Eckol from Ecklonia cava Suppresses Immunoglobulin E-mediated Mast Cell Activation and Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
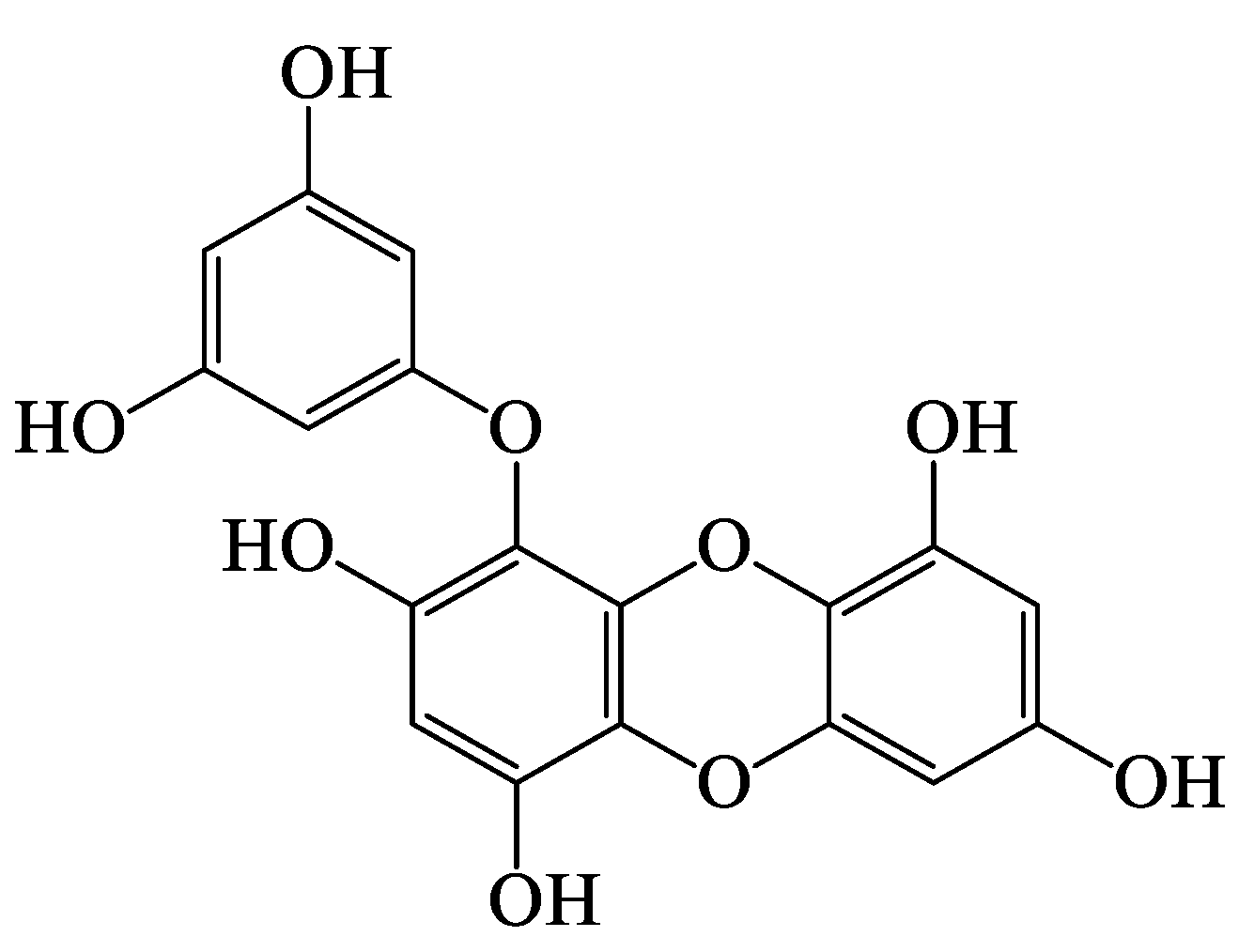
2.1. Material, Extraction, and Isolation
2.2. Animals
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Preparation and Stimulation of BMCMC
2.5. Degranulation Assay
2.6. Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) for Cytokine mRNA Levels
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for Cytokines Production
2.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis for Expression and Binding of IgE of FcεRI
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. PCA Test
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Eckol on β-Hexosaminidase Release in IgE/BSA-Stimulated BMCMC
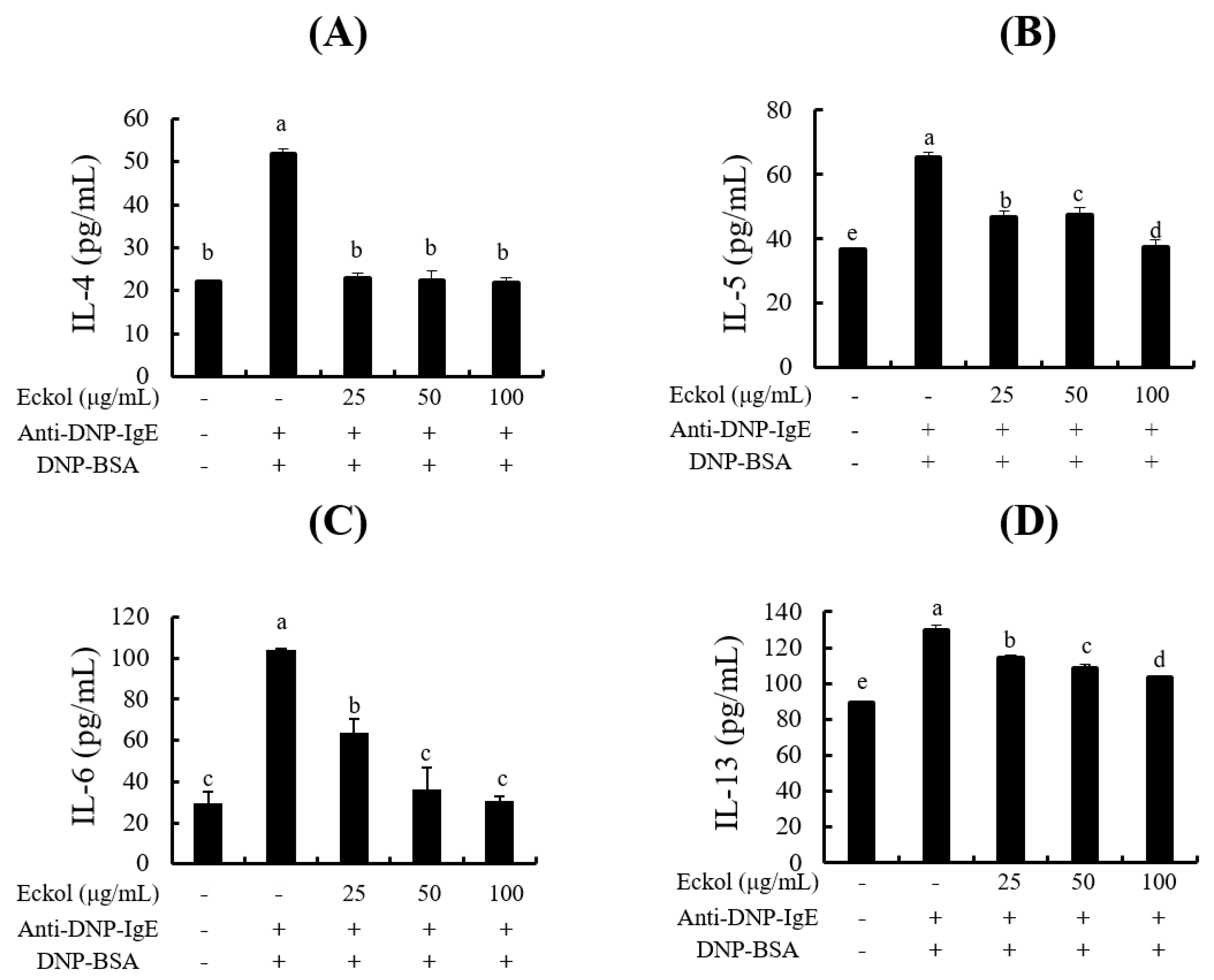
3.2. Effects of Eckol on Cytokine Production in IgE/BSA-Stimulated BMCMC
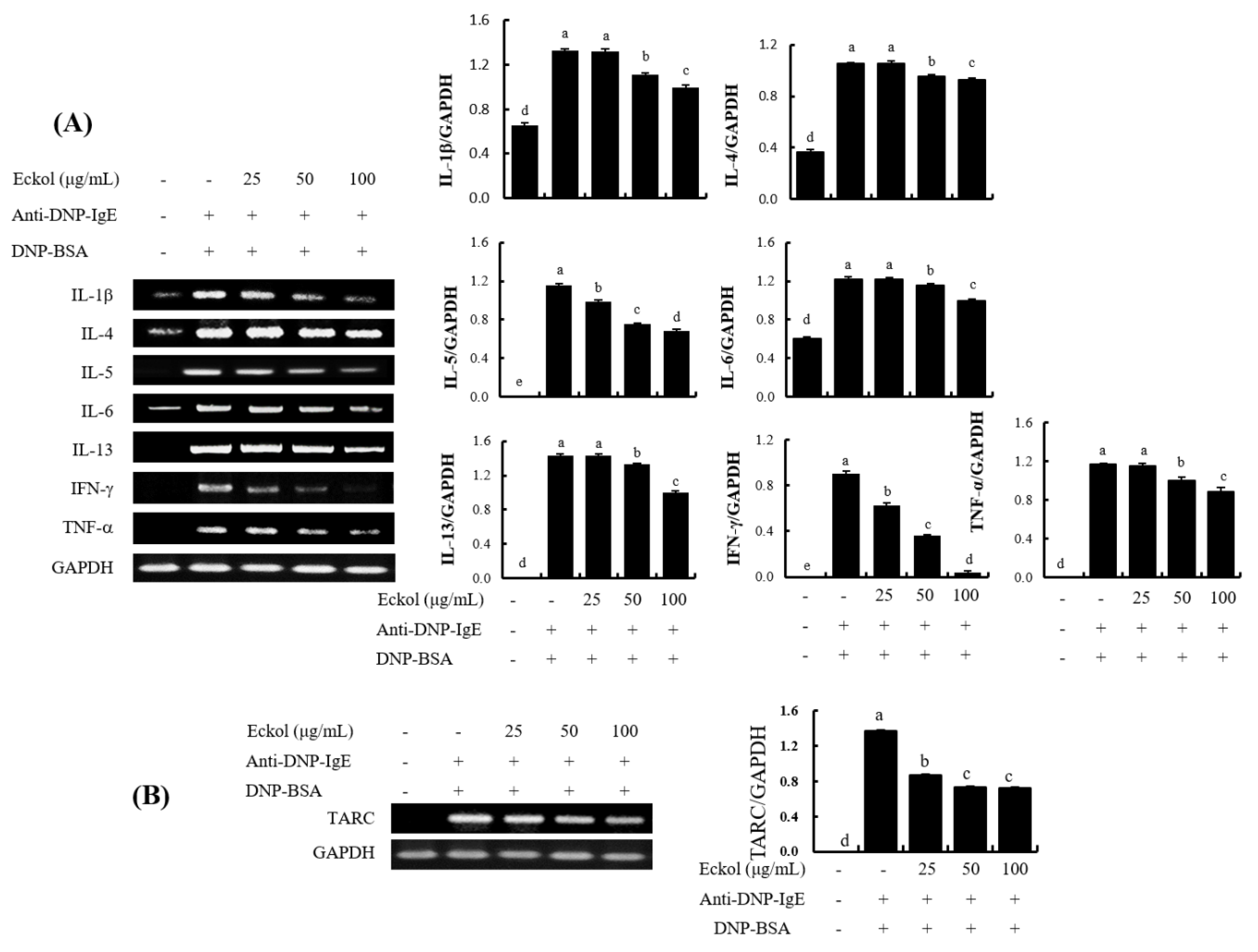
3.3. Effects of Eckol on Cytokine mRNA Levels in IgE/BSA-Stimulated BMCMC
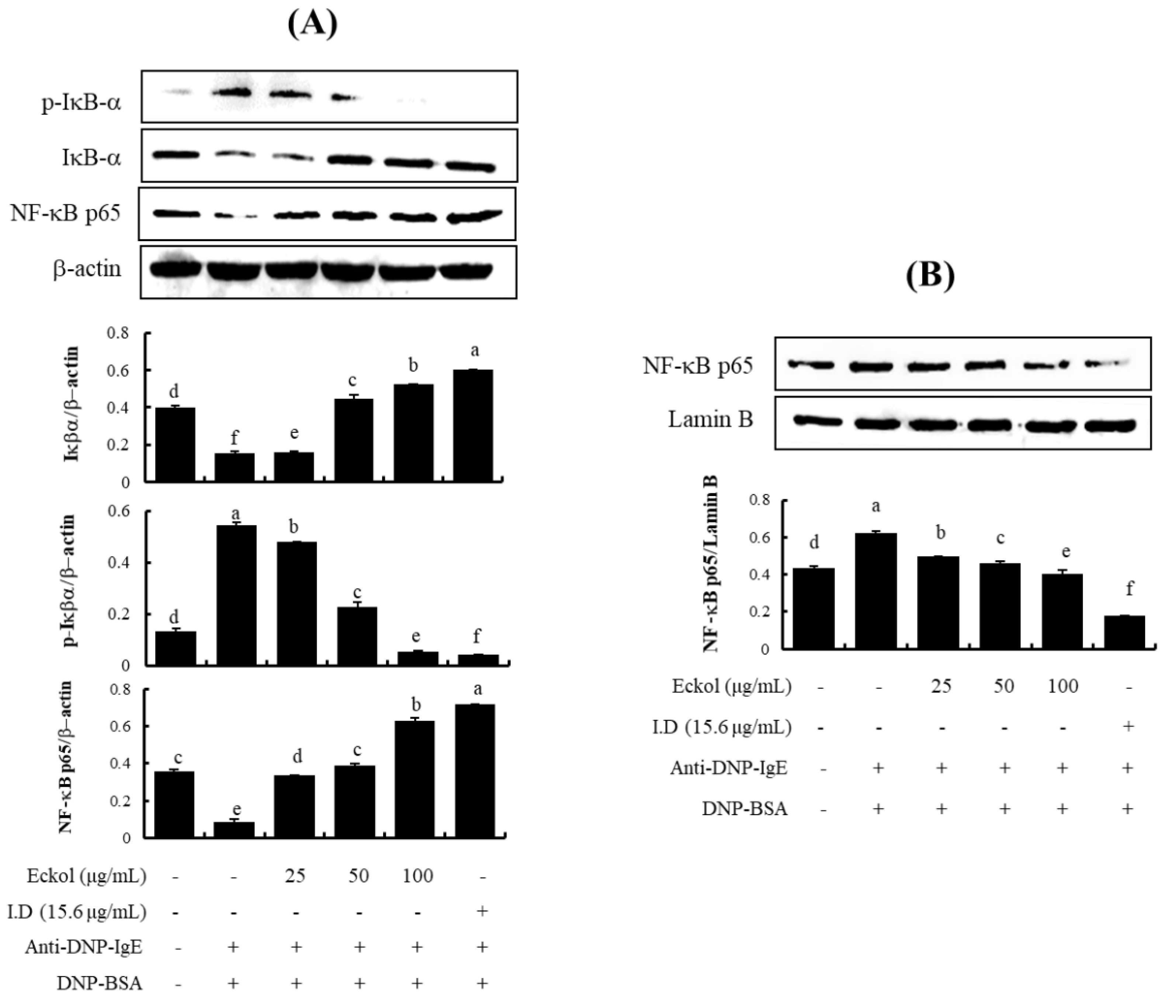
3.4. Effects of Eckol on NF-κB Activation in IgE/BSA-Stimulated BMCMC
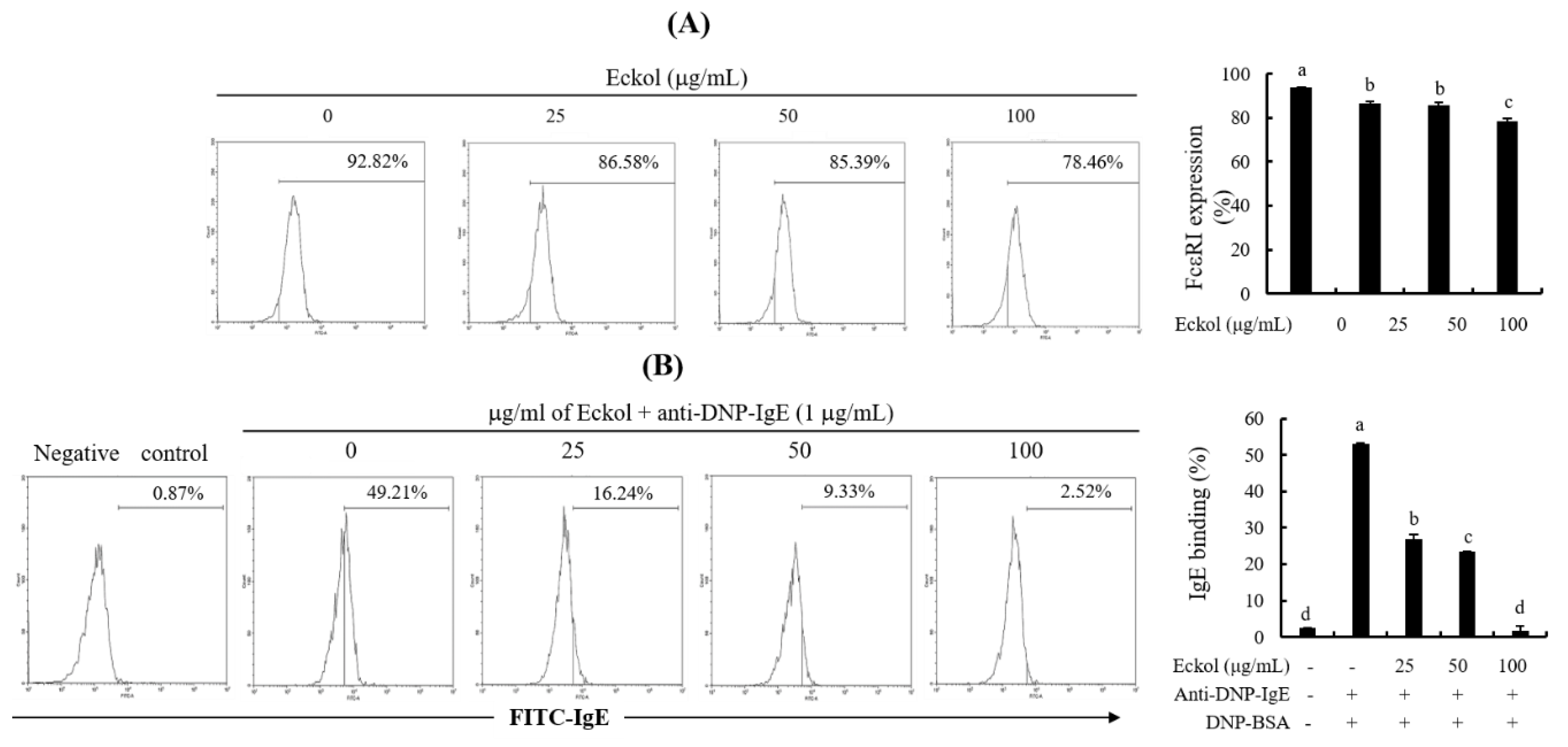
3.5. Effects of Eckol on FcεRI Expression and Binding of IgE to FcεRI.
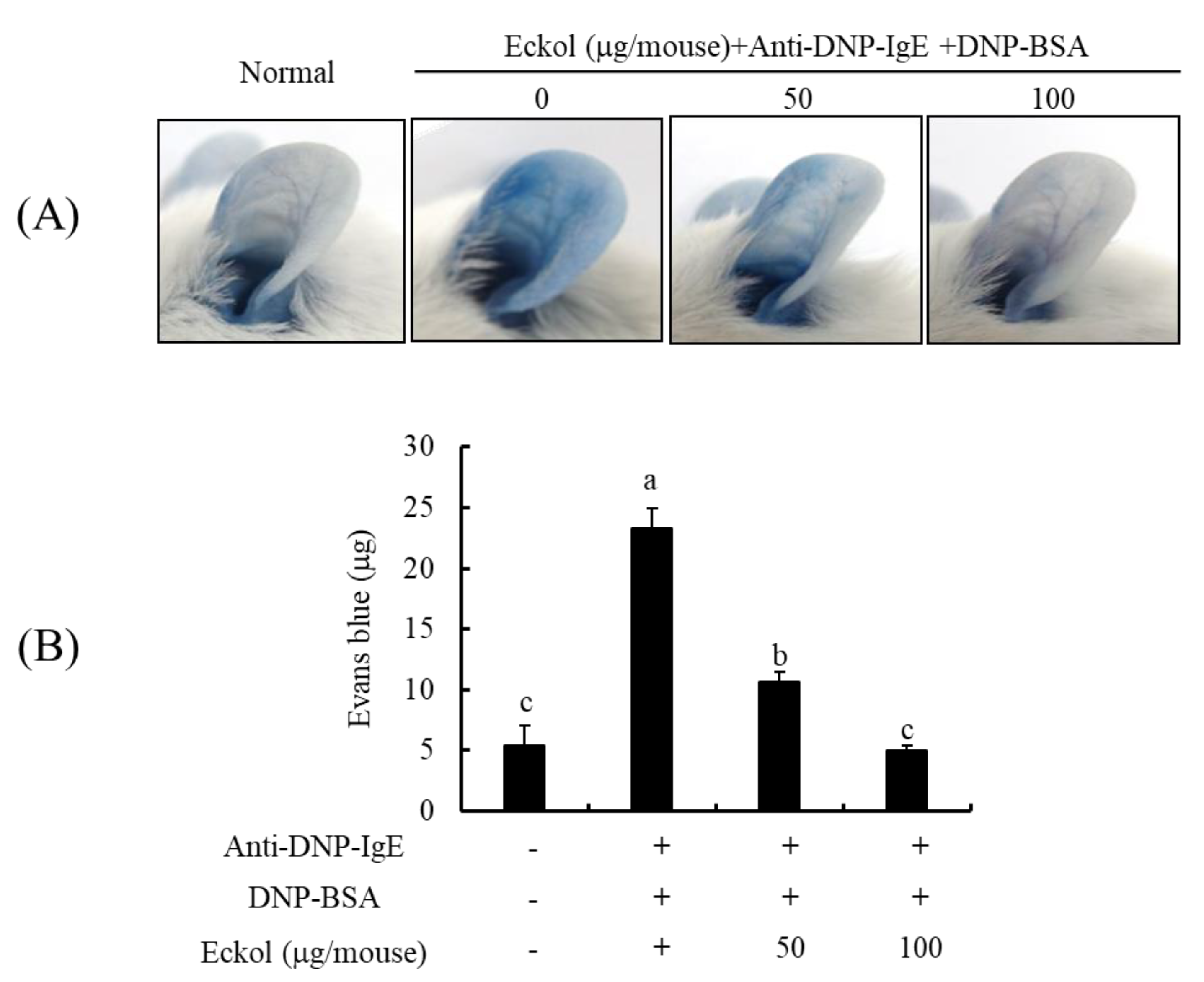
3.6. Effects of Eckol on IgE/BSA-Induced PCA Reaction in Mice Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muhammad, S.A.; Muhammad, J.; Muhammad, S.; Muhammad, K.P.; Shaista, H.; Viqar, U.A. Metabolites of marine algae collected from Karachi-coasts of Arabian Sea. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2000, 6, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Manandhar, B.; Paudel, P.; Seong, S.H.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Characterizing Eckol as a Therapeutic Aid: A Systematic Review. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, B.; Wagle, A.; Seong, S.H.; Paudel, P.; Kim, H.R.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Phlorotannins with potential anti-tyrosinase and antioxidant activity isolated from the marine seaweed Ecklonia stolonifera. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.H.; Castaneda, H.G. Preparation and chromatographic analysis of phlorotannins. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 51, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Son, B.W.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Inhibitory phlorotannins from the edible brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera on total reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.C.; Cha, S.H.; Wijesinghe, W.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, E.A.; Song, C.B.; Jeon, Y.J. Protective effect of marine algae phlorotannins against AAPH-induced oxidative stress in zebrafish embryo. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Y.J.; Lee, M.; Shin, T.; Yoon, N.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.R. Eckol enhances heme oxygenase-1 expression through activation of Nrf2/JNK pathway in HepG2 cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 15638–15652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.C.; Kang, K.A.; Zhang, R.; Piao, M.J.; Kim, G.Y.; Kang, M.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, N.H.; Surh, Y.J.; Hyun, J.W. Up-regulation of Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression by eckol, a phlorotannin compound, through activation of Erk and PI3K/Akt. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Shin, T.S.; Lee, M.S.; Park, J.Y.; Park, K.E.; Yoon, N.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, J.S.; Jang, B.C.; Byun, D.S.; et al. Isolation and identification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Kang, K.; Jeon, J.S.; Jho, E.H.; Kim, C.Y.; Nho, C.W.; Um, B.H. Isolation of phlorotannins from Eisenia bicyclis and their hepatoprotective effect against oxidative stress induced by tert-butyl hyperoxide. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 165, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Youn, K.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, M.R.; Yoon, E.; Kim, O.Y.; Jun, M. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Property of Phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava on Aβ25-35-Induced Damage in PC12 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J. Protective Effect of Eckol against Acute Hepatic Injury Induced by Carbon Tetrachloride in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, E300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, S.; Yan, D.; Wang, J. Eckol inhibits Reg3A-induced proliferation of human SW1990 pancreatic cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. 2019, 18, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Guo, J.; Hu, X.M.; Zhao, S.Q.; Li, S.L.; Wang, J. An in vivo anti-tumor effect of eckol from marine brown algae by improving the immune response. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jun, M. Dual BACE1 and Cholinesterase Inhibitory Effects of Phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava-An In Vitro and in Silico Study. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, E91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, A.X.; Hyun, Y.J.; Piao, M.J.; Fernando, P.D.S.M.; Kang, K.A.; Ahn, M.J.; Yi, J.M.; Kang, H.K.; Koh, Y.S.; Lee, N.H.; et al. Eckol Inhibits Particulate Matter 2.5-Induced Skin Keratinocyte Damage via MAPK Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, E444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.H. Does exposure to indoor allergens contribute to the development of asthma and allergy? Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010, 10, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, S.S.; Mistry, K.J.; Kakade, A.M.; Niphadkar, P.V. Role played by Th2 type cytokines in IgE mediated allergy and asthma. Lung India. 2010, 27, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Gordon, J.R.; Wershil, B.K. Cytokine production by mast cells and basophils. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1991, 3, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczyk, C.; Frandji, P.; Botros, H.G.; Poncet, P.; Lapeyre, J.; Peronet, R.; David, B.; Mécheri, S. Mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells and mast cell lines constitutively produce B cell growth and differentiation activities. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, K.; Tsai, M.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells as sources of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakahara, S.; Fujii, Y.; Nakao, T.; Tsuritani, K.; Hara, T.; Saito, H.; Ra, C. Gene expression profiles for FcεRI, cytokines and chemokines upon FcεRI activation in human cultured mast cells derived from peripheral blood. Cytokine 2001, 16, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakimi, J.C.; Seals, J.A.; Kondas, L.; Pettine, W.; Danko, W.; Kochan, J. The α subunit of the human IgE receptor (FcεRI) is sufficient for high affinity IgE binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 22079–22081. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siraganian, R.P. Mast cell signal transduction from the high-affinity IgE receptor. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, G.; Amagai, Y.; Matsuda, A.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, W.W.; Jung, K.S.; Oida, K.; Kang, H.; Ishizaka, S.; Matsuda, K.; et al. Dieckol, a phlorotannin of Ecklonia cava, suppresses IgE-mediated mast cell activation and passive cutaneous anaphylactic reaction. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 968–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, H.; Killoran, K.E.; Mitre, E. Measuring local anaphylaxis in mice, Journal of visualized experiments. JoVE 2014, 92, e52005. [Google Scholar]
- Kinet, J.P.; Blank, U.; Brini, A.; Jouvin, M.H.; Kuster, H.; Mejan, O.; Ra, C. The high affinity receptor for immunologlobulin E: A target for therapy of allergic diseases. Int. Arch. Aller. Immunol. 1991, 94, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaven, M.A.; Metzer, H. Signal transduction by Fc receptors: The FcεRI case. Immunol. Today 1993, 14, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Takatsu, K. Role of cytokines in allergic airway inflammation. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 142, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; Douglas, I.; Jahnke, A.; Ghosh, S.; Pober, J.S. A sustained reduction in IkB-β may contribute to persistent NF-kB activation in human endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 16317–16322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.J.; Hwang, Y.J.; Yang, H.J.; Park, K.I. Effect of Rhus verniciflua extract on IgE-antigen-mediated allergic reaction in rat basophilic leukemic RBL-2H3 mast cells and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in mice. Evid. Based Complement Altermat. Med. 2019, 6497691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiuru, P.; D’Auria, M.V.; Muller, C.D.; Tammela, P.; Vuorela, H.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J. Exploring marine resources for bioactive compounds. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loureiro, C.; Medema, M.H.; van der Oost, J.; Sipkema, D. Exploration and exploitation of the environment for novel specialized metabolites. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 50, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Le, Q.T.; Kim, M.M.; Kim, S.K. Anti-allergic Effects of Phlorotannins on Histamine Release via Binding Inhibition between IgE and FcεRI. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 12073–12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessner, A.; Mohrs, K.; Mohrs, M. Mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils acquire constitutive IL-4 and IL-13 transcripts during lineage differentiation that are sufficient for rapid cytokine production. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, J.J.; Baker, B.; Ryan, J.J. Mast cell production and response to IL-4 and IL-13. Cytokine 2015, 75, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, E.J.; Kim, H.-S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Herath, K.H.I.N.M.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Jee, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, T.; Shim, S.-Y.; Ahn, G. Eckol from Ecklonia cava Suppresses Immunoglobulin E-mediated Mast Cell Activation and Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis in Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051361
Han EJ, Kim H-S, Sanjeewa KKA, Herath KHINM, Jeon Y-J, Jee Y, Lee J, Kim T, Shim S-Y, Ahn G. Eckol from Ecklonia cava Suppresses Immunoglobulin E-mediated Mast Cell Activation and Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis in Mice. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051361
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Eui Jeong, Hyun-Soo Kim, K.K.A. Sanjeewa, K.H.I.N.M. Herath, You-Jin Jeon, Youngheun Jee, Jeongjun Lee, Taehee Kim, Sun-Yup Shim, and Ginnae Ahn. 2020. "Eckol from Ecklonia cava Suppresses Immunoglobulin E-mediated Mast Cell Activation and Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis in Mice" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051361
APA StyleHan, E. J., Kim, H.-S., Sanjeewa, K. K. A., Herath, K. H. I. N. M., Jeon, Y.-J., Jee, Y., Lee, J., Kim, T., Shim, S.-Y., & Ahn, G. (2020). Eckol from Ecklonia cava Suppresses Immunoglobulin E-mediated Mast Cell Activation and Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis in Mice. Nutrients, 12(5), 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051361






