Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of the Eleutherococcus senticosus, Achyranthes japonica, and Atractylodes japonica Mixed Extract Fermented with Nuruk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Vigeo
2.2. Reagents and Antibodies
2.3. Mice Care and Ethics Statement
2.4. LPS-Mediated Bone Loss Mouse Model
2.5. Micro-Computed Tomography (Micro-CT) and Histopathology
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Preparation of Mouse Bone Marrow Macrophages (BMMs) and Osteoclast Differentiation
2.8. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.10. Filamentous-Actin (F-Actin) Assay
2.11. Resorption Pit Assay
2.12. Western Blotting
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
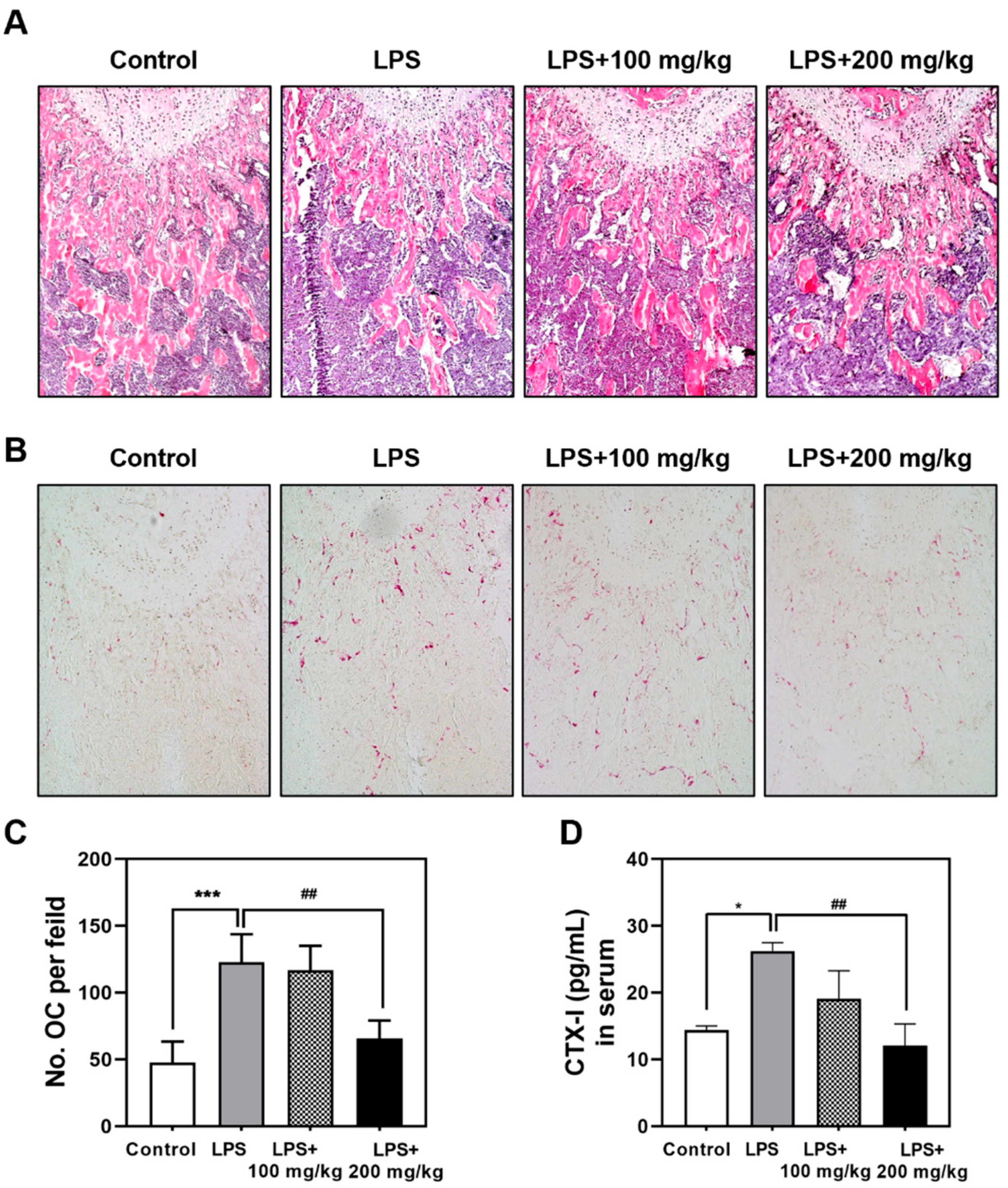
3.1. Oral Administration of Vigeo Ameliorates LPS-Induced Bone Loss In Vivo
3.2. Vigeo Effectively Attenuates LPS-Induced Osteoclast Activation In Vivo
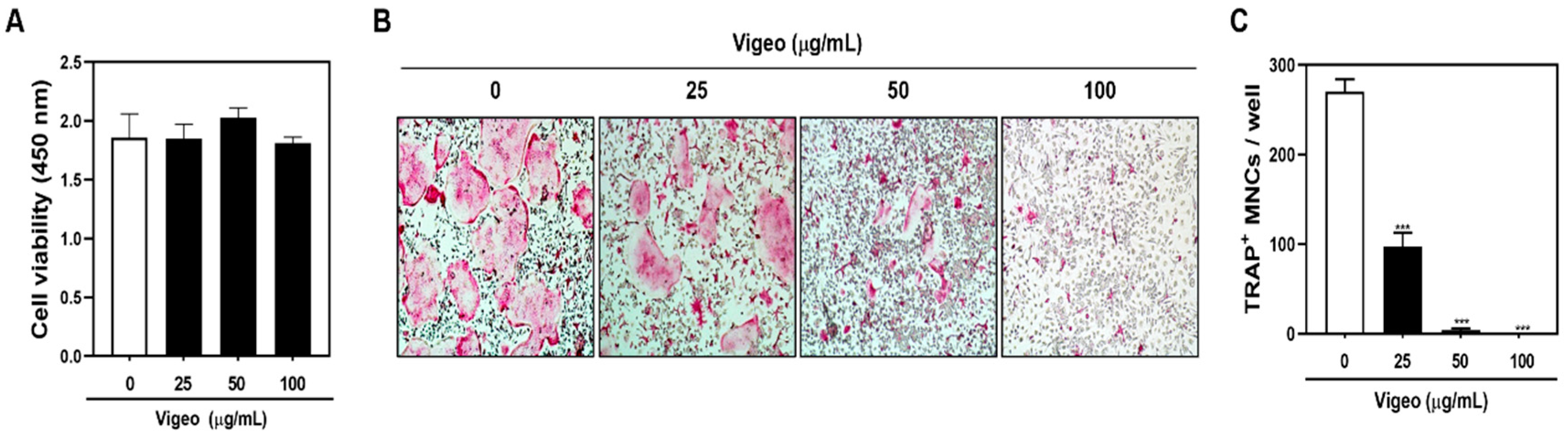
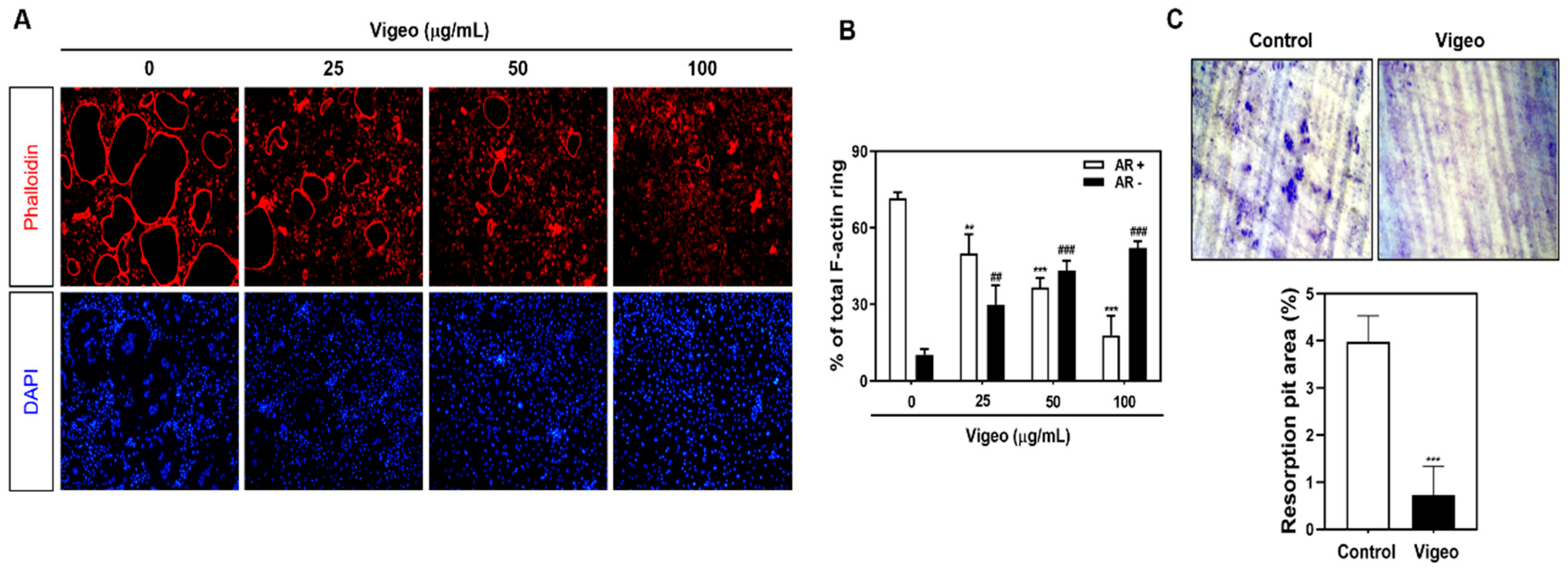
3.3. Vigeo Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Resorption In Vitro
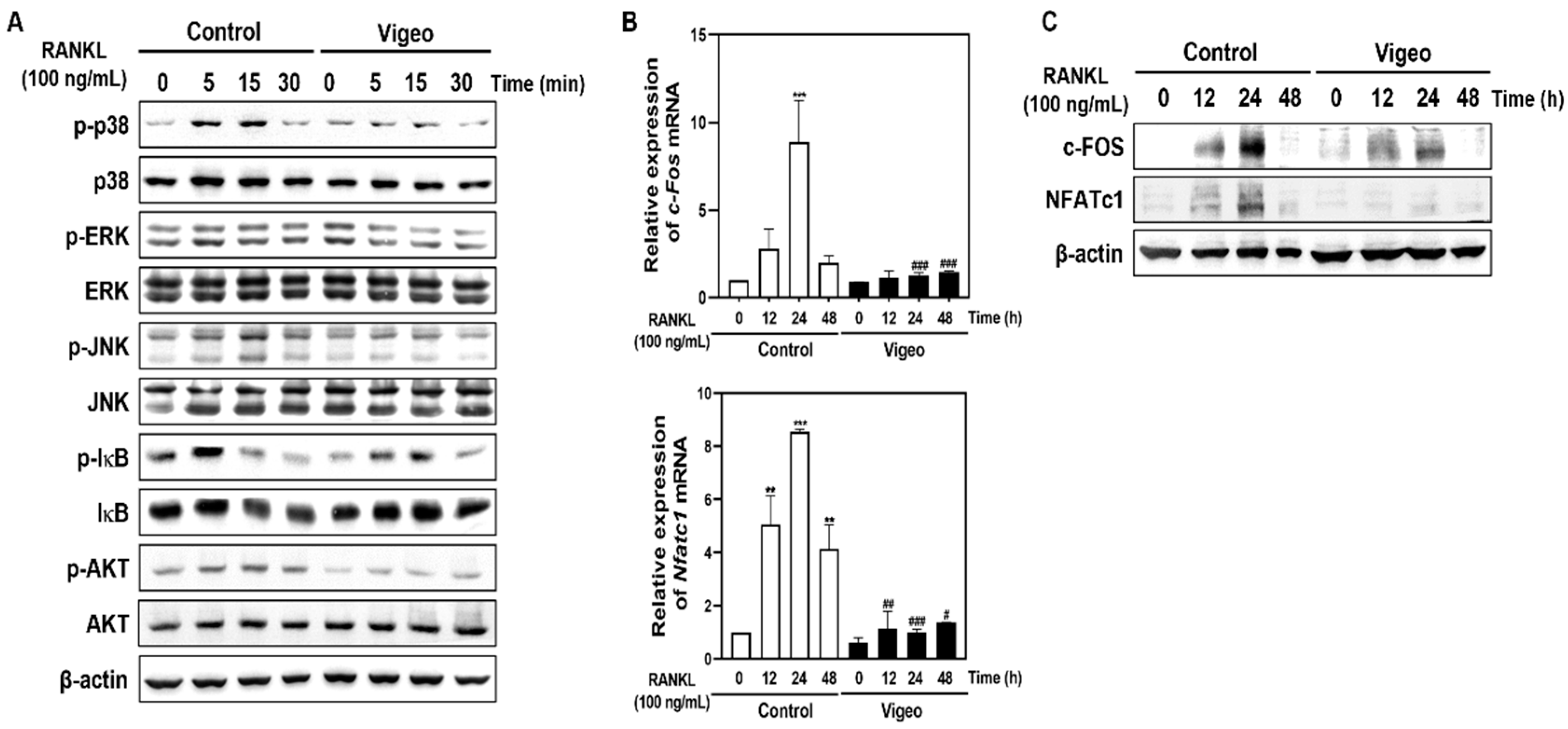
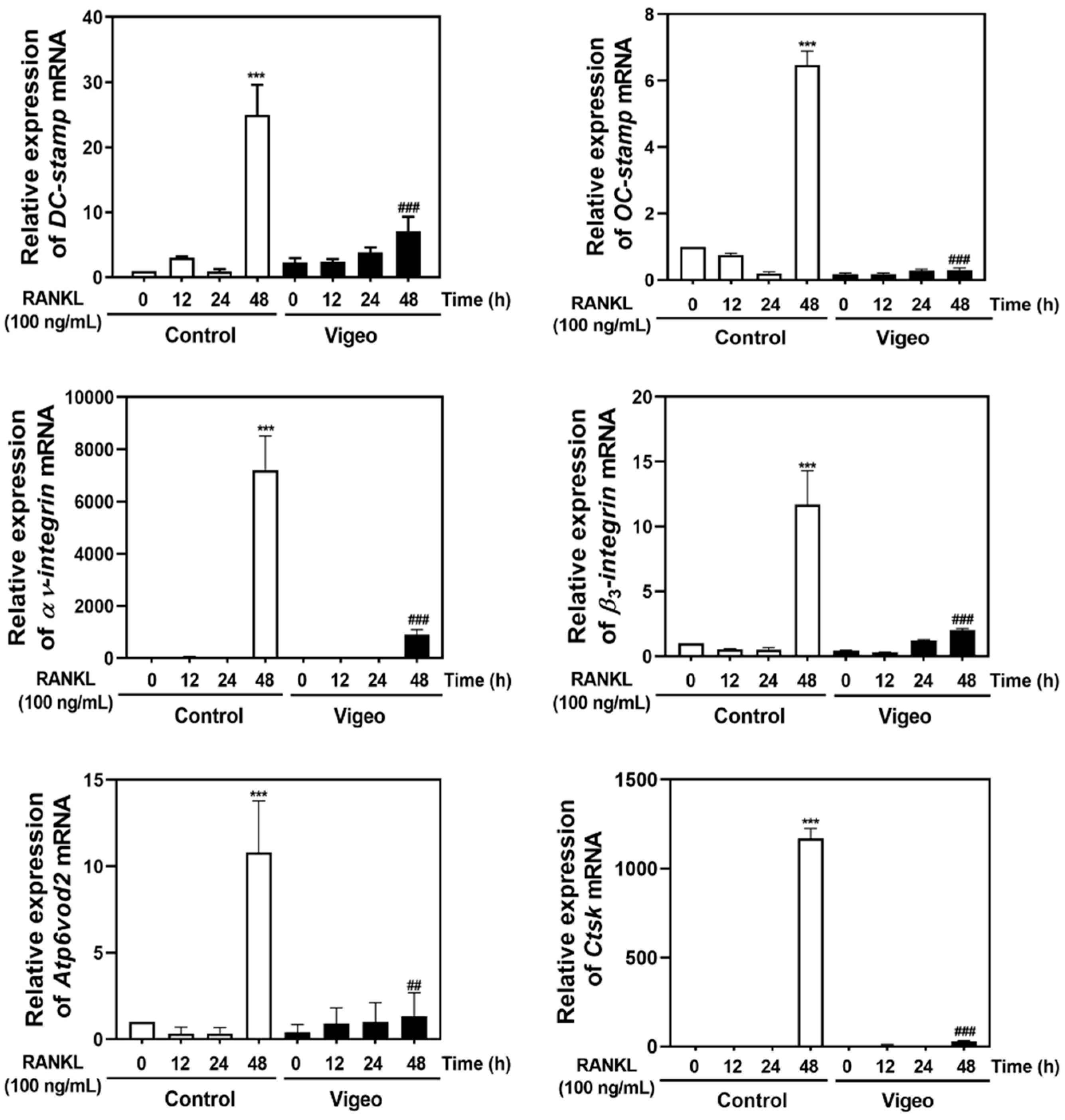
3.4. Vigeo Inhibits RANKL-Activated Osteoclast Differentiation Signaling Pathways and Osteoclast Specific Genes In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanis, J.A.; Melton, L.J.; Christiansen, C.; Johnston, C.C.; Khaltaev, N. The diagnosis of osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1994, 9, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, S.; Kyomugasho, C.; Celus, M.; Hendrickx, M.E.G.; Grauwet, T. Barriers impairing mineral bioaccessibility and bioavailability in plant-based foods and the perspectives for food processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 826–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xutian, S.; Zhang, J.; Louise, W. New exploration and understanding of traditional Chinese medicine. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2009, 37, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, Y.H.; Baek, J.M.; Park, S.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, M.S.; Oh, J.M.; Kim, J.Y. Stauntonia hexaphylla (Lardizabalaceae) leaf methanol extract inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption activity via proteasome-mediated degradation of c-Fos protein and suppression of NFATc1 expression. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, D.W.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Cha, S.H.; Kim, Y.T. Preventive Effects of Eleutherococcus senticosus Bark extract in OVX-induced osteoporosis in rats. Molecules 2013, 18, 7998–8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzello, C.G.; Coda, R.; Macías, D.S.; Pinto, D.; Marzani, B.; Filannino, P.; Giuliani, G.; Paradiso, V.M.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Lactic acid fermentation as a tool to enhance the functional features of Echinacea spp. Microb. Cell Fact. 2013, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, V.; Amoa-Awua, W.K.A.; Brimer, L. Degradation of cyanogenic glycosides by Lactobacillus plantarum strains from spontaneous cassava fermentation and other microorganisms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 53, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, S.; Malik, K.A.; Ah Kang, S.; Kim, H.Y. Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.C.; Jeong, I.K.; Ahn, K.J.; Chung, H.Y. The effects of Acanthopanax senticosus extract on bone turnover and bone mineral density in Korean postmenopausal women. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2009, 27, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, R.G.; Shin, K.M.; Ha, J.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, K.T. In vivo anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of liriodendrin isolated from the stem bark of Acanthopanax senticosus. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 610–616. [Google Scholar]
- Kropotov, A.V.; Kolodnyak, O.L.; Koldaev, V.M. Effects of Siberian ginseng extract and ipriflavone on the development of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2002, 133, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chang, Z.; Ma, R.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Kong, L.; Hao, D. Eleutherococcus senticosus inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation by attenuating the NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 4514–4521. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.G.; Lee, E.J.; Park, W.D.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, E.O.; Choi, S.W. Anti-inflammatory and anti-osteoarthritis effects of fermented Achyranthes japonica Nakai. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Park, K.K.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, S.E.; Hwang, J.K. Cornus kousa F. Buerger ex Miquel increases glucose uptake through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and insulin sensitization. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, Y.M.; Kim, O.J.; Jo, E.S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Ahn, M.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Ha, J.M.; Kim, A. Anti-inflammatory effects of the combined extracts of Achyranthes japonica nakai and Aralia continentalis kitagawa in vitro and in vivo. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Kim, D.; Suminda, G.G.D.; Min, Y.; Yang, J.; Kim, M.; Zhao, Y.; Chosh, M.; Son, Y.O. Inhibitory effects of IL-6-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-3 and -13 by Achyranthes japonica Nakai root in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis mice models. Pharmaceutical 2021, 14, 776. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Kang, S.N.; Shin, D.; Hur, I.C.; Kim, I.S.; Jin, S.K. Antioxidant activities of Achyranthes japonica Nakai extract and its application to the pork sausages. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Bae, H.; Lee, N.Y.; Shin, Y.C.; Kim, S.H.; Ko, S.G. Atractylodes japonica koidzumi inhibits the production of proinflammatory cytokines through inhibition of the NF-kappaB/IkappaB signal pathway in HMC-1 human mast cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.T.; Chen, L.G.; Chou, D.S.; Liang, W.L.; Wang, C.C. Anti-oxidative abilities of essential oils from Atractylodes ovate rhizome. Evid. -Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 204892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Jung, H.W.; Park, Y.K. The roots of Atractylodes japonica Koidzumi promote adipogenic differentiation via activation of the insulin signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 cells. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Cheon, Y.H.; Kwak, S.C.; Baek, J.M.; Yoon, K.H.; Lee, M.S.; Oh, J. Emodin regulates bone remodeling by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and stimulating osteoblast formation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.O.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Ji, H.; Lee, E.O.; Lee, H.J. Comparison of the main components and bioactivity of Rhus verniciflua Stokes extracts by different detoxification processing methods. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.A.; Hyun, Y.J.; Choo, M.K.; Oh, J.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, D.H. Protective effect of fermented red ginseng on a transient focal ischemic rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.S.; Won, T.J.; Nam, S.Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, Y.C.; Park, S.Y.; Park, H.Y.; Hwang, K.W.; Lee, D.I. Therapeutic advantages of medicinal herbs fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum, in topical application and its activities on atopic dermatitis. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Tzeng, W.S.; Shyu, Y.T. Lactic acid bacterial fermentation on the production of functional antioxidant herbal Anoectochilus formosanus Hayata. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.C.; Cho, W.K.; Oh, J.H.; Im, G.Y.; Jeong, Y.H.; Yang, M.C.; Ma, J.Y. Fermentation by Lactobacillus enhances anti-inflammatory effect of Oyaksungisan on LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cells. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, A.R.; Kim, H.; Lee, E.; Kim, T.W.; Shin, W.C.; Kim, J.H. Restoration of traditional Korean nuruk and analysis of the brewing characteristics. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Jung, S.K.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, G.W.; Lee, H.J. Nuruk extract inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced production of nitrite and interleukin-6 in RAW 264.7 cells through blocking activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1423–1426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Kwak, H.Y.; Jung, L.; Heo, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, G.W.; Baek, N.I. Sterols isolated from Nuruk (Rhizopus oryzae KSD-815) inhibit the migration of cancer cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asagiri, M.; Takayanagi, H. The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone 2007, 40, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, T.J.; Yoo, Y.C.; Lee, S.W.; Shin, K.S.; Choi, W.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Ha, E.S.; Jo, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Park, W.M. Anti-metastatic activity of Acanthopanax senticosus extract and its possible immunological mechanism of action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 93, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, S.G.; Kang, S.K.; Chung, S.H. Acanthopanax senticosus reverses fatty liver disease and hyperglycemia in ob/ob mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2006, 29, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Sumiyoshi, M. Effects of various Eleutherococcus senticosus cortex on swimming time, natural killer activity and corticosterone level in forced swimming stressed mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 95, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| Gapdh | TCAAGAAGGTGGTGAAGCAG | AGTGGGAGTTGCTGTTGAAGT |
| c-Fos | GGTGAAGACCGTGTCAGGAG | TATTCCGTTCCCTTCGGATT |
| Nfatc1 | GAGTACACCTTCCAGCACCTT | TATGATGTCGGGGAA AGAGA |
| DC-stamp | TCCTCCATGAACAAACAGTTCCA | AGACGTGGTTTAGGAATGCAGCTC |
| OC-stamp | ATGAGGACCATCAGGGCAGCCACG | GGAGAAGCTGGGTCAGTAGTTCGT |
| αv-integrin | ACAAGCTCACTCCCATCACC | ATATGAGCCTGCCGACTGAC |
| β3-integrin | GGAGTGGCTGATCCAGATGT | TCTGACCATCTTCCCTGTCC |
| Atp6v0d2 | GACCCTGTGGCACTTTTTGT | GTGTTTGAGCTTGGGGAGAA |
| Cathepsin K (Ctsk) | CCAGTGGGAGCTATGGAAGA | CTCCAGGTTATGGGCAGAGA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eun, S.Y.; Cheon, Y.-H.; Park, G.D.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, M.S. Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of the Eleutherococcus senticosus, Achyranthes japonica, and Atractylodes japonica Mixed Extract Fermented with Nuruk. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113904
Eun SY, Cheon Y-H, Park GD, Chung CH, Lee CH, Kim J-Y, Lee MS. Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of the Eleutherococcus senticosus, Achyranthes japonica, and Atractylodes japonica Mixed Extract Fermented with Nuruk. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113904
Chicago/Turabian StyleEun, So Young, Yoon-Hee Cheon, Gyeong Do Park, Chong Hyuk Chung, Chang Hoon Lee, Ju-Young Kim, and Myeung Su Lee. 2021. "Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of the Eleutherococcus senticosus, Achyranthes japonica, and Atractylodes japonica Mixed Extract Fermented with Nuruk" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113904
APA StyleEun, S. Y., Cheon, Y.-H., Park, G. D., Chung, C. H., Lee, C. H., Kim, J.-Y., & Lee, M. S. (2021). Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of the Eleutherococcus senticosus, Achyranthes japonica, and Atractylodes japonica Mixed Extract Fermented with Nuruk. Nutrients, 13(11), 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113904






