Impact of Obesity in Kidney Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Epidemiology
1.2. Pathology
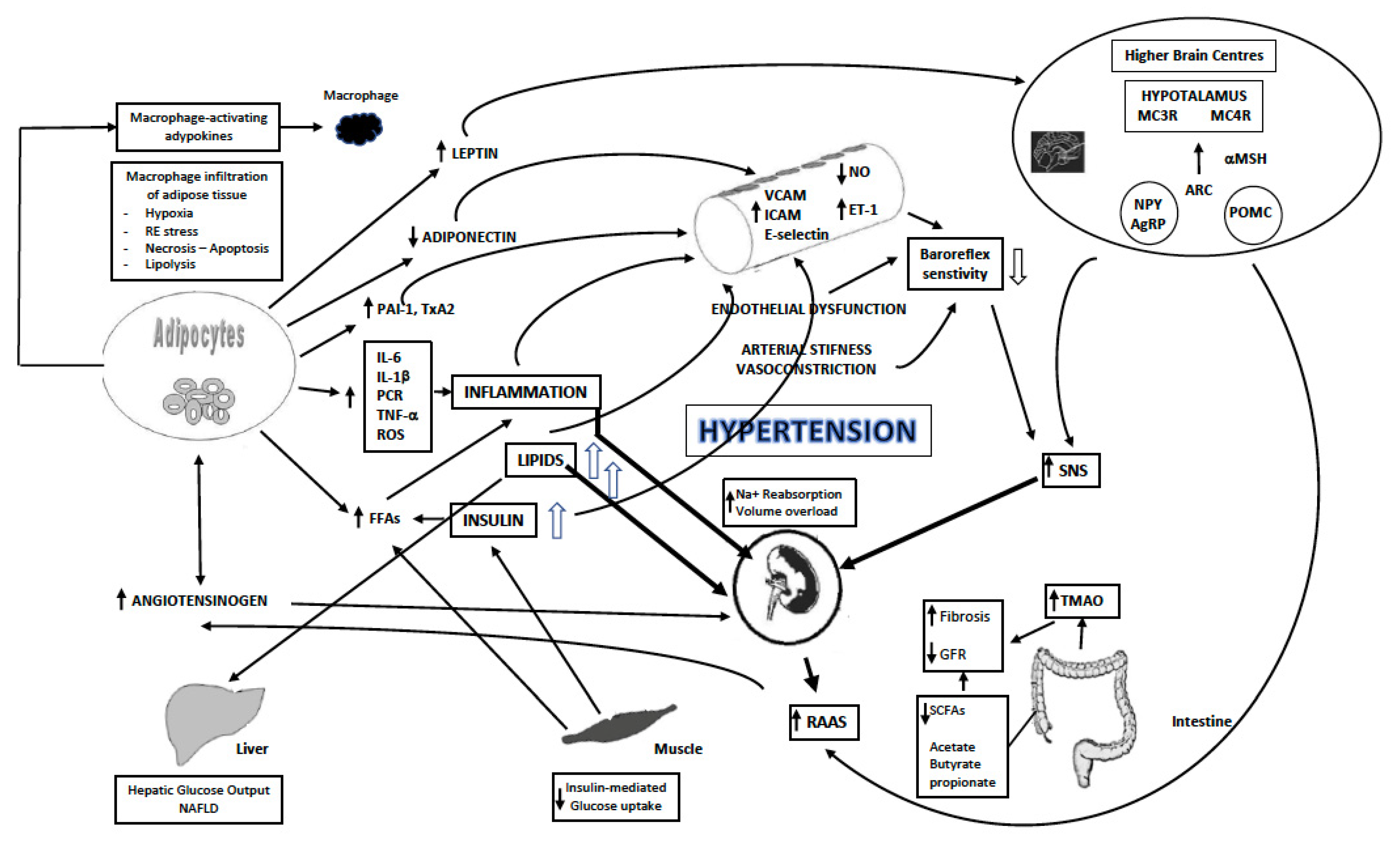
1.3. Mechanisms
1.4. Endothelial Dysfunction and Changes in Vascular Structure
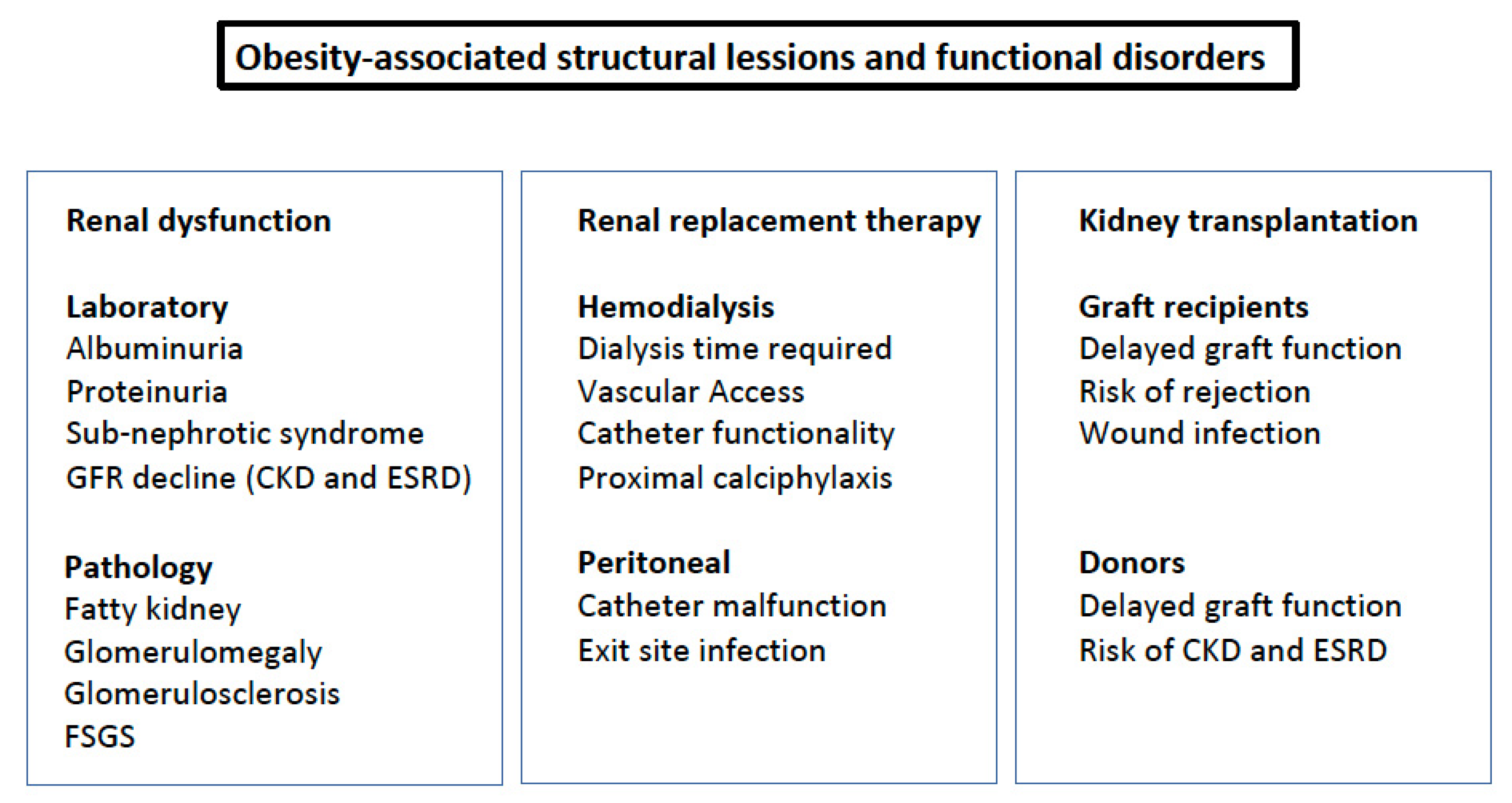
2. Clinical Consequences
2.1. Urinary Albumin Excretion and Proteinuria
2.2. Sub-Nephrotic Syndrome
2.3. Progression to CKD and ESRD
2.4. Nephrolithiasis
2.5. Renal Replacement Therapy
2.6. Kidney Transplantation
2.7. Renal Cancer
2.8. Fatty Kidney
2.9. Other Obesity-Associated Conditions and Renal Damage
3. Treatment of Obesity and Renal Damage
3.1. Life Style Intervention
3.2. Medications
3.3. Bariatric Surgery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.-Y. Chronic Kidney Disease and the Risks of Death, Cardiovascular Events, and Hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Van Der Velde, M.; Astor, B.C.; Woodward, M.; Levey, A.S.; De Jong, P.E.; Coresh, J.; Gansevoort, R.T. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: A collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, D.; Grams, M.; Sang, Y.; Black, C.; Cirillo, M.; Djurdjev, O.; Iseki, K.; Jassal, S.K.; Kimm, H.; Kronenberg, F.; et al. Associations of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with mortality and renal failure by sex: A meta-analysis. BMJ 2013, 346, f324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Lin, F.; Banerjee, T.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Eberhardt, M.S.; Morgenstern, H.; Pavkov, M.E.; Saran, R.; Powe, N.R.; et al. Trends in Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounkpatin, H.O.; Harris, S.; Fraser, S.D.S.; Day, J.; Mindell, J.S.; Taal, M.W.; O’Donoghue, D.; Roderick, P.J. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in adults in England: Comparison of nationally representative cross-sectional surveys from 2003 to 2016. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iseki, K.; Ikemiya, Y.; Kinjo, K.; Inoue, T.; Iseki, C.; Takishita, S. Body mass index and the risk of development of end-stage renal disease in a screened cohort. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polemiti, E.; Baudry, J.; Kuxhaus, O.; Jäger, S.; Bergmann, M.M.; Weikert, C.; Schulze, M.B. BMI and BMI change following incident type 2 diabetes and risk of microvascular and macrovascular complications: The EPIC-Potsdam study. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stengel, B.; Tarver–Carr, M.E.; Powe, N.R.; Eberhardt, M.S.; Brancati, F.L. Lifestyle Factors, Obesity and the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease. Epidemiology 2003, 14, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, M.; Kawar, B.; El Nahas, A.M. Influence of Obesity on Progression of Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nephron 2009, 113, c16–c23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.L.; You, Z.; Gitomer, B.; Brosnahan, G.; Torres, V.E.; Chapman, A.B.; Perrone, R.D.; Steinman, T.I.; Abebe, K.Z.; Rahbari-Oskoui, F.F.; et al. Overweight and Obesity Are Predictors of Progression in Early Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 29, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.N.; Mohsen, A.; Green, D.; Hoefield, R.A.; Summers, L.K.; Middleton, R.J.; O’Donoghue, D.J.; Kalra, P.A.; New, D.I. Body mass index has no effect on rate of progression of chronic kidney disease in non-diabetic subjects. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2776–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, C.; Borrelli, S.; Minutolo, R.; Chiodini, P.; De Nicola, L.; Conte, G. A systematic review and meta-analysis suggests obesity predicts onset of chronic kidney disease in the general population. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Muntner, P.; Hamm, L.L.; Jones, D.W.; Batuman, V.; Fonseca, V.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. The metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in U.S. adults. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, L.; Carnethon, M.; Fortmann, S.P. Association between microalbuminuria and the metabolic syndrome: NHANES III. Am. J. Hypertens. 2003, 16, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gu, D.; Chen, C.-S.; Wu, X.; Hamm, L.L.; Muntner, P.; Batuman, V.; Lee, C.-H.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Association between the metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in Chinese adults. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Shiohira, Y.; Uezu, Y.; Higa, A.; Iseki, K. Metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in Okinawa, Japan. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, I.; Han, J.H.; Myung, S.C.; Kwak, K.W.; Kim, T.-H.; Park, S.W.; Choi, N.Y.; Chung, W.H.; Ahn, S.H. Association between metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in the Korean population. Nephrology 2009, 14, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Chang, Y.; Woo, H.-Y.; Lee, K.-B.; Kim, S.-G.; Kim, D.-I.; Kim, W.S.; Suh, B.-S.; Jeong, C.; Yoon, K. Time-Dependent Association Between Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of CKD in Korean Men Without Hypertension or Diabetes. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurella, M.; Lo, J.C.; Chertow, G.M. Metabolic Syndrome and the Risk for Chronic Kidney Disease among Nondiabetic Adults. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chu, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Hsieh, P.-C.; Chung, T.-C.; Bai, C.-H.; You, S.-L.; Hwang, L.-C.; Lin, C.-M.; Sun, C.-A. Impact of metabolic syndrome on the incidence of chronic kidney disease: A Chinese cohort study. Nephrology 2012, 17, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, T.; Kiyohara, Y.; Kubo, M.; Yonemoto, K.; Tanizaki, Y.; Doi, Y.; Hirakata, H.; Iida, M. Metabolic Syndrome and CKD in a General Japanese Population: The Hisayama Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 48, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucove, J.; Vupputuri, S.; Heiss, G.; North, K.; Russell, M. Metabolic Syndrome and the Development of CKD in American Indians: The Strong Heart Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 51, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Tao, Q.; Zhan, S. Metabolic syndrome and the development of chronic kidney disease among 118 924 non-diabetic Taiwanese in a retrospective cohort. Nephrology 2010, 15, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.; Sehgal, A.R.; Kashyap, S.R.; Srinivas, T.R.; Kirwan, J.P.; Navaneethan, S.D. Metabolic Syndrome and Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidbeygi, E.; Safabakhsh, M.; Aghdam, S.D.; Mohammed, S.H.; Alizadeh, S. Metabolic syndrome and its components are related to a higher risk for albuminuria and proteinuria: Evidence from a meta-analysis on 10,603,067 subjects from 57 studies. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 13, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, A.K.T.D.C.; Dos Santos, A.M.; Salgado, J.V.; Hortegal, E.V.; Da Silva, A.A.M.; Filho, N.S. Estimated Visceral Adipose Tissue, but Not Body Mass Index, Is Associated with Reductions in Glomerular Filtration Rate Based on Cystatin C in the Early Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Nephrol. 2014, 2014, 574267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiskulnam, P.; Thokanit, N.S.; Katavetin, P.; Susanthitaphong, P.; Srisawat, N.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Tungsanga, K.; Eiam-Ong, S. The magnitude of obesity and metabolic syndrome among diabetic chronic kidney disease population: A nationwide study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammit, A.R.; Katz, M.J.; Derby, C.; Bitzer, M.; Lipton, R.B. Chronic Kidney Disease in Non-Diabetic Older Adults: Associated Roles of the Metabolic Syndrome, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.-R.; Kim, H.; Park, J.T.; Chang, T.I.; Yoo, T.-H.; Kang, S.-W.; Choi, K.H.; Sung, S.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.; et al. Obesity, Metabolic Abnormality, and Progression of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Lu, F.-H.; Chang, C.-J.; Wang, R.-S.; Yang, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-F.; Wu, J.-S. Metabolic abnormalities, but not obesity per se, associated with chronic kidney disease in a Taiwanese population. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, K.E.; Bowden, R.G.; Funderburk, L.K.; Forsse, J.S.; Ylitalo, K.R. Metabolic Health, Obesity, and Renal Function: 2013–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Life 2021, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchini, A.P. Obesity hypertension*1. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, S50–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsis, V.; Stabouli, S.; Papakatsika, S.; Rizos, Z.; Parati, G. Mechanisms of obesity-induced hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.E.; Crook, E.D.; Jones, D.W.; Wofford, M.R.; Dubbert, P.M. Mechanisms of Obesity-Associated Cardiovascular and Renal Disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2002, 324, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambham, N.; Markowitz, G.S.; Valeri, A.M.; Lin, J.; D’Agati, V.D. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: An emerging epidemic. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deji, N.; Kume, S.; Araki, S.-I.; Soumura, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Isshiki, K.; Chin-Kanasaki, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Koya, D.; Haneda, M.; et al. Structural and functional changes in the kidneys of high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2009, 296, F118–F126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, A.; Romero, R.; Lopez, D.; Navarro, M.; Esteve, A.; Perez, N.; Alastrue, A.; Ariza, A. Renal injury in the extremely obese patients with normal renal function. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.P.; Patel, T.V.; Farag, Y.M.; Florez, A.; Rennke, H.G.; Singh, A.K. Kidney pathological changes in metabolic syndrome: A Cross-sectional Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redon, J.; Lurbe, E. The Kidney in Obesity. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2015, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsis, V.; Jordan, J.; Micic, D.; Finer, N.; Leitner, D.R.; Toplak, H.; Tokgozoglu, L.; Athyros, V.; Elisaf, M.; Filippatos, T.D.; et al. Obesity and cardiovascular risk. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antza, C.; Stabouli, S.; Kotsis, V. Gut microbiota in kidney disease and hypertension. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groop, P.-H.; Forsblom, C.; Thomas, M.C. Mechanisms of Disease: Pathway-selective insulin resistance and microvascular complications of diabetes. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 1, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronavalli, S.; Duka, I.; Bakris, G.L. The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 4, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cosmo, S.; Menzaghi, C.; Prudente, S.; Trischitta, V. Role of insulin resistance in kidney dysfunction: Insights into the mechanism and epidemiological evidence. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 28, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, G.; Chen, S.; Han, D.C.; Ziyadeh, F.N. Leptin and renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, J.M.; Wang, Z.V.; Park, A.S.D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Hu, M.C.; Moe, O.W.; Susztak, K.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin Promotes Functional Recovery after Podocyte Ablation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybyciński, J.; Dziedziejko, V.; Puchałowicz, K.; Domański, L.; Pawlik, A. Adiponectin in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, J.; Bergsten, A.; Qureshi, A.; Heimbürger, O.; Bárány, P.; Lönnqvist, F.; Lindholm, B.; Nordfors, L.; Alvestrand, A.; Stenvinkel, P. Elevated resistin levels in chronic kidney disease are associated with decreased glomerular filtration rate and inflammation, but not with insulin resistance. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, A.A.; Malik, A.R.; Klee, G.G.; Turner, S.T.; Rule, A.D.; Mosley, J.T.H.; Kullo, I.J. Association of plasma resistin with glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria in hypertensive adults. Hypertension 2007, 50, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, S.L.; Salimi, S.; Pierre, V.; Giffuni, J.; Katzel, L.; Parsa, A. Microvascular endothelial dysfunction is associated with albuminuria and CKD in older adults. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, N.W.; Karim, F.; Straznicky, N.E.; Fernandez, S.; Evans, R.; Head, G.; Kaye, D.M. Augmented endothelial-specific L-arginine transport prevents obesity-induced hypertension. Acta Physiol. 2014, 212, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, H.-J.; Mayer, C.; Mangge, H.; Fauler, G.; Grandits, N.; Wilders-Truschnig, M. Obesity reduces the bioavailability of nitric oxide in juveniles. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, N.; Head, G.; Kaye, D.M. Say NO to obesity-related hypertension: Role of the l-arginine–nitric oxide pathway. Hypertension 2016, 67, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Hawkins, M.; Abramowitz, M.K. Association of sarcopenia with eGFR and misclassification of obesity in adults with CKD in the United States. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintam, K.; Chang, A.R. Strategies to Treat Obesity in Patients with CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Yang, D.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Ye, B.; Ni, Z. The prevalence of microalbuminuria and its relationships with the components of metabolic syndrome in the general population of China. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoenes, M.; Reil, J.C.; Khan, B.V.; Bramlage, P.; Volpe, M.; Kirch, W.; Böhm, M. Abdominal obesity is associated with microalbuminuria and an elevated cardiovascular risk profile in patients with hypertension. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2009, 5, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandie Shaw, P.K.C.; Berger, S.P.; Mallat, M.; Frölich, M.; Dekker, F.; Rabelink, T.J. Central Obesity Is an Independent Risk Factor for Albuminuria in Nondiabetic South Asian Subjects. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1840–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Du, N.; Peng, H.; Chao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, H.; Li, H. Interaction of obesity and central obesity on elevated urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurbe, E.; Torro, M.I.; Alvarez, J.; Aguilar, F.; Fernandez-Formoso, J.A.; Redon, J. Prevalence and factors related to urinary albumin excretion in obese youths. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 2230–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, N.; Jenkins, T.M.; Nehus, E.; Inge, T.H.; Michalsky, M.; Harmon, C.M.; Helmrath, M.A.; Brandt, M.L.; Courcoulas, A.; Moxey-Mims, M.; et al. Kidney function in severely obese adolescents undergoing bariatric surgery. Obesity 2014, 22, 2319–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goknar, N.; Öktem, F.; Özgen, I.T.; Torun, E.; Kucukkoc, M.; Demir, A.D.; Cesur, Y. Determination of early urinary renal injury markers in obese children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 30, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakkis, J.I.; Weir, M.R. Obesity and Kidney Disease. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Conde, M.; Llop, E.; Carrillo, C.F.; Tormo, B.; Abad, J.; Rodriguez, L.; Perelló, C.; Gomez, M.L.; Martínez-Porras, J.L.; Puga, N.F.; et al. Estimation of visceral fat is useful for the diagnosis of significant fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 6658–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agati, V.D.; Chagnac, A.; de Vries, A.; Levi, M.; Porrini, E.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Praga, M. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: Clinical and pathologic characteristics and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.S.; Larson, M.; Leip, E.P.; Culleton, B.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Levy, D. Predictors of new-onset kidney disease in a community- based population. JAMA 2004, 291, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejerblad, E.; Fored, C.M.; Lindblad, P.; Fryzek, J.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Nyrén, O. Obesity and risk for chronic renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.R.; Grams, M.E.; Ballew, S.; Bilo, H.; Correa, A.; Evans, M.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Hosseinpanah, F.; Iseki, K.; Kenealy, T.; et al. Adiposity and risk of decline in glomerular filtration rate: Meta-analysis of individual participant data in a global consortium. BMJ 2019, 364, k5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurusinghe, S.; Brown, R.D.; Cai, X.; Samuel, C.S.; Ricardo, S.D.; Thomas, M.C.; Kett, M.M. Does a nephron deficit exacerbate the renal and cardiovascular effects of obesity? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Okada, H.; Senmaru, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Asano, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Oda, Y.; Hasegawa, G.; Toda, H.; et al. Metabolically Healthy Obesity and Risk of Incident CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-M.; Sung, J.; Lee, K. Longitudinal relationships of metabolic syndrome and obesity with kidney function: Healthy Twin Study. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, B.; Hanks, L.J.; Tanner, R.M.; Muntner, P.; Kramer, H.; McClellan, W.M.; Warnock, D.G.; Judd, S.E.; Gutiérrez, O.M. Obesity, metabolic health, and the risk of end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, S.; Wu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, Y.; Shao, X.; Holthöfer, H.; Zou, H. Association between metabolically unhealthy overweight/obesity and chronic kidney disease: The role of inflammation. Diabetes Metab. 2014, 40, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; McCulloch, C.E.; Iribarren, C.; Darbinian, J.; Go, A.S. Body mass index and risk for end-stage renal disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 144, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitt, E.; Pscheidt, C.; Concin, H.; Kramar, R.; Lhotta, K.; Nagel, G. Anthropometric and metabolic risk factors for ESRD are disease-specific: Results from a large population-based cohort study in Austria. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, J.; Brozek, W.; Concin, H.; Nagel, G.; Kerschbaum, J.; Lhotta, K.; Ulmer, H.; Zitt, E. The Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Obesity-Related Risk of End-Stage Kidney Disease in Austrian Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e212612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.L.; Molnar, M.Z.; Naseer, A.; Mikkelsen, M.K.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kovesdy, C.P. Association of age and BMI with kidney function and mortality: A cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartling, O.; Rydell, H.; Stendahl, M.; Segelmark, M.; Lagerros, Y.T.; Evans, M. CKD Progression and Mortality among Men and Women: A Nationwide Study in Sweden. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 190–199.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siener, R.; Glatz, S.; Nicolay, C.; Hesse, A. The Role of Overweight and Obesity in Calcium Oxalate Stone Formation. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, T.S.; Cuffy, M.C.; Linares-Cervantes, I.; Govil, A. Impact of obesity on dialysis and transplant and its management. Semin. Dial. 2020, 33, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiskulnam, P.; Johansen, K.L. The obesity paradox: A further consideration in dialysis patients. Semin. Dial. 2019, 32, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.P.; White, J.; López-Hernández, F.J.; Docherty, N.G.; Le Roux, C.W. Metabolic Surgery to Treat Obesity in Diabetic Kidney Disease, Chronic Kidney Disease, and End-Stage Kidney Disease; What Are the Unanswered Questions? Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B.; Ławiński, J.; Olszewski, R.; Gluba-Brzózka, A. The Role of Metabolic Factors in Renal Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.C.; Hwang, S.-J.; Porter, S.A.; Massaro, J.; Hoffmann, U.; Fox, C.S. Fatty Kidney, Hypertension, and Chronic Kidney Disease: The Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension 2011, 58, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praga, M.; Morales, E. The Fatty Kidney: Obesity and Renal Disease. Nephron 2016, 136, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanly, P.J.; Ahmed, S.B. Sleep Apnea and the Kidney: Is sleep apnea a risk factor for chronic kidney disease? Chest 2014, 146, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Tabibian, J.H.; Ekstedt, M.; Kechagias, S.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hultcrantz, R.; Hagström, H.; Yoon, S.K.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; et al. Association of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camara, N.; Iseki, K.; Kramer, H.; Liu, Z.-H.; Sharma, K. Kidney disease and obesity: Epidemiology, mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, M.D.; Filipp, S.L.; Musani, S.K.; Sims, M.; Okusa, M.D.; Gurka, M.J. Metabolic Syndrome Severity and Risk of CKD and Worsened GFR: The Jackson Heart Study. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2018, 43, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, E.; Valero, M.A.; León, M.; Hernández, E.; Praga, M. Beneficial effects of weight loss in overweight patients with chronic proteinuric nephropathies. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 41, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshinnia, F.; Wilt, T.J.; Duval, S.; Esmaeili, A.; Ibrahim, H.N. Weight loss and proteinuria: Systematic review of clinical trials and comparative cohorts. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 25, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneethan, S.D.; Yehnert, H.; Moustarah, F.; Schreiber, M.J.; Schauer, P.R.; Beddhu, S. Weight Loss Interventions in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, V.M.R.; Wei, G.; Baird, B.C.; Murtaugh, M.; Chonchol, M.B.; Raphael, K.; Greene, T.; Beddhu, S. High dietary fiber intake is associated with decreased inflammation and all-cause mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Liu, S.-M.; Lau, W.L.; Khazaeli, M.; Nazertehrani, S.; Farzaneh, S.H.; Kieffer, D.A.; Adams, S.H.; Martin, R.J. High Amylose Resistant Starch Diet Ameliorates Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; McGuire, D.K.; Bain, S.C.; Bhatt, D.L.; Leiter, L.A.; Mazer, C.D.; Fries, T.M.; Pratley, R.E.; Rasmussen, S.; Vrazic, H.; et al. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists liraglutide and semaglutide on cardiovascular and renal outcomes across body mass index categories in type 2 diabetes: Results of the LEADER and SUSTAIN 6 trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2487–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, K.; Lakshmanan, M.C.; Rayner, B.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Woodward, D.B.; Botros, F.T. Body weight and eGFR during dulaglutide treatment in type 2 diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic kidney disease (AWARD-7). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirica, B.M.; Bohula, E.A.; Dwyer, J.P.; Qamar, A.; Inzucchi, S.E.; McGuire, D.K.; Keech, A.C.; Smith, S.R.; Murphy, S.A.; Im, K.; et al. Lorcaserin and Renal Outcomes in Obese and Overweight Patients in the CAMELLIA-TIMI 61 Trial. Circulation 2019, 139, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janež, A.; Fioretto, P. SGLT2 Inhibitors and the Clinical Implications of Associated Weight Loss in Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 2249–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Lachin, J.; Fitchett, D.; Von Eynatten, M.; Mattheus, M.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Zinman, B.; et al. Empagliflozin and Progression of Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, R.H.; Bonaca, M.P.; Raz, I.; Zelniker, T.A.; Mosenzon, O.; Cahn, A.; Kuder, J.; Murphy, S.A.; Bhatt, D.L.; Leiter, L.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Previous Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2019, 139, 2516–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; De Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, F.; Grant, P.J.; Aboyans, V.; Bailey, C.J.; Ceriello, A.; Delgado, V.; Federici, M.; Filippatos, G.; Grobbee, E.D.; Hansen, T.B.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 255–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Fagbote, C.O.; Zhuo, M.; Hawley, C.E.; Paik, J.M. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for diabetic kidney disease: A primer for deprescribing. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheurlen, K.M.; Probst, P.; Kopf, S.; Nawroth, P.P.; Billeter, A.T.; Müller-Stich, B.P. Metabolic surgery improves renal injury independent of weight loss: A meta-analysis. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, A.; Peltonen, M.; Sjöström, C.D.; Andersson-Assarsson, J.C.; Taube, M.; Sjöholm, K.; Le Roux, C.W.; Carlsson, L.M.S.; Svensson, P.-A. Incidence of end-stage renal disease following bariatric surgery in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funes, D.R.; Blanco, D.G.; Gómez, C.O.; Frieder, J.S.; Menzo, E.L.; Szomstein, S.; White, K.P.; Rosenthal, R.J. Metabolic Surgery Reduces the Risk of Progression From Chronic Kidney Disease to Kidney Failure. Ann. Surg. 2019, 270, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.N.; Wahed, A.S.; Wang, J.; Courcoulas, A.P.; Dakin, G.; Hinojosa, M.W.; Kimmel, P.L.; Mitchell, J.E.; Pomp, A.; Pories, W.J.; et al. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on CKD Risk. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.H.; Wong, M.S.; Perez, R.V.; Li, C.-S.; Lin, T.-C.; Troppmann, C. Renal Transplant Wound Complications in the Modern Era of Obesity. J. Surg. Res. 2012, 173, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Mrad, R.M.; Abu-Alfa, A.K.; Ziyadeh, F.N. Effects of weight reduction regimens and bariatric surgery on chronic kidney disease in obese patients. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2013, 305, F613–F617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Patients | Study Endpoint | OR (CI 95%) for Chronic Kidney Disease |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. [13] | 6217 US adults | chronic kidney disease and microalbuminuria | 2.60 (1.68–4.03) versus non metabolic syndrome |
| Palaniappan et al. [14] | 6217 American adults | microalbuminuria | OR 2.2 (1.44–3.34) and 4.1 (2.45–6.74) for women and men versus non metabolic syndrome. |
| Chen et al. [15] | 15,160 Chinese adults | chronic kidney disease | 1.64 (1.16–2.32) versus non metabolic syndrome |
| Tanaka et al. [16] | 6980 Japanese adults | chronic kidney disease | <60 years; 1.69 (i.35–2.11) versus non metabolic syndrome |
| Chang et al. [17] | 60,921 Korean adults | chronic kidney disease | 1.68 (0.57–1.80) versus non metabolic syndrome |
| Ryu et al. [18] | 10,685 Korean healthy men/40,616.8 person-years | prospective, chronic kidney disease | 2.00 (1.46–2.73) |
| Kurella et al. [19] | 10,096 US adults/9 years of follow-up | prospective, CKD | 1.43 (1.18–1.73) |
| Yang et al. [20] | 4248 Chinese adults/5.40 years of follow-up | prospective chronic kidney disease | 1.42 (1.03–1.73) |
| Ninomiya et al. [21] | 1440 adults/5 years of follow up | prospective, chronic kidney disease | 2.08 (1.23–3.52) |
| Lucove et al. [22] | 1484 Native Americans/10 years follow up | prospective, chronic kidney disease | 1.3 (1.10–1.60) |
| Sun et al. [23] | 118,924 Taiwanese/3.7 years follow up | prospective, chronic kidney disease | 1.30 (1.24–1.36) |
| Chen J [24] | 26,601 subjects | chronic kidney disease | 1.99 (1.57–2.53) |
| Rashidbeygi E et al. [25] | 10,603,067 participants | meta-analysis albuminuria and proteinuria | 1.92 (1.71–2.15) and 2.08 (1.85–2.34) |
| Thomas et al. [24] | 30,146 adults | meta-analysis chronic kidney disease | 1.55 (1.34–1.80) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotsis, V.; Martinez, F.; Trakatelli, C.; Redon, J. Impact of Obesity in Kidney Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124482
Kotsis V, Martinez F, Trakatelli C, Redon J. Impact of Obesity in Kidney Diseases. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124482
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotsis, Vasilios, Fernando Martinez, Christina Trakatelli, and Josep Redon. 2021. "Impact of Obesity in Kidney Diseases" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124482
APA StyleKotsis, V., Martinez, F., Trakatelli, C., & Redon, J. (2021). Impact of Obesity in Kidney Diseases. Nutrients, 13(12), 4482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124482






