Acute and Subacute Oral Toxicity of Mumefural, Bioactive Compound Derived from Processed Fruit of Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc., in ICR Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Material
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Acute Toxicity Study
2.4. Subacute (4 Weeks) Toxicity Study
2.4.1. General Observations
2.4.2. Clinical Pathology
2.4.3. Necropsy and Organ Weight Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity Study
3.2. Subacute (4 Weeks) Toxicity Study
3.2.1. Mortality and Clinical Signs
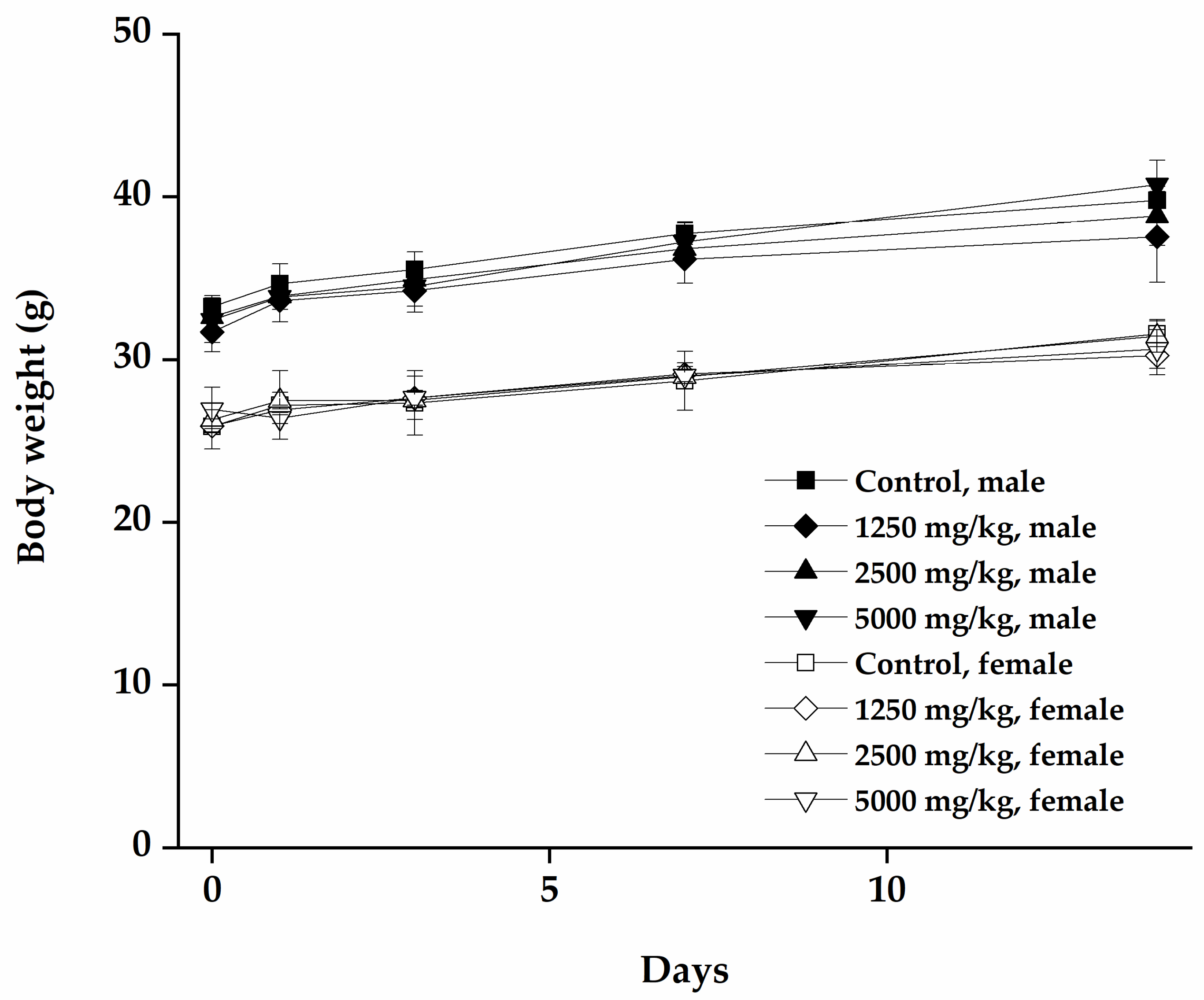
3.2.2. Changes in Body Weight and Food Consumption
3.2.3. Hematology and Serum Biochemistry
3.2.4. Relative Organ Weights and Necropsy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, B.; Shin, M. Encyclopedia of Illustrated Korean Natural Drugs; Young Lim Sa: Seoul, Korea, 1990; p. 845. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, A.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Park, J.; Kye, S.; Benza, R.L.; Passineau, M.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Nyunoya, T. A Novel Compound, “FA-1” Isolated from Prunus mume, Protects Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells and Keratinocytes from Cigarette Smoke Extract-Induced Damage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.L. Essentials of Chinese Medicine; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 2, p. 273. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, M. A Systematic Review of Ume Health Benefits; St. Catherine University: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2016; 5-2016. [Google Scholar]
- Takemura, S.; Yoshimasu, K.; Fukumoto, J.; Mure, K.; Nishio, N.; Kishida, K.; Yano, F.; Mitani, T.; Takeshita, T.; Miyashita, K. Safety and adherence of Umezu polyphenols in the Japanese plum (Prunus mume) in a 12-week double-blind randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial to evaluate antihypertensive effects. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2014, 19, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, B.S.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S.; Ryuk, J.A.; Park, S. Prunus mume and Lithospermum erythrorhizon Extracts Synergistically Prevent Visceral Adiposity by Improving Energy Metabolism through Potentiating Hypothalamic Leptin and Insulin Signalling in Ovariectomized Rats. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. ECAM 2013, 2013, 750986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, T.; Takagi, H.; Naganuma, A.; Koitabashi, E.; Uehara, S.; Sakamoto, N.; Kudo, T.; Sato, K.; Kakizaki, S. Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma responds to MK615, a compound extract from the Japanese apricot “Prunus mume”. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, K.; Kawahara, K.; Matsushita, S.; Hashiguchi, T.; Maruyama, I.; Kanekura, T. MK615, a Prunus mume Steb. Et Zucc (‘Ume’) extract, attenuates the growth of A375 melanoma cells by inhibiting the ERK1/2-Id-1 pathway. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta, A.; Accinni, R.; Dellanoce, C.; Tonini, A.; Cardot, J.M.; Bussiere, A. Efficacy of a Standardized Extract of Prunus mume in Liver Protection and Redox Homeostasis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.P.; Heo, M.Y. Biological screening of 100 plant extracts for cosmetic use (II): Anti-oxidative activity and free radical scavenging activity. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 1997, 19, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Bang, J.H.; Lee, J.; Han, J.S.; Kang, H.W.; Jeon, W.K. Fructus mume Ethanol Extract Prevents Inflammation and Normalizes the Septohippocampal Cholinergic System in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Bang, J.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, I.S.; Han, J.S.; Hwang, B.Y.; Jeon, W.K. Fructus mume alleviates chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced white matter and hippocampal damage via inhibition of inflammation and downregulation of TLR4 and p38 MAPK signaling. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, T.; Ota, K.; Inaba, N.; Kishida, K.; Koyama, H.A. Antimicrobial Activity of the Phenolic Compounds of Prunus mume against Enterobacteria. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Ma, J.; Jeon, W.K.; Han, J.S. Fructus mume extracts alleviate cognitive impairments in 5XFAD transgenic mice. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Jeon, W.K.; Lee, K.W.; Park, Y.H.; Han, J.S. Ameliorating Effects of Ethanol Extract of Fructus mume on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. ECAM 2015, 2015, 102734. [Google Scholar]
- Chuda, Y.; Ono, H.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Nagata, T.; Kikuchi, Y. Mumefural, citric acid derivative improving blood fluidity from fruit-juice concentrate of Japanese apricot (Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showing Metabocard for Mumefural (HMDB0035179). Available online: https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0035179 (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Sun, M.-F.; Chang, T.-T.; Chen, K.-C.; Yang, S.-C.; Chang, K.-W.; Tsung-Ying, T.; Chen, H.-Y.; Tsai, F.-J.; Lin, J.-G.; Chen, C. Treat Alzheimer’s disease by traditional Chinese medicine? Mol. Simul. 2011, 37, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Chang, S.S.; Chan, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y. Discovery of novel insomnia leads from screening traditional Chinese medicine database. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 32, 776–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Kadowaki, A.; Onishi, Y.; Gato, N.; Ujike, M.; Odagiri, T.; Tashiro, M.; Suzuki, Y. Mumefural and related HMF derivatives from Japanese apricot fruit juice concentrate show multiple inhibitory effects on pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Kim, M.S.; Jeon, W.K. Mumefural Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion via Regulating the Septohippocampal Cholinergic System and Neuroinflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimura, H.; Kikuchi, M.; Kato, S.; Sekita, W.; Sasaki, I. Practical synthesis of mumefural, a component of Japanese apricot juice concentrate. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 7638–7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, H.; Gato, N.; Nagatomo, H.; Chuda, Y.; Ono, H.; Yoshida, M. Quantitative analysis method for mumefural in Japanese apricot fruit [Prunus mume] juice concentrate. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. (Jpn.) 2003, 50, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneyuki, M. Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and its Implementation in Japan. Natl. Inst. Occup. Saf. Health 2010, 65, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.P.; Dinger, N.; Levine, B.S. Stress produced by gavage administration in the rat. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2000, 39, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arantes-Rodrigues, R.; Henriques, A.; Pinto-Leite, R.; Faustino-Rocha, A.; Pinho-Oliveira, J.; Teixeira-Guedes, C.; Seixas, F.; Gama, A.; Colaco, B.; Colaco, A.; et al. The effects of repeated oral gavage on the health of male CD-1 mice. Lab Anim. (N. Y.) 2012, 41, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-S.; Han, C.-H.; Lee, C.; Hwang, B.-Y.; Jung, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jeon, W.-K. Simultaneous determination and acute toxicity study of Fructus mume extracts in ICR mice. J. Soc. Prev. Korean Med. 2011, 15, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, M.; Kume, H.; Kadowaki, A.; Gato, N.; Nishihira, J. Effects and safety of daily ingestion of plum extract on blood pressure:randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled parallel group comparison study. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2017, 7, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middendorf, P.J.; Williams, P.L. Nephrotoxicity: Toxic responses of the kidney. Princ. Toxicol. Environ. Ind. Appl. 2000, 129–143. [Google Scholar]
- Mebius, R.E.; Kraal, G. Structure and function of the spleen. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Control | 1250 mg/kg | 2500 mg/kg | 5000 mg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ||||
| No observable abnormality | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 |
| Female | ||||
| No observable abnormality | 3/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 2/3 |
| Increased respiration rate | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 |
| Squeak | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 |
| Piloerection | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 |
| Decreased locomotor activity | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 |
| Dose (mg/kg) | Survival a | Mean Body Weight (g) | Final Weight Relative to Control (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Change | ||||
| Male | ||||||
| Control | 3/3 | 33.2 ± 0.69 | 39.8 ± 1.11 | 6.6 ± 0.42 | ||
| 1250 | 3/3 | 31.7 ± 1.22 | 37.5 ± 2.79 | 5.8 ± 2.20 | 94.22 | |
| 2500 | 3/3 | 32.6 ± 0.80 | 38.8 ± 1.81 | 6.2 ± 2.61 | 97.49 | |
| 5000 | 3/3 | 32.4 ± 1.38 | 40.8 ± 1.49 | 8.3 ± 1.37 | 102.51 | |
| Female | ||||||
| Control | 3/3 | 25.9 ± 1.40 | 31.6 ± 0.79 | 5.7 ± 0.69 | ||
| 1250 | 3/3 | 25.9 ± 0.42 | 30.2 ± 1.18 | 4.3 ± 1.13 | 95.57 | |
| 2500 | 3/3 | 26.3 ± 0.58 | 31.4 ± 1.00 | 5.1 ± 1.24 | 99.97 | |
| 5000 | 3/3 | 26.92 ± 1.38 | 30.6 ± 1.18 | 3.7 ± 0.21 | 96.84 | |
| Control | 1250 mg/kg | 2500 mg/kg | 5000 mg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ||||
| No observable abnormality | 5/5 | 4/5 | 5/5 | 5/5 |
| Constantly squeaked | 0/5 | 1/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 |
| Female | ||||
| No observable abnormality | 5/5 | 5/5 | 4/5 | 5/5 |
| Death | 0/5 | 0/5 | 1/5 | 0/5 |
| Dose (mg/kg) | Survival a | Mean Body Weight (g) | Final Weight Relative to Control (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Change | ||||
| Male | ||||||
| Control | 5/5 | 32.9 ± 1.63 | 36.9 ± 4.20 | 4.0 ± 2.89 | ||
| 1250 | 5/5 | 33.3 ± 1.54 | 35.4 ± 2.49 | 2.0 ± 1.03 | 95.93 | |
| 2500 | 5/5 | 32.9 ± 1.76 | 35.8 ± 1.73 | 2.9 ± 2.46 | 97.02 | |
| 5000 | 5/5 | 32.2 ± 1.36 | 34.2 ± 2.53 | 2.0 ± 3.60 | 92.68 | |
| Female | ||||||
| Control | 5/5 | 25.5 ± 1.11 | 29.6 ± 0.70 | 4.1 ± 0.71 | ||
| 1250 | 5/5 | 25.2 ± 1.29 | 28.8 ± 0.93 | 3.6 ± 0.46 | 90.18 | |
| 2500 | 4/5 | 25.4 ± 1.48 | 27.4 ± 1.57 | 1.5 ± 1.80 | 92.57 | |
| 5000 | 5/5 | 25.8 ± 1.25 | 28.3 ± 1.34 | 2.5 ± 0.68 * | 95.61 | |
| Day | Control | Food Consumption (g/day) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1250 mg/kg | 2500 mg/kg | 5000 mg/kg | ||
| Male | ||||
| 1 | 5.4 ± 0.91 | 5.4 ± 0.77 | 5.3 ± 0.66 | 4.6 ± 2.12 |
| 7 | 4.7 ± 1.00 | 5.4 ± 0.85 | 5.1 ± 0.33 | 5.2 ± 0.65 |
| 14 | 4.4 ± 0.31 | 4.8 ± 1.23 | 5.2 ± 1.23 | 4.3 ± 0.73 |
| 21 | 5.0 ± 0.82 | 5.2 ± 0.23 | 4.2 ± 1.07 | 4.6 ± 0.23 |
| 27 | 4.6 ± 0.62 | 5.5 ± 1.00 | 4.5 ± 0.76 | 4.6 ± 0.63 |
| Female | ||||
| 1 | 5.1 ± 0.57 | 3.4 ± 0.65 | 3.8 ± 2.97 | 3.7 ± 0.53 |
| 7 | 4.5 ± 0.04 | 4.9 ± 0.25 | 4.0 ± 0.34 | 5.0 ± 0.79 |
| 14 | 4.4 ± 0.54 | 4.4 ± 0.63 | 3.8 ± 0.05 | 4.5 ± 0.68 |
| 21 | 4.5 ± 0.80 | 3.2 ± 0.21 | 4.1 ± 0.65 | 4.5 ± 0.73 |
| 27 | 4.6 ± 0.06 | 3.8 ± 0.07 * | 3.7 ± 0.24 | 5.0 ± 1.07 |
| Control | 1250 mg/kg | 2500 mg/kg | 5000 mg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ||||
| WBC (103/μL) | 1.26 ± 0.92 | 1.37 ± 0.26 | 1.26 ± 0.56 | 0.96 ± 0.43 |
| RBC (106/μL) | 8.70 ± 0.75 | 9.00 ± 0.49 | 9.17 ± 0.34 | 8.88 ± 0.28 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 13.9 ± 1.0 | 14.4 ± 0.7 | 14.2 ± 0.8 | 14.3 ± 0.3 |
| HCT (%) | 44.8 ± 3.6 | 45.8 ± 2.0 | 45.8 ± 1.7 | 45.8 ± 0.8 |
| MCV (fL) | 51.5 ± 0.6 | 50.9 ± 1.4 | 50.0 ± 0.9 | 51.6 ± 0.8 |
| MCH (pg) | 16.0 ± 0.4 | 16.0 ± 0.6 | 15.4 ± 0.3 | 16.1 ± 0.4 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 31.1 ± 0.5 | 31.4 ± 0.5 | 30.9 ± 0.6 | 31.1 ± 0.5 |
| RDW (%) | 12.1 ± 0.3 | 12.3 ± 0.6 | 12.1 ± 0.8 | 12.3 ± 0.4 |
| HDW (g/dL) | 2.05 ± 0.09 | 2.11 ± 0.09 | 2.06 ± 0.07 | 2.12 ± 0.13 |
| PLT (103/μL) | 1130.6 ± 165.3 | 1231.4 ± 144.5 | 1236.0 ± 153.9 | 1190.0 ± 148.2 |
| MPV (fL) | 4.88 ± 0.33 | 4.86 ± 0.40 | 4.82 ± 0.31 | 4.88 ± 0.28 |
| NEU (%) | 18.8 ± 14.7 | 18.4 ± 6.8 | 23.3 ± 6.4 | 21.4 ± 6.2 |
| LYM (%) | 66.1 ± 25.8 | 73.6 ± 12.4 | 67.9 ± 7.0 | 73.3 ± 6.2 |
| MONO (%) | 0.60 ± 0.29 | 3.24 ± 5.69 | 1.42 ± 1.07 | 0.70 ± 0.24 |
| EOS (%) | 13.88 ± 23.73 | 4.30 ± 2.96 | 6.30 ± 6.38 | 3.80 ± 1.56 |
| BASO (%) | 0.12 ± 0.08 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.08 | 0.02 ± 0.04 |
| LUC (%) | 0.40 ± 0.16 | 0.38 ± 0.13 | 0.90 ± 0.80 | 0.76 ± 1.20 |
| Female | ||||
| WBC (103/μL) | 2.11 ± 1.23 | 2.00 ± 0.64 | 2.00 ± 1.17 | 2.59 ± 2.19 |
| RBC (106/μL) | 9.00 ± 0.39 | 9.20 ± 0.69 | 8.72 ± 0.23 | 9.04 ± 0.53 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 14.5 ± 0.8 | 14.4 ± 0.7 | 13.9 ± 0.2 | 14.3 ± 0.9 |
| HCT (%) | 45.9 ± 1.9 | 46.1 ± 2.7 | 45.2 ± 0.8 | 45.6 ± 2.9 |
| MCV (fL) | 51.1 ± 0.6 | 50.2 ± 1.2 | 51.8 ± 1.0 | 50.4 ± 1.4 |
| MCH (pg) | 16.1 ± 0.5 | 15.7 ± 0.5 | 15.9 ± 0.4 | 15.8 ± 0.6 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 31.6 ± 0.8 | 31.4 ± 0.5 | 30.8 ± 0.7 | 31.5 ± 0.4 |
| RDW (%) | 12.6 ± 0.5 | 12.4 ± 0.4 | 13.0 ± 0.2 | 13.3 ± 0.8 |
| HDW (g/dL) | 2.13 ± 0.07 | 2.14 ± 0.08 | 2.20 ± 0.08 | 2.17 ± 0.06 |
| PLT (103/μL) | 1292.8 ± 135.5 | 1165.6 ± 91.9 | 1084.8 ± 77.2 | 1218.2 ± 132.6 |
| MPV (fL) | 5.02 ± 0.55 | 4.90 ± 0.72 | 5.40 ± 0.79 | 5.32 ± 0.40 |
| NEU (%) | 14.3 ± 3.8 | 16.1 ± 3.1 | 16.3 ± 4.7 | 18.0 ± 7.4 |
| LYM (%) | 77.0 ± 6.7 | 78.9 ± 3.7 | 77.6 ± 5.0 | 76.4 ± 8.0 |
| MONO (%) | 0.90 ± 0.29 | 0.60 ± 0.25 | 0.95 ± 0.50 | 0.62 ± 0.27 |
| EOS (%) | 7.24 ± 4.39 | 3.96 ± 1.39 | 4.55 ± 0.45 | 4.40 ± 1.35 |
| BASO (%) | 0.24 ± 0.32 | 0.10 ± 0.07 | 0.13 ± 0.10 | 0.12 ± 0.08 |
| LUC (%) | 0.34 ± 0.11 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | 0.48 ± 0.10 | 0.48 ± 0.29 |
| Control | 1250 mg/kg | 2500 mg/kg | 5000 mg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ||||
| AST (U/L) | 62.6 ± 3.5 | 66.6 ± 26.5 | 60.5 ± 6.0 | 66.8 ± 8.5 |
| ALT (U/L) | 34.6 ± 3.4 | 31.4 ± 4.4 | 30.5 ± 7.0 | 37.2 ± 10.9 |
| ALP (U/L) | 71.9 ± 20.7 | 68.2 ± 15.5 | 73.3 ± 6.2 | 71.6 ± 20.9 |
| CPK (U/L) | 89.6 ± 36.0 | 104.4 ± 67.3 | 94.2 ± 18.9 | 77.2 ± 26.2 |
| TBIL (mg/dL) | 0.182 ± 0.048 | 0.151 ± 0.033 | 0.149 ± 0.036 | 0.145 ± 0.042 |
| GLU (mg/dL) | 205.9 ± 39.2 | 207.2 ± 38.0 | 193.2 ± 43.5 | 180.3 ± 62.2 |
| TCHO (mg/dL) | 217.8 ± 22.0 | 196.8 ± 25.7 | 197.2 ± 49.6 | 183.2 ± 50.2 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 72.0 ± 18.6 | 85.4 ± 31.4 | 58.0 ± 11.3 | 63.8 ± 19.2 |
| TP (g/dL) | 5.55 ± 0.14 | 5.33 ± 0.27 | 5.24 ± 0.11 * | 5.28 ± 0.11 |
| ALB (g/dL) | 2.68 ± 0.11 | 2.69 ± 0.19 | 2.68 ± 0.07 | 2.75 ± 0.05 |
| A/G ratio | 0.94 ± 0.05 | 1.02 ± 0.05 * | 1.05 ± 0.05 ** | 1.09 ± 0.07 ** |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 20.5 ± 1.4 | 23.3 ± 7.6 | 21.5 ± 6.8 | 19.2 ± 6.8 |
| CRE (mg/dL) | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.03 |
| IP (mg/dL) | 8.67 ± 0.77 | 7.50 ± 1.19 | 6.59 ± 1.40 | 7.30 ± 1.10 |
| Ca2+ (mg/dL) | 9.07 ± 0.33 | 9.11 ± 0.22 | 8.92 ± 0.22 | 8.77 ± 0.23 |
| Na+ (mmol/L) | 147.7 ± 6.3 | 152.8 ± 0.7 | 149.8 ± 6.8 | 149.4 ± 5.5 |
| K+ (mmol/L) | 5.23 ± 0.35 | 5.45 ± 0.35 | 5.49 ± 0.50 | 4.98 ± 0.47 |
| Cl− (mmol/L) | 112.9 ± 3.5 | 117.9 ± 1.6* | 119.0 ± 3.9 ** | 117.9 ± 2.8 * |
| Female | ||||
| AST (U/L) | 115.8 ± 83.6 | 85.4 ± 14.8 | 114.1 ± 42.3 | 87.4 ± 28.5 |
| ALT (U/L) | 37.0 ± 17.8 | 35.4 ± 13.1 | 49.0 ± 18.2 | 33.0 ± 5.1 |
| ALP (U/L) | 76.5 ± 11.8 | 103.9 ± 24.9 | 84.3 ± 3.0 | 89.3 ± 24.5 |
| CPK (U/L) | 94.6 ± 39.9 | 81.3 ± 34.9 | 151.3 ± 112.2 | 120.2 ± 50.5 |
| TBIL (mg/dL) | 0.097 ± 0.046 | 0.066 ± 0.036 | 0.093 | 0.083 ± 0.018 |
| GLU (mg/dL) | 190.7 ± 24.6 | 171.6 ± 37.6 | 205.4 ± 75.1 | 165.0 ± 28.2 |
| TCHO (mg/dL) | 137.4 ± 18.9 | 127.3 ± 32.2 | 132.0 ± 30.0 | 92.4 ± 22.6 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 51.2 ± 10.0 | 68.3 ± 16.1 | 60.0 ± 11.2 | 50.6 ± 8.1 |
| TP (g/dL) | 5.31 ± 0.03 | 5.50 ± 0.16 | 5.25 ± 0.15 | 5.19 ± 0.20 |
| ALB (g/dL) | 2.94 ± 0.10 | 3.08 ± 0.08 | 2.93 ± 0.11 | 2.91 ± 0.14 |
| A/G ratio | 1.24 ± 0.09 | 1.27 ± 0.05 | 1.26 ± 0.03 | 1.28 ± 0.09 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 18.4 ± 3.7 | 18.8 ± 5.0 | 17.7 ± 5.0 | 19.8 ± 5.7 |
| CRE (mg/dL) | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.01 |
| IP (mg/dL) | 8.81 ± 1.55 | 7.47 ± 1.37 | 8.59 ± 2.48 | 7.44 ± 0.78 |
| Ca2+ (mg/dL) | 9.06 ± 0.36 | 9.26 ± 0.39 | 8.94 ± 0.25 | 9.20 ± 0.14 |
| Na+ (mmol/L) | 147.3 ± 5.6 | 151.7 ± 2.1 | 152.4 ± 2.0 | 154.4 ± 1.4 * |
| K+ (mmol/L) | 6.35 ± 0.48 | 5.79 ± 0.44 | 6.54 ± 0.94 | 5.14 ± 0.43 * |
| Cl− (mmol/L) | 112.6 ± 2.3 | 115.6 ± 1.9 | 120.0 ± 3.9 * | 119.8 ± 2.8 * |
| Control | 1250 mg/kg | 2500 mg/kg | 5000 mg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ||||
| Final body weight (g) | 33.97 ± 4.41 | 32.89 ± 2.50 | 33.03 ± 1.92 | 30.93 ± 2.58 |
| Adrenal gland-left (% of body weight) | 0.0025 ± 0.0005 | 0.0029 ± 0.0004 | 0.0027 ± 0.0002 | 0.0026 ± 0.0004 |
| Adrenal gland-right (% of body weight) | 0.0026 ± 0.0004 | 0.0026 ± 0.0004 | 0.0024 ± 0.0005 | 0.0029 ± 0.0007 |
| Thymus (% of body weight) | 0.0490 ± 0.0195 | 0.0462 ± 0.0108 | 0.0459 ± 0.0179 | 0.0461 ± 0.0128 |
| Spleen (% of body weight) | 0.1054 ± 0.0191 | 0.0900 ± 0.0169 | 0.0812 ± 0.0105 * | 0.0796 ± 0.0079 * |
| Kidney-left (% of body weight) | 0.2505 ± 0.0350 | 0.2424 ± 0.0178 | 0.2504 ± 0.0173 | 0.2309 ± 0.0206 |
| Kidney-right (% of body weight) | 0.2528 ± 0.0344 | 0.2528 ± 0.0211 | 0.2658 ± 0.0142 | 0.2300 ± 0.0135 |
| Heart (% of body weight) | 0.1735 ± 0.0133 | 0.1564 ± 0.0167 | 0.1593 ± 0.0038 | 0.1569 ± 0.0169 |
| Lung (% of body weight) | 0.2170 ± 0.0239 | 0.1988 ± 0.0250 | 0.1947 ± 0.0105 | 0.2061 ± 0.0194 |
| Brain (% of body weight) | 0.4821 ± 0.0204 | 0.4839 ± 0.0238 | 0.4614 ± 0.0217 | 0.4904 ± 0.0335 |
| Liver (Gall bladder) (% of body weight) | 1.5452 ± 0.1490 | 1.7238 ± 0.3261 | 1.5987 ± 0.1777 | 1.4266 ± 0.2516 |
| Female | ||||
| Final body weight (g) | 27.30 ± 1.29 | 26.52 ± 1.03 | 25.74 ± 1.19 | 26.18 ± 1.84 |
| Adrenal gland-left (% of body weight) | 0.0061 ± 0.0014 | 0.0056 ± 0.0006 | 0.0062 ± 0.0012 | 0.0057 ± 0.0010 |
| Adrenal gland-right (% of body weight) | 0.0059 ± 0.0013 | 0.0049 ± 0.0005 | 0.0052 ± 0.0010 | 0.0051 ± 0.0010 |
| Thymus (% of body weight) | 0.0634 ± 0.0123 | 0.0682 ± 0.0226 | 0.0531 ± 0.0142 | 0.0537 ± 0.0164 |
| Spleen (% of body weight) | 0.1018 ± 0.0199 | 0.1014 ± 0.0281 | 0.0899 ± 0.0105 | 0.0982 ± 0.0213 |
| Kidney-left (% of body weight) | 0.1589 ± 0.0164 | 0.1616 ± 0.0123 | 0.1568 ± 0.0095 | 0.1639 ± 0.0223 |
| Kidney-right (% of body weight) | 0.1714 ± 0.0131 | 0.1778 ± 0.0118 | 0.1616 ± 0.0089 | 0.1657 ± 0.0170 |
| Heart (% of body weight) | 0.1301 ± 0.0049 | 0.1301 ± 0.0084 | 0.1271 ± 0.0135 | 0.1286 ± 0.0159 |
| Lung (% of body weight) | 0.1890 ± 0.0192 | 0.1833 ± 0.0186 | 0.1857 ± 0.0072 | 0.1947 ± 0.0101 |
| Brain (% of body weight) | 0.4791 ± 0.0172 | 0.4730 ± 0.0302 | 0.4583 ± 0.0184 | 0.4694 ± 0.0210 |
| Liver (Gall bladder) (% of body weight) | 1.1607 ± 0.0976 | 1.1848 ± 0.1420 | 1.1380 ± 0.0999 | 1.1288 ± 0.0933 |
| Control | 1250 mg/kg | 2500 mg/kg | 5000 mg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ||||
| No observable abnormality | 4/5 | 5/5 | 5/5 | 5/5 |
| Thymus size | 1/5 (Decreased size) | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 |
| Female | ||||
| No observable abnormality | 5/5 | 5/5 | 4/5 | 5/5 |
| Thymus size | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/4 | 0/5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Han, M.; Jeon, W.K. Acute and Subacute Oral Toxicity of Mumefural, Bioactive Compound Derived from Processed Fruit of Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc., in ICR Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051328
Kim J, Han M, Jeon WK. Acute and Subacute Oral Toxicity of Mumefural, Bioactive Compound Derived from Processed Fruit of Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc., in ICR Mice. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051328
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jungim, Mira Han, and Won Kyung Jeon. 2020. "Acute and Subacute Oral Toxicity of Mumefural, Bioactive Compound Derived from Processed Fruit of Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc., in ICR Mice" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051328
APA StyleKim, J., Han, M., & Jeon, W. K. (2020). Acute and Subacute Oral Toxicity of Mumefural, Bioactive Compound Derived from Processed Fruit of Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc., in ICR Mice. Nutrients, 12(5), 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051328





