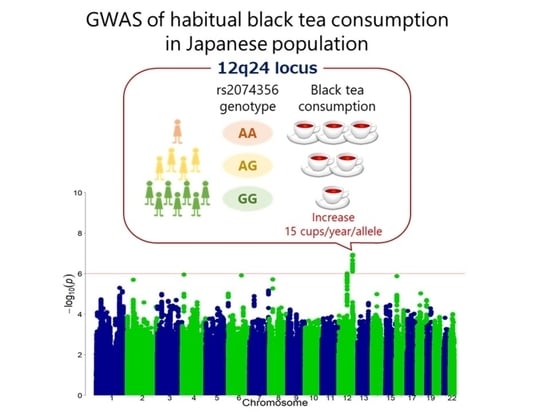
A Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies the Association between the 12q24 Locus and Black Tea Consumption in Japanese Populations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Black Tea Consumption
2.3. Adjustment Variables
2.4. DNA Sampling, Genotype, Quality Control, and Genotype Imputation
2.5. Genome-Wide Association and Meta-Analysis
2.6. Confounding Factor Adjustment and Subgroup Analysis
3. Results
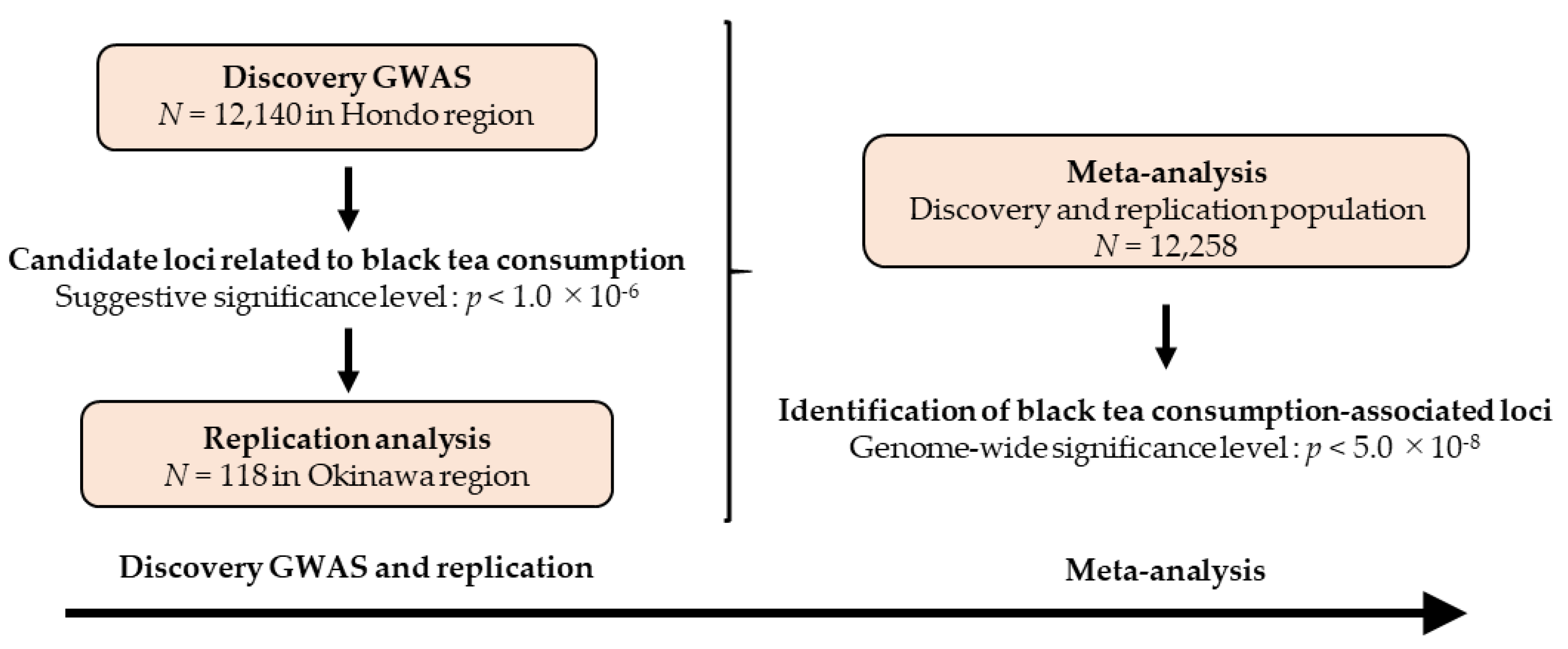
3.1. Research Flow and Characteristics of the Study Participants
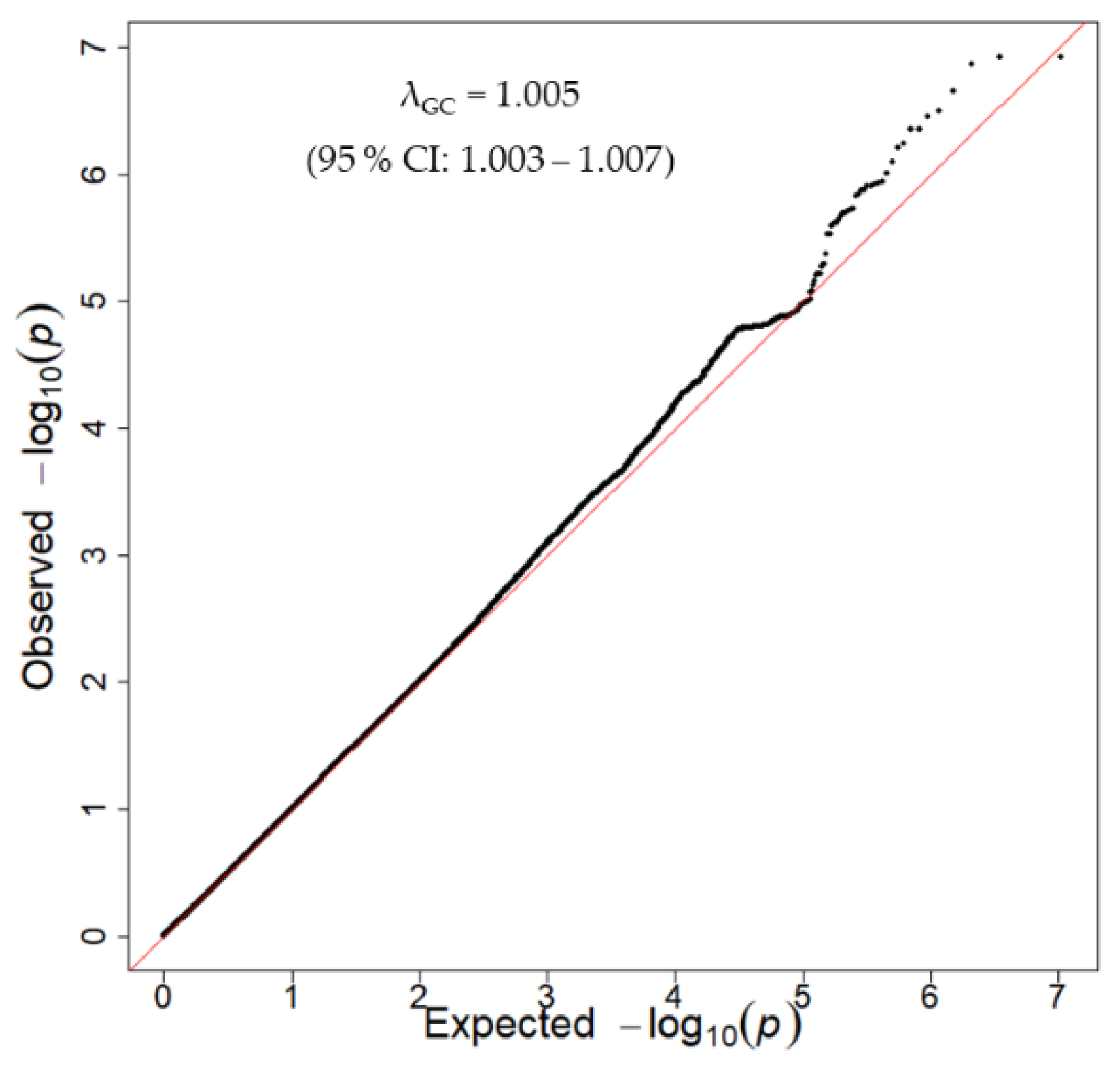
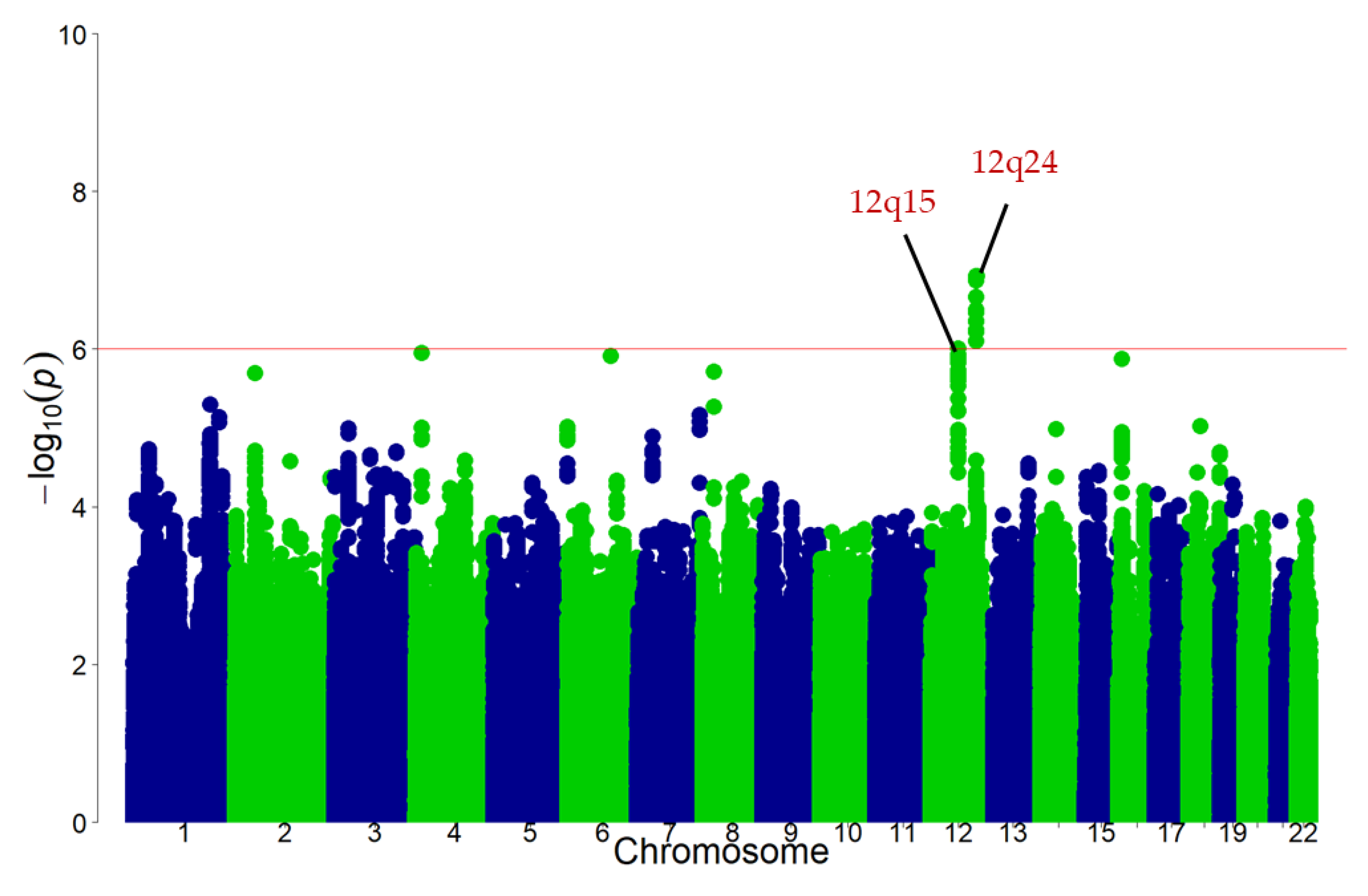
3.2. Discovery GWAS
3.3. Replication Stage and Meta-Analysis
3.4. Adjustment for Potential Confounding Factors
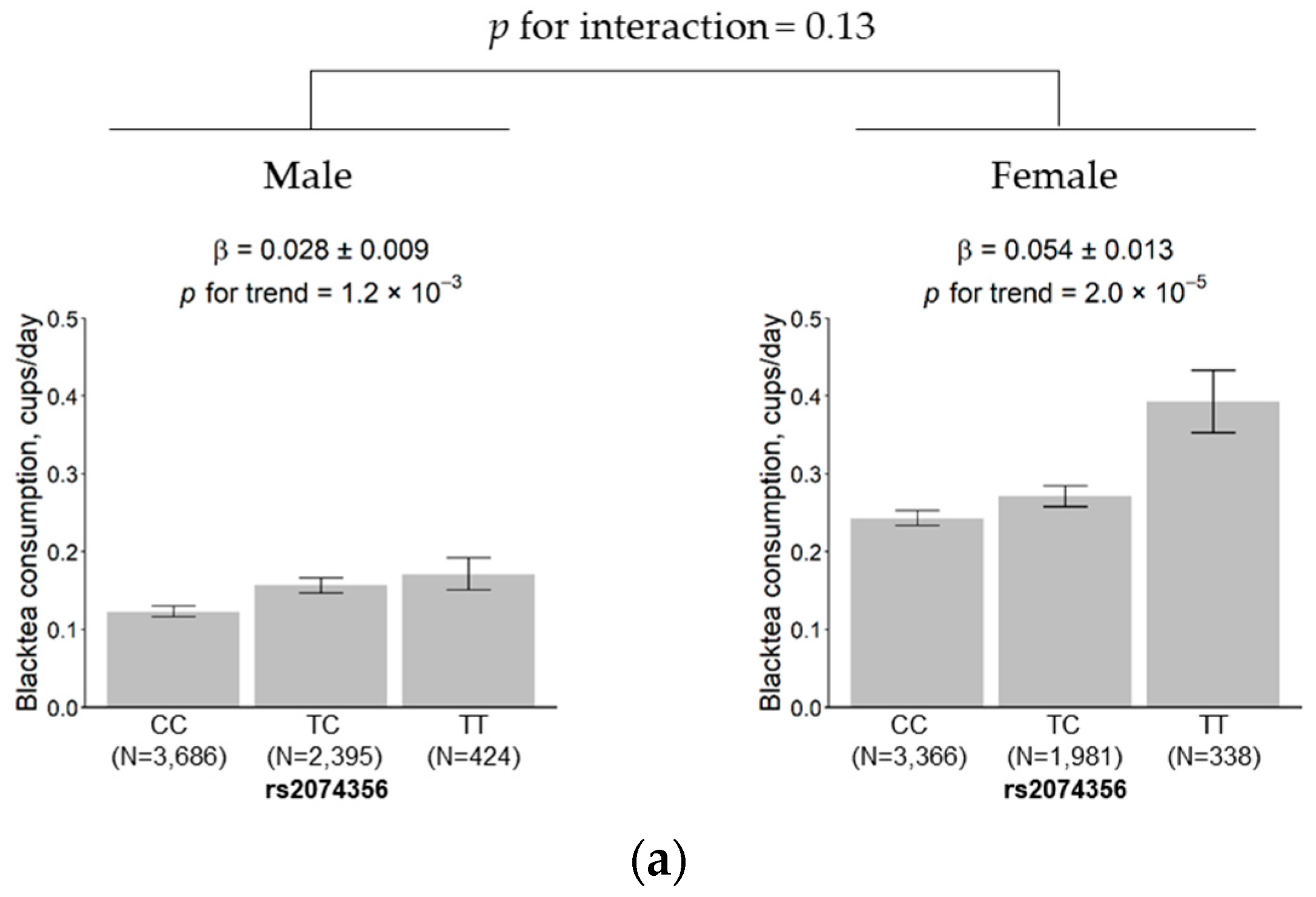
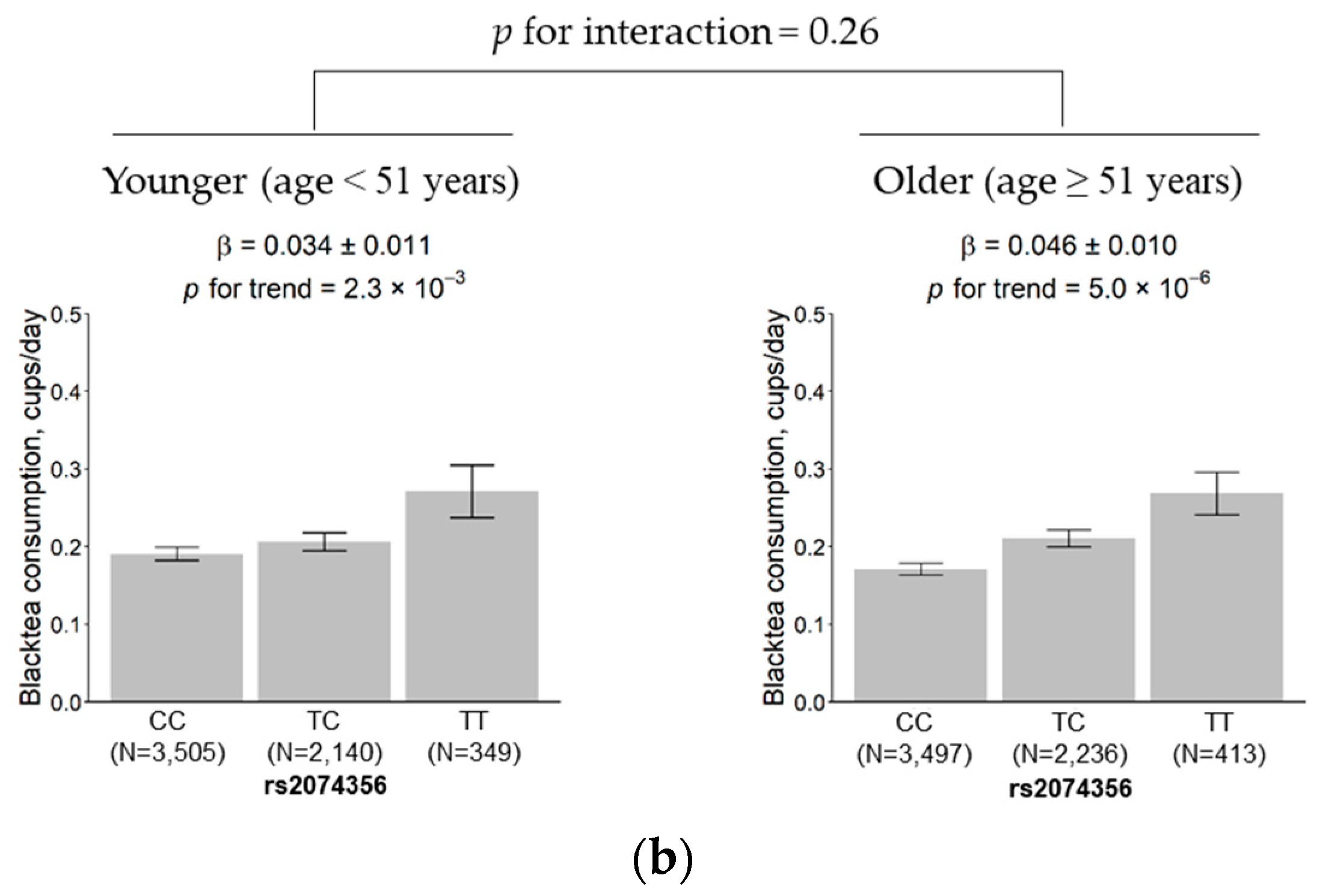
3.5. Subgroup Analysis According to Sex and Age
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leung, L.K.; Su, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.-Y. Theaflavins in Black Tea and Catechins in Green Tea Are Equally Effective Antioxidants. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheang, W.S.; Ngai, C.Y.; Tam, Y.Y.; Tian, X.Y.; Wong, W.T.; Zhang, Y.; Lau, C.W.; Chen, Z.Y.; Bian, Z.X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Black tea protects against hypertension-associated endothelial dysfunction through alleviation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.R.; Anton, S.; Melville, L.; Houston, N.P.; Dayal, S.; McDougall, G.J.; Stewart, D.; Rena, G. Black tea polyphenols mimic insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signalling to the longevity factor FOXO1a. Aging Cell 2008, 7, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gothandam, K.; Ganesan, V.S.; Ayyasamy, T.; Ramalingam, S. Antioxidant potential of theaflavin ameliorates the activities of key enzymes of glucose metabolism in high fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Redox Rep. Commun. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, L.; Liu, W.; Elashoff, D. Green and black tea consumption and risk of stroke: A meta-analysis. Stroke 2009, 40, 1786–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robino, A.; Concas, M.P.; Catamo, E.; Gasparini, P. A Brief Review of Genetic Approaches to the Study of Food Preferences: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, N.; Akiyama, M.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, M.; Takahashi, A.; Momozawa, Y.; Ikegawa, S.; Ikeda, M.; Iwata, N.; Hirata, M.; et al. GWAS of 165,084 Japanese individuals identified nine loci associated with dietary habits. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2020, 4, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, M.; Nogawa, S.; Kawafune, K.; Hachiya, T.; Takahashi, S.; Jia, H.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. Identification of the 12q24 locus associated with fish intake frequency by genome-wide meta-analysis in Japanese populations. Genes Nutr. 2019, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgenson, E.; Thai, K.K.; Hoffmann, T.J.; Sakoda, L.C.; Kvale, M.N.; Banda, Y.; Schaefer, C.; Risch, N.; Mertens, J.; Weisner, C.; et al. Genetic contributors to variation in alcohol consumption vary by race/ethnicity in a large multi-ethnic genome-wide association study. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillen, E.E.; Chen, X.-D.; Almasy, L.; Yang, F.; He, H.; Li, X.; Wang, X.-Y.; Liu, T.-Q.; Hao, W.; Deng, H.-W.; et al. ALDH2 is associated to alcohol dependence and is the major genetic determinant of “daily maximum drinks” in a GWAS study of an isolated rural Chinese sample. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2014, 165B, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Chen, J.; Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; et al. Common variants at 12q24 are associated with drinking behavior in Han Chinese. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Nogawa, S.; Kawafune, K.; Hachiya, T.; Takahashi, S.; Igarashi, M.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. GWAS of habitual coffee consumption reveals a sex difference in the genetic effect of the 12q24 locus in the Japanese population. BMC Genet. 2019, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa-Senda, H.; Hachiya, T.; Shimizu, A.; Hosono, S.; Oze, I.; Watanabe, M.; Matsuo, K.; Ito, H.; Hara, M.; Nishida, Y.; et al. A genome-wide association study in the Japanese population identifies the 12q24 locus for habitual coffee consumption: The J-MICC Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirastu, N.; Kooyman, M.; Robino, A.; van der Spek, A.; Navarini, L.; Amin, N.; Karssen, L.C.; Van Duijn, C.M.; Gasparini, P. Non-additive genome-wide association scan reveals a new gene associated with habitual coffee consumption. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawafune, K.; Hachiya, T.; Nogawa, S.; Takahashi, S.; Jia, H.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. Strong association between the 12q24 locus and sweet taste preference in the Japanese population revealed by genome-wide meta-analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.L.; Patterson, N.J.; Plenge, R.M.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Shadick, N.A.; Reich, D. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi-Kabata, Y.; Nakazono, K.; Takahashi, A.; Saito, S.; Hosono, N.; Kubo, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Kamatani, N. Japanese population structure, based on SNP genotypes from 7003 individuals compared to other ethnic groups: Effects on population-based association studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachiya, T.; Komaki, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ohmomo, H.; Tanno, K.; Hozawa, A.; Tamiya, G.; Yamamoto, M.; Ogasawara, K.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis in Japanese populations identifies novel variants at the TMC6–TMC8 and SIX3–SIX2 loci associated with HbA1c. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimanoe, C.; Hachiya, T.; Hara, M.; Nishida, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Sutoh, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Hishida, A.; Kawai, S.; Okada, R.; et al. A genome-wide association study of coping behaviors suggests FBXO45 is associated with emotional expression. Genes Brain Behav. 2019, 18, e12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Genomes Project Consortium; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.R.; Altshuler, D.M.; Durbin, R.M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Bentley, D.R.; Chakravarti, A.; Clark, A.G.; Donnelly, P.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, P.-R.; Danecek, P.; Palamara, P.F.; Fuchsberger, C.; Reshef, Y.A.; Finucane, H.K.; Schoenherr, S.; Forer, L.; McCarthy, S.; Abecasis, G.R.; et al. Reference-based phasing using the Haplotype Reference Consortium panel. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schönherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willer, C.J.; Li, Y.; Abecasis, G.R. METAL: Fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans. Bioinformatics (Oxford) 2010, 26, 2190–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Go, M.J.; Hu, C.; Hong, C.B.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, D.-J.; Kim, N.H.; et al. Large-scale genome-wide association studies in East Asians identify new genetic loci influencing metabolic traits. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Mo, X.B.; Xu, T.; Bu, X.Q.; Lei, S.F.; Zhang, Y.H. Novel Genes Affecting Blood Pressure Detected Via Gene-Based Association Analysis. G3 (Bethesda) 2015, 5, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Zheng, W.; Okada, Y.; Takeuchi, F.; Tabara, Y.; Hwang, J.Y.; Dorajoo, R.; Li, H.; Tsai, F.J.; Yang, X.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in East Asian-ancestry populations identifies four new loci for body mass index. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 5492–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, M.C.; Monda, K.L.; Yu, K.; Paynter, N.; Azzato, E.M.; Bennett, S.N.; Berndt, S.I.; Boerwinkle, E.; Chanock, S.; Chatterjee, N.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies regions on 7p21 (AHR) and 15q24 (CYP1A2) as determinants of habitual caffeine consumption. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josse, A.R.; Da Costa, L.A.; Campos, H.; El-Sohemy, A. Associations between polymorphisms in the AHR and CYP1A1-CYP1A2 gene regions and habitual caffeine consumption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higdon, J.V.; Frei, B. Coffee and Health: A Review of Recent Human Research. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Youn, J.; Kim, A.N.; Kang, M.; Kim, K.; Sung, J.; Lee, J.E. Interactions of Habitual Coffee Consumption by Genetic Polymorphisms with the Risk of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Combined. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.M.; Roy, S.; Nielsen, E.; Paul, M.; Maul, R.; Paun, A.; Koentgen, F.; Raval, F.M.; Szomolanyi-Tsuda, E.; Pitha, P.M. Unique contribution of IRF-5-Ikaros axis to the B-cell IgG2a response. Genes Immun. 2012, 13, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabsch, T.; Holzapfel, C. A Scientific Perspective of Personalised Gene-Based Dietary Recommendations for Weight Management. Nutrients 2019, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Discovery | Replication |
|---|---|---|
| N | 12,140 | 118 |
| Female (%) | 46.8 | 45.8 |
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 50.3 ± 13.2 | 49.0 ± 12.3 |
| Black tea consumption, cups/day (mean ± SD) | 0.20 ± 0.51 | 0.15 ± 0.41 |
| Drinking frequency, times/week (mean ± SD) | 2.21 ± 2.67 | 2.63 ± 2.76 |
| Alcohol consumption, g/day (means ± SD) | 7.10 ± 11.94 | 9.87 ± 15.02 |
| Coffee consumption, cups/day (mean ± SD) | 1.70 ± 1.50 | 1.64 ± 1.28 |
| Sweet taste preference, (mean ± SD) | 3.74 ± 0.90 | 3.72 ± 0.89 |
| BMI, kg/m2 (mean ± SD) | 23.1 ± 3.7 | 23.9 ± 4.0 |
| SNP | Chr | Position | Gene | EA | NEA | Population | EAF | Beta | SE (Beta) | pAssociation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs2074356 | 12 | 112645401 | HECTD4 | T | C | Discovery | 0.244 | 0.040 | 0.008 | 1.2 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.174 | 0.184 | 0.070 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.243 | 0.042 | 0.008 | 2.4 × 10−8 | ||||||
| rs144504271 | 12 | 112627350 | HECTD4 | A | G | Discovery | 0.264 | 0.041 | 0.008 | 1.2 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.190 | 0.183 | 0.072 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.263 | 0.042 | 0.008 | 3.1 × 10−8 | ||||||
| rs12231737 | 12 | 112574616 | TRAFD1 | T | C | Discovery | 0.266 | 0.041 | 0.008 | 1.4 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.192 | 0.187 | 0.072 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.265 | 0.043 | 0.008 | 4.3 × 10−8 | ||||||
| rs116873087 | 12 | 112511913 | NAA25 | C | G | Discovery | 0.263 | 0.041 | 0.008 | 2.2 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.189 | 0.186 | 0.074 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.262 | 0.043 | 0.008 | 5.8 × 10−8 | ||||||
| rs11066132 | 12 | 112468206 | NAA25 | T | C | Discovery | 0.261 | 0.040 | 0.008 | 3.2 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.188 | 0.188 | 0.074 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.260 | 0.042 | 0.008 | 9.6 × 10−8 | ||||||
| rs78069066 | 12 | 112337924 | MAPKAPK5 TMEM116 | A | G | Discovery | 0.267 | 0.039 | 0.008 | 3.5 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.189 | 0.177 | 0.072 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.266 | 0.040 | 0.008 | 1.1 × 10−7 | ||||||
| rs4646776 | 12 | 112230019 | ALDH2 | C | G | Discovery | 0.264 | 0.037 | 0.007 | 4.4 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.187 | 0.171 | 0.070 | 0.02 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.263 | 0.039 | 0.007 | 1.4 × 10−7 | ||||||
| rs671 | 12 | 112241766 | ALDH2 | A | G | Discovery | 0.264 | 0.037 | 0.007 | 4.5 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.186 | 0.171 | 0.070 | 0.02 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.263 | 0.039 | 0.007 | 1.5 × 10−7 | ||||||
| rs11066001 | 12 | 112119171 | BRAP | C | T | Discovery | 0.262 | 0.038 | 0.008 | 6.2 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.185 | 0.175 | 0.072 | 0.02 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.261 | 0.039 | 0.008 | 1.6 × 10−7 | ||||||
| rs11066015 | 12 | 112168009 | ACAD10 | A | G | Discovery | 0.263 | 0.037 | 0.007 | 5.7 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.187 | 0.171 | 0.070 | 0.02 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.262 | 0.038 | 0.007 | 1.8 × 10−7 | ||||||
| rs3782886 | 12 | 112110489 | BRAP | C | T | Discovery | 0.264 | 0.037 | 0.008 | 7.9 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.186 | 0.175 | 0.072 | 0.02 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.263 | 0.039 | 0.008 | 2.6 × 10−7 | ||||||
| rs1981764 | 12 | 68217659 | DYRK2– IFNG | G | A | Discovery | 0.123 | 0.049 | 0.010 | 9.9 × 10−7 |
| Replication | 0.119 | −0.021 | 0.087 | 0.81 | ||||||
| Meta-analysis | 0.127 | 0.048 | 0.010 | 1.4 × 10−6 |
| Adjustment Variables | Beta | SE (Beta) | p Association |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, Sex, Population structure (5 PCs) | 0.040 | 0.008 | 1.2 × 10−7 |
| Age, Sex, Population structure (5 PCs), Drinking frequency | 0.033 | 0.008 | 3.8 × 10−5 |
| Age, Sex, Population structure (5 PCs), Alcohol consumption | 0.037 | 0.008 | 3.1 × 10−6 |
| Age, Sex, Population structure (5 PCs), Coffee consumption | 0.045 | 0.008 | 9.9 × 10−9 |
| Age, Sex, Population structure (5 PCs), Sweet preference | 0.039 | 0.008 | 3.0 × 10−7 |
| Age, Sex, Population structure (5 PCs), BMI | 0.040 | 0.008 | 9.9 × 10−8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furukawa, K.; Igarashi, M.; Jia, H.; Nogawa, S.; Kawafune, K.; Hachiya, T.; Takahashi, S.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. A Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies the Association between the 12q24 Locus and Black Tea Consumption in Japanese Populations. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103182
Furukawa K, Igarashi M, Jia H, Nogawa S, Kawafune K, Hachiya T, Takahashi S, Saito K, Kato H. A Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies the Association between the 12q24 Locus and Black Tea Consumption in Japanese Populations. Nutrients. 2020; 12(10):3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103182
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurukawa, Kyohei, Maki Igarashi, Huijuan Jia, Shun Nogawa, Kaoru Kawafune, Tsuyoshi Hachiya, Shoko Takahashi, Kenji Saito, and Hisanori Kato. 2020. "A Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies the Association between the 12q24 Locus and Black Tea Consumption in Japanese Populations" Nutrients 12, no. 10: 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103182
APA StyleFurukawa, K., Igarashi, M., Jia, H., Nogawa, S., Kawafune, K., Hachiya, T., Takahashi, S., Saito, K., & Kato, H. (2020). A Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies the Association between the 12q24 Locus and Black Tea Consumption in Japanese Populations. Nutrients, 12(10), 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103182