Differential Influence of Soluble Dietary Fibres on Intestinal and Hepatic Carbohydrate Response
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Experimental Procedure
2.2. Liver Triglyceride and Histological Analysis
2.3. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR
2.4. Microbial 16S rRNA Sequencing (Preparation and Analysis)
2.5. H NMR Metabolomics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
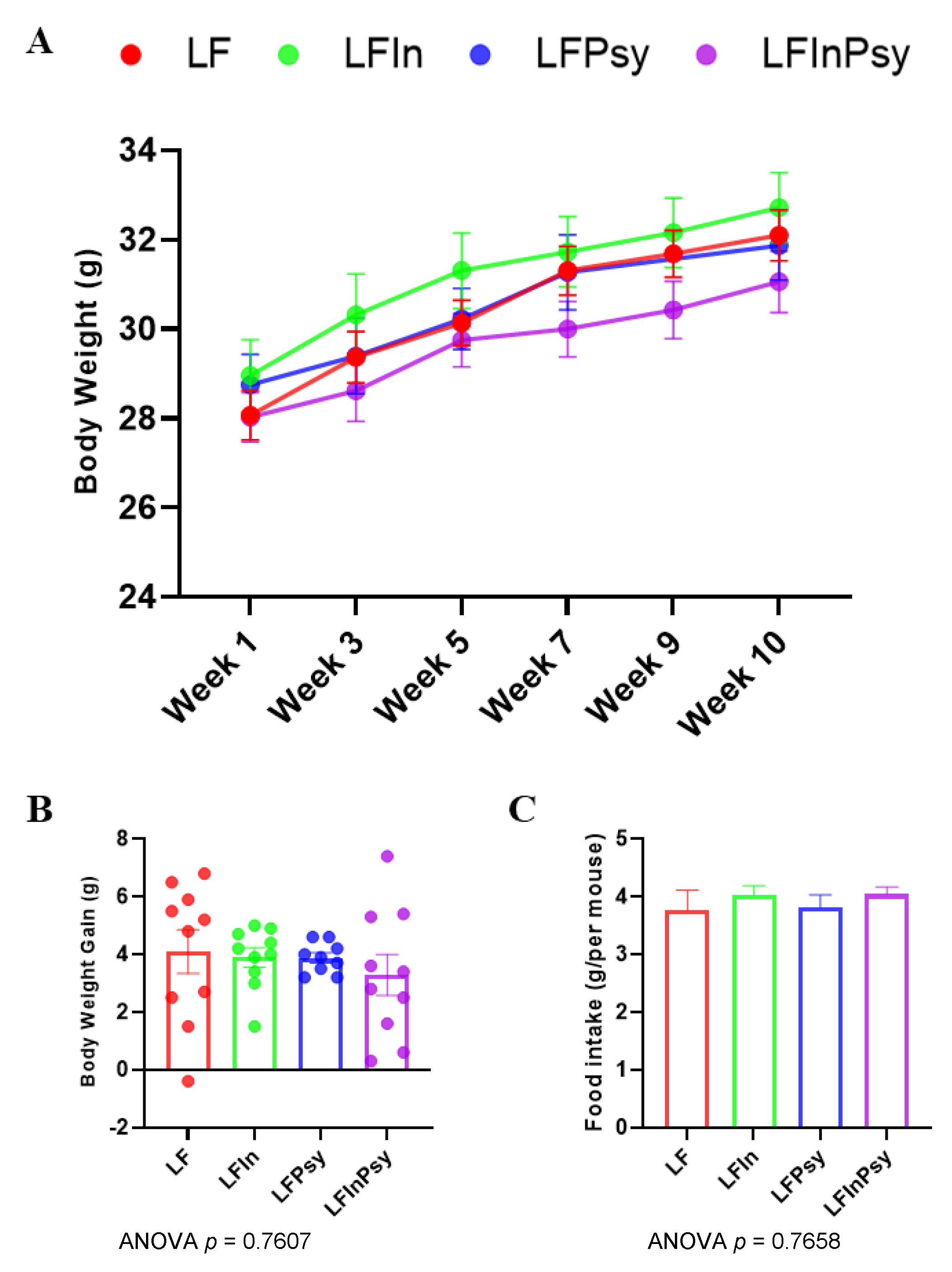
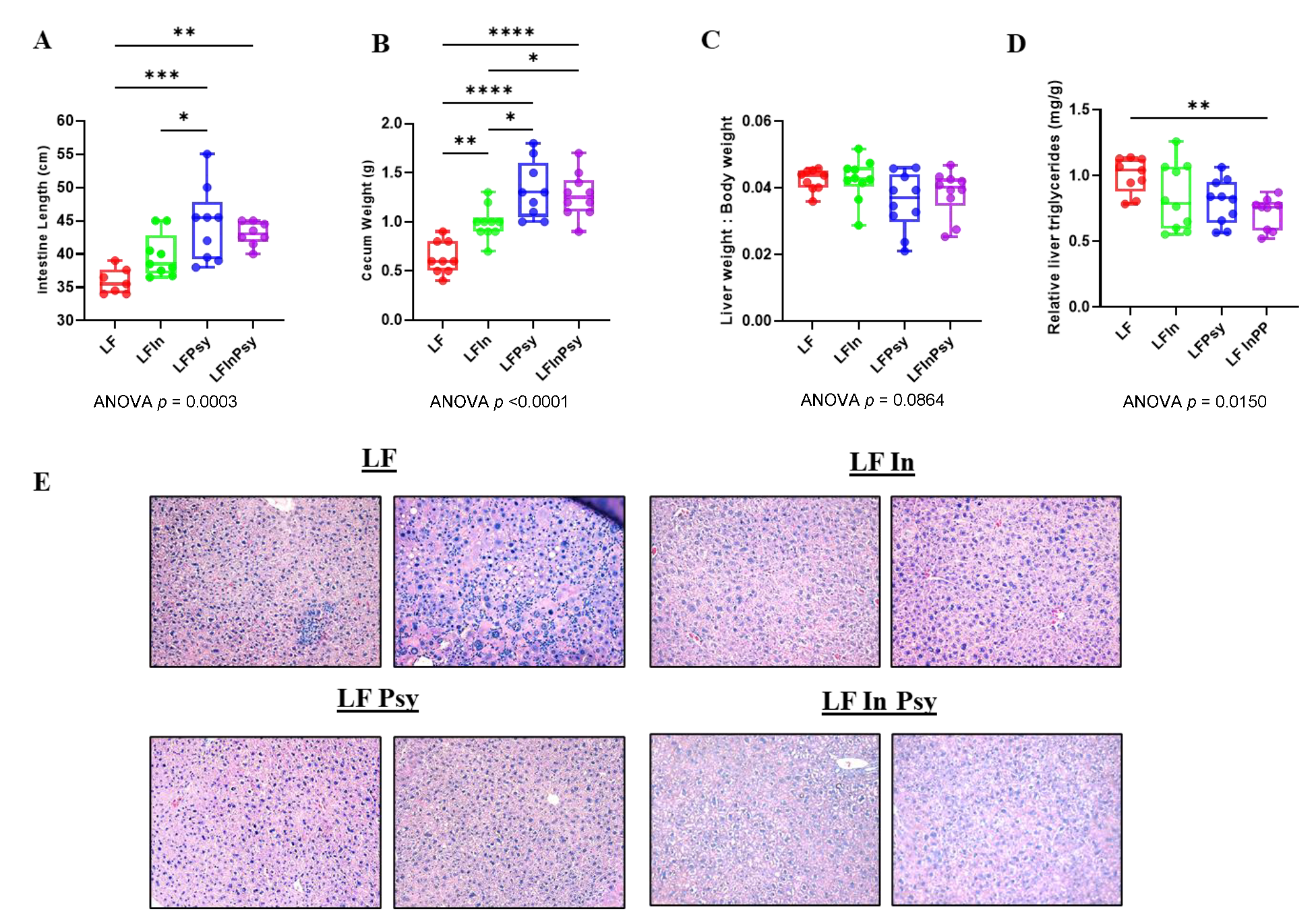
3.1. Addition of DFs Has Profound Morphological Implications, Independant of Body Weight Gain
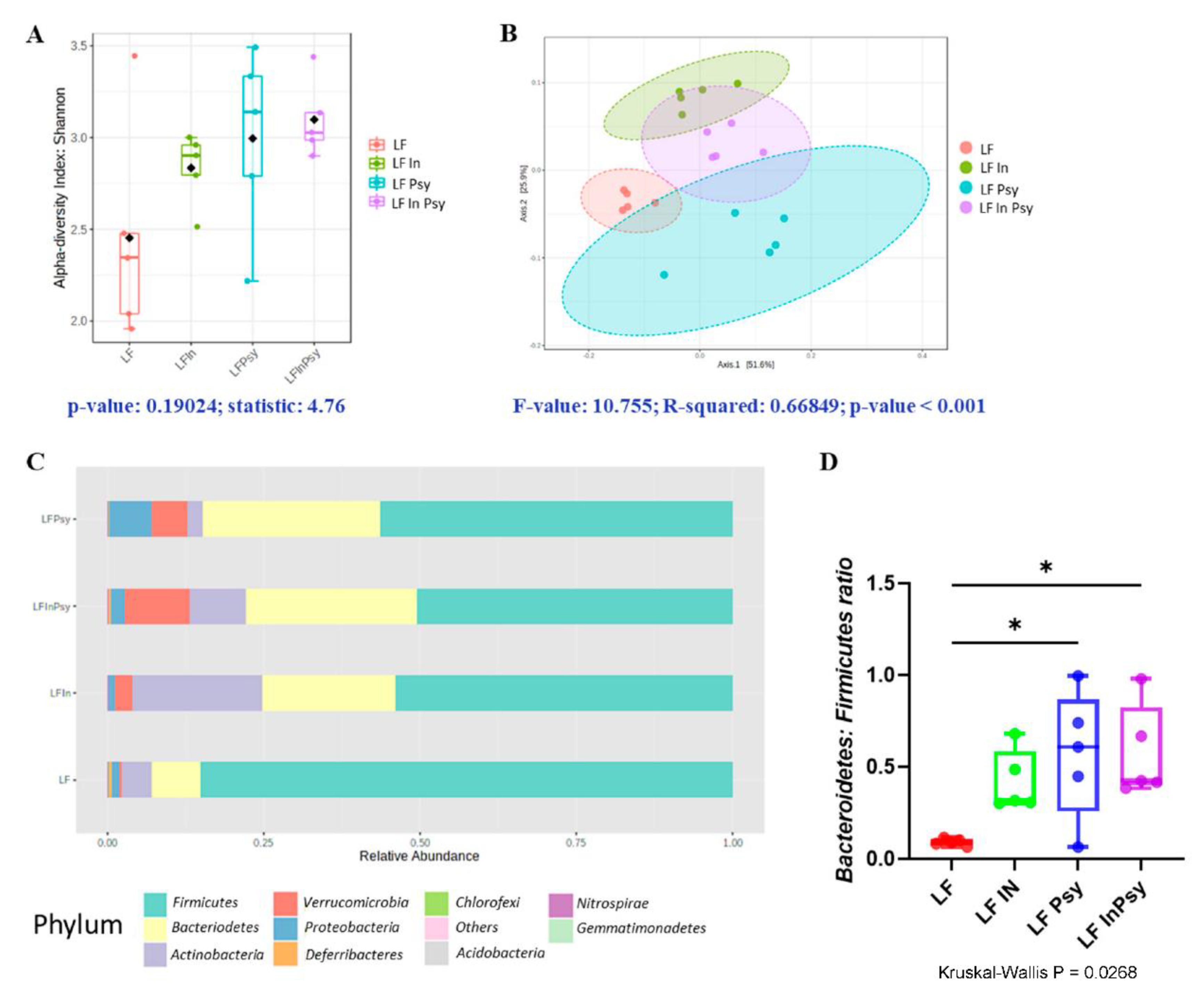
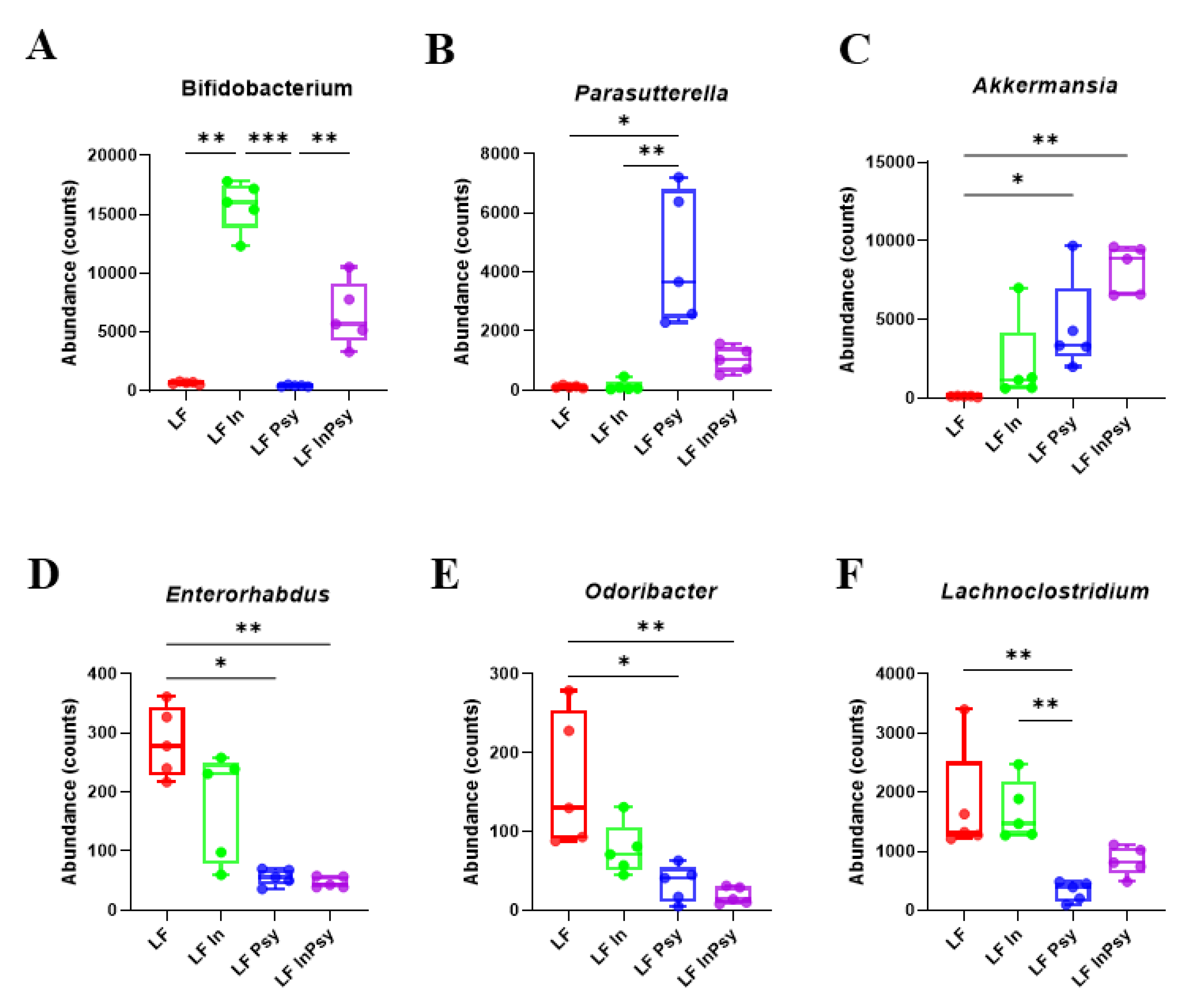
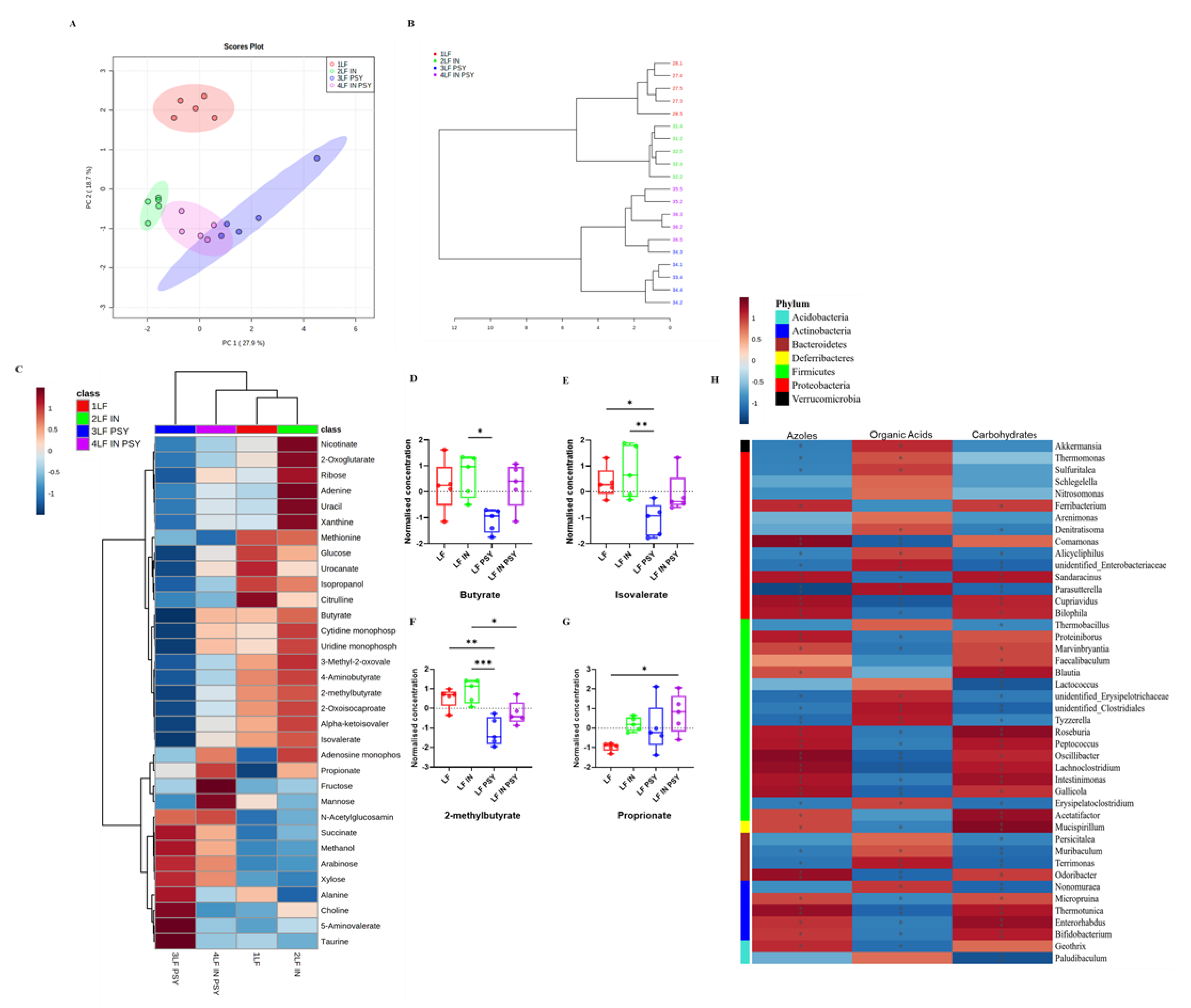
3.2. Psyllium and Inulin Result in Divergent Modulation of the Cecal Microbiota
3.3. DFs Have a Profound Impact on Cecal Metabolomic Profile
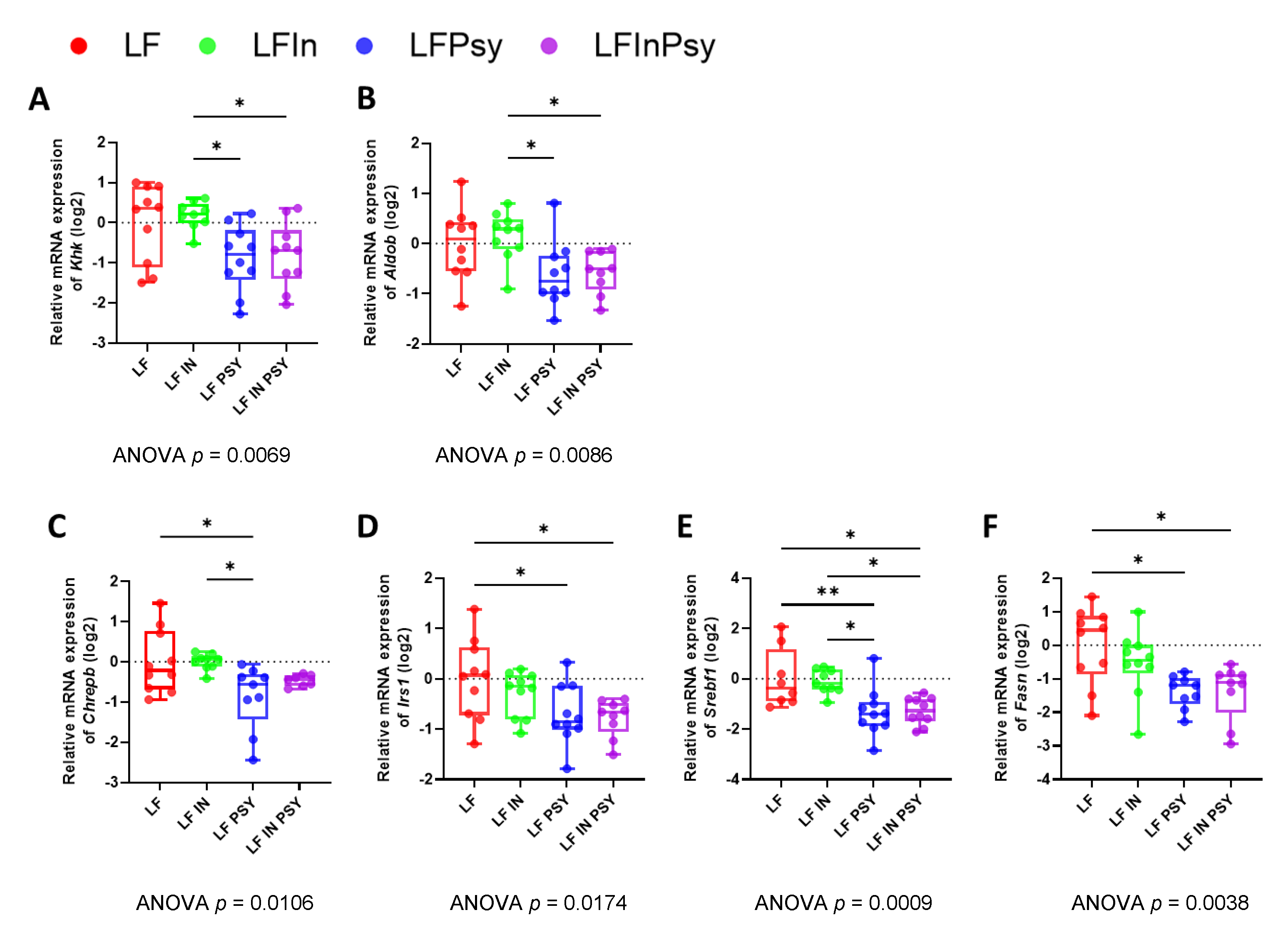
3.4. Soluble DF Addition Alters Intestinal Carbohydrate Response
3.5. The Addition of Psyllium Leads to Altered Hepatic Carbohydrate Response and Lipogenesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harris, R.M.; Rose, A.M.C.; Soares-Wynter, S.; Unwin, N. Ultra-processed food consumption in Barbados: Evidence from a nationally representative, cross-sectional study. J. Nutr. Sci. 2021, 10, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.M.; Champ, M.M.; Cloran, S.J.; Fleith, M.; van Lieshout, L.; Mejborn, H.; Burley, V.J. Dietary fibre in Europe: Current state of knowledge on definitions, sources, recommendations, intakes and relationships to health. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 149–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P. Dietary Fiber Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses. J. Chiropr. Med. 2018, 17, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.K.; Rossi, M.; Bajka, B.; Whelan, K. Dietary fibre in gastrointestinal health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.; Wolever, T.M.; Jenkins, A.L.; Taylor, R.H. Dietary fibre, carbohydrate metabolism and diabetes. Mol. Aspects Med. 1987, 9, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelson, M.; Tan, S.M.; Clarke, R.E.; de Pasquale, C.; Thallas-Bonke, V.; Nguyen, T.V.; Penfold, S.A.; Harcourt, B.E.; Sourris, K.C.; Lindblom, R.S.; et al. Processed foods drive intestinal barrier permeability and microvascular diseases. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantu-Jungles, T.M.; Hamaker, B.R. New View on Dietary Fiber Selection for Predictable Shifts in Gut Microbiota. mBio 2020, 11, e02179-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eswaran, S.; Muir, J.; Chey, W.D. Fiber and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, T.M.; Kabisch, S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Weickert, M.O. The Health Benefits of Dietary Fibre. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Chen, G.-C.; Wang, X.-P.; Qin, L.; Bai, Y. Dietary Fiber and Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis and Review of Related Mechanisms. Nutrients 2017, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, B.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Fang, Y.; Cui, J.; Wan, J. Dietary fiber intake and risk of metabolic syndrome: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.W.; Baird, P.; Davis, R.H., Jr.; Ferreri, S.; Knudtson, M.; Koraym, A.; Waters, V.; Williams, C.L. Health benefits of dietary fiber. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhrstad, M.C.W.; Tunsjø, H.; Charnock, C.; Telle-Hansen, V.H. Dietary Fiber, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolic Regulation—Current Status in Human Randomized Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laukens, D.; Brinkman, B.M.; Raes, J.; De Vos, M.; Vandenabeele, P. Heterogeneity of the gut microbiome in mice: Guidelines for optimizing experimental design. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauzour, D.; Rodriguez-Ramiro, I.; Rushbrook, S.; Ipharraguerre, I.R.; Bevan, D.; Davies, S.; Tejera, N.; Mena, P.; de Pascual-Teresa, S.; Del Rio, D.; et al. n-3 Fatty acids combined with flavan-3-ols prevent steatosis and liver injury in a murine model of NAFLD. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, A.T.; Wolfe, D. Tissue Processing and Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining. In Histopathology: Methods and Protocols; Day, C.E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, K.; Ohashi, K.; Taminishi, S.; Okano, T.; Yoshioka, A.; Shima, M. Reference gene selection for real-time RT-PCR in regenerating mouse livers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Su, Y. Normalizing genes for real-time polymerase chain reaction in epithelial and nonepithelial cells of mouse small intestine. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 399, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, T.T.T.; Corsini, S.; Kellingray, L.; Hegarty, C.; Le Gall, G.; Narbad, A.; Müller, M.; Tejera, N.; O’Toole, P.W.; Minihane, A.M.; et al. APOE genotype influences the gut microbiome structure and function in humans and mice: Relevance for Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. Faseb J. 2019, 33, 8221–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.-É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Yu, G.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y.; Wells, P.M.; Steves, C.J.; Ju, F.; Fu, J. M2IA: A web server for microbiome and metabolome integrative analysis. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3493–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhariwal, A.; Chong, J.; Habib, S.; King, I.L.; Agellon, L.B.; Xia, J. MicrobiomeAnalyst: A web-based tool for comprehensive statistical, visual and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W180–W188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Liang, D.; Wei, R.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Jia, W.; Chen, T. Evaluation of metabolite-microbe correlation detection methods. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 567, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, J.; Brandmaier, S.; Leonhardt, J.; Scheerer, M.F.; Mohney, R.P.; Xu, T.; Bi, J.; Rotter, M.; Troll, M.; Chi, S.; et al. Metformin Effect on Nontargeted Metabolite Profiles in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and in Multiple Murine Tissues. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3776–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, Q.; Hu, J.; Gao, H.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.; Zuo, S.; Fang, Q.; Huang, X.; Yin, J.; et al. Bioactive Dietary Fibers Selectively Promote Gut Microbiota to Exert Antidiabetic Effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7000–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, N.C.; Saltzman, E.; Roberts, S.B. Dietary fiber and weight regulation. Nutr. Rev. 2001, 59, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, M.; McKay, J.; Pal, S. Effects of daily consumption of psyllium, oat bran and polyGlycopleX on obesity-related disease risk factors: A critical review. Nutrition 2019, 57, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, H.; Wang, K.; Bhagavathula, A.S.; Almuhairi, S.J.; Ryan, P.M.; Rahmani, J.; Dang, M.; et al. The effect of psyllium consumption on weight, body mass index, lipid profile, and glucose metabolism in diabetic patients: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Miles-Brown, J.; Pellizzon, M.; Ulman, E.; Ricci, M.; Zhang, L.; Patterson, A.D.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Gewirtz, A.T. Lack of soluble fiber drives diet-induced adiposity in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G528–G541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, C.L.; Williams, P.A.; Garden, K.E.; Thomson, L.M.; Ross, A.W. Dose-Dependent Effects of a Soluble Dietary Fibre (Pectin) on Food Intake, Adiposity, Gut Hypertrophy and Gut Satiety Hormone Secretion in Rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morita, T.; Kasaoka, S.; Hase, K.; Kiriyama, S. Psyllium Shifts the Fermentation Site of High-Amylose Cornstarch toward the Distal Colon and Increases Fecal Butyrate Concentration in Rats. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.; Wada, S.; Yang, S.; Gosis, B.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lee, G.; Arany, Z.; Rabinowitz, J.D. The small intestine shields the liver from fructose-induced steatosis. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopman, W.P.; Houben, P.G.; Speth, P.A.; Lamers, C.B. Glucomannan prevents postprandial hypoglycaemia in patients with previous gastric surgery. Gut 1988, 29, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sierra, M.; García, J.J.; Fernández, N.; Diez, M.J.; Calle, A.P. Therapeutic effects of psyllium in type 2 diabetic patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibson, G.R.; Beatty, E.R.; Wang, X.; Cummings, J.H. Selective stimulation of bifidobacteria in the human colon by oligofructose and inulin. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRorie, J.W., Jr. Psyllium is not fermented in the human gut. NeuroGastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 1681–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalanka, J.; Major, G.; Murray, K.; Singh, G.; Nowak, A.; Kurtz, C.; Silos-Santiago, I.; Johnston, J.M.; de Vos, W.M.; Spiller, R. The Effect of Psyllium Husk on Intestinal Microbiota in Constipated Patients and Healthy Controls. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, H.S.; Cho, C.H.; Yun, M.S.; Jang, S.J.; You, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Han, D.; Cha, K.H.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, K.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila secretes a glucagon-like peptide-1-inducing protein that improves glucose homeostasis and ameliorates metabolic disease in mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopchand, D.E.; Carmody, R.N.; Kuhn, P.; Moskal, K.; Rojas-Silva, P.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Raskin, I. Dietary Polyphenols Promote Growth of the Gut Bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila and Attenuate High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2847–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greer, R.L.; Dong, X.; Moraes, A.C.; Zielke, R.A.; Fernandes, G.R.; Peremyslova, E.; Vasquez-Perez, S.; Schoenborn, A.A.; Gomes, E.P.; Pereira, A.C.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila mediates negative effects of IFNγ on glucose metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, T.; Kong, J.Y.; Stothard, P.; Willing, B.P. Defining the role of Parasutterella, a previously uncharacterized member of the core gut microbiota. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, L.; Kang, K.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Chang, B. FOXO4 ameliorates alcohol-induced chronic liver injury via inhibiting NF-κB and modulating gut microbiota in C57BL/6J mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.-C.; Guo, W.-L.; Li, L.; Yu, X.-D.; Liu, B. Polysaccharide peptides from Ganoderma lucidum ameliorate lipid metabolic disorders and gut microbiota dysbiosis in high-fat diet-fed rats. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 57, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.S.; Li, L.; Rui, J.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Cui, D.; Xu, B. Tomato seed oil attenuates hyperlipidemia and modulates gut microbiota in C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4275–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.-K.; Seo, S.-H.; Park, S.-E.; Kim, H.-W.; Kim, E.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Pyo, J.-Y.; Cho, K.-M.; Kwon, S.-J.; Park, D.-H.; et al. Gut Microbiome and Metabolome Profiles Associated with High-Fat Diet in Mice. Metabolites 2021, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefura, T.; Zapała, B.; Gosiewski, T.; Skomarovska, O.; Dudek, A.; Pędziwiatr, M.; Major, P. Differences in Compositions of Oral and Fecal Microbiota between Patients with Obesity and Controls. Medicina 2021, 57, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Long, H.; Muhindo, E.M.; Liu, R.; Sui, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M. Lactobacillus rhamnosus LRa05 Ameliorate Hyperglycemia through a Regulating Glucagon-Mediated Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8797–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Geng, R.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, S.G.; Huang, K.; Tong, T. Oleuropein Ameliorates Advanced Stage of Type 2 Diabetes in db/db Mice by Regulating Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menni, C.; Fauman, E.; Erte, I.; Perry, J.R.; Kastenmüller, G.; Shin, S.Y.; Petersen, A.K.; Hyde, C.; Psatha, M.; Ward, K.J.; et al. Biomarkers for type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose using a nontargeted metabolomics approach. Diabetes 2013, 62, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Guo, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis A6 Alleviates Obesity Associated with Promoting Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Function of Adipose Tissue in Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Phylum | p Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|
| Actinobacteria | 0.000892 | 0.008173 |
| Proteobacteria | 0.001026 | 0.008173 |
| Verrucomicrobia | 0.002157 | 0.009708 |
| Deferribacteres | 0.005 | 0.016724 |
| Firmicutes | 0.011603 | 0.029836 |
| Genus | p Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|
| Bifidobacterium | 0.00053615 | 0.035856 |
| Parasutterella | 0.00098285 | 0.035856 |
| Lachnoclostridium | 0.0012329 | 0.035856 |
| Odoribacter | 0.0019303 | 0.035856 |
| Akkermansia | 0.0021574 | 0.035856 |
| Enterorhabdus | 0.0023009 | 0.035856 |
| Phylum. | Genus. | Metabolic Class | Metabolite | R | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verrucomicrobia | Akkermansia | Amino Acids | Citrulline | −0.71 | 0.022 |
| Carbohydrates | Glucose | −0.733 | 0.016 | ||
| Others | 3-Methyl-2-oxovalerate | −0.782 | 7.5 × 10−3 | ||
| Proteobacteria | Parasutterella | Amino Acids | Citrulline | −0.77 | 9.2 × 10−3 |
| Carbohydrates | Glucose | −0.673 | 0.033 | ||
| Actinobacteria | Enterorhabdus | Amino Acids | Citrulline | 0.758 | 0.011 |
| Carbohydrates | Glucose | 0.758 | 0.011 | ||
| Others | 3-Methyl-2-oxovalerate | 0.806 | 4.9 × 10−3 | ||
| Proteobacteria | Odoribacter | Amino Acids | Citrulline | 0.806 | 4.9 × 10−3 |
| Others | 3-Methyl-2-oxovalerate | 0.915 | 2 × 10−4 | ||
| Firmicutes | Lachnoclostridium | Amino Acids | Citrulline | 0.77 | 9.2 × 10−3 |
| Carbohydrates | Glucose | 0.721 | 0.019 | ||
| Others | 3-Methyl-2-oxovalerate | 0.842 | 2.2 × 10−3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pontifex, M.G.; Mushtaq, A.; Le Gall, G.; Rodriguez-Ramiro, I.; Blokker, B.A.; Hoogteijling, M.E.M.; Ricci, M.; Pellizzon, M.; Vauzour, D.; Müller, M. Differential Influence of Soluble Dietary Fibres on Intestinal and Hepatic Carbohydrate Response. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124278
Pontifex MG, Mushtaq A, Le Gall G, Rodriguez-Ramiro I, Blokker BA, Hoogteijling MEM, Ricci M, Pellizzon M, Vauzour D, Müller M. Differential Influence of Soluble Dietary Fibres on Intestinal and Hepatic Carbohydrate Response. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124278
Chicago/Turabian StylePontifex, Matthew G., Aleena Mushtaq, Gwenaëlle Le Gall, Ildefonso Rodriguez-Ramiro, Britt Anne Blokker, Mara E. M. Hoogteijling, Matthew Ricci, Michael Pellizzon, David Vauzour, and Michael Müller. 2021. "Differential Influence of Soluble Dietary Fibres on Intestinal and Hepatic Carbohydrate Response" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124278
APA StylePontifex, M. G., Mushtaq, A., Le Gall, G., Rodriguez-Ramiro, I., Blokker, B. A., Hoogteijling, M. E. M., Ricci, M., Pellizzon, M., Vauzour, D., & Müller, M. (2021). Differential Influence of Soluble Dietary Fibres on Intestinal and Hepatic Carbohydrate Response. Nutrients, 13(12), 4278. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124278








