Effect of Polyglucosamine on Weight Loss and Metabolic Parameters in Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Participants
2.5. Intervention and Control Group
2.6. Outcomes
2.7. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.8. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
3. Results
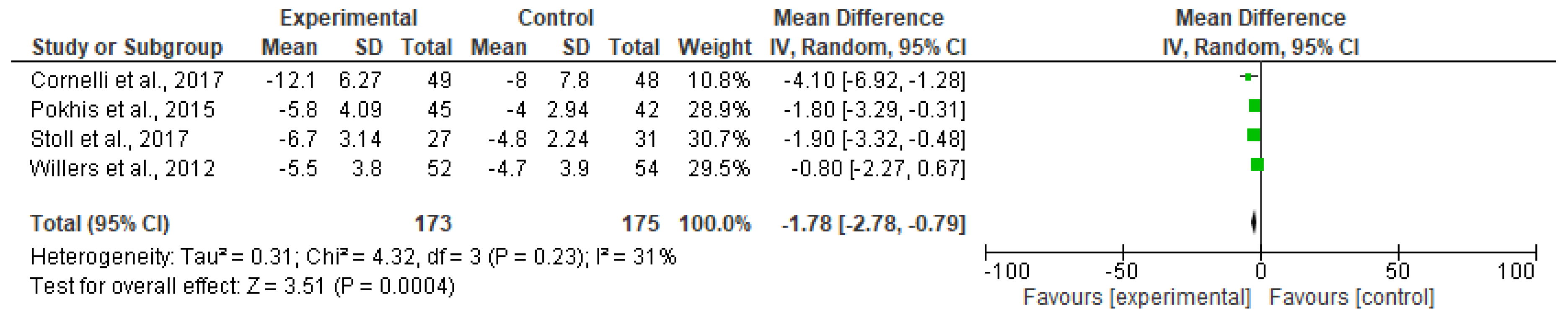
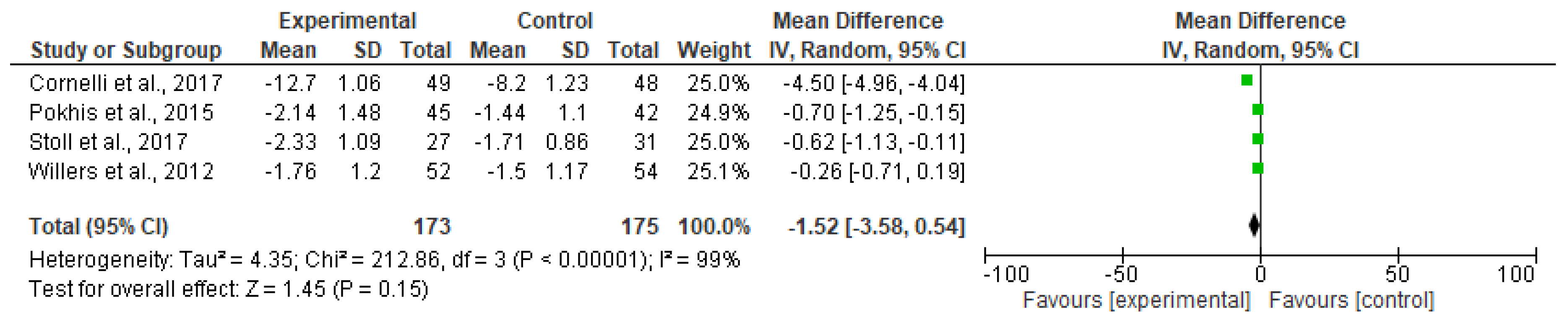
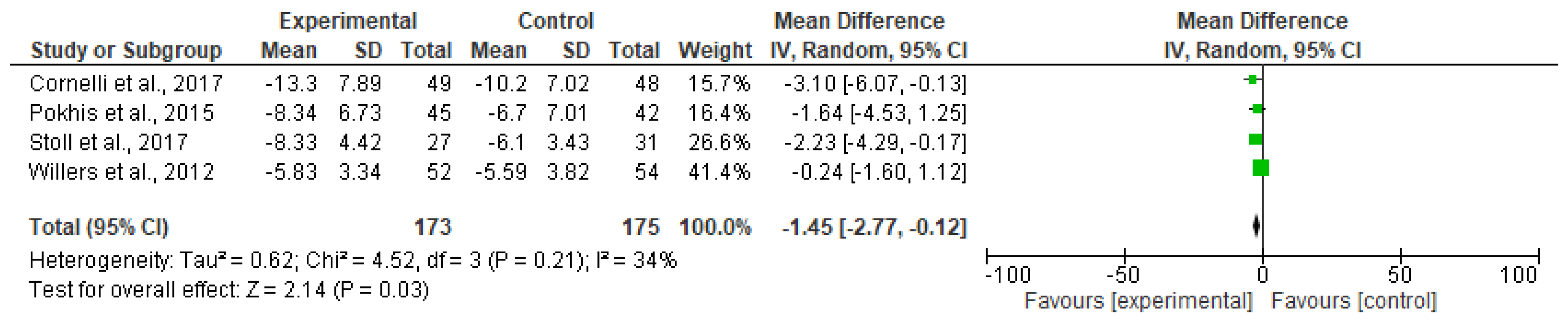
3.1. Meta-Analyzed Data
3.2. Risk of Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klein, S.; Fontana, L.; Young, V.L.; Coggan, A.R.; Kilo, C.; Patterson, B.W.; Mohammed, B.S. Absence of an effect of liposuction on insulin action and risk factors for coronary heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2549–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.D.; Guo, J. Obesity energetics: body weight regulation and the effects of diet composition. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apovian, C.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Bessesen, D.H.; McDonnell, M.E.; Murad, M.H.; Pagotto, U.; Ryan, D.H.; Still, C.D. Pharmacological management of obesity: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 342–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelli, U. Body weight reduction with L112: Review of double blind randomized controlled clinical trials. Curr. Res. Diabetes Obes. J. 2018, 6, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Baak, M.A.; Mariman, E.C.M. Dietary strategies for weight loss maintenance. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, D.; Preuss, H.G. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Prevention; Bagchi, D., Preuss, H.G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780429192296. [Google Scholar]
- Padwal, R.S.; Majumdar, S.R. Drug treatments for obesity: Orlistat, sibutramine, and rimonabant. Lancet 2007, 369, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA Recommends Against the Continued Use of Meridia (sibutramine). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-fda-recommends-against-continued-use-meridia-sibutramine (accessed on 7 April 2020).
- Moraru, C.; Mincea, M.M.; Frandes, M.; Timar, B.; Ostafe, V. A meta-analysis on randomised controlled clinical trials evaluating the effect of the dietary supplement chitosan on weight loss, lipid parameters and blood pressure. Medicina 2018, 54, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicińska, P.; Pytel, E.; Maćczak, A.; Koter-Michalak, M. The use of various diet supplements in metabolic syndrome. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2015, 69, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelli, U.; Belcaro, G. Meta-analysis of studies on body weight and cholesterol reduction using the chitosan derivative polyglucosamine L112. Res. Artic. Gen. Med. Open 2018, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Stoll, M.; Bitterlich, N.; Cornelli, U. Randomised, double-blind, clinical investigation to compare orlistat 60 milligram and a customized polyglucosamine, two treatment methods for the management of overweight and obesity. BMC Obes. 2017, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, A.M.; Yanovski, J.A.; Calis, K.A. Orlistat, a new lipase inhibitor for the management of obesity. Pharmacotherapy 2000, 20, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokhis, K.; Bitterlich, N.; Cornelli, U.; Cassano, G. Efficacy of polyglucosamine for weight loss-confirmed in a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical investigation. BMC Obes. 2015, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelli, U.; Belcaro, G.; Recchia, M.; D’Orazio, N. Long-term treatment of overweight and obesity with polyglucosamine (PG L112): Randomized study compared with placebo in subjects after caloric restriction. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2017, 1, e000919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willers, J.; Plötz, S.; Hahn, A. The combination of a high-protein formuladiet and polyglucosamine decreases bodyweight and parameters of glucose and lipidmetabolism in overweight and obese men and women. Eur. J. Food Res. Rev. 2012, 2, 29–45. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. PRISMA group preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. The cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondiolotti, G.; Bareggi, S.R.; Frega, N.G.; Strabioli, S.; Cornelli, U. Activity of two different polyglucosamines, L112 and FF45, on body weight in male rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 567, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar]
- Espeland, M.; Pi-Sunyer, X.; Blackburn, G.; Brancati, F.L.; Bray, G.A.; Bright, R.; Clark, J.M.; Curtis, J.M.; Foreyt, J.P.; Graves, K.; et al. Reduction in weight and cardiovascular disease risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes one-year results of the look ahead trial. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, R.R.; Bolin, P.; Brancati, F.L.; Bray, G.A.; Clark, J.M.; Coday, M.; Crow, R.S.; Curtis, J.M.; Egan, C.M.; Espeland, M.A.; et al. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, D.; Toyomura, K.; Fukumoto, J.; Ueda, N.; Ohnaka, K.; Adachi, M.; Takayanagi, R.; Kono, S. Waist circumference and cardiovascular risk factors in Japanese men and women. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2009, 16, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppitt, S.D.; Keogh, G.F.; Prentice, A.M.; Williams, D.E.M.; Sonnemans, H.M.W.; Valk, E.E.J.; Robinson, E.; Wareham, N.J. Long-term effects of ad libitum low-fat, high-carbohydrate diets on body weight and serum lipids in overweight subjects with metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 75, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubro, S.; Astrup, A. Randomised comparison of diets for maintaining obese subjects’ weight after major weight loss: Ad lib, low fat, high carbohydrate dietv fixed energy intake. BMJ 1997, 314, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciutto, A. Lipid-lowering effect of chitosan dietary integrator hypocaloric diet in obese subjects. Acta Toxicol. Ther. 1995, 16, 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Macchi, G. A new approach to the treatment of obesity: chitosan’s effects on body weight reduction and plasma cholesterol’s levels. Acta Toxicol. Ther. 1996, 17, 303–322. [Google Scholar]
- Zahorska-Markiewicz, B.; Krotkiewski, M.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M.; Zurakowski, A. Effect of chitosan in complex management of obesity. Pol. Merkur. Lek. 2002, 13, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Pittler, M.H.; Abbot, N.C.; Harkness, E.F.; Ernst, E. Randomized, double-blind trial of chitosan for body weight reduction. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffer, S.; Sampalis, J. Efficacy and safety of chitosan HEP-40TM in the management of hypercholesterolemia: A randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial. Altern. Med. Rev. 2007, 12, 265. [Google Scholar]
- Aldekhail, N.M.; Logue, J.; McLoone, P.; Morrison, D.S. Effect of orlistat on glycaemic control in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obesity Rev. 2015, 16, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author/Year of Publication | Subjects, Sex (Polyglucosamine vs. Placebo) | Population (Age, BMI) | Treatment Duration | Polyglucosamine Dosage | Control Group | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pokhis et al., 2015 [14] | Total: 115 (36 M, 79 F) (45 vs. 42) | 21–75 years, BMI of >26 and <45 kg/m2 | 26 weeks | 850 mg PG tablets twice daily + 6–7 MET-h/week activity + caloric restriction | 6–7 MET-h/week activity + caloric restriction | Weight, BMI, and waist circumference |
| Cornelli et al., 2017 [15] | Total: 100 (50 M, 50 F) (49 vs. 48) | 25–65 years, BMI of >30 and <35 kg/m2 | 12 months | Two 400 mg PG tablets twice daily + caloric restriction + 8 MET-h/week | Caloric restriction + 8 MET-h/week | Weight, BMI, waist circumference |
| Willers et al., 2012 [16] | Total: 120 (61 M, 59 F) (52 vs. 54) | 30–60 years, BMI of 28–35 kg/m2 | 12 weeks | Two 400 mg PG tablets/day + Protein-rich formula diet | High protein-rich formula diet | Weight, BMI, waist and hip circumference, waist to hip ratio, blood glucose, and lipid parameters |
| Stoll et al., 2017 [12] | Total: 64 (28M, 36 F) (27 vs. 31) | 21–70 years, BMI of >28 and <45 kg/m2 | 12 weeks | Two PG tablets twice/day | One orlistat capsule three times/day | Weight, BMI, waist circumference |
| Study, Year | Random-Sequence Generation | Allocation Concealment | Participant-Personnel Blinding | Outcome-Assessment Blinding | Incomplete Outcome Data | Selective Reporting | Other Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cornelli et al., 2017 [15] | Low | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low |
| Pokhis et al., 2015 [14] | Low | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low |
| Stoll et al., 2017 [12] | Low | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low |
| Willers et al., 2012 [16] | Low | Unclear | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perna, S.; Basharat, S.N.M.; Ali, K.F.; Eid, A.; Gasparri, C.; Infantino, V.; Faliva, M.A.; Naso, M.; Cazzola, R.; Cestaro, B.; et al. Effect of Polyglucosamine on Weight Loss and Metabolic Parameters in Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082365
Perna S, Basharat SNM, Ali KF, Eid A, Gasparri C, Infantino V, Faliva MA, Naso M, Cazzola R, Cestaro B, et al. Effect of Polyglucosamine on Weight Loss and Metabolic Parameters in Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082365
Chicago/Turabian StylePerna, Simone, Sana N. M. Basharat, Khawla F. Ali, Abdulla Eid, Clara Gasparri, Vittoria Infantino, Milena A. Faliva, Maurizio Naso, Roberta Cazzola, Benvenuto Cestaro, and et al. 2020. "Effect of Polyglucosamine on Weight Loss and Metabolic Parameters in Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 12, no. 8: 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082365
APA StylePerna, S., Basharat, S. N. M., Ali, K. F., Eid, A., Gasparri, C., Infantino, V., Faliva, M. A., Naso, M., Cazzola, R., Cestaro, B., & Rondanelli, M. (2020). Effect of Polyglucosamine on Weight Loss and Metabolic Parameters in Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 12(8), 2365. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082365






