Conservative Treatment for Childhood and Adolescent Obesity: Real World Follow-Up Profiling and Clinical Evolution in 1300 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Excellent Responder Group
2.3. Metabolically Healthy Group
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Follow-Up Characterization
3.1.1. Time of Follow-Up and Drop-Out
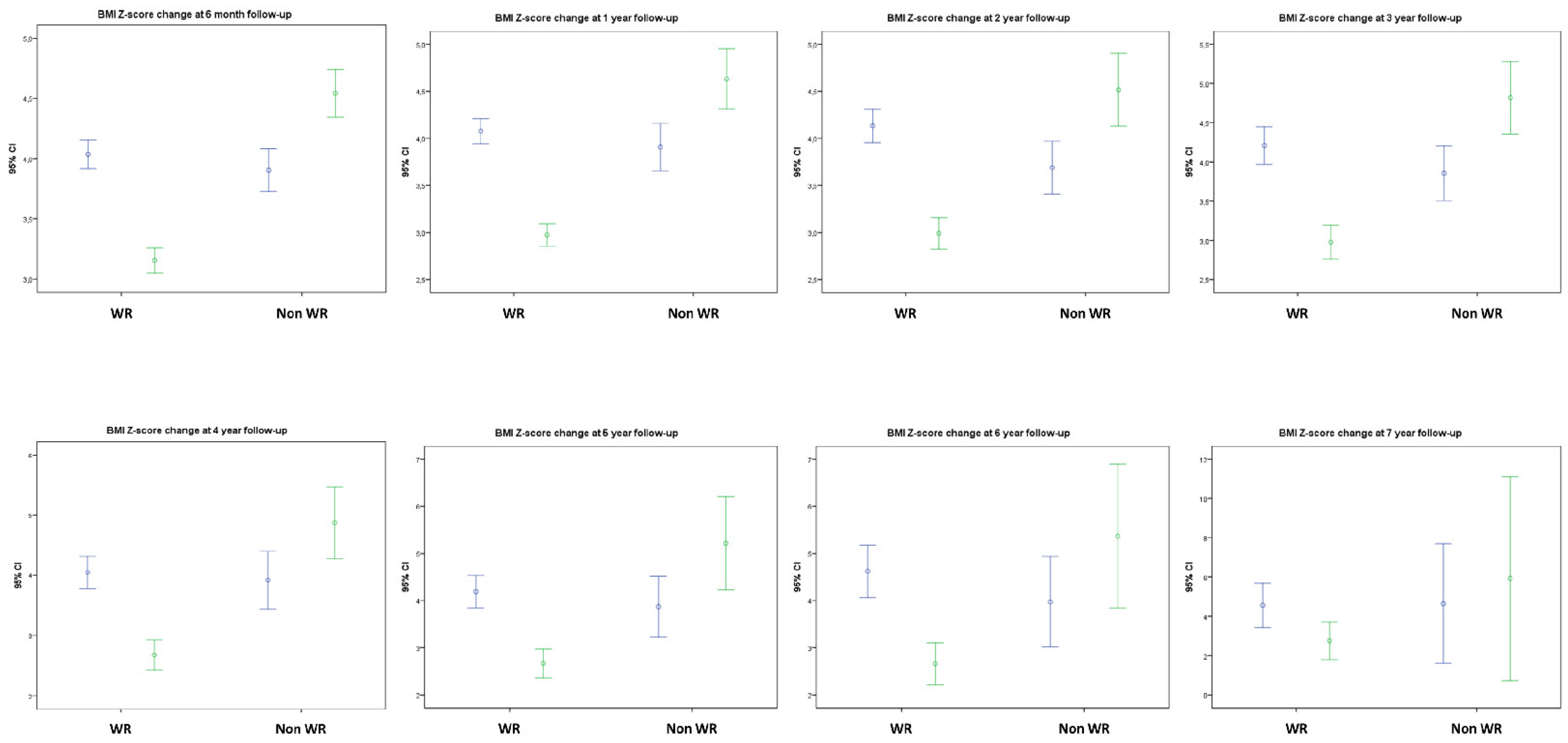
3.1.2. BMI Evolution and Lifestyle Changes
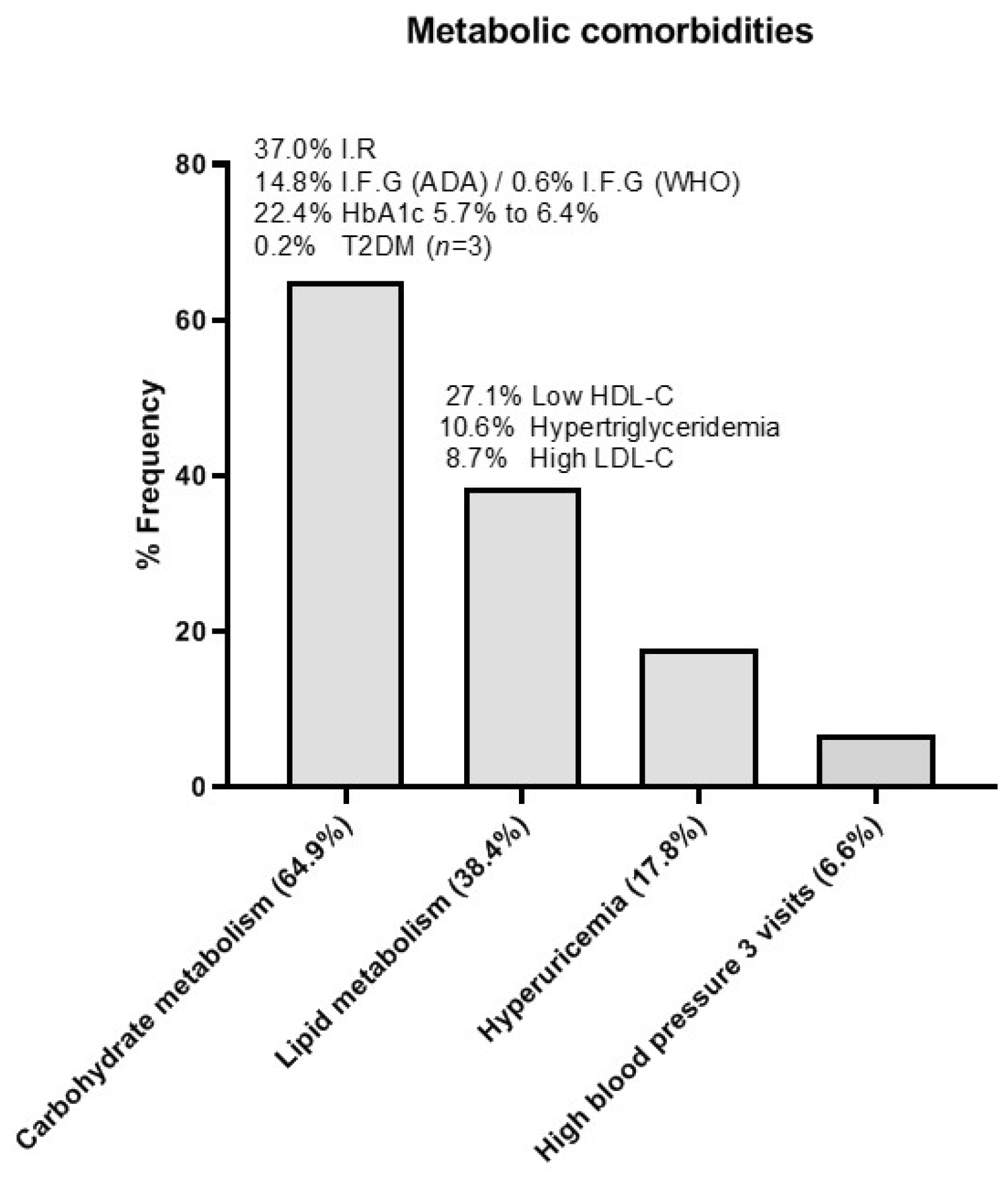
3.1.3. Metabolic Evolution
3.1.4. Growth and Puberty throughout Follow-Up
3.2. The Excellent Responder Cohort
3.3. “Metabolically Healthy” Cohort
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Intervention and BMI Changes on Metabolic Comorbidities
4.2. Influence of BMI on Puberty and Growth
4.3. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srivastava, G.; Browne, N.; Kyle, T.K.; O’Hara, V.; Browne, A.; Nelson, T.; Puhl, R. Caring for US Children: Barriers to Effective Treatment in Children with the Disease of Obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2021, 29, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styne, D.M.; Arslanian, S.A.; Connor, E.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Murad, M.H.; Silverstein, J.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Pediatric obesity-assessment, treatment, and prevention: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 709–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupo de trabajo de la Guía de Práctica Clínica sobre la Prevención y el Tratamiento de la Obesidad Infantojuvenil; Centro Cochrane Iberoamericano, Coordinador. Guía de Práctica Clínica sobre la Prevención y el Tratamiento de la Obesidad Infantojuvenil. Plan de Calidad para el Sistema Nacional de Salud del Ministerio de Sanidad y Política Social; Guías de Práctica Clínica en el SNS: AATRM Nº 2007/25; Agència d’Avaluació de Tecnologia i Recerca Mèdiques: Barcelona, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.A.; Gray, E.; Jones, T.L.; Han, J.C.; Burton, E.T. Waitlist management in a pediatric weight management clinic: Implementing an orientation session. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Garrido, N.; Bernal-Jiménez, M.A.; Anti-Cano, M.J. Evaluation of Obesity Management Recorded in Electronic Clinical History: A Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.R.; Bowen-Jallow, K.A.; Stanford, F.C. A call to action: Multi-disciplinary care and treatment of obesity in pediatrics. Pediatr. Investig. 2021, 5, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, J.; Nosworthy, N.M.; Holt, N.L.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; Avis, J.L.; Rasquinha, A.; Ball, G.D. Attrition and the Management of Pediatric Obesity: An Integrative Review. Child. Obes. 2016, 10, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinehr, T.; Widhalm, K.; l’Allemand, D.; Wiegand, S.; Wabitsch, M.; Holl, R.W.; APV-Wiss Study Group and German Competence Net Obesity. Two-year follow-up in 21,784 overweight children and adolescents with lifestyle intervention. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009, 17, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksel, E.; Gündüzoʇlu, N.Ç.; Topçu, S. The perception of obese persons: Cross cultural considerations. Holist. Nurs. Pract. 2015, 29, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, R.W.; Ye, L.; Sereika, S.M.; Zheng, Y.; Mattos, M.; Acharya, S.D.; Ewing, L.J.; Danford, C.; Hu, L.; Imes, C.C.; et al. Socio-demographic, anthropometric, and psychosocial predictors of attrition across behavioral weight-loss trials. Eat. Behav. 2016, 20, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yackobovitch-Gavan, M.; Steinberg, D.M.; Endevelt, R.; Benyamini, Y. Factors associated with dropout in a group weight-loss programme: A longitudinal investigation. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 28 (Suppl. 2), 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos-Moreno, G.A.; Martinez-Villanueva, J.; Gonzalez-Leal, R.; Chowen, J.A.; Argente, J. Sex, puberty, and ethnicity have a strong influence on growth and metabolic comorbidities in children and adolescents with obesity: Report on 1300 patients (the Madrid Cohort). Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, A.; Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Niklasson, A.; Martínez-Villanueva, J.; Argente, J.; Albertsson-Wikland, K. The pubertal growth spurt is diminished in children with severe obesity. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Karlberg, J. BMI in childhood and its association with height gain, timing of puberty, and final height. Pediatr. Res. 2001, 49, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno, L.A. Effects of diet on growth of children with obesity. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, S147–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.L.; Hunt, L.P.; Cooper, A.; Shield, J.P.H. What reduction in BMI SDS is required in obese adolescents to improve body composition and cardiometabolic health? Arch. Dis. Child. 2010, 95, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, P.; Svensson, V.; Kowalski, J.; Nyberg, G.; Ekblom, Ö.; Marcus, C. Importance of age for 3-year continuous behavioral obesity treatment success and dropout rate. Obes. Facts 2012, 5, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.E.; Mason, T.B.; Wang, W.L.; Schumacher, L.M.; Pellegrini, C.A.; Goldschmidt, A.B.; Unick, J.L. Dynamic associations between anxiety, stress, physical activity, and eating regulation over the course of a behavioral weight loss intervention. Appetite 2021, 168, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primeau, V.; Coderre, L.; Karelis, A.D.; Brochu, M.; Lavoie, M.E.; Messier, V.; Sladek, R.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. Characterizing the profile of obese patients who are metabolically healthy. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damanhoury, S.; Newton, A.S.; Rashid, M.; Hartling, L.; Byrne, J.L.S.; Ball, G.D.C. Defining metabolically healthy obesity in children: A scoping review. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 1476–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, R.L.; Kuk, J.L.; Ambler, K.A.; Dhaliwal, J.; Ball, G.D. Predictors of metabolically healthy obesity in children. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vukovic, R.; Dos Santos, T.J.; Ybarra, M.; Atar, M. Children with metabolically healthy obesity: A review. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomazini, F.; de Carvalho, B.S.; de Araujo, P.X.; Franco, M.D.C. High uric acid levels in overweight and obese children and their relationship with cardiometabolic risk factors: What is missing in this puzzle? J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, M.; Castellet, J.; Narvaiza, J.L.; Rincón, J.M.; Ruiz, I.; Sánchez, E.; Sobradillo, B.; Zurimendi, A. Curvas y Tablas de Crecimiento, 2nd ed.; Instituto de Investigación Sobre Crecimiento y Desarrollo, Fundación Faustino Orbegozo, Editorial Garsi: Madrid, Spain, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegal, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity world-wide: International survey. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2000, 320, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar]
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The Fourth Report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greulich, W.W.; Pyle, S.I. Radiographic Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Hand and Wrist, 2nd ed.; Standford University Press: Standford, CA, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Zeller, M.; Kirk, S.; Claytor, R.; Khoury, P.; Grieme, J.; Santangelo, M.; Daniels, S. Predictors of attrition from a pediatric weight management program. J. Pediatr. 2004, 144, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, R.; Ramasamy, V.; Sturgiss, E.; Dunbar, J.; Boyle, J. Shared medical appointments for weight loss: A systematic review. Fam. Pract. 2021, 18, cmab105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inclán-López, P.; Bartolomé-Gutiérrez, R.; Martínez-Castillo, D.; Rabanales-Sotos, J.; Guisado-Requena, I.M.; Martínez-Andrés, M. Parental Perception of Weight and Feeding Practices in SchoolChildren: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, R.; Kengneson, C.C.; Bodnaruc, A.M.; Gunter, A.; Giroux, I. Factors Influencing Parents’ and Children’s Misperception of Children’s Weight Status: A Systematic Review of Current Research. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 373–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordeleau, M.; Leduc, G.; Blanchet, C.; Drapeau, V.; Alméras, N. Body Size Misperception and Dissatisfaction in Elementary School Children. Child. Obes. 2021, 17, 467–475. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Villanueva, J.; González-Leal, R.; Argente, J.; Martos-Moreno, G.Á. Parental obesity is associated with the severity of childhood obesity and its comorbidities. An. Pediatr. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 90, n224–n231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Martínez-Villanueva, J.; González-Leal, R.; Argente, J. The importance of socioeconomic factors in obesity studies. Authors reply. An. Pediatr. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 91, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batterham, M.; Tapsell, L.C.; Charlton, K.E. Predicting dropout in dietary weight loss trials using demographic and early weight change characteristics: Implications for trial design. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 10, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mameli, C.; Krakauer, J.C.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Bosetti, A.; Ferrari, C.M.; Schneider, L.; Borsani, B.; Arrigoni, S.; Pendezza, E.; Zuccotti, G.V. Effects of a multidisciplinary weight loss intervention in overweight and obese children and adolescents: 11 years of experience. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vine, M.; Hargreaves, M.B.; Briefel, R.R.; Orfield, C. Expanding the Role of Primary Care in the Prevention and Treatment of Childhood Obesity: A Review of Clinic- and Community-Based Recommendations and Interventions. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 172035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.J.; Wan, Q.Q.; Liu, C.Y.; Feng, X.L.; Shang, S.M. Determinants of patient loyalty to healthcare providers: An integrative review. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2017, 29, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiandani, D.; Wharton, S.; Rotondi, M.A.; Ardern, C.I.; Kuk, J.L. Predictors of early attrition and successful weight loss in patients attending an obesity management program. BMC Obes. 2016, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caixàs, A.; Villaró, M.; Arraiza, C.; Montalvá, J.C.; Lecube, A.; Fernández-García, J.M.; Corio, R.; Bellido, D.; Llisterri, J.L.; Tinahones, F.J. SEEDO-SEMERGEN consensus document on continuous care of obesity between Primary Care and Specialist Hospital Units 2019. Med. Clin. 2020, 155, 267.e1–267.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Martínez-Villanueva, J.; González-Leal, R.; Barrios, V.; Sirvent, S.; Hawkins, F.; Chowen, J.A.; Argente, J. Ethnicity Strongly Influences Body Fat Distribution Determining Serum Adipokine Profile and Metabolic Derangement in Childhood Obesity. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 551103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Total Cohort (n = 1300) | Caucasians (n = 986/75.8%) | Latinos (n = 247/19.0%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prepubertal | Pubertal | Prepubertal | Pubertal | Prepubertal | Pubertal | |
| n | 693 (53.3%) | 607 (46.7%) | 525 (53.2%) | 461 (46.8%) | 130 (52.6%) | 117 (47.4%) |
| Sex | F 263 (38.0%) M 430 (62.0%) | F 351 (57.8%) M 256 (42.2%) | F 192 (36.6%) M 333 (63.4%) | F 271 (58.8%) M 190 (41.2%) | F 56 (43.1%) M 74 (56.9%) | F 66 (56.4%) M 51 (43.6%) |
| Age (years) | 8.26 ± 2.54 | 12.96 ± 1.97 | 8.47 ± 2.38 | 13.10 ± 1.94 | 7.68 ± 2.82 | 12.53 ± 2.05 |
| BMI-SDS | 4.21 ± 1.52 | 3.77 ± 1.43 | 4.14 ± 1.42 | 3.71 ± 1.36 | 4.38 ± 1.84 | 3.81 ± 1.39 |
| Glucose (mg/dl) | 91.65 ± 7.00 | 93.44 ± 6.70 | 91.34 ± 7.08 | 93.27 ± 6.70 | 92.83 ± 6.58 | 94.17 ± 6.85 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.45 ± 0.34 | 5.47 ± 0.30 | 5.45 ± 0.34 | 5.45 ± 0.30 | 5.43 ± 0.34 | 5.53 ± 0.28 |
| Insulin (µU/mL) | 11.78 ± 6.94 | 17.19 ± 10.74 | 11.47 ± 6.37 | 16.51 ± 10.44 | 13.01 ± 8.46 | 18.98 ± 11.39 |
| HOMA | 2.70 ± 1.65 | 4.01 ± 2.66 | 2.63 ± 1.56 | 3.85 ± 2.63 | 2.99 ± 1.86 | 4.43 ± 2.67 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 99.72 ± 26.31 | 93.36 ± 24.27 | 99.87 ± 26.03 | 93.56 ± 24.42 | 101.97 ± 27.58 | 93.16 ± 24.30 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 47.33 ± 11.10 | 43.93 ± 9.84 | 47.83 ± 10.85 | 44.50 ± 9.99 | 45.34 ± 11.56 | 40.94 ± 8.51 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 74.64 ± 44.34 | 85.63 ± 53.60 | 72.75 ± 43.51 | 82.69 ± 53.78 | 82.61 ± 45.90 | 97.2 ± 54.40 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 4.47 ± 0.92 | 5.28 ± 1.11 | 4.51 ± 0.89 | 5.30 ± 1.05 | 4.30 ± 0.92 | 5.11 ± 1.12 |
| Baseline | Second Visit (p vs. Baseline) | Last Visit (p vs. Baseline) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snacking | 81.9% | 55.9% (p < 0.001) | 57.2% (p < 0.001) |
| Eating compulsivity | 74.0% | 50.6% (p < 0.001) | 47.3% (p < 0.001) |
| Lack of scheduled physical activity | 74.7% | 53.1% (p < 0.001) | 49.8% (p < 0.001) |
| Age (Years) | 10.41 ± 3.19 |
| BMI-SDS | 4.24 ± 1.46 |
| Ethnicity: | |
| - Caucasian | 78.6 |
| - Latino | 18.1 |
| - Others | 4.3 |
| Sex (%) | |
| Female | 38.5 |
| Male | 61.5 |
| Pubertal status (%) | |
| Prepubertal | 57.10 (70.1% males/29.9% females) |
| Pubertal | 42.90 (50.0% males/50.0% females) |
| Baseline (n = 252) | After Weight Reduction (n = 252) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (SDS) | 3.99 ± 1.43 | 2.69 ± 1.21 | p < 0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 94.39 ± 7.10 | 92.20 ± 6.78 | p < 0.01 |
| Insulin (mcU/mL) | 15.25 ± 8.35 | 10.73 ± 5.28 | p < 0.001 |
| HOMA index | 3.58 ± 2.07 | 2.47 ± 1.27 | p < 0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 151.93 ± 29.99 | 146.35 ± 30.20 | p < 0.01 |
| LDL-c (mg/dL) | 93.52 ± 27.92 | 87.76 ± 24.81 | p < 0.001 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 43.66 ± 10.06 | 46.13 ± 11.70 | p < 0.001 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 74.03 ± 48.19 | 63.10 ± 37.58 | p < 0.001 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.05 ± 1.20 | 4.98 ± 1.14 | N.S. (p = 0.07) |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 39.00 ± 20.98 | 40.63 ± 20.76 | N.S. |
| Total proteins (g/dL) | 7.25 ± 0.42 | 7.24 ± 0.46 | N.S. |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.09 ± 0.27 | 4.17 ± 0.28 | p < 0.01 |
| 25 [Vitamin D] (ng/mL) | 22.54 ± 5.82 | 24.45 ± 6.90 | N.S. |
| All MH (n = 505) | Insulin < 15 μU/mL (n = 376) | Insulin ≥ 15 μU/mL (n = 129) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 10.14 ± 3.20 | 11.62 ± 2.58 | p < 0.001 |
| BMI-SDS | 3.66 ± 1.25 | 4.12 ± 378 | p < 0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 113.46 ± 11.68 | 118.26 ± 12.57 | p < 0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 58.83 ± 6.89 | 61.68 ± 6.71 | p < 0.001 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 90.35 ± 5.32 | 91.68 ± 4.73 | p < 0.05 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 4.41 ± 0.79 | 4.63 ± 0.85 | p < 0.01 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 51.01 ± 9.15 | 48.41 ± 7.32 | p < 0.01 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 55.54 ± 22.10 | 68.47 ± 24.27 | p < 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Martínez-Villanueva Fernández, J.; Frías-Herrero, A.; Martín-Rivada, Á.; Argente, J. Conservative Treatment for Childhood and Adolescent Obesity: Real World Follow-Up Profiling and Clinical Evolution in 1300 Patients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3847. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113847
Martos-Moreno GÁ, Martínez-Villanueva Fernández J, Frías-Herrero A, Martín-Rivada Á, Argente J. Conservative Treatment for Childhood and Adolescent Obesity: Real World Follow-Up Profiling and Clinical Evolution in 1300 Patients. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3847. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113847
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartos-Moreno, Gabriel Á., Julián Martínez-Villanueva Fernández, Alicia Frías-Herrero, Álvaro Martín-Rivada, and Jesús Argente. 2021. "Conservative Treatment for Childhood and Adolescent Obesity: Real World Follow-Up Profiling and Clinical Evolution in 1300 Patients" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3847. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113847
APA StyleMartos-Moreno, G. Á., Martínez-Villanueva Fernández, J., Frías-Herrero, A., Martín-Rivada, Á., & Argente, J. (2021). Conservative Treatment for Childhood and Adolescent Obesity: Real World Follow-Up Profiling and Clinical Evolution in 1300 Patients. Nutrients, 13(11), 3847. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113847






