Plasma and Red Blood Cell PUFAs in Home Parenteral Nutrition Paediatric Patients—Effects of Lipid Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aim of the Study
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. PUFA Profile
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Biochemical Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Ethical Aspects
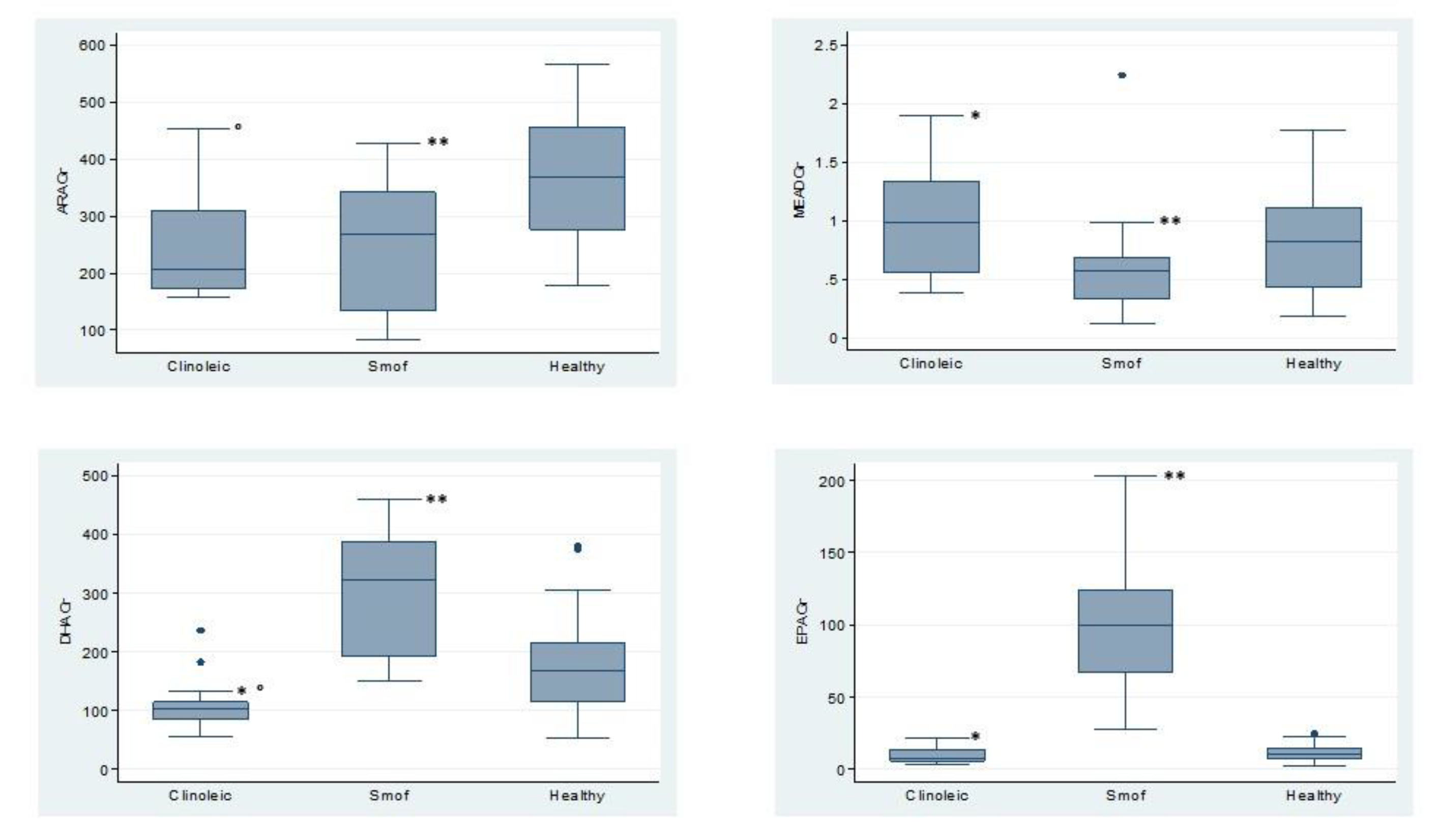
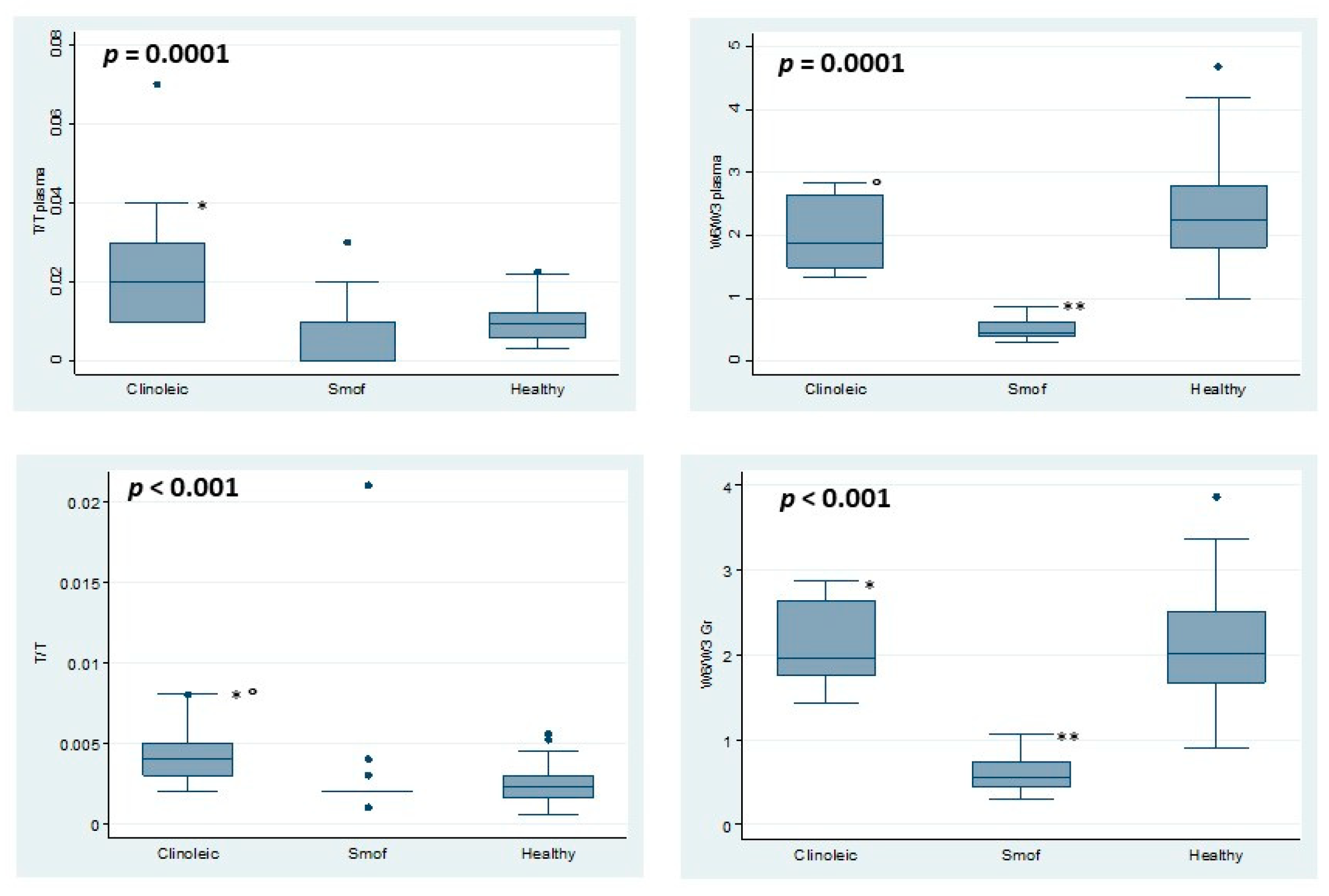
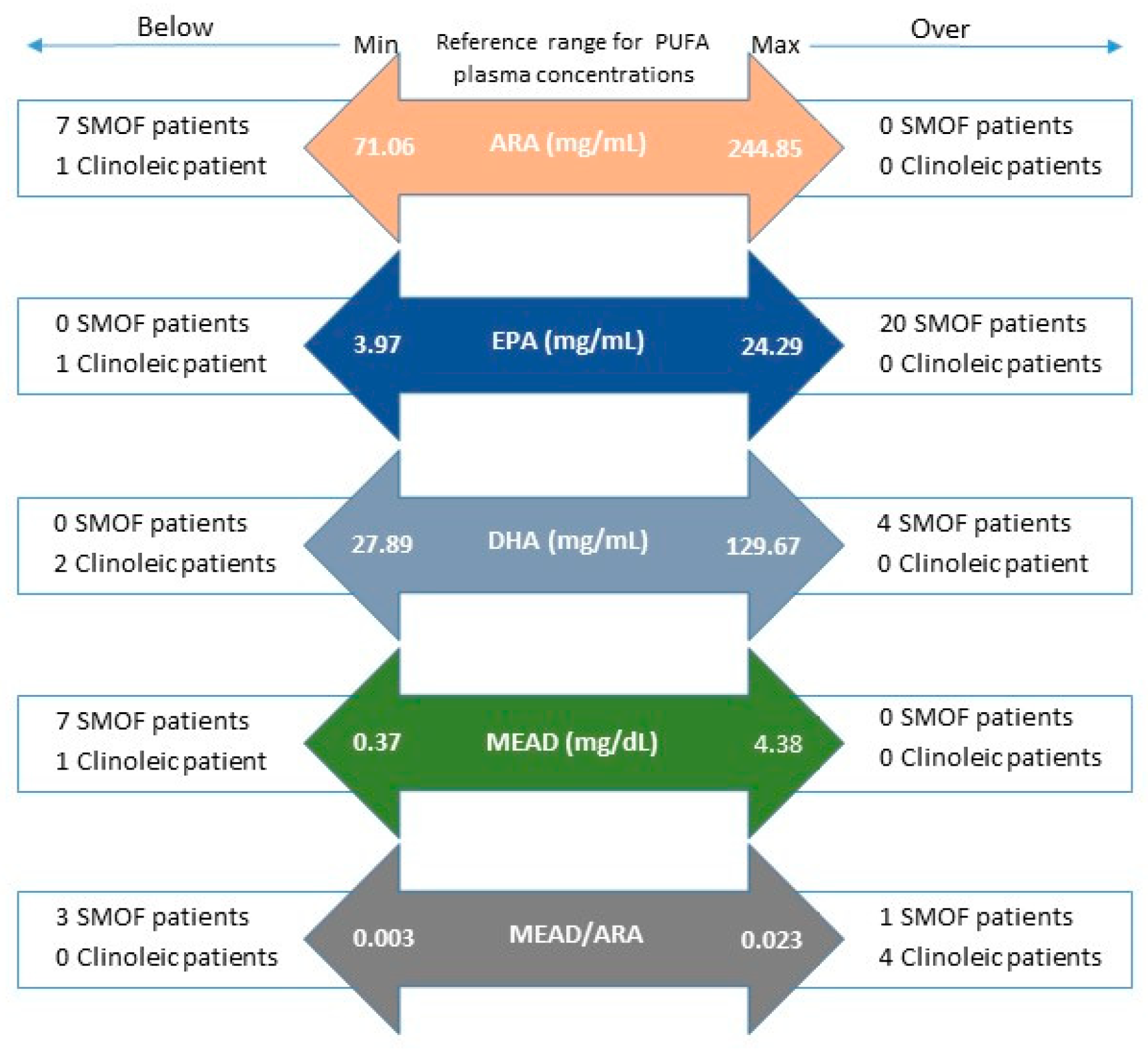
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goulet, O.; Ruemmele, F. Causes and Management of Intestinal Failure in Children. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, S16–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet, O.; Joly, F.; Corriol, O.; Colomb-Jung, V. Some new insights in intestinal failure-associated liver disease. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2009, 14, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, O.J. Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease and the Use of Fish Oil-Based Lipid Emulsions. World. Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 112, 90–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavicchi, M.; Beau, P.; Crenn, P.; Degott, C.; Messing, B. Prevalence of Liver Disease and Contributing Factors in Patients Receiving Home Parenteral Nutrition for Permanent Intestinal Failure. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 132, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomb, V.; Jobert-Giraud, A.; Lacaille, F.; Goulet, O.; Fournet, J.-C.; Ricour, C. Role of Lipid Emulsions in Cholestasis Associated with Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition in Children. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2000, 24, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, C.; Shamir, R.; Simchowitz, V.; Lohner, S.; Cai, W.; Decsi, T.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; et al. Espghan/Espen/Espr/Cspen guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Complications. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2418–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapillonne, A.; Mis, N.F.; Goulet, O.; Akker, C.H.V.D.; Wu, J.; Koletzko, B.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; et al. Espghan/Espen/Espr/Cspen guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Lipids. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2324–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet, O.; Lambe, C. Intravenous lipid emulsions in pediatric patients with intestinal failure. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2017, 22, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gura, K.M.; Duggan, C.P.; Collier, S.B.; Jennings, R.W.; Folkman, J.; Bistrian, B.R.; Puder, M. Reversal of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease in Two Infants With Short Bowel Syndrome Using Parenteral Fish Oil: Implications for Future Management. Pediatrics 2006, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gura, K.M.; Lee, S.; Valim, C.; Zhou, J.; Kim, S.; Modi, B.P.; Arsenault, D.A.; Strijbosch, R.A.M.; Lopes, S.; Duggan, C.P.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of a Fish-Oil-Based Fat Emulsion in the Treatment of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e678–e686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puder, M.; Valim, C.; Meisel, J.A.; Le, H.D.; De Meijer, V.E.; Robinson, E.M.; Zhou, J.; Duggan, C.; Gura, K.M. Parenteral Fish Oil Improves Outcomes in Patients With Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Injury. Trans. Meet. Am. Surg. Assoc. 2009, 127, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diamond, I.R.; Sterescu, A.; Pencharz, P.B.; Kim, J.H.; Wales, P.W. Changing the Paradigm: Omegaven for the Treatment of Liver Failure in Pediatric Short Bowel Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 48, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meijer, V.E.; Le, H.D.; Meisel, J.A.; Gura, K.M.; Puder, M. Parenteral Fish Oil as Monotherapy Prevents Essential Fatty Acid Deficiency in Parenteral Nutrition–dependent Patients. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hojsak, I.; Colomb, V.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; Mis, N.F.; Hulst, J.M.; Indrio, F.; et al. ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition Position Paper. Intravenous Lipid Emulsions and Risk of Hepatotoxicity in Infants and Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 776–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wales, P.W.; Allen, N.; Worthington, P.; George, D.; Compher, C.; Teitelbaum, D.; Malone, A.; Jaksic, T.; Ayers, P.; Baroccas, A.; et al. A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seida, J.C.; Mager, D.R.; Hartling, L.; VanderMeer, B.; Turner, J.M. Parenteral ω-3 Fatty Acid Lipid Emulsions for Children With Intestinal Failure and Other Conditions. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2012, 37, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klek, S. Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Modern Parenteral Nutrition: A Review of the Current Evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martindale, R.G.; Berlana, D.; Boullata, J.I.; Cai, W.; Calder, P.C.; Deshpande, G.H.; Evans, D.; Garcia-De-Lorenzo, A.; Goulet, O.J.; Li, A.; et al. Summary of Proceedings and Expert Consensus Statements From the International Summit “Lipids in Parenteral Nutrition ”. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, S7–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, C.J.; Calder, P.C. Influence of different intravenous lipid emulsions on fatty acid status and laboratory and clinical outcomes in adult patients receiving home parenteral nutrition: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goulet, O.; Lambe, C.; Talbotec, C.; Poisson, C.; Rocha, A.; Postaire, M.; Clément, R.; Lamazière, A.; Maubert, M.; Wolff, C. Intravenous lipid emulsion containing 15% fish oil provides a new red blood cell fatty acids profile [abstract]. Transplantation 2017, 101, S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, C.; Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B. High-throughput analysis of fatty acid composition of plasma glycerophospholipids[S]. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 51, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derevlean, L.; D’Onofrio, V.; Lezo, A.; Massarenti, P.; Mengozzi, G.; Puccinelli, M. Standardization of Routine Quantification of Polyunsaturated Acids in Pediatric Total Parenteral Nutrition. Nutrition 2020, 110916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, A.; Alladio, E.; Casalini, V.; Puccinelli, M.P.; Massarenti, P.; Pazzi, M.; Aprile, S.; De Francesco, A.; Mengozzi, G.; D’Avolio, A. Novel "Matrix-Corrected Calibration" study for the detection of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in plasma and erythrocytes by means of a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry approach optimized to follow up long-term parental patients. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 176, 112764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klem, S.; Klingler, M.; Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B. Efficient and Specific Analysis of Red Blood Cell Glycerophospholipid Fatty Acid Composition. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, J.H.; Roumiantsev, S.; Singh, R. PediTools Electronic Growth Chart Calculators: Applications in Clinical Care, Research, and Quality Improvement. J. Med. Int. Res. 2020, 22, e16204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, C.; Demmelmair, H.; Sausenthaler, S.; Herbarth, O.; Heinrich, J.; Koletzko, B. Fatty Acid Composition of Serum Glycerophospholipids in Children. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 826–831.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.-J.; Sun, L.-L.; Li, M.-Y.; Ding, C.-L.; Su, Y.-C.; Sun, L.-J.; Xue, S.-H.; Yan, F.; Zhao, C.-H.; Wang, W. Comparison of Formulas Based on Lipid Emulsions of Olive Oil, Soybean Oil, or Several Oils for Parenteral Nutrition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meisel, J.A.; Le, H.D.; De Meijer, V.E.; Nose, V.; Gura, K.M.; Mulkern, R.V.; Akhavan Sharif, M.R.; Puder, M. Comparison of 5 intravenous lipid emulsions and their effects on hepatic steatosis in a murine model. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimund, J.-M.; Rahmi, G.; Escalin, G.; Pinna, G.; Finck, G.; Muller, C.D.; Duclos, B.; Baumann, R. Efficacy and safety of an olive oil-based intravenous fat emulsion in adult patients on home parenteral nutrition. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 21, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Gibson, S.; Jawhari, A.; Atlan, P.; Le Brun, A.; Farthing, M.; Forbes, A. Safe and efficacious prolonged use of an olive oil-based lipid emulsion (ClinOleic) in chronic intestinal failure. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, K.; Atlan, P.; Joly, F.; Le Brun, A.; Evard, D.; Perennec, V.; Roux-Haguenau, D.; Bereziat, G.; Messing, B. A 3-month double-blind randomised study comparing an olive oil- with a soyabean oil-based intravenous lipid emulsion in home parenteral nutrition patients. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 94, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kłęk, S.; Chambrier, C.; Singer, P.; Rubin, M.; Bowling, T.; Staun, M.; Joly, F.; Rasmussen, H.; Strauss, B.J.; Wanten, G.; et al. Four-week parenteral nutrition using a third generation lipid emulsion (SMOFlipid)—A double-blind, randomised, multicentre study in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramlich, L.; Ireton-Jones, C.; Miles, J.M.; Morrison, M.; Pontes-Arruda, A. Essential Fatty Acid Requirements and Intravenous Lipid Emulsions. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anez-Bustillos, L.; Dao, D.T.; A Baker, M.; Fell, G.L.; Puder, M.; Gura, K.M. Intravenous Fat Emulsion Formulations for the Adult and Pediatric Patient: Understanding the Differences. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kish-Trier, E.; Schwarz, E.; Pasquali, M.; Yuzyuk, T. Quantitation of total fatty acids in plasma and serum by GC-NCI-MS. Clin. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 2, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.D.; Meisel, J.A.; De Meijer, V.E.; Gura, K.M.; Puder, M. The essentiality of arachidonic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2009, 81, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, U. Essential Fatty Acids—A Review. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2006, 7, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet, O.; Antébi, H.; Wolf, C.; Talbotec, C.; Alcindor, L.-G.; Corriol, O.; Lamor, M.; Colomb-Jung, V. A New Intravenous Fat Emulsion Containing Soybean Oil, Medium-Chain Triglycerides, Olive Oil, and Fish Oil. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, B.P.; Mitchell, P.D.; Gura, K.M.; Potemkin, A.K.; Squires, R.H.; Puder, M.; Duggan, C.P. Growth in Infants and Children With Intestinal Failure-associated Liver Disease Treated With Intravenous Fish Oil. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicario, C.; González-Périz, A.; Rius, B.; Morán-Salvador, E.; García-Alonso, V.; Lozano, J.J.; Bataller, R.; Cofán, M.; Kang, J.X.; Arroyo, V.; et al. Molecular interplay between Δ5/Δ6 desaturases and long-chain fatty acids in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 2014, 63, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanten, G.J.; Calder, P.C. Immune modulation by parenteral lipid emulsions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Patients and HPN Characteristics | Clinoleic® n = 15 Mediana (IQR) | SMOF® n = 23 Mediana (IQR) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients’ age (years) | 8.4 (1.6–18.6) | 3.3 (0.9–16.9) | 0.097 |
| Causes of IF—n (%) Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS) Motility disorders (CIPO) Congenital enteropathies Other | 9 (60%) 3 (20%) 1 (7%) 2 (13%) | 16 (70%) 1 (4%) 4 (17%) 2 (9%) | 0.670 |
| PN duration (months) | 22.2 (9.8–202) | 21.1 (6.9–104) | 0.362 |
| PN bags/week | 7 (3–7) | 7 (5–7) | 0.115 |
| Nr lipid infusions/week | 6 (3–7) | 6 (5–7) | 0.643 |
| Lipid intake (g/kg/day) | 1.03 (0.5–1.7) | 1.3 (0.5–2.5) | 0.064 |
| Lipid intake (% kcal) | 24.5 (20.1–36.3) | 21.5 (6.7–40.3) | 0.066 |
| Glucose intake (% kcal) | 65.1 (46.0–71.0) | 65.2 (48.9–86.1) | 0.347 |
| Aminoacid intake (g/kg/day) | 1.05 (0.2–1.8) | 1.3 (0.7–3.2) | 0.002 |
| PN energy provision (Kcal/kg/day) | 40.99 (12.0–62.7) | 54.4 (23.9–82.8) | 0.002 |
| PN energy (% BEE) Energy intake (% BEE) | 100 (30–100) | 100 (74–118) | 0.057 |
| BMI/WFL Z-score <−2 | 0 (0%) | 5/23 (21.7%) | 0.046 |
| Weight for age Z-score <−2 | 3/15 (20%) | 13/23 (56.5%) | 0.221 |
| Height for age Z-score <−2 | 2/15 (13.3%) | 9/23 (39.1%) | 0.050 |
| Product Name | Clinoleic® | Smof® Lipid |
|---|---|---|
| Lipid source | 20% soybean oil, 80% olive oil | 30% soybean oil, 30% MCT, 25% olive oil, 15% fish oil |
| Soybean oil (g/L) | 40 | 60 |
| MCT (g/L) | 0 | 60 |
| Olive oil (g/L) | 160 | 50 |
| Fish oil (g/L) | 0 | 30 |
| Lipidic composition | ||
| Linoleic acid (%; g/L) | 18.5; 18 | 21.4; 58 |
| α-Linolenic acid (%; g/L) | 2; 2 | 2.5; 6 |
| Arachidonic acid (g/L) | 0,6 | 1 |
| EPA (%; g/L) | 0; 0 | 3; 6 |
| DHA (%; g/L) | 0; 0 | 2; 1 |
| ω-6: ω-3 ratio | 9:1 | 2.5:1 |
| α-Tocopherol (mg/L) | 32 | 200 |
| Phytosterols (mg/L) | 327 ± 8 | 47.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lezo, A.; D’Onofrio, V.; Puccinelli, M.P.; Capriati, T.; De Francesco, A.; Bo, S.; Massarenti, P.; Gandullia, P.; Marin, M.; Derevlean, L.; et al. Plasma and Red Blood Cell PUFAs in Home Parenteral Nutrition Paediatric Patients—Effects of Lipid Emulsions. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123748
Lezo A, D’Onofrio V, Puccinelli MP, Capriati T, De Francesco A, Bo S, Massarenti P, Gandullia P, Marin M, Derevlean L, et al. Plasma and Red Blood Cell PUFAs in Home Parenteral Nutrition Paediatric Patients—Effects of Lipid Emulsions. Nutrients. 2020; 12(12):3748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123748
Chicago/Turabian StyleLezo, Antonella, Valentina D’Onofrio, Maria Paola Puccinelli, Teresa Capriati, Antonella De Francesco, Simona Bo, Paola Massarenti, Paolo Gandullia, Marta Marin, Liliana Derevlean, and et al. 2020. "Plasma and Red Blood Cell PUFAs in Home Parenteral Nutrition Paediatric Patients—Effects of Lipid Emulsions" Nutrients 12, no. 12: 3748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123748
APA StyleLezo, A., D’Onofrio, V., Puccinelli, M. P., Capriati, T., De Francesco, A., Bo, S., Massarenti, P., Gandullia, P., Marin, M., Derevlean, L., Baldini, L., Longo, F., & Diamanti, A. (2020). Plasma and Red Blood Cell PUFAs in Home Parenteral Nutrition Paediatric Patients—Effects of Lipid Emulsions. Nutrients, 12(12), 3748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123748