Effect of Luteolin and Apigenin on the Production of Il-31 and Il-33 in Lipopolysaccharides-Activated Microglia Cells and Their Mechanism of Action
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.5. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
2.6. Measurement of Cytokine Production
2.7. Nuclear Protein Extraction and Western Blot
2.8. Immunofluorescence
2.9. NF-κB and STAT DNA Binding Activity Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
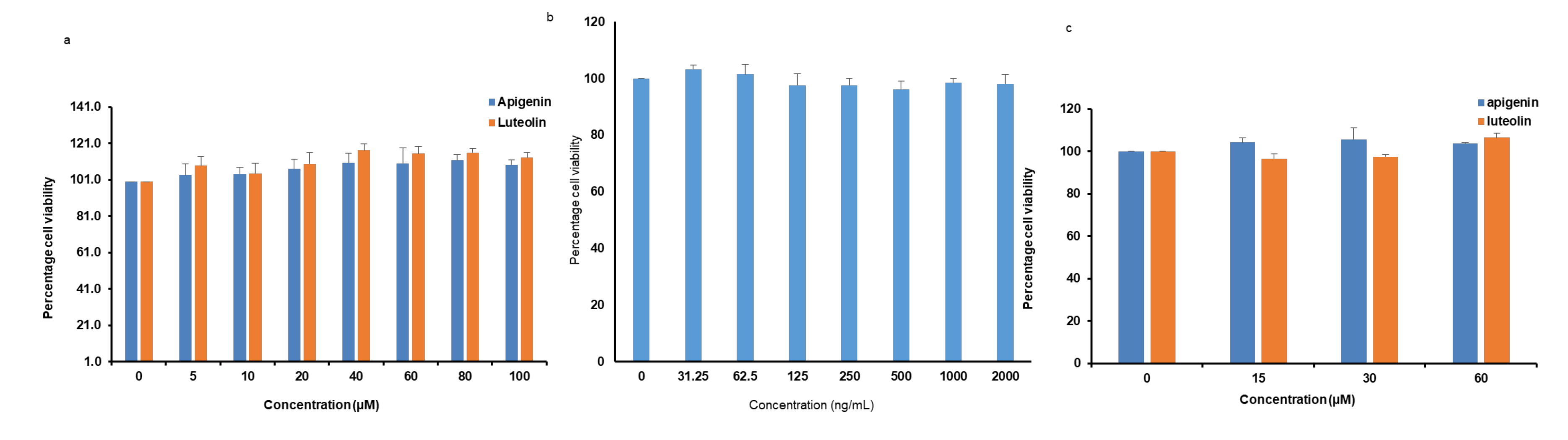
3.1. Effects of Apigenin, Luteolin, and LPS on Cytotoxicity to Microglia Cells
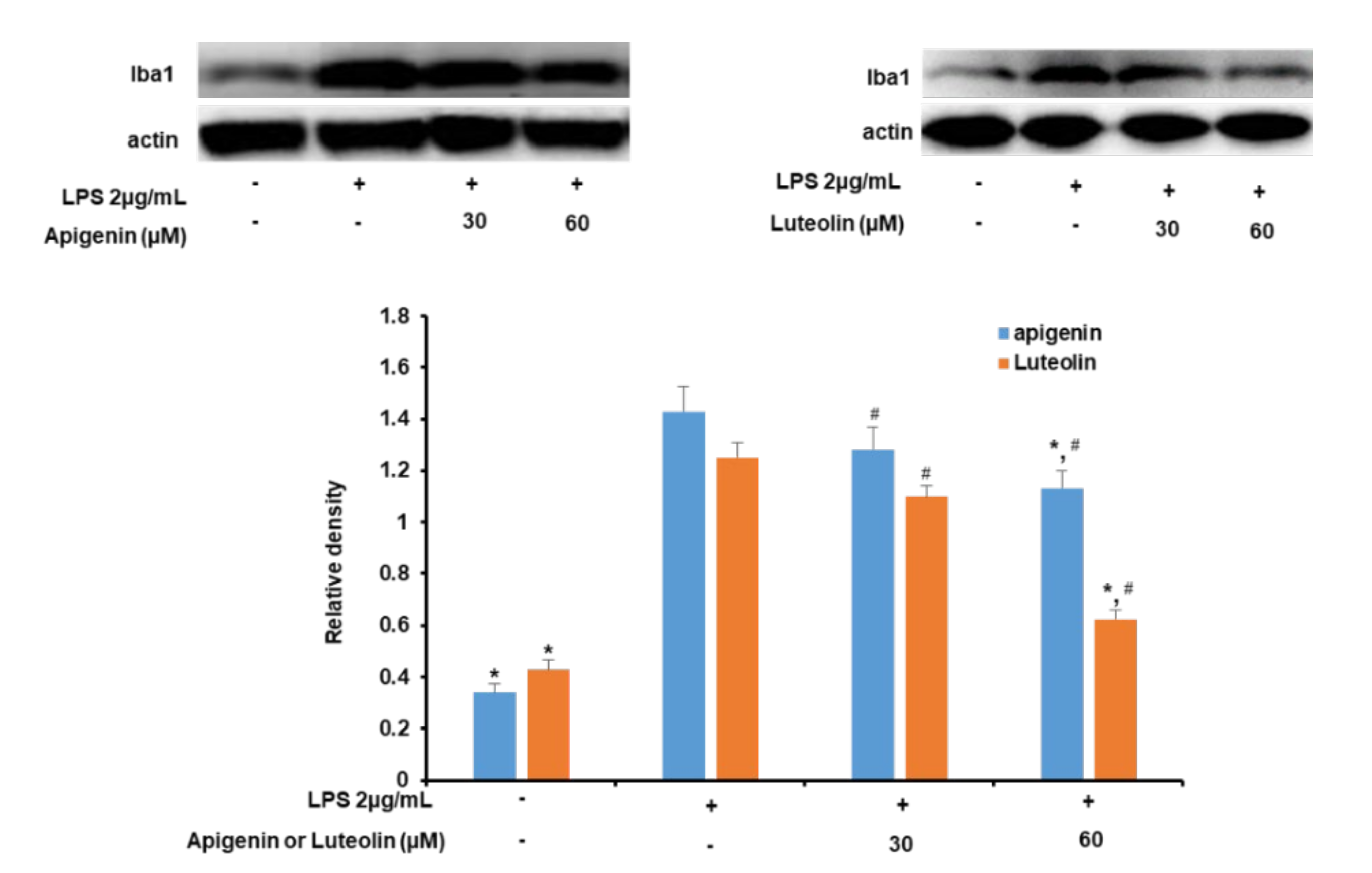
3.2. Effects of Apigenin and Luteolin on Iba-1 Expression in Stimulated Microglia
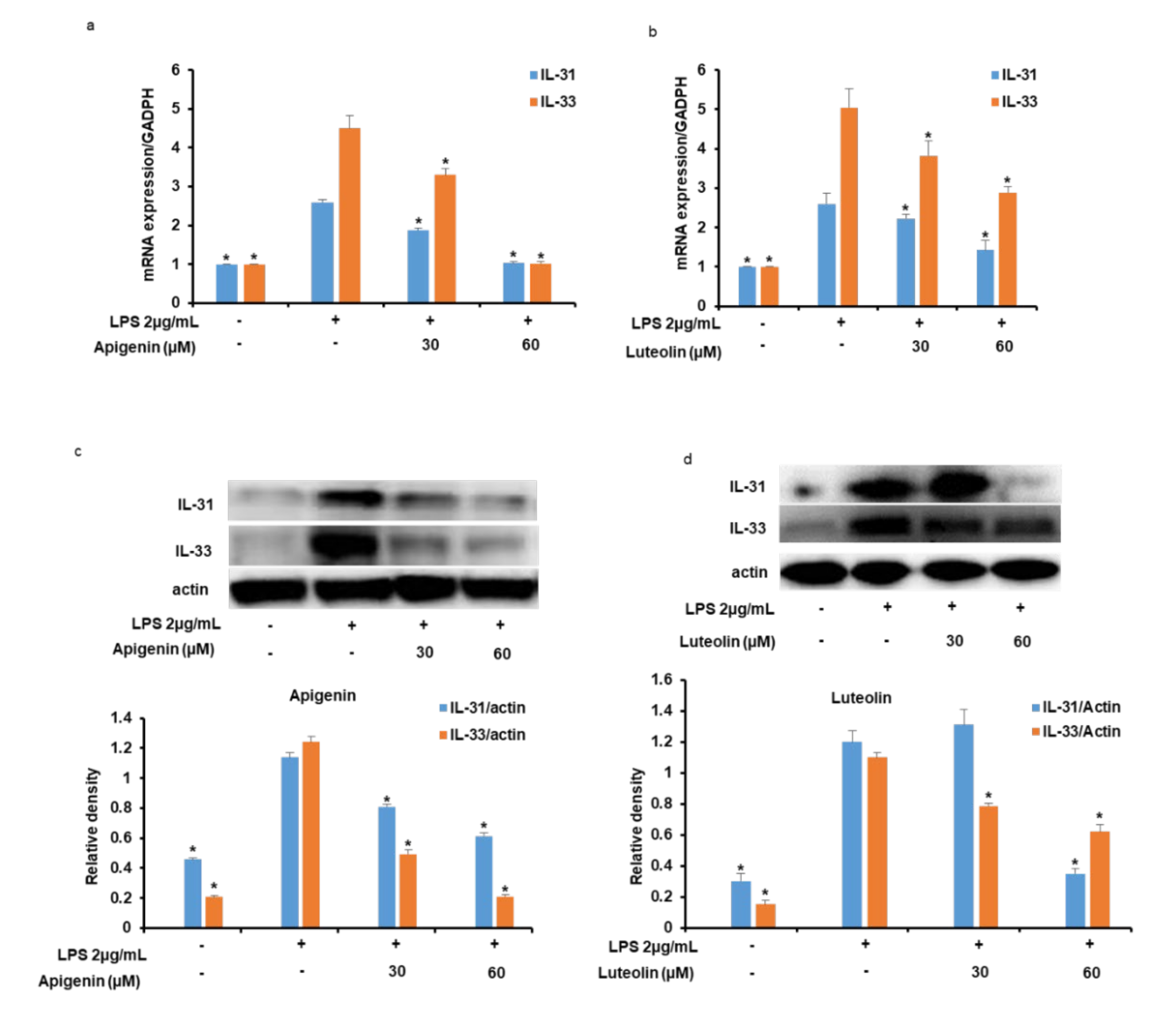
3.3. Effects of Apigenin and Luteolin on IL-31 and IL-33 mRNA and Protein Expression in Stimulated Microglia
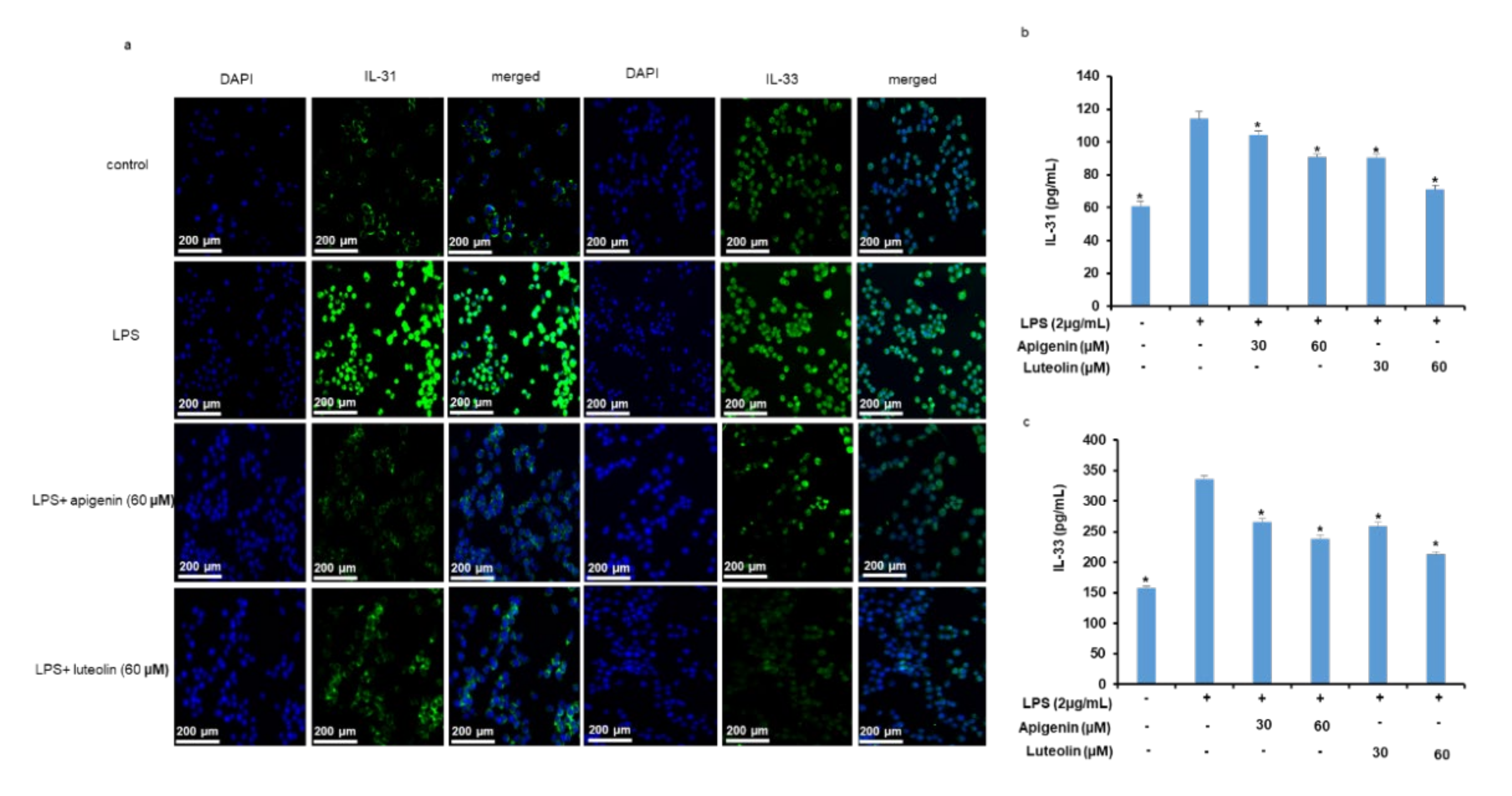
3.4. Effects of Apigenin and Luteolin on IL-31 and IL-33 Secretion In Stimulated Microglia
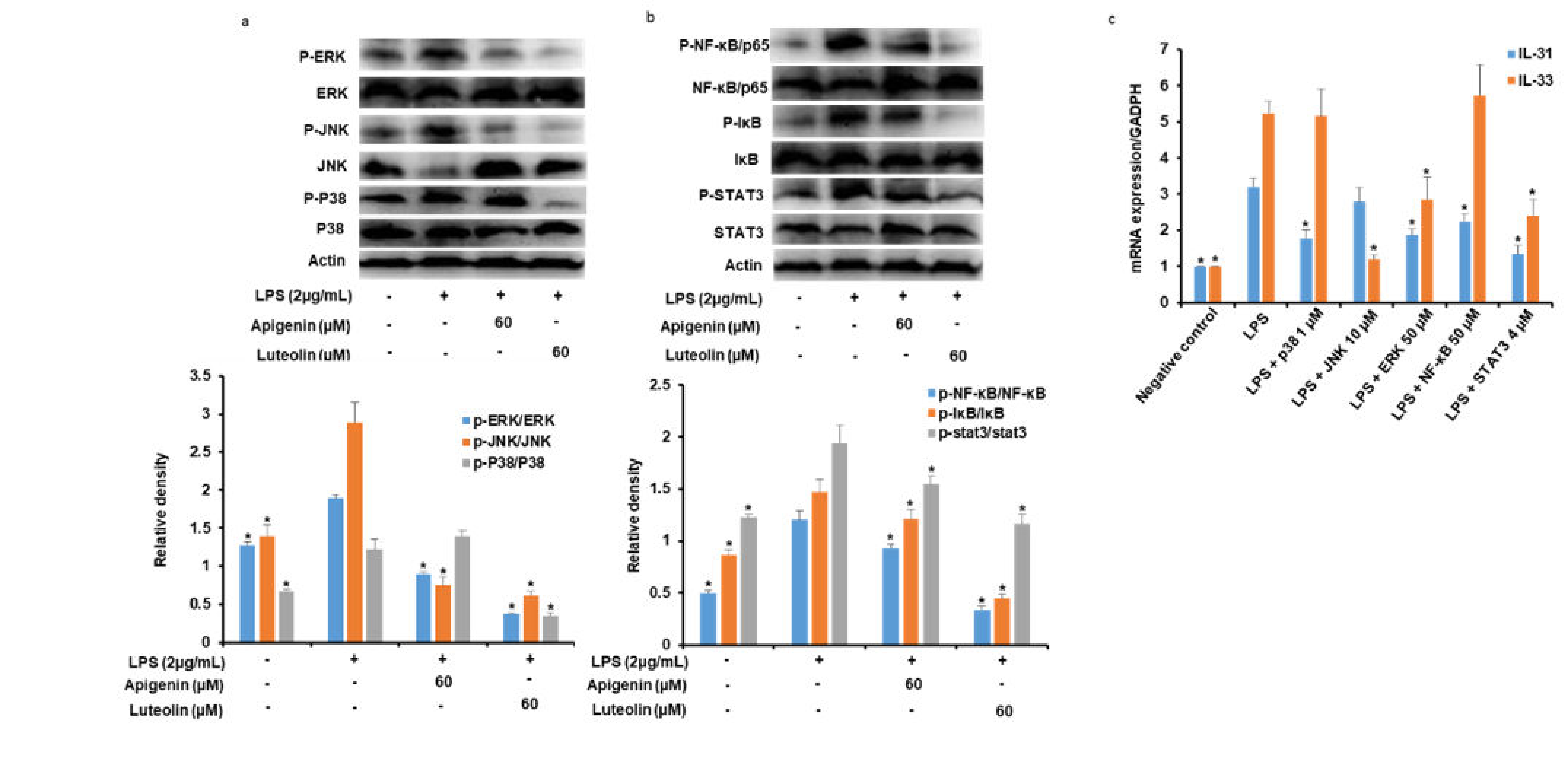
3.5. Effects of Apigenin and Luteolin on MAPK Pathway in Stimulated Microglia
3.6. Effects of Apigenin and Luteolin on NF-κB and STAT3Ppathways in Stimulated Microglia
3.7. Effects of Potent Inhibitors of MAPK, NF-κB, and STAT3 Pathways on IL-31 and IL-33 Production in Stimulated Microglia
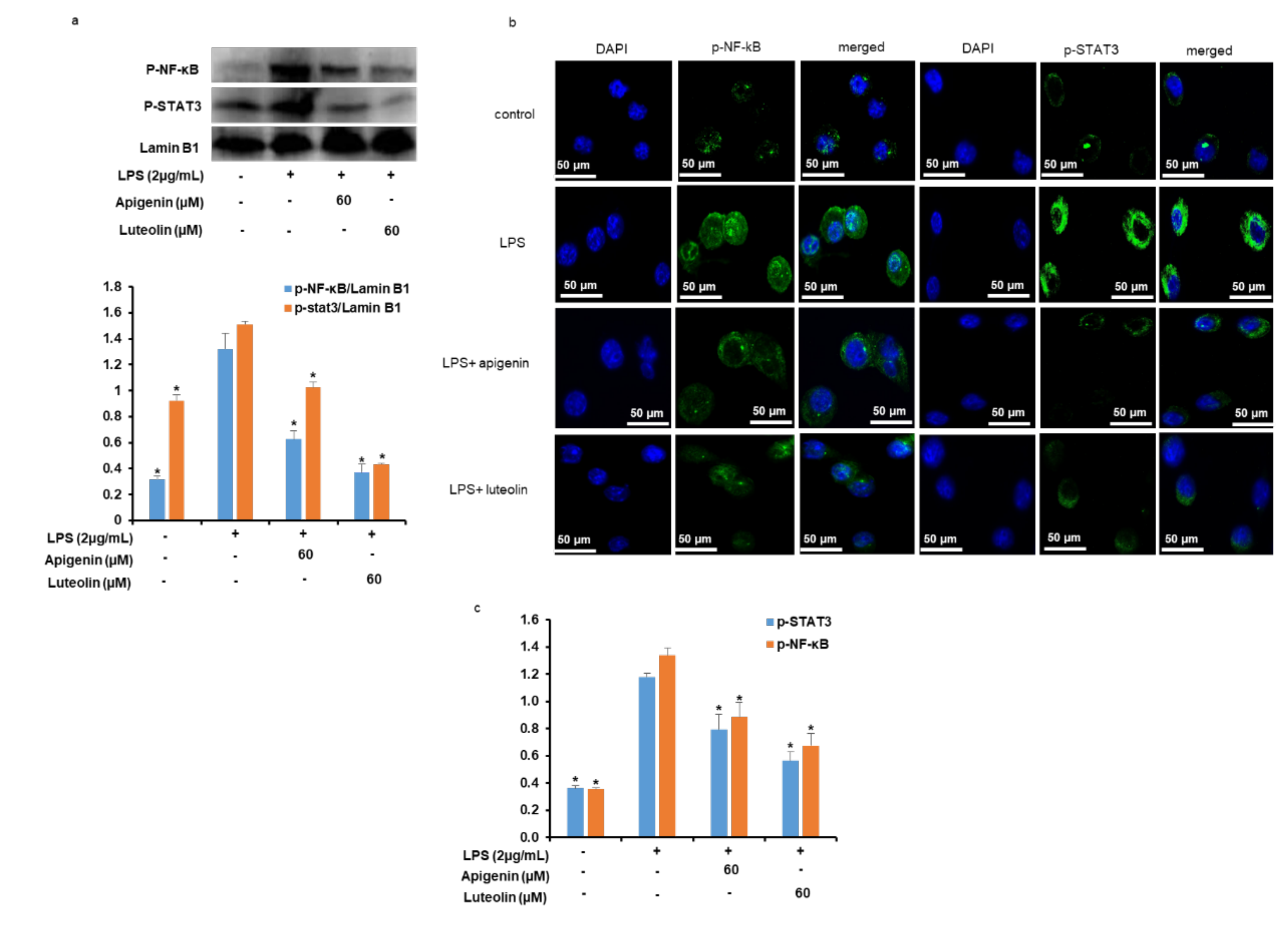
3.8. Effects of Apigenin and Luteolin on NF-κB/p65 and STAT3 Nuclear Translocation and DNA Binding Activities in Stimulated Microglia
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Askew, K.; Li, K.; Olmos-Alonso, A.; Garcia-Moreno, F.; Liang, Y.; Richardson, P.; Tipton, T.; Chapman, M.A.; Riecken, K.; Beccari, S.; et al. Coupled Proliferation and Apoptosis Maintain the Rapid Turnover of Microglia in the Adult Brain. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeffel, G.; Chen, J.; Lavin, Y.; Low, D.; Almeida Francisca, F.; See, P.; Beaudin Anna, E.; Lum, J.; Low, I.; Forsberg, E.C.; et al. C-Myb+ erythro-myeloid progenitor-derived fetal monocytes give rise to adult tissue-resident macrophages. Immunity 2015, 42, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, V.H.; Nicoll, J.A.; Holmes, C. Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjalkens, R.B.; Popichak, K.A.; Kirkley, K.A. Inflammatory Activation of Microglia and Astrocytes in Manganese Neurotoxicity. Adv. Neurobiol. 2017, 18, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, B.F.; Patsinakidis, N.; Raap, U. Role of the Pruritic Cytokine IL-31 in Autoimmune Skin Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Salvo, E.; Ventura-Spagnolo, E.; Casciaro, M.; Navarra, M.; Gangemi, S. IL-33/IL-31 Axis: A Potential Inflammatory Pathway. Med. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3858032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabryelska, A.; Kuna, P.; Antczak, A.; Białasiewicz, P.; Panek, M. IL-33 mediated inflammation in chronic respiratory diseases—understanding the role of the member of il-1 superfamily. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Liao, X.; Lu, J.; Yao, S.; Wu, F.; Zhu, X.; Shi, D.; Wen, S.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H. IL-33/ST2 plays a critical role in endothelial cell activation and microglia-mediated neuroinflammation modulation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, S.; Kawanokuchi, J.; Parajuli, B.; Jin, S.; Doi, Y.; Noda, M.; Sonobe, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Mizuno, T.; Suzumura, A. Production and functions of IL-33 in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 2011, 1385, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tai, Y.; Achanta, S.; Kaelberer, M.M.; Caceres, A.I.; Shao, X.; Fang, J.; Jordt, S.-E. IL-33/ST2 signaling excites sensory neurons and mediates itch response in a mouse model of poison ivy contact allergy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7572–E7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M.; Yamamura, K.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Nakahara, T.; Fukui, Y. Emerging role of interleukin-31 and interleukin-31 receptor in pruritus in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2018, 73, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginwala, R.; Bhavsar, R.; Chigbu, D.I.; Jain, P.; Khan, Z.K. Potential Role of Flavonoids in Treating Chronic Inflammatory Diseases with a Special Focus on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Apigenin. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.P.; Vafeiadou, K.; Williams, R.J.; Vauzour, D. Neuroinflammation: Modulation by flavonoids and mechanisms of action. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghitu, A.; Schwiebs, A.; Radeke, H.H.; Avram, S.; Zupko, I.; Bor, A.; Pavel, I.Z.; Dehelean, C.A.; Oprean, C.; Bojin, F.; et al. A Comprehensive Assessment of Apigenin as an Antiproliferative, Proapoptotic, Antiangiogenic and Immunomodulatory Phytocompound. Nutrients 2019, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, E.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, M.S. Luteolin-Enriched Artichoke Leaf Extract Alleviates the Metabolic Syndrome in Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miean, K.H.; Mohamed, S. Flavonoid (myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin) content of edible tropical plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3106–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balez, R.; Steiner, N.; Engel, M.; Muñoz, S.S.; Lum, J.S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Vallotton, P.; Sachdev, P.; O’Connor, M.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of apigenin against inflammation, neuronal excitability and apoptosis in an induced pluripotent stem cell model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.K.; Lee, P.; Park, J.A.; Oh, H.R.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Lee, E.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, K.R.; Kim, S.Y. Apigenin inhibits the production of NO and PGE2 in microglia and inhibits neuronal cell death in a middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced focal ischemia mice model. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.H.; Bi, W.; Qi, R.B.; Wang, H.D.; Lu, D.X. Luteolin inhibits microglial inflammation and improves neuron survival against inflammation. Int. J. Neurosci. 2011, 121, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.D.; Rytych, J.L.; Amin, R.; Johnson, R.W. Dietary Luteolin Reduces Proinflammatory Microglia in the Brain of Senescent Mice. Rejuvenation Res. 2015, 19, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Kelley, K.W.; Johnson, R.W. Luteolin reduces IL-6 production in microglia by inhibiting JNK phosphorylation and activation of AP-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Li, F.; Wu, Q.; Gong, Q.; Lu, Y.; Shi, J. Protective effects of icariin on brain dysfunction induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, B.; Jukes, J.-P.; Vergara-Irigaray, N.; Errea, O.; Villoslada, P.; Perry, V.H.; Newman, T.A. Systemic inflammation induces axon injury during brain inflammation. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Ehrhart, J.; Bai, Y.; Sanberg, P.R.; Bickford, P.; Tan, J.; Shytle, R.D. Apigenin and luteolin modulate microglial activation via inhibition of STAT1-induced CD40 expression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rachman Isnadi, M.F.; Chin, V.K.; Abd Majid, R.; Lee, T.Y.; Atmadini Abdullah, M.; Bello Omenesa, R.; Osamah Ibraheem, Z.; Basir, R. Critical Roles of IL-33/ST2 Pathway in Neurological Disorders. Med. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 5346413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.K.Y.; Hung, K.-W.; Yuen, M.Y.F.; Zhou, X.; Mak, D.S.Y.; Chan, I.C.W.; Cheung, T.H.; Zhang, B.; Fu, W.-Y.; Liew, F.Y.; et al. IL-33 ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and cognitive decline. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2705–E2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, S.R.; Sprecher, C.; Hammond, A.; Bilsborough, J.; Rosenfeld-Franklin, M.; Presnell, S.R.; Haugen, H.S.; Maurer, M.; Harder, B.; Johnston, J.; et al. Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces dermatitis in mice. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, J. neuroprotective effects of luteolin against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Gortzi, O.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Daglia, M.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Nabavi, S.M. Luteolin as an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agent: A brief review. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Sonego, S.; Gyengesi, E.; Rangel, A.; Niedermayer, G.; Karl, T.; Münch, G. OP-25—anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effect of apigenin: studies in the gfap-il6 mouse model of chronic neuroinflammation. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M. Spinal dorsal horn astrocytes: New players in chronic itch. Allergol. Int. off. J. Jpn. Soc. Allergol. 2017, 66, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vainchtein, I.D.; Chin, G.; Cho, F.S.; Kelley, K.W.; Miller, J.G.; Chien, E.C.; Liddelow, S.A.; Nguyen, P.T.; Nakao-Inoue, H.; Dorman, L.C.; et al. Astrocyte-derived interleukin-33 promotes microglial synapse engulfment and neural circuit development. Science 2018, 359, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairlie-Clarke, K.; Barbour, M.; Wilson, C.; Hridi, S.U.; Allan, D.; Jiang, H.-R. Expression and function of il-33/st2 axis in the central nervous system under normal and diseased conditions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.M., Jr.; Yang, L.; Cordell, B. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor augments beta-amyloid-induced interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and nitric oxide production by microglial cells. J. Boil. Chem. 1998, 273, 20967–20971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.-Y.; Sul, D.; Hwang, B.Y.; Hwang, K.W.; Yoo, K.-Y.; Park, S.-Y. Suppression of LPS-induced inflammatory responses by inflexanin B in BV2 microglial cells. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 91, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, M.; Mackman, N. LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-J.; Lin, W.-W.; Chen, H.-L.; Chang, Y.-H.; Ou, H.-C.; Kuo, J.-S.; Hong, J.-S.; Jeng, K.-C.G. Silymarin protects dopaminergic neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting microglia activation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, Y. NF-κB activation and IκBα dynamism involved in iNOS and chemokine induction in astroglial cells. Life Sci. 2001, 68, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, G.; Hao, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yu, Z. The role of the JAK2-STAT3 pathway in pro-inflammatory responses of EMF-stimulated N9 microglial cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che, D.N.; Cho, B.O.; Kim, J.-s.; Shin, J.Y.; Kang, H.J.; Jang, S.I. Effect of Luteolin and Apigenin on the Production of Il-31 and Il-33 in Lipopolysaccharides-Activated Microglia Cells and Their Mechanism of Action. Nutrients 2020, 12, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030811
Che DN, Cho BO, Kim J-s, Shin JY, Kang HJ, Jang SI. Effect of Luteolin and Apigenin on the Production of Il-31 and Il-33 in Lipopolysaccharides-Activated Microglia Cells and Their Mechanism of Action. Nutrients. 2020; 12(3):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030811
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe, Denis Nchang, Byoung Ok Cho, Ji-su Kim, Jae Young Shin, Hyun Ju Kang, and Seon Il Jang. 2020. "Effect of Luteolin and Apigenin on the Production of Il-31 and Il-33 in Lipopolysaccharides-Activated Microglia Cells and Their Mechanism of Action" Nutrients 12, no. 3: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030811
APA StyleChe, D. N., Cho, B. O., Kim, J.-s., Shin, J. Y., Kang, H. J., & Jang, S. I. (2020). Effect of Luteolin and Apigenin on the Production of Il-31 and Il-33 in Lipopolysaccharides-Activated Microglia Cells and Their Mechanism of Action. Nutrients, 12(3), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030811





