Is There an Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Erectile Dysfunction? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
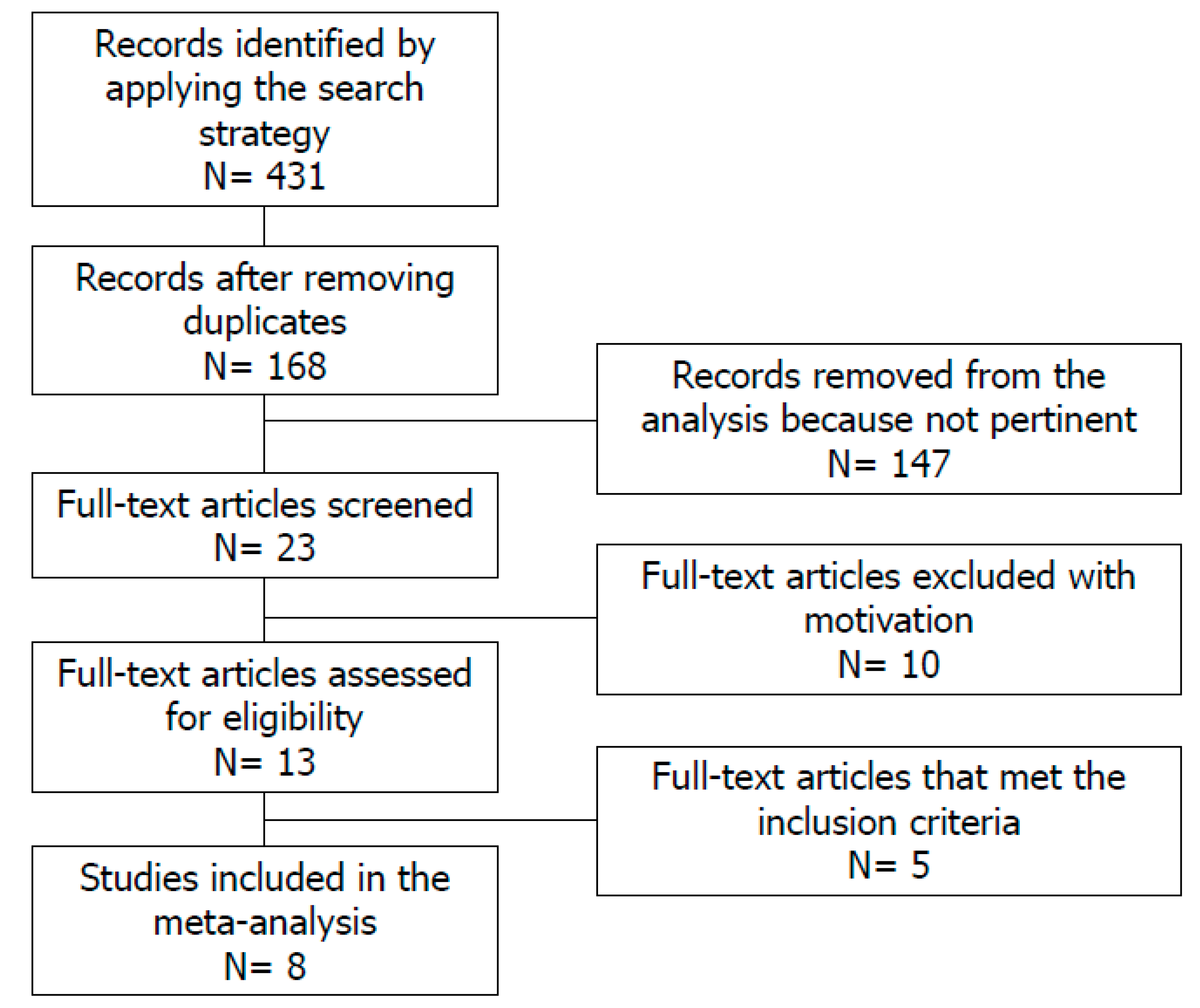
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source
2.2. Study Selection
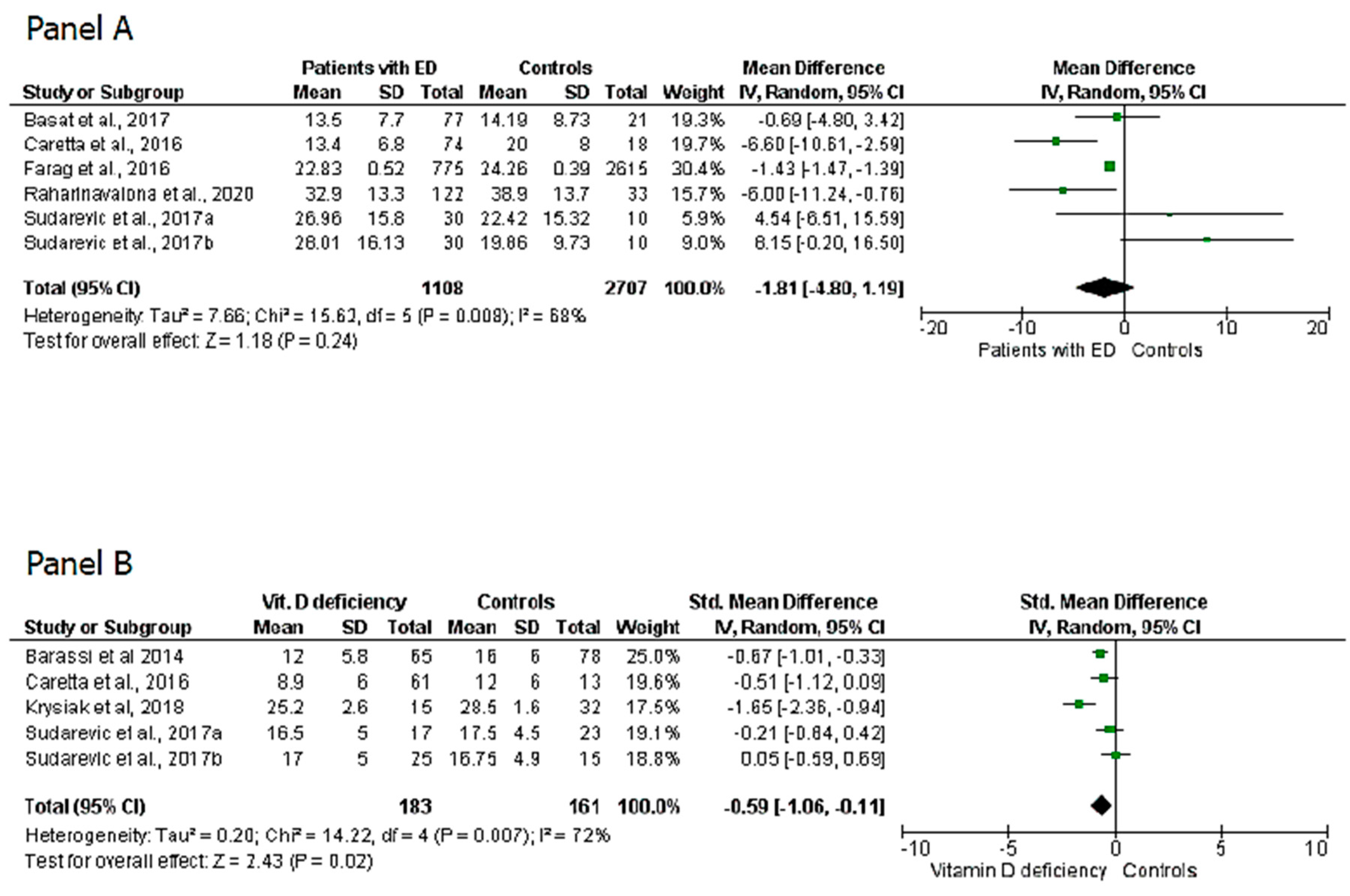
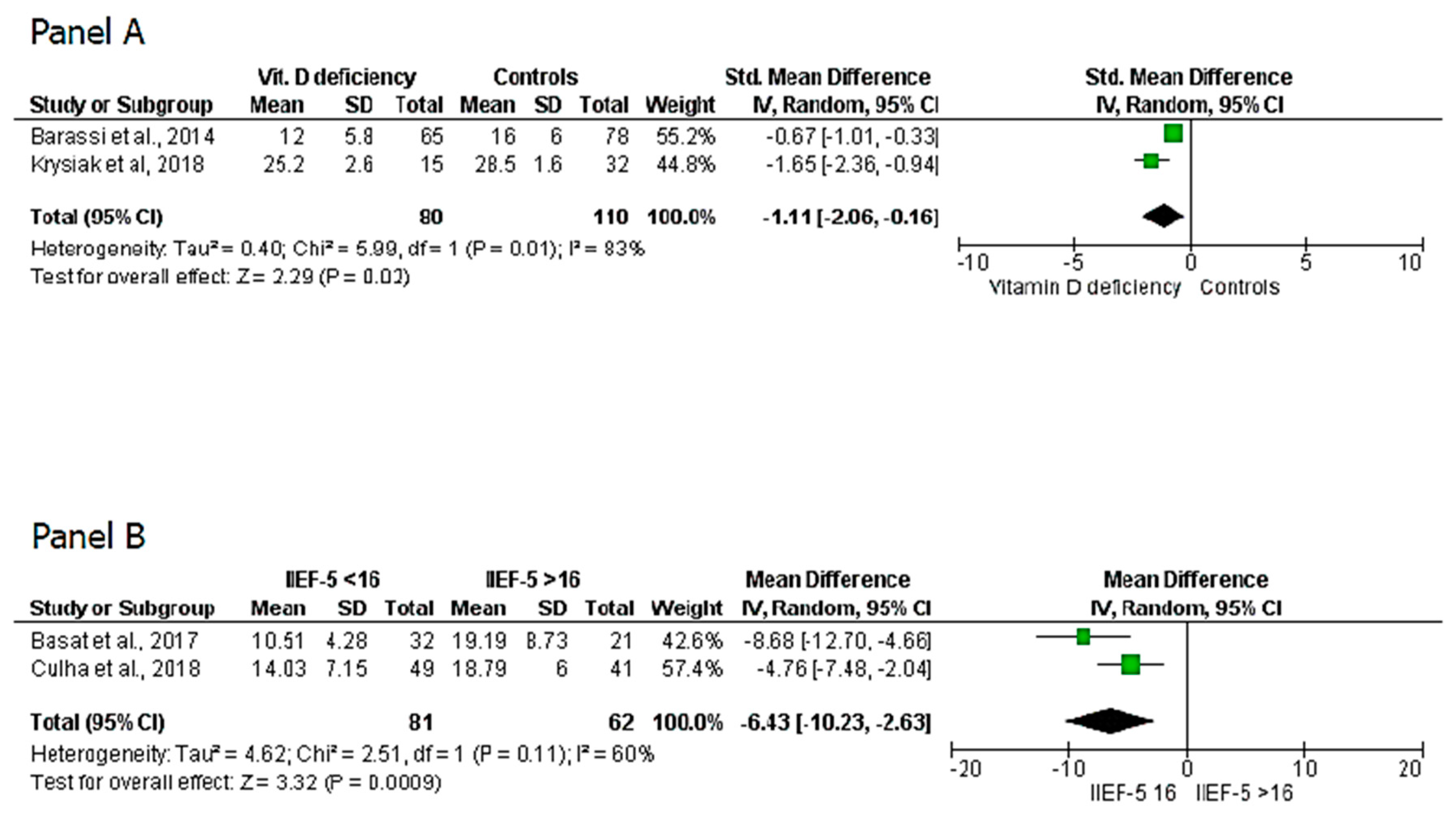
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holick, M.F.; Chen, T. Vitamin D deficiency: A worldwide problem with health consequences. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1080S–1086S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D. Vitamin D: Newer Concepts of Its Metabolism and Function at the Basic and Clinical Level. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvz038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, J.W.; Meyer, M.B.; Lee, S.-M.; Onal, M.; Benkusky, N.A. The vitamin D receptor: Contemporary genomic approaches reveal new basic and translational insights. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresta, C.; Strapazzon, G.; De Toni, L.; Perilli, L.; Di Mambro, A.; Muciaccia, B.; Sartori, L.; Selice, R. Bone mineral density and testicular failure: Evidence for a role of vitamin D 25-hydroxylase in human testis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E646–E652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vignera, S.; Condorelli, R.A.; Cimino, L.; Russo, G.I.; Morgia, G.; Calogero, A.E. Late-onset hypogonadism: The advantages of treatment with human chorionic gonadotropin rather than testosterone. Aging Male 2016, 19, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, P.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, H. Serum vitamin D levels and erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Andrologia 2019, 51, e13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarevic, B.; Begić, I.; Simunović, D.; Kuvezdić, H.; Seric, V.; Zibar, L. Vitamin D Status in Renal Transplant recipients is not Associated with Erectile Dysfunction. Acta Clin. Croat. 2017, 56, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raharinavalona, S.A.; Chevalier, N.; Gruel, C.; N’Toutoum, A.; Céphise, F.V. What is the best biological parameter to predict erectile dysfunction in men aged >55 years with type 2 diabetes? J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basat, S.; Sivritepe, R.; Ortaboz, D.; Çalık, E.S.; Küçük, E.V.; Şimşek, B.; Atay, S.; Çalışgan, A.; Calisgan, A. The relationship between vitamin D level and erectile dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Aging Male 2018, 21, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, Y.M.; Guallar, E.; Zhao, D.; Kalyani, R.R.; Blaha, M.J.; Feldman, D.I.; Martin, S.S.; Lutsey, P.L.; Billups, K.L.; Michos, E.D. Vitamin D deficiency is independently associated with greater prevalence of erectile dysfunction: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001-2004. Atherosclerosis 2016, 252, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caretta, N.; De Kreutzenberg, S.V.; Valente, U.; Guarneri, G.; Ferlin, A.; Avogaro, A.; Foresta, C. Hypovitaminosis D is associated with erectile dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Endocrine 2016, 53, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirabassi, G.; Sudano, M.; Salvio, G.; Cutini, M.; Muscogiuri, G.; Corona, G.; Balercia, G. Vitamin D and Male Sexual Function: A Transversal and Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 3720813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canguven, O.; Talib, R.A.; El Ansari, W.; Yassin, D.-J.; Al Naimi, A. Vitamin D treatment improves levels of sexual hormones, metabolic parameters and erectile function in middle-aged vitamin D deficient men. Aging Male 2017, 20, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidir, V.; Altuntas, A.; Inal, S.; Akpinar, A.; Orhan, H.; Sezer, M.T. Sexual dysfunction in dialysis patients: Does vitamin D deficiency have a role? Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 22491–22496. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, A.; Wildbolz, A.; Descoeudres, C.; Hennes, U.; A Dambacher, M.; A Fischer, J.; Weidmann, P. Influence of 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol on sexual dysfunction and related endocrine parameters in patiens on maintenance hemodialysis. Clin. Nephrol. 1980, 13, 208–214. [Google Scholar]
- Bellastella, G.; Maiorino, M.I.; Olita, L.; Capuano, A.; Rafaniello, C.; Giugliano, D.; Esposito, K. Vitamin D Deficiency in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Hypogonadism. J. Sex. Med. 2014, 11, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, X. Vitamin D Deficiency as a Potential Marker of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Urology 2016, 97, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, U.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B.; et al. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in EpidemiologyA Proposal for Reporting. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analysis. 2011. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, R.; Szwajkosz, A.; Okopień, B. The effect of low vitamin D status on sexual functioning and depressive symptoms in apparently healthy men: A pilot study. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2018, 30, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barassi, A.; Pezzilli, R.; Colpi, G.M.; Romanelli, M.C.; D’Eril, G.V.M. Vitamin D and Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2014, 11, 2792–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culha, M.G.; Atalay, H.A.; Canat, L.; Alkan, I.; Özbir, S.; Can, O.; Ötünçtemur, A. The relationship between erectile dysfunction severity, mean platelet volume and vitamin D levels. Aging Male 2018, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Cainzos-Achirica, M.; Feldman, D.I.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Nasir, K.; Miner, M.M.; Billups, K.L.; Blaha, M.J.; Information, P.E.K.F.C. Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Men with Vascular Erectile Dysfunction: The View of the Preventive Cardiologist. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheem, O.A.; Su, J.J.; Wilson, J.R.; Hsieh, T.M. The Association of Erectile Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Critical Review. Am. J. Men’s Heal. 2017, 11, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirhosseini, N.; Rainsbury, J.; Kimball, S. Vitamin D Supplementation, Serum 25(OH)D Concentrations and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimalawansa, S.J. Vitamin D and cardiovascular diseases: Causality. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Boil. 2018, 175, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, N.; Sorenson, C.M.; Sheibani, N. Vitamin D and regulation of vascular cell function. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H753–H765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Meza, C.A.; Clarke, H.; Kim, J.-S.; Hickner, R. Vitamin D and Endothelial Function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, K.; Fujii, H.; Kono, K.; Goto, S.; Kitazawa, R.; Kitazawa, S.; Hirata, M.; Shinohara, M.; Fukagawa, M.; Nishi, S. Vitamin D Activates the Nrf2-Keap1 Antioxidant Pathway and Ameliorates Nephropathy in Diabetic Rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2014, 27, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, R.A.; Khalafalla, K.; Canguven, O. The role of vitamin D supplementation on erectile function. Türk Üroloji Dergisi/Turk. J. Urol. 2017, 43, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Leung, P.S.C.; Adamopoulos, I.; Gershwin, M.E. The implication of vitamin D and autoimmunity: A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otunctemur, A.; Bozkurt, M.; Besiroglu, H.; Polat, E.C.; Ozcan, L.; Ozbek, E. Erectile Dysfunction Is Positively Correlated with Mean Platelet Volume and Platelet Count, but Not with Eosinophil Count in Peripheral Blood. Urol. J. 2015, 12, 2347–2352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.C.; Kim, J.; Seo, M.-S.; Hong, S.W.; Cho, E.S.; Kim, J.-K. Inverse relationship between vitamin D levels and platelet indices in Korean adults. Hematology 2017, 22, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzonek-Szlacheta, I.; Hudzik, B.; Nowak, J.; Szkodziński, J.; Nowak, J.; Gąsior, M.; Zubelewicz-Szkodzińska, B. Mean platelet volume is associated with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Hear. Vessel. 2018, 33, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, M.B.; Grant, W.B. Does vitamin D deficiency contribute to erectile dysfunction? Dermato-Endocrinology 2012, 4, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Canguven, O.; Al-Malki, A.H. Vitamin D and Male Erectile Function: An Updated Review. World J. Men’s Heal. 2020, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.-Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Yi, L.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, X.; Tang, Y. Comparison of the simplified International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) in patients of erectile dysfunction with different pathophysiologies. BMC Urol. 2014, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouidrat, Y.; Pizzol, D.; Cosco, T.D.; Thompson, T.; Carnaghi, M.; Bertoldo, A.; Solmi, M.; Stubbs, B.; Veronese, N. High prevalence of erectile dysfunction in diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 145 studies. Diabet. Med. 2017, 34, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatiki, M.; Rapti, E.; Karras, S.; Ajjan, R.A.; Kotsa, K. Vitamin D and diabetes mellitus: Causal or casual association? Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiuk, J.V.; Tadros, N.N. Erectile dysfunction in renal failure and transplant patients. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Bahnasawy, M.S.; El-Assmy, A.; Dawood, A.; Abobieh, E.; Dein, B.A.; El-Din, A.B.; El-Hamady, S.D. Effect of the use of internal iliac artery for renal transplantation on penile vascularity and erectile function: A prospective study. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 2335–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gontero, P.; Oderda, M.; Filippini, C.; Fontana, F.; Lazzarich, E.; Stratta, P.; Turello, E.; Tizzani, A.; Frea, B. Does kidney transplantation onto the external iliac artery affect the haemodynamic parameters of the cavernosal arteries? Asian J. Androl. 2012, 14, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.C.; Tajar, A.; Beynon, J.M.; Pye, S.; Silman, A.J.; Finn, J.D.; O’Neill, T.W.; Bartfai, G.; Casanueva, F.F.; Forti, G.; et al. Identification of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Morgentaler, A.; Sforza, A.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Meta-analysis of Results of Testosterone Therapy on Sexual Function Based on International Index of Erectile Function Scores. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajar, A.; Forti, G.; O’Neill, T.W.; Lee, D.; Silman, A.J.; Finn, J.D.; Bartfai, G.; Boonen, S.; Casanueva, F.F.; Giwercman, A.; et al. Characteristics of Secondary, Primary, and Compensated Hypogonadism in Aging Men: Evidence from the European Male Ageing Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travison, T.G.; Araujo, A.B.; Kupelian, V.; O’Donnell, A.B.; McKinlay, J.B. The Relative Contributions of Aging, Health, and Lifestyle Factors to Serum Testosterone Decline in Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, C.; Galdiero, M.; Pivonello, C.; Garifalos, F.; Menafra, D.; Cariati, F.; Salzano, C.; Galdiero, G.; Piscopo, M.; Vece, A.; et al. The role of vitamin D in male fertility: A focus on the testis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, T.; Rashed, L.A.; Sabry, D.; Osman, I.; Nabil, N.; Kareem, F.; Mostafa, I.A. Serum l-carnitine and vitamin D levels may be low among oral sildenafil citrate non-responders. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2018, 31, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Sample Size | No. of ED Patients | No. of Control | 25(OH)D3 Levels in ED Patients | 25(OH)D3 Levels in Control Group | No. of Vitamin Ddeficiency Patients | No. of Vitamin D Normal Patients | IIEF Score in Vitamin D Deficiency Patients | IIEF Score in Patients with Normal Levels of 25(OH)D3 or with Insufficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farag et al., 2016 | 3390 | 775 | 2615 | 22.83 ± 0.52 | 24.26 ± 0.39 | / | / | / | / |
| Basat et al., 2017 | 98 | 77 | 21 | 13.54 ± 7.24 | 14.19 ± 8.73 | / | / | / | / |
| Culha et al., 2018 | 90 | 90 | / | 18.79 ± 6 in mild ED 14.03 ± 7.15 in severe ED | / | / | / | / | / |
| Krysiak et al., 2018 | 47 | 11 | 36 | / | / | 15 | 32 | 25.2 ± 2.6 | 28.5 ± 1.6 |
| Barassi et al., 2014 | 143 | 143 | / | 18.2 ± 8.07 (A-ED) 22.5 ± 5.3 (BL-ED) 25.3 ± 11.6 (NA-ED) | / | 65 | 78 | 12 ± 5.8 | 16 ± 4 |
| Sudarevic et al., 2017 | 40 | 30 | 10 | 26.96 ± 15.8 (summer value) 28.01 ± 16.13 (winter value) | 22.42 ± 15.32 (summer value) 19.86 ± 9.73 (winter value) | 17 Summer 25 Winter | 23 Summer 15 winter | 16.5 ± 5 (summer value) 17 ± 5 (winter value) | 17.5 ± 4.5 (summer value) 16.75 ± 4.9 (winter value) |
| Raharinavalona et al., 2020 | 155 | 122 | 33 | 32.9 ± 13.3 | 38.9 ± 13.7 | / | / | / | / |
| Caretta et al., 2016 | 92 | 74 | 18 | 13.4 ± 6.8 | 20 ± 8 | 34 | 13 | 8.9 ± 6 | 12 ± 6 |
| Source | Study Design | No. of ED Patients | No. of Controls | No. of Vitamin D Deficiency Patients | No. of Vitamin D Normal Patients | Outcomes | Selection | Comparability | Exposure or Outcome | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farag et al. 2016 (11) | Cross-sectional | 775 | 2615 | / | / | Difference in 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with and without ED | *** | * | * | Moderate |
| Basat et al. 2017 (10) | Cross-sectional | 77 | 21 | / | / | Difference in 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with and without ED | *** | * | * | Moderate |
| Krysiak et al. 2018 (22) | Cross-sectional | 11 | 36 | 15 | 32 | Difference in IEFF-15 score in patients with or without vitamin D deficiency | ** | * | ** | Moderate |
| Barassi et al. 2014 (23) | Cross-sectional | 143 | / | 65 | 78 | Difference in 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with different form of ED and difference in IIEF-5 score in patients with or without vitamin D deficiency | *** | ** | * | Moderate |
| Sudarevic et al., 2017 (8) | Cross-sectional | 30 | 10 | 17 | 23 | Difference in 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with and without ED and difference in IIEF-5 score in patients with or without vitamin D deficiency | ** | * | ** | Moderate |
| Raharinavalona et., 2020 (9) | Cross-sectional | 122 | 33 | / | / | Difference in 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with and without ED | *** | * | ** | Moderate |
| Culha et Al 2018 (24) | Cross-sectional | 90 | / | / | / | Difference in 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with severe form of ED than patients with mild form | *** | * | ** | Moderate |
| Caretta et al. 2016 (12) | Cross-sectional | 74 | 18 | 34 | 13 | Difference in 25(OH)D3 levels in patients with and without ED and difference in IIEF-5 score in patients with or without vitamin D deficiency | *** | ** | * | Moderate |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crafa, A.; Cannarella, R.; Condorelli, R.A.; La Vignera, S.; Calogero, A.E. Is There an Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Erectile Dysfunction? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051411
Crafa A, Cannarella R, Condorelli RA, La Vignera S, Calogero AE. Is There an Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Erectile Dysfunction? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051411
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrafa, Andrea, Rossella Cannarella, Rosita A. Condorelli, Sandro La Vignera, and Aldo E. Calogero. 2020. "Is There an Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Erectile Dysfunction? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051411
APA StyleCrafa, A., Cannarella, R., Condorelli, R. A., La Vignera, S., & Calogero, A. E. (2020). Is There an Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Erectile Dysfunction? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 12(5), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051411








