The Fermented Soy Product ImmuBalanceTM Suppresses Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Asthma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
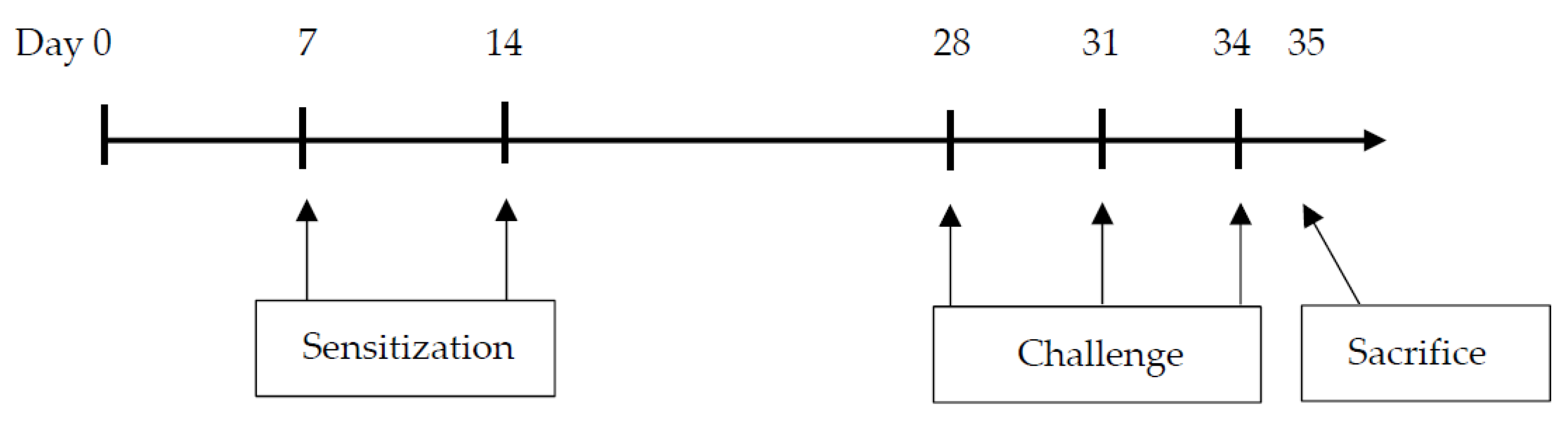
2.2. Sensitization and Airway Challenge Protocol
2.3. Diets
2.4. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) Analysis and Measurement of Cytokine Levels
2.5. Analysis of Lung Tissue
2.6. Measurement of Serum OVA-Specific IgE
2.7. Measurement of SCFAs in the Cecum
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
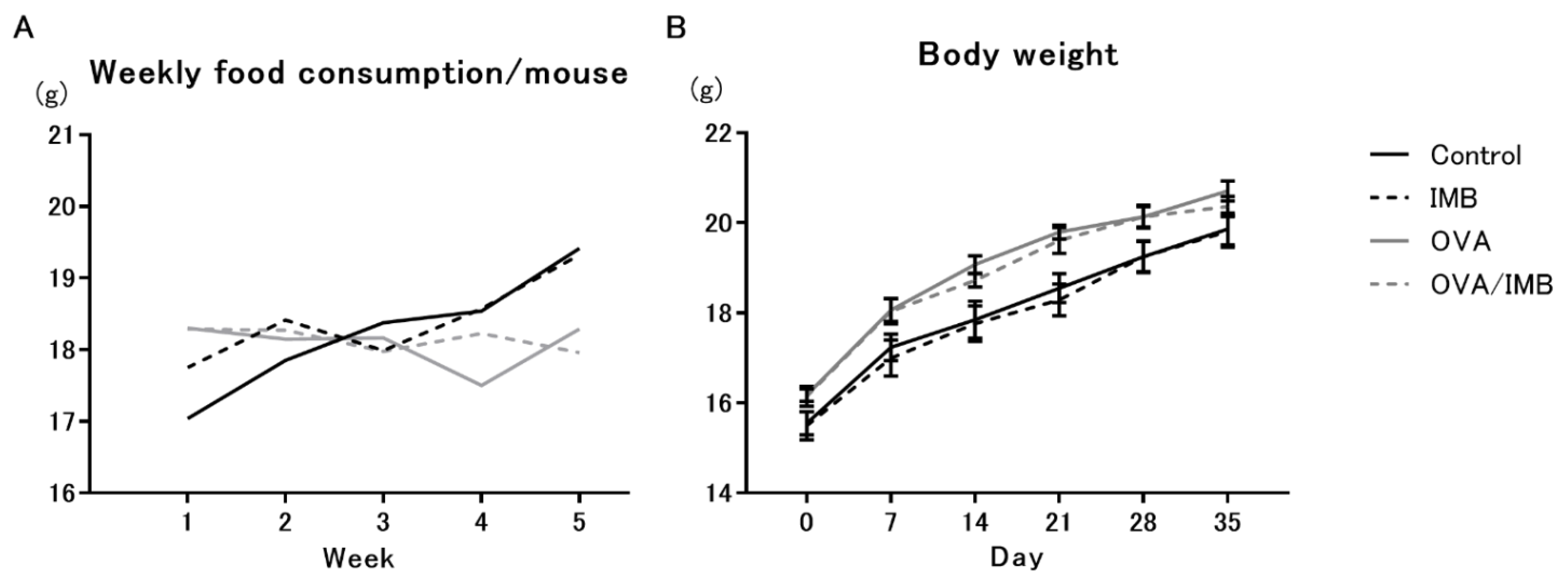
3.1. Diet Consumption and Changes in Body Weight
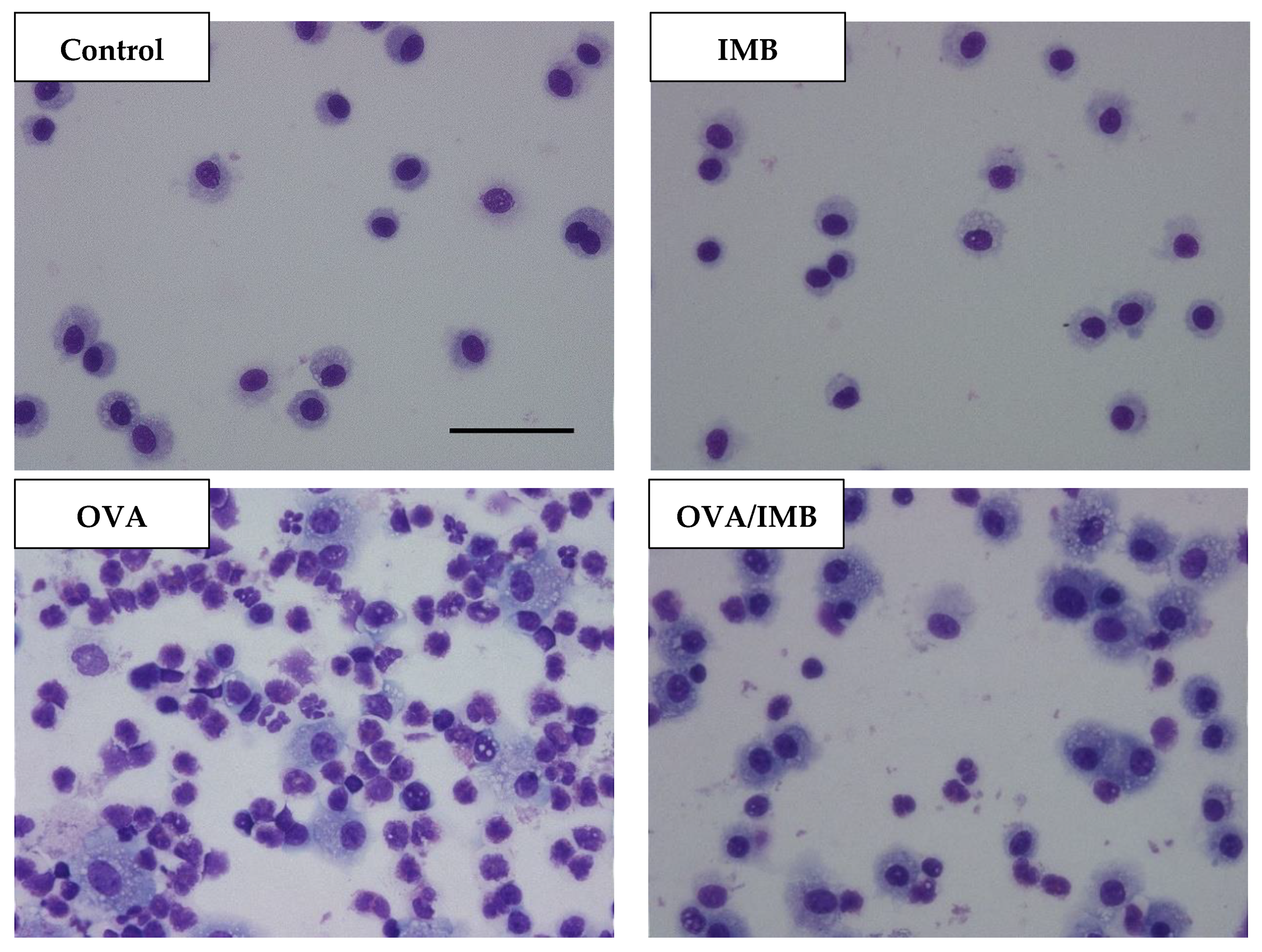
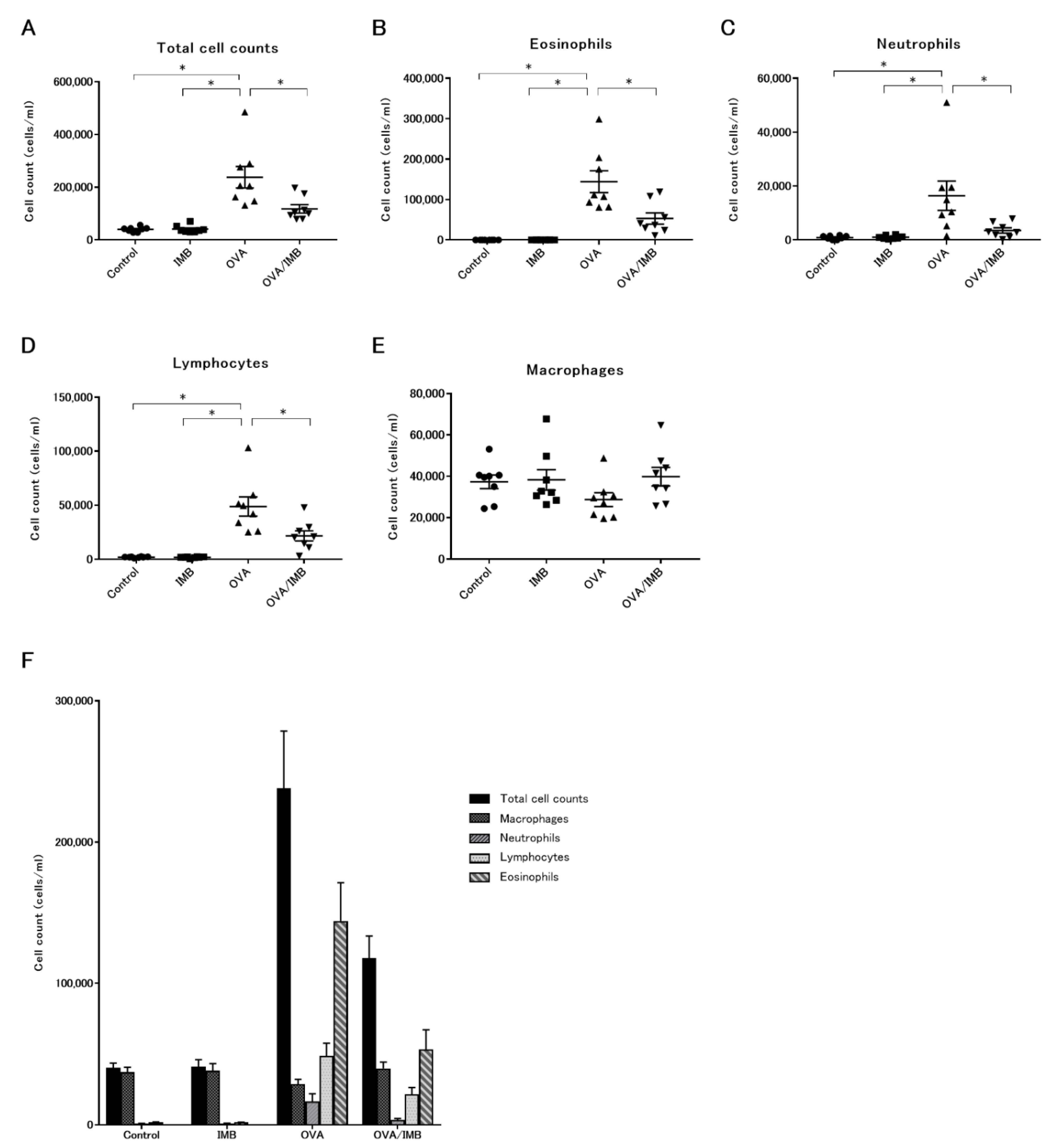
3.2. ImmuBalance Decreased the Number of Eosinophils and Other Inflammatory Cells in BALF
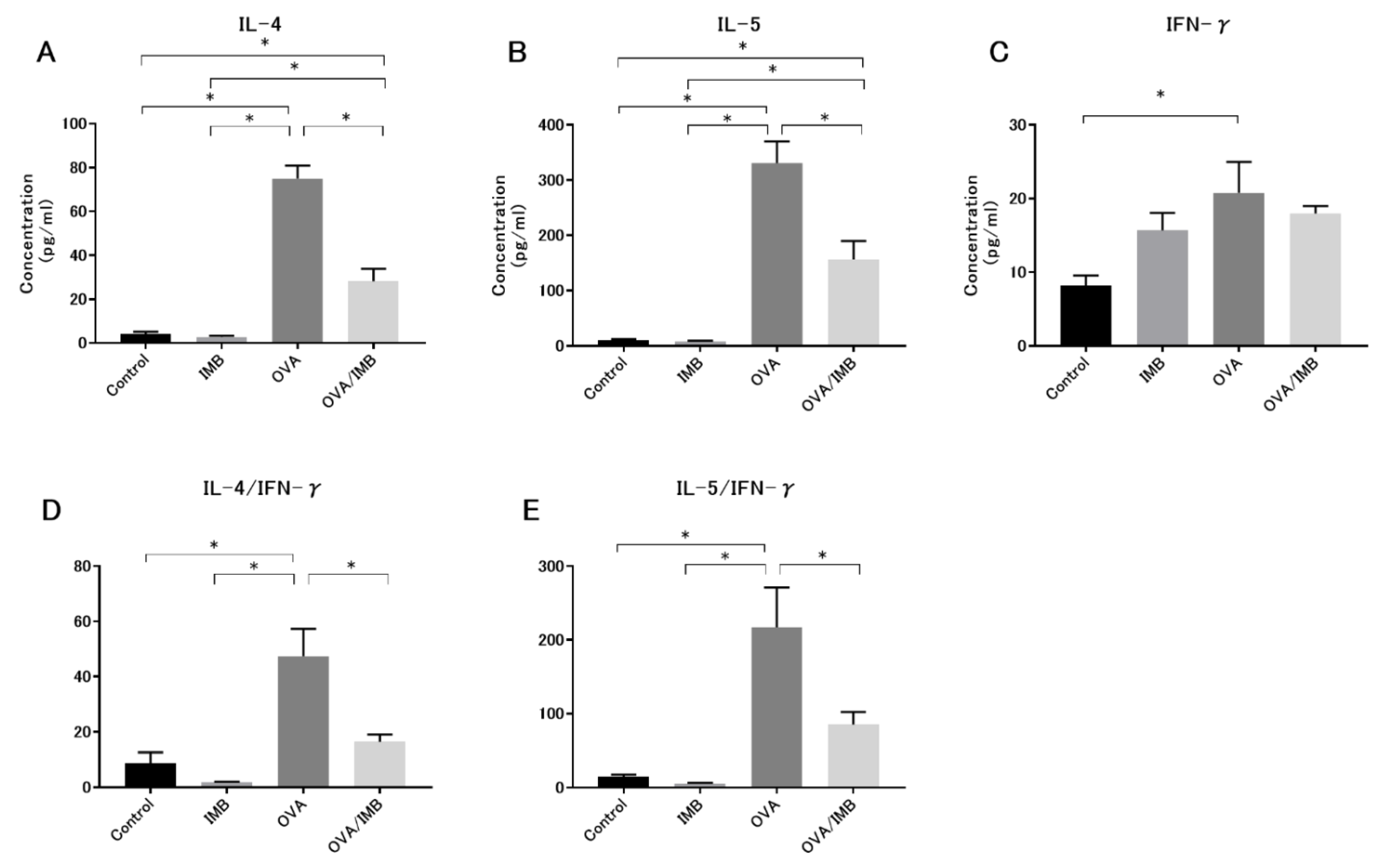
3.3. ImmuBalance Regulated the Th1- and Th2-Related Cytokines in BALF
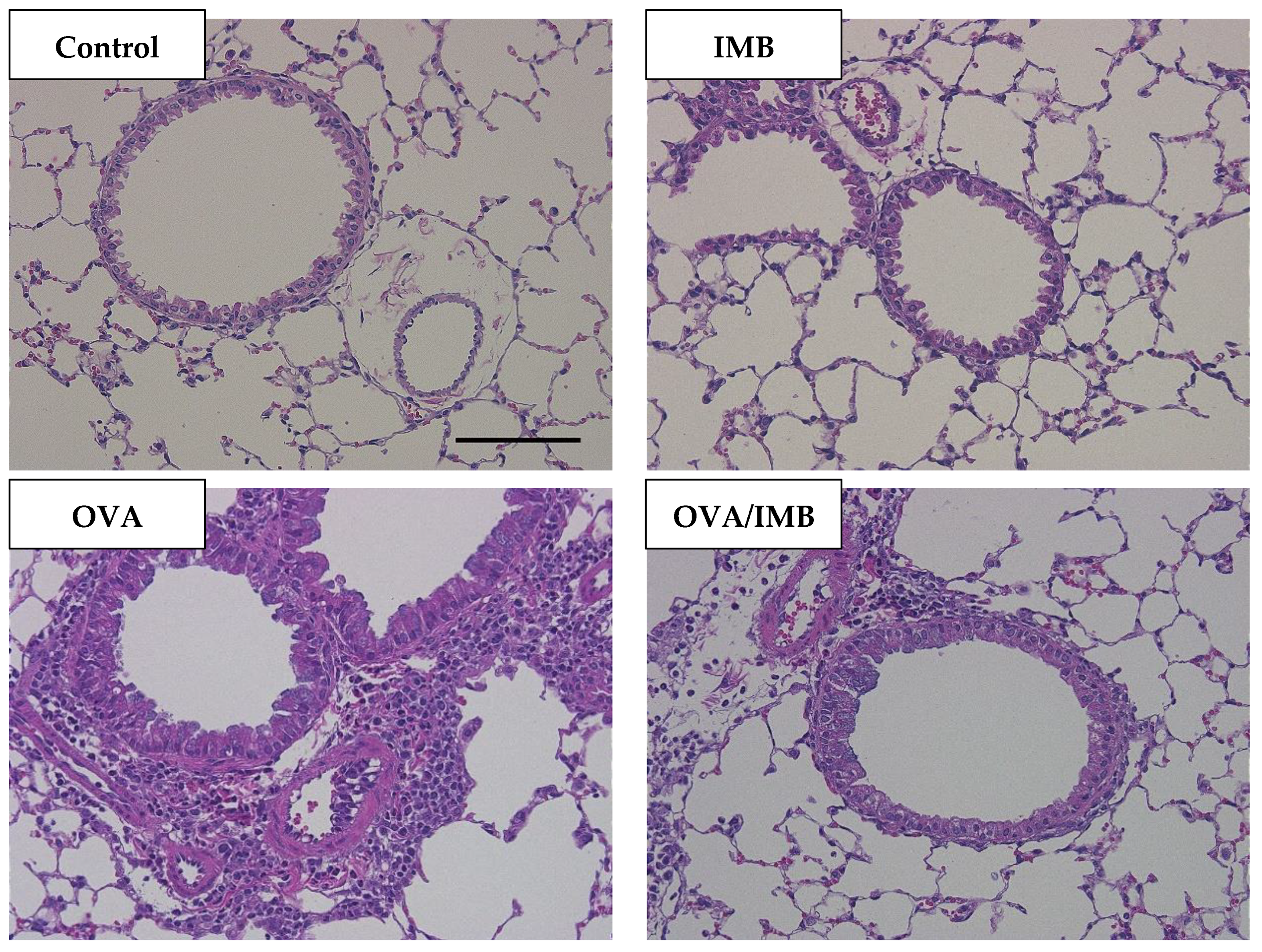
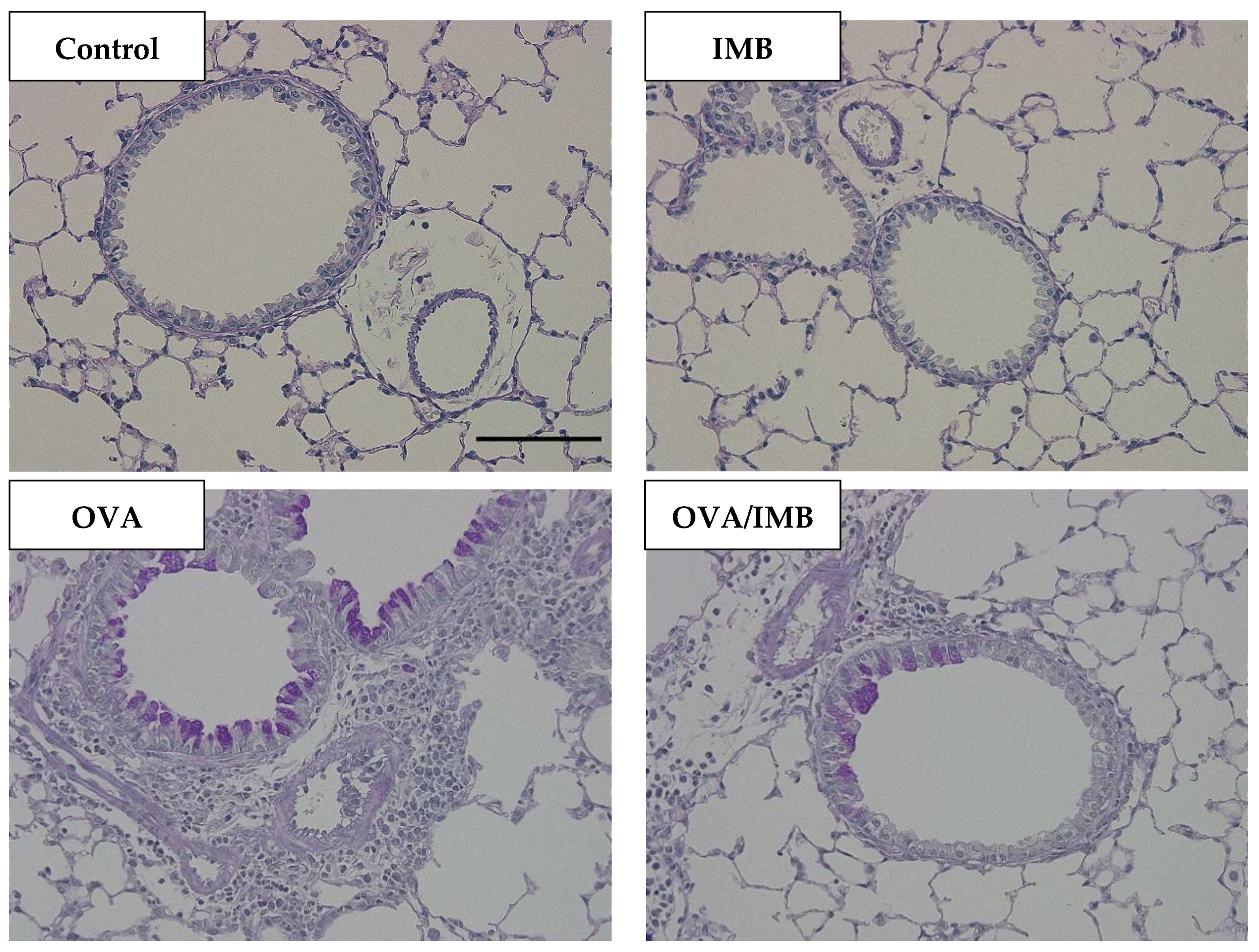
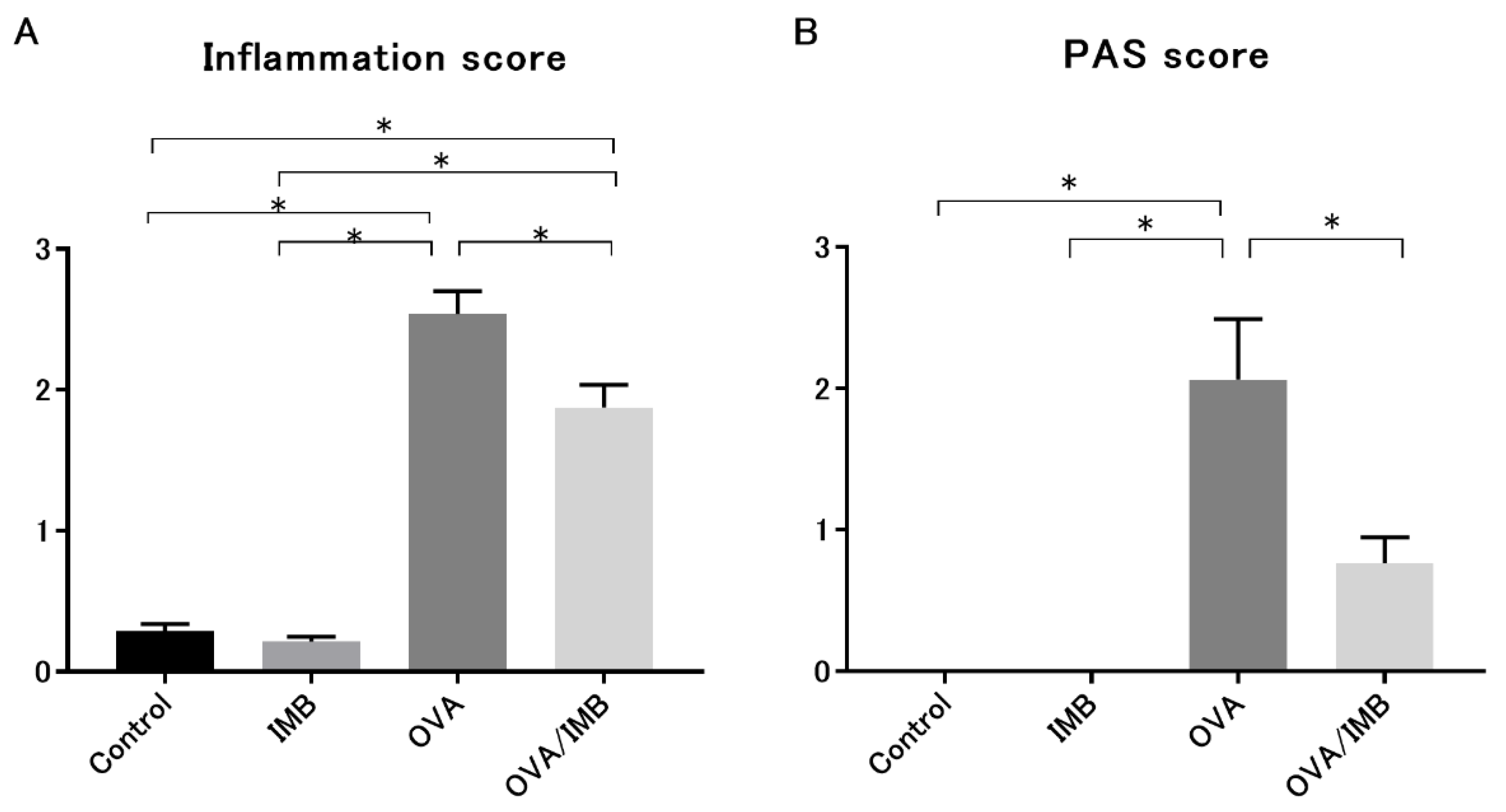
3.4. ImmuBalance Ameliorated OVA-Induced Histological Changes in Lung
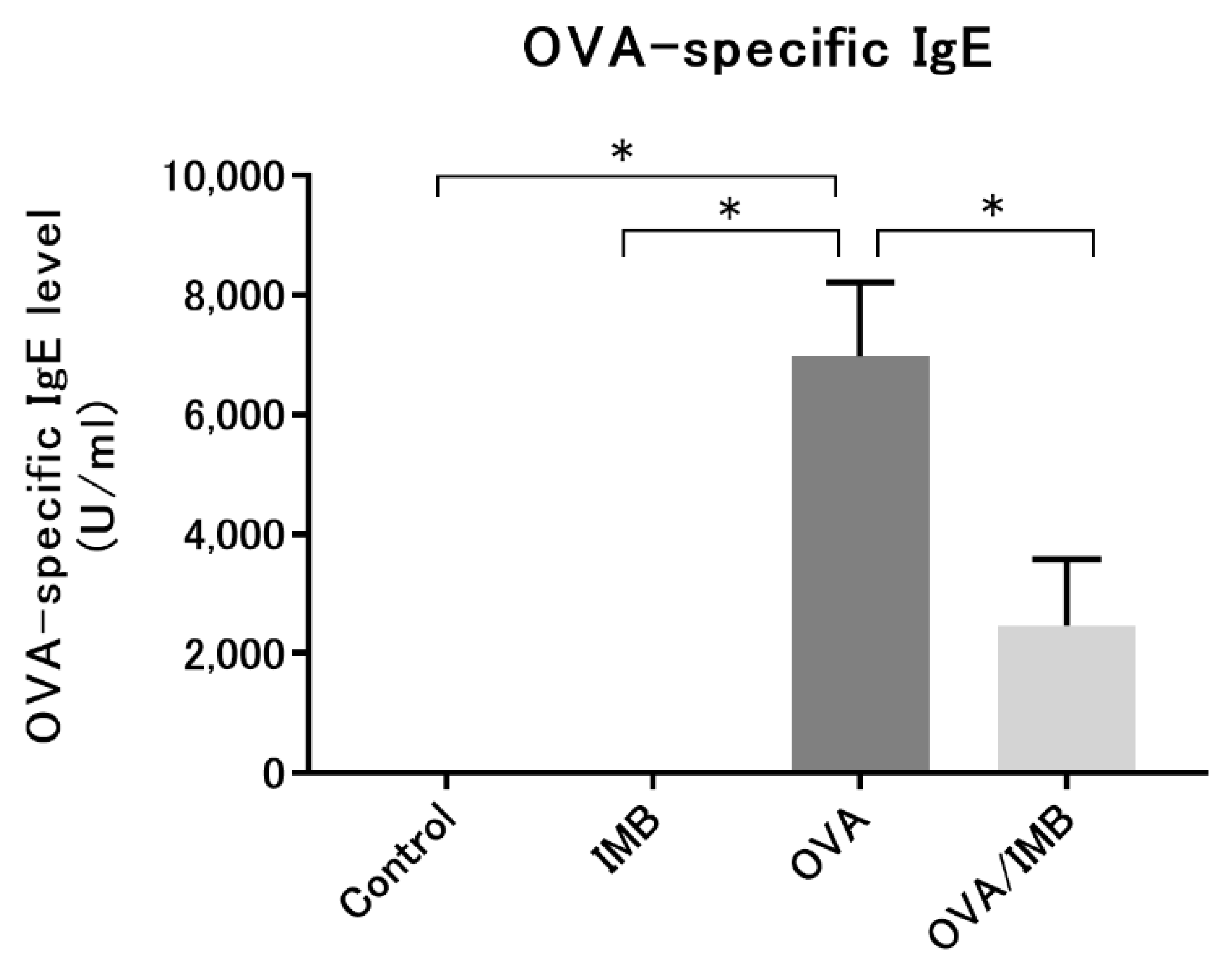
3.5. ImmuBalance Reduced the Serum OVA-Specific IgE Levels in OVA-Challenged Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kattan, J. The Prevalence and Natural History of Food Allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman, H.; Räisänen, P.; Hedman, L.; Stridsman, C.; Andersson, M.; Lindberg, A.; Lundbäck, B.; Rönmark, E. Increased prevalence of allergic asthma from 1996 to 2006 and further to 2016-results from three population surveys. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, M.; Penn, J.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Lima, H.; Sehmi, R. Atopic March: Collegium Internationale Allergologicum Update 2020. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.W.; Leung, T.F.; Ko, F.W. Changing prevalence of allergic diseases in the Asia-pacific region. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2013, 5, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holgate, S.T. The airway epithelium is central to the pathogenesis of asthma. Allergol. Int. 2008, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, S.C.; Brown, R.E.; Cerulli, A.; Vidaurre, C.F. The cumulative burden of oral corticosteroid side effects and the economic implications of steroid use. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 975–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Ahmet, A.; Ward, L.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Mandelcorn, E.D.; Leigh, R.; Brown, J.P.; Cohen, A.; Kim, H. A practical guide to the monitoring and management of the complications of systemic corticosteroid therapy. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, D.B.; Trudo, F.; Voorham, J.; Xu, X.; Kerkhof, M.; Ling Zhi Jie, J.; Tran, T.N. Adverse outcomes from initiation of systemic corticosteroids for asthma: Long-term observational study. J. Asthma Allergy 2018, 11, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bime, C.; Wei, C.Y.; Holbrook, J.; Smith, L.J.; Wise, R.A. Association of dietary soy genistein intake with lung function and asthma control: A post-hoc analysis of patients enrolled in a prospective multicentre clinical trial. Prim. Care Respir. J. 2012, 21, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyake, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Ohya, Y.; Miyamoto, S.; Matsunaga, I.; Yoshida, T.; Hirota, Y.; Oda, H. Soy, isoflavones, and prevalence of allergic rhinitis in Japanese women: The Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroni, D.G.; Nuzzi, G.; Trambusti, I.; Di Cicco, M.E.; Comberiati, P. Microbiome Composition and Its Impact on the Development of Allergic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trompette, A.; Gollwitzer, E.S.; Yadava, K.; Sichelstiel, A.K.; Sprenger, N.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Blanchard, C.; Junt, T.; Nicod, L.P.; Harris, N.L.; et al. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorburn, A.N.; McKenzie, C.I.; Shen, S.; Stanley, D.; Macia, L.; Mason, L.J.; Roberts, L.K.; Wong, C.H.; Shim, R.; Robert, R.; et al. Evidence that asthma is a developmental origin disease influenced by maternal diet and bacterial metabolites. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cait, A.; Hughes, M.R.; Antignano, F.; Cait, J.; Dimitriu, P.A.; Maas, K.R.; Reynolds, L.A.; Hacker, L.; Mohr, J.; Finlay, B.B.; et al. Microbiome-driven allergic lung inflammation is ameliorated by short-chain fatty acids. Mucosal. Immunol. 2018, 11, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thio, C.L.; Chi, P.Y.; Lai, A.C.; Chang, Y.J. Regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cell-dependent airway hyperreactivity by butyrate. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1867–1883.e1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theiler, A.; Bärnthaler, T.; Platzer, W.; Richtig, G.; Peinhaupt, M.; Rittchen, S.; Kargl, J.; Ulven, T.; Marsh, L.M.; Marsche, G.; et al. Butyrate ameliorates allergic airway inflammation by limiting eosinophil trafficking and survival. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Sasaki, H.; Shiga, K.; Miyakawa, H.; Shibata, S. The Timing Effects of Soy Protein Intake on Mice Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2019, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Q.; Cheng, D.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Lao, C.; Xia, Y.; Liu, W.; Gong, X.; Hu, D.; Li, B.; et al. Improvement of Colonic Immune Function with Soy Isoflavones in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Molecules 2019, 24, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamoto, K. Cell biology of the Koji mold Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otsuka, Y.; Pan, W. Effects of the novel symbiotic ImmuBalance as a food supplement in relieving clinical symptoms of Japanese cedar pollinosis: A pilot study. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, S73–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.; Tanaka, A.; Pan, W.; Okamoto, N.; Oida, K.; Kingyo, N.; Amagai, Y.; Xia, Y.; Jang, H.; Nishikawa, S.; et al. Supplementation of the fermented soy product ImmuBalance™ effectively reduces itching behavior of atopic NC/Tnd mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 67, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Pan, W.; Takebe, M.; Schofield, B.; Sampson, H.; Li, X.M. Therapeutic effects of a fermented soy product on peanut hypersensitivity is associated with modulation of T-helper type 1 and T-helper type 2 responses. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 1808–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, L.X.; Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Yin, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.R. Dietary Fermented Soy Extract and Oligo-Lactic Acid Alleviate Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice via Inhibition of Inflammation and Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, M.; Sagara, H.; Takahashi, F.; Harada, N.; Nishio, K.; Mori, A.; Ushio, H.; Shimizu, K.; Okada, T.; Ota, M.; et al. Role of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 in the pathogenesis of allergic airway inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 296, L30–L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanashiro, J.; Muraosa, Y.; Toyotome, T.; Hirose, K.; Watanabe, A.; Kamei, K. Schizophyllum commune induces IL-17-mediated neutrophilic airway inflammation in OVA-induced asthma model mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busse, W.W.; Lemanske, R.F. Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauwe, J.V. Interleukin-5 as a potential target for asthma treatment. Drug News Perspect. 2000, 13, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Bringe, N.A.; Berhow, M.A.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. beta-Conglycinins among sources of bioactives in hydrolysates of different soybean varieties that inhibit leukemia cells in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4012–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Bi, X.; Yu, B.; Chen, D. Isoflavones: Anti-Inflammatory Benefit and Possible Caveats. Nutrients 2016, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takaoka, O.; Mori, T.; Ito, F.; Okimura, H.; Kataoka, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Koshiba, A.; Kusuki, I.; Shigehiro, S.; Amami, T.; et al. Daidzein-rich isoflavone aglycones inhibit cell growth and inflammation in endometriosis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 181, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, K.; Asai, K.; Kubo, H.; Sugitani, A.; Kyomoto, Y.; Okamoto, A.; Yamada, K.; Ijiri, N.; Watanabe, T.; Hirata, K.; et al. Isoflavone Aglycones Attenuate Cigarette Smoke-Induced Emphysema via Suppression of Neutrophilic Inflammation in a COPD Murine Model. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, L.J.; Holbrook, J.T.; Wise, R.; Blumenthal, M.; Dozor, A.J.; Mastronarde, J.; Williams, L.; Centers, A.L.A.A.C.R. Dietary intake of soy genistein is associated with lung function in patients with asthma. J. Asthma 2004, 41, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Bando, N.; Tsuji, H.; Okajima, H.; Nishikawa, K.; Sasaoka, K. Investigation of the IgE-binding proteins in soybeans by immunoblotting with the sera of the soybean-sensitive patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1991, 37, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izumi, T.; Piskula, M.K.; Osawa, S.; Obata, A.; Tobe, K.; Saito, M.; Kataoka, S.; Kubota, Y.; Kikuchi, M. Soy isoflavone aglycones are absorbed faster and in higher amounts than their glucosides in humans. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.W.; Kim, I.D.; Bilal, S.; Shahzad, R.; Saeed, M.T.; Adhikari, B.; Nabi, R.B.S.; Kyo, J.R.; Shin, D.H. Effects of Bacterial Fermentation on the Biochemical Constituents and Antioxidant Potential of Fermented and Unfermented Soybeans Using Probiotic Bacillus subtilis (KCTC 13241). Molecules 2017, 22, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frias, J.; Song, Y.S.; Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; González de Mejia, E.; Vidal-Valverde, C. Immunoreactivity and amino acid content of fermented soybean products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, C.; Ozeki, K.; Naito, M.; Suzuki, M.; Izumi, H. Analyses of functional ingredient in ImmuBalance® fermented soybean. Nagoya J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 2, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitaka, Y.; Hamada, H.; Uesugi, D.; Kuboki, A.; Shimoda, K.; Iwaki, T.; Kiriake, Y.; Saikawa, T. Synthesis of Daidzein Glycosides, α-Tocopherol Glycosides, Hesperetin Glycosides by Bioconversion and Their Potential for Anti-Allergic Functional-Foods and Cosmetics. Molecules 2019, 24, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, L.J.; Kalhan, R.; Wise, R.A.; Sugar, E.A.; Lima, J.J.; Irvin, C.G.; Dozor, A.J.; Holbrook, J.T.; American Lung Association Asthma Clinical Research Centers. Effect of a soy isoflavone supplement on lung function and clinical outcomes in patients with poorly controlled asthma: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2015, 313, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadotani, H.; Asai, K.; Miyamoto, A.; Iwasaki, K.; Kawai, T.; Nishimura, M.; Tohda, M.; Okamoto, A.; Sato, K.; Yamada, K.; et al. The Fermented Soy Product ImmuBalanceTM Suppresses Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Asthma. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103380
Kadotani H, Asai K, Miyamoto A, Iwasaki K, Kawai T, Nishimura M, Tohda M, Okamoto A, Sato K, Yamada K, et al. The Fermented Soy Product ImmuBalanceTM Suppresses Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Asthma. Nutrients. 2021; 13(10):3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103380
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadotani, Hideaki, Kazuhisa Asai, Atsushi Miyamoto, Kohei Iwasaki, Takahiro Kawai, Misako Nishimura, Mitsunori Tohda, Atsuko Okamoto, Kanako Sato, Kazuhiro Yamada, and et al. 2021. "The Fermented Soy Product ImmuBalanceTM Suppresses Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Asthma" Nutrients 13, no. 10: 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103380
APA StyleKadotani, H., Asai, K., Miyamoto, A., Iwasaki, K., Kawai, T., Nishimura, M., Tohda, M., Okamoto, A., Sato, K., Yamada, K., Ijiri, N., Watanabe, T., & Kawaguchi, T. (2021). The Fermented Soy Product ImmuBalanceTM Suppresses Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Asthma. Nutrients, 13(10), 3380. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103380






