I., Tragomalou, A., & Ioakimidis, I. (2021). Fast Eating Is Associated with Increased BMI among High-School Students. Nutrients, 13(3), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030880










