Sarcopenia Severity Based on Computed Tomography Image Analysis in Patients with Cirrhosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. CT Image Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Body Composition Analysis in Donors and Patients with Cirrhosis
3.3. Sex-Specific Cut-Off Values for Sarcopenia
3.4. Clinical Features of Patients with Cirrhosis and Sarcopenia
3.5. Survival of Patients with Cirrhosis and Sarcopenia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carey, E.J.; Lai, J.C.; Sonnenday, C.; Tapper, E.B.; Tandon, P.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Dunn, M.A.; Tsien, C.; Kallwitz, E.R.; Ng, V.; et al. A North American Expert Opinion Statement on Sarcopenia in Liver Transplantation. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1816–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, M.; Bhanji, R.A.; Mazurak, V.C.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Sarcopenia in cirrhosis: From pathogenesis to interventions. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Jang, J.W. Sarcopenia in the prognosis of cirrhosis: Going beyond the MELD score. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7637–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Punyanitya, M.; Wang, Z.; Gallagher, D.; St.-Onge, M.P.; Albu, J.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Heshka, S. Total body skeletal muscle and adipose tissue volumes: Estimation from a single abdominal cross-sectional image. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2004, 97, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, E.J.; Lai, J.C.; Wang, C.W.; Dasarathy, S.; Lobach, I.; Montano-Loza, A.J.; Dunn, M.A. Fitness, Life Enhancement, and Exercise in Liver Transplantation Consortium. A multicenter study to define sarcopenia in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2017, 23, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, M.; Tandon, P.; Moctezuma-Velazquez, C.; Ghosh, S.; Baracos, V.E.; Mazurak, V.C.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Low subcutaneous adiposity associates with higher mortality in female patients with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.D.; Jones, E.; Yanovski, J.A.; Shankar, R.; Feuerstein, I.; Falloon, J. Visceral abdominal-fat accumulation associated with use of indinavir. Lancet 1998, 351, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsiopoulos, N.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Lyons, W.; Gallagher, D.; Ross, R. Cadaver validation of skeletal muscle measurement by magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1998, 85, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, J.; Esfandiari, N.; Baracos, V.E.; Buteau, F.A.; Frenette, J.; Putman, C.T.; Mazurak, V.C. Measurement of skeletal muscle radiation attenuation and basis of its biological variation. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2014, 210, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedher, S.; Fouthaili, N.; Maoui, A.; Lahiani, S.; Salem, M.; Bouzid, K. The Diagnostic and Prognostic Values of C-Reactive Protein and Procalcitonin during Bacterial Infections in Decompensated Cirrhosis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 591547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.J.; Yu, L.J. Oxidative stress, molecular inflammation and sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1509–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeranki, S.; Tyagi, S.C. Defective homocysteine metabolism: Potential implications for skeletal muscle malfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 15074–15091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, T.C.; Gomes, T.L.; Pichard, C.; Laviano, A.; Pimentel, G.D. High neutrophil to lymphocytes ratio is associated with sarcopenia risk in hospitalized cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaitzakis, E. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14686–14695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moctezuma-Velazquez, C.; Ebadi, M.; Bhanji, R.A.; Stirnimann, G.; Tandon, P.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Limited performance of subjective global assessment compared to computed tomography-determined sarcopenia in predicting adverse clinical outcomes in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2696–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, N.D.; Zhang, P.; Singal, A.G.; Derstine, B.A.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Barman, P.; Waljee, A.K.; Su, G.L. Body Composition Predicts Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Transarterial Chemoembolization. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, E.B.; Zhang, P.; Garg, R.; Nault, T.; Leary, K.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Su, G.L. Body Composition Predicts Mortality and Decompensation in Compensated Cirrhosis Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. JHEP Rep. 2019, 2, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, A.J.; Avery, A.; Keating, S.E.; Ward, L.C.; Coombes, J.S.; Macdonald, G.A. Computerised tomography skeletal muscle and adipose surface area values in a healthy Caucasian population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, J.; Shasthry, V.; Kaal, C.R.; Anand, L.; Bhardwaj, A.; Pandit, V.; Arora, A.; Rajesh, S.; Pamecha, V.; Jain, V.; et al. Characterization of body composition and definition of sarcopenia in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis: A computed tomography based study. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMartini, A.; Cruz, R.J., Jr.; Dew, M.A.; Myaskovsky, L.; Goodpaster, B.; Fox, K.; Kim, K.H.; Fontes, P. Muscle mass predicts outcomes following liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2013, 19, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapaliya, S.; Runkana, A.; McMullen, M.R.; Nagy, L.E.; McDonald, C.; Prasad, S.V.N.; Dasarathy, S. Alcohol-induced autophagy contributes to loss in skeletal muscle mass. Autophagy 2014, 10, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, C.H.; Frost, R.A.; Svanberg, E.; Vary, T.C. IGF-I/IGFBP-3 ameliorates alterations in protein synthesis, eIF4E availability, and myostatin in alcohol-fed rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 286, E916–E926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.M.; Sawyer, M.B.; Ghosh, S.; Lieffers, J.R.; Esfandiari, N.; Antoun, S.; Baracos, V.E. Central tenet of cancer cachexia therapy: Do patients with advanced cancer have exploitable anabolic potential? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
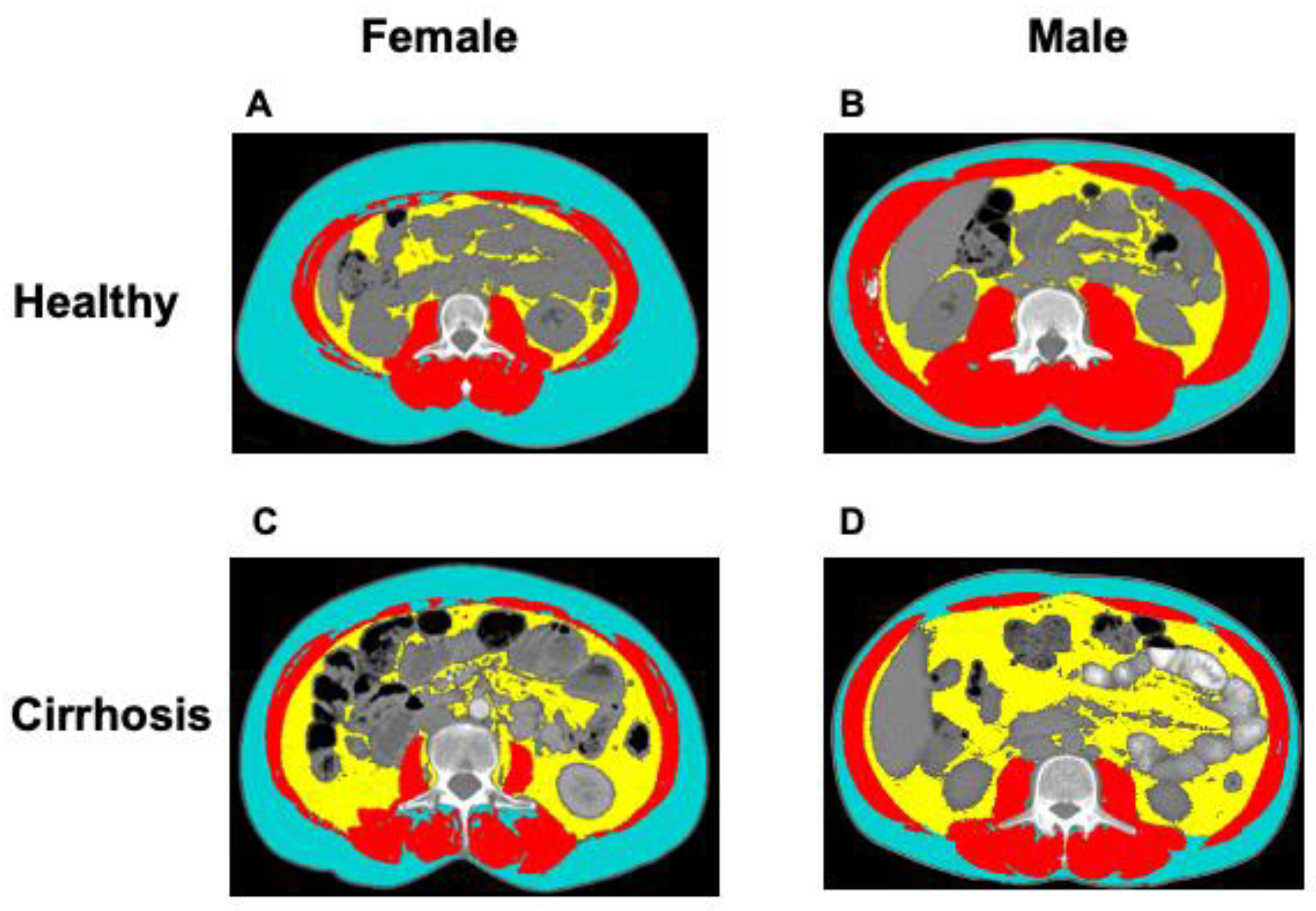



| Donor | Cirrhosis | p-Value Female (Donor vs. Cirrhosis) | p-Value Male (Donor vs. Cirrhosis) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female (n = 74) | Male (n = 55) | p-Value | Female (n = 195) | Male (n = 408) | p-Value | |||
| Age, years | 33 ± 1 | 35 ± 1 | 0.20 | 56 ± 0.7 | 57 ± 0.4 | 0.17 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| BMI, (kg/m2) | 25 ± 0.4 | 26 ± 0.5 | 0.009 | 27 ± 0.5 | 28 ± 0.3 | 0.95 | <0.001 | 0.04 |
| SMI, (cm2/m2) | 44 ± 0.8 | 57 ± 1 | <0.001 | 45 ± 0.7 | 53 ± 0.4 | <0.001 | 0.27 | 0.002 |
| SATI, (cm2/m2) | 65 ± 4 | 47 ± 3 | 0.001 | 68 ± 4 | 49 ± 2 | <0.001 | 0.60 | 0.57 |
| VATI, (cm2/m2) | 14 ± 1 | 32 ± 3 | <0.001 | 32 ± 2 | 40 ± 1 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.08 |
| Muscle radiodensity, HU | 43 ± 0.6 | 44 ± 0.7 | 0.37 | 32 ± 0.6 | 37 ± 0.4 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Female | Male | |
|---|---|---|
| Skeletal muscle index two SD below the mean of a young healthy donor | 30 | 42 |
| Skeletal muscle index one SD below the mean of a young healthy donor | 37 | 50 |
| Severe-Sarcopenic | <30 | <42 |
| Sarcopenic | 30 ≤ SMI < 37 | 45 ≤ SMI < 50 |
| Non-sarcopenic | ≥37 | ≥50 |
| Non-Sarcopenic (n = 415) | Sarcopenic (n = 138) | Severe-Sarcopenic (n = 50) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 57 ± 0.4 | 56 ± 0.8 | 58 ± 1 | 0.37 |
| Sex, male | 255 (61) | 112 (81) | 41 (82) | <0.001 |
| Cirrhosis ethology | ||||
| NASH | 98 (24) | 33 (24) | 5 (10) | 0.09 |
| Alcohol | 73 (18) | 40 (29) | 22 (44) | <0.001 |
| Hepatitis C | 180 (43) | 48 (35) | 15 (30) | 0.06 |
| Hepatitis B | 27 (7) | 7 (5) | 4 (8) | 0.73 |
| Autoimmune liver diseases | 34 (8) | 10 (7) | 3 (6) | 0.83 |
| Hepatic encephalopathy | 116 (28) | 52 (38) | 26 (52) | 0.001 |
| Refractory ascites | 88 (21) | 49 (36) | 21 (42) | <0.001 |
| MELD score | 14 ± 0.4 | 15 ± 0.7 | 16 ± 1 | 0.12 |
| Severe-malnutrition (SGA C) | 15 (8) | 6 (8) | 10 (33) | 0.001 |
| CRP> 20, mg/mL | 54 (19) | 19 (22) | 16 (42) | 0.01 |
| Vitamin D deficiency (<50 nmol/L) | 204 (57) | 66 (59) | 32 (73) | 0.14 |
| Albumin, g/L | 33 ± 0.3 | 32 ± 0.6 | 33 ± 0.9 | 0.24 |
| WBC, 109/L | 5.7 ± 0.2 | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 6.7 ± 0.5 | 0.23 |
| Neutrophil count, 109/L | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.2 | 5.2 ± 0.5 *,¥ | 0.001 |
| Lymphocyte count, 109/L | 1.2 ± 0.04 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.06 | 0.09 |
| Platelet, 109/L | 102 ± 3 | 124 ± 8 * | 116 ± 7 | 0.005 |
| Homocysteine, µmol/L | 13 ± 0.4 | 14 ± 1 | 18 ± 2 * | 0.007 |
| CRP, mg/mL | 16 ± 2 | 16 ± 3 | 28 ± 8 | 0.13 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 29 ± 0.3 | 25 ± 0.4 * | 23 ± 0.9 * | <0.001 |
| SATI, cm2/m2 | 64 ± 2 | 37 ± 2 * | 30 ± 3 * | <0.001 |
| VATI, cm2/m2 | 41 ± 1 | 30 ± 2 * | 25 ± 2 * | <0.001 |
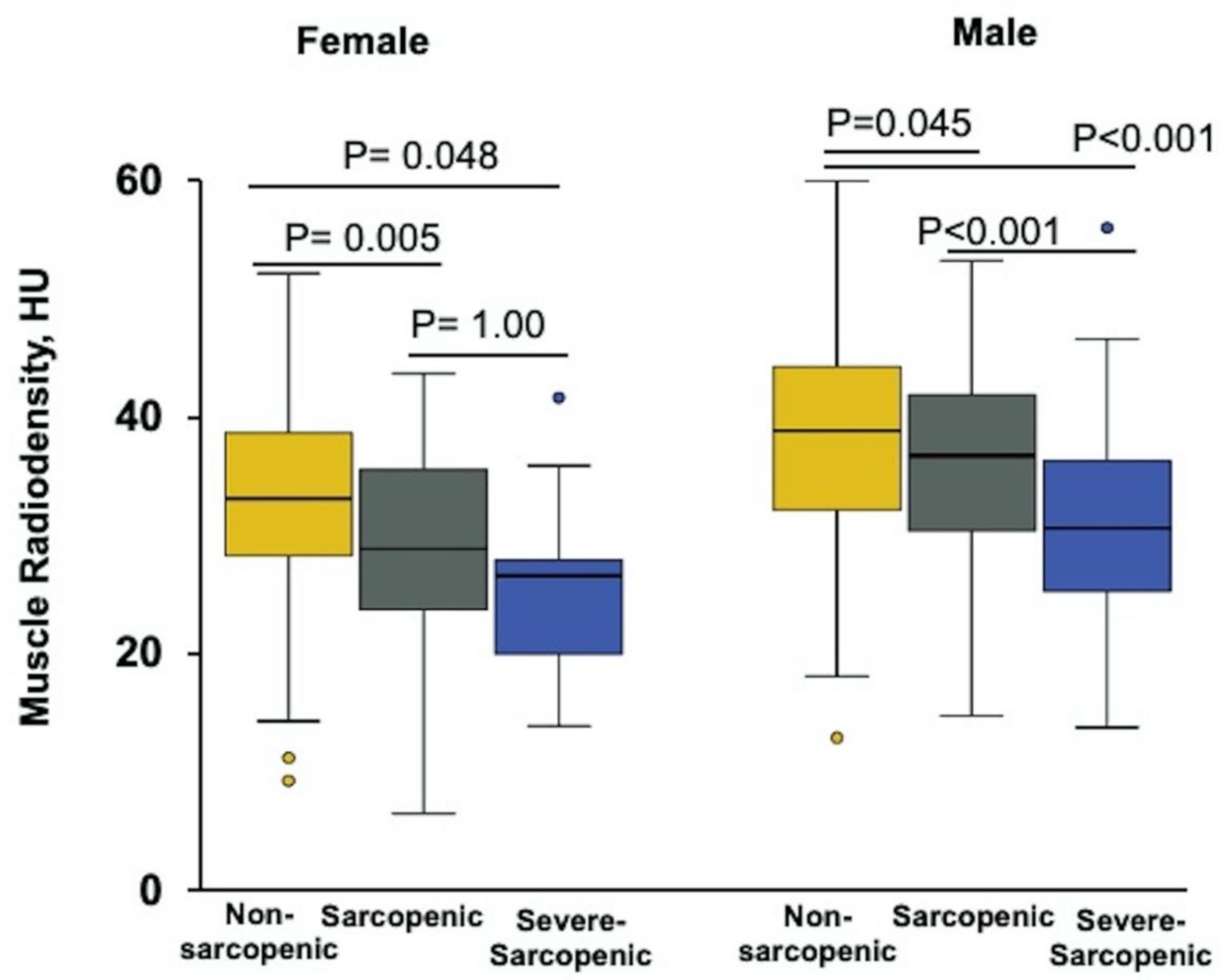
| Muscle radiodensity, HU | 36 ± 0.4 | 34 ± 0.8 * | 29 ± 1 *,¥ | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio | 4.5 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 7.5 ± 1 *,¥ | 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebadi, M.; Bhanji, R.A.; Dunichand-Hoedl, A.R.; Mazurak, V.C.; Baracos, V.E.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Sarcopenia Severity Based on Computed Tomography Image Analysis in Patients with Cirrhosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113463
Ebadi M, Bhanji RA, Dunichand-Hoedl AR, Mazurak VC, Baracos VE, Montano-Loza AJ. Sarcopenia Severity Based on Computed Tomography Image Analysis in Patients with Cirrhosis. Nutrients. 2020; 12(11):3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113463
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbadi, Maryam, Rahima A. Bhanji, Abha R. Dunichand-Hoedl, Vera C. Mazurak, Vickie E. Baracos, and Aldo J. Montano-Loza. 2020. "Sarcopenia Severity Based on Computed Tomography Image Analysis in Patients with Cirrhosis" Nutrients 12, no. 11: 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113463
APA StyleEbadi, M., Bhanji, R. A., Dunichand-Hoedl, A. R., Mazurak, V. C., Baracos, V. E., & Montano-Loza, A. J. (2020). Sarcopenia Severity Based on Computed Tomography Image Analysis in Patients with Cirrhosis. Nutrients, 12(11), 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113463







