Effects of Polyphenols on Insulin Resistance
Abstract
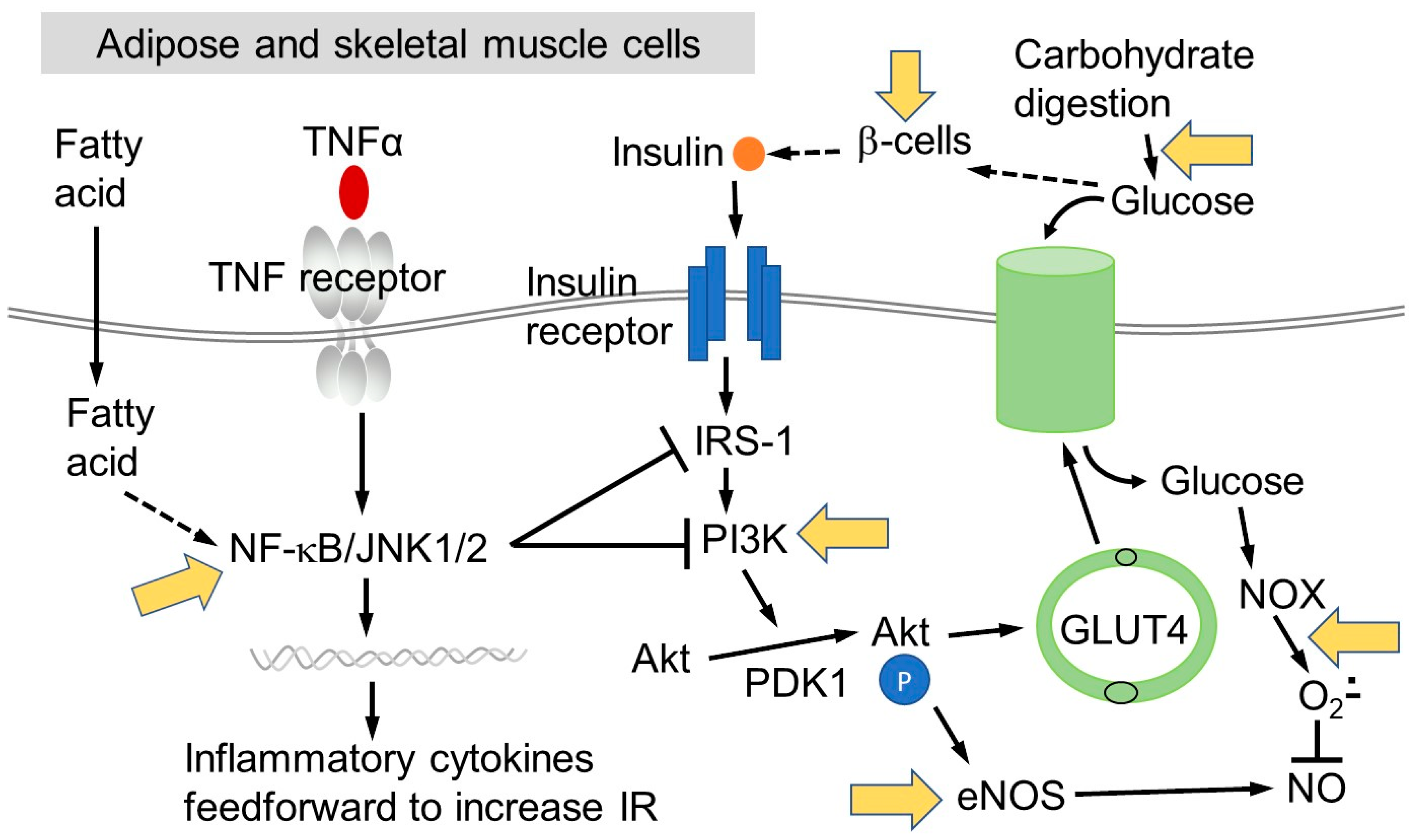
1. Insulin Resistance
1.1. Characteristics of Insulin Resistance
1.2. Measurement of Insulin Resistance
1.3. The Role of Chronic Inflammation in Insulin Resistance
2. Factors that Affect IR
2.1. Macronutrient Intake
2.2. Lipid Metabolism
2.3. Gut Microbiota and Exercise
3. Dietary (Poly)phenols
3.1. Sources and Intake
3.2. Metabolism of (Poly)phenols
3.3. General Epidemiology on (Poly)Phenol-Rich Foods and IR/t2D Risk
3.4. Interventions Using Foods
3.4.1. Cocoa and (−)-Epicatechin
3.4.2. Green Tea
3.4.3. Anthocyanins and Berries
3.4.4. Quercetin and Onions
3.4.5. Phenolic Acids and Other Phenolic Compounds
3.4.6. Stilbenes and Wine
3.4.7. Hesperidin and Citrus Fruits
3.4.8. Pomegranate and Ellagitannins
3.4.9. (Poly)phenols from Nuts
4. Mechanisms in the Pathway of Developing IR That May Be Affected by (Poly)phenols
4.1. Effects of (Poly)phenols on Starch Digestion
4.2. Effects of (Poly)phenols on Glucose Transport
4.3. Attenuation of Impaired Insulin Signalling and Pro-Inflammatory Pathways by (Poly)phenols
5. Cell Models for Protection of β-Cells against Oxidative Damage
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moller, D.E.; Kaufman, K.D. Metabolic Syndrome: A Clinical and Molecular Perspective. Annu. Rev. Med. 2005, 56, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.-K.; Saltiel, A.R. Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory Mechanisms in Obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for Insulin Resistance: Common Threads and Missing Links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kau, A.L.; Ahern, P.P.; Griffin, N.W.; Goodman, A.L.; Gordon, J.I. Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune system. Nature 2011, 474, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-Gut Microbiota Metabolic Interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.M.; Olefsky, J.M. The Origins and Drivers of Insulin Resistance. Cell 2013, 152, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, M.P. Insulin action and resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.A. Defining and Characterizing the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, S151–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K.; Maezono, K.; Osman, A.; Pendergrass, M.; Patti, M.E.; Pratipanawatr, T.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Kahn, C.R.; Mandarino, L.J. Insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase– and MAP kinase–mediated signaling in human muscle. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiki, M.; Klip, A. Minireview: Recent Developments in the Regulation of Glucose Transporter-4 Traffic: New Signals, Locations, and Partners. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 5071–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Tobin, J.D.; Andres, R. Glucose clamp technique: A method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am. J. Physiol. 1979, 237, E214–E223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and ?-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudenski, A.S.; Matthews, D.R.; Levy, J.C.; Turner, R.C. Understanding “insulin resistance”: Both glucose resistance and insulin resistance are required to model human diabetes. Metabolism 1991, 40, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sullivan, G.; Yue, L.Q.; Katz, A.; Quon, M.J. QUICKI is a useful index of insulin sensitivity in subjects with hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E804–E812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: Comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szosland, K.; Lewiński, A. In quest for method of insulin resistance assessment in everyday clinical practice—Insulin resistance indices. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2016, 10, S120–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. The Product of Fasting Glucose and Triglycerides as Surrogate for Identifying Insulin Resistance in Apparently Healthy Subjects. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2008, 6, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borai, A.; Livingstone, C.; Kaddam, I.; Ferns, G. Selection of the appropriate method for the assessment of insulin resistance. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2011, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonora, E.; Kiechl, S.; Willeit, J.; Oberhollenzer, F.; Egger, G.; Meigs, J.B.; Bonadonna, R.C.; Muggeo, M. Insulin Resistance as Estimated by Homeostasis Model Assessment Predicts Incident Symptomatic Cardiovascular Disease in Caucasian Subjects From the General Population: The Bruneck Study. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, A.J.; Williams, K.; Stern, M.P.; Haffner, S.M. Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance in Relation to the Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease: The San Antonio Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Yuan, M. Inflammation and the IKKβ/IκB/NF-κB axis in obesity—And diet-induced insulin resistance. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.K.S.; Peraldi, P.; Budavari, A.; Ellis, R.; White, M.F.; Spiegelman, B.M. IRS-1-Mediated Inhibition of Insulin Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activity in TNF-alpha- and Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance. Science 1996, 271, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zick, Y. Insulin resistance: A phosphorylation-based uncoupling of insulin signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkan, M.C.; Hevener, A.L.; Greten, F.R.; Maeda, S.; Li, Z.-W.; Long, J.M.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Poli, G.; Olefsky, J.; Karin, M. IKK-β links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, O.; Olefsky, J.M. The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Yuan, M.; Frantz, D.F.; Melendez, P.A.; Hansen, L.; Lee, J.; Shoelson, S.E. Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-β and NF-κB. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itani, S.I.; Ruderman, N.B.; Schmieder, F.; Boden, G. Lipid-induced insulin resistance in human muscle is associated with changes in diacylglycerol, protein kinase C, and IkappaB-alpha. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2005–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, G.K.; Yu, J.G.; Ofrecio, J.; Olefsky, J.M. Increased p85/55/50 expression and decreased phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase activity in insulin-resistant human skeletal muscle. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, K.N.; Cruzat, V.; Carlessi, R.; De Bittencourt, P.I.H.; Newsholme, P. Molecular Events Linking Oxidative Stress and Inflammation to Insulin Resistance and β-Cell Dysfunction. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 181643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rave, K.; Roggen, K.; Dellweg, S.; Heise, T.; Dieck, H.T. Improvement of insulin resistance after diet with a whole-grain based dietary product: Results of a randomized, controlled cross-over study in obese subjects with elevated fasting blood glucose. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, N.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Liu, S.; Saltzman, E.; Wilson, P.W.; Jacques, P.F. Carbohydrate nutrition, insulin resistance, and the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liese, A.D.; Roach, A.K.; Sparks, K.C.; Marquart, L.; D’Agostino, R.B., Jr.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Whole-grain intake and insulin sensitivity: The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, O.Y.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, S.Y. Consumption of whole grain and legume powder reduces insulin demand, lipid peroxidation, and plasma homocysteine concentrations in patients with coronary artery disease: Randomized controlled clinical trial. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.A.; Jacobs, D.R.; Pins, J.J.; Raatz, S.K.; Gross, M.D.; Slavin, J.L.; Seaquist, E.R. Effect of whole grains on insulin sensitivity in overweight hyperinsulinemic adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 75, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, G.; Leeds, A.; Trew, G.; Margara, R.; Dornhorst, A. Insulin sensitivity in women at risk of coronary heart disease and the effect of a low glycemic diet. Metabolism 1998, 47, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, J.A.; De La Sacristana, A.G.; Romero, I.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Latre, J.; Sánchez, E.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; López-Miranda, J.; Perez-Jimenez, F. Monounsaturated Fat-Rich Diet Prevents Central Body Fat Distribution and Decreases Postprandial Adiponectin Expression Induced by a Carbohydrate-Rich Diet in Insulin-Resistant Subjects. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramel, A.; Martinez, A.; Kiely, M.; Morais, G.; Bandarra, N.M.; Thorsdottir, I. Beneficial effects of long-chain n-3 fatty acids included in an energy-restricted diet on insulin resistance in overweight and obese European young adults. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartweg, J.; Perera, R.; Montori, V.M.; Dinneen, S.F.; Neil, A.H.; Farmer, A.; Neil, H.A.W. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, CD003205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, O.P.; Dahl, D.B.; Brechtel, K.; Machann, J.; Haap, M.; Maier, T.; Loviscach, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Claussen, C.D.; Schick, F.; et al. Effects of Intravenous and Dietary Lipid Challenge on Intramyocellular Lipid Content and the Relation With Insulin Sensitivity in Humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2579–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehleman, T.L.; Peters, S.J.; Heigenhauser, G.J.F.; Spriet, L.L. Enzymatic regulation of glucose disposal in human skeletal muscle after a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisschop, P.H.; De Metz, J.; Ackermans, M.T.; Endert, E.; Pijl, H.; Kuipers, F.; Meijer, A.J.; Sauerwein, H.P.; Romijn, J.A. Dietary fat content alters insulin-mediated glucose metabolism in healthy men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brøns, C.; Jensen, C.B.; Storgaard, H.; Hiscock, N.J.; White, A.; Appel, J.S.; Jacobsen, S.; Nilsson, E.; Larsen, C.M.; Astrup, A.; et al. Impact of short-term high-fat feeding on glucose and insulin metabolism in young healthy men. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Frankenberg, A.D.; Marina, A.; Song, X.; Callahan, H.S.; Kratz, M.; Utzschneider, K.M. A high-fat, high-saturated fat diet decreases insulin sensitivity without changing intra-abdominal fat in weight-stable overweight and obese adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 56, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, L.E.H.; Van Schinkel, L.D.; Guigas, B.; Streefland, T.C.M.; Jonker, J.T.; Van Klinken, J.B.; Van Der Zon, G.C.M.; Lamb, H.J.; Smit, J.W.; Pijl, H.; et al. A 5-Day High-Fat, High-Calorie Diet Impairs Insulin Sensitivity in Healthy, Young South Asian Men but Not in Caucasian Men. Diabetes 2014, 63, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, C.K.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammation and Lipid Signaling in the Etiology of Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, E.; Magkos, F.; Mohammed, B.S.; Pietka, T.; Abumrad, N.A.; Patterson, B.W.; Okunade, A.; Klein, S. Intrahepatic fat, not visceral fat, is linked with metabolic complications of obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15430–15435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, E.; Tamboli, R.A.; Magkos, F.; Marks–Shulman, P.A.; Eckhauser, A.W.; Richards, W.O.; Klein, S.; Abumrad, N.N. Surgical Removal of Omental Fat Does Not Improve Insulin Sensitivity and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Obese Adults. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic Endotoxemia Initiates Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Maiya, G.A.; Shastry, B.; Vaishali, K.; Ravishankar, N.; Hazari, A.; Gundmi, S.; Jadhav, R. Exercise and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marson, E.C.; Delevatti, R.S.; Prado, A.K.G.; Netto, N.; Kruel, L.F.M. Effects of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise training on insulin resistance markers in overweight or obese children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev. Med. 2016, 93, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, C.D.; Clifford, M.N.; Mena, P.; McDougall, G.J.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Cassidy, A.; Del Rio, D.; Kuhnert, N.; Manach, C.; Pereira-Caro, G.; et al. Recommendations for standardizing nomenclature for dietary (poly)phenol catabolites. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1051–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.; Fukagawa, N.K.; Bilia, A.R.; Johnson, E.J.; Kwon, O.; Prakash, V.; Miyazawa, T.; Clifford, M.N.; Kay, C.D.; Crozier, A.; et al. Terms and nomenclature used for plant-derived components in nutrition and related research: Efforts toward harmonization. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 78, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Spencer, J.P.; Tognolini, M.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Dietary (Poly)phenolics in Human Health: Structures, Bioavailability, and Evidence of Protective Effects Against Chronic Diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1818–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.N.; Van Der Hooft, J.J.; Crozier, A. Human studies on the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of tea polyphenols. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1619S–1630S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neveu, V.; Perez-Jimenez, J.; Vos, F.; Crespy, V.; Du Chaffaut, L.; Mennen, L.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Cruz, J.; Wishart, D.; et al. Phenol-Explorer: An online comprehensive database on polyphenol contents in foods. Database 2010, 2010, bap024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.; Kay, C.D.; Crozier, A. The Bioavailability, Transport, and Bioactivity of Dietary Flavonoids: A Review from a Historical Perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1054–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Actis-Goretta, L.; Lévèques, A.; Giuffrida, F.; Romanov-Michailidis, F.; Viton, F.; Barron, D.; Duenas-Paton, M.; Gonzalez-Manzano, S.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Williamson, G.; et al. Elucidation of (−)-epicatechin metabolites after ingestion of chocolate by healthy humans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.F.; Borge, G.I.A.; Piskula, M.K.; Tudose, A.; Tudoreanu, L.; Valentová, K.; Williamson, G.; Dos Santos, C.N. Bioavailability of Quercetin in Humans with a Focus on Interindividual Variation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 714–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.N.; Kerimi, A.; Williamson, G. Bioavailability and metabolism of chlorogenic acids (acyl-quinic acids) in humans. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1299–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, Z.; Ghiasvand, R.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. Empirically derived dietary patterns and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis on prospective observational studies. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 19, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ros, R.; Forouhi, N.G.; Sharp, S.J.; González, C.A.; Buijsse, B.; Guevara, M.; Van Der Schouw, Y.T.; Amiano, P.; Boeing, H.; Bredsdorff, L.; et al. The Association Between Dietary Flavonoid and Lignan Intakes and Incident Type 2 Diabetes in European Populations: The EPIC-InterAct study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3961–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-F.; Yang, B.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J.-J.; Li, D. Apple and pear consumption and type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Pan, A.; Malik, V.S.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B. Caffeinated and caffeine-free beverages and risk of type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 97, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Chen, M.; van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B. Caffeinated and Decaffeinated Coffee Consumption and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and a Dose-Response Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.B.; Yu, S.H.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, S.R.; Oh, S.J.; Jee, S.H.; Lee, J.E. Association Between Coffee Consumption and Circulating Levels of Adiponectin and Leptin. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, A.; Welch, A.A.; Spector, T.; MacGregor, A.; Cassidy, A. Intakes of Anthocyanins and Flavones Are Associated with Biomarkers of Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Women. J. Nutr. 2013, 144, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, D.; Lippi, C.; Necozione, S.; Desideri, G.; Ferri, C. Short-term administration of dark chocolate is followed by a significant increase in insulin sensitivity and a decrease in blood pressure in healthy persons. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, D.; Desideri, G.; Necozione, S.; Lippi, C.; Casale, R.; Properzi, G.; Blumberg, J.B.; Ferri, C. Blood Pressure Is Reduced and Insulin Sensitivity Increased in Glucose-Intolerant, Hypertensive Subjects after 15 Days of Consuming High-Polyphenol Dark Chocolate. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desideri, G.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Grassi, D.; Necozione, S.; Ghiadoni, L.; Mastroiacovo, D.; Raffaele, A.; Ferri, L.; Bocale, R.; Lechiara, M.C.; et al. Benefits in Cognitive Function, Blood Pressure, and Insulin Resistance Through Cocoa Flavanol Consumption in Elderly Subjects With Mild Cognitive Impairment. Hypertension 2012, 60, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stote, K.S.; Clevidence, B.A.; Novotny, J.A.; Henderson, T.; Radecki, S.V.; Baer, D.J. Effect of cocoa and green tea on biomarkers of glucose regulation, oxidative stress, inflammation and hemostasis in obese adults at risk for insulin resistance. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrime, M.G.; Bauer, S.R.; McDonald, A.C.; Chowdhury, N.H.; Coltart, C.E.M.; Ding, E.L. Flavonoid-Rich Cocoa Consumption Affects Multiple Cardiovascular Risk Factors in a Meta-Analysis of Short-Term Studies. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dower, J.I.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Gijsbers, L.; Zock, P.L.; Kromhout, D.; Hollman, P.C.H. Effects of the pure flavonoids epicatechin and quercetin on vascular function and cardiometabolic health: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tian, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, L.; Ying, X.; Tian, H.; Nie, M. Effects of green tea or green tea extract on insulin sensitivity and glycaemic control in populations at risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 27, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhou, R.; Wang, B.; Chen, K.; Shi, L.-Y.; Zhu, J.-D.; Mi, M.-T. Effect of green tea on glucose control and insulin sensitivity: A meta-analysis of 17 randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-X.; Xu, Y.-L.; Li, S.-H.; Hui, R.; Wu, Y.; Huang, X.-H. Effects of green tea catechins with or without caffeine on glycemic control in adults: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshzad, E.; Shab-Bidar, S.; Mohammadpour, Z.; Djafarian, K. Effect of anthocyanin supplementation on cardio-metabolic biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, C.; Kiely, M.; Lyons, J.; Lucey, A. The Effect of Berry-Based Food Interventions on Markers of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Health: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, A.J.; Cash, K.C.; Johnson, W.D.; Champagne, C.M.; Cefalu, W.T. Bioactives in Blueberries Improve Insulin Sensitivity in Obese, Insulin-Resistant Men and Women. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1764–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokayem, M.; Blond, E.; Vidal, H.; Lambert, K.; Meugnier, E.; Feillet-Coudray, C.; Coudray, C.; Pesenti, S.; Luyton, C.; Lambert-Porcheron, S.; et al. Grape Polyphenols Prevent Fructose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Insulin Resistance in First-Degree Relatives of Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, R.; Xia, M. Anthocyanin increases adiponectin secretion and protects against diabetes-related endothelial dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E975–E988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostadmohammadi, V.; Milajerdi, A.; Ayati, E.; Kolahdooz, F.; Asemi, Z. Effects of quercetin supplementation on glycemic control among patients with metabolic syndrome and related disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Williamson, G. Quercetin lowers plasma uric acid in pre-hyperuricaemic males: A randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarpour-Sadegh, F.; Montazeri, V.; Adili, A.; Esfehani, A.; Rashidi, M.-R.; Pirouzpanah, S. Consumption of Fresh Yellow Onion Ameliorates Hyperglycemia and Insulin Resistance in Breast Cancer Patients During Doxorubicin-Based Chemotherapy: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2016, 16, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bule, M.; Abdurahman, A.; Nikfar, S.; Abdollahi, M.; Amini, M. Antidiabetic effect of quercetin: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaposhnikov, S.; Hatzold, T.; El Yamani, N.; Stavro, P.M.; Lorenzo, Y.; Dusinska, M.; Reus, A.; Pasman, W.; Collins, A. Coffee and oxidative stress: A human intervention study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 57, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikpayam, O.; Najafi, M.; Ghaffari, S.; Jafarabadi, M.A.; Sohrab, G.; Roshanravan, N. Effects of green coffee extract on fasting blood glucose, insulin concentration and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR): A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bock, M.; Derraik, J.G.B.; Brennan, C.M.; Biggs, J.B.; Morgan, P.E.; Hodgkinson, S.C.; Hofman, P.L.; Cutfield, W.S. Olive (Olea europaea L.) Leaf Polyphenols Improve Insulin Sensitivity in Middle-Aged Overweight Men: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, S.; Konings, E.; Bilet, L.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Van De Weijer, T.; Goossens, G.H.; Hoeks, J.; Van Der Krieken, S.; Ryu, D.; Kersten, S.; et al. Calorie Restriction-like Effects of 30 Days of Resveratrol Supplementation on Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Profile in Obese Humans. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, R.; Cozzolino, D.; Guardasole, V.; Angelini, V.; Zarra, E.; Matarazzo, M.; Cittadini, A.; Sacca, L.; Torella, R. Red wine consumption improves insulin resistance but not endothelial function in type 2 diabetic patients. Metabolism 2005, 54, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerdeman, J.; Del Rio, D.; Calani, L.; Eringa, E.C.; Smulders, Y.M.; Serné, E.H. Red wine polyphenols do not improve obesity-associated insulin resistance: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 20, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Chen, X.; Bao, L. Effects of wine on blood pressure, glucose parameters, and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medicine 2019, 98, e15771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausenblas, H.A.; Schoulda, J.A.; Smoliga, J.M. Resveratrol treatment as an adjunct to pharmacological management in type 2 diabetes mellitus-systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, C.; Qiu, S.; Yuan, X.; Li, L. Effects of resveratrol on glucose control and insulin sensitivity in subjects with type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgary, S.; Karimi, R.; Momtaz, S.; Naseri, R.; Farzaei, M.H. Effect of resveratrol on metabolic syndrome components: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerdeman, J.; Van Poelgeest, E.; Ket, J.C.; Eringa, E.C.; Serné, E.H.; Smulders, Y.M. Do grape polyphenols improve metabolic syndrome components? A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams-Rad, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Ramezani-Jolfaie, N.; Zarei, S.; Mohsenpour, M.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. Hesperidin supplementation has no effect on blood glucose control: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liao, D.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y. Lack of efficacy of pomegranate supplementation for glucose management, insulin levels and sensitivity: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandari, S.; Hatami, E.; Ziaei, R.; Ghavami, A.; Yamchi, A.M. The effect of pomegranate (Punica granatum) supplementation on metabolic status in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 52, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasalvar, C.; Bolling, B.W. Review of nut phytochemicals, fat-soluble bioactives, antioxidant components and health effects. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, S68–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, P.; Hassanipour, S.; Sisakht, M.; Daryabeygi-Khotbehsara, R.; Savardashtaki, A.; Fathalipour, M. The effectiveness of pistachio on glycemic control and insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes, prediabetes and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, E.P.; Guan, V.; Tapsell, L.C.; Probst, Y.C. Effect of walnut consumption on markers of blood glucose control: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, D.L.; Eliasziw, M.; Chen, C.-Y.O.; Blumberg, J.B. A Pecan-Rich Diet Improves Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, J.; Thorwald, M.; De La Cruz, N.; Vu, E.; Asghar, S.A.; Kuse, Q.; Rios, L.K.D.; Ortiz, R.M. Glucoregulatory and Cardiometabolic Profiles of Almond vs. Cracker Snacking for 8 Weeks in Young Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liu, J.-F.; Chang, W.-H.; Chen, C.-M. Almond consumption improved glycemic control and lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2011, 60, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, J.H. Reversible Insulin Resistance in Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Horm. Metab. Res. 1996, 28, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, K.; Whaley-Connell, A.T.; Stump, C.S.; Ibdah, J.A.; Sowers, J.R. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance: Role of inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R673–R680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Ehses, J.A.; Maedler, K.; Schumann, D.M.; Ellingsgaard, H.; Eppler, E.; Reinecke, M. Mechanisms of -Cell Death in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, S108–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzen, S.; Drinkgern, J.; Tiedge, M. Low antioxidant enzyme gene expression in pancreatic islets compared with various other mouse tissues. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G. Possible effects of dietary polyphenols on sugar absorption and digestion. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 57, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ni, X.; Kai, G.; Chen, X. A Review on Structure–Activity Relationship of Dietary Polyphenols Inhibiting α-Amylase. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Royall, P.G.; Gaisford, S.; Williams, G.R.; Edwards, C.H.; Warren, F.J.; Flanagan, B.M.; Ellis, P.R.; Butterworth, P.J. Structural and enzyme kinetic studies of retrograded starch: Inhibition of α-amylase and consequences for intestinal digestion of starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madariaga, H.; Lee, P.C.; Heitlinger, L.A.; Lebenthal, E. Effects of graded alpha-glucosidase inhibition on sugar absorption in vivo. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1988, 33, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Rubin, B.R.; Orme, C.M.; Karpikov, A.; Yu, C.; Bogan, J.S.; Toomre, D.K. Dual-mode of insulin action controls GLUT4 vesicle exocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, F.; Yang, X.; Franklin, B.S.; Hoelscher, M.; Schmitz, T.; Bedorf, J.; Nickenig, G.; Werner, N. High glucose condition increases NADPH oxidase activity in endothelial microparticles that promote vascular inflammation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 98, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Mann, G.E. Vascular NAD(P)H oxidase activation in diabetes: A double-edged sword in redox signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiasson, J.-L.; Josse, R.G.; Gomis, R.; Hanefeld, M.; Karasik, A.; Laakso, M. Acarbose for prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus: The STOP-NIDDM randomised trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerimi, A.; Nyambe-Silavwe, H.; Gauer, J.S.; Tomas-Barberan, F.; Williamson, G. Pomegranate juice, but not an extract, confers a lower glycemic response on a high–glycemic index food: Randomized, crossover, controlled trials in healthy subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, M.; Quezada-Calvillo, R.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Nichols, B.L.; Hamaker, B.R. Dietary Phenolic Compounds Selectively Inhibit the Individual Subunits of Maltase-Glucoamylase and Sucrase-Isomaltase with the Potential of Modulating Glucose Release. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3873–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forester, S.C.; Gu, Y.; Lambert, J.D. Inhibition of starch digestion by the green tea polyphenol, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piparo, E.L.; Scheib, H.; Frei, N.; Williamson, G.; Grigorov, M.; Chou, C.J. Flavonoids for Controlling Starch Digestion: Structural Requirements for Inhibiting Human α-Amylase. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyambe-Silavwe, H.; Williamson, G. Polyphenol- and fibre-rich dried fruits with green tea attenuate starch-derived postprandial blood glucose and insulin: A randomised, controlled, single-blind, cross-over intervention. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauer, J.S.; Tumova, S.; Lippiat, J.D.; Kerimi, A.; Williamson, G. Differential patterns of inhibition of the sugar transporters GLUT2, GLUT5 and GLUT7 by flavonoids. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 152, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.-J.; Kornmann, F.; Fuhrmann, G.F. The inhibitory effects of flavonoids and antiestrogens on the Glut1 glucose transporter in human erythrocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2003, 146, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Kwon, O.; Chen, S.; Daruwala, R.; Eck, P.; Park, J.B.; Levine, M. Flavonoid Inhibition of Sodium-dependent Vitamin C Transporter 1 (SVCT1) and Glucose Transporter Isoform 2 (GLUT2), Intestinal Transporters for Vitamin C and Glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 15252–15260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Rodriguez, J.A.; Aydin, E.; Gauer, J.S.; Pyner, A.; Williamson, G.; Kerimi, A. Green and Chamomile Teas, but not Acarbose, Attenuate Glucose and Fructose Transport via Inhibition of GLUT2 and GLUT5. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, M.J.; Kerimi, A.; Mouly, V.; Tumova, S.; Williamson, G. Gut microbiome catabolites as novel modulators of muscle cell glucose metabolism. FASEB J. 2018, 33, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Bian, H.-X.; Xu, N.; Bao, B.; Liu, J. Quercetin reduces obesity-associated ATM infiltration and inflammation in mice: A mechanism including AMPKα1/SIRT1. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugani, C.B.; Klip, A. Glucose transporter 4: Cycling, compartments and controversies. EMBO Rep. 2005, 6, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, P.A.; Clifford, M.N.; Crozier, A.; Day, A.J.; Donovan, J.L.; Manach, C.; Williamson, G. How should we assess the effects of exposure to dietary polyphenols in vitro? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Oteiza, P.I. Dietary flavonoids: Role of (−)-epicatechin and related procyanidins in cell signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Prieto, M.A.; Bettaieb, A.; Haj, F.G.; Fraga, C.G.; Oteiza, P.I. (−)-Epicatechin prevents TNFα-induced activation of signaling cascades involved in inflammation and insulin sensitivity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-Y.; Wu, T.-T.; Zhou, S.-H.; Bao, Y.-Y.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Fan, J.; Huang, Y.-P. Apigenin suppresses GLUT-1 and p-AKT expression to enhance the chemosensitivity to cisplatin of laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 cells: An in vitro study. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3938–3947. [Google Scholar]
- Bettaieb, A.; Prieto, M.A.V.; Lanzi, C.R.; Miatello, R.M.; Haj, F.G.; Fraga, C.G.; Oteiza, P.I. (−)-Epicatechin mitigates high-fructose-associated insulin resistance by modulating redox signaling and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonini, E.; Wang, Z.; Bettaieb, A.; Adamo, A.M.; Daveri, E.; Mills, D.A.; Kalanetra, K.M.; Haj, F.G.; Karakas, S.; Oteiza, P.I. (−)-Epicatechin protects the intestinal barrier from high fat diet-induced permeabilization: Implications for steatosis and insulin resistance. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senaphan, K.; Kukongviriyapan, U.; Sangartit, W.; Pakdeechote, P.; Pannangpetch, P.; Prachaney, P.; Greenwald, S.E.; Kukongviriyapan, V. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Changes in a Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome Induced by High-Carbohydrate, High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6446–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youl, E.; Bardy, G.; Magous, R.; Cros, G.; Sejalon, F.; Virsolvy, A.; Richard, S.; Quignard, J.; Gross, R.; Petit, P.; et al. Quercetin potentiates insulin secretion and protects INS-1 pancreatic β-cells against oxidative damage via the ERK1/2 pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youl, E.; Magous, R.; Cros, G.; Oiry, C. MAP Kinase cross talks in oxidative stress-induced impairment of insulin secretion. Involvement in the protective activity of quercetin. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 28, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardy, G.; Virsolvy, A.; Quignard, J.F.; Ravier, M.A.; Bertrand, G.; Dalle, S.; Cros, G.; Magous, R.; Richard, S.; Oiry, C. Quercetin induces insulin secretion by direct activation of L-type calcium channels in pancreatic beta cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Wang, W.; Fan, C.-Y.; Wang, M.-X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.-H.; Kong, L.-D. Quercetin Preservesβ-Cell Mass and Function in Fructose-Induced Hyperinsulinemia through Modulating Pancreatic Akt/FoxO1 Activation. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 303902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Chan, C.B. Epicatechin potentiation of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in INS-1 cells is not dependent on its antioxidant activity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, M.Á.; Fernández-Millán, E.; Ramos, S.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L. Cocoa flavonoid epicatechin protects pancreatic beta cell viability and function against oxidative stress. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 58, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Xiang, J.; Shan, W.; Li, M.; Zhou, W.; Han, X.; Chen, F. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits Ethanol-Induced Apoptosis Through Neurod1 Regulating CHOP Expression in Pancreatic β-Cells. Anat. Rec. 2016, 299, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaprakasam, B.; Vareed, S.K.; Olson, L.K.; Nair, M.G. Insulin Secretion by Bioactive Anthocyanins and Anthocyanidins Present in Fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suantawee, T.; Elazab, S.T.; Hsu, W.H.; Yao, S.; Cheng, H.; Adisakwattana, S. Cyanidin Stimulates Insulin Secretion and Pancreatic β-Cell Gene Expression through Activation of l-type Voltage-Dependent Ca2+ Channels. Nutrients 2017, 9, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Buya, M.; Qin, W.; Sun, C.; Cai, H.; Xie, Q.; Xu, B.; Wu, Y. Anthocyanins from Chinese Bayberry Extract Activate Transcription Factor Nrf2 in β Cells and Negatively Regulate Oxidative Stress-Induced Autophagy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8765–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adisakwattana, S.; Moonsan, P.; Yibchok-Anun, S. Insulin-releasing properties of a series of cinnamic acid derivatives in vitro and in vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7838–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Niu, Q.; Song, H.; Wei, S.; Wang, S.; Yao, L.; Li, Y.-P. Polysaccharides from Portulaca oleracea L. regulated insulin secretion in INS-1 cells through voltage-gated Na(+) channel. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assali, E.A.; Shlomo, D.; Zeng, J.; Taddeo, E.P.; Trudeau, K.M.; Erion, K.A.; Colby, A.H.; Grinstaff, M.W.; Liesa, M.; Las, G.; et al. Nanoparticle-mediated lysosomal reacidification restores mitochondrial turnover and function in β cells under lipotoxicity. FASEB J. 2018, 33, 4154–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramenzoni, L.L.; Zuellig, R.A.; Hussain, A.; Lehmann, R.; Heumann, C.; Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R. Bacterial supernatants elevate glucose-dependent insulin secretion in rat pancreatic INS-1 line and islet β-cells via PI3K/AKT signaling. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 452, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, Y.-M.; Jung, K.; Chin, Y.-W.; Kang, K.S. Alpha-Mangostin Improves Insulin Secretion and Protects INS-1 Cells from Streptozotocin-Induced Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, L.E.; Nicholas, L.M.; Filipsson, K.; Sun, J.; Medina, A.; Fex, M.; Mulder, H.; Spégel, P.; Al-Majdoub, M. Glycogen metabolism in the glucose-sensing and supply-driven beta-cell. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 4242–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, L.; Han, K.-S.; Bains, K.; Singh, H. Indian culinary plants enhance glucose-induced insulin secretion and glucose consumption in INS-1 β-cells and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, E.P.; Lin, J.-K. Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) and Rutin Suppress the Glucotoxicity through Activating IRS2 and AMPK Signaling in Rat Pancreatic β Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9817–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nahdi, A.M.; John, A.; Raza, H. Cytoprotective Effects of N-Acetylcysteine on Streptozotocin- Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in RIN-5F Pancreatic β-Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-C.; Hsu, C.-C.; Liu, S.-H.; Su, C.-C.; Yen, C.-C.; Lee, M.-J.; Chen, K.-L.; Ho, T.-J.; Hung, D.-Z.; Wu, C.-C.; et al. Cadmium Induces Apoptosis in Pancreatic β-Cells through a Mitochondria-Dependent Pathway: The Role of Oxidative Stress-Mediated c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondas, D.; Tomas, A.; Soto-Ribeiro, M.; Wehrle-Haller, B.; Halban, P.A. Novel Mechanistic Link between Focal Adhesion Remodeling and Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 287, 2423–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, J.-I.; Earaki, K.; Yamato, E.; Ikegami, H.; Asano, T.; Shibasaki, Y.; Oka, Y.; Yamamura, K.-I. Establishment of a Pancreatic β Cell Line That Retains Glucose-Inducible Insulin Secretion: Special Reference to Expression of Glucose Transporter Isoforms. Endocrinology 1990, 127, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Ahn, I.S.; Kwon, D.Y.; Ko, B.S.; Jun, W.K. Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 Suppress Triglyceride Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and Enhance β-Cell Insulin Secretion and Viability in Min6 CellsviaPKA-Dependent Pathways. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 2815–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaluri, N.; Modi, S.; Rodríguez, M.L.; Stancáková, A.; Kuusisto, J.; Kokkola, T.; Laakso, M. Simvastatin Impairs Insulin Secretion by Multiple Mechanisms in MIN6 Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, U.G.; Ilievski, V.; Unterman, T.G.; Watanabe, K. Porphyromonas gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide Upregulates Insulin Secretion From Pancreatic β Cell Line MIN6. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, S.; McClenaghan, N.H.; McCluskey, J.T.; Flatt, P.R. Cellular responses of novel human pancreatic β-cell line, 1.1B4 to hyperglycemia. Islets 2013, 5, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.D.; Vasu, S.; McClenaghan, N.H.; Flatt, P.R. Implanting 1.1B4 human β-cell pseudoislets improves glycaemic control in diabetic severe combined immune deficient mice. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, S.; McClenaghan, N.H.; Flatt, P.R. Molecular Mechanisms of Toxicity and Cell Damage by Chemicals in a Human Pancreatic Beta Cell Line, 1.1B4. Pancreas 2016, 45, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, S.; McClenaghan, N.H.; McCluskey, J.T.; Flatt, P.R. Effects of lipotoxicity on a novel insulin-secreting human pancreatic β-cell line, 1.1B4. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.D.; Vasu, S.; McClenaghan, N.H.; Flatt, P.R. Pseudoislet formation enhances gene expression, insulin secretion and cytoprotective mechanisms of clonal human insulin-secreting 1.1B4 cells. Eur. J. Physiol. 2015, 467, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravassard, P.; Hazhouz, Y.; Pechberty, S.; Bricout-Neveu, E.; Armanet, M.; Czernichow, P.; Scharfmann, R. A genetically engineered human pancreatic β cell line exhibiting glucose-inducible insulin secretion. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3589–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsonkova, V.G.; Sand, F.W.; Wolf, X.A.; Grunnet, L.G.; Ringgaard, A.K.; Ingvorsen, C.; Winkel, L.; Kalisz, M.; Dalgaard, K.; Bruun, C.; et al. The EndoC-βH1 cell line is a valid model of human beta cells and applicable for screenings to identify novel drug target candidates. Mol. Metab. 2018, 8, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozzi, F.; Nardelli, T.R.; Lopes, M.; Millard, I.; Barthson, J.; Igoillo-Esteve, M.; Grieco, F.A.; Villate, O.; Oliveira, J.M.; Casimir, M.; et al. Cytokines induce endoplasmic reticulum stress in human, rat and mouse beta cells via different mechanisms. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teraoku, H.; Lenzen, S. Dynamics of Insulin Secretion from EndoC-βH1 β-Cell Pseudoislets in Response to Glucose and Other Nutrient and Nonnutrient Secretagogues. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 2309630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfmann, R.; Didiesheim, M.; Richards, P.; Chandra, V.; Oshima, M.; Albagli, O. Mass production of functional human pancreatic β-cells: Why and how? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Organism | Characteristics | Studies and Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| INS-1 | Rat | β-cell line secreting insulin in response to glucose. Line is stable with time, with high glucose-induced insulin secretion | Polysaccharide-induced insulin secretion [149] Lipotoxicity [150] Bacteria [151] Cytotoxic effects of mangostin [152] Glycogen metabolism [153] Effect of Indian culinary plants [154] |
| RIN | Rat | Exhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion | [155,156,157] |
| Min6 | Mouse | Releases insulin in response to glucose, but high passage cells have impaired insulin secretion | [158] Establishment [159] Ginseng root-treated [160] Statin-treated [161] [162] |
| 1.1B4 | Human | Secretes low levels of insulin when glucose-stimulated | Cellular response to hyperglycaemia [163] [164,165,166,167] |
| EndoCβH1 | Human | Secretes insulin in response to a glucose challenge, but slow growing and difficult to culture | Characterisation [168] Validity in drug screening against mouse model [169] [170,171] Further studies listed in review [172] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williamson, G.; Sheedy, K. Effects of Polyphenols on Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103135
Williamson G, Sheedy K. Effects of Polyphenols on Insulin Resistance. Nutrients. 2020; 12(10):3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103135
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliamson, Gary, and Katherine Sheedy. 2020. "Effects of Polyphenols on Insulin Resistance" Nutrients 12, no. 10: 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103135
APA StyleWilliamson, G., & Sheedy, K. (2020). Effects of Polyphenols on Insulin Resistance. Nutrients, 12(10), 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103135





