Association of Ultrasound-Derived Metrics of the Quadriceps Muscle with Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Recruitment
2.2. Ultrasound Measures
2.2.1. QMT Assessment
2.2.2. RFCSA Measurement
2.3. Nutritional Status Assessment
2.3.1. Anthropometry
2.3.2. Body Composition
2.3.3. Laboratory Investigations
2.3.4. Dietary Assessment
2.3.5. Nutritional Risk Assessment
2.3.6. Handgrip Strength Test
2.3.7. Protein Energy Wasting Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics as per PEW Identification
3.2. Nutritional Status Assessment and US Measures
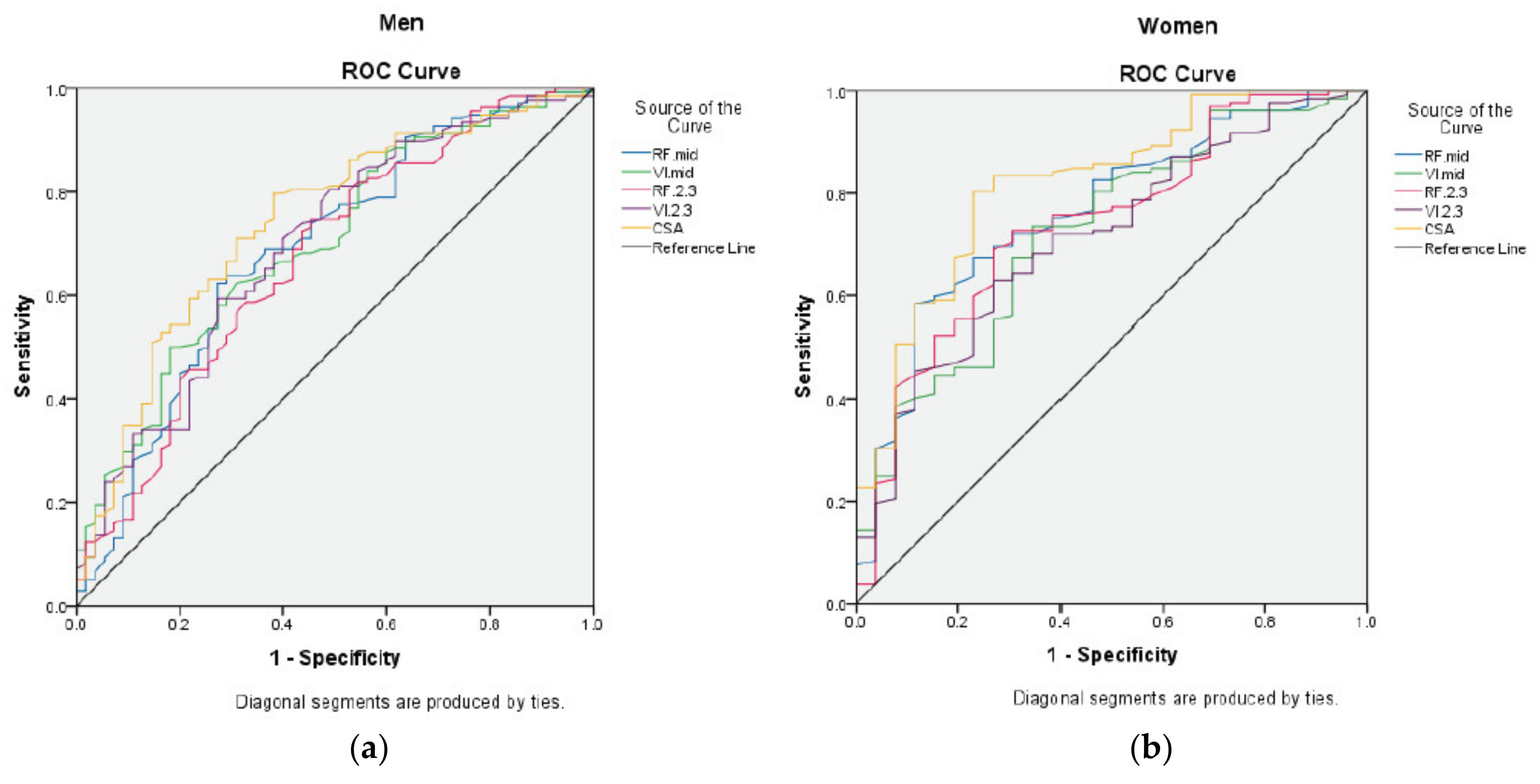
3.3. Assessment of US, BIS, and HGS Methods for PEW Risk
3.4. Development of the Gender-Specific Value of US Measures for PEW Risk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOR | Adjusted odds ratio |
| ATM | Adipose tissue mass |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BCM | Body cell mass |
| BIA | Bio-impedance analysis |
| BIS | Bio-impedance spectroscopy |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CSA | Cross-sectional area |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DEI | Dietary energy intake |
| FTI | Fat tissue index |
| FTM | Fat tissue mass |
| HD | Hemodialysis |
| HGS | Handgrip strength |
| hsCRP | High-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| IBW | Ideal body weight |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| ISAK | International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry |
| ISRNM | International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism |
| LBM | Lean body mass |
| LTI | Lean tissue index |
| LTM | Lean tissue mass |
| MAC | Mid-arm circumference |
| MAMA | Mid-arm muscle area |
| MAMC | Mid-arm muscle circumference |
| MIS | Malnutrition–inflammation score |
| PATCH | Palm Tocotrienol in Chronic Hemodialysis |
| PEW | Protein energy wasting |
| QMT | Quadriceps muscle thickness |
| RF | Rectus femoris |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TSF | Triceps skinfold |
| US | Ultrasound |
| VI | Vastus intermedius |
References
- Fouque, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.D.; Cano, N.; Chauveau, P.; Cuppari, L.; A Franch, H.; Guarnieri, G.L.; Ikizler, T.; A Kaysen, G.; et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein–energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, J.J.; Thomas, F.; Nagy, K.; Arogundade, F.; Avesani, C.M.; Chan, M.; Chmielewski, M.; Cordeiro, A.C.; Espinosa-Cuevas, A.; Fiaccadori, E.; et al. Global Prevalence of Protein-Energy Wasting in Kidney Disease: A Meta-analysis of Contemporary Observational Studies From the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtzakis, M.; Wischmeyer, P. Bedside ultrasound measurement of skeletal muscle. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workeneh, B.T.; E Mitch, W. Review of muscle wasting associated with chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1128S–1132S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.J.; Johansen, K.L.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P.; Cuppari, L.; Avesani, C.M. Screening for muscle wasting and dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, K.; Eston, R. Kinanthropometry and Exercise Physiology, 4th ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, S.F.; Mohktar, M.S.; Ibrahim, F. The Theory and Fundamentals of Bioimpedance Analysis in Clinical Status Monitoring and Diagnosis of Diseases. Sensors 2014, 14, 10895–10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamney, P.W.; Wabel, P.; Moissl, U.M.; Müller, M.J.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Korth, O.; Fuller, N.J. A whole-body model to distinguish excess fluid from the hydration of major body tissues. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahathevan, S.; Khor, B.; Yeong, C.H.; Tan, T.H.; Mohaideen, A.K.M.; Ng, H.M.; Ong, G.R.; Narayanan, S.S.; Gafor, A.H.A.; Goh, B.L.; et al. Validity of Ultrasound Imaging in Measuring Quadriceps Muscle Thickness and Cross-Sectional Area in Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, C.A.G.; Zepeda, E.M.; Méndez, O.A.L. Bedside Ultrasound Measurement of Rectus Femoris: A Tutorial for the Nutrition Support Clinician. J. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 2017, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Delsante, M.; Di Motta, T.; Cantarelli, C.; Pioli, S.; Grassi, G.; Batini, V.; Gregorini, M.; Fiaccadori, E.; et al. Noninvasive evaluation of muscle mass by ultrasonography of quadriceps femoris muscle in End-Stage Renal Disease patients on hemodialysis. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarborough, D.M.; Krebs, D.E.; Harris, B.A. Quadriceps muscle strength and dynamic stability in elderly persons. Gait Posture 1999, 10, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruther, W.; Benesch, T.; Zorn, C.; Paternostro-Sluga, T.; Quittan, M.; Fialka-Moser, V.; Spiss, C.; Kainberger, F.; Crevenna, R. Muscle wasting in intensive care patients: Ultrasound observation of the M. quadriceps femoris muscle layer. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2008, 40, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.K.; Houchen, L.; Harrison, S.; Singh, S.J.; Morgan, M.D.; Steiner, M.C. Ultrasound assessment of lower limb muscle mass in response to resistance training in COPD. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; McManus, C.; Smith, J.; Stevens, V.; Nixon, D.W. Anthropometric measurement of muscle mass: Revised equations for calculating bone-free arm muscle area. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 36, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.-J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ikizler, T.; Block, G.; Avram, M.M.; Kopple, J.D. Malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome in dialysis patients: Causes and consequences. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 42, 864–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garagarza, C.; Flores, A.L.; Valente, A. Influence of Body Composition and Nutrition Parameters in Handgrip Strength: Are There Differences by Sex in Hemodialysis Patients? Nutr. Clin. Pr. 2017, 33, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, F.R.U.; Antunes, A.A.U.; Vannini, F.C.D.U.; Silveira, L.V.A.U.; Martin, L.C.U.; Barretti, P.; Caramori, J.C.T. Validity of malnutrition scores for predicting mortality in chronic hemodialysis patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2013, 45, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoyama, N.; Qureshi, A.R.; Avesani, C.M.; Lindholm, B.; Bàràny, P.; Heimbürger, O.; Cederholm, T.; Stenvinkel, P.; Carrero, J.J. Comparative Associations of Muscle Mass and Muscle Strength with Mortality in Dialysis Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchengast, S. Gender Differences in Body Composition from Childhood to Old Age: An Evolutionary Point of View. J. Life Sci. 2010, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, V.A.; Oliveira, D.; Cupolilo, E.N.; Miranda, C.S.; Colugnati, F.A.B.; Mansur, H.N.; Fernandes, N.M.D.S.; Bastos, M.G. Rectus femoris muscle mass evaluation by ultrasound: Facilitating sarcopenia diagnosis in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease stages. Clinics 2018, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M.; et al. The FNIH Sarcopenia Project: Rationale, Study Description, Conference Recommendations, and Final Estimates. J. Gerontol. Ser. A. Boil. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscaritoli, M.; Molfino, A.; Bollea, M.R.; Fanelli, F.R. Malnutrition and wasting in renal disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2009, 12, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-K.; Lee, W.-J.; Peng, L.-N.; Liu, L.-K.; Arai, H.; Akishita, M. Recent Advances in Sarcopenia Research in Asia: 2016 Update From the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 767.e1–767.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T.J.; Gould, D.W.; Nixon, D.G.D.; Watson, E.L.; Smith, A. Quality over quantity? Association of skeletal muscle myosteatosis and myofibrosis on physical function in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2019, 34, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.M.; Ward, K.; Sidhu, P.S.; Puthucheary, Z.; Steier, J.; Jolley, C.J.; Rafferty, G.F.; Polkey, M.I.; Moxham, J. Ultrasound measurement of rectus femoris cross-sectional area and the relationship with quadriceps strength in COPD. Thorax 2009, 64, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappe, T.A.; Lindquist, D.M.; Carrithers, J.A. Muscle-specific atrophy of the quadriceps femoris with aging. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 2070–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.; Murthy, S.; Tainter, C.R.; Lee, J.; Riddell, K.; Fintelmann, F.J.; Grabitz, S.D.; Timm, F.P.; Levi, B.; Kurth, T.; et al. Can Sarcopenia Quantified by Ultrasound of the Rectus Femoris Muscle Predict Adverse Outcome of Surgical Intensive Care Unit Patients as well as Frailty? A Prospective, Observational Cohort Study. Ann. Surg. 2016, 264, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, Y.; Ullo, I.; Massarenti, S.; Esposito, P.; Prencipe, M.A.; Ciancio, G.; Provenzano, M.; Fiorini, F.; Andreucci, M.; Storari, A.; et al. Ultrasonography of Quadriceps Femoris Muscle and Subcutaneous Fat Tissue and Body Composition by BIVA in Chronic Dialysis Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, C.; DeChicco, R.; Nowak, D.; Lopez, R.; He, L.; Jacob, S.; Kirby, D.F.; Rahman, N.; Cresci, G. Use of Bedside Ultrasound to Assess Muscle Changes in the Critically Ill Surgical Patient. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, D.W.; Watson, E.L.; Wilkinson, T.J.; Wormleighton, J.; Xenophontos, S.; Viana, J.L.; Smith, A. Ultrasound assessment of muscle mass in response to exercise training in chronic kidney disease: A comparison with MRI. J. Cachexia Sarcopeni. 2019, 10, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Kimura, Y.; Ishiyama, D.; Nishio, N.; Otobe, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ohji, S.; Koyama, S.; Sato, A.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Synergistic effect of bodyweight resistance exercise and protein supplementation on skeletal muscle in sarcopenic or dynapenic older adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Bozzoli, L.; Fani, F.; Antoniotti, R.; Maggiore, U.; Fiaccadori, E. Reliability of bedside ultrasound for measurement of quadriceps muscle thickness in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

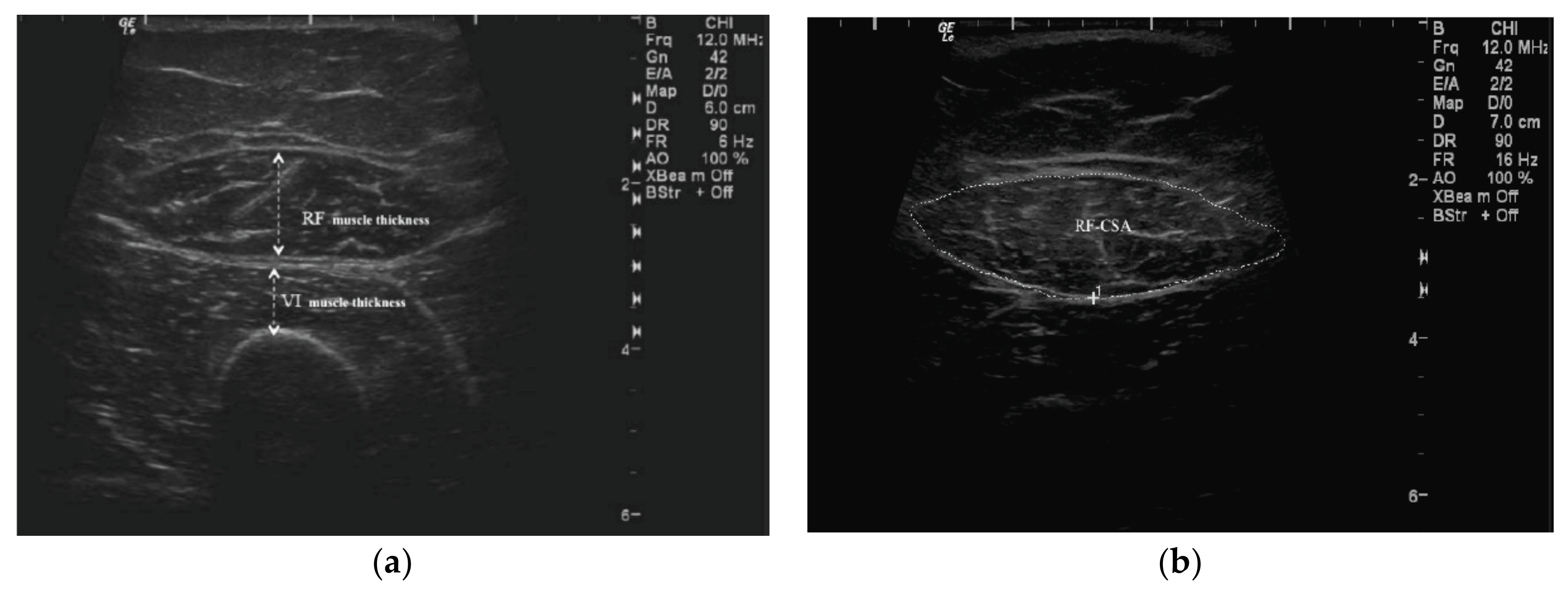
| Variables a,b | Overall (n = 351) | PEW c (n = 81) | Non-PEW (n = 270) | p-Value d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 55.18 ± 14.04 | 52.79 ±15.84 | 55.89 ± 13.40 | 0.112 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 193 (55.0) | 55 (67.9) | 138 (51.1) | 0.008 |
| Female | 158 (45.0) | 26 (32.1) | 132 (48.9) | |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| Malay | 102 (29.1) | 25 (30.9) | 77 (28.5) | 0.118 |
| Chinese | 190 (54.1) | 37 (45.7) | 153 (56.7) | |
| Indian | 59 (16.8) | 19 (23.5) | 40 (14.8) | |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Diabetes | 146 (41.6) | 24 (29.6) | 122 (45.2) | 0.013 |
| Hypertension | 274 (78.1) | 55 (67.9) | 219 (81.1) | 0.012 |
| CVD | 56 (16.0) | 11 (13.6) | 45 (16.7) | 0.506 |
| Dialysis vintage (months) | 82 ± 72 | 85 ± 88 | 80 ± 67 | 0.632 |
| Dialysis adequacy (Kt/V) | 1.65 (1.40–1.87) | 1.71 (1.41–2.04) | 1.63 (1.39–1.83) | 0.100 |
| Biochemistry Markers | ||||
| • Serum urea (mmol/L) | 19.2 (15.60–22.85) | 17.05 (14.38–20.08) | 20.15 (16.38–23.40) | <0.001 |
| • Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 814 (672–951) | 738 (624–884) | 834 (704–976) | 0.001 |
| • Serum albumin (g/L) | 40 (37–42) | 37 (35–42) | 40 (38–42) | <0.001 |
| • hsCRP (mg/L) | 3.50 (1.60–7.60) | 3.48 (1.44–6.45) | 3.53 (1.70–7.96) | 0.563 |
| • IL–6 (pg/mL) | 3.71 (2.33–5.99) | 4.43 (2.30–8.90) | 3.63 (2.33–5.69) | 0.166 |
| • Serum bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 20.64 (18.87–22.63) | 21.25 (19.88–23.14) | 20.53 (18.38–22.42) | 0.009 |
| Dietary Intake | ||||
| • DEI (kcal/kg IBW) | 24.37 (20.82–28.85) | 21.34 (18.86–23.60) | 25.80 (21.97–29.86) | <0.001 |
| • DPI (g/kg IBW) | 0.89 (0.71–1.12) | 0.81 (0.65–1.02) | 0.93 (0.74–1.16) | 0.002 |
| MIS | 5 (3–8) | 9 (5–11) | 5 (3–7) | <0.001 |
| Overall (n = 351) | Men (n = 193) | Women (n = 158) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable a | PEW (n = 81) Median (IQR) | Non-PEW (n = 270) Median (IQR) | PEW (n = 55) Median (IQR) | Non-PEW (n = 138) Median (IQR) | PEW (n = 26) Median (IQR) | Non-PEW (n = 132) Median (IQR) |
| Anthropometrics | ||||||
| Weight (kg) | 50.60 (44.45–59.35) | 63.00 (54.25–71.08) b | 56.00 (49.50–62.70) | 67.15 (59.88–74.30) b | 43.05 (38.60–47.18) | 57.35 (50.10–65.86) b |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.09 (18.51–22.04) | 25.08 (22.96–27.90) b | 20.62 (19.12–22.36) | 25.06 (23.46–27.50) b | 18.66 (16.98–20.48) | 25.09 (22.27–28.56) b |
| MAC (cm) | 24.55 (22.53–26.58) | 30.10 (27.90–32.76) b | 25.25 (23.20–27.65) | 30.18 (28.05–32.40) b | 22.58 (21.13–25.89) | 30.05 (27.25–33.71) b |
| TSF (mm) | 11.80 (8.60–15.75) | 16.75 (12.98–23.18) b | 11.30 (8.20–14.90) | 14.80 (11.45–19.50) b | 12.75 (9.73–17.28) | 20.50 (15.55–30.65) b |
| MAMC (cm) | 20.37 (18.70–22.94) | 24.35 (22.34–26.10) b | 22.05 (19.83–23.52) | 25.17 (23.71–26.47) b | 18.49 (17.53–19.48) | 23.03 (21.32–25.23) b |
| MAMA (cm2) | 23.95 (20.00–31.89) | 38.87 (32.07–45.33) b | 28.67 (21.29–34.05) | 40.71 (34.79–46.03) b | 20.13 (17.39–23.71) | 35.79 (29.84–44.17) b |
| Mid-thigh girth (cm) | 42.10 (39.70–46.08) | 48.90 (45.38–52.45) b | 43.30 (40.70–47.00) | 48.75 (45.50–52.21) b | 40.06 (38.38–42.80) | 49.00 (45.23–53.05) b |
| Body Composition and Physical Strength Test | ||||||
| LTM (kg) | 31.30 (27.00–35.10) | 31.30 (26.60–38.30) | 34.05 (29.20–37.48) | 38.00 (33.70–43.60) c | 26.60 (22.40–29.90) | 26.85 (23.20–29.70) |
| FTM (kg) | 13.50 (9.70–20.00) | 22.00 (17.10–27.10) b | 14.40 (10.00–21.25) | 21.10 (15.50–25.10) b | 11.30 (8.35–16.35) | 24.05 (18.00–28.65) b |
| LTI (kg/m2) | 11.80 (10.90–13.50) | 12.90 (11.10–14.60) c | 12.35 (11.15–14.43) | 14.10 (12.90–16.50) b | 11.40 (10.50–12.20) | 11.45 (10.10–12.90) |
| FTI (kg/m2) | 7.30 (5.50–10.00) | 12.10 (9.20–15.60) b | 7.95 (5.33–10.53) | 11.00 (8.20–12.90) b | 7.00 (5.55–9.45) | 14.10 (10.73–16.88) b |
| ATM (kg) | 18.30 (13.20–27.30) | 30.00 (23.20–36.80) b | 19.60 (13.60–28.98) | 28.70 (21.10–34.20) b | 15.40 (11.45–22.20) | 32.70 (24.43–39.03) b |
| BCM (kg) | 16.50 (14.00–19.30) | 17.30 (14.10–21.60) | 18.20 (14.88–21.43) | 21.20 (18.30–25.40) b | 13.30 (11.55–15.60) | 14.50 (11.75–16.48) |
| HGS (kg) | 17.50 (13.40–22.70) | 18.30 (14.05–24.60) | 19.50 (15.60–26.00) | 23.10 (18.25–28.95) c | 13.85 (10.23–16.93) | 14.95 (12.10–18.10) |
| US Measures | ||||||
| RFMID (cm) | 1.55 (1.32–1.86) | 1.77 (1.55–2.03) b | 1.74 (1.48–1.97) | 1.97 (1.74–2.19) b | 1.33 (1.13–1.49) | 1.59 (1.41–1.77) b |
| VIMID (cm) | 1.26 (0.95–1.67) | 1.65 (1.29–2.10) b | 1.45 (0.97–1.65) | 1.71 (1.39–2.15) b | 1.16 (0.90–1.69) | 1.61 (1.22–2.05) b |
| RF2/3 (cm) | 1.20 (0.98–1.48) | 1.42 (1.16–1.63) b | 1.31 (1.09–1.60) | 1.55 (1.30–1.76) b | 1.01 (0.79–1.19) | 1.27 (1.03–1.46) b |
| VI2/3 (cm) | 0.98 (0.75–1.25) | 1.27 (0.99–1.63) b | 1.01 (0.76–1.34) | 1.28 (1.05–1.63) b | 0.94 (0.71–1.20) | 1.22 (0.91–1.64) b |
| RFCSA (cm2) | 5.21 (4.10–6.21) | 6.27 (5.09–7.44) b | 5.81 (5.08–6.68) | 7.18 (6.07–8.25) b | 4.06 (3.11–4.56) | 5.52 (4.61–6.32) b |
| Parameters | AUC | 95% CI | p-Value | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFMID (cm) | 0.639 | 0.57–0.71 | <0.001 | 0.531 | 0.748 |
| VIMID (cm) | 0.702 | 0.64–0.77 | <0.001 | 0.827 | 0.474 |
| RF2/3 (cm) | 0.647 | 0.58–0.72 | <0.001 | 0.593 | 0.663 |
| VI2/3 (cm) | 0.696 | 0.63–0.76 | <0.001 | 0.654 | 0.656 |
| RFCSA (cm2) | 0.686 | 0.62–0.75 | <0.001 | 0.728 | 0.556 |
| BIS–LTM | 0.515 | 0.45–0.58 | 0.693 | 0.797 | 0.300 |
| BIS–LTI | 0.581 | 0.51–0.65 | 0.029 | 0.658 | 0.539 |
| BIS–BCM | 0.545 | 0.48–0.61 | 0.229 | 0.772 | 0.378 |
| HGS | 0.532 | 0.46–0.60 | 0.380 | 0.620 | 0.491 |
| US Measures | Men | Women | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | 95% CI | p-Value | AUC | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| RFMID (cm) | 0.68 | 0.60–0.77 | <0.001 | 0.75 | 0.64–0.85 | <0.001 |
| VIMID (cm) | 0.71 | 0.63–0.79 | <0.001 | 0.69 | 0.58–0.80 | 0.004 |
| RF2/3 (cm) | 0.67 | 0.59–0.76 | <0.001 | 0.72 | 0.60–0.83 | 0.001 |
| VI2/3 (cm) | 0.70 | 0.62–0.79 | <0.001 | 0.70 | 0.58–0.81 | 0.003 |
| RFCSA (cm2) | 0.74 | 0.66–0.82 | <0.001 | 0.80 | 0.70–0.90 | <0.001 |
| Men (<6.00 cm2) | Women (<4.47 cm2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.618 | 0.769 |
| Specificity | 0.797 | 0.803 |
| PEW Risk | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | |||
| Low RFCSA | 8.00 | 4.62–13.86 | <0.001 |
| High RFCSA | Reference | ||
| Adjusted a | |||
| Low RFCSA | 8.63 | 4.80–15.50 | <0.001 |
| High RFCSA | Reference |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahathevan, S.; Khor, B.-H.; Singh, B.K.S.; Sabatino, A.; Fiaccadori, E.; Daud, Z.A.M.; Ali, M.S.; Narayanan, S.S.; Tallman, D.; Chinna, K.; et al. Association of Ultrasound-Derived Metrics of the Quadriceps Muscle with Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113597
Sahathevan S, Khor B-H, Singh BKS, Sabatino A, Fiaccadori E, Daud ZAM, Ali MS, Narayanan SS, Tallman D, Chinna K, et al. Association of Ultrasound-Derived Metrics of the Quadriceps Muscle with Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2020; 12(11):3597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113597
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahathevan, Sharmela, Ban-Hock Khor, Birinder Kaur Sadu Singh, Alice Sabatino, Enrico Fiaccadori, Zulfitri Azuan Mat Daud, Mohammad Syafiq Ali, Sreelakshmi Sankara Narayanan, Dina Tallman, Karuthan Chinna, and et al. 2020. "Association of Ultrasound-Derived Metrics of the Quadriceps Muscle with Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 12, no. 11: 3597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113597
APA StyleSahathevan, S., Khor, B.-H., Singh, B. K. S., Sabatino, A., Fiaccadori, E., Daud, Z. A. M., Ali, M. S., Narayanan, S. S., Tallman, D., Chinna, K., Goh, B.-L., Gafor, A. H. A., Ahmad, G., Morad, Z., Khosla, P., Karupaiah, T., & on behalf of the PATCH Study Investigators. (2020). Association of Ultrasound-Derived Metrics of the Quadriceps Muscle with Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 12(11), 3597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113597








