Dietary Exposure and Risk Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 for Children Aged 1 to 9 Years Old in Serbia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Extraction of Milk Samples for LC-MS/MS
2.3.1. Standard Solution Preparation
2.3.2. Chromatographic and MS Parameters
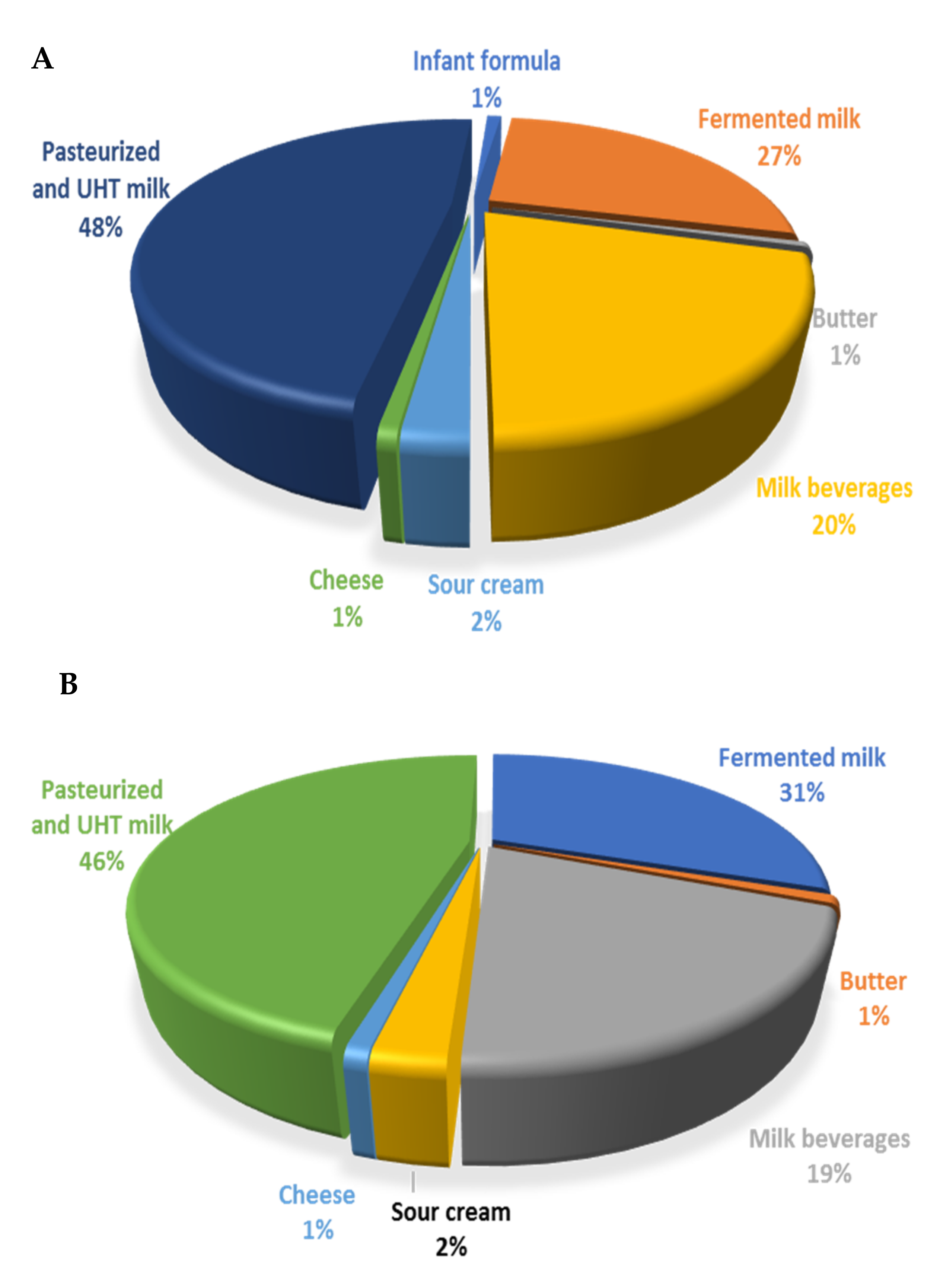
2.4. National Food Consumption Survey on Toddlers and Children
2.5. Health Risk Assessment
2.6. Exposure Assessment
2.7. Risk Characterization
2.8. Assessment of Liver Cancer Risk—The Carcinogenic Potency
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of AFM1 in Milk and Milk-Based Food
3.2. Dietary Exposure Assessment
3.3. Risk Characterization/Cancer Risk Attributable to AFM1
4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medina, A.; González, J.M.; Sainz, M.J. Impact of global warming on mycotoxins. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 18, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, N.; Keller, N.P. A call to arms: Mustering secondary metabolites for success and survival of an opportunistic pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udovicki, B.; Audenaert, K.; De Saeger, S.; Rajkovic, A. Overview on the mycotoxins incidence in Serbia in the period 2004–2016. Toxins 2018, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milićević, D.; Škrinjar, M.; Baltić, T. Real and perceived risks for mycotoxin contamination in foods and feeds: Challenges for food safety control. Toxins 2010, 2, 572–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milićević, D.; Spirić, D.; Radičević, T.; Velebit, B.; Stefanović, S.; Milojević, L.; Janković, S. A review of the current situation of aflatoxin M 1 in cow’s milk in Serbia: Risk assessment and regulatory aspects. Food Addit. Contam. A 2017, 34, 1617–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milićević, D.; Nastasijevic, I.; Petrovic, Z. Mycotoxin in the food supply chain—Implications for public health program. J. Environ. Sci. Health C 2016, 34, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleadin, J.; Frece, J.; Markov, K. Mycotoxins in food and feed. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 89, 297–345. [Google Scholar]
- Milicević, D.; Udovički, B.; Petrović, Z.; Janković, S.; Radulović, S.; Gurinović, M.; Rajković, A. Current status of mycotoxin contamination of food and feeds and associated public health risk in Serbia. Meat Technol. 2020, 61, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, C.P.; Miller, J.D.; Groopman, J.D. (Eds.) Mycotoxin Control in Low and Middle-Income Countries; (IARC Working Group Reports, No. 9.); International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2015. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK350558/2015 (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- De Ruyck, K.; De Boevre, M.; Huybrechts, I.; De Saeger, S. Dietary mycotoxins, co-exposure, and carcinogenesis in humans: Short review. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2015, 766, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). Chemical Agents and Related Occupations; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 225–248. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Regulation (EC) No 165/2010 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 26 February 2010 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards aflatoxins. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L50/8, 12. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Serbian Regulation. Maximum allowed contents of contaminants in food and feed. Off. Bull. Repub. Serbia 2020, 132/2020. Available online: https://www.paragraf.rs (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.C.S.; Jiang, J.Y.; Goggins, W.B.; Liang, M.; Fang, Y.; Fung, F.D.H.; Leung, C.; Wang, H.H.X.; Wong, G.L.H.; Wong, V.W.S.; et al. International incidence and mortality trends of liver cancer: A global profile. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfamariam, K.; De Boevre, M.; Kolsteren, P.; Belachew, T.; Mesfin, A.; De Saeger, S.; Lachat, C. Dietary mycotoxins exposure and child growth. immune system. morbidity. and mortality: A systematic literature review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3321–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiola, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Manyes, L.; Meca, G.; Ritieni, A. Risk analysis of main mycotoxins occurring in food for children: An overview. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 84, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraica, M.; Richter, D.; Rašić, D. Mycotoxicoses in children. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assuncao, R.; Vasco, E.; Nunes, B.; Loureiro, S.; Martins, C.; Alvito, P. Single-compound and cumulative risk assessment of mycotoxins present in breakfast cereals consumed by children from Lisbon region. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 86, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulin, M.; Bemrah, N.; Nougadere, A.; Volatier, J.L.; Sirot, V.; Leblanc, J.C. Assessment of infant exposure to food chemicals: The French total diet study design. Food Addit. Contam. A 2014, 31, 1226–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.; Raiola, A.; Mañes, J.; Ritieni, A. Presence of mycotoxin in commercial infant formulas and baby foods from Italian market. Food Control 2014, 39, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.C. Milk nutritional composition and its role in human health. Nutrition 2014, 30, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milićević, D.; Spirić, D.; Janković, S.; Velebit, B.; Radičević, T.; Petrović, Z.; Stefanović, S. Aflatoxin M1 in processed milk: Occurrence and seasonal variation with an emphasis on risk assessment of human exposure in Serbia. In Proceedings of the 59th International Meat Industry Conference MEATCON2017, Zlatibor, Serbia, 1–4 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milićević, D.; Petronijević, R.; Petrović, Z.; Đjinović-Stojanović, J.; Jovanović, J.; Baltić, T.; Janković, S. Impact of climate change on aflatoxin M1 contamination of raw milk with special focus on climate conditions in Serbia. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5202–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekovic, M.; Gurinovic, M.; Milesevic, J.; Glibetic, M. National Food Consumption Survey among children from 1–9 years in Serbia–final deliverable. EFSA Supporting Publ. 2021, 18, 6994E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, M.; Milesevic, J.; Zekovic, M.; Gurinovic, M.; Glibetic, M. The development and validation of food atlas for portion size estimation in the Balkan region. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurinović, M.; Milešević, J.; Kadvan, A.; Nikolić, M.; Zeković, M.; Djekić-Ivanković, M.; Glibetić, M. Development, features and application of DIET ASSESS & PLAN (DAP) software in supporting public health nutrition research in Central Eastern European Countries (CEEC). Food Chem. 2018, 238, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JECFA—Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of certain contaminants in food: Eighty-third report of the joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives. WHO Tech. Rep. Ser. 2017, 1002, 1–166. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/254893 (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- EFSA. Management of left-censored data in dietary exposure assessment of chemical substances. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1557. [Google Scholar]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.R.; Leblanc, J.C.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. (EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain) Scientific opinion—Risk assessment of aflatoxins in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 112. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO/UN. Safety Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food: Prepared by the Eighty-Third Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); WHO Food Additives Series, No. 74; FAO JECFA Monographs 19 bis; World Health Organization; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kos, J.; Lević, J.; Đuragić, O.; Kokić, B.; Miladinović, I. Occurrence and estimation of aflatoxin M1 exposure in milk in Serbia. Food Control 2014, 38, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrbić, B.; Živančev, J.; Antić, I.; Godula, M. Levels of aflatoxin M1 in different types of milk collected in Serbia: Assessment of human and animal exposure. Food Control 2014, 40, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomašević, I.; Petrović, J.; Jovetić, M.; Raičcević, S.; Milojević, M.; Miočinović, J. Two year survey on the occurrence and seasonal variation of aflatoxin M1 in milk and milk products in Serbia. Food Control 2015, 56, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walte, H.G.; Schwake-Anduschus, C.; Geisen, R.; Fritsche, J. Aflatoxin: Food chain transfer from feed to milk. J. Consum. Protect. Food Saf. 2016, 11, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kos, J.; Janić Hajnal, E.; Šarić, B.; Jovanov, P.; Mandić, A.; Đuragić, O.; Kokić, B. Aflatoxins in maize harvested in the Republic of Serbia over the period 2012–2016. Food Addit. Contam. B 2018, 11, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrbić, B.; Antić, I.; Živančev, J. Presence of aflatoxin M1 in white and hard cheese samples from Serbia. Food Control 2015, 50, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milicevic, D.; Jankovic, S.; Muric, K.; Petrovic, Z.; Petronijevic, R.; Raseta, M.; Djinovic-Stojanovic, J. Safety of milk and whey from Zlatibor region in relation to aflatoxin M1 contamination: A seasonal study. In Proceedings of the 60th International Meat Industry Conference MEATCON2019, Kopaonik, Serbia, 22–25 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costamagna, D.; Gaggiotti, M.; Chiericatti, C.A.; Costabel, L.; Audero, G.M.L.; Taverna, M.; Signorini, M.L. Quantification of aflatoxin M1 carry-over rate from feed to soft cheese. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torović, L.; Popović, N.; Živkov-Baloš, M.; Jakšić, S. Risk estimates of hepatocellular carcinoma in Vojvodina (Serbia) related to aflatoxin M1 contaminated cheese. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 103, 104122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Asi, M.R. Assessment of aflatoxin M1 in milk and milk products from Punjab, Pakistan. Food Control 2013, 30, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnaa, N.S.; Wu, F. Aflatoxin M1 in milk: A global occurrence, intake & exposure assessment. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 110, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper-Goodman, T. Uncertainties in the risk assessment of three mycotoxins: Aflatoxin, ochratoxin, and zearalenone. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1990, 68, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.I.I.; Wild, C.P.; Baan, R.A.; Gelderblom, W.C.A.; Miller, J.D.; Riley, R.T.; Wu, F. Improving Public Health through Mycotoxin Control; IARC WHO: Lyon, France, 2012; pp. 225–248. ISBN 978-92-832-2158-6. [Google Scholar]
- Makori, N.; Matemu, A.; Kimanya, M.; Kassim, N. Inadequate management of complementary foods contributes to the risk of aflatoxin exposure and low nutrition status among children. World Mycotoxin J. 2019, 12, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Naeem, I.; Gong, Y.Y.; Routledge, M.N.; Akhtar, S.; Riaz, M.; Ramalho, L.N.Z.; de Oliveira, C.A.F.; Ismail, Z. Early life exposure to dietary aflatoxins, health impact and control perspectives: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 112, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, F. Global burden of aflatoxin-induced hepatocellular carcinoma: A risk assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Institute of Public Health of Serbia “Dr Milan Jovanovic Batut” The Report on Infectious Diseases in the Republic of Serbia for 2019. 2020. Available online: https://www.batut.org.rs/download/izvestaji/Godisnji%20izvestaj%20o%20zaraznim%20bolestima%202019.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2021).
| Type of Sample | n/N (%) | Mean (ng kg−1 ± SD) of All Samples | Mean Positives (ng kg−1 ± SD) | Median Positives (ng kg−1) | Q1 Positives (ng kg−1) | Q3 Positives (ng kg−1) | Range (ng kg−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LB | MB | UB | P95 | |||||||
| Infant formula | 14/92 (15.2) | 1.6 ± 0.004 | 3.76 ± 0.003 | 5.88 ± 0.002 | 12.5 | 10.0 ± 0.002 | 11.0 | 8.00 | 13.00 | 8.0–14.0 |
| Fermented milk products | 158/775 (20.3) | 9.58 ± 0.02 | 11.5 ± 0.02 | 13.56 ± 0.02 | 57.0 | 47.0 ± 0.022 | 38.0 | 34.0 | 56.25 | 25.0–174.0 |
| Clotted cream | 0/48 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | <5.0 | |
| Butter | 14/143 (10) | 5.20 ± 0.01 | 7.44 ± 0.016 | 9.70 ± 0.01 | 47.0 | 53.0 ± 0.016 | 47.0 | 41.75 | 58.0 | 39.0–92.0 |
| Milk beverages | 145/714 (20) | 4.22 ± 0.01 | 6.21 ± 0.011 | 8.20 ± 0.01 | 23.0 | 20.77 ± 0.02 | 14.0 | 10.50 | 22.50 | 5.0–117.0 |
| Sour cream | 19/132 (14) | 6.90 ± 0.02 | 9.04 ± 0.018 | 11.18 ± 0.02 | 48.0 | 47.95 ± 0.002 | 39.0 | 31.0 | 60.0 | 25.0–103.0 |
| Cheese | 7/404 (2) | 1.36 ± 0.01 | 3.82 ± 0.014 | 6.28 ± 0.01 | 5.0 | 7.89 ± 0.08 | 49.0 | 40.0 | 58.0 | 39.0–276.0 |
| Pasteurized and UHT milk | 574/725 (79) | 22.34 ± 0.02 | 22.87 ± 0.018 | 23.40 ± 0.01 | 53.0 | 28.22 ± 0.016 | 25.00 | 19.00 | 35.0 | 5.0–132.0 |
| Milk powder | 67/201 (33) | 9.12 ± 0.02 | 10.79 ± 0.020 | 12.46 ± 0.02 | 47.0 | 27.37 ± 0.03 | 16.00 | 9.00 | 36.00 | 5.0–155.0 |
| Whey liquid | 13/90 (14) | 14.82 ± 0.05 | 16.96 ± 0.05 | 19.10 ± 0.05 | 70.0 | 102.6 ± 0.10 | 70.0 | 20.50 | 211.0 | 5.0–278.0 |
| Total | 1012/3404 (29.7) | 9.47 ± 0.02 | 11.23 ± 0.02 | 12.99 ± 0.02 | 44.0 | 31.86 ± 0.026 | 27.00 | 16.00 | 38.00 | 5.0–278.0 |
| Age Group | Body Weight (kg) | N | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |
| Toddlers, 1–3 years | 14 | 13 | 98 | 91 |
| Children, 3–9 years | 24 | 24 | 159 | 150 |
| Age Group | Infant Formula | Fermented Milk Products | Clotted Cream | Butter | Milk Beverages | Sour Cream | Cheese | Pasteurized and UHT Milk | Whey Liquid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toddlers. 1–3 years | M | 31.51 | 133.40 | 9.94 | 4.88 | 230.00 | 15.00 | 22.50 | 102.87 | - |
| F | 29.93 | 115.76 | 8.72 | 5.30 | 213.30 | 17.47 | 24.40 | 112.05 | - | |
| Children. 3–9 years | M | - | 153.24 | 13.31 | 7.95 | 220.83 | 16.58 | 27.19 | 99.55 | 250.0 |
| F | - | 150.50 | 13.60 | 8.02 | 199.75 | 15.05 | 26.94 | 93.58 | - | |
| Average | 30.72 | 138.23 | 11.41 | 6.54 | 215.97 | 16.02 | 25.25 | 102.01 | 250.0 | |
| Food Group | Exposure (ng kg−1 bw day−1) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toddlers, 1–3 Years | Children, 3–9 Years | |||||||||||
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |||||||||
| LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | |
| Infant formula | 0.004 | 0.014 | 0.029 | 0.004 | 0.014 | 0.029 | ||||||
| Fermented milk products | 0.091 | 0.129 | 0.543 | 0.085 | 0.121 | 0.508 | 0.061 | 0.087 | 0.364 | 0.060 | 0.085 | 0.358 |
| Butter | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.019 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.016 |
| Milk beverages | 0.069 | 0.135 | 0.378 | 0.069 | 0.134 | 0.377 | 0.039 | 0.075 | 0.212 | 0.035 | 0.068 | 0.191 |
| Sour cream | 0.007 | 0.012 | 0.051 | 0.009 | 0.015 | 0.065 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.033 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.030 |
| Cheese | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.008 | 0.003 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.005 |
| Pasteurized and UHT milk | 0.164 | 0.172 | 0.389 | 0.193 | 0.202 | 0.457 | 0.093 | 0.097 | 0.220 | 0.087 | 0.091 | 0.207 |
| Whey liquid | 0.154 | 0.177 | 0.199 | |||||||||
| Total | 0.340 | 0.475 | 1.415 | 0.365 | 0.501 | 1.463 | 0.201 | 0.277 | 0.850 | 0.190 | 0.262 | 0.807 |
| Food Group | MOE | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toddlers, 1–3 Years | Children, 3–9 Years | |||||||||||
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |||||||||
| LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | |
| Infant formula | 1,076,492 | 292,923 | 137,791 | 1,085,686 | 295,425 | 138,968 | ||||||
| Fermented milk products | 43,819 | 30,958 | 7365 | 46,890 | 33,127 | 7881 | 65,393 | 46,200 | 10,991 | 66,566 | 47,028 | 11,188 |
| Butter | 2,206,810 | 1,183,032 | 244,158 | 1,886,792 | 1,011,476 | 208,752 | 2,322,206 | 1,244,894 | 256,925 | 2,301,937 | 1,234,028 | 254,682 |
| Milk beverages | 57,696 | 29,692 | 10,586 | 57,851 | 29,772 | 10,614 | 103,015 | 53,015 | 18,901 | 113,886 | 58,610 | 20,896 |
| Sour cream | 541,063 | 333,930 | 77,778 | 431,381 | 266,237 | 62,011 | 839,146 | 517,899 | 120,627 | 924,455 | 570,549 | 132,890 |
| Cheese | 1,830,065 | 396,320 | 497,778 | 1,567,020 | 339,355 | 426,230 | 2,596,110 | 562,215 | 706,142 | 2,679,887 | 580,358 | 728,929 |
| Pasteurized and UHT milk | 24,368 | 23,264 | 10,271 | 20,773 | 19,832 | 8756 | 43,166 | 41,211 | 18,195 | 45,920 | 43,840 | 19,356 |
| Whey liquid | 25,911 | 22,642 | 20,105 | |||||||||
| Average | 825,759 | 327,160 | 140,818 | 728,056 | 285,032 | 123,316 | 856,421 | 355,439 | 164,555 | 1,022,109 | 422,402 | 194,657 |
| Food Group | Liver Cancer Risk (Case/100,000 Persons) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toddlers, 1–3 Years | Children, 3–9 Years | |||||||||||
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |||||||||
| LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | |
| Infant formula | 0.00001 | 0.00003 | 0.00006 | 0.00001 | 0.00003 | 0.00006 | ||||||
| Fermented milk products | 0.00018 | 0.00025 | 0.00106 | 0.00017 | 0.00024 | 0.00099 | 0.00012 | 0.00017 | 0.00071 | 0.00012 | 0.00017 | 0.00070 |
| Butter | 0.00000 | 0.00001 | 0.00003 | 0.00000 | 0.00001 | 0.00004 | 0.00000 | 0.00001 | 0.00003 | 0.00000 | 0.00001 | 0.00003 |
| Milk beverages | 0.00014 | 0.00026 | 0.00074 | 0.00013 | 0.00026 | 0.00074 | 0.00008 | 0.00015 | 0.00041 | 0.00007 | 0.00013 | 0.00037 |
| Sour cream | 0.00001 | 0.00002 | 0.00010 | 0.00002 | 0.00003 | 0.00013 | 0.00001 | 0.00002 | 0.00006 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00006 |
| Cheese | 0.00000 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00000 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00000 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00000 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 |
| Pasteurized and UHT milk | 0.00032 | 0.00034 | 0.00076 | 0.00038 | 0.00039 | 0.00089 | 0.00018 | 0.00019 | 0.00043 | 0.00017 | 0.00018 | 0.00040 |
| Whey liquid | 0.00030 | 0.00034 | 0.00039 | |||||||||
| Total | 0.00066 | 0.00093 | 0.00276 | 0.00071 | 0.00098 | 0.00286 | 0.00069 | 0.00089 | 0.00166 | 0.00037 | 0.00037 | 0.00158 |
| Food Group | Liver Cancer Risk (Case/100,000 Persons) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toddlers, 1–3 Years | Children, 3–9 Years | |||||||||||
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |||||||||
| LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | LB | UB | P95 | |
| Infant formula | 0.00002 | 0.00007 | 0.00016 | 0.00002 | 0.00007 | 0.00016 | ||||||
| Fermented milk products | 0.00049 | 0.00070 | 0.00294 | 0.00046 | 0.00065 | 0.00275 | 0.00033 | 0.00047 | 0.00197 | 0.00033 | 0.00046 | 0.00194 |
| Butter | 0.00001 | 0.00002 | 0.00009 | 0.00001 | 0.00002 | 0.00010 | 0.00001 | 0.00002 | 0.00008 | 0.00001 | 0.00002 | 0.00009 |
| Milk beverages | 0.00038 | 0.00073 | 0.00205 | 0.00037 | 0.00073 | 0.00204 | 0.00021 | 0.00041 | 0.00115 | 0.00019 | 0.00037 | 0.00104 |
| Sour cream | 0.00004 | 0.00006 | 0.00028 | 0.00005 | 0.00008 | 0.00035 | 0.00003 | 0.00004 | 0.00018 | 0.00002 | 0.00004 | 0.00016 |
| Cheese | 0.00001 | 0.00005 | 0.00004 | 0.00001 | 0.00006 | 0.00005 | 0.00001 | 0.00004 | 0.00003 | 0.00001 | 0.00004 | 0.00003 |
| Pasteurized and UHT milk | 0.00089 | 0.00093 | 0.00211 | 0.00104 | 0.00109 | 0.00247 | 0.00050 | 0.00053 | 0.00119 | 0.00047 | 0.00049 | 0.00112 |
| Whey liquid | 0.00084 | 0.00096 | 0.00108 | |||||||||
| Total | 0.00184 | 0.00257 | 0.00766 | 0.00197 | 0.00271 | 0.00792 | 0.00109 | 0.00150 | 0.00460 | 0.00103 | 0.00142 | 0.00437 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milićević, D.R.; Milešević, J.; Gurinović, M.; Janković, S.; Đinović-Stojanović, J.; Zeković, M.; Glibetić, M. Dietary Exposure and Risk Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 for Children Aged 1 to 9 Years Old in Serbia. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124450
Milićević DR, Milešević J, Gurinović M, Janković S, Đinović-Stojanović J, Zeković M, Glibetić M. Dietary Exposure and Risk Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 for Children Aged 1 to 9 Years Old in Serbia. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124450
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilićević, Dragan R., Jelena Milešević, Mirjana Gurinović, Saša Janković, Jasna Đinović-Stojanović, Milica Zeković, and Maria Glibetić. 2021. "Dietary Exposure and Risk Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 for Children Aged 1 to 9 Years Old in Serbia" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124450
APA StyleMilićević, D. R., Milešević, J., Gurinović, M., Janković, S., Đinović-Stojanović, J., Zeković, M., & Glibetić, M. (2021). Dietary Exposure and Risk Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 for Children Aged 1 to 9 Years Old in Serbia. Nutrients, 13(12), 4450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124450








