Dietary Magnesium Alleviates Experimental Murine Colitis through Modulation of Gut Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Bacterial DNA Purification, Amplification, and Sequencing
3. Results
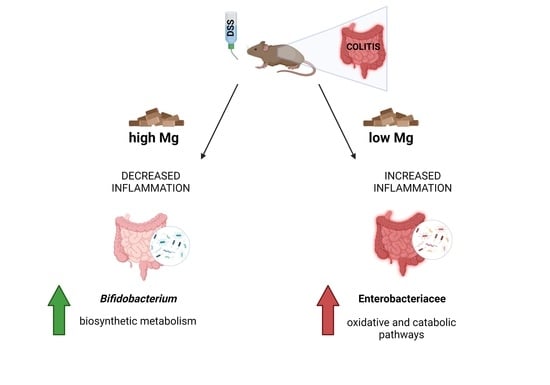
3.1. Dietary Magnesium Modulates Experimental Colitis
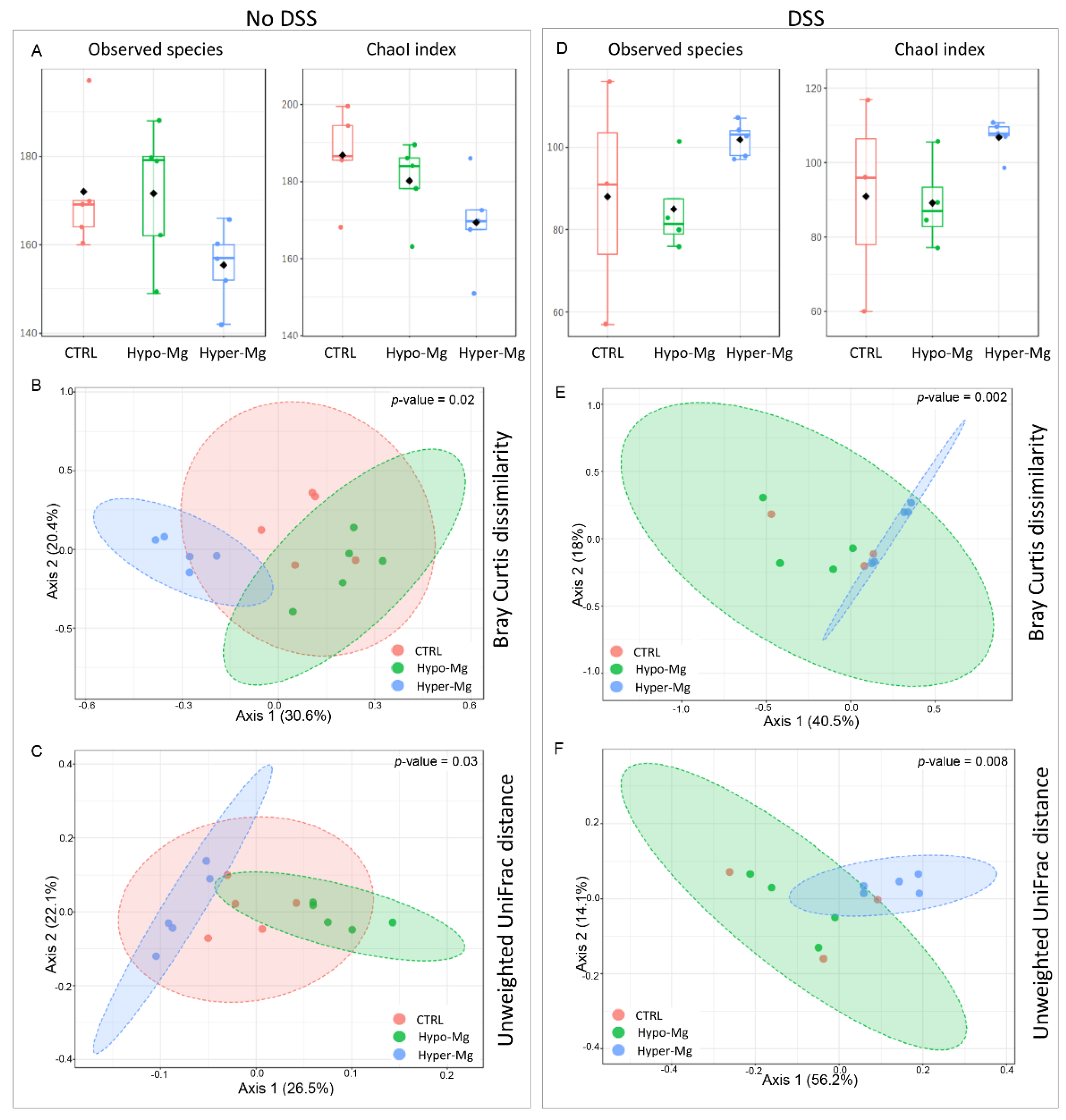
3.2. Dietary Magnesium Modulates Intestinal Microbiota
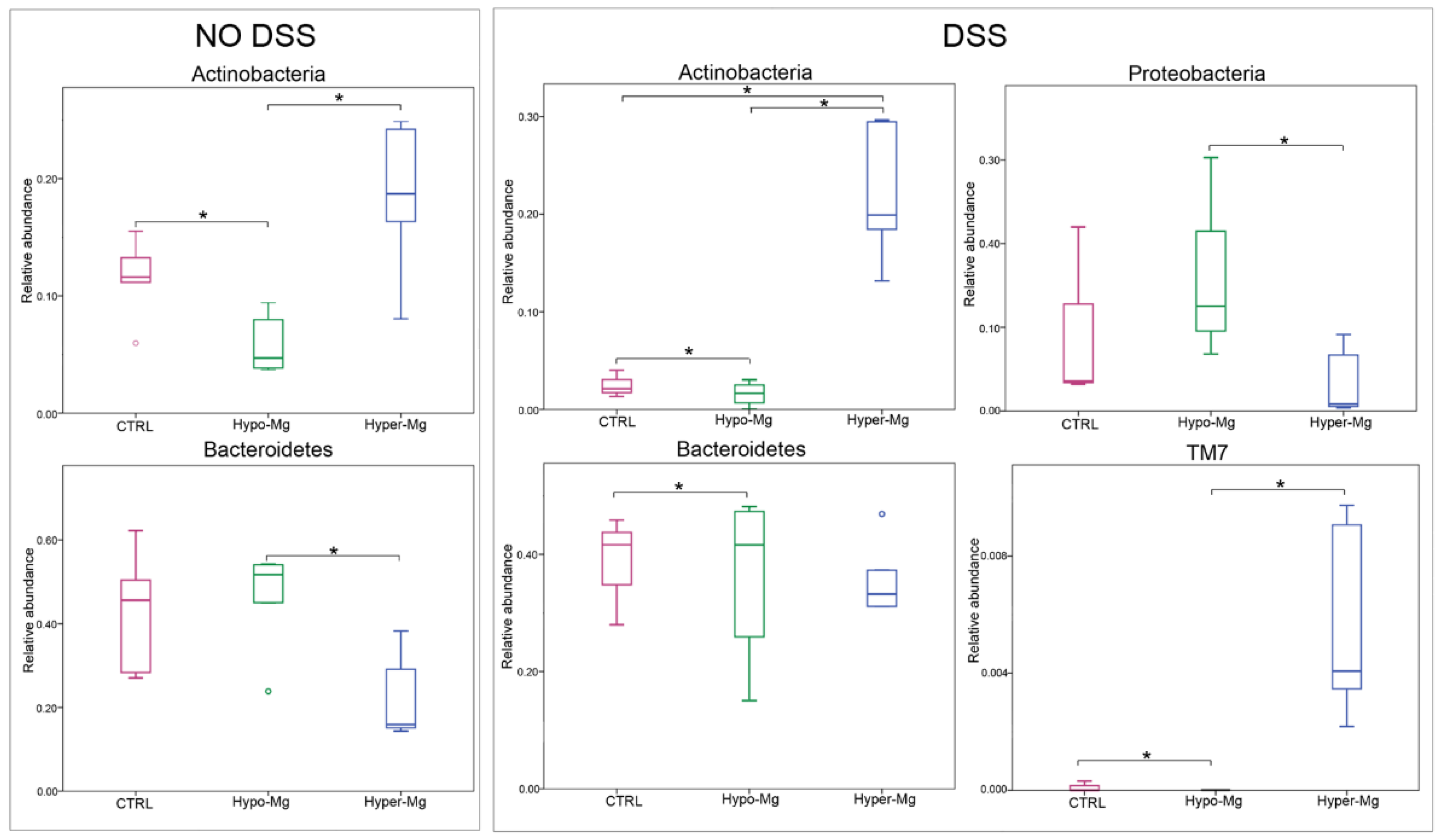
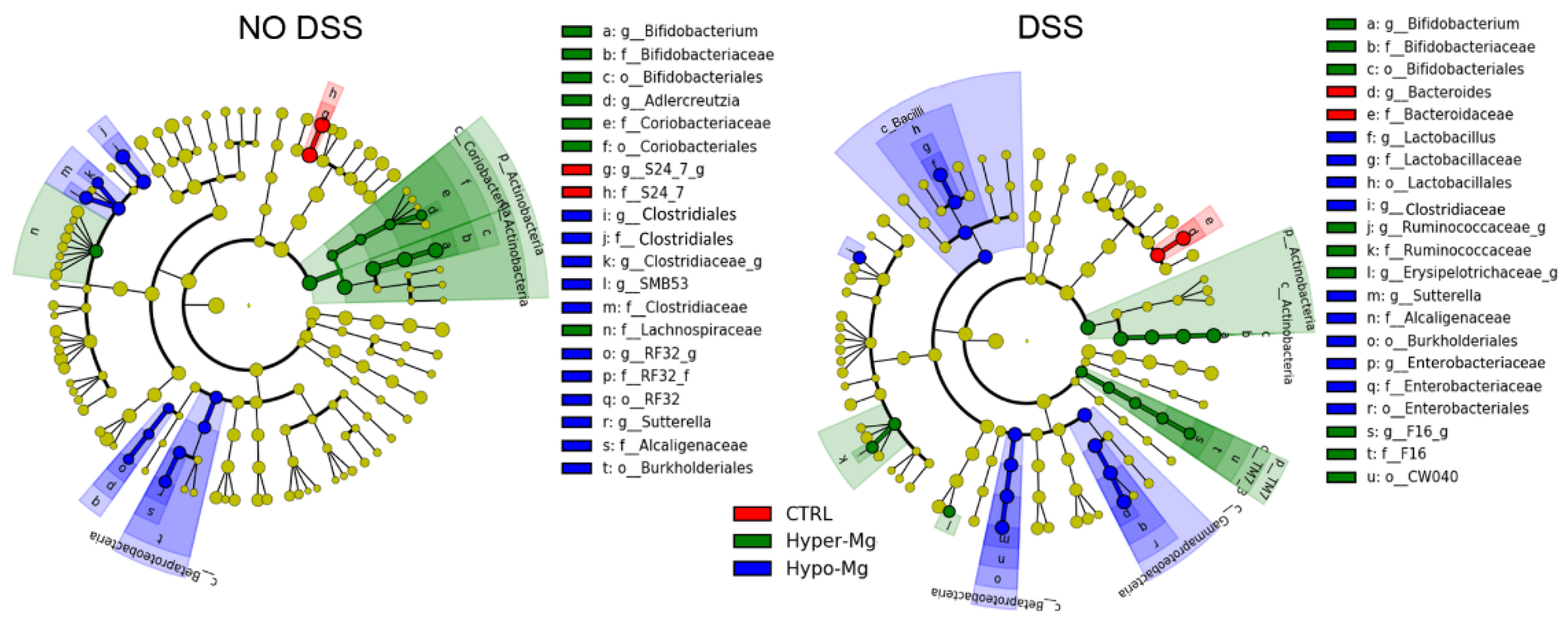
3.2.1. Microbiota Composition
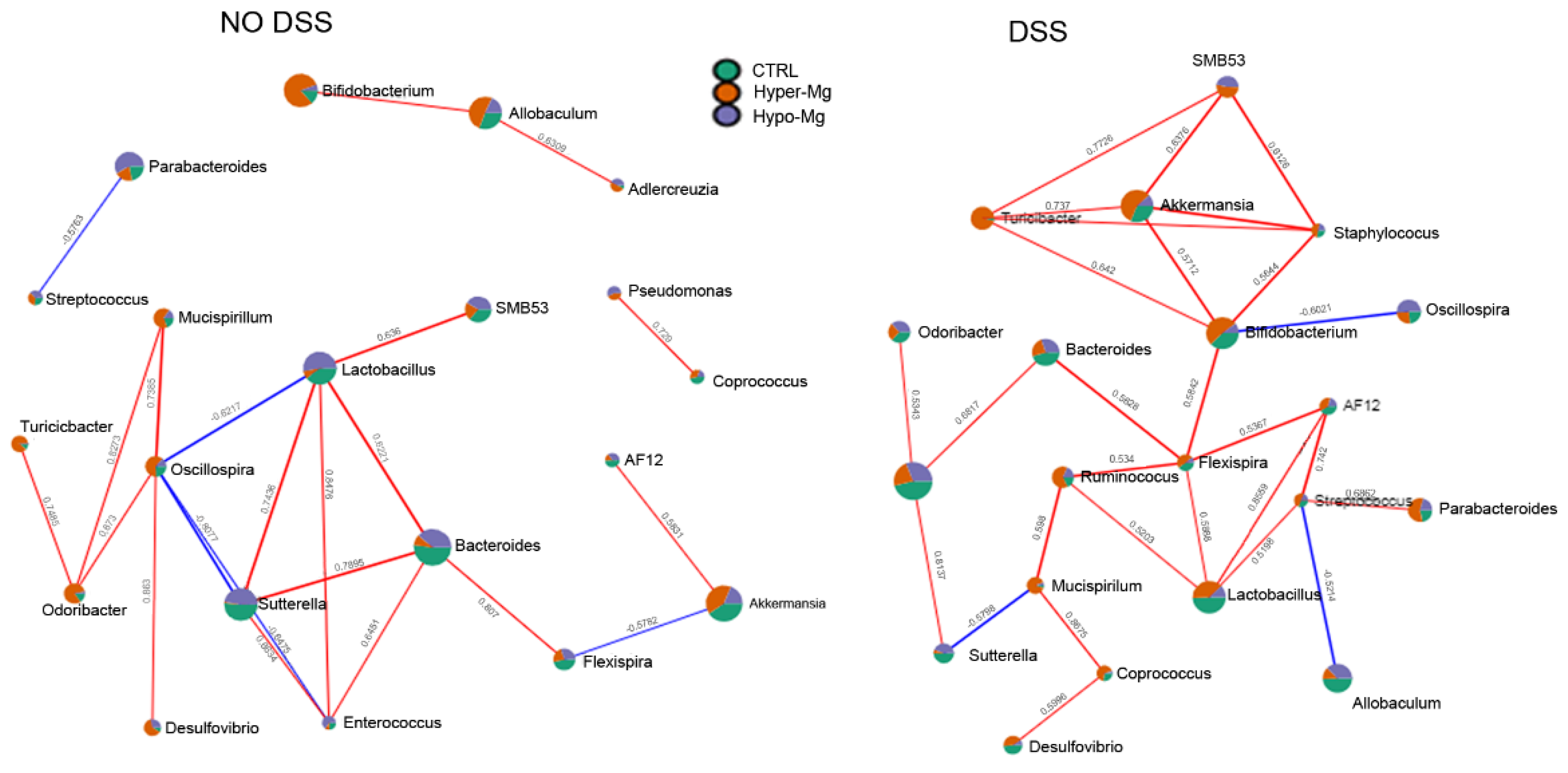
3.2.2. Co-Occurrence and Co-Exclusion Patterns
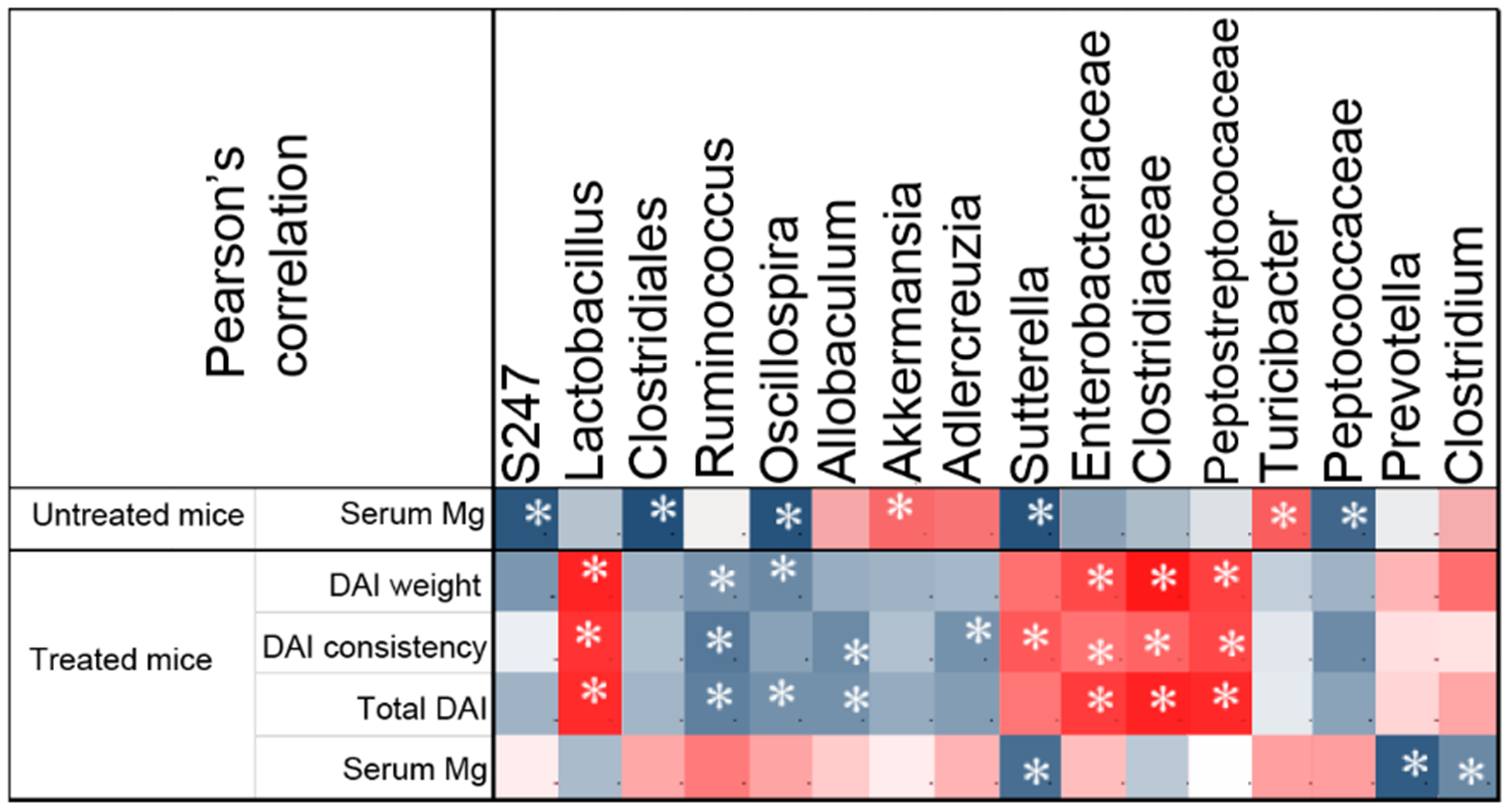
3.2.3. Correlation between Gut Microbial Taxa and Colitis Severity
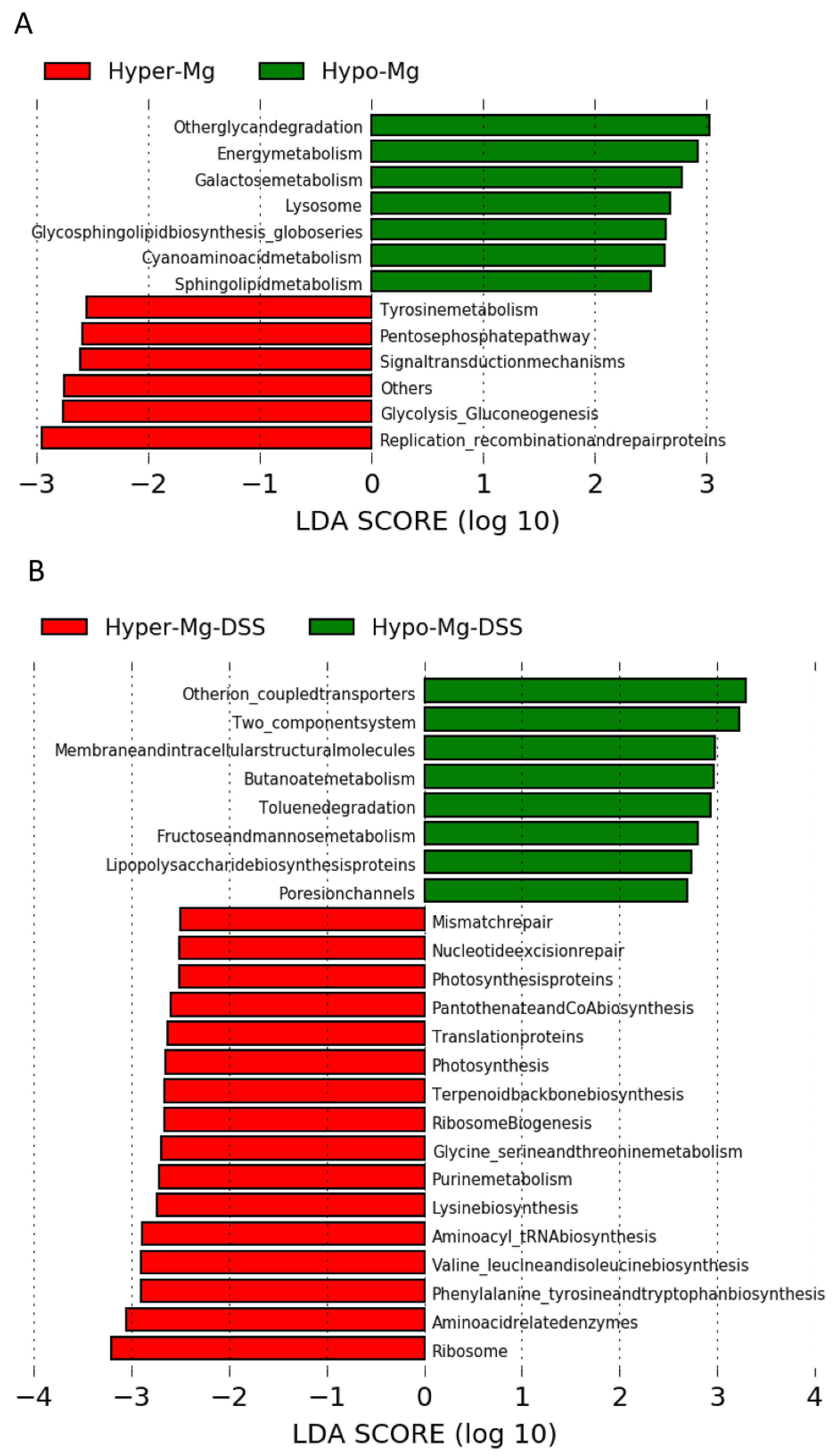
3.2.4. Microbial Functional Profiling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mentella, M.C.; Scaldaferri, F.; Pizzoferrato, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Miggiano, G.A.D. Nutrition, IBD and Gut Microbiota: A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, C.L.; Weir, T.L. The Gut Microbiota at the Intersection of Diet and Human Health. Science 2018, 362, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quagliariello, A.; Del Chierico, F.; Reddel, S.; Russo, A.; Onetti Muda, A.; D’Argenio, P.; Angelino, G.; Romeo, E.F.; Dall’Oglio, L.; De Angelis, P.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplant in Two Ulcerative Colitis Pediatric Cases: Gut Microbiota and Clinical Course Correlations. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, F.M.; Vesa, C.M.; Gheorghe, G.; Diaconu, C.C.; Stoicescu, M.; Munteanu, M.A.; Babes, E.E.; Tit, D.M.; Toma, M.M.; Bungau, S. Highlighting the Relevance of Gut Microbiota Manipulation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisshof, R.; Chermesh, I. Micronutrient Deficiencies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapani, V.; Petito, V.; Di Agostini, A.; Arduini, D.; Hamersma, W.; Pietropaolo, G.; Luongo, F.; Arena, V.; Stigliano, E.; Lopetuso, L.R.; et al. Dietary Magnesium Alleviates Experimental Murine Colitis Through Upregulation of the Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 6 Channel. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, J.A.; Castiglioni, S.; Locatelli, L.; Zocchi, M.; Mazur, A. Magnesium and Inflammation: Advances and Perspectives. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 115, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, E.A.; Hollands, K.; Kriner, M.A.; Lee, E.-J.; Park, S.-Y.; Pontes, M.H. Bacterial Mg2+ Homeostasis, Transport, and Virulence. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2013, 47, 625–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, J.C.; Shin, D.; Zwir, I.; Latifi, T.; Hadley, T.J.; Groisman, E.A. Evolution of a Bacterial Regulon Controlling Virulence and Mg2+ Homeostasis. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véscovi, E.G.; Soncini, F.C.; Groisman, E.A. Mg2+ as an Extracellular Signal: Environmental Regulation of Salmonella Virulence. Cell 1996, 84, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachikian, B.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Deldicque, L.; De Backer, F.C.; Catry, E.; Dewulf, E.M.; Sohet, F.M.; Bindels, L.B.; Everard, A.; Francaux, M.; et al. Changes in Intestinal Bifidobacteria Levels Are Associated with the Inflammatory Response in Magnesium-Deficient Mice. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, G.; Pyndt Jørgensen, B.M.; Elfving, B.; Nielsen, D.S.; Kihl, P.; Lund, S.; Sørensen, D.B.; Wegener, G. Dietary Magnesium Deficiency Alters Gut Microbiota and Leads to Depressive-like Behaviour. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015, 27, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyndt Jørgensen, B.; Winther, G.; Kihl, P.; Nielsen, D.S.; Wegener, G.; Hansen, A.K.; Sørensen, D.B. Dietary Magnesium Deficiency Affects Gut Microbiota and Anxiety-like Behaviour in C57BL/6N Mice. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015, 27, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommers, L.M.M.; Ederveen, T.H.A.; Wijst, J.; Overmars-Bos, C.; Kortman, G.A.M.; Boekhorst, J.; Bindels, R.J.M.; Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J. Low Gut Microbiota Diversity and Dietary Magnesium Intake are Associated with the Development of PPI-induced Hypomagnesemia. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 11235–11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, E.K.; Long-Smith, C.M.; Murphy, A.; Patterson, E.; Murphy, K.; O’Gorman, D.M.; Stanton, C.; Nolan, Y.M. Dietary Supplementation with a Magnesium-Rich Marine Mineral Blend Enhances the Diversity of Gastrointestinal Microbiota. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnich, N.; Rodrigues, M.; Sauvanet, P.; Chevarin, C.; Denis, S.; Le Goff, O.; Faure-Imbert, D.; Hanh, T.; Roques, C.F.; Chassaing, B.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Natural Mineral Waters on Intestinal Inflammation and the Mucosa-Associated Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Chiriaco, M.; Foligno, S.; Reddel, S.; Salvatori, G.; Cifaldi, C.; Faraci, S.; Finocchi, A.; Rossi, P.; et al. Gut Mucosal and Fecal Microbiota Profiling Combined to Intestinal Immune System in Neonates Affected by Intestinal Ischemic Injuries. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME Allows Analysis of High-Throughput Community Sequencing Data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and Clustering Orders of Magnitude Faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Dubosarskiy, I.; Murray, S.R.; Andersen, G.L. Comprehensive Aligned Sequence Construction for Automated Design of Effective Probes (CASCADE-P) Using 16S RDNA. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for Comprehensive Statistical, Functional, and Meta-Analysis of Microbiome Data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhariwal, A.; Chong, J.; Habib, S.; King, I.L.; Agellon, L.B.; Xia, J. MicrobiomeAnalyst: A Web-Based Tool for Comprehensive Statistical, Visual and Meta-Analysis of Microbiome Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W180–W188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive Functional Profiling of Microbial Communities Using 16S RRNA Marker Gene Sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubucker, S.; Segata, N.; Goll, J.; Schubert, A.M.; Izard, J.; Cantarel, B.L.; Rodriguez-Mueller, B.; Zucker, J.; Thiagarajan, M.; Henrissat, B.; et al. Metabolic Reconstruction for Metagenomic Data and Its Application to the Human Microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehbacher, T.; Rehman, A.; Lepage, P.; Hellmig, S.; Fölsch, U.R.; Schreiber, S.; Ott, S.J. Intestinal TM7 Bacterial Phylogenies in Active Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuoka, T. Bifidobacteria and Their Role in Human Health. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1990, 6, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Linglong, P.; Weixia, D.; Hong, W. Protective Effects of Bifidobacterium on Intestinal Barrier Function in LPS-Induced Enterocyte Barrier Injury of Caco-2 Monolayers and in a Rat NEC Model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodes, L. Effect of Probiotics Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium on Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides and Inflammatory Cytokines: An In Vitro Study Using a Human Colonic Microbiota Model. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Bhatia, R.; Khare, P.; Sharma, S.; Rajarammohan, S.; Bishnoi, M.; Bhadada, S.K.; Sharma, S.S.; Kaur, J.; Kondepudi, K.K. Anti-Inflammatory Bifidobacterium Strains Prevent Dextran Sodium Sulfate Induced Colitis and Associated Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Guan, X.-X.; Tang, Y.-J.; Sun, J.-F.; Wang, X.-K.; Wang, W.-D.; Fan, J.-M. Clinical Effects and Gut Microbiota Changes of Using Probiotics, Prebiotics or Synbiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 2855–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topouzian, N.; Joseph, B.J.; Bezkorovainy, A. Effect of Various Metals and Calcium Metabolism Inhibitors on the Growth of Bifidobacterium Bifidum Var. Pennsylvanicus. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1984, 3, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenkamp, G.C.; Veerkamp, J.H. Effects of Antibiotics on Metabolism of Peptidoglycan, Protein, and Lipids in Bifidobacterium Bifidum Subsp. Pennsylvanicus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1976, 10, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagi, T.; Belzer, C. The Interaction of Akkermansia Muciniphila with Host-Derived Substances, Bacteria and Diets. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4833–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.; Wu, W.; Yang, L.; Lv, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Fang, D.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; et al. Administration of Akkermansia Muciniphila Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, T.; Fujii, K.; Seki, T.; Aoyama, M.; Azuma, A.; Kawasome, H. Novel Gut Microbiota Modulator, Which Markedly Increases Akkermansia Muciniphila Occupancy, Ameliorates Experimental Colitis in Rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Legorreta, A.; Soriano-Pérez, L.A.; Flores-Buendía, A.M.; Medina-Campos, O.N.; Noriega, L.G.; Granados-Portillo, O.; Nambo-Venegas, R.; Tovar, A.R.; Mendoza-Vargas, A.; Barrera-Oviedo, D.; et al. Effect of Dietary Magnesium Content on Intestinal Microbiota of Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljewicz, M.; Siemianowska, E.; Cichosz, G.; Tońska, E. The Effect of Probiotics (Lactobacillus Rhamnosus HN001, Lactobacillus Paracasei LPC-37, and Lactobacillus Acidophilus NCFM) on the Availability of Minerals from Dutch-Type Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 4824–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielik, V.; Kolisek, M. Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Minerals in Relation to a Healthy Gut Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, M.; Miura, T.; Hirakata, S.; Hosoyama, A.; Sugino, S.; Umeno, A.; Murotomi, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Koike, T. Comparative Analysis of the Intestinal Flora in Type 2 Diabetes and Nondiabetic Mice. Exp. Anim. 2017, 66, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommers, L.M.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M.; de Baaij, J.H.F. Hypomagnesemia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Vicious Circle? Diabetes 2016, 65, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, N.W.; de Zoete, M.R.; Cullen, T.W.; Barry, N.A.; Stefanowski, J.; Hao, L.; Degnan, P.H.; Hu, J.; Peter, I.; Zhang, W.; et al. Immunoglobulin A Coating Identifies Colitogenic Bacteria in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell 2014, 158, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.M.; de Zoete, M.R.; Palm, N.W.; Laenen, Y.; Bright, R.; Mallette, M.; Bu, K.; Bielecka, A.A.; Xu, F.; Hurtado-Lorenzo, A.; et al. Immunoglobulin A Targets a Unique Subset of the Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 83–93.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldelli, V.; Scaldaferri, F.; Putignani, L.; Del Chierico, F. The Role of Enterobacteriaceae in Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, E.R.; Winter, M.G.; Duerkop, B.A.; Spiga, L.; Furtado de Carvalho, T.; Zhu, W.; Gillis, C.C.; Büttner, L.; Smoot, M.P.; Behrendt, C.L.; et al. Microbial Respiration and Formate Oxidation as Metabolic Signatures of Inflammation-Associated Dysbiosis. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konikoff, T.; Gophna, U. Oscillospira: A Central, Enigmatic Component of the Human Gut Microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lyu, W.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Y. Allobaculum Involves in the Modulation of Intestinal ANGPTLT4 Expression in Mice Treated by High-Fat Diet. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 690138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.A.; Xu, Z.; Knight, R. Meta-Analyses of Human Gut Microbes Associated with Obesity and IBD. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 4223–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Berberine and Metformin during the Treatment of High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Beneficial Effects of Ginger on Prevention of Obesity through Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 699–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everard, A.; Lazarevic, V.; Gaïa, N.; Johansson, M.; Ståhlman, M.; Backhed, F.; Delzenne, N.M.; Schrenzel, J.; François, P.; Cani, P.D. Microbiome of Prebiotic-Treated Mice Reveals Novel Targets Involved in Host Response during Obesity. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, C.; Baldridge, M.T.; Wallace, M.A.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; Virgin, H.W.; Stappenbeck, T.S. Vertically Transmitted Faecal IgA Levels Determine Extra-Chromosomal Phenotypic Variation. Nature 2015, 521, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O. Sutterella Species, IgA-Degrading Bacteria in Ulcerative Colitis. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Sphingolipids and Their Metabolism in Physiology and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, P.-F.; Karla, C.; Edgar Alejandro, M.-T.; Sara Elva, E.-P.; Gemma, F.; Luz, C. Sphingolipids as Mediators in the Crosstalk between Microbiota and Intestinal Cells: Implications for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 9890141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M. Magnesium in Man: Implications for Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapani, V.; Wolf, F.I. Dysregulation of Mg2+ Homeostasis Contributes to Acquisition of Cancer Hallmarks. Cell Calcium 2019, 83, 102078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Chierico, F.; Trapani, V.; Petito, V.; Reddel, S.; Pietropaolo, G.; Graziani, C.; Masi, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; Putignani, L.; Scaldaferri, F.; et al. Dietary Magnesium Alleviates Experimental Murine Colitis through Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4188. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124188
Del Chierico F, Trapani V, Petito V, Reddel S, Pietropaolo G, Graziani C, Masi L, Gasbarrini A, Putignani L, Scaldaferri F, et al. Dietary Magnesium Alleviates Experimental Murine Colitis through Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4188. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124188
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Chierico, Federica, Valentina Trapani, Valentina Petito, Sofia Reddel, Giuseppe Pietropaolo, Cristina Graziani, Letizia Masi, Antonio Gasbarrini, Lorenza Putignani, Franco Scaldaferri, and et al. 2021. "Dietary Magnesium Alleviates Experimental Murine Colitis through Modulation of Gut Microbiota" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4188. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124188
APA StyleDel Chierico, F., Trapani, V., Petito, V., Reddel, S., Pietropaolo, G., Graziani, C., Masi, L., Gasbarrini, A., Putignani, L., Scaldaferri, F., & Wolf, F. I. (2021). Dietary Magnesium Alleviates Experimental Murine Colitis through Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Nutrients, 13(12), 4188. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124188