Sweet Taste Antagonist Lactisole Administered in Combination with Sucrose, But Not Glucose, Increases Energy Intake and Decreases Peripheral Serotonin in Male Subjects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
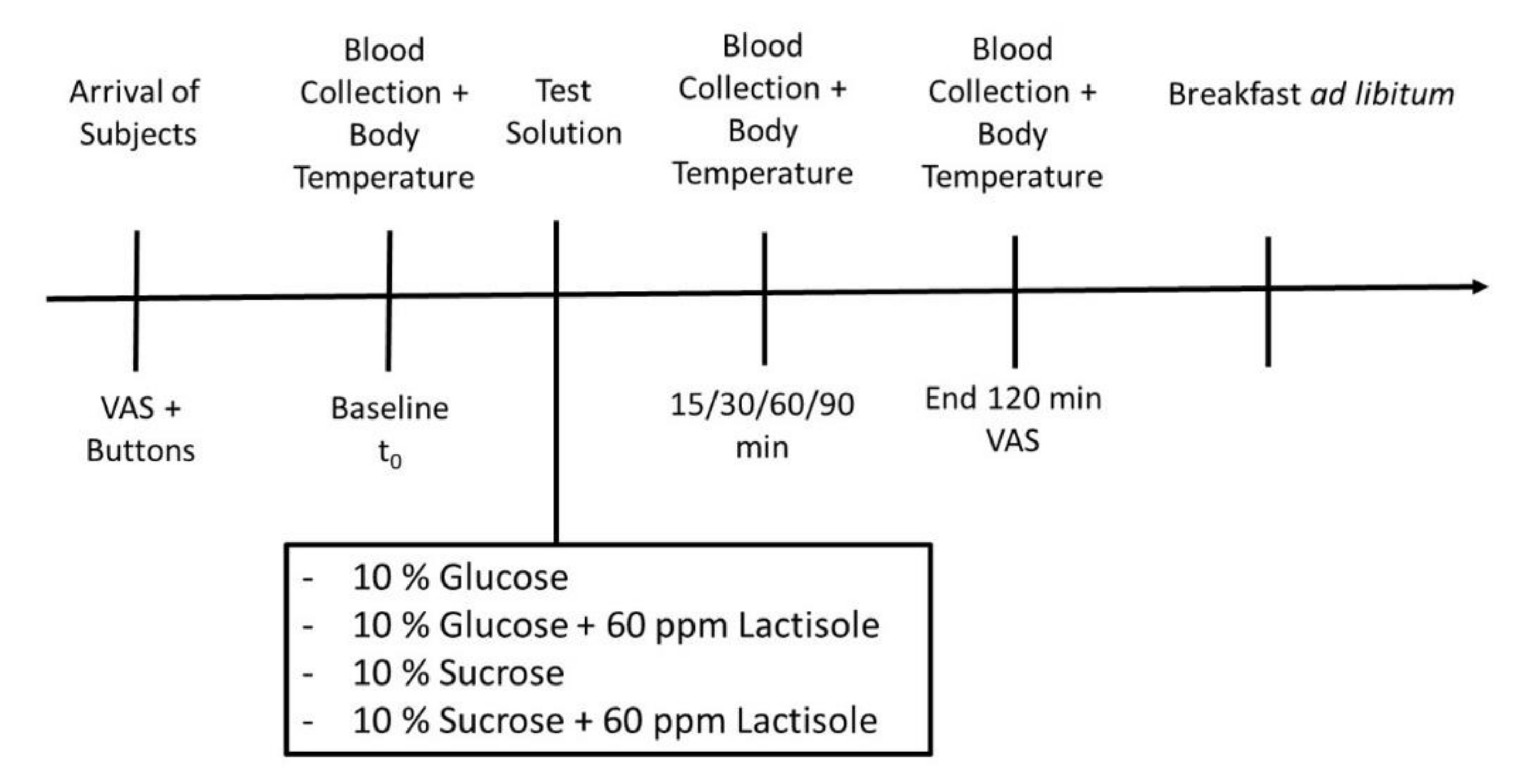
2.2. Study Design and Intervention
2.2.1. Subjects’ Rating of Hunger
2.2.2. Total Energy Intake
2.3. Blood Sample Collection
2.4. Determination of Postprandial Ghrelin, CCK, and Serotonin Plasma Concentrations
2.5. Body Core and Skin Temperature
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
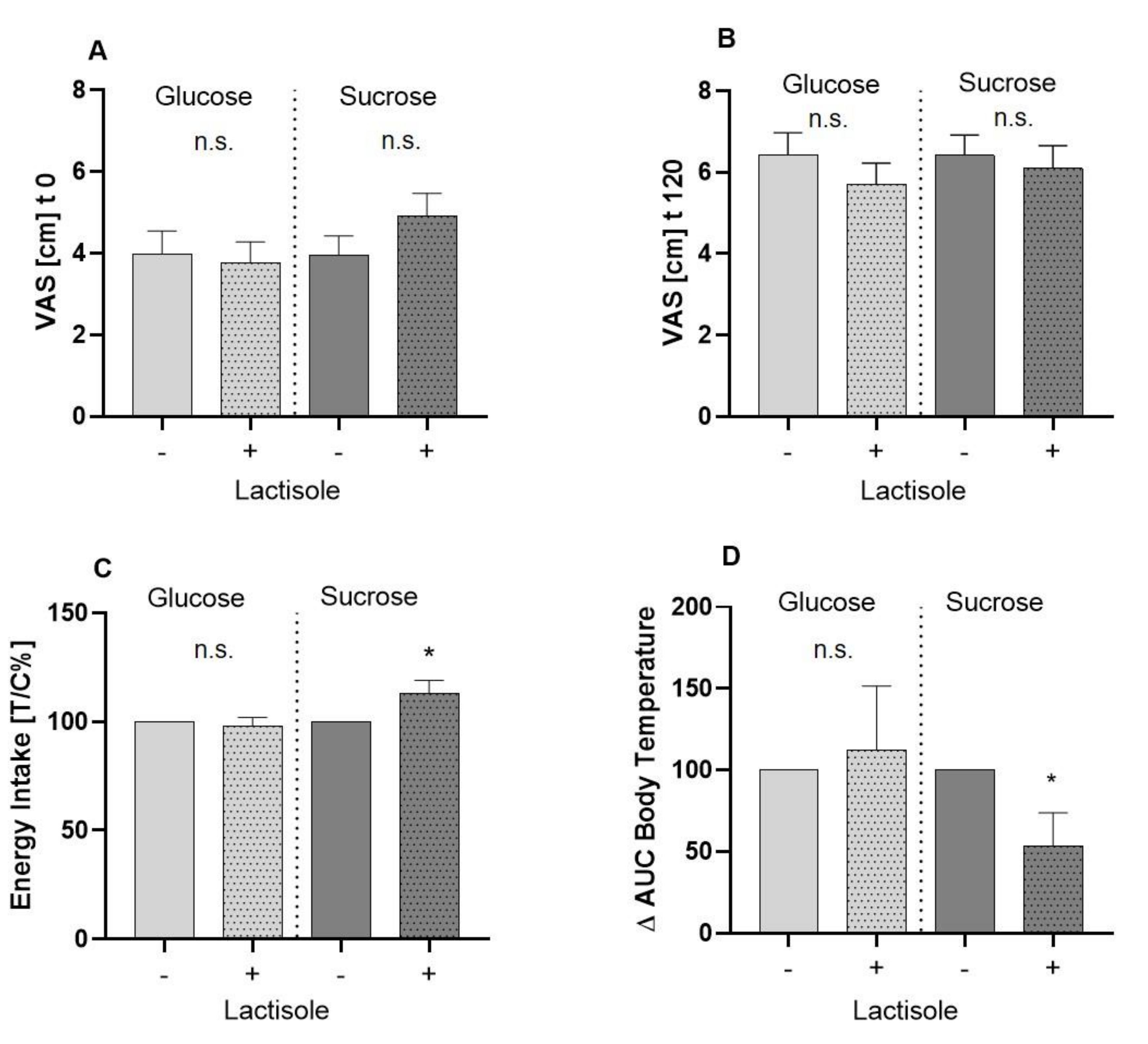
3.1. Assessment of Subjects’ Feeling of Hunger by Means of Visual Analogue Scale
3.2. Total Energy Intake after an Ad Libitum Breakfast
3.3. Body Core and Body Skin Temperature
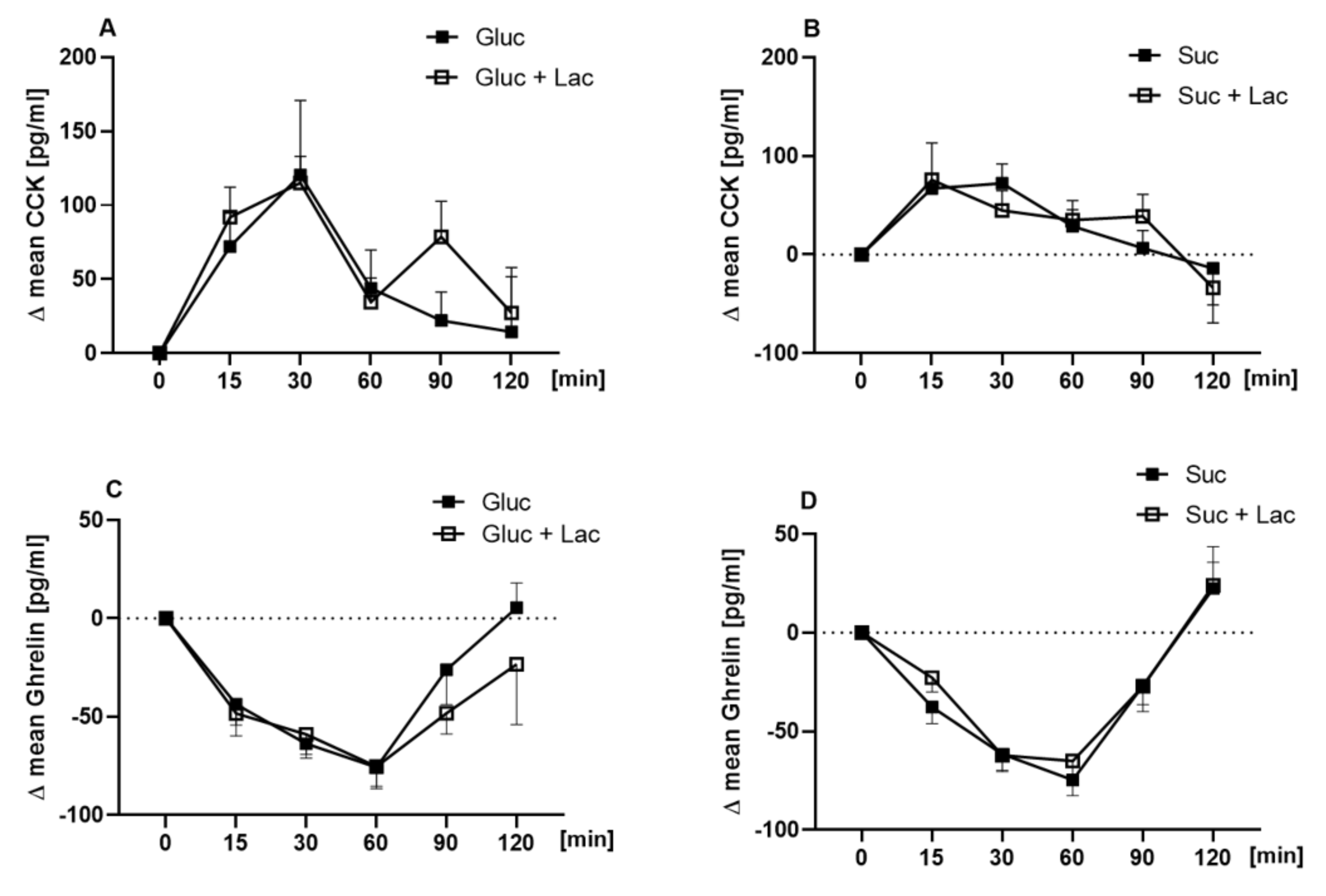
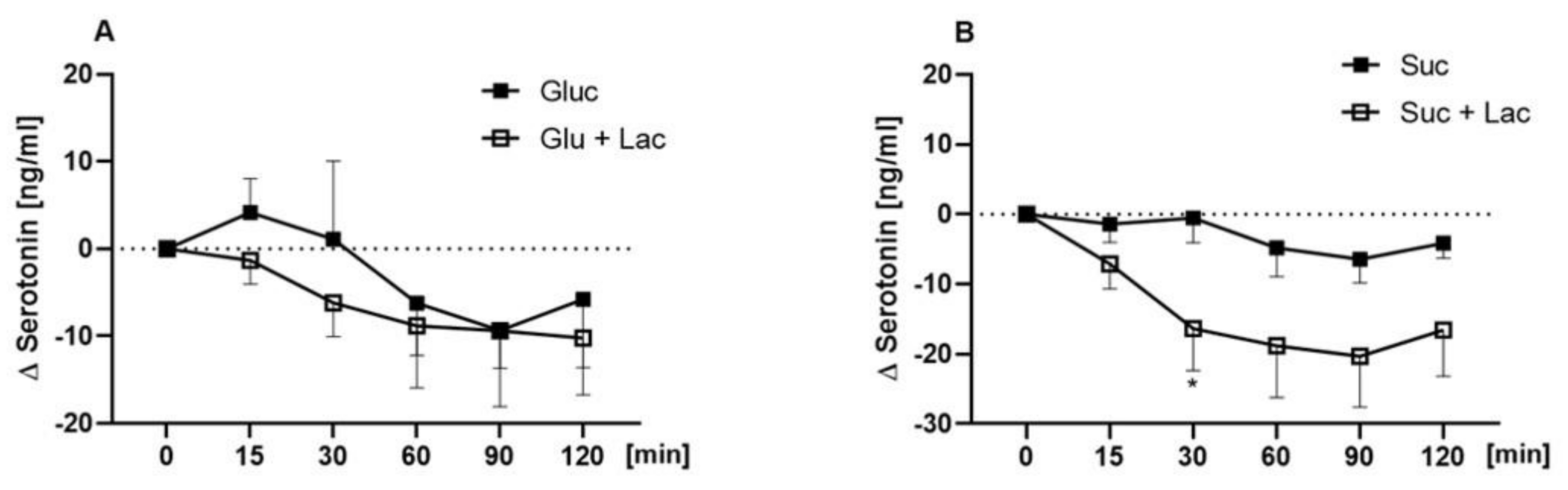
3.4. Plasma Concentrations of Ghrelin, CCK, and Serotonin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jayasinghe, S.N.; Kruger, R.; Walsh, D.C.I.; Cao, G.; Rivers, S.; Richter, M.; Breier, B.H. Is Sweet Taste Perception Associated with Sweet Food Liking and Intake? Nutrients 2017, 9, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.Y.; Lacy, K.E.; McBride, R.; Keast, R.S. The Association between Sweet Taste Function, Anthropometry, and Dietary Intake in Adults. Nutrients 2016, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feeney, E.; O’Brien, S.; Scannell, A.; Markey, A.; Gibney, E.R. Genetic variation in taste perception: Does it have a role in healthy eating? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2011, 70, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.H. Sugars, sweetness, and food intake. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavin, J.H.; French, S.J.; Read, N.W. Comparison of oral and gastric administration of sucrose and maltose on gastric emptying rate and appetite. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Cui, M.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Z.; Snyder, L.A.; Benard, L.M.; Osman, R.; Margolskee, R.F.; Max, M. Lactisole interacts with the transmembrane domains of human T1R3 to inhibit sweet taste. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15238–15246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, N.; Roper, S.D. The cell biology of taste. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 190, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezencon, C.; le Coutre, J.; Damak, S. Taste-signaling proteins are coexpressed in solitary intestinal epithelial cells. Chem. Senses 2007, 32, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Kokrashvili, Z.; Theodorakis, M.J.; Carlson, O.D.; Kim, B.J.; Zhou, J.; Kim, H.H.; Xu, X.; Chan, S.L.; Juhaszova, M.; et al. Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15069–15074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.A.; Owyang, C. Sugars, Sweet Taste Receptors, and Brain Responses. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, I.; Nakagawa, Y.; Hamano, K.; Medina, J.; Li, L.; Nagasawa, M. Glucose-Sensing Receptor T1R3: A New Signaling Receptor Activated by Glucose in Pancreatic β-Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelam, B. Satiation, satiety and their effects on eating behaviour. Nutr. Bull. 2009, 34, 126–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, S.C.; D’Alessio, D.A. Central control of body weight and appetite. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, B.; Wang, Y. Appetite regulation and weight control: The role of gut hormones. Nutr. Diabetes 2012, 2, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.M.; Young, R.L.; Leong, L.; Rogers, G.B.; Spencer, N.J.; Jessup, C.F.; Keating, D.J. The Diverse Metabolic Roles of Peripheral Serotonin. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Rolland, V.; Wilson, S.A.; Westerterp, K.R. Satiety related to 24 h diet-induced thermogenesis during high protein/carbohydrate vs high fat diets measured in a respiration chamber. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerspach, A.C.; Steinert, R.E.; Schonenberger, L.; Graber-Maier, A.; Beglinger, C. The role of the gut sweet taste receptor in regulating GLP-1, PYY, and CCK release in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zopun, M.; Lieder, B.; Holik, A.K.; Ley, J.P.; Hans, J.; Somoza, V. Noncaloric Sweeteners Induce Peripheral Serotonin Secretion via the T1R3-Dependent Pathway in Human Gastric Parietal Tumor Cells (HGT-1). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7044–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruszt, S.; Garami, A. The short- and long-term effects of food intake on thermogenesis. Temperature 2014, 1, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, L.B.; Moller, P.; Flint, A.; Martens, M.; Raben, A. Effect of sensory perception of foods on appetite and food intake: A review of studies on humans. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2003, 27, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, C.M.; Wendelin, M.; Lutsch, D.; Schleining, G.; Dürrschmid, K.; Ley, J.P.; Krammer, G.E.; Lieder, B. Structure-dependent effects of sweet and sweet taste affecting compounds on their sensorial properties. Food Chem. 2020, 7, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Vigues, S.; Hobbs, J.R.; Conn, G.L.; Munger, S.D. Distinct Contributions of T1R2 and T1R3 Taste Receptor Subunits to the Detection of Sweet Stimuli. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1948–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asarian, L.; Geary, N. Modulation of appetite by gonadal steroid hormones. Philos. Trans. R Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sclafani, A.; Pérez, C. Cypha™ Propionic acid, 2-(4-methoxyphenol) salt inhibits sweet taste in humans, but not in rats. Physiol. Behav. 1997, 61, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochkogler, C.; Lieder, B.; Rust, P.; Berry, D.; Meier-Menches, S.; Pignitter, M.; Riva, A.; Leitinger, A.; Bruk, A.; Wagner, S.; et al. A 12-week intervention with nonivamide, a TRPV1 agonist, prevents a dietary-induced body fat gain and increases peripheral serotonin in moderately overweight subjects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 61, 1600731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoeger, V.; Lieder, B.; Riedel, J.; Schweiger, K.; Hoi, J.; Ruzsanyi, V.; Klieber, M.; Rust, P.; Hans, J.; Ley, J.P.; et al. Wheat Protein Hydrolysate Fortified With l-Arginine Enhances Satiation Induced by the Capsaicinoid Nonivamide in Moderately Overweight Male Subjects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1900133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochkogler, C.M.; Rohm, B.; Hojdar, K.; Pignitter, M.; Widder, S.; Ley, J.P.; Krammer, G.E.; Somoza, V. The capsaicin analog nonivamide decreases total energy intake from a standardized breakfast and enhances plasma serotonin levels in moderately overweight men after administered in an oral glucose tolerance test: A randomized, crossover trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. ISO 9886:2004 Ergonomics—Evaluation of Thermal Strain by Physiological Measurements; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.Y.; Tucker, R.M. Sweet Taste as a Predictor of Dietary Intake: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.Y.; Friel, J.K.; Mackay, D.S. Effect of sucralose and aspartame on glucose metabolism and gut hormones. Nutr. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.H.; Catherine, N.L.; Woodend, D.M.; Wolever, T.M. Inverse association between the effect of carbohydrates on blood glucose and subsequent short-term food intake in young men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat-Larquemin, L.; Oppert, J.M.; Bellisle, F.; Guy-Grand, B. Sweet taste of aspartame and sucrose: Effects on diet-induced thermogenesis. Appetite 2000, 34, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, J.P.; Fink, H. Serotonin controlling feeding and satiety. Behav. Brain. Res. 2015, 277, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Merahbi, R.; Löffler, M.; Mayer, A.; Sumara, G. The roles of peripheral serotonin in metabolic homeostasis. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, S.; Stevens, R. Peripherally administered 5-hydroxytryptamine elicits the full behavioural sequence of satiety. Physiol. Behav. 1991, 50, 1075–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, J.D.; Rowland, N. Peripherally administered serotonin decreases food intake in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1981, 15, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochkogler, C.; Liszt, K.; Lieder, B.; Stöger, V.; Stübler, A.; Pignitter, M.; Hans, J.; Widder, S.; Ley, J.; Krammer, G.; et al. Appetite-Inducing Effects of Homoeriodictyol: Two Randomized, Cross-Over Interventions. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2017, 61, 1700459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, T.P.; Melichar, J.K.; Nutt, D.J.; Donaldson, L.F. Human Taste Thresholds Are Modulated by Serotonin and Noradrenaline. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 26, 12664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolskee, R.F.; Dyer, J.; Kokrashvili, Z.; Salmon, K.S.H.; Ilegems, E.; Daly, K.; Maillet, E.L.; Ninomiya, Y.; Mosinger, B.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. T1R3 and gustducin in gut sense sugars to regulate expression of Na+-glucose cotransporter 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15075–15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, A.T.; Balakrishnan, A.; Rhoads, D.B.; Tavakkolizadeh, A. Rapid upregulation of sodium-glucose transporter SGLT1 in response to intestinal sweet taste stimulation. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, K.K.; Sukumaran, S.K.; Kotha, R.; Gilbertson, T.A.; Margolskee, R.F. Glucose transporters and ATP-gated K+ (KATP) metabolic sensors are present in type 1 taste receptor 3 (T1r3)-expressing taste cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5431–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.M.; Loo, D.D.; Hirayama, B.A. Biology of human sodium glucose transporters. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 733–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, S.S.; Booth, B.J.; Sattely-Miller, E.A.; Graham, B.G.; Gibes, K.M. Selective Inhibition of Sweetness by the Sodium Salt of ± 2-(4-Methoxyphenoxy) propanoic Acid. Chem. Senses 1999, 24, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
| n | 27 |
|---|---|
| Gender | Male |
| Age [years] | 28 ± 5 |
| Body Weight [kg] | 77.4 ± 12 |
| Height [m] | 1.81 ± 0.1 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 23.8 ± 2.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schweiger, K.; Grüneis, V.; Treml, J.; Galassi, C.; Karl, C.M.; Ley, J.P.; Krammer, G.E.; Lieder, B.; Somoza, V. Sweet Taste Antagonist Lactisole Administered in Combination with Sucrose, But Not Glucose, Increases Energy Intake and Decreases Peripheral Serotonin in Male Subjects. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103133
Schweiger K, Grüneis V, Treml J, Galassi C, Karl CM, Ley JP, Krammer GE, Lieder B, Somoza V. Sweet Taste Antagonist Lactisole Administered in Combination with Sucrose, But Not Glucose, Increases Energy Intake and Decreases Peripheral Serotonin in Male Subjects. Nutrients. 2020; 12(10):3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103133
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchweiger, Kerstin, Verena Grüneis, Julia Treml, Claudia Galassi, Corinna M. Karl, Jakob P. Ley, Gerhard E. Krammer, Barbara Lieder, and Veronika Somoza. 2020. "Sweet Taste Antagonist Lactisole Administered in Combination with Sucrose, But Not Glucose, Increases Energy Intake and Decreases Peripheral Serotonin in Male Subjects" Nutrients 12, no. 10: 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103133
APA StyleSchweiger, K., Grüneis, V., Treml, J., Galassi, C., Karl, C. M., Ley, J. P., Krammer, G. E., Lieder, B., & Somoza, V. (2020). Sweet Taste Antagonist Lactisole Administered in Combination with Sucrose, But Not Glucose, Increases Energy Intake and Decreases Peripheral Serotonin in Male Subjects. Nutrients, 12(10), 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103133







