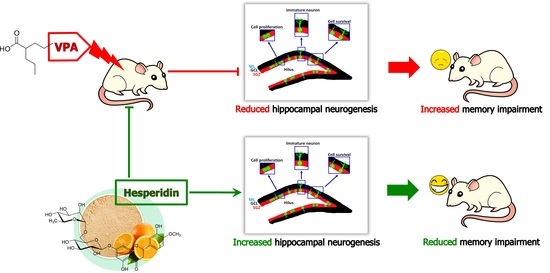
Hesperidin Reduces Memory Impairment Associated with Adult Rat Hippocampal Neurogenesis Triggered by Valproic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rat Model
2.2. Drug Administration
2.3. Behavioural Testing
2.4. Immunohistochemistry for Hippocampal Neurogenesis Markers
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
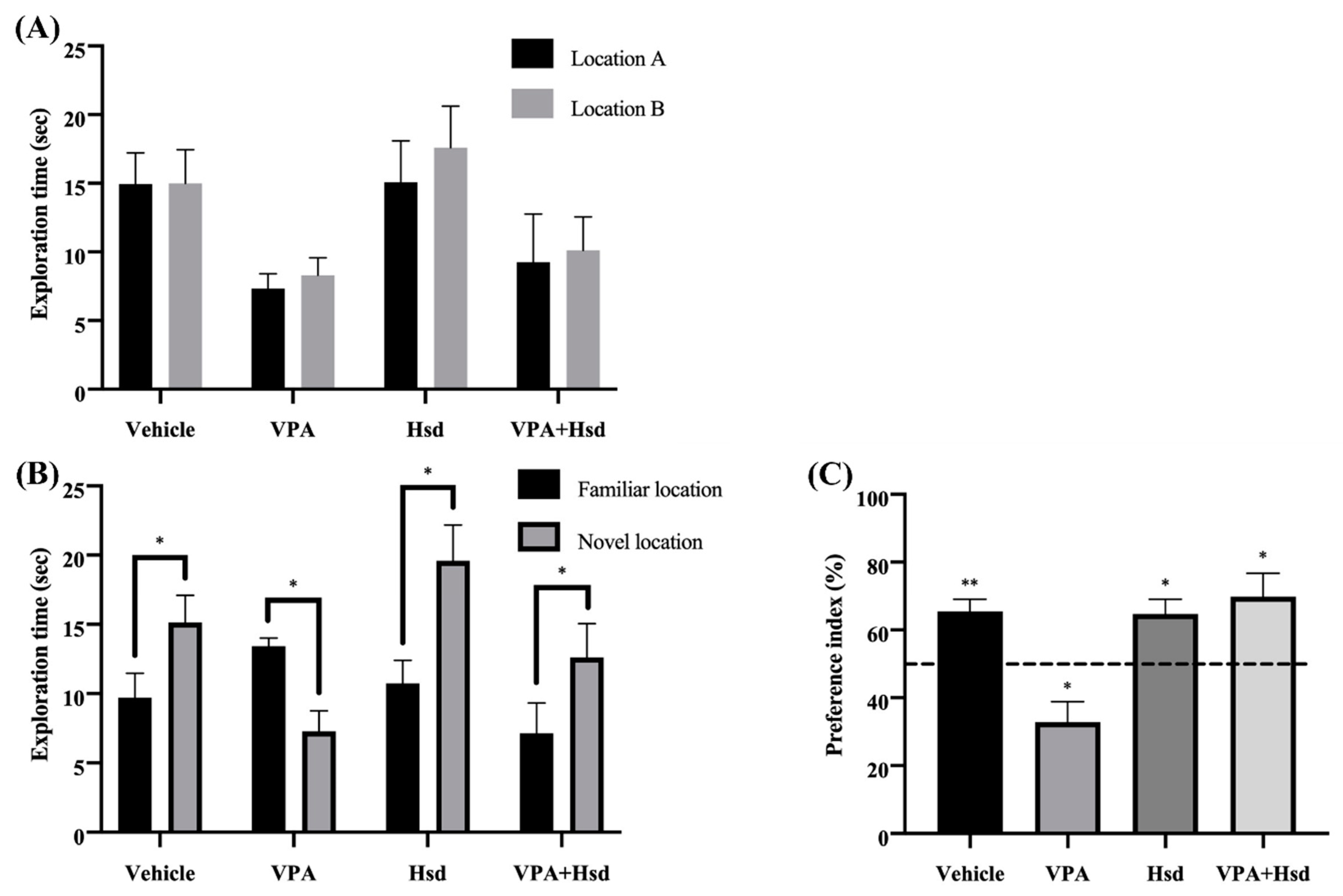
3.1. Effects of Valproic Acid (VPA) and Hesperidin (Hsd) on Memory Evaluated by Novel Object Location (NOL) Test
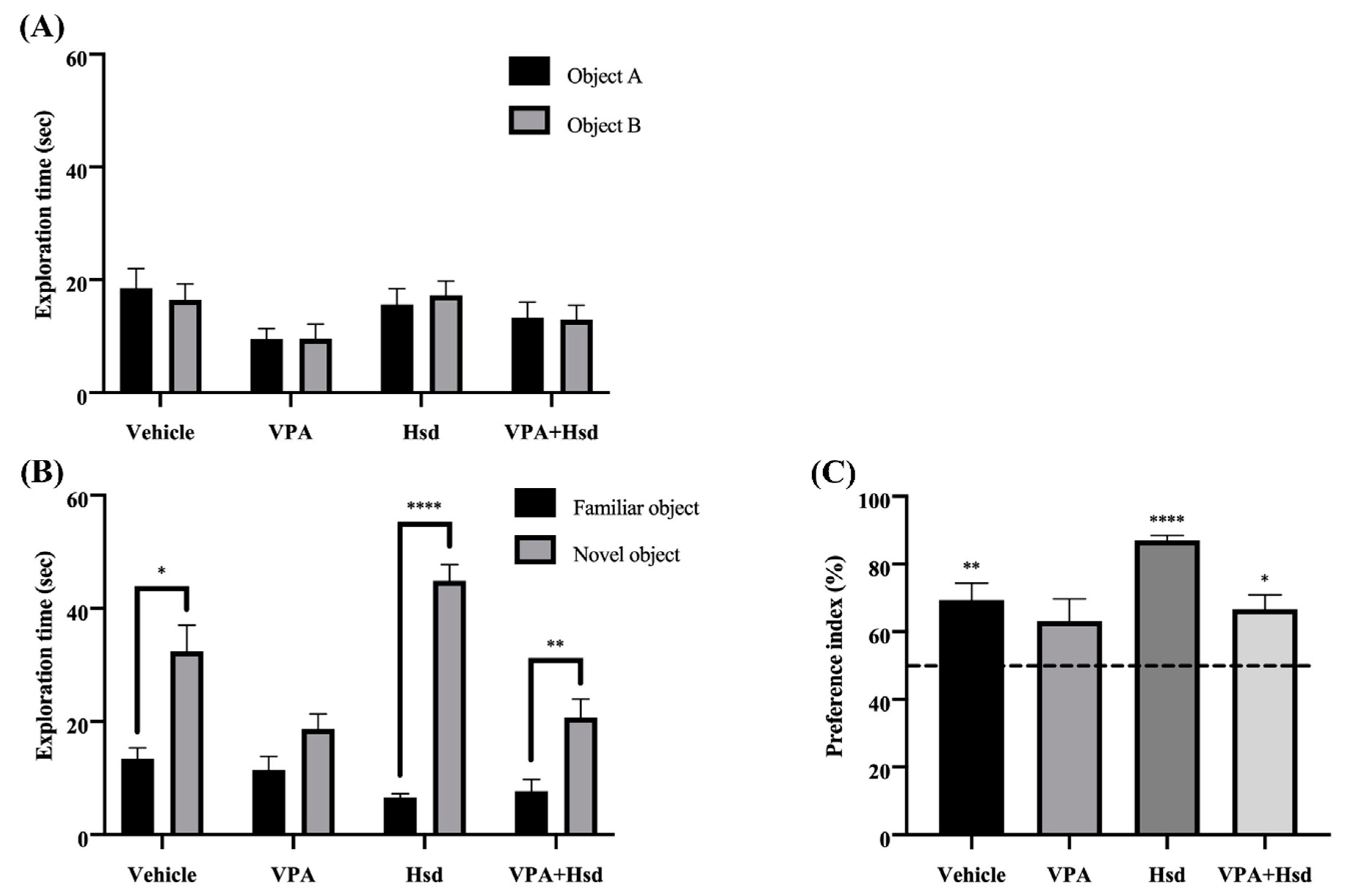
3.2. Effects of VPA and Hsd on Memory Evaluated by Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test
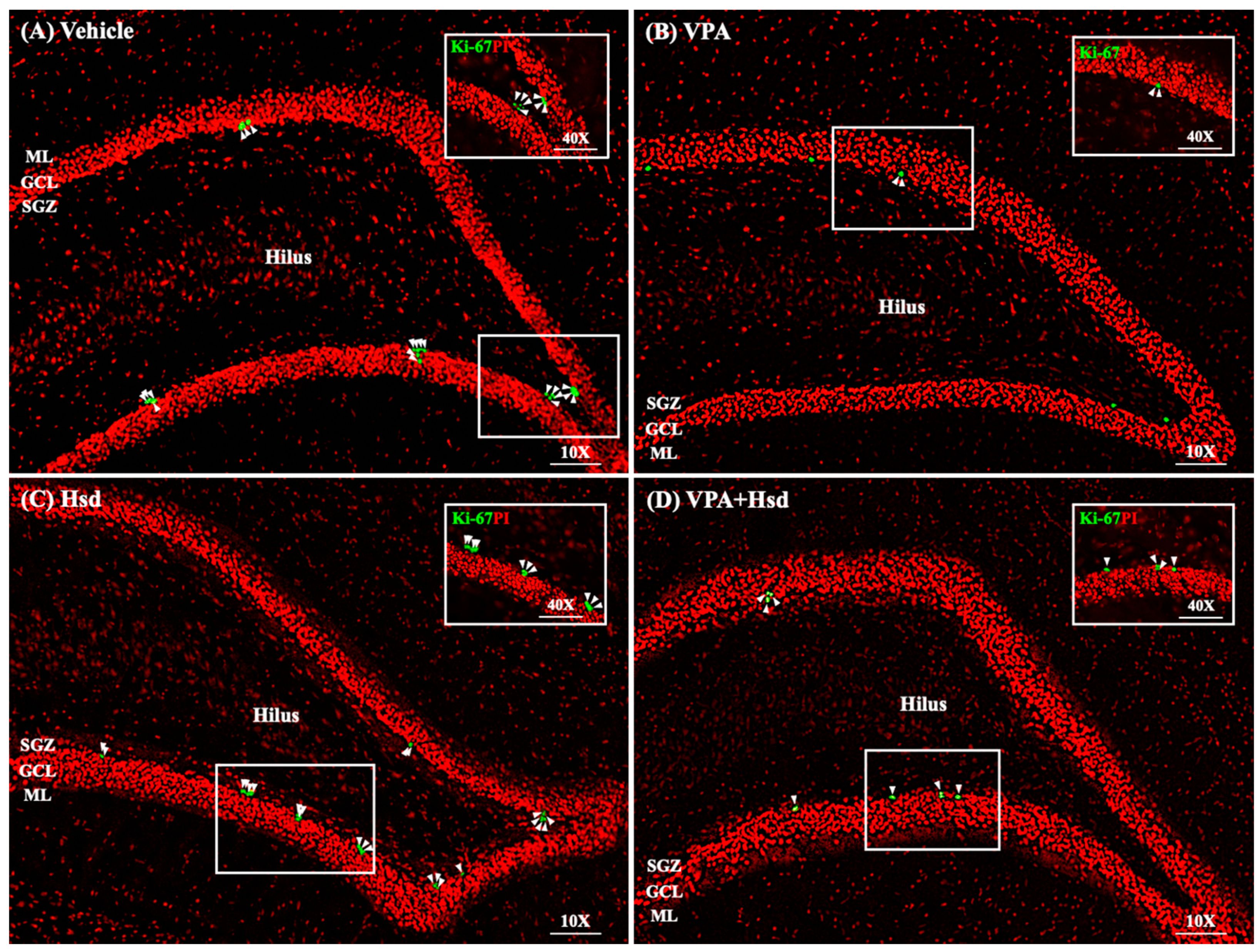
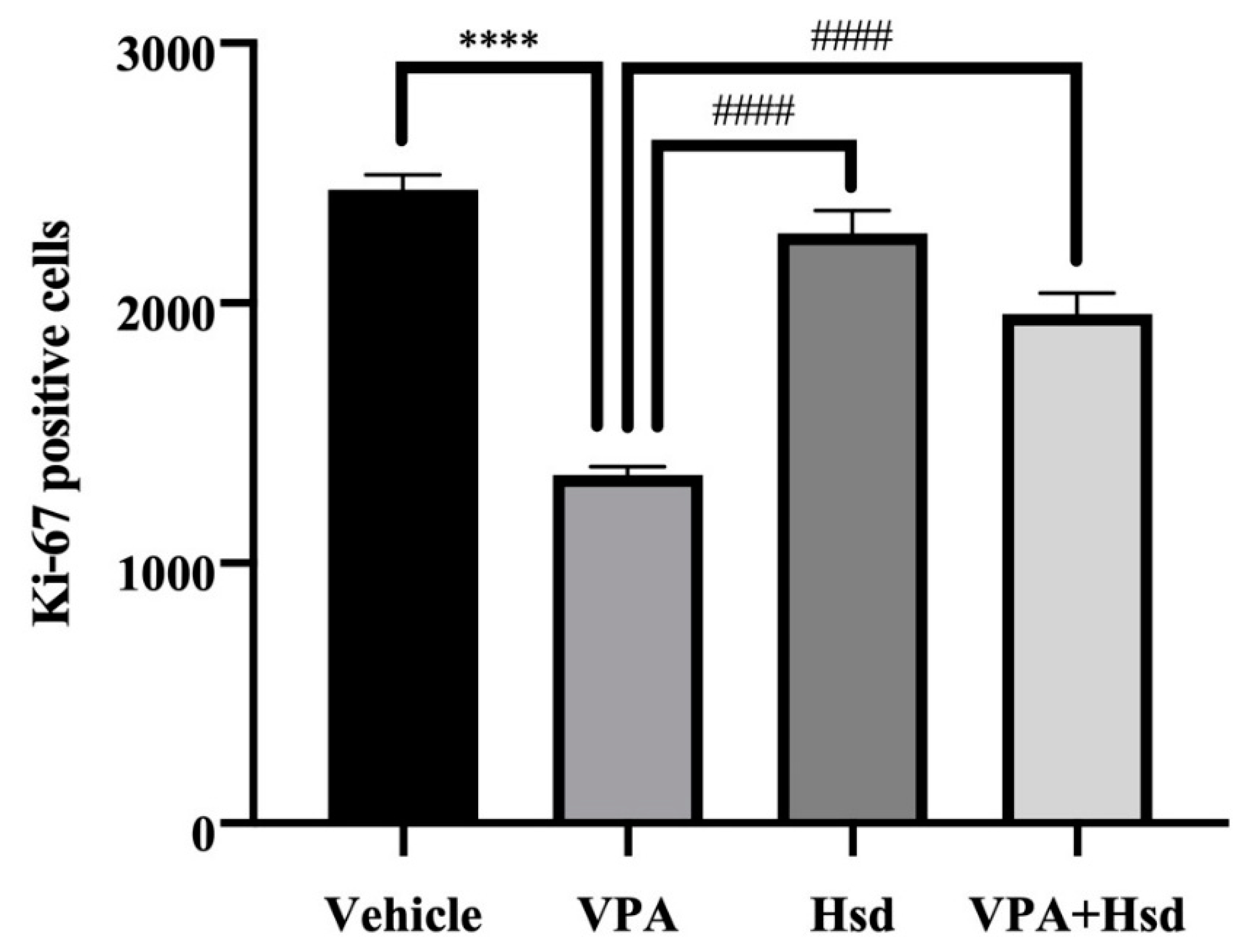
3.3. Effects of VPA and Hsd on the Ki-67 Positive Cell Count in the Hippocampus
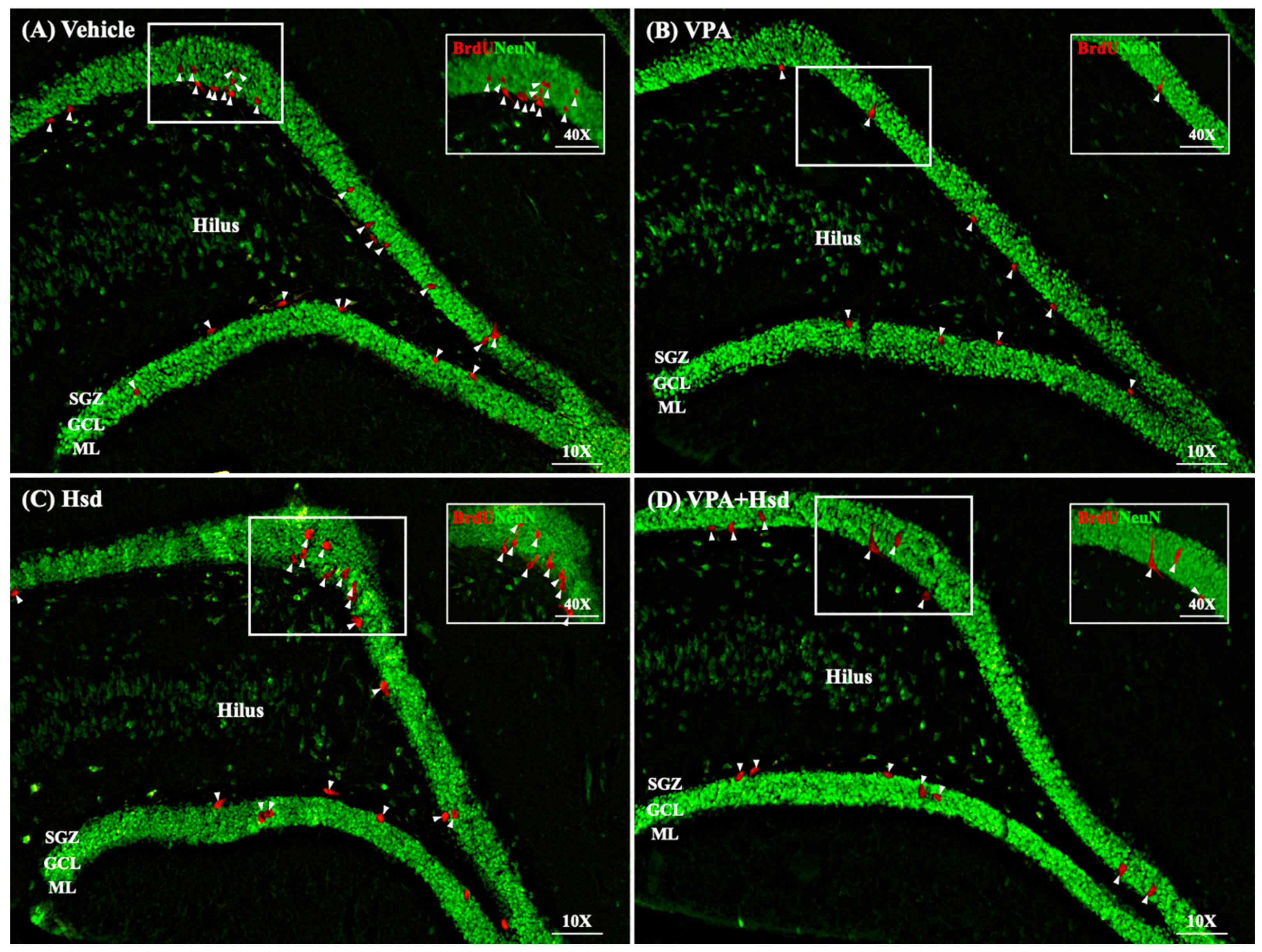
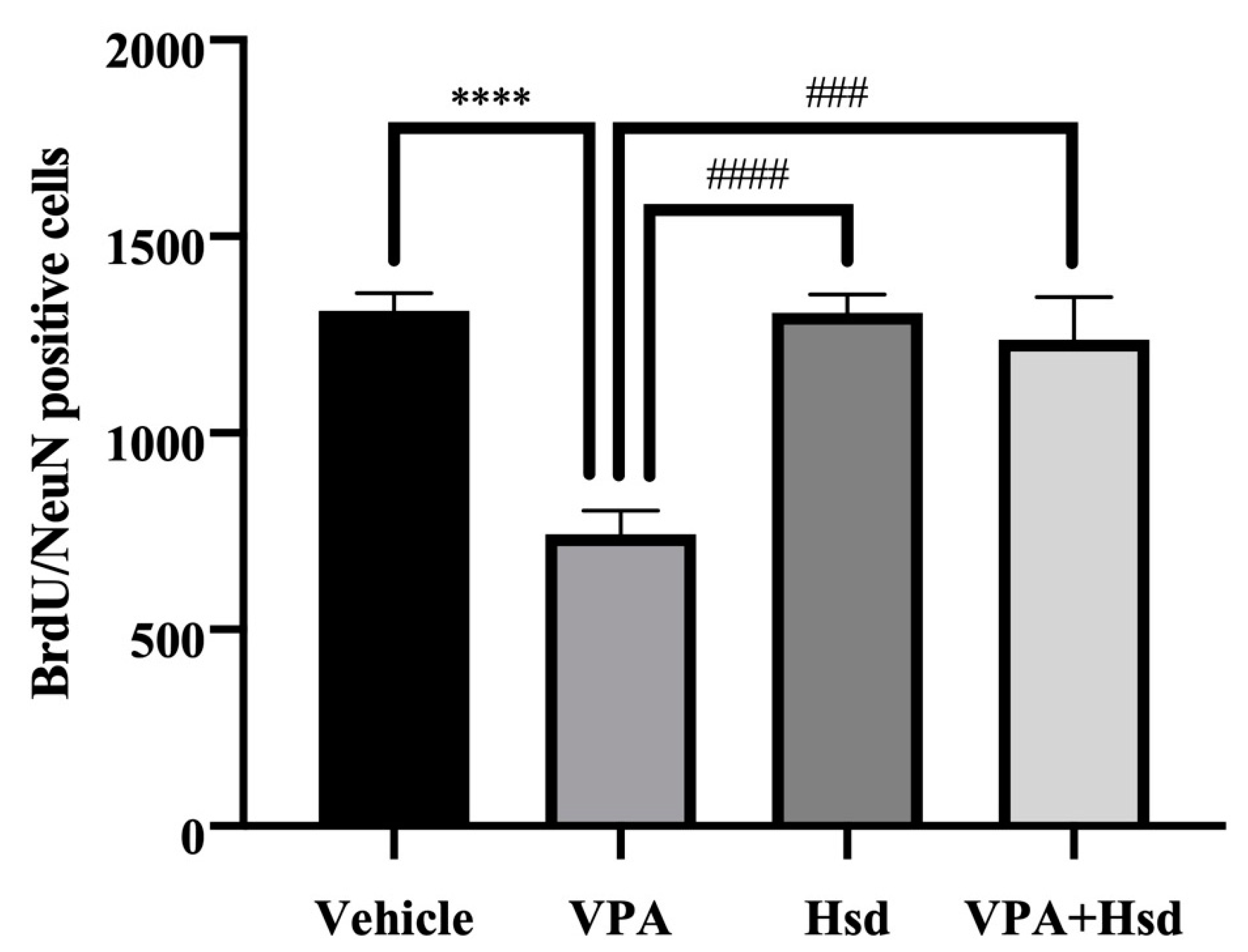
3.4. Effects of VPA and Hsd on Neuronal Cell Survival
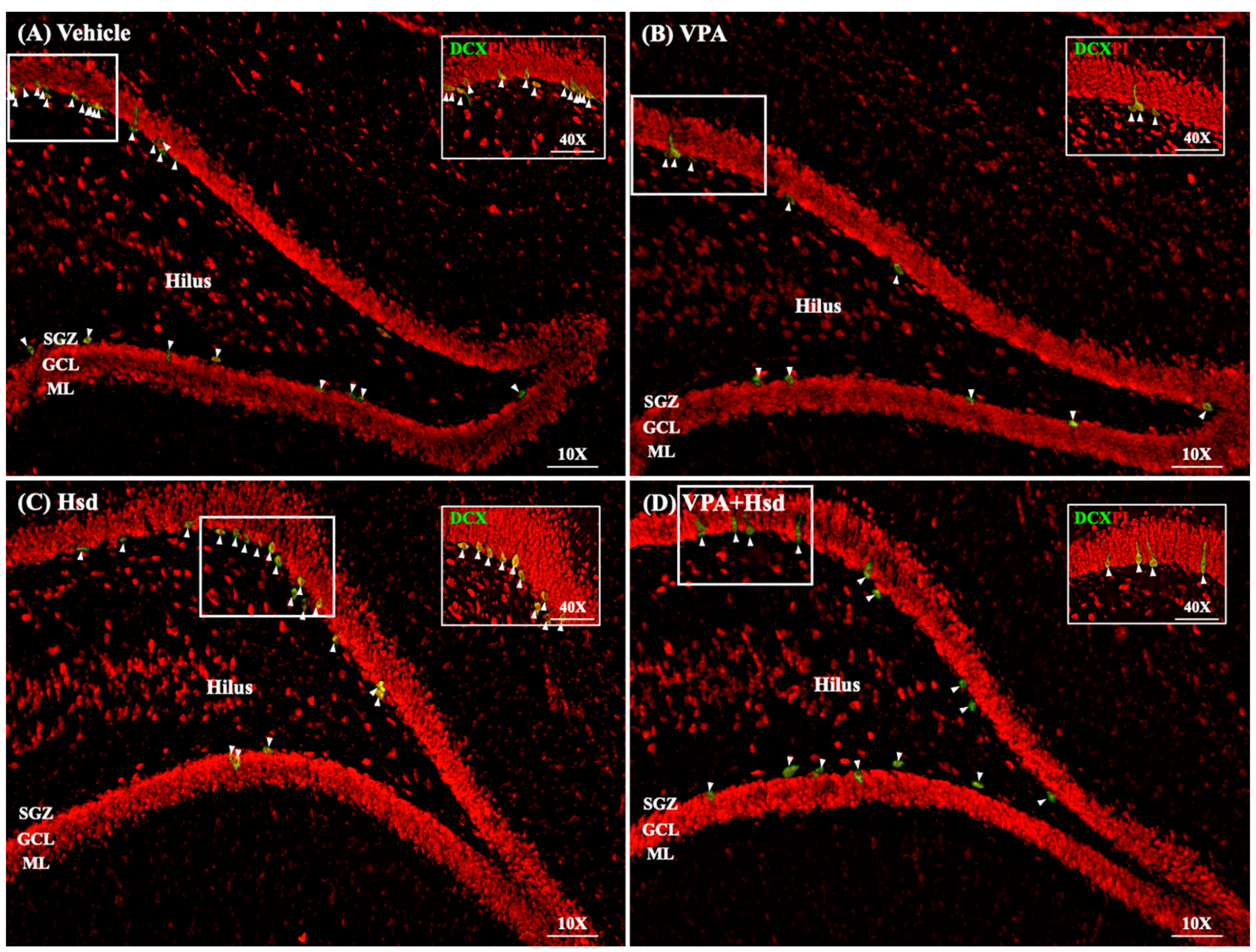
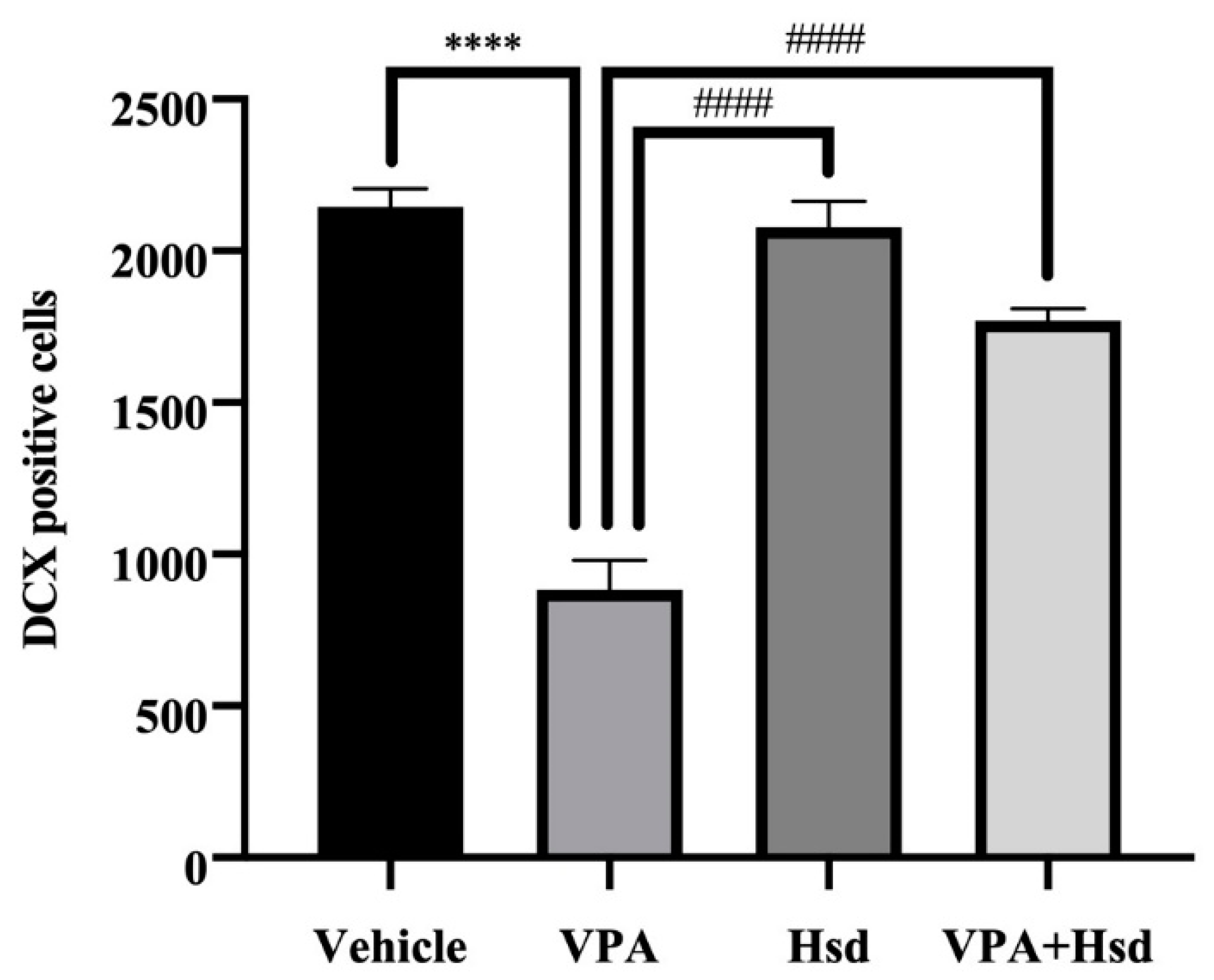
3.5. Effects of VPA and Hsd on Immature Neuron
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Hernández, J.; Zaldívar-Machorro, V.J.; Villanueva-Porras, D.; Avila, E.V.; Chavarría, A. A Potential Alternative against Neurodegenerative Diseases: Phytodrugs. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 8378613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H. Antioxidative effects of hesperetin against lead acetate-induced oxidative stress in rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2013, 45, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Dong, W. Hesperetin induces the apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via mitochondrial pathway mediated by the increased intracellular reactive oxygen species, ATP and calcium. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, M.K.; Sharma, N.; Dobhal, M.P.; Joshi, Y.C. Flavonoids: A versatile source of anticancer drugs. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajialyani, M.; Farzaei, M.H.; Echeverría, J.; Nabavi, S.M.; Uriarte, E.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. Hesperidin as a Neuroprotective Agent: A Review of Animal and Clinical Evidence. Molecules 2019, 24, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenmozhi, A.J.; Raja, T.R.W.; Janakiraman, U.; Manivasagam, T. Neuroprotective effect of hesperidin on aluminium chloride induced Alzheimer’s disease in Wistar rats. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naewla, S.; Sirichoat, A.; Pannangrong, W.; Chaisawang, P.; Wigmore, P.; Welbat, J.U. Hesperidin Alleviates Methotrexate-Induced Memory Deficits via Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Adult Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.T.; Schafer, S.; Gage, F.H. Adult Neurogenesis in the Hippocampus: From Stem Cells to Behavior. Cell 2016, 167, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Sahay, A.; Duman, R.S.; Hen, R. Functional Differentiation of Adult-Born Neurons along the Septotemporal Axis of the Dentate Gyrus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a018978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Kitamura, T.; Saitoh, Y.; Ohkawa, N.; Kondo, T.; Inokuchi, K. Adult Neurogenesis Conserves Hippocampal Memory Capacity. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 6854–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umka, J.; Mustafa, S.; ElBeltagy, M.; Thorpe, A.; Latif, L.; Bennett, G.; Wigmore, P. Valproic acid reduces spatial working memory and cell proliferation in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 2010, 166, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, C.U. Mechanisms of action of valproate: A commentatory. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 37, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, C.T.; Johnson, L.G. Comparative Neurocognitive Effects of 5 Psychotropic Anticonvulsants and Lithium. MedGenMed: Medscape Gen. Med. 2006, 8, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Senturk, V.; Goker, C.; Bilgic, A.; Olmez, S.; Tugcu, H.; Öncü, B.; Atbasoglu, E.C. Impaired verbal memory and otherwise spared cognition in remitted bipolar patients on monotherapy with lithium or valproate. Bipolar Disord. 2007, 9, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranarochana, A.; Chaisawang, P.; Sirichoat, A.; Pannangrong, W.; Wigmore, P.; Welbat, J.U. Protective effects of melatonin against valproic acid-induced memory impairments and reductions in adult rat hippocampal neurogenesis. Neuroscience 2019, 406, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottay, D.; Neergheen-Bhujun, V.S. Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Effects of Traditional Herbal Medicines used in the Management of Neurodegenerative Diseases in Mauritius. Arch. Med. Biomed. Res. 2016, 2, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéniche, A.; Philippe, D.; Buyukpamukcu, E.; Bastien, P.; Bourassa, S.; Bernard, D.; Delatre, C.; Castiel-Hogounenc, I. The natural flavonoid, hesperidin improves skin aging surface parameters following oral intake. In Proceedings of the European Society for Dermatological Research Meeting, Salzburg, Austria, 19–22 September 2012; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327832482 (accessed on 2 December 2021).
- Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, M.; Kuno, T. Cancer chemoprevention by citrus pulp and juices containing high amounts of beta-cryptoxanthin and hesperidin. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 516981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, S.L.; Aggleton, J.P. Extending the spontaneous preference test of recognition: Evidence of object-location and object-context recognition. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 99, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, T.M.; Burton, G.J. Methodological problems in placental morphometry: Apologia for the use of stereology based on sound sampling practice. Placenta 1988, 9, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeltagy, M.; Mustafa, S.; Umka, J.; Lyons, L.; Salman, A.; Dormon, K.; Allcock, C.; Bennett, G.; Wigmore, P. The effect of 5-fluorouracil on the long-term survival and proliferation of cells in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 88, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabogal-Guaqueta, A.M.; Munoz-Manco, J.I.; Ramirez-Pineda, J.R.; Lamprea-Rodriguez, M.; Osorio, E.; Cardona-Gomez, G.P. The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and protects cognitive and emotional function in aged triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Neuropharmacology 2015, 93, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghbelinejad, S.; Nassiri-Asl, M.; Naserpour Farivar, T.; Abbasi, E.; Sheikhi, M.; Taghiloo, M.; Farsad, F.; Samimi, A.; Hajiali, F. Rutin activates the MAPK pathway and BDNF gene expression on beta-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 224, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.X.; Wang, S.-W.; Yu, X.-L.; Su, Y.-J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, W.-W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.-J.; Liu, R.-T. Rutin improves spatial memory in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice by reducing Abeta oligomer level and attenuating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 264, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, N.J.; Squire, L.R.; Clark, R.E. Spatial memory, recognition memory, and the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14515–14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbeltagy, M.; Mustafa, S.; Umka, J.; Lyons, L.; Salman, A.; Tu, C.-Y.G.; Bhalla, N.; Bennett, G.; Wigmore, P.M. Fluoxetine improves the memory deficits caused by the chemotherapy agent 5-fluorouracil. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Cysique, L.; Maruff, P.; Brew, B.J. Valproic acid is associated with cognitive decline in HIV-infected individuals: A clinical observational study. BMC Neurol. 2006, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, K.J.; Loring, D.W.; Hulihan, J.F.; Kamin, M.; Karim, R. Differential cognitive and behavioral effects of topiramate and valproate. Neurology 2003, 60, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Shehata, G.; Bateh, A.E.-A.M.; Hamed, S.; A Rageh, T.; Elsorogy, Y.B. Neuropsychological effects of antiepileptic drugs (carbamazepine versus valproate) in adult males with epilepsy. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2009, 5, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y. Hesperidin alleviates cognitive impairment, mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 1209–12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, L.R.; Wixted, J.; Clark, R.E. Recognition memory and the medial temporal lobe: A new perspective. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turriziani, P.; Oliveri, M.; Salerno, S.; Costanzo, F.; Koch, G.; Caltagirone, C.; Carlesimo, G.A. Recognition Memory and Prefrontal Cortex: Dissociating Recollection and Familiarity Processes Using rTMS. Behav. Neurol. 2008, 19, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevins, R.A.; Besheer, J. Object recognition in rats and mice: A one-trial non-matching-to-sample learning task to study ‘recognition memory’. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takuma, K.; Hara, Y.; Kataoka, S.; Kawanai, T.; Maeda, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Takano, E.; Hayata-Takano, A.; Hashimoto, H.; Ago, Y.; et al. Chronic treatment with valproic acid or sodium butyrate attenuates novel object recognition deficits and hippocampal dendritic spine loss in a mouse model of autism. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 126, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, I.; Diniz, L.P.; Buosi, A.; Neves, G.; Stipursky, J.; Carvalho Alcantara Gomes, F. Flavonoid Hesperidin Induces Synapse Formation and Improves Memory Performance through the Astrocytic TGF-beta1. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.S.; Jesse, C.R.; Ruff, J.R.; Espinosa, D.D.O.; Gomes, N.S.; Altvater, E.E.T.; Donato, F.; Giacomeli, R.; Boeira, S.P. Hesperidin reverses cognitive and depressive disturbances induced by olfactory bulbectomy in mice by modulating hippocampal neurotrophins and cytokine levels and acetylcholinesterase activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 789, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, D.; Lucki, I. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis: Regulation, functional implications, and contribution to disease pathology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 232–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabatake, Y.; Sailor, K.; Ming, G.-L.; Song, H. Adult Neurogenesis and Hippocampal Memory Function: New Cells, More Plasticity, New Memories? Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 18, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Spalding, K.; Bergmann, O.; Alkass, K.; Bernard, S.; Salehpour, M.; Huttner, H.B.; Boström, E.; Westerlund, I.; Vial, C.; Buchholz, B.; et al. Dynamics of Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Adult Humans. Cell 2013, 153, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welbat, J.U.; Sirichoat, A.; Chaijaroonkhanarak, W.; Prachaney, P.; Pannangrong, W.; Pakdeechote, P.; Sripanidkulchai, B.; Wigmore, P. Asiatic Acid Prevents the Deleterious Effects of Valproic Acid on Cognition and Hippocampal Cell Proliferation and Survival. Nutrients 2016, 8, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell Physiol. 2000, 182, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirichoat, A.; Suwannakot, K.; Chaisawang, P.; Pannangrong, W.; Aranarochana, A.; Wigmore, P.; Welbat, J.U. Melatonin attenuates 5-fluorouracil-induced spatial memory and hippocampal neurogenesis impairment in adult rats. Life Sci. 2020, 248, 117468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.; Nakashima, K.; Kuwabara, T.; Mejia, E.; Gage, F.H. Histone deacetylase inhibition-mediated neuronal differentiation of multipotent adult neural progenitor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16659–16664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, H.; Buchsbaum, R.; Weintraub, D.; Pierro, J., Jr.; Stanley, R.; Hirsch, L. Patient-reported cognitive side effects of antiepileptic drugs: Predictors and comparison of all commonly used antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy Behav. 2009, 14, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpay, J.; Aldenkamp, A.; van Donselaar, C. Complaints associated with the use of antiepileptic drugs: Results from a community-based study. Seizure 2005, 14, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtowicz, J.M.; Kee, N. BrdU assay for neurogenesis in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusel’Nikova, V.V.; Korzhevskiy, D.E. NeuN as a Neuronal Nuclear Antigen and Neuron Differentiation Marker. Acta Naturae 2015, 7, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.M.; Hotsenpiller, G.; Peterson, D.A. Acute Psychosocial Stress Reduces Cell Survival in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis without Altering Proliferation. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2734–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliandi, B.; Tanemura, K.; Igarashi, K.; Tominaga, T.; Furukawa, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Moriyama, N.; Ikegami, D.; Abematsu, M.; Sanosaka, T.; et al. Reduced Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Cognitive Impairments following Prenatal Treatment of the Antiepileptic Drug Valproic Acid. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.; Yan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.-J.; Yu, H.-P.; Tu, Z.; Guo, X.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Li, X.-J.; et al. Maternal valproic acid exposure leads to neurogenesis defects and autism-like behaviors in non-human primates. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimouchi, A.; Yokota, H.; Ono, S.; Matsumoto, C.; Tamai, T.; Takumi, H.; Narayanan, S.P.; Kimura, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Caldwell, R.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of water-dispersible hesperetin in retinal ischemia reperfusion injury. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 60, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, G.; Perez-Garcia, C.G.; Gleeson, J.G. Selective Expression of Doublecortin and LIS1 in Developing Human Cortex Suggests Unique Modes of Neuronal Movement. Cereb. Cortex 2002, 12, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, H.Y.; Wojtowicz, J.M. Dynamics of neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 385, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aranarochana, A.; Kaewngam, S.; Anosri, T.; Sirichoat, A.; Pannangrong, W.; Wigmore, P.; Welbat, J.U. Hesperidin Reduces Memory Impairment Associated with Adult Rat Hippocampal Neurogenesis Triggered by Valproic Acid. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4364. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124364
Aranarochana A, Kaewngam S, Anosri T, Sirichoat A, Pannangrong W, Wigmore P, Welbat JU. Hesperidin Reduces Memory Impairment Associated with Adult Rat Hippocampal Neurogenesis Triggered by Valproic Acid. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4364. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124364
Chicago/Turabian StyleAranarochana, Anusara, Soraya Kaewngam, Tanaporn Anosri, Apiwat Sirichoat, Wanassanun Pannangrong, Peter Wigmore, and Jariya Umka Welbat. 2021. "Hesperidin Reduces Memory Impairment Associated with Adult Rat Hippocampal Neurogenesis Triggered by Valproic Acid" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4364. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124364
APA StyleAranarochana, A., Kaewngam, S., Anosri, T., Sirichoat, A., Pannangrong, W., Wigmore, P., & Welbat, J. U. (2021). Hesperidin Reduces Memory Impairment Associated with Adult Rat Hippocampal Neurogenesis Triggered by Valproic Acid. Nutrients, 13(12), 4364. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124364