Dairy Consumption at Snack Meal Occasions and the Overall Quality of Diet during Childhood. Prospective and Cross-Sectional Analyses from the IDEFICS/I.Family Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
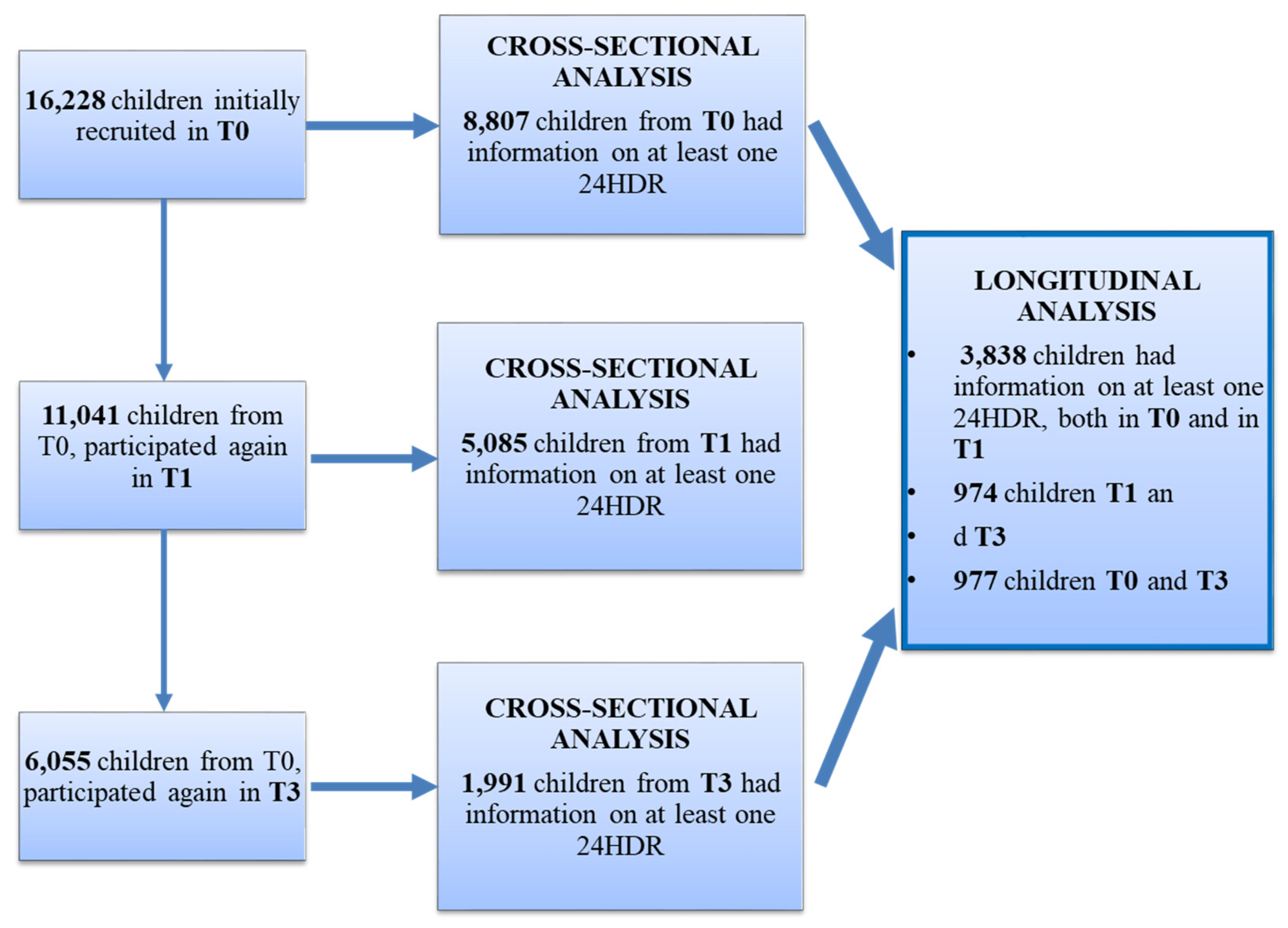
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Diet Quality Index
2.4. Body Mass Index
2.5. Sociodemographic Factors
2.6. Intervention
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| CVD | cardiovascular diseases |
| CEHQ | Children’s Eating Habits Questionnaire |
| CINDI | Countrywide Integrated Non-communicable Disease Intervention program |
| DQI | dietary quality index; FBDG: food-based dietary guidelines |
| FCT | food composition tables |
| FFQ | food frequency questionnaire |
| HDR | hours dietary recall |
| HELENA-DIAT | HELENA-DIetary Assessment Tool |
| HELENA | Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence |
| IDEFICS | Identification and prevention of Dietary- and lifestyle induced health EFfects In Children and infantS |
| ISCED | International Standard Classification of Education |
| SACANA | Self-Administered Children, Adolescents, and Adult Nutrition Assessment |
| SACINA | Self-Administered Children and Infant Nutrition Assessment |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for Social Sciences |
| TEI | total energy intake |
| UK | United Kingdom |
Appendix A
| Preferable | IDEFICS (T0/T1): Water, wholemeal bread, wholemeal cereals, unsweetened breakfast cereals, raw vegetables, fresh fruit, cooked meat, eggs, fresh fish, plain yogurt I.Family (T3) additionally: replacement foods (e.g., tofu), poultry boiled, canned fish, vegetable oils |
| Intermediate | IDEFICS (T0/T1): light soft drinks, fruit juices, milk, white bread, cereals (pasta and rice…), sweetened breakfast cereals, cooked vegetables, sweetened fruit, nuts, ketchup, fried meat, cold cults, fried eggs, fried fish, sweetened yogurt, cheese, butter and margarine I.Family (T3) additioanlly: coffee and tea, dried fruits |
| Low | IDEFICS (T0/T1): Soft drinks, chocolates, salty snacks, ice-creams, biscuits, candies, chocolate/nut-based spread, fried potatoes, mayonnaise I.Family (T3) additionally: poultry fried |
References
- Howarth, N.C.; Huang, T.T.; Roberts, S.B.; Lin, B.H.; McCrory, M.A. Eating patterns and dietary composition in relation to BMI in younger and older adults. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, R.R. 2nd plenary session of ‘body weight balance and regulation’. Role of dietary carbohydrate and frequent eating in body-weight control. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2000, 59, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, C.; Braegger, C.; Decsi, T.; Kolacek, S.; Koletzko, B.; Mihatsch, W.; Moreno, L.A.; Puntis, J.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. Role of dietary factors and food habits in the development of childhood obesity: A commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUropean Food Information Council (EUFIC) (2007) Is Eating between Meals Good for Our Health? EUFIC: Brussels, Belgium, 2007.
- van den Heuvel, E.G.H.M.; Steijns, J.M.J.M. Dairy products and bone health: how strong is the 444 scientific evidence? Nutr. Res. Rev. 2018, 31, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.A.; Bel-Serrat, S.; Santaliestra-Pasias, A.; Bueno, G. Dairy products, yogurt consumption, and cardiometabolic risk in children and adolescents. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, L.A.; Cifelli, C.J.; Miller, G.D. The Role of Dairy Products in Healthy Weight and Body Composition in Children and Adolescents. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2011, 7, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, G.L.; Emmett, P.M.; Northstone, K.; Jebb, S.A. Tracking a dietary pattern associated with increased adiposity in childhood and adolescence. Obesity 2014, 22, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.; Burrows, T.; Collins, C.E. Systematic review of diet quality indices and their associations with health-related outcomes in children and adolescents. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 27, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyncke, K.; Cruz Fernandez, E.; Fajo-Pascual, M.; Cuenca-Garcia, M.; De Keyzer, W.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Moreno, L.A.; Beghin, L.; Breidenassel, C.; Kersting, M.; et al. Validation of the Diet Quality Index for Adolescents by comparison with biomarkers, nutrient and food intakes: The HELENA study. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 109, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, W.; Bammann, K.; de Henauw, S.; Halford, J.; Palou, A.; Pigeot, I.; Siani, A.; Sjostrom, M. Understanding and preventing childhood obesity and related disorders–IDEFICS: A European multilevel epidemiological approach. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, W.; Bammann, K.; Siani, A.; Buchecker, K.; De Henauw, S.; Iacoviello, L.; Hebestreit, A.; Krogh, V.; Lissner, L.; Marild, S.; et al. The IDEFICS cohort: design, characteristics and participation in the baseline survey. Int. J. Obes 2011, 35, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, W.; Siani, A.; Adan, R.; De Henauw, S.; Eiben, G.; Gwozdz, W.; Hebestreit, A.; Hunsberger, M.; Kaprio, J.; Krogh, V.; et al. Cohort Profile: The transition from childhood to adolescence in European children-how I.Family extends the IDEFICS cohort. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langeheine, M.; Pohlabeln, H.; Lauria, F.; Veidebaum, T.; Tornaritis, M.; Molnar, D.; Eiben, G.; de Henauw, S.; Moreno, L.A.; Williams, G.; et al. Attrition in the European Child Cohort IDEFICS/I.Family: Exploring Associations Between Attrition and Body Mass Index. Front Pediatr. 2018, 6, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereecken, C.A.; Covents, M.; Sichert-Hellert, W.; Alvira, J.M.; Le Donne, C.; De Henauw, S.; De Vriendt, T.; Phillipp, M.K.; Beghin, L.; Manios, Y.; et al. Development and evaluation of a self-administered computerized 24-h dietary recall method for adolescents in Europe. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, S26–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebestreit, A.; Bornhorst, C.; Pala, V.; Barba, G.; Eiben, G.; Veidebaum, T.; Hadjigergiou, C.; Molnar, D.; Claessens, M.; Fernandez-Alvira, J.M.; et al. Dietary energy density in young children across Europe. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, S124–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebestreit, A.; Barba, G.; De Henauw, S.; Eiben, G.; Hadjigeorgiou, C.; Kovacs, E.; Krogh, V.; Moreno, L.A.; Pala, V.; Veidebaum, T.; et al. Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations between energy intake and BMI z-score in European children. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCance, W. The Composition of Foods, 6th ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Food Standards Agency: London, UK, 2002.
- Bel-Serrat, S.; Mouratidou, T.; Pala, V.; Huybrechts, I.; Bornhorst, C.; Fernandez-Alvira, J.M.; Hadjigeorgiou, C.; Eiben, G.; Hebestreit, A.; Lissner, L.; et al. Relative validity of the Children’s Eating Habits Questionnaire-food frequency section among young European children: The IDEFICS Study. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 17, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfer, A.; Hebestreit, A.; Ahrens, W.; Krogh, V.; Sieri, S.; Lissner, L.; Eiben, G.; Siani, A.; Huybrechts, I.; Loit, H.M.; et al. Reproducibility of food consumption frequencies derived from the Children’s Eating Habits Questionnaire used in the IDEFICS study. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, S61–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huybrechts, I.; Vereecken, C.; De Bacquer, D.; Vandevijvere, S.; Van Oyen, H.; Maes, L.; Vanhauwaert, E.; Temme, L.; De Backer, G.; De Henauw, S. Reproducibility and validity of a diet quality index for children assessed using a FFQ. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster-Rasmussen, R.; Siersma, V.; Halldorsson, T.I.; de Fine Olivarius, N.; Henriksen, J.E.; Heitmann, B.L. Missing portion sizes in FFQ--alternatives to use of standard portions. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 18, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkevage, J.; Mayen, A.L.; Zuleta, C.; DiGirolamo, A.M.; Stein, A.D.; Ramirez-Zea, M. Relative Validity of Three Food Frequency Questionnaires for Assessing Dietary Intakes of Guatemalan Schoolchildren. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgian Health Council. De actieve voedingsdriehoekeen praktische voedingsen beweeggids (Nutritional Recommendations for Belgium. Revised version 2012); Belgian Health Council: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.J.; Freeman, J.V.; Preece, M.A. British 1990 growth reference centiles for weight, height, body mass index and head circumference fitted by maximum penalized likelihood. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO Institute for Statistics. International Standard Classification of Education ISCED 2011; UNESCO: Montreal, QC, CA, 2012; ISBN 978-92-9189-123-8. [Google Scholar]
- De Henauw, S.; Baranowski, T.; Pigeot, I. Special Issue: Prevention of childhood obesity: Results from the IDEFICS study. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- EUFIC. The European Food Information Council.10 Healthy Lifestyle Tips for Adults. Last Revision: 7 June 2017 [14 June 2017]. Available online: http://www.eufic.org/en/healthy-living/article/10-healthy-lifestyle-tips-for-adults (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- Leech, R.M.; Worsley, A.; Timperio, A.; McNaughton, S.A. Characterizing eating patterns: A comparison of eating occasion definitions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellisle, F. Meals and snacking, diet quality and energy balance. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 134, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicklas, T.A.; Yang, S.J.; Baranowski, T.; Zakeri, I.; Berenson, G. Eating patterns and obesity in children. The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2003, 25, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julián, C.; Santaliestra-Pasías, A.; Miguel-Berges, M.; Moreno, L. Frequency and quality of mid-afternoon snack among Spanish children. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelder, S.H.; Perry, C.L.; Klepp, K.I.; Lytle, L.L. Longitudinal tracking of adolescent smoking, physical activity, and food choice behaviors. Am. J. Public Health 1994, 84, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verloigne, M.; Van Lippevelde, W.; Maes, L.; Brug, J.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I. Family- and school-based correlates of energy balance-related behaviours in 10-12-year-old children: A systematic review within the ENERGY (EuropeaN Energy balance Research to prevent excessive weight Gain among Youth) project. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 1380–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, M.; Hakansson, N.N.; Wolk, A. Association between dairy food consumption and weight change over 9 y in 19,352 perimenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Troy, L.M.; Rogers, G.T.; Fox, C.S.; McKeown, N.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Jacques, P.F. Longitudinal association between dairy consumption and changes of body weight and waist circumference: The Framingham Heart Study. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Hao, T.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Changes in diet and lifestyle and long-term weight gain in women and men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Sayon-Orea, C.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; de la Fuente, C.; Gea, A.; Bes-Rastrollo, M. Yogurt consumption, weight change and risk of overweight/obesity: The SUN cohort study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santaliestra-Pasias, A.M.; González-Gil, E.M.; Pala, V.; Intemann, T.; Hebestreit, A.; Russo, P.; Van Aart, C.; Galli, C.; Veidebaum, T.; Molnar, D.; et al. Prospective associations between lifestyle behaviors and dairy consumption: The IDEFICS study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panahi, S.; Fernandez, M.A.; Marette, A.; Tremblay, A. Yogurt, diet quality and lifestyle factors. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 71, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A. Yogurt and dairy product consumption to prevent cardiometabolic diseases: Epidemiologic and experimental studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1235S–1242S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Livingston, K.A.; Fox, C.S.; Meigs, J.B.; Jacques, P.F. Yogurt consumption is associated with better diet quality and metabolic profile in American men and women. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, M.; Johansson, G.; Berglund, L.; Vessby, B.; de Faire, U.; Hellenius, M.L. Associations between the intake of dairy fat and calcium and abdominal obesity. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerlikaya, O.; Acu, M.; Kinik, O. Importance of dairy products in cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, D.K. Dairy consumption and pre-school, school-age and adolescent obesity in developed countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, M.; Baars, T.; Guyenet, S. The relationship between high-fat dairy consumption and obesity, cardiovascular, and metabolic disease. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Hollis, J.H.; Jacques, P.F. The associations between yogurt consumption, diet quality, and metabolic profiles in children in the USA. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkin, B.M. Technology, transport, globalization and the nutrition transition food policy. Food Policy 2006, 31, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M. Global nutrition dynamics: The world is shifting rapidly toward a diet linked with noncommunicable diseases. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, A.; Anderson, C.; McCullough, F. Associations between children’s diet quality and watching television during meal or snack consumption: A systematic review. Matern. Child Nutr. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutishauser, I.H. Dietary intake measurements. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| T0 | T1 | T3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | Girls | Boys | Girls | Boys | Girls | |||||||
| 2–6 y | 6–10 y | 2–6 y | 6–10 y | 2–6 y | 6–12 y | 2–6 y | 6–12 y | <10 y | ≥10 y | <10 y | ≥10 y | |
| N | 1961 | 2504 | 1814 | 2528 | 501 | 2076 | 445 | 2063 | 450 | 575 | 418 | 548 |
| BMI z-score * | 0.18 (1.18) | 0.54 (1.25) | 0.21 (1.11) | 0.54 (1.17) | 0.24 (1.20) | 0.61 (1.22) | 0.27 (1.19) | 0.60 (1.17) | 0.50 (1.24) | 0.57 (1.28) | 0.29 (1.21) | 0.34 (1.21) |
| Education of the Families (ISCED 2011) T0 | ||||||||||||
| High education | 888 | 1064 | 832 | 1122 | 253 | 987 | 249 | 991 | 241 | 310 | 260 | 278 |
| Medium education | 905 | 1220 | 847 | 1204 | 214 | 931 | 175 | 927 | 188 | 245 | 144 | 241 |
| Low education | 168 | 220 | 135 | 202 | 34 | 158 | 21 | 145 | 21 | 20 | 14 | 29 |
| Country | ||||||||||||
| Italy | 483 | 558 | 388 | 553 | 129 | 657 | 101 | 612 | 64 | 112 | 50 | 107 |
| Estonia | 131 | 215 | 138 | 254 | 148 | 351 | 131 | 390 | 109 | 95 | 85 | 84 |
| Cyprus | 168 | 263 | 163 | 273 | 6 | 149 | 9 | 159 | 11 | 30 | 11 | 35 |
| Belgium | 116 | 83 | 105 | 76 | 34 | 166 | 35 | 148 | 28 | 34 | 24 | 38 |
| Sweden | 296 | 326 | 272 | 320 | 70 | 207 | 60 | 204 | 57 | 87 | 74 | 67 |
| Germany | 372 | 528 | 369 | 513 | 31 | 206 | 38 | 203 | 38 | 96 | 48 | 66 |
| Hungary | 224 | 392 | 247 | 395 | 17 | 90 | 18 | 87 | 29 | 25 | 20 | 30 |
| Spain | 171 | 139 | 132 | 144 | 66 | 250 | 53 | 260 | 45 | 45 | 46 | 40 |
| Region | ||||||||||||
| Control | 918 | 1146 | 821 | 1201 | 250 | 1088 | 226 | 1065 | 224 | 241 | 186 | 231 |
| Intervention | 1043 | 1358 | 993 | 1327 | 251 | 988 | 219 | 998 | 226 | 334 | 232 | 317 |
| T0 (2007–2008) | T1 (2009–2010) | T3 (2013–2014) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | Girls | Boys | Girls | Boys | Girls | |||||||
| 2–6 y | 6–10 y | 2–6 y | 6–10 y | 2–6 y | 6–12 y | 2–6 y | 6–12 y | <10 y | ≥10 y | <10 y | ≥10 y | |
| Diet Quality Index (DQI) | 79.97 (16.03) | 80.7 (18.04) | 80.62 (16.12) | 83.22 (17.36) | 85.69 (19.09) | 85.22 (18.98) | 87.75 (18.02) | 87.90 (19.32) | 99.76 (16.82) | 97.86 (18.43) | 101.26 (18.56) | 100.85 (18.54) |
| Total energy intake (kcal/day) | 1460.25 (509.69) | 1675.2 (568.23) | 1374.55 (502.57) | 1529.91 (512.75) | 1634.04 (512.72) | 1774.23 (571.07) | 1503.72 (516.58) | 1619.30 (546.67) | 1648.12 (688.47) | 1611.99 (650.67) | 1485.81 (624.40) | 1482.05 (570.48) |
| Total Dairy intake (g/day) | 334.98 (241.84) | 318.52 (259.12) | 303.78 (232.57) | 270.34 (227.84) | 368.29 (240.99) | 322.90 (258.65) | 326.51 (235.56) | 282.67 (217.55) | 254.35 (234.82) | 233.52 (211.30) | 239.90 (218.76) | 209.64 (218.83) |
| Breakfast | ||||||||||||
| Milk (g/day) | 91.65 (108.40) | 81.99 (102.58) | 81.50 (109.20) | 68.42 (95.64) | 93.01 (105.67) | 101.01 (109.21) | 83.77 (101.28) | 85.54 (98.19) | 82.39 (105.70) | 90.42 (109.42) | 74.75 (97.52) | 60.73 (86.92) |
| Yogurt (g/day) | 15.88 (54.35) | 13.95 (53.02) | 13.38 (47.33) | 12.01 (47.72) | 17.09 (54.97) | 14.52 (52.88) | 14.71 (46.42) | 15.41 (53.01) | 13.82 (50.98) | 12.81 (51.47) | 14.31 (47,47) | 12.84 (45.03) |
| Milk + yogurt (g/day) | 107.52 (114.57) | 95.93 (109.33) | 94.87 (113.38) | 80.43 (101.39) | 110.10 (112.07) | 115.53 (112.43) | 98.48 (101.12) | 100.95 (102.19) | 96.21 (111.50) | 103.23 (113.29) | 89.06 (104.68) | 73.57 (92.78) |
| Cheese (g/day) | 2.81 (14.91) | 2.10 (10.87) | 2.75 (16.77) | 2.01 (10.72) | 2.42 (17.89) | 2.20 (13.56) | 2.22 (13.23) | 2.45 (12.74) | 2.93 (18.51) | 2.91 (11.78) | 4.33 (15.82) | 2.92 (14.88) |
| Milky desserts + sweetened milk (g/day) | 18.43 (59.55) | 18.85 (60.80) | 15.0 (55.25) | 18.0 (57.38) | 9.91 (39.58) | 13.27 (50.81) | 14.38 (51.88) | 14.70 (52.09) | 19.11 (62.77) | 16.27 (61.13) | 17.86 (59.63) | 19.53 (60.09) |
| Lunch | ||||||||||||
| Milk (g/day) | 17.94 (54.56) | 21.06 (66.53) | 16.55 (49.79) | 15.57 (56.80) | 28.76 (68.95) | 20.57 (63.58) | 23.03 (63.68) | 16.52 (54.93) | 19.89 (59.72) | 17.22 (60.40) | 20.45 (62.79) | 13.60 (55.78) |
| Yogurt (g/day) | 7.93 (34.60) | 6.80 (32.38) | 5.31 (27.95) | 6.53 (31.57) | 6.12 (30.47) | 9.29 (37.73) | 7.48 (36.98) | 7.89 (33.81) | 6.08 (31.51) | 6.95 (33.40) | 4.95 (26.53) | 5.20 (28.56) |
| Milk + yogurt (g/day) | 25.86 (63.77) | 27.85 (72.77) | 21.86 (56.56) | 22.10 (63.71) | 34.88 (73.83) | 29.86 (72.11) | 30.51 (71.31) | 24.41 (62.64) | 25.97 (67.12) | 24.17 (68.12) | 25.40 (68.52) | 18.80 (61.52) |
| Cheese (g/day) | 4.76 (26.32) | 5.14 (21.89) | 5.57 (22.08) | 6.05 (26.21) | 8.93 (27.65) | 6.19 (24.24) | 7.01 (25.01) | 6.0 (23.03) | 5.15 (22.16) | 3.14 (16.42) | 3.29 (16.71) | 4.06 (22.16) |
| Milky desserts + sweetened milk (g/day) | 4.76 (26.32) | 6.63 (37.93) | 4.63 (32.40) | 6.04 (29.57) | 9.3343 (40.37) | 8.91 (39.96) | 8.87 (36.58) | 8.92 (38.27) | 19.11 (62.77) | 16.27 (61.13) | 17.86 (59.63) | 19.53 (60.09) |
| Dinner | ||||||||||||
| Milk (g/day) | 31.82 (77.85) | 37.53 (88.72) | 29.60 (71.51) | 27.85 (74.04) | 46.62 (86.76) | 33.59 (81.77) | 39.13 (82.87) | 28.67 (74.64) | 29.21 (83.20) | 20.52 (63.42) | 24.16 (66.39) | 23.57 (72.32) |
| Yogurt (g/day) | 11.16 (43.63) | 8.33 (37.91) | 8.75 (37.16) | 6.57 (31.09) | 9.56 (39.47) | 8.57 (37.95) | 9.94 (35.80) | 9.60 (38.29) | 7.08 (37.16) | 7.24 (41.46) | 8.06 (37.65) | 7.24 (35.13) |
| Milk + yogurt (g/day) | 42.98 (88.38) | 45.86 (94.60) | 38.35 (78.99) | 34.43 (78.51) | 56.18 (93.29) | 42.16 (87.77) | 49.08 (88.711) | 38.27 (81.77) | 36.29 (89.57) | 27.76 (74.37) | 32.22 (74.44) | 30.80 (80.52) |
| Cheese (g/day) | 5.57 (20.68) | 6.35 (23.29) | 6.22 (23.95) | 6.07 (24.40) | 7.39(25.55) | 7.80 (27.85) | 7.93 (30.45) | 6.91 (24.30) | 5.54 (19.36) | 5.04 (20.79) | 5.47 (21.27) | 5.06 (21.46) |
| Milky desserts + sweetened milk (g/day) | 10.99 (43.65) | 14.01 (52.42) | 9.83 (42.30) | 9.29 (41.32) | 8.27 (34.45) | 7.52 (34.48) | 6.20 (28.03) | 6.99 (31.20) | 19.11 (62.77) | 16.27 (61.13) | 17.86 (59.63) | 19.53 (60.09) |
| T0 (2007–2008) | T1 (2009–2010) | T3 (2013–2014) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | Girls | Boys | Girls | Boys | Girls | |||||||
| 2–6 y | 6–10 y | 2–6 y | 6–10 y | 2–6 y | 6–12 y | 2–6 y | 6–12 y | <10 y | ≥10 y | <10 y | ≥10 y | |
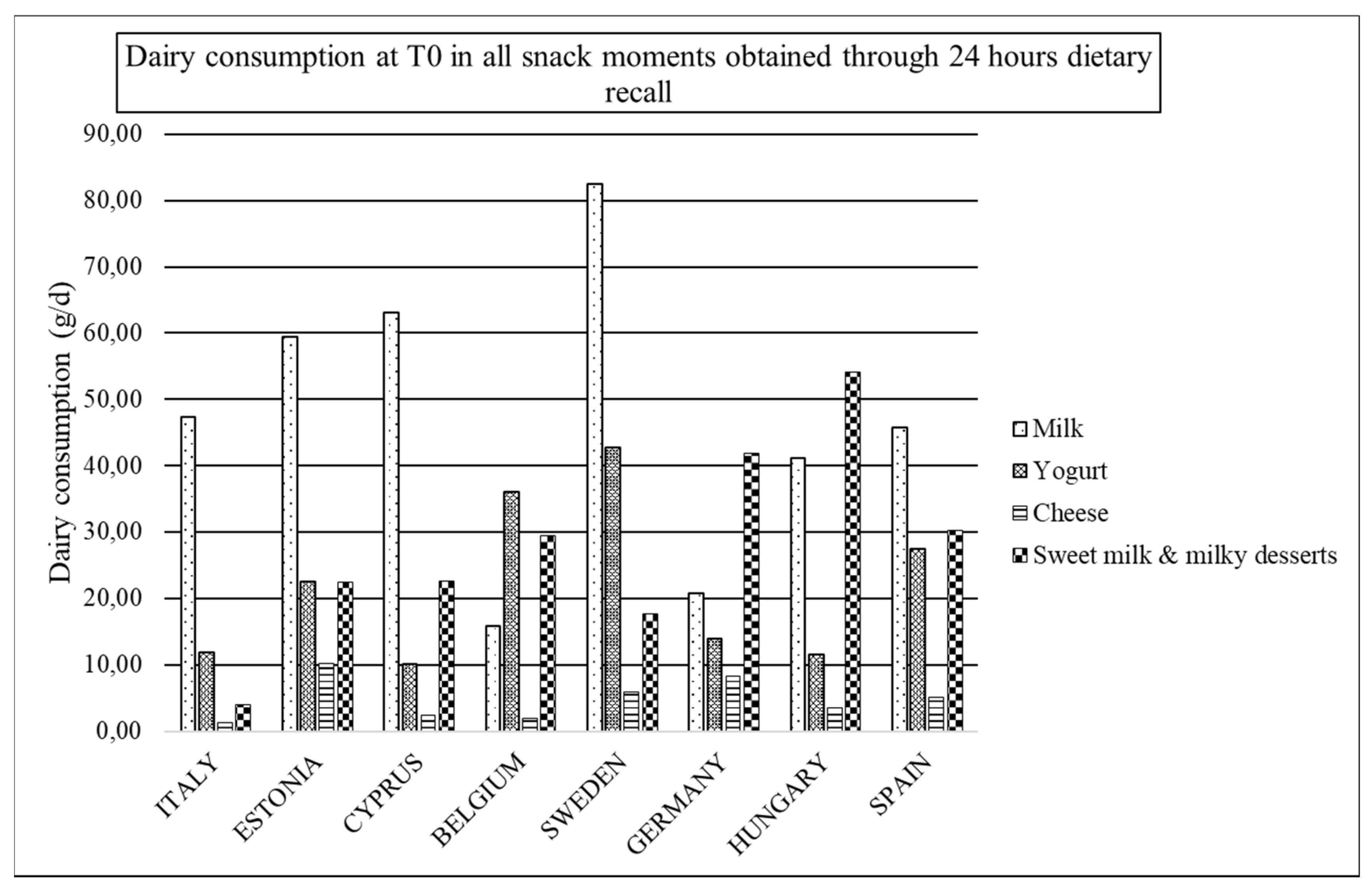
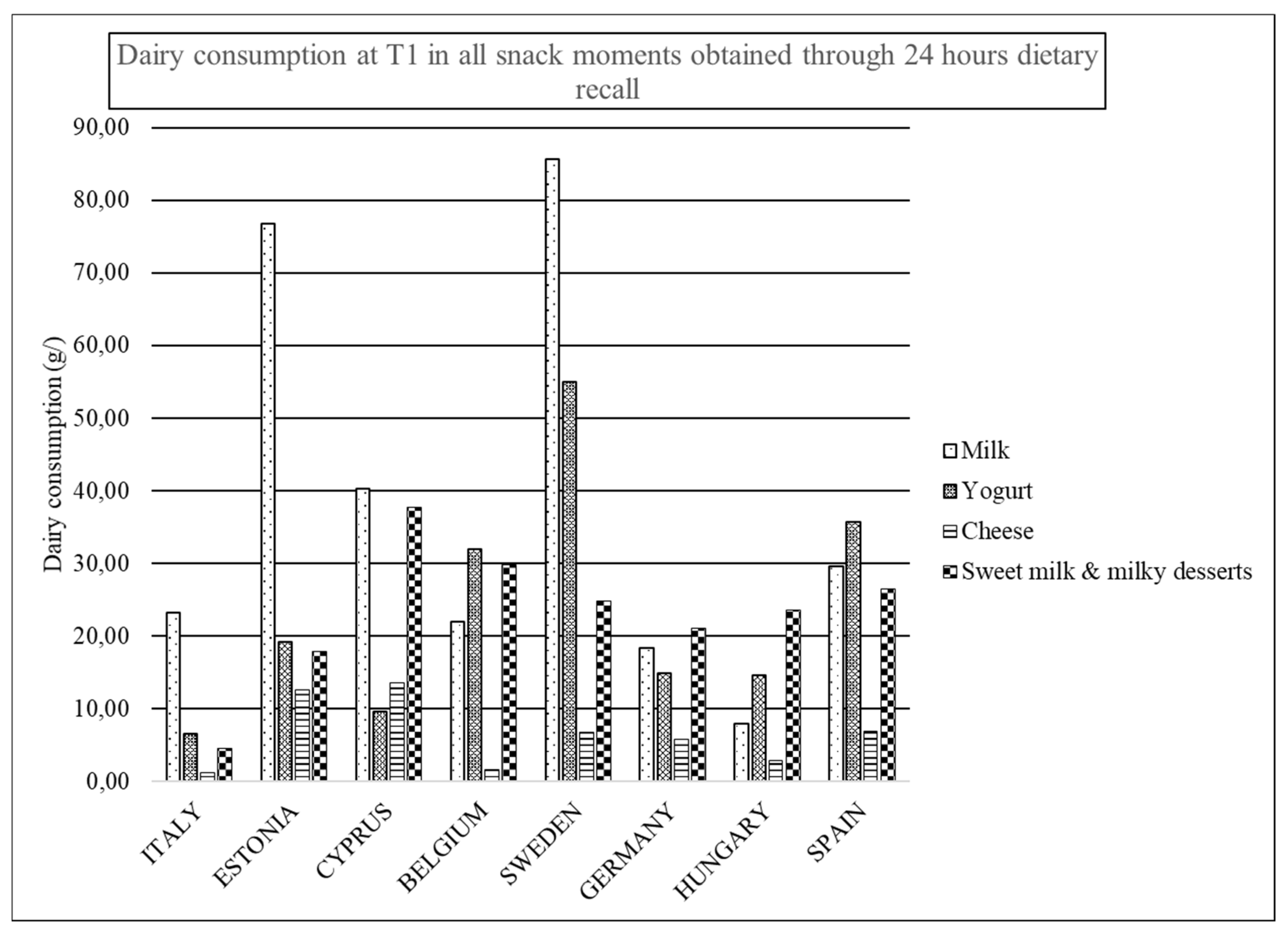
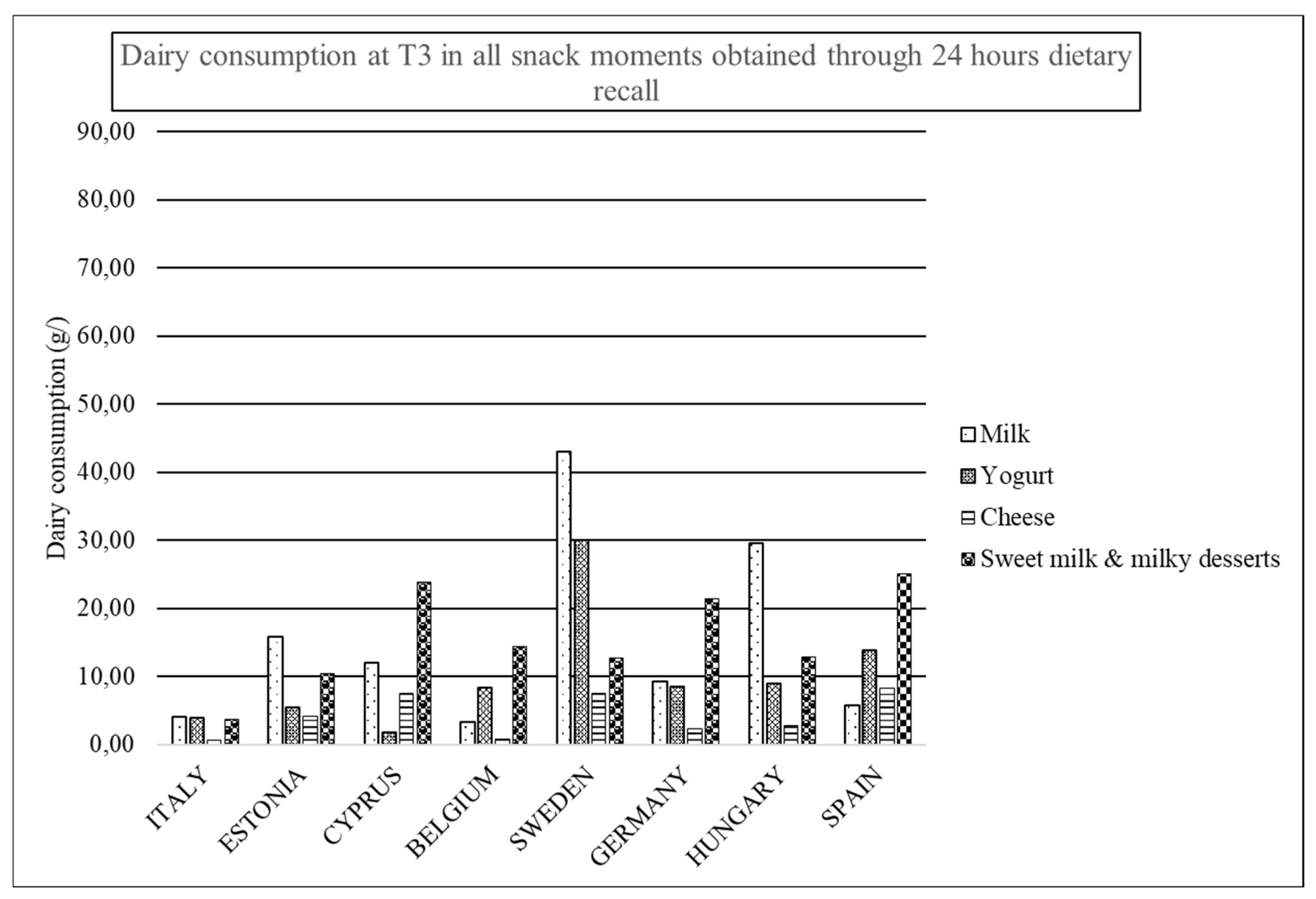
| All Snacks | ||||||||||||
| Milk | 56.19 (107.24) | 44.21 (96.46) | 53.25 (98.03) | 38.27 (85.70) | 65.18 (105.80) | 41.95 (104.65) | 55.3 (100.27) | 31.86 (82.24) | 20.08 (67.87) | 15.30 (60.70) | 13.90 (49.47) | 12.50 (50.40) |
| Yogurt | 22.82 (64.18) | 18.60 (64.27) | 20.49 (58.75) | 16.25 (53.78) | 31.75 (71.75) | 21.57 (65.00) | 24.79 (61.20) | 17.17 (53.32) | 11.15 (43.62) | 9.10 (43.11) | 12.73 (47.15) | 9.35 (46.02) |
| Milk + yogurt | 79.0 (123.33) | 62.81 (117.68) | 73.74 (110.84) | 54.52 (101.14) | 96.93 (120.76) | 63.52 (121.63) | 80.09 (114.39) | 49.03 (96.46) | 31.23 (81.24) | 24.39 (73.17) | 26.63 (68.95) | 21.85 (71.41) |
| Cheese | 4.66 (17.82) | 5.19 (19.14) | 4.89 (17.53) | 4.54 (14.52) | 6.11 (24.35) | 6.19 (20.82) | 6.17 (24.38) | 6.07 (20.00) | 3.52 (20.47) | 3.30 (21.74) | 4.39 (28.20) | 3.27 (17.63) |
| Milky desserts + sweetened milk | 26.71 (76.55) | 27.81 (78.17) | 26.06 (73.29) | 26.77 (79.95) | 17.84 (54.88) | 19.74 (64.80) | 15.57 (53.75) | 17.96 (61.27) | 12.18 (50.76) | 10.16 (51.12) | 14.76 (56.62) | 14.70 (54.13) |
| Mid-Morning Snack | ||||||||||||
| Milk | 5.62 (37.97) | 7.06 (37.31) | 6.74 (31.62) | 8.92 (40.37) | 15.52 (57.68) | 5.22 (31.39) | 12.02 (46.36) | 3.38 (25.80) | 2.65 (25.46) | 1.85 (20.79) | 1.84 (17.11) | 2.53 (25.68) |
| Yogurt | 4.97 (28.56) | 3.98 (36.07) | 4.28 (24.83) | 2.98 (20.92) | 5.24 (28.92) | 4.63 (27.20) | 5.45 (28.57) | 3.56 (22.38) | 2.61 (20.23) | 0.96 (11.86) | 1.68 (13.42) | 0.55 (7.39) |
| Milk + yogurt | 10.59 (47.47) | 11.04 (52.94) | 11.01 (39.82) | 11.90 (44.88) | 20.76 (64.58) | 9.85 (41.12) | 17.47 (53.23) | 6.94 (33.80) | 5.26 (32.30) | 2.80 (23.86) | 3.52 (21.60) | 3.078 (26.67) |
| Mid-Afternoon Snack | ||||||||||||
| Milk | 20.0 (59.83) | 18.90 (64.26) | 19.04 (56.46) | 14.66 (53.59) | 27.18 (66.59) | 20.03 (66.15) | 29.70 (70.63) | 18.34 (61.91) | 10.21 (46.01) | 8.62 (46.96) | 8.97 (41.74) | 6.03 (33.35) |
| Yogurt | 12.74 (45.01) | 8.90 (40.01) | 12.04 (43.94) | 8.43 (37.76) | 15.45 (49.04) | 10.24 (42.81) | 14.25 (46.07) | 9.23 (38.52) | 5.54 (30.16) | 3.73 (26.79) | 5.35 (35.12) | 5.622 (32.71) |
| Milk + yogurt | 32.74 (74.24) | 27.80 (76.23) | 31.08 (70.06) | 23.10 (65.54) | 42.65 (78.59) | 30.27 (77.86) | 43.96 (83.28) | 27.58 (72.05) | 15.75 (56.64) | 12.35 (54.30) | 14.32 (54.10) | 11.66 (49.43) |
| After-Dinner Snack | ||||||||||||
| Milk | 30.57 (76.31) | 18.25 (58.92) | 27.48 (70.75) | 14.68 (51.15) | 22.46 (67.60) | 16.69 (59.16) | 13.573 (52.99) | 10.14 (45.60) | 7.22 (41.18) | 4.83 (31.98) | 3.09 (22.65) | 3.93 (24.63) |
| Yogurt | 5.11 (32.82) | 5.72 (34.34) | 4.17 (28.86) | 4.84 (31.36) | 11.05 (46.01) | 6.71 (39.05) | 5.09 (29.69) | 4.38 (29.39) | 3.0 (25.17) | 4.41 (29.35) | 5.70 (30.13) | 3.18 (28.98) |
| Milk + yogurt | 35.67 (81.69) | 23.98 (67.58) | 31.65 (75.45) | 19.53 (59.05) | 33.52 (80.93) | 23.40 (70.36) | 18.66 (60.16) | 14.52 (54.14) | 10.22 (48.25) | 9.24 (42.92) | 8.78 (37.62) | 7.12 (37.70) |
| T0 | T1 | T3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Means | (CI 95%) p-Values | Means | (CI 95%) p-Values | Means | (CI 95%) p-Values | ||
| All Snacks | |||||||
| Milk (g/day) | NON CONSUMERS (N) CONSUMERS (N) | 85.91 (6640) 87.21 (2160) | (−0.06, 1.71) 0.06 | 86.17 (4082) 88.22 (1002) | (−0.24, 2.39) 0.11 | 99.73 (1831) 100.88 (160) | (−2.46, 3.40) 0.75 |
| Yogurt (g/day) | NON CONSUMERS (N) CONSUMERS (N) | 86.06 (7754) 87.41 (1042) | (−0.43, 1.92) 0.22 | 85.92 (4429) 90.96 (654) | (2.66, 5.73) <0.001 | 99.68 (1867) 101.96 (124) | (−1.68, 4.88) 0.34 |
| Milk + yogurt (g/day) | NON CONSUMERS (N) CONSUMERS (N) | 85.74 (5843) 87.18 (2957) | (0.06, 1.68) 0.04 | 85.47 (3538) 89.09 (1546) | (1.44, 3.71) <0.001 | 99.60 (1720) 101.27 (271) | (−1.32, 3.34) 0.40 |
| Cheese (g/day) | NON CONSUMERS (N) CONSUMERS (N) | 85.34 (7453) 88.35 (1346) | (1.02, 3.13) <0.001 | 85.92 (4262) 89.95 (821) | (1.39, 4.21) <0.001 | 99.56 (1845) 103.16 (146) | (−0.03, 6.06) 0.052 |
| Milky desserts (g/day) | NON CONSUMERS (N) CONSUMERS (N) | 86.25 (8203) 85.81 (593) | (−2.69, 0.35) 0.13 | 86.50 (4709) 87.40 (374) | (−1.56, 2.39) 0.68 | 99.93 (1869) 98.18 (122) | (−5.32, 1.28) 0.23 |
| Sweetened milk (g/day) | NON CONSUMERS (N) CONSUMERS (N) | 86.32 (7405) 85.71 (1392) | (−2.21, −0.12) 0.03 | 86.38 (4442) 87.90 (641) | (−0.87, 2.25) 0.39 | 99.75 (1930) 102.33 (61) | (−2.95, 6.25) 0.48 |
| T0–T1 | T1–T3 | T0–T3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean DQI (n) | (CI 95%) p-Values | Mean DQI (n) | (CI 95%) p-Values | Mean DQI (n) | (CI 95%) p-Values | ||
| All Snacks | |||||||
| Milk | UNHEALTHY TRACKING HEALTHY TRACKING | 85.46 (3039) 88.11 (799) | (0.26, 3.20) 0.02 | 98.85 (908) 101.27 (66) | (−2.35, 6.88) 0.34 | 98.74 (914) 100.71 (77) | (−3.12, 5.20) 0.62 |
| Yogurt | UNHEALTHY TRACKING HEALTHY TRACKING | 85.49 (3388) 89.91 (450) | (1.70, 5.36) <0.001 | 98.86 (921) 101.73 (53) | (−3.14, 7.05) 0.45 | 98.79 (928) 100.47 (63) | (−4.06, 5.0) 0.84 |
| Milk + yogurt | UNHEALTHY TRACKING HEALTHY TRACKING | 84.90 (2675) 88.56 (1163) | (1.36, 3.96) <0.001 | 98.65 (860) 101.75 (114) | (−0.95, 6.26) 0.15 | 98.59 (859) 100.85 (132) | (−2.09, 4.48) 0.48 |
| Cheese | UNHEALTHY TRACKING HEALTHY TRACKING | 85.14 (3235) 89.59 (603) | (1.74, 5.0) <0.001 | 98.63 (913) 104.85 (61) | (0.43, 9.95) 0.03 | - | - |
| Milky desserts + sweetened milk* | HEALTHY TRACKING UNHEALTHY TRACKING | 86.34 (450) 85.97 (3388) | (−1.36, 2.31) 0.61 | 96.81 (120) 99.33 (854) | (−0.07, 6.96) 0.054 | 98.11 (85) 98.97 (906) | (−2.61, 5.27) 0.51 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iglesia, I.; Intemann, T.; De Miguel-Etayo, P.; Pala, V.; Hebestreit, A.; Wolters, M.; Russo, P.; Veidebaum, T.; Papoutsou, S.; Nagy, P.; et al. Dairy Consumption at Snack Meal Occasions and the Overall Quality of Diet during Childhood. Prospective and Cross-Sectional Analyses from the IDEFICS/I.Family Cohort. Nutrients 2020, 12, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030642
Iglesia I, Intemann T, De Miguel-Etayo P, Pala V, Hebestreit A, Wolters M, Russo P, Veidebaum T, Papoutsou S, Nagy P, et al. Dairy Consumption at Snack Meal Occasions and the Overall Quality of Diet during Childhood. Prospective and Cross-Sectional Analyses from the IDEFICS/I.Family Cohort. Nutrients. 2020; 12(3):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030642
Chicago/Turabian StyleIglesia, Iris, Timm Intemann, Pilar De Miguel-Etayo, Valeria Pala, Antje Hebestreit, Maike Wolters, Paola Russo, Toomas Veidebaum, Stalo Papoutsou, Peter Nagy, and et al. 2020. "Dairy Consumption at Snack Meal Occasions and the Overall Quality of Diet during Childhood. Prospective and Cross-Sectional Analyses from the IDEFICS/I.Family Cohort" Nutrients 12, no. 3: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030642
APA StyleIglesia, I., Intemann, T., De Miguel-Etayo, P., Pala, V., Hebestreit, A., Wolters, M., Russo, P., Veidebaum, T., Papoutsou, S., Nagy, P., Eiben, G., Rise, P., De Henauw, S., & Moreno, L. A., on behalf of the IDEFICS/I.Family consortia. (2020). Dairy Consumption at Snack Meal Occasions and the Overall Quality of Diet during Childhood. Prospective and Cross-Sectional Analyses from the IDEFICS/I.Family Cohort. Nutrients, 12(3), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030642








