Raphani Semen (Raphanus sativus L.) Ameliorates Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating De Novo Lipogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Ethical Statement
2.4. Animal Experiments
2.5. Blood Serum Analysis
2.6. Cytokine Measurement
2.7. Hepatic TG Measurement
2.8. Hepatic FFA Measurement
2.9. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.10. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.11. RNA Isolation and Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.12. Immunofluorescence (IF) Assay
2.13. Cell Culture and PA-Induced Lipid Accumulation in HepG2 Cells
2.14. Cell Cytotoxicity
2.15. LDH Measurement
2.16. BODIPYTM Staining
2.17. Oil Red O Staining
2.18. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. RSWE Attenuates Fatty Liver Phenotypes in AFLD Mice
3.2. RSWE Regulates De Novo Lipogenesis in the Liver of AFLD Mice
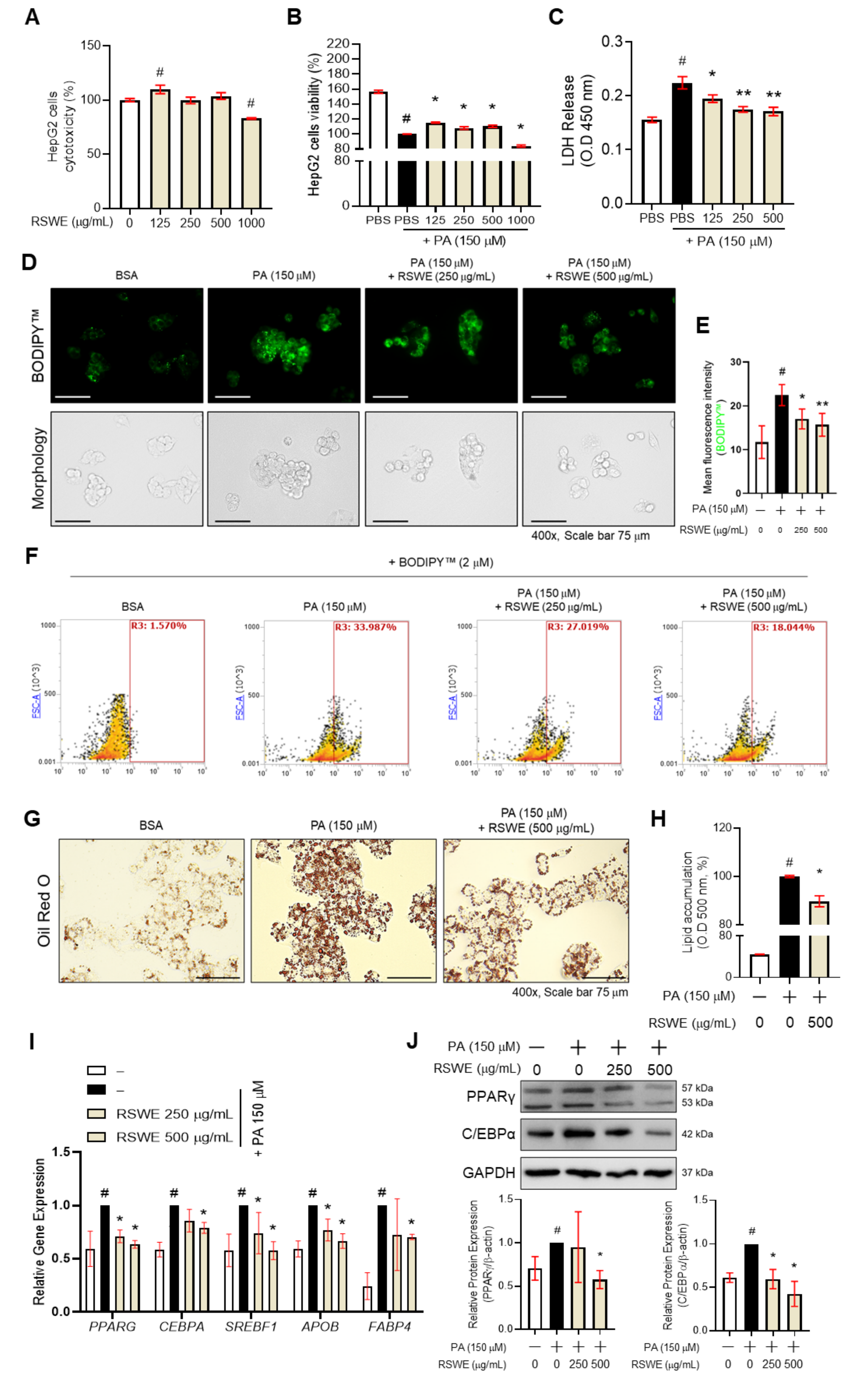
3.3. RSWE Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in PA-Induced Steatosis HepG2 Cells
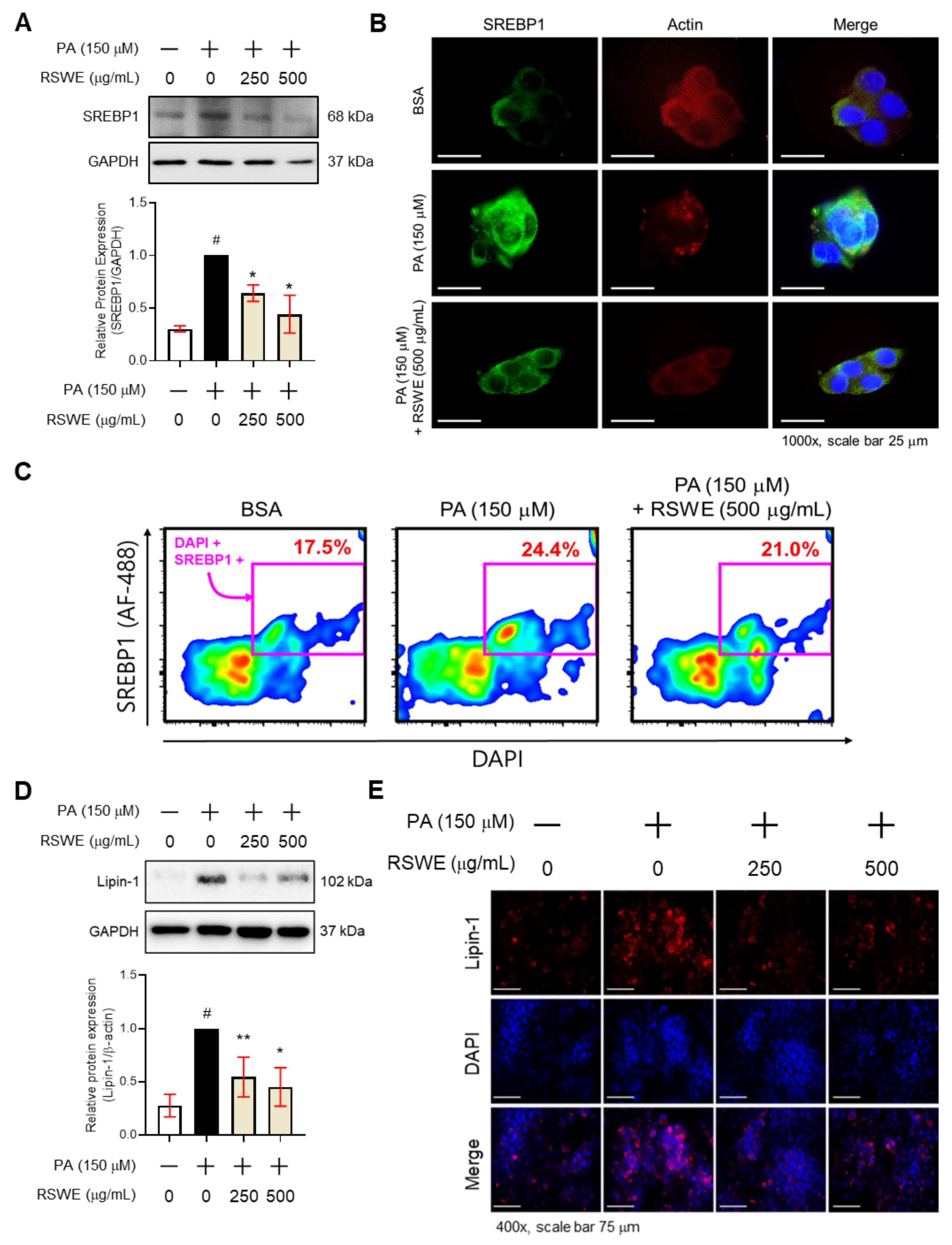
3.4. RSWE Regulates SREBP1 and Lipin-1 in PA-Induced Steatosis HepG2 Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, H.; Shen, Y.; Ren, Y.; Mou, Q.; Lin, T.; Zhu, L.; Ren, T. Combined intake of blueberry juice and probiotics ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunction by activating SIRT1 in alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellentani, S.; Saccoccio, G.; Masutti, F.; Giacca, M.; Miglioli, L.; Monzoni, A.; Tiribelli, C. Risk factors for alcoholic liver disease. Addict. Biol. 2000, 5, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-J.; Xiao, P.; Xu, H.-Q.; Niu, J.-Q.; Gao, Y.-H. Growing burden of alcoholic liver disease in China: A review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Han, J.; Lee, C.; Yoon, M.; Jung, Y. Pathophysiological Aspects of Alcohol Metabolism in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ge, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, W.; Dong, C. Disturbance of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in hepatic lipid metabolism in rats fed with high fat diet. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 146, 111848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, G.; Barak, P.; Das, S.; Kamat, S.S.; Mallik, R. Kinesin-dependent mechanism for controlling triglyceride secretion from the liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12958–12963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. The SREBP Pathway: Regulation of Cholesterol Metabolism by Proteolysis of a Membrane-Bound Transcription Factor. Cell 1997, 89, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, H.M.; Holloway, G.P.; Steinberg, G.R. AMPK regulation of fatty acid metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis: Implications for obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 366, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, H.; Guicciardi, M.E.; Gores, G.J. Hepatocyte death: A clear and present danger. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 1165–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.-C.; Cho, S.-W.; Kook, S.-H.; Chun, S.-R.; Bhattarai, G.; Poudel, S.B.; Kim, M.-K.; Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, J.-C. Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of the seeds of Raphanus sativus L. in experimental ulcerative colitis models. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 179, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sham, T.T.; Yuen, A.C.; Ng, Y.F.; Chan, C.O.; Mok, D.K.; Chan, S.W. A review of the phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of raphani semen. Evid. -Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 636194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Bai, C.; Liu, T.; He, J.; Gu, X. The effect of Raphanus sativus L. seeds on regulation of intestinal motility in rats consuming a high-calorie diet. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillari, J.; Iori, R.; Papi, A.; Orlandi, M.; Bartolini, G.; Gabbanini, S.; Pedulli, G.F.; Valgimigli, L. Kaiware Daikon (Raphanus sativus L.) extract: A naturally multipotent chemopreventive agent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7823–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kook, S.-H.; Choi, K.-C.; Lee, Y.-H.; Cho, H.-K.; Lee, J.-C. Raphanus sativus L. seeds prevent LPS-stimulated inflammatory response through negative regulation of the p38 MAPK-NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Moon, E.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.R. 4-Methylthio-butanyl derivatives from the seeds of Raphanus sativus and their biological evaluation on anti-inflammatory and antitumor activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, A.; Mathews, S.; Ki, S.H.; Wang, H.; Gao, B. Mouse model of chronic and binge ethanol feeding (the NIAAA model). Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, W.Y.; Choe, S.K.; Park, J.; Um, J.Y. Black Raspberry (Rubus coreanus Miquel) Promotes Browning of Preadipocytes and Inguinal White Adipose Tissue in Cold-Induced Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, Y.; Park, J.; Kim, H.L.; Sim, J.E.; Youn, D.H.; Kang, J.; Lim, S.; Jeong, M.Y.; Yang, W.M.; Lee, S.G.; et al. Vanillic acid attenuates obesity via activation of the AMPK pathway and thermogenic factors in vivo and in vitro. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Kang, J.; Park, W.Y.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y.; Kang, M.W.; Kwak, H.J.; Um, J.Y. Vanillic Acid Improves Comorbidity of Cancer and Obesity through STAT3 Regulation in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese and B16BL6 Melanoma-Injected Mice. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.Y.; Park, J.; Ahn, K.S.; Kwak, H.J.; Um, J.Y. Ellagic acid induces beige remodeling of white adipose tissue by controlling mitochondrial dynamics and SIRT3. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhuja, P. Pathology of alcoholic liver disease, can it be differentiated from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis? World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 16474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osna, N.A.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Kharbanda, K.K. Alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis and current management. Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2017, 38, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, S.Y.; Seo, Y.; Bang, C.Y.; Woo, S.H.; Kang, M. Protective effects of Gymnaster koraiensis extract on ethanol-induced fatty liver in rats. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2020, 20, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.M.; Brunt, E.M. Pathological features of fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, B.; Dadabhai, A.S.; Jang, Y.Y.; Gurakar, A.; Mezey, E. Current Management of Alcoholic Hepatitis and Future Therapies. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.S.; Ong, M.; Qu, X. Optimal management for alcoholic liver disease: Conventional medications, natural therapy or combination? World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Stewart, A.G.; Woodman, O.L.; Ritchie, R.H.; Qin, C.X. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A review of its mechanism, models and medical treatments. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederbaum, A.I. Alcohol metabolism. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.H.; Ginsberg, H.N. Increased very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) secretion, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linton, M.F.; Yancey, P.G.; Davies, S.S.; Jerome, W.G.; Linton, E.F.; Song, W.L.; Doran, A.C.; Vickers, K.C. The Role of Lipids and Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA. Copyright © 2000–2021; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.; Carr, R. Alcohol effects on hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Zhuge, J.; Wang, X.; Bai, J.; Cederbaum, A.I. Cytochrome P450 2E1 contributes to ethanol-induced fatty liver in mice. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, H.K.; Bataller, R.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Mueller, S.; Szabo, G.; Tsukamoto, H. Alcoholic liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBose-Boyd, R.A.; Ye, J. SREBPs in lipid metabolism, insulin signaling, and beyond. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, J. The role of lipin-1 in the pathogenesis of alcoholic fatty liver. Alcohol Alcohol. 2015, 50, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Csaki, L.S.; Reue, K. Lipins: Multifunctional lipid metabolism proteins. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 30, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.K.; Park, J.E.; Lee, M.; Hardwick, J.P. Hepatic lipid homeostasis by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma 2. Liver Res. 2018, 2, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Genes | Forward (5′ to 3′) | Reverse (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| m-Apob | TTGGCAAACTGCATAGCATCC | TCAAATTGGGACTCTCCTTTAGC |
| m-Atgl | ATATCCCACTTTAGCTCCAGGG | CAAGTTGTCTGAAATGCCGC |
| m-Cd36 | ATGGGCTGTGATCGGAACTG | GTCTTCCCAATAAGCATGTCTCC |
| m-Cebpa | CAAGAACAGCAACGAGTACCG | GTCACTGGTCAACTCCAGCAC |
| m-Chrebp | CCAGCCTCAAGGTGAGCAAA | CATGTCCCGCATCTGGTCA |
| m-Cpt1a | CTCCGCCTGAGCCATGAAG | CACCAGTGATGATGCCATTCT |
| m-Cpt1b | GCACACCAGGCAGTAGCTTT | CAGGAGTTGATTCCAGACAGGTA |
| m-Cyp2e1 | CGTTGCCTTGCTTGTCTGGA | AAGAAAGGAATTGGGAAAGGTCC |
| m-Fas | TATCAAGGAGGCCCATTTTGC | TGTTTCCACTTCTAAACCATGCT |
| m-Gapdh | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA |
| m-Hsl | CTGAGATTGAGGTGCTGTCG | CAAGGGAGGTGAGAGGGTAAC |
| m-Lpin1 | CATGCTTCGGAAAGTCCTTCA | GGTTATTCTTTGGCGTCAACCT |
| m-Ppara | AGAGCCCCATCTGTCCTCTC | ACTGGTAGTCTGCAAAACCAAA |
| m-Pparg | TTTTCAAGGGTGCCAGTTTC | TTATTCATCAGGGAGGCCAG |
| m-Scd1 | TTCTTGCGATACACTCTGGTGC | CGGGATTGAATGTTCTTGTCGT |
| m-Srebf1 | GCAGCCACCATCTAGCCTG | GCAGCCACCATCTAGCCTG |
| h-APOB | GCAGGCCGAAGCTGTTTTG | GCACACGTTTCAGCCACTG |
| h-CEBPA | TGTATACCCCTGGTGGGAGA | TCATAACTCCGGTCCCTCTG |
| h-FABP4 | ACTGGGCCAGGAATTTGACG | CTCGTGGAAGTGACGCCTT |
| h-GAPDH | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
| h-PPARG | TACTGTCGGTTTCAGAAATGCC | GTCAGCGGACTCTGGATTCAG |
| h-SREBF1 | ACAGTGACTTCCCTGGCCTAT | ACAGTGACTTCCCTGGCCTAT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, W.Y.; Song, G.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.J.; Hong, S.; Park, J.; Um, J.-Y. Raphani Semen (Raphanus sativus L.) Ameliorates Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating De Novo Lipogenesis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124448
Park WY, Song G, Noh JH, Kim T, Kim JJ, Hong S, Park J, Um J-Y. Raphani Semen (Raphanus sativus L.) Ameliorates Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating De Novo Lipogenesis. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124448
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Woo Yong, Gahee Song, Joon Hak Noh, Taegon Kim, Jae Jin Kim, Seokbeom Hong, Jinbong Park, and Jae-Young Um. 2021. "Raphani Semen (Raphanus sativus L.) Ameliorates Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating De Novo Lipogenesis" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124448
APA StylePark, W. Y., Song, G., Noh, J. H., Kim, T., Kim, J. J., Hong, S., Park, J., & Um, J.-Y. (2021). Raphani Semen (Raphanus sativus L.) Ameliorates Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating De Novo Lipogenesis. Nutrients, 13(12), 4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124448








