Lactobacillus Brevis OPK-3 from Kimchi Prevents Obesity and Modulates the Expression of Adipogenic and Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Adipose Tissue of Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Bacterial Cultures
2.2. Animals and Diets
2.3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
2.4. Lipid Profiles Assay and Hepatic Histology
2.5. Detection of Cytokine Production
2.6. RNA Isolation and Hybridization of Microarray
2.7. Analysis of Microarray Data
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
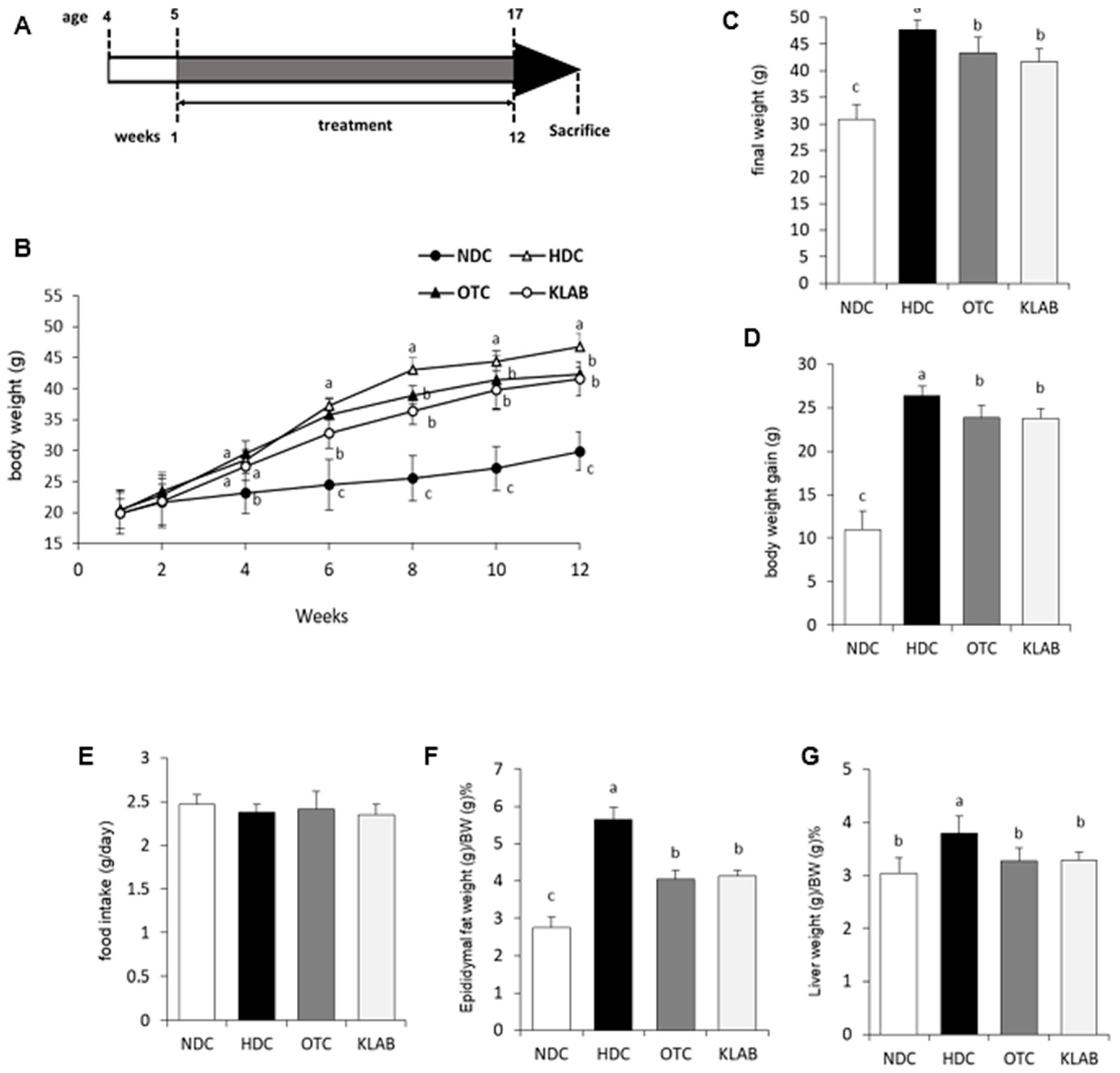
3.1. Changes in Body Weight and Tissue Weight
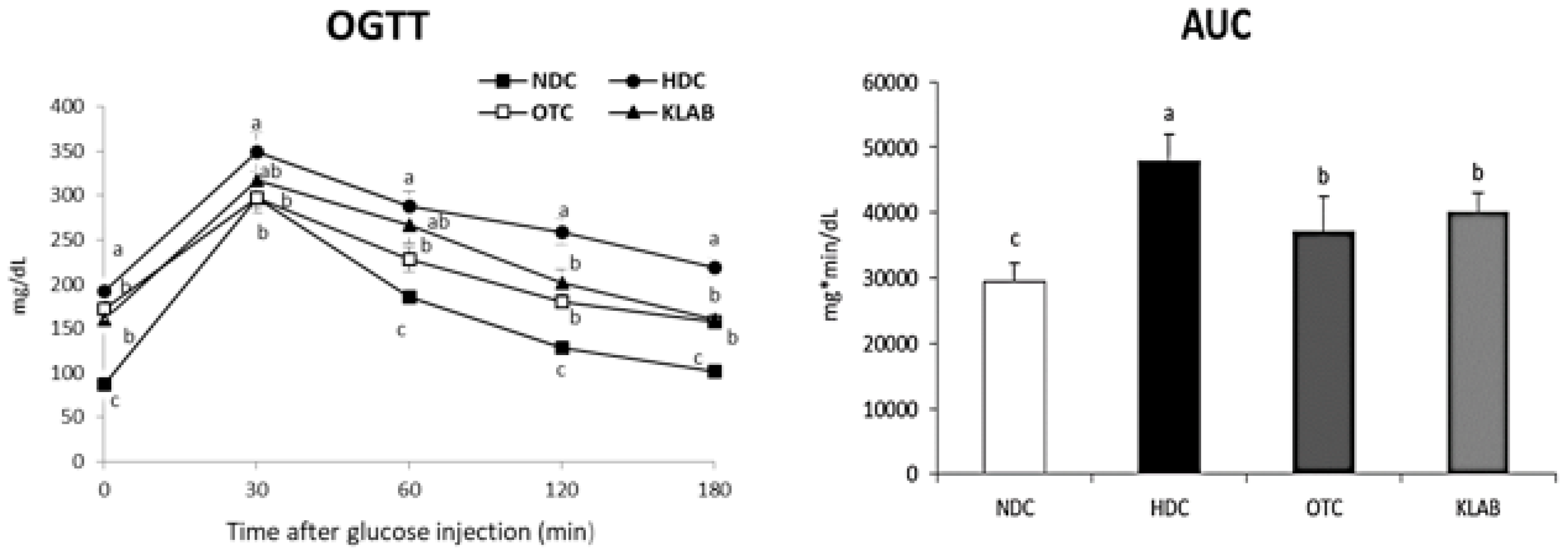
3.2. Blood Glucose Measurements
3.3. Serum and Hepatic Lipids
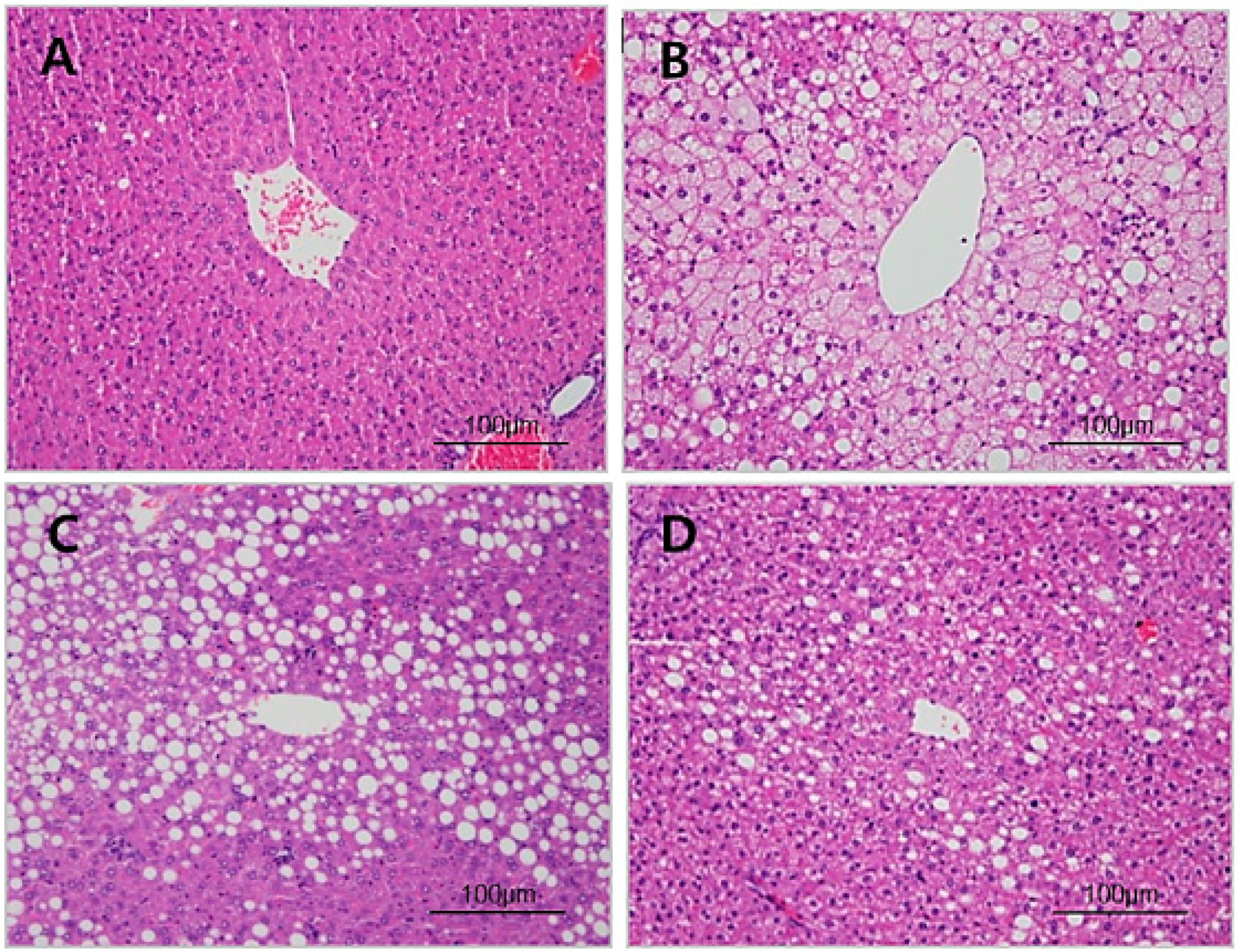
3.4. Histopathology of Liver
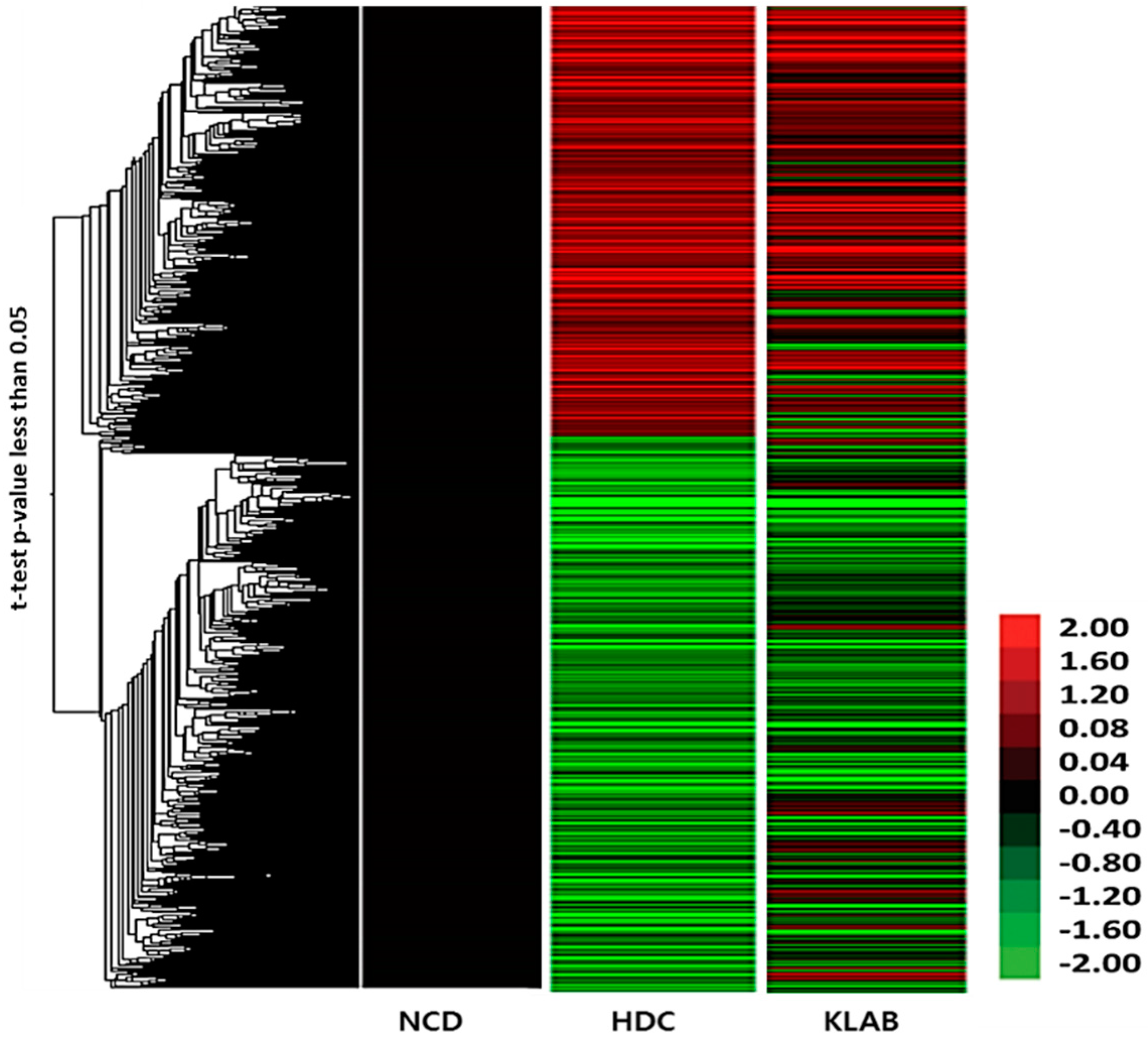
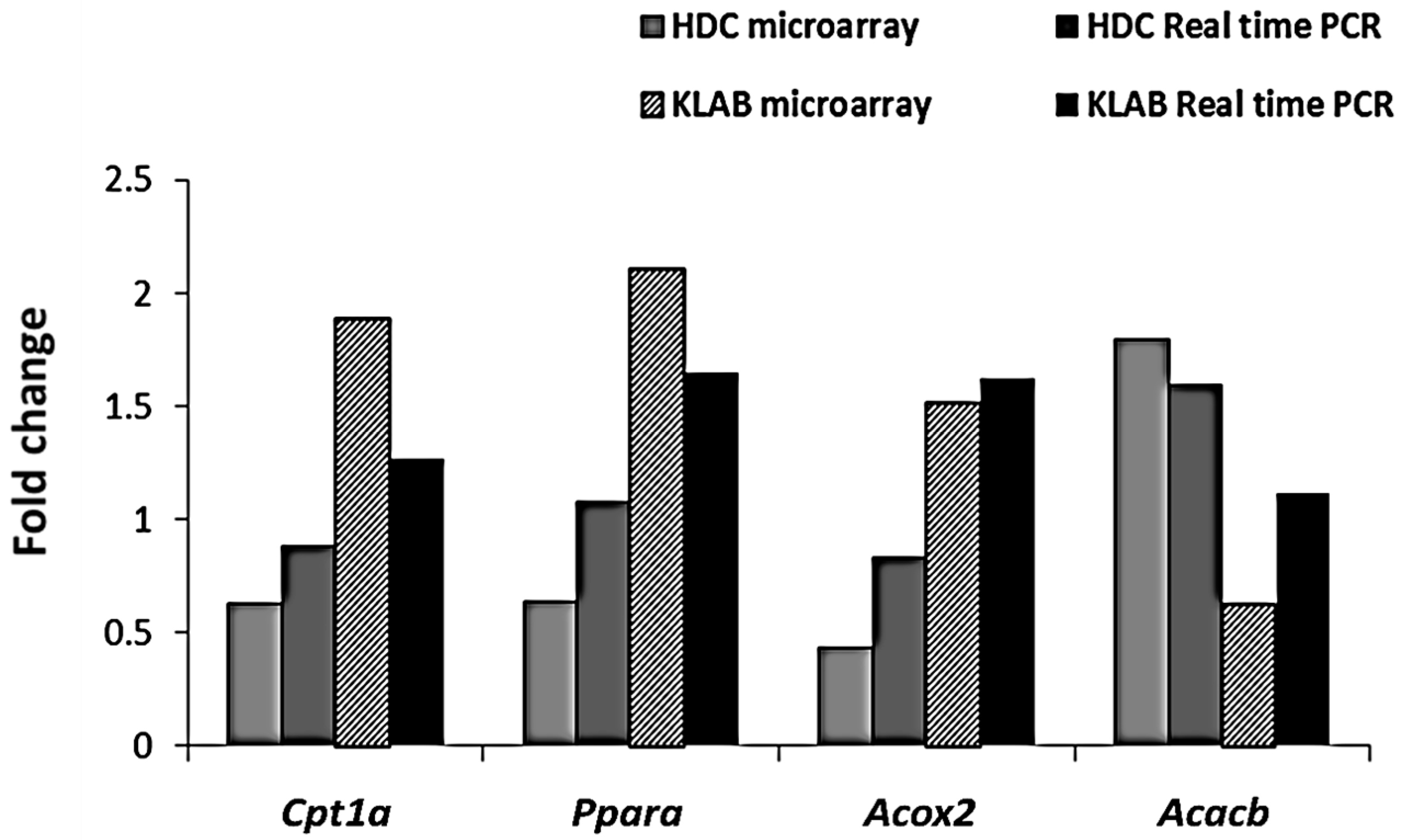
3.5. Microarray Analysis of Liver Tissue Gene Expression Profiles
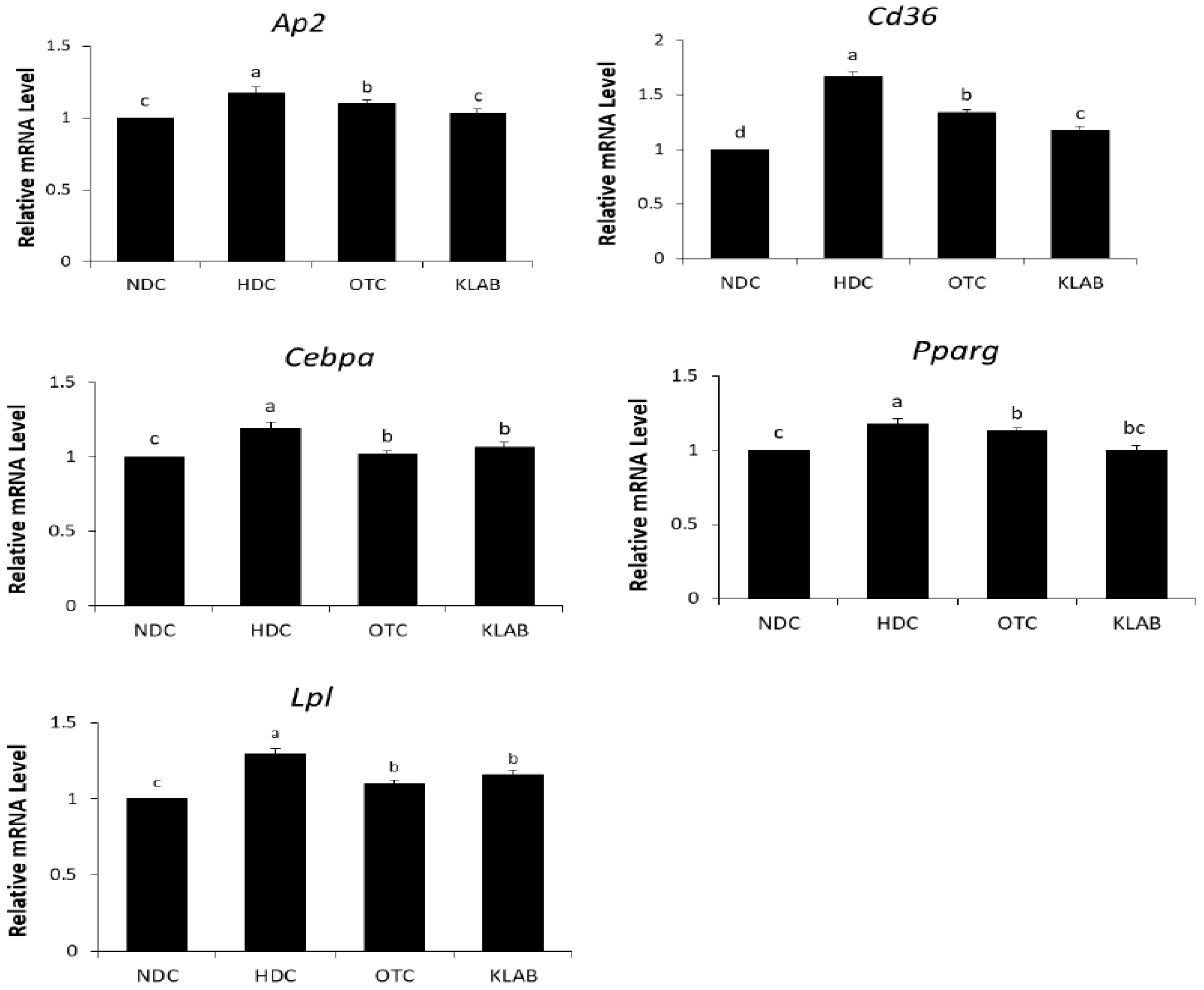
3.6. Expression of Adipogenic Regulating Gene in Adipose Tissue
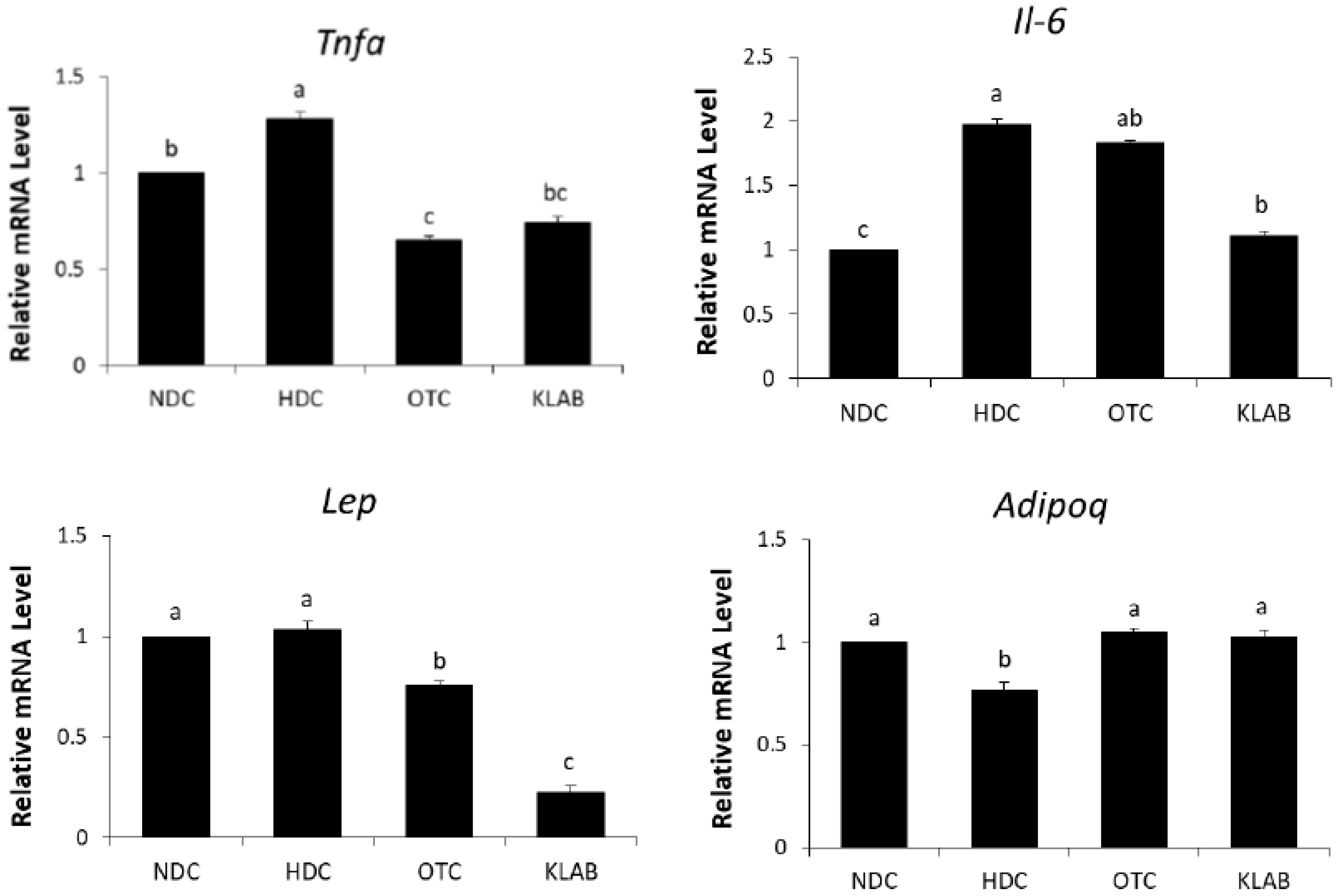
3.7. Expression of Inflammation Related Genes in Adipose Tissue
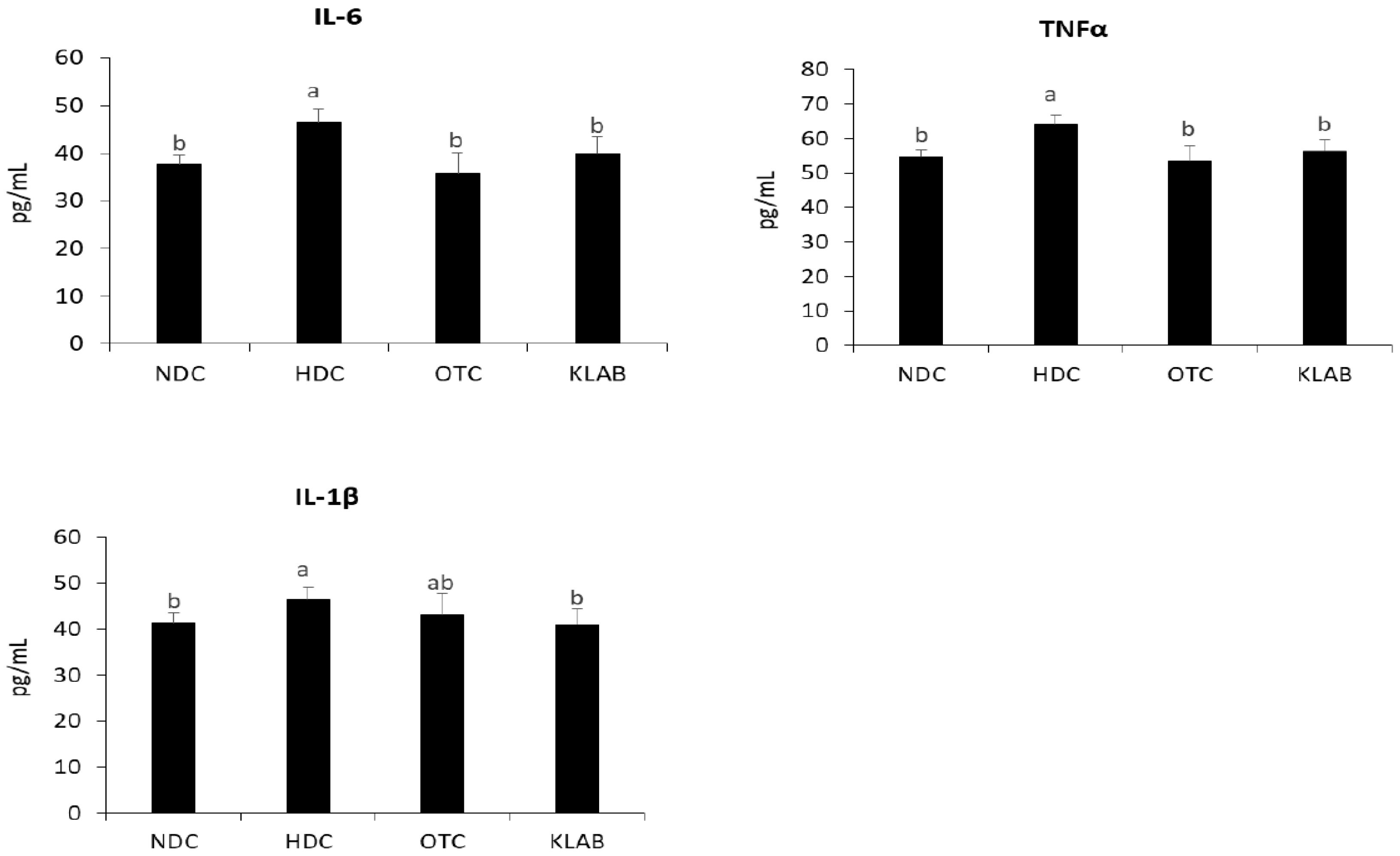
3.8. Inflammatory Cytokines in Serum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rocchini, A.P. Childhood obesity and a diabetes epidemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 854–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, R.H. Mechanisms of the components of the metabolic syndrome that predispose to diabetes and atherosclerotic CVD. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 66, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornier, M.A.; Dabelea, D.; Hernandez, T.L.; Lindstrom, R.C.; Steig, A.J.; Stob, N.R.; Van Pelt, R.E.; Wang, H.; Eckel, R.H. The Metabolic Syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 777–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J.P.; McKinley, B.; Eckel, R.H. The metabolic syndrome and inflammation. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2004, 2, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegaard, J.I.; Chawla, A. Pleiotropic actions of insulin resistance and inflammation in metabolic homeostasis. Science 2013, 339, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, K.; Froguel, P.; Wolowczuk, I. Adipose tissue in obesity-related inflammation and insulin resistance: Cells, cytokines, and chemokines. ISRN Inflamm. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Chun, J.; Cha, C.J.; Park, W.S.; Jeon, C.O.; Bae, J.W. Bacterial community analysis during fermentation of ten representative kinds of kimchi with barcoded pyrosequencing. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Ko, C.Y.; Ha, D.M. Microfloral changes of the lactic acid bacteria during kimchi fermentation and identification of the isolates. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 20, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Chun, J.; Han, H.U. Leuconostoc kimchii sp. nov., a new species from kimchi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.A.; Heo, G.Y.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, B.Y.; Miheen, T.I.; Kim, C.K.; Ahn, J.S. Change of microbial communities in kimchi fermentation at low temperature. Korean J. Microbiol. 2003, 39, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.M.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, D.W.; Song, J.C.; Suh, H.J.; Chang, U.J.; Kim, J.M. Identification of the lactic acid bacteria in kimchi according to initial and over-ripened fermentation using PCR and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.; Prasad, J. Probiotics, immunomodulation, and health benefits. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 606, 423–454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mennigen, R.; Bruewer, M. Effect of probiotics on intestinal barrier function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1165, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.A.; An, H.M.; Kim, J.R.; Kim, M.J.; Cha, M.G.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, K.O.; et al. Hypocholesterolemic effect of sonication-killed Bifidobacterium longum isolated from healthy adult Koreans in high cholesterol fed rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S.J. The health effects of cultured milk products with viable and non-viable bacteria. Int. Dairy. Journal. 1998, 8, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Cui, Y.; Yin, Y.N.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J.W.; Wang, Z.G.; Fu, N.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.H.; Liu, X.W.; et al. Effects of two Lactobacillus strains on lipid metabolism and intestinal microflora in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Velasquez, M.T.; Hansen, C.T.; Mohamed, A.I.; Bhathena, S.J. Modulation of carbohydrate metabolism and peptide hormones by soybean isoflavones and probiotics in obesity and diabetes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, N.; Okubo, T.; Sonoyama, K. Lactobacillus plantarum strain No. 14 reduces adipocyte size in mice fed high-fat diet. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 235, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Oh, S.H.; Cha, Y.S. Lactobacillus plantarum LG42 isolated from Gajami Sik-Hae inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocyte. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Jung, S.R.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D.; Lim, S.I. Lactobacillus plantarum Strain Ln4 Attenuates Diet-Induced Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Changes in Hepatic mRNA Levels Associated with Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Nutrients 2018, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, J.H.; Park, K.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Bae, M.O.; Lee, M.K.; Oh, S.H. Production and characterization of kimchi with enhanced levels of γ-aminobutyric acid. Food. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 17, 940–946. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.J.; Oh, S.H. Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria strains with ornithine producing capacity from natural sea salt. J. Microbiol. 2010, 248, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J. Preparation and characterization of kimchi using lactic acid bacteria having GABA and ornithine producing capacity and its some functional properties. Master’s Thesis, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, South Korea, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, Y.J.; Soh, J.R.; Yu, J.J.; Sohn, H.S.; Cha, Y.S.; Oh, S.H. Intracellular lipid accumulation inhibitory effect of Weissella koreensis OK1-6 isolated from Kimchi on differentiating adipocyte. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.B. Effect of growth hormone on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 1987, 8, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Oh, S.H.; Cha, Y.S. Lactobacillus brevis OPK-3 isolated from kimchi inhibits adipogenesis and exerts anti-inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocyte. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 4, 2514–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, E. Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730: A clinically proven probiotic. Nutrafoods 2004, 3, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.L.; Geier, M.S.; Yazbeck, R.; Torres, D.M.; Butler, R.N.; Howarth, G.S. Lactobacillus fermentum BR11 and fructo-oligosaccharide partially reduce jejunal inflammation in a model of intestinal mucositis in rats. Nutr. Cancer 2008, 60, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Yadav, H.; Sinha, P.R. Antioxidant and cholesterol assimilation activities of selected lactobacilli and lactococci cultures. J. Dairy. Res. 2009, 76, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, H.Q.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Hang, X.M.; Qin, H.L. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum LP-Onlly on gut flora and colitis in interleukin-10 knockout mice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane-Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- de la Serre, C.B.; Ellis, C.L.; Lee, J.; Hartman, A.L.; Rutledge, J.C.; Raybould, H.E. Propensity to high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats is associated with changes in the gut microbiota and gut inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G440–G448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, M.; Ogawa, A.; Higurashi, S.; Kadooka, Y. Anti-obesity effect of Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055 accompanied by inhibition of pro-inflammatory gene expression in the visceral adipose tissue in diet-induced obese mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2004, 53, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, T.; Nagata, Y.; Kado, S.; Uchida, K.; Kato, I.; Hashimoto, S.; Yokokura, T. Prevention of onset in an insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus model, NOD mice, by oral feeding of Lactobacillus casei. APMIS 1997, 105, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Velásquez-Mejía, E.P.; Carmona, J.A.; Abad, J.M.; Escobar, J.S. Gut microbiota is associated with obesity and cardiometabolic disease in a population in the midst of Westernization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.V.; Cortez-Pinto, H. Diet, Microbiota, Obesity, and NAFLD: A Dangerous Quartet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterveer, M.H.; van Dijk, T.H.; Tietge, U.J.; Boer, T.; Havinga, R.; Stellaard, F.; Groen, A.K.; Kuipers, F.; Reijngoud, D.J. High fat feeding induces hepatic fatty acid elongation in mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmiel-Haggai, M.; Cederbaum, A.I.; Nieto, N. A high-fat diet leads to the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese rats. The FASEB Journal 2005, 19, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postic, C.; Girard, J. Contribution of de novo fatty acid synthesis to hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance: Lessons from genetically engineered mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elam, R.P. Morphological changes in adult males from resistance exercise and amino acid supplementation. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 1988, 28, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Evain-Brion, D.; Donnadieu, M.; Roger, M.; Job, J. Simultaneous study of somatotrophic and corticotrophic pituitary secretions during ornithine infusion test. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 1982, 17, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota de Sá, P.; Richard, A.J.; Hang, H.; Stephens, J.M. Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 7, 635–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Auwerx, J.; Leroy, P.; Schoonjans, K. Lipoprotein lipase: Recent contributions from molecular biology. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1992, 29, 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoonjans, K.; Peinado-Onsurbe, J.; Lefebvre, A.M.; Heyman, R.A.; Briggs, M.; Deeb, S.; Staels, B.; Auwerx, J. PPARalpha and PPARgamma activators direct a distinct tissue-specific transcriptional response via a PPRE in the lipoprotein lipase gene. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 5336–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Koo, B.S.; Kang, M.K.; Rho, H.W.; Sohn, H.S.; Jhee, E.C.; Park, J.W. Retinoic acid inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2002, 34, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, M.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Maeda, K.; Nagaretani, H.; Kishida, K.; Maeda, N.; et al. Adiponectin specifically increased tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 through interleukin-10 expression in human macrophages. Circulation 2004, 109, 2046–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.M.; Wolf, D.; Rumpold, H.; Enrich, B.; Tilg, H. Adiponectin induces the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-1RA in human leukocytes. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 323, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulster-Radcliffe, M.C.; Ajuwon, K.M.; Wang, J.; Christian, J.A.; Spurlock, M.E. Adiponectin differentially regulate cytokines in porcine macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M. Interplay between obesity and associated metabolic disorders: New insights into the gut microbiota. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Million, M.; Maraninchi, M.; Henry, M.; Armougom, F.; Richet, H.; Carrieri, P.; Valero, R.; Raccah, D.; Vialettes, B.; Raoult, D. Obesity-associated gut microbiota is enriched in Lactobacillus reuteri and depleted in Bifidobacterium animalis and Methanobrevibacter smithii. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 6, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ingredient (g) | † Normal Diet | ‡ High Fat Diet | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDC | HDC | OTC | KLAB | |
| Casein, lactic | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| L-cystine | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Corn Starch | 315 | - | - | - |
| Maltodextrin | 35 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
| Sucrose | 350 | 68.8 | 68.8 | 68.8 |
| Cellulose | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Soybean Oil | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Lard | 20 | 245 | 245 | 245 |
| Mineral Mix | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Dicalcium Phosphate | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| Calcium Carbonate | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Potassium Citrate | 16.5 | 16.5 | 16.5 | 16.5 |
| Vitamin Mix | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Choline Bitarate | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| FD&C Yellow Dye #5 | 0.05 | - | - | - |
| FD&C Blue Dye #1 | - | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Total | 1055.05 | 773.85 | 773.85 | 773.85 |
| Kcal | 4057 | 4057 | 4057 | 4057 |
| Kcal/g | 3.8 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 5.2 |
| Oral administration | DW | DW | L-ornithine | Lb. brevis OPK-3 |
| Groups | NDC | HDC | OTC | KLAB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum (mg/dL) | ||||
| TG | 94.34 ± 17.26 c | 140.72 ± 16.40 a | 109.57 ± 3.55 bc | 99.07 ± 11.64 c |
| TC | 155.35 ± 18.1 c | 314.65 ± 56.06 a | 304.12 ± 47.70 b | 307.01 ± 22.94 b |
| HDL-c | 92.89 ± 6.28 c | 102.57 ± 7.33 b | 116.32 ± 10.08 a | 118.50 ± 8.72 a |
| HDL-c/TC | 53.45 ± 2.22 | 34.07 ± 4.35 | 36.90 ± 2.23 | 36.58 ± 4.13 |
| Liver (mg/g) | ||||
| TG | 10.24 ± 2.03 b | 31.45 ± 4.08 a | 27.13 ± 2.16 a | 19.59 ± 5.20 b |
| TC | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| Symbol | Gene Name | Fold Change | Accession ID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDC | KLAB | |||
| Immunity and inflammation response | ||||
| Anxa1 | annexin A1 | 4.01 | 0.61 | NM_009071 |
| Igj | immunoglobulin joining chain | 2.67 | 0.54 | NM_152839 |
| Myd88 | myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 | 1.52 | 0.66 | NM_010851 |
| Lipid metabolic process | ||||
| Slc27a1 | solute carrier family 27 (fatty acid transporter), member 1 | 0.58 | 2.15 | NM_011977 |
| Gpx3 | glutathione peroxidase 3 | 3.17 | 0.62 | NM_008161 |
| Ldlr | low density lipoprotein receptor | 1.50 | 0.65 | NM_010700 |
| Agpat5 | 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 5 | 1.74 | 0.64 | NM_026792 |
| Cpt1a | carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a, liver | 0.63 | 1.88 | NM_013495 |
| Acacb | acetyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase beta | 1.80 | 0.62 | NM_133904 |
| Ppara | peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha | 0.64 | 2.10 | NM_011144 |
| Acox2 | acyl-Coenzyme A oxidase 2 | 0.43 | 1.51 | NM_053115 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.E.; Oh, S.-H.; Cha, Y.-S. Lactobacillus Brevis OPK-3 from Kimchi Prevents Obesity and Modulates the Expression of Adipogenic and Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Adipose Tissue of Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030604
Park JE, Oh S-H, Cha Y-S. Lactobacillus Brevis OPK-3 from Kimchi Prevents Obesity and Modulates the Expression of Adipogenic and Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Adipose Tissue of Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients. 2020; 12(3):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030604
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jung Eun, Suk-Heung Oh, and Youn-Soo Cha. 2020. "Lactobacillus Brevis OPK-3 from Kimchi Prevents Obesity and Modulates the Expression of Adipogenic and Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Adipose Tissue of Diet-Induced Obese Mice" Nutrients 12, no. 3: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030604
APA StylePark, J. E., Oh, S.-H., & Cha, Y.-S. (2020). Lactobacillus Brevis OPK-3 from Kimchi Prevents Obesity and Modulates the Expression of Adipogenic and Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Adipose Tissue of Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients, 12(3), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030604




